T2K experiment on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
T2K (" Tokai to Kamioka") is a
 Except for the
Except for the
 The Pi-Zero () Detector (P0D) contains 40 plastic scintillator module planes, which in the central part are interleaved with 2.8 cm thick bags fillable of water and thick brass sheets, and in two peripheral regions scintillator modules are sandwiched with lead sheets. By comparison of the amount of interaction between modes with and without water in the bags, it is possible to extract the number of neutrino interactions occurring on the water – the target material inside the far detector Super-Kamiokande.
The size of the entire active P0D volume is around 2.1 m × 2.2 m × 2.4 m (X×Y×Z) and its mass with and without water is 15.8 and 12.9 tons respectively.
The main goal of the Pi-Zero Detector is a measurement of neutral
The Pi-Zero () Detector (P0D) contains 40 plastic scintillator module planes, which in the central part are interleaved with 2.8 cm thick bags fillable of water and thick brass sheets, and in two peripheral regions scintillator modules are sandwiched with lead sheets. By comparison of the amount of interaction between modes with and without water in the bags, it is possible to extract the number of neutrino interactions occurring on the water – the target material inside the far detector Super-Kamiokande.
The size of the entire active P0D volume is around 2.1 m × 2.2 m × 2.4 m (X×Y×Z) and its mass with and without water is 15.8 and 12.9 tons respectively.
The main goal of the Pi-Zero Detector is a measurement of neutral
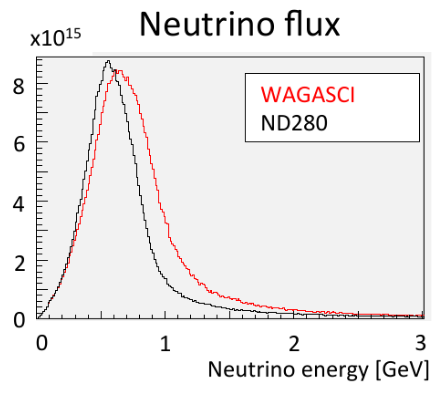 WAGASCI-BabyMIND is a new detector located next to the INGRID and ND280 detectors, devoted to
WAGASCI-BabyMIND is a new detector located next to the INGRID and ND280 detectors, devoted to
 Super-Kamiokande detector is located 1000 m underground in the Mozumi Mine, under Mount Ikeno in the Kamioka area of Hida city. It is a stainless steel cylindrical tank of about 40 m height and diameter, filled with 50,000 tons of
Super-Kamiokande detector is located 1000 m underground in the Mozumi Mine, under Mount Ikeno in the Kamioka area of Hida city. It is a stainless steel cylindrical tank of about 40 m height and diameter, filled with 50,000 tons of
 The current design of the ND280 detector is optimized for the detection and reconstruction of forward-going leptons ( muons and
The current design of the ND280 detector is optimized for the detection and reconstruction of forward-going leptons ( muons and
T2K Experiment Official Website
Super-Kamiokande Realtime Monitor
Neutrino physics – The T2K experiment – YouTube
Inside Japan's Big Physics , Part one: Super Kamiokande – YouTube
{{Neutrino detectors Accelerator neutrino experiments Science and technology in Japan CERN experiments Fixed-target experiments
particle physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) an ...
experiment studying the oscillations
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
of the accelerator neutrinos. The experiment is conducted in Japan by the international cooperation of about 500 physicists and engineers with over 60 research institutions from several countries from Europe, Asia and North America and it is a recognized CERN experiment (RE13). T2K collected data within its first phase of operation from 2010 till 2021. The second phase of data taking ( T2K-II) is expected to start in 2023 and last until commencement of the successor of T2K – the Hyper-Kamiokande experiment in 2027.
T2K was the first experiment which observed the appearance of electron neutrino
The electron neutrino () is an elementary particle which has zero electric charge and a spin of . Together with the electron, it forms the first generation of leptons, hence the name electron neutrino. It was first hypothesized by Wolfgang Pauli ...
s in a muon neutrino
The muon neutrino is an elementary particle which has the symbol () and zero electric charge. Together with the muon it forms the second generation of leptons, hence the name muon neutrino. It was discovered in 1962 by Leon Lederman, Melvin Schwar ...
beam. It also provided the world best measurement of oscillation parameter ''θ''23 and a hint of a significant matter-antimatter asymmetry in neutrino oscillations. The measurement of the neutrino-antineutrino oscillation asymmetry may bring us closer to the explanation of the existence of our matter-dominated Universe.
