TLR 4 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Toll-like receptor 4 is a
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
that in humans is encoded by the ''TLR4'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
. TLR4 is a transmembrane protein, member of the toll-like receptor
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. They are single-pass membrane-spanning receptors usually expressed on sentinel cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells, that recognize ...
family, which belongs to the pattern recognition receptor
Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) play a crucial role in the proper function of the innate immune system. PRRs are germline-encoded host sensors, which detect molecules typical for the pathogens. They are proteins expressed, mainly, by cells of ...
(PRR) family. Its activation leads to an intracellular signaling pathway NF-κB
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) is a protein complex that controls transcription of DNA, cytokine production and cell survival. NF-κB is found in almost all animal cell types and is involved in cellular ...
and inflammatory cytokine production which is responsible for activating the innate immune system
The innate, or nonspecific, immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies (the other being the adaptive immune system) in vertebrates. The innate immune system is an older evolutionary defense strategy, relatively speaking, and is the ...
.
TLR4 expressing cells are myeloid
Myeloid tissue, in the bone marrow sense of the word '' myeloid'' ('' myelo-'' + '' -oid''), is tissue of bone marrow, of bone marrow cell lineage, or resembling bone marrow, and myelogenous tissue (''myelo-'' + '' -genous'') is any tissue o ...
(erythrocytes, granulocytes, macrophages) rather than lymphoid
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid o ...
(T-cells, B-cells, NK cells). Most myeloid cells also express high levels of CD14
CD14 (cluster of differentiation 14) is a human protein made mostly by macrophages as part of the innate immune system. It helps to detect bacteria in the body by binding lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP). ...
, which facilitates activation of TLR4 by LPS.
It is most well known for recognizing lipopolysaccharide
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide that are bacterial toxins. They are composed of an O- antigen, an outer core, and an inner core all joined by a covalent bond, and are found in the out ...
(LPS), a component present in many Gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall ...
(e.g. ''Neisseria'' spp.) and selected Gram-positive bacteria
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.
Gram-positive bac ...
. Its ligands also include several viral proteins, polysaccharide, and a variety of endogenous proteins such as low-density lipoprotein, beta-defensins, and heat shock protein. Palmitic acid
Palmitic acid (hexadecanoic acid in IUPAC nomenclature) is a fatty acid with a 16-carbon chain. It is the most common saturated fatty acid found in animals, plants and microorganisms.Gunstone, F. D., John L. Harwood, and Albert J. Dijkstra. The ...
and lauric acid
Lauric acid, systematically dodecanoic acid, is a saturated fatty acid with a 12-carbon atom chain, thus having many properties of medium-chain fatty acids. It is a bright white, powdery solid with a faint odor of bay oil or soap. The salts and ...
are also a TLR4 agonists
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agon ...
, and chronic inflammatory responses via cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in au ...
release can result from high dietary intake of these nutrients. However, unsaturated omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids serve as TLR4 antagonists and can negate the inflammation caused by a high-fat diet.
TLR4 has also been designated as CD284 (cluster of differentiation
The cluster of differentiation (also known as cluster of designation or classification determinant and often abbreviated as CD) is a protocol used for the identification and investigation of cell surface molecules providing targets for immunophen ...
284). The molecular weight of TLR4 is approximately 95 kDa.
Function
TLR4 is a member of thetoll-like receptor
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. They are single-pass membrane-spanning receptors usually expressed on sentinel cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells, that recognize ...
(TLR) family, which plays a fundamental role in pathogen recognition and activation of innate immunity
The innate, or nonspecific, immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies (the other being the adaptive immune system) in vertebrates. The innate immune system is an older evolutionary defense strategy, relatively speaking, and is the ...
. They recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns ( PAMPs) that are expressed on infectious agents, and mediate the production of cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in au ...
s necessary for the development of effective immunity. TLRs are highly conserved from plants to ''Drosophila
''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many speci ...
'' to humans and share structural and functional similarities.
The various TLRs exhibit different patterns of expression. This receptor is most abundantly expressed in placenta
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas and waste exchange between the physically separate mate ...
, and in myelomonocytic subpopulation of the leukocytes
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mu ...
.
It cooperates with LY96
Lymphocyte antigen 96, also known as "Myeloid Differentiation factor 2 (MD-2)," is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LY96'' gene.
The protein encoded by this gene is involved in binding lipopolysaccharide with Toll-Like Receptor (TLR4 ...
(also referred as MD-2) and CD14
CD14 (cluster of differentiation 14) is a human protein made mostly by macrophages as part of the innate immune system. It helps to detect bacteria in the body by binding lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP). ...
to mediate in signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellula ...
events induced by lipopolysaccharide
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide that are bacterial toxins. They are composed of an O- antigen, an outer core, and an inner core all joined by a covalent bond, and are found in the out ...
