The
border
Borders are usually defined as geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other subnational entities. Political borders c ...
between
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
and the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
is the longest international border in the world. The terrestrial boundary (including boundaries in the
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
, Atlantic, and Pacific coasts) is long. The land border has two sections: Canada's border with the
contiguous United States to its south, and with the U.S. state of
Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S. ...
to its west. The bi-national
International Boundary Commission
The International Boundary Commission (french: Commission de la frontière internationale) is a bi-national organization responsible for surveying and mapping the Canada–United States border. The commission was created in 1908 and made permanen ...
deals with matters relating to marking and maintaining the boundary, and the
International Joint Commission
The International Joint Commission (french: Commission mixte internationale) is a bi-national organization established by the governments of the United States and Canada under the Boundary Waters Treaty of 1909. Its responsibilities were expa ...
deals with issues concerning boundary waters. The agencies currently responsible for facilitating legal passage through the international boundary are the
Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) and
U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP).
History
18th century

The
Treaty of Paris of 1783
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal perso ...
ended the
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
between
Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It i ...
and the United States. In the second article of the Treaty, the parties agreed on all boundaries of the United States, including, but not limited to, the boundary to the north along then-
British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestow ...
. The agreed-upon boundary included the line from the northwest angle of
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
to the northwesternmost head of the
Connecticut River and proceeded down along the middle of the river to the
45th parallel of north latitude.
The parallel had been established in the 1760s as the boundary between the provinces of
Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
and
New York (including what would later become the
State of Vermont). It was
surveyed and marked by John Collins and Thomas Valentine from 1771 to 1773.
The
St. Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting ...
and the Great Lakes became the boundary further west, between the United States and what is now
Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
. Northwest of
Lake Superior
Lake Superior in central North America is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. and the third-largest by volume, holding 10% of the world's surface fresh wa ...
, the boundary followed rivers to the
Lake of the Woods. From the
northwesternmost point of the Lake of the Woods, the boundary was agreed to go straight west until it met the
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
. In fact, that line never meets the river since
the river's source is further south.
Jay Treaty (1794)
The
Jay Treaty
The Treaty of Amity, Commerce, and Navigation, Between His Britannic Majesty and the United States of America, commonly known as the Jay Treaty, and also as Jay's Treaty, was a 1794 treaty between the United States and Great Britain that averted ...
of 1794 (effective 1796) created the
International Boundary Commission
The International Boundary Commission (french: Commission de la frontière internationale) is a bi-national organization responsible for surveying and mapping the Canada–United States border. The commission was created in 1908 and made permanen ...
, which was charged with surveying and mapping the boundary. It also provided for the removal of British military and administration from
Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at t ...
, as well as other frontier outposts on the U.S. side. The Jay Treaty was superseded by the
Treaty of Ghent
The Treaty of Ghent () was the peace treaty that ended the War of 1812 between the United States and the United Kingdom. It took effect in February 1815. Both sides signed it on December 24, 1814, in the city of Ghent, United Netherlands (now in ...
(effective 1815) concluding the
War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States, United States of America and its Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom ...
, which included pre-war boundaries.
19th century

Signed in December 1814, the Treaty of Ghent ended the War of 1812, returning the boundaries of British North America and the United States to the state they were prior to the war. In the following decades, the United States and the United Kingdom concluded several treaties that settled the major boundary disputes between the two, enabling the border to be
demilitarized. The
Rush–Bagot Treaty
The Rush–Bagot Treaty or Rush–Bagot Disarmament was a treaty between the United States and Great Britain limiting naval armaments on the Great Lakes and Lake Champlain, following the War of 1812. It was ratified by the United States Senate o ...
of 1817 provided a plan for demilitarizing the two combatant sides in the War of 1812 and also laid out preliminary principles for drawing a border between British North America and the United States.
London Convention (1818)
The
Treaty of 1818 saw expansion of both British North America and the US, where the boundary extended westward along the
49th parallel, from the
Northwest Angle at Lake of the Woods to the
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico ...
. The treaty extinguished British claims to the south of that line up to the
Red River Valley, which was part of
Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land (french: Terre de Rupert), or Prince Rupert's Land (french: Terre du Prince Rupert, link=no), was a territory in British North America which comprised the Hudson Bay drainage basin; this was further extended from Rupert's Land t ...
. The treaty also extinguished U.S. claims to land north of that line in the watershed of the
Missouri River, which was part of the
Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase (french: Vente de la Louisiane, translation=Sale of Louisiana) was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. In return for fifteen million dollars, or app ...
. This amounted to three small areas, consisting of the northern part of the drainages of the
Milk River (today in southern
Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
and southwestern
Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a province in western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dak ...
), the
Poplar River (Saskatchewan), and
Big Muddy Creek (Saskatchewan). Along the 49th parallel, the border vista is theoretically straight, but in practice follows the 19th-century surveyed border markers and varies by several hundred feet in spots.
Webster–Ashburton Treaty (1842)

Disputes over the interpretation of the border treaties and mistakes in surveying required additional negotiations, which resulted in the
Webster–Ashburton Treaty
The Webster–Ashburton Treaty, signed August 9, 1842, was a treaty that resolved several border issues between the United States and the British North American colonies (the region that became Canada). Signed under John Tyler's presidency, it r ...
of 1842. The treaty resolved the
Aroostook War
The Aroostook War (sometimes called the Pork and Beans WarLe Duc, Thomas (1947). The Maine Frontier and the Northeastern Boundary Controversy. ''The American Historical Review'' Vol. 53, No. 1 (Oct., 1947), pp. 30–41), or the Madawaska War, wa ...
, a dispute over the boundary between
Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and ...
,
New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only province with both English and ...
, and the
Province of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report on th ...
. The treaty redefined the border between
New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec to the nor ...
, Vermont, and New York on the one hand, and the Province of Canada on the other, resolving the
Indian Stream dispute and the
Fort Blunder
Fort Montgomery on Lake Champlain is the second of two American forts built at the northernmost point of the American part of the lake: a first, unnamed fort built on the same site in 1816 and Fort Montgomery built in 1844.
The current massive s ...
dilemma at the outlet to
Lake Champlain
Lake Champlain ( ; french: Lac Champlain) is a natural freshwater lake in North America. It mostly lies between the US states of New York and Vermont, but also extends north into the Canada, Canadian province of Quebec.
The New York portion of t ...
.
The part of the 45th parallel that separates Quebec from the U.S. states of Vermont and New York had first been surveyed from 1771 to 1773 after it had been declared the boundary between New York (including what later became Vermont) and Quebec. It was surveyed again after the War of 1812. The U.S. federal government began to construct fortifications just south of the border at
Rouses Point, New York
Rouses Point is a village in Clinton County, New York, United States, along the 45th parallel. The population was 2,209 at the 2010 census. The village is named after Jacques Rouse, a French Canadian soldier who fought alongside the Americans du ...
, on Lake Champlain. After a significant portion of the construction was completed, measurements revealed that at that point, the actual 45th parallel was three-quarters of a mile (1.2 km) south of the surveyed line. The fort, which became known as "
Fort Blunder
Fort Montgomery on Lake Champlain is the second of two American forts built at the northernmost point of the American part of the lake: a first, unnamed fort built on the same site in 1816 and Fort Montgomery built in 1844.
The current massive s ...
", was in Canada, which created a dilemma for the U.S. that was not resolved until a provision of the treaty left the border on the meandering line as surveyed. The border along the
Boundary Waters
The Boundary Waters, also called the Quetico-Superior Country, is a region of wilderness straddling the Canada–United States border between Ontario and Minnesota, in the area just west of Lake Superior. While "Boundary Waters" is a common name ...
in present-day Ontario and
Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
between Lake Superior and the Northwest Angle was also redefined.