The intense beam of muon neutrinos is produced in the J-PARC
J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex) is a high intensity proton accelerator facility. It is a joint project between KEK and JAEA and is located at the Tokai campus of JAEA. J-PARC aims for the frontier in materials and life scienc ...
facility (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex) in Tokai on the east coast of Japan. The beam is directed towards the Super-Kamiokande
Super-Kamiokande (abbreviation of Super-Kamioka Neutrino Detection Experiment, also abbreviated to Super-K or SK; ja, スーパーカミオカンデ) is a Neutrino detector, neutrino observatory located Kamioka Observatory, under Mount Ikeno ...
far detector located away in the city of Hida, Gifu prefecture. The properties and composition of the neutrino flux are first measured by a system of near detectors located from the beam production place at the J-PARC site, and then again in the Super-Kamiokande detector. Comparison of the content of different neutrino flavours in these two locations allows measurement of the oscillations probability on the way between near and far detectors. Super-Kamiokande is able to detect interactions of both, muon and electron neutrinos, and thus measure the disappearance of muon neutrino flux, as well as electron neutrino appearance in the beam.
Physics program
T2K experiment was proposed in 2003 with the following measurement goals: * The discovery of the →oscillations
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
, and thus the confirmation that the last unknown mixing angle ''θ''13 is not zero.
* Precise measurement of the oscillation parameters Δ''m'' and ''θ''23 via muon neutrino disappearance studies.
* Search for sterile neutrino
Sterile neutrinos (or inert neutrinos) are hypothetical particles (neutral leptons – neutrinos) that are believed to interact only via gravity and not via any of the other fundamental interactions of the Standard Model. The term ''sterile neutri ...
oscillations, which could be observed as a deficit of neutral current
Weak neutral current interactions are one of the ways in which subatomic particles can interact by means of the weak force. These interactions are mediated by the Z boson. The discovery of weak neutral currents was a significant step towa ...
neutrino interactions.
* Measurements of various interaction cross-sections for different types of neutrinos and targets in an energy range of few GeV.
Since the start of the data taking in 2010, the T2K experiment succeeded to provide a list of world-class results:
* The confirmation of electron neutrino appearance in the muon neutrino beam (→), which was the first time when neutrinos produced in one flavour was explicitly observed in another flavour.
* The most precise measurement of the ''θ''23 parameter.
* Limits on a sterile neutrino
Sterile neutrinos (or inert neutrinos) are hypothetical particles (neutral leptons – neutrinos) that are believed to interact only via gravity and not via any of the other fundamental interactions of the Standard Model. The term ''sterile neutri ...
oscillation parameters based on studies in the near ND280 and far Super-Kamiokande detectors.
* Various cross-section measurements of electron and muon neutrinos and antineutrinos, including inclusive charged current (CC) interactions, CC interactions without pions and with single pion in the final state, coherent pion production, neutral current
Weak neutral current interactions are one of the ways in which subatomic particles can interact by means of the weak force. These interactions are mediated by the Z boson. The discovery of weak neutral currents was a significant step towa ...
interactions, etc. on different targets such as carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon mak ...
, water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
and iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
.
* The first significant constraint on the ''δ''CP parameter, responsible for the matter-antimatter asymmetry in the neutrino oscillations.
''δ''CP takes values from -''π'' to ''π'' (i.e. from −180° to 180°) and can be measured by comparing oscillations of neutrinos to those of antineutrinos. The CP symmetry would be conserved, and thus the oscillation probabilities would be the same for neutrinos and antineutrinos, for ''δ''CP equal to 0 or ±''π''. T2K provided the first and the strongest yet constraint on ''δ''CP, rejecting at the 3σ (99.7%) significance level almost half of the possible values, ruling out the both CP conserving points at the significance level of 95% and giving a strong hint that CP violation may be large in the neutrino sector. The CP violation is one of the conditions proposed by the Russian physicist Andrei Sakharov
Andrei Dmitrievich Sakharov ( rus, Андрей Дмитриевич Сахаров, p=ɐnˈdrʲej ˈdmʲitrʲɪjevʲɪtɕ ˈsaxərəf; 21 May 192114 December 1989) was a Soviet nuclear physicist, dissident, nobel laureate and activist for n ...