(LPS) found in most gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall ...
. Mutations in this gene have been associated with differences in LPS responsiveness.
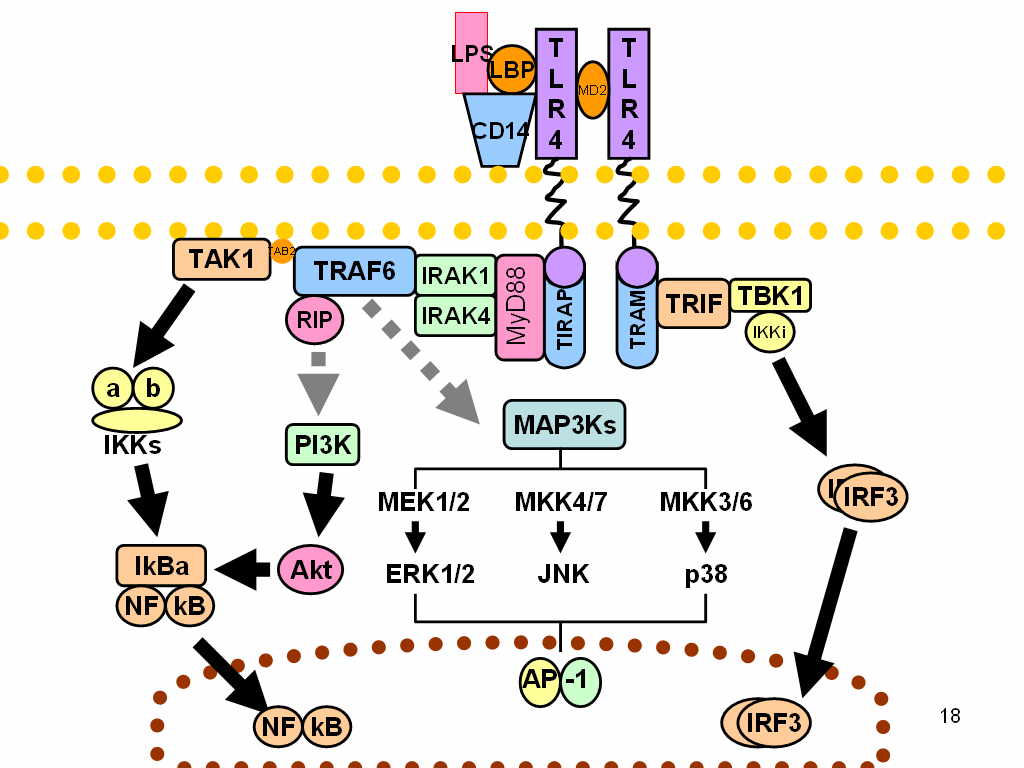
TLR4 signaling responds to signals by forming a complex using an extracellular leucine-rich repeat domain (LRR) and an intracellular toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain. LPS stimulation induces a series of interactions with several accessory proteins which form the TLR4 complex on the cell surface. LPS recognition is initiated by an LPS binding to an LBP protein. This LPS-LBP complex transfers the LPS to CD14
CD14 (cluster of differentiation 14) is a human protein made mostly by macrophages as part of the innate immune system. It helps to detect bacteria in the body by binding lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP). ...
. CD14
CD14 (cluster of differentiation 14) is a human protein made mostly by macrophages as part of the innate immune system. It helps to detect bacteria in the body by binding lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP). ...
is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane protein that binds the LPS-LBP complex and facilitates the transfer of LPS to MD-2 protein, which is associated with the extracellular domain of TLR4. LPS binding promotes the dimerization of TLR4/MD-2. The conformational changes of the TLR4 induce the recruitment of intracellular adaptor proteins containing the TIR domain which is necessary to activate the downstream signaling pathway.
Several transcript variants of this gene have been found, but the protein-coding potential of most of them is uncertain.
Most of the reported effects of TLR4 signaling in tumors are pro-carcinogenic mainly due to contributions of proinflammatory cytokine signaling (whose expression is driven by TLR-mediated signals) to tumor-promoting microenvironment.
Signaling
Upon LPS recognition, conformational changes in the TLR4 receptors result in recruitment of intracellular TIR-domains containing adaptor molecules. These adaptors are associated with the TLR4 cluster via homophilic interactions between the TIR domains. There are four adaptor proteins involved in two major intracellular signaling pathways.
MyD88 – dependent pathway
The MyD88-dependent pathway is regulated by two adaptor-associated proteins: Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response Gene 88 ( MyD88) and TIR Domain-Containing Adaptor Protein (TIRAP
TIRAP is an adapter molecule associated with toll-like receptors.
The innate immune system recognizes microbial pathogens through Toll-like receptors (TLRs), which identify pathogen-associated molecular patterns. Different TLRs recognize different ...