Oregon Treaty (1846)
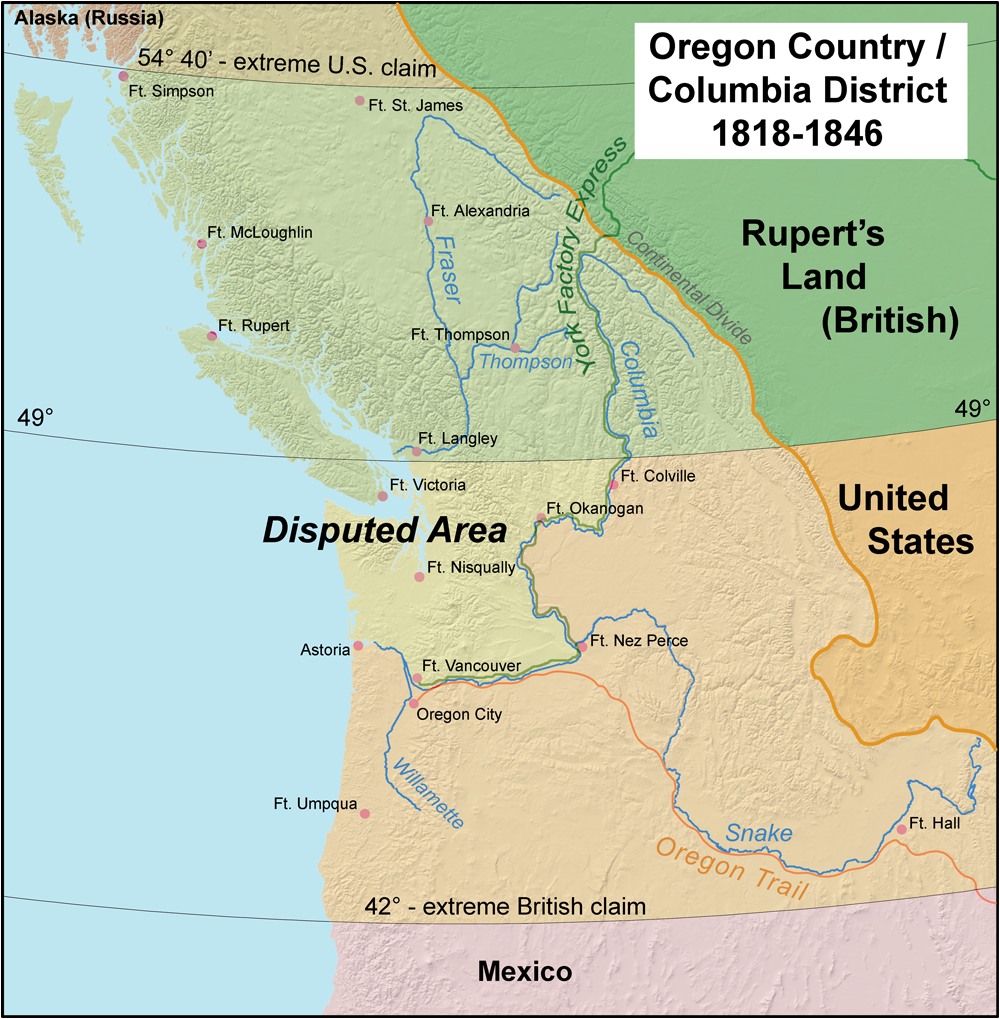
An
1844 boundary dispute during the
Presidency of James K. Polk led to a call for the northern boundary of the U.S. west of the Rockies to be
54°40′N related to the southern boundary of Russia's
Alaska Territory. However, Great Britain wanted a border that followed the
Columbia River to the Pacific Ocean. The dispute was resolved in the
Oregon Treaty of 1846, which established the 49th parallel as the boundary through the Rockies.
Boundary surveys (mid–19th century)
The Northwest Boundary Survey (1857–1861) laid out the land boundary. However, the water boundary was not settled for some time. After the
Pig War in 1859, arbitration in 1872 established the border between the
Gulf Islands
The Gulf Islands are a group of islands in the Salish Sea between Vancouver Island and the mainland coast of British Columbia.
Etymology
The name "Gulf Islands" comes from "Gulf of Georgia," the original term used by George Vancouver in his ...
and the
San Juan Islands
The San Juan Islands are an archipelago in the Pacific Northwest of the United States between the U.S. state of Washington and Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. The San Juan Islands are part of Washington state, and form the core of ...
.
The
International Boundary Survey (or, the "Northern Boundary Survey" in the US) began in 1872. Its mandate was to establish the border as agreed to in the Treaty of 1818. Archibald Campbell led the way for the United States, while Donald Cameron, supported by chief astronomer
Samuel Anderson, headed the British team. This survey focused on the border from the Lake of the Woods to the summit of the Rocky Mountains.
20th century
In 1903, following a dispute that arose because of the
Klondike Gold Rush, a joint United Kingdom–Canada–U.S. tribunal established the
boundary of southeast Alaska.
On April 11, 1908, the United Kingdom and the United States agreed, under Article IV of the Treaty of 1908 "concerning the boundary between the United States and the Dominion of Canada from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean", to survey and delimit the boundary between Canada and the U.S. through the St. Lawrence River and Great Lakes, in accordance with modern surveying techniques, and thus accomplished several changes to the border. In 1925, the International Boundary Commission's temporary mission became permanent for maintaining the survey and mapping of the border; maintaining boundary monuments and buoys; and keeping the border clear of brush and vegetation for . This "
border vista" extends for on each side of the line.
In 1909, under the
Boundary Waters Treaty
The Boundary Waters Treaty is the 1909 treaty between the United States and Canada providing mechanisms for resolving any dispute over any waters bordering the two countries. The treaty covers the
Canada, as a dominion of the Crown of Britain ...
, the
International Joint Commission
The International Joint Commission (french: Commission mixte internationale) is a bi-national organization established by the governments of the United States and Canada under the Boundary Waters Treaty of 1909. Its responsibilities were expa ...
was established for Canada and the U.S. to investigate and approve projects that affect the waters and waterways along the border.
21st century
As a result of the 2001
September 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated suicide terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked four commer ...
, the Canada–U.S. border was shut without any warning, and no goods or people were allowed to cross. In the wake of the impromptu border closure, procedures were jointly developed to ensure that commercial traffic could cross the border even if people were restricted from crossing. These procedures were later used for a border closure caused by the
COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
in 2020.
2020–2021 closure

In response to the
COVID-19 pandemic in Canada
The COVID-19 pandemic in Canada is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (). It is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (). Most cases over the course of the pandemic have been in Ontario, Que ...
and the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, the governments of Canada and the United States agreed to close the border to "non-essential" travel on March 21, 2020, for an initial period of 30 days. The closure has been extended 15 times since then; it expired on July 21, 2021. However, in mid-June 2021, the Canadian government announced it will ease some entry requirements for fully vaccinated Canadian nationals, permanent residents, and foreign nationals starting on July 5, 2021. In mid-July, the Canadian government announced that fully vaccinated American citizens and permanent residents can visit Canada starting August 9, 2021. The American government reopened its land border to fully vaccinated Canadian citizens effective November 8, 2021. Provided that COVID cases remain stable and/or decline, fully vaccinated international visitors can enter Canada starting September 7. The 2020–21 closure was reportedly the first blanket, long-term closure of the border since the War of 1812.
Essential travel, as defined by Canadian and US regulations, includes travel for employment or education purposes. "Non-essential" travel to Canada, includes travel "for an optional or discretionary purpose, such as tourism, recreation or entertainment." The U.S. Department of Homeland Security issued defined non-essential travel to include "tourism purposes (e.g., sightseeing, recreation, gambling, or attending cultural events)" and gave an extensive, non-exhaustive definition of what sorts of travel qualify as essential.
Business advocacy groups, noting the substantial economic impact of the closure on both sides of the border, called for more nuanced restrictions in place of the blanket ban on non-essential travel. The Northern Border Caucus, a group in the
US Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washin ...
composed of members from border communities, made similar suggestions to the governments of both countries. Beyond the closure itself, US President
Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who served as the 45th president of the United States from 2017 to 2021.
Trump graduated from the Wharton School of the University of P ...
also initially suggested the idea of deploying United States military personnel near the border with Canada in connection with the pandemic. He later abandoned the idea following vocal opposition from Canadian officials.
Security
Law enforcement approach
The International Boundary is commonly referred to as the world's "longest undefended border", though this is true only in the military sense, as civilian law enforcement is present. It is illegal to cross the border outside border controls, as anyone crossing the border must be checked per immigration and customs laws. The relatively low level of security measures stands in contrast to that of the
United States–Mexico border
United may refer to:
Places
* United, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community
* United, West Virginia, an unincorporated community
Arts and entertainment Films
* ''United'' (2003 film), a Norwegian film
* ''United'' (2011 film), a BBC Two f ...