, necessary to produce
Produce is a generalized term for many farm-produced crops, including fruits and vegetables (grains, oats, etc. are also sometimes considered ''produce''). More specifically, the term ''produce'' often implies that the products are fresh and g ...
the excess of matter with respect to antimatter at the early universe, which forms now our matter-built Universe. CP violation
In particle physics, CP violation is a violation of CP-symmetry (or charge conjugation parity symmetry): the combination of C-symmetry (charge symmetry) and P-symmetry ( parity symmetry). CP-symmetry states that the laws of physics should be th ...
in quark section was confirmed already in 1964, but it is too small to explain the observed matter-antimatter imbalance. The strong CP violation in the neutrino sector could lead to matter excess production through the process called leptogenesis and thus such measurement would be important step to understand how the Universe were formed.
The NOvA experiment is the other neutrino oscillation experiment capable to measure ''δ''CP through the comparison between → and → oscillation channels. NOvA is conducted in the USA
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
and measures accelerator neutrino oscillation at the distance of 810 km on the way between beam production place in Fermilab
Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab), located just outside Batavia, Illinois, near Chicago, is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory specializing in high-energy particle physics. Since 2007, Fermilab has been opera ...
and far detector in Ash River, Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
. NOvA provided a less precise measurement of ''δ''CP, which is in slight tension with the T2K result. The T2K best-fit point lies in the region disfavoured by NOvA at the confidence level of 90%. There are ongoing works to obtain a joint fit to data from both experiments to quantify consistency between them.
Future upgrades of T2K is expected to provide more precise measurements of Δ''m'' and ''θ''23 parameters, cross-section measurements which will extend our understanding of neutrino interactions and thus improve theoretical models used in neutrino generators, as well as further constrain on the ''δ''CP phase and confirmation if the CP symmetry is conserved or violated in the neutrino oscillation at the 3σ significance level in the T2K-II and 5σ in the Hyper-Kamiokande Hyper-Kamiokande is a neutrino observatory being constructed on the site of the Kamioka Observatory, near Kamioka, Japan.
The project started in 2010 as a successor to Super-Kamiokande. It was ranked as among the 28 top priority projects of the J ...
experiment.
Neutrino beam
T2K uses a muon neutrino or muon antineutrino beam produced at theJ-PARC
J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex) is a high intensity proton accelerator facility. It is a joint project between KEK and JAEA and is located at the Tokai campus of JAEA. J-PARC aims for the frontier in materials and life scienc ...
facility using a proton beam gradually accelerated to 30 GeV by a system of three accelerators: first to 400 MeV energy by the Linac linear accelerator, then up to 3 GeV by the RCS (Rapid Cycle Synchrotron), and finally up to 30 GeV by the MR synchrotron (Main Ring). Protons collide with a graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on lar ...
target, producing meson
In particle physics, a meson ( or ) is a type of hadronic subatomic particle composed of an equal number of quarks and antiquarks, usually one of each, bound together by the strong interaction. Because mesons are composed of quark subparticles, ...
s, mainly pion
In particle physics, a pion (or a pi meson, denoted with the Greek letter pi: ) is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the lightest mesons and, more gene ...
s and kaon
KAON (Karlsruhe ontology) is an ontology infrastructure developed by the University of Karlsruhe and the Research Center for Information Technologies in Karlsruhe.
Its first incarnation was developed in 2002 and supported an enhanced version of ...
s, which are then focused by a set of three magnetic horns and directed into a tunnel called the decay volume. Depending on the horns polarity, either positive or negative particles are focused. Positive pions and kaons decay mainly into and , forming a muon neutrino beam, while negative pions and kaons decay mainly into and , forming a muon antineutrino beam. All remaining hadron
In particle physics, a hadron (; grc, ἁδρός, hadrós; "stout, thick") is a composite subatomic particle made of two or more quarks held together by the strong interaction. They are analogous to molecules that are held together by the e ...
s and charged leptons are stopped by a 75-ton block of graphite (so-called beam dump) and in the ground, while neutrinos travel underground towards the far detector.