). TIRAP-MyD88 regulates early NF-κβ activation and production of proinflammatory cytokine An inflammatory cytokine or proinflammatory cytokine is a type of signaling molecule (a cytokine) that is secreted from immune cells like helper T cells (Th) and macrophages, and certain other cell types that promote inflammation. They include inte ...
s, such as IL-12. MyD88 signaling involves the activation of IL-1 Receptor-Associated Kinases ( IRAKs) and the adaptor molecules TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 6 (TRAF6
TRAF6 is a TRAF human protein.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF receptor associated factor (TRAF) protein family. TRAF proteins are associated with, and mediate signal transduction from members of the TNF recep ...
). TRAF6 induces the activation of TAK1 (Transforming growth factor-β-Activated Kinase 1) that leads to the activation of MAPK cascades (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase) and IKK (IκB Kinase). IKKs' signaling pathway leads to the induction of the transcription factor NF-κB
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) is a protein complex that controls transcription of DNA, cytokine production and cell survival. NF-κB is found in almost all animal cell types and is involved in cellular ...
, while activation of MAPK cascades lead to the activation of another transcription factor AP-1. Both of them have a role in the expression of proinflammatory cytokines. The activation of NF-κB via TAK-1 is complex, and it starts by the assembly of a protein complex called the signalosome, which is made of a scaffolding protein, called NEMO. The protein complex is made from two different κB kinases, called IKKα and IKKβ. This causes the addition of a small regulatory protein to the signalosome called ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. Fo ...
, that acts to initiate the release of the NF-κB protein, which coordinates translocation in the nucleus of cytokines.
MyD88 – independent pathway
This TRIF-dependent pathway involves the recruitment of the adaptor proteins TIR-domain-containing adaptor inducing interferon-β (TRIF
TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β (TRIF) is an adapter in responding to activation of toll-like receptors (TLRs). It mediates the rather delayed cascade of two TLR-associated signaling cascades, where the other one is dependent ...
) and TRIF-related Adaptor Molecule (TRAM). TRAM-TRIF signals activate the transcription factor Interferon Regulatory Factor-3 (IRF3
Interferon regulatory factor 3, also known as IRF3, is an interferon regulatory factor.
Function
IRF3 is a member of the interferon regulatory transcription factor (IRF) family. IRF3 was originally discovered as a homolog of IRF1 and IRF2. ...
) via TRAF3
TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRAF3 gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF receptor associated factor (TRAF) protein family. TRAF proteins associate wit ...
. IRF3 activation induces the production of type 1 interferons.
SARM – TRIF-mediated pathway
A fifth TIR-domain-containing adaptor protein called Sterile α and HEAT (Armadillo motif) (SARM) is a TLR4 signaling pathway inhibitor. SARM activation by LPS-binding inhibits -TRIF-mediated pathways but does not inhibit MyD88-mediated pathways. This mechanism prevents an excessive activation in response to LPS which may lead to inflammation-induced damage such assepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
.
Evolutionary history
TLR4 originated when TLR2 and TLR4 diverged about 500 million years ago near the beginning of vertebrate evolution. Sequence alignments of human and great ape TLR4 exons have demonstrated that not much evolution has occurred in human TLR4 since our divergence from our last common ancestor with chimpanzees; human and chimp TLR4 exons only differ by three substitutions while humans and baboons are 93.5% similar in the extracellular domain. Notably, humans possess a greater number of early stop codons in TLR4 than great apes; in a study of 158 humans worldwide, 0.6% had a nonsense mutation. This suggests that there are weaker evolutionary pressures on the human TLR4 than on our primate relatives. The distribution of human TLR4 polymorphisms matches the out-of-Africa migration, and it is likely that the polymorphisms were generated in Africa before migration to other continents.Interactions
TLR4 has been shown tointeract
Advocates for Informed Choice, doing business as, dba interACT or interACT Advocates for Intersex Youth, is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization using innovative strategies to advocate for the legal and human rights of children with intersex trai ...
with:
* Lymphocyte antigen 96
Lymphocyte antigen 96, also known as "Myeloid Differentiation factor 2 (MD-2)," is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LY96'' gene.
The protein encoded by this gene is involved in binding lipopolysaccharide with Toll-Like Receptor (TL ...
,
* Myd88, and
* TOLLIP
Toll interacting protein, also known as TOLLIP, is an inhibitory adaptor protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TOLLIP'' gene.
Function and regulation
It is an inhibitory adaptor protein within Toll-like receptors (TLR). The TLR pathway i ...
.
* Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow t ...
,
Intracellular trafficking of TLR4 is dependent on the GTPase Rab-11a, and knock down of Rab-11a results in hampered TLR4 recruitment to ''E. coli''-containing phagosomes and subsequent reduced signal transduction through the MyD88-independent pathway.