(one-third length of Canada–U.S. border), which is actively patrolled by U.S. Customs and Border Protection personnel to prevent
illegal migration and
drug trafficking.

Parts of the International Boundary cross through mountainous terrain or heavily forested areas, but significant portions also cross remote prairie farmland and the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence River, in addition to the maritime components of the boundary at the
Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
,
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
, and
Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, N ...
oceans. The border also runs through the middle of the
Akwesasne Nation and even divides some buildings found in communities in New England and Quebec.
The U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) identifies the chief issues along the border as domestic and international terrorism; drug smuggling and smuggling of products (such as
tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
) to evade customs duties; and illegal immigration.
A June 2019 U.S.
Government Accountability Office report identified specific staffing and resource shortfalls faced by the CBP on the Northern border that adversely affect enforcement actions; the U.S. Border Patrol "identified an insufficient number of agents that limited patrol missions along the northern border" while
CBP Air and Marine Operations
Air and Marine Operations (AMO) is a federal law enforcement component within U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP), an agency of the United States Department of Homeland Security (DHS). AMO's mission is to protect the American people and na ...
"identified an insufficient number of agents along the northern border, which limited the number and frequency of air and maritime missions."
[
There are eight U.S. Border Patrol sectors based on the Canada–U.S. border, each covering a designated "area of responsibility"; the sectors are (from west to east) based in Blaine, Washington; ]Spokane, Washington
Spokane ( ) is the largest city and county seat of Spokane County, Washington, United States. It is in eastern Washington, along the Spokane River, adjacent to the Selkirk Mountains, and west of the Rocky Mountain foothills, south of the Cana ...
; Havre, Montana
Havre ( ) is the county seat and largest city in Hill County, Montana, United States. Havre is nicknamed the crown jewel of the Hi-Line. It is said to be named after the city of Le Havre in France. As of the 2020 census the population was 9,362 ...
; Grand Forks, North Dakota; Detroit, Michigan
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at ...
; Buffalo, New York
Buffalo is the second-largest city in the U.S. state of New York (behind only New York City) and the seat of Erie County. It is at the eastern end of Lake Erie, at the head of the Niagara River, and is across the Canadian border from Sou ...
; Swanton, Vermont; and Houlton, Maine.[
Following the September 11 attacks in the United States, security along the border was dramatically tightened by the two countries in both populated and rural areas. Both nations are also actively involved in detailed and extensive tactical and strategic intelligence sharing.
In December 2010, Canada and the United States were negotiating an agreement titled "Beyond the Border: A Shared Vision for Perimeter Security and Competitiveness" which would give the U.S. more influence over Canada's border security and immigration controls, and more information would be shared by Canada with the U.S.
]
Security measures
 Residents of both nations who own property adjacent to the border are forbidden to build within the boundary vista without permission from the International Boundary Commission. They are required to report such construction to their respective governments.
All persons crossing the border are required to report to the customs agency of the country they have entered. Where necessary, fences or vehicle blockades are used. In remote areas, where staffed border crossings are not available, there are hidden sensors on roads, trails, railways, and wooded areas, which are located near crossing points. There is no
Residents of both nations who own property adjacent to the border are forbidden to build within the boundary vista without permission from the International Boundary Commission. They are required to report such construction to their respective governments.
All persons crossing the border are required to report to the customs agency of the country they have entered. Where necessary, fences or vehicle blockades are used. In remote areas, where staffed border crossings are not available, there are hidden sensors on roads, trails, railways, and wooded areas, which are located near crossing points. There is no border zone
Border control refers to measures taken by governments to monitor and regulate the movement of people, animals, and goods across land, air, and maritime borders. While border control is typically associated with international borders, it a ...
; the U.S. Customs and Border Protection routinely sets up checkpoints as far as into U.S. territory.
In August 2020, the United States constructed of short cable fencing along the border between Abbotsford, British Columbia, and Whatcom County, Washington
Whatcom County is a county located in the northwestern corner of the U.S. state of Washington, bordered by the Canadian Lower Mainland (the Metro Vancouver and Fraser Valley Regional Districts of British Columbia) to the north, Okanogan ...
.
Identification
Prior to 2007, American and Canadian citizens were only required to produce a birth certificate and driver's license/government-issued identification card when crossing the Canada–United States border.U.S. Department of Homeland Security
The United States Department of Homeland Security (DHS) is the U.S. federal executive department responsible for public security, roughly comparable to the interior or home ministries of other countries. Its stated missions involve anti-terr ...
(DHS) announced the final rule of the Western Hemisphere Travel Initiative
The Western Hemisphere Travel Initiative (WHTI) is the implementation of the requirement to show a passport or other acceptable document to enter the United States, for nationals of certain North American jurisdictions who were previously exempt ...
(WHTI), which pertained to new identification requirements for travelers entering the United States. This rule, which marked the first phase of the initiative, was implemented on January 23, 2007, specifying six forms of identification acceptable for crossing the U.S. border (depending on mode):
* a valid passport—required in order to enter by air;
* a United States Passport Card
The United States passport card is an optional national identity card and a travel document issued by the U.S. federal government in the size of a credit card. Like a U.S. passport book, the passport card is only issued to U.S. nationals ex ...
;
* a state enhanced driver's license—available in the States of Michigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
, Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
, New York, Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...
, Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
, as well as in the provinces of British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
, Manitoba
, image_map = Manitoba in Canada 2.svg
, map_alt = Map showing Manitoba's location in the centre of Southern Canada
, Label_map = yes
, coordinates =
, capital = Winn ...
, Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
, and Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
;
* a trusted traveler program card (i.e. NEXUS
NEXUS is a joint Canada Border Services Agency and U.S. Customs and Border Protection-operated Trusted Traveler and expedited border control program designed for pre-approved, low-risk travelers. Members of the program can avoid waits at border ...
, FAST, or SENTRI
The Secure Electronic Network for Travelers Rapid Inspection (SENTRI) provides expedited U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) processing, at the U.S.-Mexico border, of pre-approved travelers considered low-risk. Voluntarily applicants must ...
);
* a valid Merchant Mariner Credential The Merchant Mariner Credential (MMC) is a credential issued by the United States Coast Guard in accordance with guidelines of the International Convention on Standards of Training, Certification and Watchkeeping for Seafarers (STCW) to United Stat ...
—to be used when traveling in conjunction with official maritime business; and
* a valid U.S. military identification card—to be used when traveling on official orders.
The requirement of a passport or an enhanced form of identification to enter the United States by air went into effect in January 2007; and went into effect for those entering the U.S. by land and sea in January 2008.[ Although the new requirements for land and sea entry went into legal effect in January 2008, its enforcement did not begin until June 2009.][ Since June 2009, every traveller arriving via a land or sea port-of-entry (including ]ferries
A ferry is a ship, watercraft or amphibious vehicle used to carry passengers, and sometimes vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A passenger ferry with many stops, such as in Venice, Italy, is sometimes called a water bus or water tax ...
) has been required to present one of the above forms of identification in order to enter the United States.
Conversely in order to cross into Canada, a traveler must also carry identification, as well as a valid visa (if necessary) when crossing the border.[ Several other documents may be used by Canadians to identify their citizenship at the border, although use of such documents requires it to be supported with additional photo identification.][
American and Canadian citizens who are members of a trusted traveler program such as FAST or NEXUS, may present their FAST or NEXUS card as an alternate form of identification when crossing the international boundary by land or sea, or when arriving by air from only Canada or the United States.][ Although permanent residents of Canada and the United States are eligible for FAST or NEXUS, they are required to travel with a passport and proof of permanent residency upon arrival at the Canadian border.][ American permanent residents who are NEXUS members also require Electronic Travel Authorization when crossing the Canadian border.][
]
Security issues
Smuggling
 Smuggling of
Smuggling of alcoholic beverages
An alcoholic beverage (also called an alcoholic drink, adult beverage, or a drink) is a drink that contains ethanol, a type of alcohol that acts as a drug and is produced by fermentation of grains, fruits, or other sources of sugar. The cons ...
( "rum running") was widespread during the 1920s, when Prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcohol ...
was in effect nationally in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
and parts of Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
.