Clinical significance
Various single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the TLR4 in humans have been identified and for some of them an association with increased susceptibility to Gram-negative bacterial infections or faster progression and a more severe course of sepsis in critically ill patients was reported.In sepsis
TLR4 can be activated by binding to the lipid A portion oflipopolysaccharide
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide that are bacterial toxins. They are composed of an O- antigen, an outer core, and an inner core all joined by a covalent bond, and are found in the out ...
found in Gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall ...
. Exaggerated and uncontrolled inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
triggered by TRL4 during infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
can lead to sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
and septic shock
Septic shock is a potentially fatal medical condition that occurs when sepsis, which is organ injury or damage in response to infection, leads to dangerously low blood pressure and abnormalities in cellular metabolism. The Third International C ...
. Infections with Gram-negative bacteria such as ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Esc ...
'' and ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic– facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. a ...
'' are the prevailing causes of severe sepsis in humans.
In insulin resistance
Fetuin-A facilitates the binding of lipids to receptors, thereby contributing toinsulin resistance
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological condition in which cells fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin.
Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the transport of glucose from blood into cells, thereby reducing blood glucose (blood sugar ...
.
In cancer progression
TLR4 expression can be detected on many tumor cells and cell lines. TLR4 is capable of activatingMAPK
A mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK or MAP kinase) is a type of protein kinase that is specific to the amino acids serine and threonine (i.e., a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase). MAPKs are involved in directing cellular responses to ...
and NF-κB
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) is a protein complex that controls transcription of DNA, cytokine production and cell survival. NF-κB is found in almost all animal cell types and is involved in cellular ...
pathways, implicating possible direct role of cell-autonomous TLR4 signaling in regulation of carcinogenesis, in particular, through increased proliferation of tumor cells, apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes ( morphology) and death. These changes in ...
inhibition and metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, the ...
. TLR4 signaling may also contribute to resistance to paclitaxel
Paclitaxel (PTX), sold under the brand name Taxol among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes ovarian cancer, esophageal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, cervical ca ...
chemotherapy in ovary cancer and siRNA
Small interfering RNA (siRNA), sometimes known as short interfering RNA or silencing RNA, is a class of double-stranded RNA at first non-coding RNA molecules, typically 20-24 (normally 21) base pairs in length, similar to miRNA, and operating ...
therapy in prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer of the prostate. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancerous tumor worldwide and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality among men. The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that su ...
. 63% of breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or ...
patients were reported to express TLR4 on tumor cells and the level of expression inversely correlated with the survival. Additionally, low MyD88 expression correlated with decreased metastasis to the lung and decreased CCL2
''For the ICAO airport code see Candle Lake Airpark, for the diradical compound see Dichlorocarbene.''
The chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2) is also referred to as monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP1) and small inducible cytokine A2. C ...
and CCL5
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5 (also CCL5) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''CCL5'' gene. The gene has been discovered in 1990 by ''in situ'' hybridisation and it is localised on 17q11.2-q12 chromosome. It is also known as RANTE ...
expression. TLR4 expression levels were the highest among TLRs in human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231
Scientists study the behaviour of isolated cells grown in the laboratory for insights into how cells function in the body in health and disease. Experiments using cell culture
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cells are ...
and TLR4 knockdown resulted in decreased proliferation and decreased IL-6 and IL-8 levels. On the other hand, TLR4 signaling in immune and inflammatory cells of tumor microenvironment
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is the environment around a tumor, including the surrounding blood vessels, immune cells, fibroblasts, signaling molecules and the extracellular matrix (ECM). The tumor and the surrounding microenvironment ...
may lead to production of proinflammatory cytokines ( TNF, IL-1β
Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) also known as leukocytic pyrogen, leukocytic endogenous mediator, mononuclear cell factor, lymphocyte activating factor and other names, is a cytokine protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IL1B'' gene."Catabolin ...
, IL-6, IL-18, etc.), immunosuppressive cytokines ( IL-10, TGF-β
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is a multifunctional cytokine belonging to the transforming growth factor superfamily that includes three different mammalian isoforms (TGF-β 1 to 3, HGNC symbols TGFB1, TGFB2, TGFB3) and many other s ...
, etc.) and angiogenic mediators (VEGF
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF, ), originally known as vascular permeability factor (VPF), is a signal protein produced by many cells that stimulates the formation of blood vessels. To be specific, VEGF is a sub-family of growth factors ...
, EGF, TGF-β, etc.).
These activities may result in further polarization of tumor-associated macrophage Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are a class of immune cells present in high numbers in the microenvironment of solid tumors. They are heavily involved in cancer-related inflammation. Macrophages are known to originate from bone marrow-derived bl ...
s, conversion of fibroblasts
A fibroblast is a type of biological cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework ( stroma) for animal tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells ...
into tumor-promoting cancer-associated fibroblasts, conversion of dendritic cells into tumor-associated DCs and activation of pro-tumorigenic functions of immature myeloid cells - Myeloid-derived Suppressor Cell
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) are a heterogeneous group of immune cells from the myeloid lineage (a family of cells that originate from bone marrow stem cells).
MDSCs expand under pathologic conditions such as chronic infection and cance ...
s (MDSC). TLR signaling has been linked to accumulation and function of MDSC at the site of tumor and it also allows mesenchymal stromal cells to counter NK cell
Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells or large granular lymphocytes (LGL), are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system that belong to the rapidly expanding family of known innate lymphoid cells (ILC) and represen ...
-mediated anti-tumor immunity. In HepG2 hepatoblastoma cells LPS increased TLR4 levels, cell proliferation
Cell proliferation is the process by which ''a cell grows and divides to produce two daughter cells''. Cell proliferation leads to an exponential increase in cell number and is therefore a rapid mechanism of tissue growth. Cell proliferation r ...
and resistance to chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemother ...
, and these phenomena could be reversed by TLR4 gene knockdown Gene knockdown is an experimental technique by which the expression of one or more of an organism's genes is reduced. The reduction can occur either through genetic modification or by treatment with a reagent such as a short DNA or RNA oligonucleot ...
. Similarly, LPS stimulation of human liver cancer cell line H7402 resulted in TLR4 upregulation, NF-κB activation, TNF, IL-6 and IL-8 production and increased proliferation that could be reversed by signal transducer
and STAT3
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is a transcription factor which in humans is encoded by the ''STAT3'' gene. It is a member of the STAT protein family.
Function
STAT3 is a member of the STAT protein family. In respons ...
inhibition. Besides the successful usage of Bacillus Calmette–Guérin in the therapy of bladder cancer
Bladder cancer is any of several types of cancer arising from the tissues of the urinary bladder. Symptoms include blood in the urine, pain with urination, and low back pain. It is caused when epithelial cells that line the bladder become ma ...
there are reports on the treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous-cell carcinomas (SCCs), also known as epidermoid carcinomas, comprise a number of different types of cancer that begin in squamous cells. These cells form on the surface of the skin, on the lining of hollow organs in the body, and on the ...
, gastric cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a cancer that develops from the lining of the stomach. Most cases of stomach cancers are gastric carcinomas, which can be divided into a number of subtypes, including gastric adenocarcinomas. Lym ...
and cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is a cancer arising from the cervix. It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Early on, typically no symptoms are seen. Later symptoms may include abnormal ...
with lyophilized streptococcal preparation OK-432 and utilization of TLR4/TLR2
Toll-like receptor 2 also known as TLR2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TLR2'' gene. TLR2 has also been designated as CD282 (cluster of differentiation 282). TLR2 is one of the toll-like receptors and plays a role in the immune sys ...
ligands – derivatives of muramyl dipeptide
Muramyl dipeptide is constituent of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria composed of N-acetylmuramic acid linked by its lactic acid moiety to the N-terminus of an L-alanine D-isoglutamine dipeptide.
It can be recognized by the immune sy ...
.
TLR4 stimulates B-cell responsiveness to Pokeweed mitogen for proliferation which can play a role in inhibiting tumor development.
In pregnancy
Activation of TLR4 in intrauterine infections leads to deregulation of prostaglandin synthesis, leading to uterine smooth muscle contraction.Asp299Gly polymorphism
Classically, TLR4 is said to be the receptor for LPS, however TLR4 has also been shown to be activated by other kinds of lipids. ''Plasmodium falciparum
''Plasmodium falciparum'' is a unicellular protozoan parasite of humans, and the deadliest species of ''Plasmodium'' that causes malaria in humans. The parasite is transmitted through the bite of a female '' Anopheles'' mosquito and causes the ...
'', a parasite known to cause the most common and serious form of malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. ...
that is seen primarily in Africa, produces glycosylphosphatidylinositol
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (), or glycophosphatidylinositol, or GPI in short, is a phosphoglyceride that can be attached to the C-terminus of a protein during posttranslational modification. The resulting GPI-anchored proteins play key roles i ...