In more recent years, Canadian officials have brought attention to drug, cigarette, and firearms smuggling from the United States, while U.S. officials have made complaints of drug smuggling via Canada. In July 2005, law enforcement personnel arrested three men who had built a tunnel under the border between British Columbia and Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
, intended for the use of smuggling marijuana, the first such tunnel known on this border. From 2007 to 2010, 147 people were arrested for smuggling marijuana on the property of a bed-and-breakfast
Bed and breakfast (typically shortened to B&B or BnB) is a small lodging establishment that offers overnight accommodation and breakfast. Bed and breakfasts are often private family homes and typically have between four and eleven rooms, wit ...
in Blaine, Washington, but agents estimate that they caught only about 5% of smugglers.Cornwall, Ontario
Cornwall is a city in Eastern Ontario, Canada, situated where the provinces of Ontario and Quebec and the state of New York converge. It is the seat of the United Counties of Stormont, Dundas, and Glengarry and is Ontario's easternmost city ...
, experiences ongoing smuggling—mostly of tobacco and firearms from the United States. The neighboring Mohawk Mohawk may refer to:
Related to Native Americans
* Mohawk people, an indigenous people of North America (Canada and New York)
*Mohawk language, the language spoken by the Mohawk people
* Mohawk hairstyle, from a hairstyle once thought to have been ...
territory of Akwesasne straddles the Ontario–Quebec–New York borders, where its First Nations
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:
* Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.
Indigenous groups
*First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including:
**First Natio ...
sovereignty prevents Ontario Provincial Police
The Ontario Provincial Police (OPP) is the provincial police service of Ontario, Canada. Under its provincial mandate, the OPP patrols provincial highways and waterways, protects provincial government buildings and officials, patrols unincorp ...
, Sûreté du Québec
The (SQ; , ) is the provincial police service for the Canadian province of Quebec. No official English name exists, but the agency's name is sometimes translated to 'Quebec Provincial Police' or QPP in English-language sources. The headquarters ...
, Royal Canadian Mounted Police
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP; french: Gendarmerie royale du Canada; french: GRC, label=none), commonly known in English as the Mounties (and colloquially in French as ) is the federal police, federal and national police service of ...
, Canada Border Services Agency, Canadian Coast Guard
The Canadian Coast Guard (CCG; french: links=no, Garde côtière canadienne, GCC) is the coast guard of Canada. Formed in 1962, the coast guard is tasked with marine search and rescue (SAR), communication, navigation, and transportation issues ...
, United States Border Patrol, United States Coast Guard
The United States Coast Guard (USCG) is the maritime security, search and rescue, and law enforcement service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the country's eight uniformed services. The service is a maritime, military, mu ...
, and New York State Police
The New York State Police (NYSP) is the state police of the state of New York in the United States. It is part of the New York State Executive Department, and employs over 5,000 sworn state troopers and 711 civilian members.
History
The Stat ...
from exercising jurisdiction over exchanges taking place within the territory.
2009 border occupation
In May 2009, the Mohawk people of Akwesasne occupied the area around the Canada Border Services Agency port of entry building to protest the Canadian government's decision to arm its border agents while operating on Mohawk territory. The north span of the Seaway International Bridge
The Seaway International Bridge is an international crossing connecting New York State, in the United States, Akwesasne Mohawk Territory, and the province of Ontario in Canada. It consists of the South and North Channel Bridges. The South Chan ...
and the CBSA inspection facilities were closed. During this occupation, the Canadian flag was replaced with the flag of the Mohawk people. Although U.S. Customs remained opened to southbound traffic, northbound traffic was blocked on the U.S. side by both American and Canadian officials. The Canadian border at this crossing remained closed for six weeks. On July 13, 2009, the CBSA opened a temporary inspection station at the north end of the north span of the bridge in the city of Cornwall, allowing traffic to once again flow in both directions.
The Mohawk people of Akwesasne have staged ongoing protests at this border. In 2014 they objected to a process that made their crossing more tedious, believing it violated their treaty rights of free passage. When traveling from the U.S. to Cornwall Island, they must first cross a second bridge into Canada, for inspection at the new Canadian border station. Discussions between inter-governmental agencies were being pursued on the feasibility of relocating the Canadian border inspection facilities on the U.S. side of the border.
2017 border crossing crisis
In August 2017, the border between Quebec and New York saw an influx of up to 500 irregular crossings each day, by individuals seeking asylum in Canada. As a result, Canada increased border security and immigration staffing in the area, reiterating the fact that crossing the border irregularly had no effect on one's asylum status.
From the beginning of January 2017 up until the end of March 2018, the RCMP intercepted 25,645 people crossing the border into Canada from an unauthorized point of entry. Public Safety Canada
Public Safety Canada (PSC; french: Sécurité publique Canada, SPC; PSP), legally incorporated as the Department of Public Safety and Emergency Preparedness (PSEPC), is the Ministry (government department), department of the Government of Canada ...
estimates another 2,500 came across in April 2018 for a total of just over 28,000.
Border lengths and regions
The length of the terrestrial boundary is long, including bodies of water and the border between Alaska and Canada that spans . Eight out of thirteen provinces and territories of Canada
Within the geographical areas of Canada, the ten provinces and three territories are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British Nort ...
and thirteen out of fifty U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...
s are located along this international boundary.
Yukon
The Canadian territory of Yukon
Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as ...
shares its entire western border with the U.S. state of Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S. ...
, beginning at the Beaufort Sea at and proceeds southwards along the 141st meridian west. At 60°18′N, the border proceeds away from the 141st meridian west in a southeastward direction, following the St. Elias Mountains. South of the 60th parallel north
The 60th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 60 degrees north of Earth's equator. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
Although it lies approximately twice as far away from the Equator as ...
, the border continues into British Columbia.
British Columbia

British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
has two international borders with the United States: with the state of Alaska along BC's northwest, and with the contiguous United States along the southern edge of the province, including (west to east) Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
, Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and Wyomi ...
, and Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columb ...
.Mt. Fairweather
Mount Fairweather (officially gazetted as Fairweather Mountain in Canada but referred to as Mount Fairweather), is the highest mountain in the Canadian province of British Columbia, with an elevation of . It is located east of the Pacific Ocean ...
at , where the border heads northwestward towards the Coast Mountains.Portland Canal
, image = Hyder Alaska IMG 0276 (22495379342).jpg
, alt =
, caption = Portland Canal from Hyder, Alaska
, image_bathymetry =
, alt_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = Alaska and British Columbia
, group =
, coordinates ...
and follows it outward to the Dixon Entrance
The Dixon Entrance (french: Entrée Dixon) is a strait about long and wide in the Pacific Ocean at the Canada–United States border, between the U.S. state of Alaska and the province of British Columbia in Canada. The Dixon Entrance is part o ...
, which takes the border down and out into the Pacific Ocean, terminating it upon reaching international waters
The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water (or their drainage basins) transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed region ...
.
BC's border along the contiguous U.S. begins southwest of Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest by ...
and northwest of the Olympic Peninsula
The Olympic Peninsula is a large arm of land in western Washington that lies across Puget Sound from Seattle, and contains Olympic National Park. It is bounded on the west by the Pacific Ocean, the north by the Strait of Juan de Fuca, and th ...
, at the terminus of international waters in the Pacific Ocean.Strait of Juan de Fuca
The Strait of Juan de Fuca (officially named Juan de Fuca Strait in Canada) is a body of water about long that is the Salish Sea's outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre ...
eastward, turning northeastward to enter Haro Strait
, image = Southern Gulf Islands, BC, Canada - panoramio.jpg
, image_size = 250px
, alt =
, caption = View of Haro Strait from South Pender Island
, image_bathymetry = Locmap-Haro-Boundary ad ...
. The border follows the strait in a northward direction, but turns sharply eastward through Boundary Pass
, image = Monarch Head (7604530136).jpg
, image_size = 250px
, alt =
, caption = View of Boundary Pass from Monarch Head, Saturna Island
, image_bathymetry = Locmap-Haro-Boundary additional l ...
, separating the Canadian Gulf Islands
The Gulf Islands are a group of islands in the Salish Sea between Vancouver Island and the mainland coast of British Columbia.
Etymology
The name "Gulf Islands" comes from "Gulf of Georgia," the original term used by George Vancouver in his ...
from the American San Juan Islands
The San Juan Islands are an archipelago in the Pacific Northwest of the United States between the U.S. state of Washington and Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. The San Juan Islands are part of Washington state, and form the core of ...
. Upon reaching the Strait of Georgia, the border turns due north and then towards the northwest, bisecting the strait until the 49th parallel north. After making a sharp turn eastbound, the border follows this parallel across the Tsawwassen Peninsula, separating Point Roberts, Washington
Point Roberts is a pene-exclave of Washington on the southernmost tip of the Tsawwassen peninsula, south of Vancouver, Canada. The area, which had a population of 1,191 at the 2020 census, is reached by land from the rest of the United States ...
from Delta, British Columbia
Delta is a city in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia, Canada, as part of Greater Vancouver. Located on the Fraser Lowland south of Fraser River's south arm, it is bordered by the city of Richmond on the Lulu Island to the north, N ...
, and continues into Alberta.
Prairies
 The entire Canada–U.S. border in the provinces of both Alberta and Saskatchewan lie on the 49th parallel north.
The entire Canada–U.S. border in the provinces of both Alberta and Saskatchewan lie on the 49th parallel north.Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columb ...
, while, farther east, Saskatchewan also shares a border with North Dakota
North Dakota () is a U.S. state in the Upper Midwest, named after the indigenous Dakota Sioux. North Dakota is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba to the north and by the U.S. states of Minnesota to the east, So ...
.Manitoba
, image_map = Manitoba in Canada 2.svg
, map_alt = Map showing Manitoba's location in the centre of Southern Canada
, Label_map = yes
, coordinates =
, capital = Winn ...
lies on the 49th parallel north. At the province's eastern end, however, the border briefly enters the Lake of the Woods, turning north at where it continues into land along the western end of Minnesota's Northwest Angle, the only part of the United States besides the state of Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S. ...
that is north of the 49th parallel. The border reaches Ontario at .
Ontario
 The province of Ontario shares its border (west to east) with the U.S. states of Minnesota,
The province of Ontario shares its border (west to east) with the U.S. states of Minnesota, Michigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
, Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
, and New York. The largest provincial international border, most of the border is a water boundary. It begins at the north-westernmost point of Minnesota's Northwest Angle (). From here, it proceeds eastward through the Angle Inlet into the Lake of the Woods, turning southward at where it continues into the Rainy River.Rainy Lake
Rainy Lake ( French: '; Ojibwe: ') is a freshwater lake with a surface area of that straddles the border between the United States and Canada. The Rainy River issues from the west side of the lake and is harnessed to make hydroelectricity for ...
, then subsequently through various smaller lakes, including Namakan Lake, Lac la Croix, and Sea Gull Lake, until it reaches the Pigeon River, which leads it out into Lake Superior. The border continues through Lake Superior and Whitefish Bay
Whitefish Bay is a large bay on the eastern end of Lake Superior between Michigan, United States, and Ontario, Canada. It is located between Whitefish Point in Michigan and Whiskey Point along the more rugged, largely wilderness Canadian Shield o ...
, into the St. Mary's River then the North Channel. At , the border turns southward into the False Detour Channel
The False Detour Channel is a short channel in Lake Huron, connecting the main body of the lake to the North Channel. Retrieved 2013-03-30 The Canada–United States border passes roughly through the middle of the channel, which separates Michiga ...
, from which it reaches Lake Huron. Through the Lake, the border heads southward until reaching the St. Clair River
The St. Clair River (french: Rivière Sainte-Claire) is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed November 7, 2011 river in central North America which flows from Lake Huron int ...
, leading it to Lake St. Clair. The border proceeds through Lake St. Clair, reaching the Detroit River
The Detroit River flows west and south for from Lake St. Clair to Lake Erie as a strait in the Great Lakes system. The river divides the metropolitan areas of Detroit, Michigan, and Windsor, Ontario—an area collectively referred to as Detro ...
, which leads it to Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also h ...
. From Lake Erie the border is led into the Niagara River, which takes it into Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The Canada–United States border ...
. From here, the boundary heads northwestward until it reaches , where it makes a sharp turn towards the northeast. The border then reaches the St. Lawrence River, proceeding through it until finally, at , the border splits from the river and continues into Quebec.
Quebec
The province of Quebec borders (west to east) the U.S. states of New York, Vermont, New Hampshire, and Maine, beginning where the Ontario-New York border ends in the St. Lawrence River at the 45th parallel north. This border heads inland towards the east, remaining on or near the parallel. At , the border begins to follow various natural features of the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
, continuing to do so until , where it begins to head northbound, then northeastward at . Finally, at , the border heads toward Beau Lake
Beau may refer to:
*Beau (name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name, nickname or surname
*Beau (guitarist) (born 1946), songwriter and 12-string guitar specialist
*Beau (grape), another name for the Italian wine grape Tr ...
, going through it and continuing into New Brunswick.
New Brunswick
The entire border of New Brunswick is shared with the U.S. state of Maine, beginning at the southern tip of Beau Lake at , subsequently proceeding to the Saint John River. The border moves through the River until , where it splits from the river and heads southward into the Chiputneticook Lakes The Chiputneticook Lakes are a group of several lakes along the international boundary between Maine and New Brunswick.
They are East Grand Lake, North Lake, Mud Lake, Spednic Lake, and Palfrey Lake.
This lake system forms the head waters of t ...
at , which subsequently leads the border to the St. Croix River. The border proceeds through the St. Croix to Passamaquoddy Bay
Passamaquoddy Bay (french: Baie de Passamaquoddy) is an inlet of the Bay of Fundy, between the U.S. state of Maine and the Canadian province of New Brunswick, at the mouth of the St. Croix River. Most of the bay lies within Canada, with its w ...
, which then leads it to Grand Manan Island
Grand Manan is a Canadian island in the Bay of Fundy. Grand Manan is also the name of an incorporated village, which includes the main island and all of its adjacent islands, except White Head Island. It is governed as a village and is part of t ...
into the middle of the Bay of Fundy. Here, the border turns towards the south and terminates upon reaching international waters.
Crossings and border straddling
Airports
The U.S. maintains pre-clearance facilities (i.e. immigration offices) at eight Canadian airports with international air service to the United States: Calgary; Edmonton
Edmonton ( ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city ancho ...
; Halifax Stanfield; Montreal–Trudeau; Ottawa Macdonald–Cartier; Toronto Island Airport (Billy Bishop Airport), Toronto–Pearson, Vancouver
Vancouver ( ) is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the ...
; and Winnipeg James Armstrong Richardson. These procedures expedite travel by allowing flights originating in Canada to land at a U.S. airport without being processed as an international arrival. Canada does not maintain equivalent personnel at U.S. airports due to the sheer number of Canada-bound flights from numerous U.S. departure locations.
Cross-border airports
One curiosity on the Canada–U.S. border is the presence of six airports and eleven seaplane bases whose runways straddle the borderline. Such airports were built prior to the U.S. entry into World War II as a way to legally transfer U.S.-built aircraft, such as the Lockheed Hudson
The Lockheed Hudson is a light bomber and coastal reconnaissance aircraft built by the American Lockheed Aircraft Corporation. It was initially put into service by the Royal Air Force shortly before the outbreak of the Second World War and p ...
, to Canada under the provisions of the ''Lend-Lease Act''. In the interest of maintaining neutrality, U.S. military pilots were forbidden to deliver combat aircraft to Canada. As result, the aircraft were flown to the border, where they landed, then were towed on their wheels over the border by tractors or horses overnight. The next day, the planes were crewed by RCAF
The Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF; french: Aviation royale canadienne, ARC) is the air and space force of Canada. Its role is to "provide the Canadian Forces with relevant, responsive and effective airpower". The RCAF is one of three environm ...
pilots and flown to other locations, typically airbases in Eastern Canada
Eastern Canada (also the Eastern provinces or the East) is generally considered to be the region of Canada south of the Hudson Bay/ Strait and east of Manitoba, consisting of the following provinces (from east to west): Newfoundland and Labrado ...
and Newfoundland, from where they were flown to the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
and deployed in the Battle of Britain
The Battle of Britain, also known as the Air Battle for England (german: die Luftschlacht um England), was a military campaign of the Second World War, in which the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the Fleet Air Arm (FAA) of the Royal Navy defende ...
.