, which can activate TLR4. Two SNPs in TLR4 are co-expressed with high penetrance
Penetrance in genetics is the proportion of individuals carrying a particular variant (or allele) of a gene (the genotype) that also express an associated trait (the phenotype). In medical genetics, the penetrance of a disease-causing mutation is t ...
in African populations (i.e. TLR-4-Asp299Gly and TLR-4-Thr399Ile). These Polymorphisms are associated with an increase in TLR4-Mediated IL-10 production—an immunomodulator—and a decrease in proinflammatory cytokine An inflammatory cytokine or proinflammatory cytokine is a type of signaling molecule (a cytokine) that is secreted from immune cells like helper T cells (Th) and macrophages, and certain other cell types that promote inflammation. They include inte ...
s. The TLR-4-Asp299Gly point mutation is strongly correlated with an increased infection rate with ''Plasmodium falciparum''. It appears that the mutation prevents TLR4 from acting as vigorously against, at least some plasmodial infections. The malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. ...
infection rate and associated morbidity are higher in TLR-4-Asp299Gly group, but mortality appears to be decreased. This may indicate that at least part of the pathogenesis of malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. ...
takes advantage of cytokine production. By reducing the cytokine production via the TLR4 mutation, the infection rate may increase, but the number of deaths due to the infection seem to decrease.
In addition, TLR4-D299G has been associated with aggressive colorectal cancer in humans. It has been shown that human colon adenocarcinomas from patients with TLR4-D299G were more frequently of an advanced stage with metastasis than those with wild-type TLR4. The same study demonstrated functionally that intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2) expressing TLR4-D299G underwent epithelial-mesenchymal transition and morphologic changes associated with tumor progression, whereas intestinal epithelial cells expressing wild-type TLR4 did not.
Animal studies
A link between the TLR4 receptor andbinge drinking
Binge drinking, or heavy episodic drinking, is drinking alcoholic beverages with an intention of becoming intoxicated by heavy consumption of alcohol over a short period of time, but definitions ( see below) vary considerably.
Binge drinking i ...
has been suggested. When genes responsible for the expression of TLR4 and GABA receptors are manipulated in rodents that had been bred and trained to drink excessively, the animals showed a "profound reduction" in drinking behaviours.
* Additionally, it has been shown that ethanol, even in the absence of LPS, can activate TLR4 signaling pathways.
High levels of TLR4 molecules and M2 tumor-associated macrophage Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are a class of immune cells present in high numbers in the microenvironment of solid tumors. They are heavily involved in cancer-related inflammation. Macrophages are known to originate from bone marrow-derived bl ...
s are associated with increased susceptibility to cancer growth in mice deprived of sleep. Mice genetically modified so that they could not produce TLR4 molecules showed normal cancer growth.
Drugs targeting TLR4
Toll-like receptor 4 has been shown to be important for the long-term side-effects ofopioid
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use ...
analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It ...
drugs. Various μ-opioid receptor
Receptor may refer to:
*Sensory receptor, in physiology, any structure which, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and responds to a n ...
ligands have been tested and found to also possess action as agonists or antagonists of TLR4, with opioid agonists such as (+)-morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies ('' Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. T ...
being TLR4 agonists, while opioid antagonists such as naloxone were found to be TLR4 antagonists. Activation of TLR4 leads to downstream release of inflammatory modulators including TNF-α and Interleukin-1
The Interleukin-1 family (IL-1 family) is a group of 11 cytokines that plays a central role in the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses to infections or sterile insults.
Discovery
Discovery of these cytokines began with studies on t ...
, and constant low-level release of these modulators is thought to reduce the efficacy of opioid drug treatment with time, and be involved in both the development of tolerance
Tolerance or toleration is the state of tolerating, or putting up with, conditionally.
Economics, business, and politics
* Toleration Party, a historic political party active in Connecticut
* Tolerant Systems, the former name of Veritas Software ...
to opioid analgesic drugs, and in the emergence of side-effects such as hyperalgesia
Hyperalgesia ( or ; 'hyper' from Greek ὑπέρ (huper, “over”), '-algesia' from Greek algos, ἄλγος (pain)) is an abnormally increased sensitivity to pain, which may be caused by damage to nociceptors or peripheral nerves and can ...
and allodynia
Allodynia is a condition in which pain is caused by a stimulus that does not normally elicit pain. For example, bad sunburn can cause temporary allodynia, and touching sunburned skin, or running cold or warm water over it, can be very painful. It i ...
that can become a problem following extended use of opioid drugs. Drugs that block the action of TNF-α or IL-1β have been shown to increase the analgesic effects of opioids and reduce the development of tolerance and other side-effects, and this has also been demonstrated with drugs that block TLR4 itself.
The response of TLR4 to opioid drugs has been found to be enantiomer
In chemistry, an enantiomer ( /ɪˈnænti.əmər, ɛ-, -oʊ-/ ''ih-NAN-tee-ə-mər''; from Ancient Greek ἐνάντιος ''(enántios)'' 'opposite', and μέρος ''(méros)'' 'part') – also called optical isomer, antipode, or optical anti ...
-independent, so the "unnatural" enantiomers of opioid drugs such as morphine and naloxone
Naloxone, sold under the brand names Narcan (4 mg) and Kloxxado (8 mg) among others, is a medication used to reverse or reduce the effects of opioids. It is commonly used to counter decreased breathing in opioid overdose. Effects begin withi ...
, which lack affinity for opioid receptors, still produce the same activity at TLR4 as their "normal" enantiomers. This means that the unnatural enantiomers of opioid antagonists, such as (+)-naloxone, can be used to block the TLR4 activity of opioid analgesic drugs, while leaving the μ-opioid receptor mediated analgesic activity unaffected. This may also be the mechanism behind the beneficial effect of ultra-low dose naltrexone on opioid analgesia.
Morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies ('' Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. T ...
causes inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
by binding to the protein lymphocyte antigen 96
Lymphocyte antigen 96, also known as "Myeloid Differentiation factor 2 (MD-2)," is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LY96'' gene.
The protein encoded by this gene is involved in binding lipopolysaccharide with Toll-Like Receptor (TL ...
, which, in turn, causes the protein to bind to Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). The morphine-induced TLR4 activation attenuates pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
suppression by opioid
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use ...
s and enhances the development of opioid tolerance
Tolerance or toleration is the state of tolerating, or putting up with, conditionally.
Economics, business, and politics
* Toleration Party, a historic political party active in Connecticut
* Tolerant Systems, the former name of Veritas Software ...
and addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to engage in certain behaviors, one of which is the usage of a drug, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use o ...
, drug abuse
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods which are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, ...
, and other negative side effects such as respiratory depression
Hypoventilation (also known as respiratory depression) occurs when ventilation is inadequate (''hypo'' meaning "below") to perform needed respiratory gas exchange. By definition it causes an increased concentration of carbon dioxide (hypercapni ...
and hyperalgesia. Drug candidates that target TLR4 may improve opioid-based pain management
Pain management is an aspect of medicine and health care involving relief of pain (pain relief, analgesia, pain control) in various dimensions, from acute and simple to chronic and challenging. Most physicians and other health professionals pr ...
therapies.
Agonists
*Buprenorphine
Buprenorphine is an opioid used to treat opioid use disorder, acute pain, and chronic pain. It can be used under the tongue (sublingual), in the cheek (buccal), by injection (intravenous and subcutaneous), as a skin patch (transdermal ...
* Carbamazepine
Carbamazepine (CBZ), sold under the trade name Tegretol among others, is an anticonvulsant medication used primarily in the treatment of epilepsy and neuropathic pain. It is used as an adjunctive treatment in schizophrenia along with other m ...
* Ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
* Fentanyl
Fentanyl, also spelled fentanil, is a very potent synthetic opioid used as a pain medication. Together with other drugs, fentanyl is used for anesthesia. It is also used illicitly as a recreational drug, sometimes mixed with heroin, cocain ...
* Levorphanol
Levorphanol (brand name Levo-Dromoran) is an opioid medication used to treat moderate to severe pain. It is the levorotatory enantiomer of the compound racemorphan. Its dextrorotatory counterpart is dextrorphan.
It was first described in Germa ...
* Lipopolysaccharide
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide that are bacterial toxins. They are composed of an O- antigen, an outer core, and an inner core all joined by a covalent bond, and are found in the out ...
s (LPS)
* Methadone
Methadone, sold under the brand names Dolophine and Methadose among others, is a synthetic opioid agonist used for chronic pain and also for opioid dependence. It is used to treat chronic pain, and it is also used to treat addiction to heroi ...
* Morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies ('' Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. T ...
* Oxcarbazepine
* Oxycodone
Oxycodone, sold under various brand names such as Roxicodone and OxyContin (which is the extended release form), is a strong, semi-synthetic opioid used medically for treatment of moderate to severe pain. It is highly addictive and a commonly ...
* Pethidine
Pethidine, also known as meperidine and sold under the brand name Demerol among others, is a synthetic opioid pain medication of the phenylpiperidine class. Synthesized in 1938 as a potential anticholinergic agent by the German chemist Otto Eis ...
* Glucuronoxylomannan from Cryptococcus
''Cryptococcus'' is a genus of fungi in the family Cryptococcaceae that includes both yeasts and filamentous species. The filamentous, sexual forms or teleomorphs were formerly classified in the genus ''Filobasidiella'', while ''Cryptococcus'' ...
* Morphine-3-glucuronide
Morphine-3-glucuronide is a metabolite of morphine produced by UGT2B7. It is not active as an opioid agonist, but does have some action as a convulsant, which does not appear to be mediated through opioid receptors, but rather through interaction ...
(inactive at opioid receptors, so selective for TLR4 activation)
* Tapentadol
Tapentadol, brand names Nucynta among others, is a centrally acting opioid analgesic of the benzenoid class with a dual mode of action as an agonist of the μ-opioid receptor and as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRI). Analgesia occurs wit ...