Piney Pinecreek Border Airport
Piney Pinecreek Border Airport is a public use general aviation airport located northwest of the central business district of Pinecreek, in Dieter Township, Roseau County, Minnesota, United States, on the Canada–US border. It is jointly own ...
is located in Piney, Manitoba and Pinecreek, Minnesota. The northwest–southeast-oriented runway straddles the border, and there are two ramps: one in the U.S. and one in Canada. The airport is owned by the Minnesota Department of Transportation.[Simpson, Victoria. 2020.]
4 Airports Shared By The U.S. And Canada
" ''WorldAtlas''. Retrieved April 29, 2020.
International Peace Garden Airport is located in Boissevain, Manitoba and Dunseith, North Dakota
Dunseith ( ) is a city in Rolette County, North Dakota, United States. The population was 632 at the 2020 census. Dunseith is best known for its proximity to the International Peace Garden. The port of entry at the Peace Garden is one of three ...
adjacent to the International Peace Garden
The International Peace Garden is a park located adjacent to the International Peace Garden Border Crossing along the Canada–United States border between the province of Manitoba and the state of North Dakota. It was established on July 14, ...
. The runway is entirely within North Dakota, but a ramp extends across the border to allow aircraft to access Canadian customs. While not jointly owned, it is operated as an international facility for customs clearance as part of the Peace Garden.
Coronach/Scobey Border Station Airport
Coronach/Scobey Border Station Airport is located southeast of Coronach, Saskatchewan, Canada and north of Scobey, Montana, United States. In the United States, the airport is known by the names Scobey Border Station Airport and East Popla ...
(or East Poplar Airport) is located in Coronach, Saskatchewan
Coronach is a community in southern Saskatchewan, Canada near the Canada–US border. It was founded in 1926 by the Canadian Pacific Railway and named after Coronach, the horse who had just won The Derby in England that year. Coronach was of ...
and Scobey, Montana
Scobey is a city in and the county seat of Daniels County, Montana, United States. The population was 999 at the 2020 census.
Scobey is known for its bird and big game hunting. The nearby Mansfield A. Daniels House is listed on the NRHP.
Hi ...
. The airport is jointly owned by the Canadian and U.S. government, with its east–west runway sited exactly on the borderline.
Coutts/Ross International Airport is located in Alberta and Montana. Like Coronach/Scobey, the east–west runway is sited exactly on the border. The airport is owned entirely by the Montana Department of Transportation (DOT) Aeronautics Division.
Del Bonita/Whetstone International Airport, located in Del Bonita, Alberta
Del Bonita is a hamlet in southern Alberta, Canada within Cardston County. It is located approximately south of Magrath at the junction of Highway 62 and Highway 501. Due to its location near the Canada–United States border, it serves as a p ...
and Del Bonita, Montana, has an east–west runway sited exactly on the border, similar to Coutts/Ross. The airport is officially owned by the state of Montana and run by the state's DOT Aeronautics Division, thus it has been assigned a U.S. identifier only. The facility is set up for both the general public (15 passengers maximum per plane) as well as the American military
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is the ...
.Sault Ste. Marie Water Aerodrome
Sault Ste. Marie Water Aerodrome is located adjacent on the St. Marys River in Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, Canada. It shares its airspace and waterway with neighbouring Sault Ste Marie International Seaplane Base in the United States.
Sault S ...
(Michigan / Ontario)
* Sand Point Lake Water Aerodrome (Minnesota / Ontario)
* International Falls SPB and Fort Frances Water Aerodrome (Minnesota / Ontario)
* Baudette International Airport and Rainy River Water Aerodrome (Minnesota / Ontario)
* Hyder Seaplane Base
Hyder Seaplane Base is a state owned, public use seaplane base located one nautical mile (2 km) southeast of the central business district of Hyder, a community in the Prince of Wales-Hyder Census Area of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is i ...
and Stewart Water Aerodrome
Stewart Water Aerodrome is located on the Portland Canal, south of Stewart, British Columbia, Canada. It shares its airspace with the nearby Stewart Aerodrome and Hyder Seaplane Base, and its water runway in the Portland Canal
, image = Hyd ...
(Alaska / British Columbia)
Land border crossings
 Currently there are 119 legal land border crossings between the United States and Canada, 26 of which take place at a bridge or tunnel. Only 2 of the 119 crossings are one-way: the Churubusco–Franklin Centre Border Crossing, where travelers may enter only the United States; and the
Currently there are 119 legal land border crossings between the United States and Canada, 26 of which take place at a bridge or tunnel. Only 2 of the 119 crossings are one-way: the Churubusco–Franklin Centre Border Crossing, where travelers may enter only the United States; and the Four Falls Border Crossing
The Four Falls Border Crossing is a one-way crossing between Fort Fairfield, Maine and Four Falls, New Brunswick on the Canada–US border. Traffic is seasonally permitted to enter Canada at this location, but people entering the United States ...
, where travelers may enter only Canada.
There are six roads that have unstaffed road crossings, and do not have border inspection services in one or both directions, where travelers are legally allowed to cross the border. Those that cross are required to report to customs, which are stationed farther within.
Trail crossings
The Fourth Connecticut Lake Trail (New Hampshire/Quebec) crosses several times while following the border vista before heading back to the United States.
= Rail crossings
=
There are 39 railroads
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prep ...
that cross the U.S.–Canada border, nine of which are no longer in use. Eleven of these railroads cross the border at a bridge or tunnel.
Only three international rail lines currently carry passengers between the U.S. and Canada. At Vancouver's Pacific Central Station
Pacific Central Station is a railway station in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, which acts as the western terminus of Via Rail's cross-country '' The Canadian'' service to Toronto and the northern terminus of Amtrak's '' Cascades'' service t ...
, passengers are required to pass through U.S. partial pre-clearance and pass their baggage through an X-ray machine
An X-ray machine is any machine that involves X-rays. It may consist of an X-ray generator and an X-ray detector.
Examples include:
*Machines for medical projectional radiography
*Machines for computed tomography
*Backscatter X-ray machines, used ...
before being allowed to board the Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in both the state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest regio ...
-bound Amtrak ''Cascades'' train, which makes no further stops before crossing the border at Blaine, Washington, where the train stops for another CBP inspection. Pre-clearance facilities are not available for the popular ''Adirondack'' (New York City to Montreal) or ''Maple Leaf'' (New York City to Toronto) trains, since these lines have stops between Montreal or Toronto and the border. Instead, passengers must clear customs at a stop located at the actual border.
Seaports
 There are 13 international ferry crossings operating between the U.S. and Canada. Two of them carry passengers only and one carries only rail cars. Four of the ferries operate only on a seasonal basis.
Similar to that of the pre-clearance facilities at Canadian airports, arrangements exist at major Canadian
There are 13 international ferry crossings operating between the U.S. and Canada. Two of them carry passengers only and one carries only rail cars. Four of the ferries operate only on a seasonal basis.
Similar to that of the pre-clearance facilities at Canadian airports, arrangements exist at major Canadian seaports
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ha ...
that handle sealed direct import shipments into the U.S. Along the East coast, ferry services operate between the province of New Brunswick and the state of Maine, while on the West coast, they operate between British Columbia and the states of Washington and Alaska. There are also several ferry services in the Great Lakes operating between the province of Ontario and the states of Michigan, New York, and Ohio. The ferry between Maine and Nova Scotia ended its operations in 2009, resuming again in 2014.
On Heart Island
Heart Island is an island in the Town of Alexandria within the Saint Lawrence River, along the northern border of the U.S. state of New York, in Jefferson County. The island is one of the most prominent within the Thousand Islands archipelago ...
in the St. Lawrence River, the Boldt Castle
Boldt Castle is a major landmark and tourist attraction in the Thousand Islands region of the U.S. state of New York. Open to guests seasonally between mid-May and mid-October, it is located on Heart Island in the Saint Lawrence River. Heart I ...
has a border control point with no specific location on the Canadian side. As such, Canadians must present identification to land on the island.
Cross-border buildings
 A
A line house
A line house is a building deliberately located so that an international boundary passes through it. One such building on the boundary between the United States and Canada is the Haskell Free Library and Opera House in Stanstead, Quebec, and De ...
is a building located so that an international boundary passes through it. There are several such buildings that exist along the U.S.–Canada border:
* The Haskell Free Library and Opera House
, image = HaskellFreeLibraryandOperaHouse.JPG
, caption = Haskell Free Library and Opera House in 2012
, location = Stanstead, Quebec, CanadaDerby Line, Vermont, U.S.
, coordinates =
, area =
, architect = Nate Beach & James Ball
, a ...
straddles the border in Derby Line, Vermont
Derby Line is an incorporated village in the town of Derby in Orleans County, Vermont, United States, slightly north of the 45th parallel, the nominal U.S.-Canada boundary. The population was 687 at the 2020 census.
The village is located o ...
, and Stanstead, Quebec.
* Private homes divided by the boundary line between Estcourt Station, Maine, and Pohénégamook, Quebec.
* Private homes divided between Beebe Plain, Quebec
Stanstead is a town in the Memphrémagog Regional County Municipality in the Estrie region of Quebec, located on the Canada–United States border across from Derby Line, Vermont.
The Town of Stanstead was created in 1995 by the merger of the ...
and Beebe Plain, Vermont
Beebe Plain is an unincorporated community in the town of Derby in Orleans County, Vermont, United States, which extends into the municipality of Stanstead, Quebec, Canada. The village is divided by the Canada–United States border between Ca ...
;
* A seasonal home divided at the intersection of Matthias Lane in Alburgh, Vermont, and Chemin au Bord de l'Eau in Noyan, Quebec;
* A house divided between Richford, Vermont
Richford is a town in Franklin County, Vermont, United States, located along the Canada–United States border. The population was 2,346 at the 2020 census.
Richford is the birthplace of R. G. LeTourneau, an industrialist who founded LeTourneau ...
, and Abercorn, Quebec.
* The Halfway House (also known as Taillon's International Hotel) is a tavern, built in 1820 before the border was surveyed, that straddles the border between Dundee, Quebec
Dundee is a township municipality in Le Haut-Saint-Laurent Regional County Municipality in the Montérégie administrative region of Quebec, Canada. At the Canada 2021 Census, the population was 386. It is primarily an agricultural area consisti ...
, and Fort Covington, New York.
The Maine–New Brunswick border divides the Aroostook Valley Country Club
The Aroostook Valley Country Club is a golf course which straddles the Canada–US border, between the U.S. state of Maine and the Canadian province of New Brunswick. The club, located near Perth-Andover, New Brunswick and Fort Fairfield, Ma ...
.
Boundary divisions
Practical exclaves
To be a true international exclave, ''all'' potential paths of travel from the exclave to the home country must cross over only the territory of a different country or countries. Like exclaves, practical exclaves are not contiguous with the ''land'' of the home country and have ''land'' access only through another country or countries. Unlike exclaves, they are not ''entirely'' surrounded by foreign territory. Hence, they are exclaves ''for practical purposes'', without meeting the strict definition.
The term ''pene-exclave,'' also known as a "functional" or "practical" exclave,Point Roberts, Washington
Point Roberts is a pene-exclave of Washington on the southernmost tip of the Tsawwassen peninsula, south of Vancouver, Canada. The area, which had a population of 1,191 at the 2020 census, is reached by land from the rest of the United States ...
: "Although physical connections by water with Point Roberts are entirely within the sovereignty of the United States, land access is only possible through Canada."
Practical exclaves of Canada
 The Quebec western portion of the Akwesasne reserve is a practical exclave of Canada because of the St. Lawrence River to the north, the St. Regis River to the east, New York State, U.S. to the south. To travel by land to elsewhere in Canada, one must drive through New York State.
The Quebec western portion of the Akwesasne reserve is a practical exclave of Canada because of the St. Lawrence River to the north, the St. Regis River to the east, New York State, U.S. to the south. To travel by land to elsewhere in Canada, one must drive through New York State.
Campobello Island
Campobello Island (, also ) is the largest and only inhabited island in Campobello, a civil parish in southwestern New Brunswick, Canada, near the border with Maine, United States. The island's permanent population in 2021 was 949. It is the s ...
is another practical exclave located at the entrance to Passamaquoddy Bay
Passamaquoddy Bay (french: Baie de Passamaquoddy) is an inlet of the Bay of Fundy, between the U.S. state of Maine and the Canadian province of New Brunswick, at the mouth of the St. Croix River. Most of the bay lies within Canada, with its w ...
, adjacent to the entrance to Cobscook Bay
Cobscook Bay is located in Washington County in the state of Maine. It opens into Passamaquoddy Bay, within the Bay of Fundy. Cobscook Bay is immediately south of the island city of Eastport, the main island of which (Moose Island) straddles the ...
, and within the Bay of Fundy. The island is part of Charlotte County, New Brunswick, but is actually physically connected by the Franklin Delano Roosevelt Bridge with Lubec, Maine
Lubec ( ) is a town in Washington County, Maine, United States. It is the easternmost municipality in the contiguous U.S. (see extreme points of the United States) and is the country's closest continental location to Africa.
The town, with a ...
, the easternmost tip of the continental United States.
Premier, British Columbia is an abandoned mining site accessible only through Hyder, Alaska.
Practical exclaves of the United States
 Alaska is a non-contiguous U.S. state bounded by the Bering Sea; the
Alaska is a non-contiguous U.S. state bounded by the Bering Sea; the Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, N ...
and Pacific oceans; and Canada's British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
and Yukon Territory
Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as ...
. Additionally, because of the terrain, several municipalities in southeast Alaska (the "Panhandle") are inaccessible by road, except via Canada. Specifically, the town of Hyder, Alaska
Hyder is a census-designated place in Prince of Wales-Hyder Census Area, Alaska, United States. The population was 87 at the 2010 census, down from 97 in 2000. Hyder is accessible by road only from Stewart, British Columbia, is popular with mot ...
, is accessible only through Stewart, British Columbia, or by floatplane. Moreover, Haines and Skagway are accessible by road only through Canada, although there are car ferries which connect them to other Alaskan places.
Point Roberts, Washington
Point Roberts is a pene-exclave of Washington on the southernmost tip of the Tsawwassen peninsula, south of Vancouver, Canada. The area, which had a population of 1,191 at the 2020 census, is reached by land from the rest of the United States ...
is bounded by British Columbia, the Strait of Georgia, and Boundary Bay.
In Minnesota, Elm Point, two small pieces of land to its west (Buffalo Bay Point), and the Northwest Angle are bounded by the province of Manitoba
, image_map = Manitoba in Canada 2.svg
, map_alt = Map showing Manitoba's location in the centre of Southern Canada
, Label_map = yes
, coordinates =
, capital = Winn ...
and Lake of the Woods.
In Vermont, the Alburgh Tongue, as well as Province Point, which is the small end of a peninsula east of Alburgh
Alburgh is a village and civil parish in the English county of Norfolk. It lies about four miles (6 km) north-east of Harleston and 16 miles (26 km) south of Norwich.
Heritage
The earliest evidence of settlement is from the Mesolith ...
, are bounded by Quebec and Lake Champlain.
Split features
Between Quebec and Vermont, Province Island is a piece of land that primarily lies in Canada, though a small portion of the island is situated in the U.S. state, lying south of the 45th parallel with a border vista marking the international boundary.
Canusa Street
Canusa Street (french: rue Canusa) is the only part of the Canada–United States border that runs down the middle of a street. The street separates Beebe Plain, Vermont, in the United States, from the Beebe Plain area of Stanstead, Quebec, ...
in Beebe Plain, VT is the only portion of the Canada–United States border split down the middle of a street.
Between North Dakota
North Dakota () is a U.S. state in the Upper Midwest, named after the indigenous Dakota Sioux. North Dakota is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba to the north and by the U.S. states of Minnesota to the east, So ...
and Manitoba, the international border splits a peninsula within a lake on the border of Rolette County, North Dakota, and the Wakopa Wildlife Management Area
Wakopa Wildlife Management Area is a wildlife management area located near Turtle Mountain Provincial Park, Manitoba, Canada. It was established in 2006 under the Manitoba Wildlife Act. It is in size.
See also
* List of wildlife management are ...
, MB. Likewise, Lake Metigoshe
Lake Metigoshe is a lake in both Bottineau County, North Dakota and the Rural Municipality of Winchester, Manitoba. The lake has a maximum depth of . It is located in the Turtle Mountains on the Canada–United States border
The border ...