(combined full μ-opioid receptor agonist and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor)
* "Unnatural" isomers such as (+)-morphine activate TLR4 but lack opioid receptor activity, although (+)-morphine also shows activity as a sigma receptor
Sigma receptors (σ-receptors) are protein cell surface receptors that bind ligands such as 4-PPBP (4-phenyl-1-(4-phenylbutyl) piperidine), SA 4503 (cutamesine), ditolylguanidine, dimethyltryptamine, and siramesine. There are two subtypes, ...
agonist.
Antagonists
* The lipid A analog eritoran acts as a TLR4 antagonist. , it was being developed as a drug against severesepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
. However, in 2013, a news story said the results against sepsis were somewhat disappointing and that it was better used to treat certain cases of severe influenza. Although it does not treat the virus itself, it could be used against the massive immune reaction called cytokine storm
A cytokine storm, also called hypercytokinemia, is a physiological reaction in humans and other animals in which the innate immune system causes an uncontrolled and excessive release of pro-inflammatory signaling molecules called cytokines. Norma ...
which often occurs later in the infection and is a major cause of mortality from severe influenza.
* Amitriptyline
Amitriptyline, sold under the brand name Elavil among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant primarily used to treat cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS), major depressive disorder and a variety of pain syndromes from neuropathic pain to fibromyalgi ...
* Cyclobenzaprine
Cyclobenzaprine (sold under the brand name Flexeril, among others) is a medication used for muscle spasms from musculoskeletal conditions of sudden onset. It is not useful in cerebral palsy. It is taken by mouth. Use is not recommended for mor ...
* Ketotifen
* Imipramine
* Mianserin
Mianserin, sold under the brand name Tolvon among others, is an atypical antidepressant that is used primarily in the treatment of depression in Europe and elsewhere in the world. It is a tetracyclic antidepressant (TeCA). Mianserin is closel ...
* Ibudilast
Ibudilast (development codes: AV-411 or MN-166) is an anti-inflammatory drug used mainly in Japan, which acts as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, inhibiting the PDE4 subtype to the greatest extent, but also showing significant inhibition of other ...
* Pinocembrin
Pinocembrin is a flavanone, a type of flavonoid. It is an antioxidant found in damiana, honey, fingerroot, and propolis.
Pinocembrin can be converted biosynthetically to pinobanksin by hydroxylation adjacent to the ketone. Studies have sho ...
* Resatorvid
Resatorvid (TAK-242) is a cyclohexane derivative that was invented by scientists at Takeda in a drug discovery campaign to identify inhibitors of the receptor TLR4. It binds directly to cysteine residue 747 intracellularly, preventing TLR4 bindi ...
* M62812
M62812 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). In animal studies it blocks TLR4-mediated cytokine release and has antiinflammatory effects, showing efficacy in animal models of arthritis and septi ...
* Naloxone
Naloxone, sold under the brand names Narcan (4 mg) and Kloxxado (8 mg) among others, is a medication used to reverse or reduce the effects of opioids. It is commonly used to counter decreased breathing in opioid overdose. Effects begin withi ...
* (+)-Naloxone
(+)-Naloxone (dextro-naloxone) is a drug which is the opposite enantiomer of the opioid antagonist drug (−)-naloxone. Unlike (-)-naloxone, (+)-naloxone has no significant affinity for opioid receptors, but instead has been discovered to act as a ...
("unnatural" isomer, lacks opioid receptor affinity so selective for TLR4 inhibition)
* Naltrexone
Naltrexone, sold under the brand name Revia among others, is a medication primarily used to manage alcohol or opioid use disorder by reducing cravings and feelings of euphoria associated with substance use disorder. It has also been foun ...
* (+)-Naltrexone
* LPS-RS
* Propentofylline
Propentofylline (HWA 285) is a xanthine derivative drug with purported neuroprotective effects.
Pharmacology
It is a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, and also acts as an adenosine reuptake inhibitor.
Uses
Propentofylline was studied as a possible tre ...
* Pentoxifylline
Pentoxifylline, also known as oxpentifylline, is a xanthine derivative used as a drug to treat muscle pain in people with peripheral artery disease. It is generic and sold under many brand names worldwide.Drugs.codrugs.com international listings ...
(and downregulate TLR4 expression)
* Tapentadol
Tapentadol, brand names Nucynta among others, is a centrally acting opioid analgesic of the benzenoid class with a dual mode of action as an agonist of the μ-opioid receptor and as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRI). Analgesia occurs wit ...
(mixed agonist/antagonist)
* TLR4-IN-C34
TLR4-IN-C34 (or C34) is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). In animal studies it blocks TLR4-mediated cytokine release and has antiinflammatory effects.
See also
* M62812
M62812 is a drug whi ...
* Palmitoylethanolamide
References
External links
* * {{TLR signaling pathway Clusters of differentiation 4 LRR proteins