, lying in the Township of Roland, borders the municipality of Winchester, Manitoba. The border splits a shoreline, putting Canadian cabins on one side and the beach and boat docks for those cabins on the U.S. side, while land access is only through Canada.
Remaining boundary disputes
 *
* Machias Seal Island
Machias Seal Island is an island in disputed water between the Gulf of Maine and the Bay of Fundy, about southeast from Cutler, Maine, and southwest of Grand Manan Island, New Brunswick. Sovereignty of the island is disputed by the United Sta ...
and North Rock
North Rock (french: Roche North) is an offshore rock near the boundary between the Gulf of Maine and the Bay of Fundy east of the North American continent. Its ownership is disputed between the Canadian province of New Brunswick and the U.S. sta ...
(Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and ...
/ New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only province with both English and ...
)
* Dixon Entrance
The Dixon Entrance (french: Entrée Dixon) is a strait about long and wide in the Pacific Ocean at the Canada–United States border, between the U.S. state of Alaska and the province of British Columbia in Canada. The Dixon Entrance is part o ...
(Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S. ...
/ British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
)
* Beaufort Sea (Alaska / Yukon
Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as ...
)
* Strait of Juan de Fuca
The Strait of Juan de Fuca (officially named Juan de Fuca Strait in Canada) is a body of water about long that is the Salish Sea's outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre ...
(Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
/ British Columbia)
See also
* Canada Border Services Agency
*United States Customs and Border Protection
United States Customs and Border Protection (CBP) is the largest federal law enforcement agency of the United States Department of Homeland Security. It is the country's primary border control organization, charged with regulating and facilit ...
** United States Border Patrol interior checkpoints
* Canada–United States relations
* Illegal immigration to Canada
Illegal immigration to Canada (also called Irregular immigration to Canada, though this terminology is contested) is the act of a person who is not a Canadian citizen or permanent resident entering or remaining in Canada in a manner contrary t ...
* Illegal immigration to the United States
* Indian barrier state, British plans to set up a new country in the Old Northwest
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolutionary War. Established in 1 ...
* John Lewis Tiarks, a British surveyor of the border
* Joseph Smith Harris
Joseph Smith Harris (April 29, 1836 – June 1, 1910) was an American surveyor, civil engineer, and railroad executive. Largely self-taught, he worked on several projects for the U.S. government, including the Coast Survey of the Mississippi ...
' account of the Northwest Boundary Survey
* Mexico–United States border
The Mexico–United States border ( es, frontera Estados Unidos–México) is an international border separating Mexico and the United States, extending from the Pacific Ocean in the west to the Gulf of Mexico in the east. The border trave ...
Footnotes
References
Citations
Further reading
* Anderson, Christopher G. 2012.
Canadian Liberalism and the Politics of Border Control, 1867–1967
'. Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press
The University of British Columbia Press (UBC Press) is a university press that is part of the University of British Columbia. It was established in 1971. The press is based in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, and has editorial offices in Kelo ...
. Studies pivotal episodes in Canadian immigration policy that shed light on more restrictive approaches today.
* Hunt, Courtney. 2008. '' Frozen River''. edited by Kate Williams. US: Sony Pictures Classics
Sony Pictures Classics Inc. is an American film production and distribution company that is a division of Sony Pictures. It was founded in 1992 by former Orion Classics heads Michael Barker, Tom Bernard and Marcie Bloom. It distributes, produce ...
. A feature film about smuggling across the border
* Paulus, Jeremy, and Ali Asgary. 2010.
Enhancing Border Security: Local Values and Preferences at the Blue Water Bridge (Point Edward, Canada)
" ''Journal of Homeland Security and Emergency'' ''Management'' 7(1): article 77.
*University of Kent
, motto_lang =
, mottoeng = Literal translation: 'Whom to serve is to reign'(Book of Common Prayer translation: 'whose service is perfect freedom')Graham Martin, ''From Vision to Reality: the Making of the University of Kent at Canterbury'' ...
. 2015.
Culture and the Canada–US Border
'' funded by Leverhulme Trust
The Leverhulme Trust () is a large national grant-making organisation in the United Kingdom. It was established in 1925 under the will of the 1st Viscount Leverhulme (1851–1925), with the instruction that its resources should be used to suppo ...
. An international research network dedicated to studying cultural representation, production and exchange on and around the Canada–US border.
External links
International Boundary Commission
{{DEFAULTSORT:Canada-United States Border
Borders of Canada
Borders of the United States
Canada–United States relations
International borders
 Signed in December 1814, the Treaty of Ghent ended the War of 1812, returning the boundaries of British North America and the United States to the state they were prior to the war. In the following decades, the United States and the United Kingdom concluded several treaties that settled the major boundary disputes between the two, enabling the border to be demilitarized. The
Signed in December 1814, the Treaty of Ghent ended the War of 1812, returning the boundaries of British North America and the United States to the state they were prior to the war. In the following decades, the United States and the United Kingdom concluded several treaties that settled the major boundary disputes between the two, enabling the border to be demilitarized. The  An 1844 boundary dispute during the Presidency of James K. Polk led to a call for the northern boundary of the U.S. west of the Rockies to be 54°40′N related to the southern boundary of Russia's Alaska Territory. However, Great Britain wanted a border that followed the Columbia River to the Pacific Ocean. The dispute was resolved in the Oregon Treaty of 1846, which established the 49th parallel as the boundary through the Rockies.
An 1844 boundary dispute during the Presidency of James K. Polk led to a call for the northern boundary of the U.S. west of the Rockies to be 54°40′N related to the southern boundary of Russia's Alaska Territory. However, Great Britain wanted a border that followed the Columbia River to the Pacific Ocean. The dispute was resolved in the Oregon Treaty of 1846, which established the 49th parallel as the boundary through the Rockies.
 In response to the
In response to the  Parts of the International Boundary cross through mountainous terrain or heavily forested areas, but significant portions also cross remote prairie farmland and the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence River, in addition to the maritime components of the boundary at the
Parts of the International Boundary cross through mountainous terrain or heavily forested areas, but significant portions also cross remote prairie farmland and the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence River, in addition to the maritime components of the boundary at the  Smuggling of
Smuggling of 
 The entire Canada–U.S. border in the provinces of both Alberta and Saskatchewan lie on the 49th parallel north. Both provinces share borders with the state of
The entire Canada–U.S. border in the provinces of both Alberta and Saskatchewan lie on the 49th parallel north. Both provinces share borders with the state of  The province of Ontario shares its border (west to east) with the U.S. states of Minnesota,
The province of Ontario shares its border (west to east) with the U.S. states of Minnesota, 
 Currently there are 119 legal land border crossings between the United States and Canada, 26 of which take place at a bridge or tunnel. Only 2 of the 119 crossings are one-way: the Churubusco–Franklin Centre Border Crossing, where travelers may enter only the United States; and the
Currently there are 119 legal land border crossings between the United States and Canada, 26 of which take place at a bridge or tunnel. Only 2 of the 119 crossings are one-way: the Churubusco–Franklin Centre Border Crossing, where travelers may enter only the United States; and the  There are 13 international ferry crossings operating between the U.S. and Canada. Two of them carry passengers only and one carries only rail cars. Four of the ferries operate only on a seasonal basis.
Similar to that of the pre-clearance facilities at Canadian airports, arrangements exist at major Canadian
There are 13 international ferry crossings operating between the U.S. and Canada. Two of them carry passengers only and one carries only rail cars. Four of the ferries operate only on a seasonal basis.
Similar to that of the pre-clearance facilities at Canadian airports, arrangements exist at major Canadian  A
A  The Quebec western portion of the Akwesasne reserve is a practical exclave of Canada because of the St. Lawrence River to the north, the St. Regis River to the east, New York State, U.S. to the south. To travel by land to elsewhere in Canada, one must drive through New York State.
The Quebec western portion of the Akwesasne reserve is a practical exclave of Canada because of the St. Lawrence River to the north, the St. Regis River to the east, New York State, U.S. to the south. To travel by land to elsewhere in Canada, one must drive through New York State.
 Alaska is a non-contiguous U.S. state bounded by the Bering Sea; the
Alaska is a non-contiguous U.S. state bounded by the Bering Sea; the  *
*