Off-axis beam
T2K is the first experiment in which the concept of off-axis neutrino beam was realized. The neutrino beam at J-PARC is designed so that it can be directed 2 to 3 degrees away from theSuper-Kamiokande
Super-Kamiokande (abbreviation of Super-Kamioka Neutrino Detection Experiment, also abbreviated to Super-K or SK; ja, スーパーカミオカンデ) is a Neutrino detector, neutrino observatory located Kamioka Observatory, under Mount Ikeno ...
far detector and one of the near detectors, ND280. The average energy of neutrinos decreases with the deviation from the beam axis. The off-axis angle was chosen to 2.5° to maximize the probability of oscillation at a distance corresponding to the far detector, which for is maximal for around 600 MeV neutrinos. In this neutrino energy range, the dominant type of neutrino interactions are charged current quasielastic interactions, for which it is possible to reconstruct the energy of the interacting neutrino only on the basis of the momentum and direction of the produced charged lepton. The higher neutrino energies are suppressed by the off-axis configuration, decreasing the number of interactions with meson production, which are background in the oscillation analysis in the T2K experiment.
Near detectors
The near detector complex is located at a distance of from the graphite target. Its purpose is to measure the neutrino flux before oscillations and to study neutrino interactions. The system consists of three main detectors: * INGRID detector (Interactive Neutrino GRID) located on the axis of the neutrino beam, * ND280 detector located 2.5° away from the beam axis, i.e. at the same angle as the far detector. * WAGASCI-BabyMIND (WAter Grid SCIntillator Detector – prototype Magnetized Iron Neutrino Detector) is a magnetised neutrino detector located at 1.5° off-axis angle, built to explore the energy spectrum variation with the off-axis angle and cross-sections at higher average neutrino energy.Signal readout
Time Projection Chamber
In physics, a time projection chamber (TPC) is a type of particle detector that uses a combination of electric fields and magnetic fields together with a sensitive volume of gas or liquid to perform a three-dimensional reconstruction of a particl ...
s in ND280, the entire active material (enabling particle tracking) of the near detectors is plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptab ...
scintillator. The light produced by traversing charged particles in the plastic scintillator bars and planes is collected by wavelength-shifting fibres
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate ...
and detected by Hamamatsu Multi-pixel photon counters located at one or both ends of the fibres. Scintillator bars are organised into layers, where bars in two neighbouring layers are perpendicular to each other providing together 3D information about the traversing particles.
INGRID detector
The main purpose of the INGRID detector is the monitoring of the direction and intensity of the beam on a daily basis by direct detection of neutrino interactions. The INGRID detector consists of 16 identical modules arranged in the shape of a cross, 7 in a vertical and 7 in a horizontal arm, plus 2 modules outside the cross. The height and width of the arms are . A single module consists of alternating layers of iron and a plastic scintillator. An additional 4 vetoVeto is a part of a detector where no activity should be registered to accept an event. Such requirement allows constraining the number of background events in a selected sample; here the background from particles produced outside of the detector. layers of the scintillator surround the module on the sides to distinguish particles entering from the outside from those produced by interactions inside the module. The total mass of iron in one module is 7.1 tons and constitutes 96% of the module weight. On the neutrino beam axis, in the middle of the cross between the vertical and horizontal arm, there is an additional module built only from layers of the plastic scintillator (Proton Module) with a mass of 0.55 tons. Its purpose is to register quasielastic interactions and compare the obtained results with the simulations.ND280 detector
The ND280 detector is used to measure the flux, energy spectrum and electron neutrino beam pollution for the same off-axis angle as for the far detector. ND280 also investigates various types of muon and electron neutrino and antineutrino interactions. All this allows estimating the expected number and type of interactions in the far detector, reducing the systematic error in the neutrino oscillations analysis associated with models of neutrino interactions and flux. ND280 is composed of the set of inner sub-detectors: Pi-Zero detector and a tracker with 2 Fine-Grained Detectors interleaved with 3 Time Projection Chambers, placed inside of a metal frame called a basket. The basket is surrounded by the electromagnetic calorimeter and a magnet recycled from the UA1 experiment producing 0.2 T uniform horizontal magnetic field and instrumented with scintillator planes constituting the Side Muon Range Detector.Pi-Zero detector
 The Pi-Zero () Detector (P0D) contains 40 plastic scintillator module planes, which in the central part are interleaved with 2.8 cm thick bags fillable of water and thick brass sheets, and in two peripheral regions scintillator modules are sandwiched with lead sheets. By comparison of the amount of interaction between modes with and without water in the bags, it is possible to extract the number of neutrino interactions occurring on the water – the target material inside the far detector Super-Kamiokande.
The size of the entire active P0D volume is around 2.1 m × 2.2 m × 2.4 m (X×Y×Z) and its mass with and without water is 15.8 and 12.9 tons respectively.
The main goal of the Pi-Zero Detector is a measurement of neutral
The Pi-Zero () Detector (P0D) contains 40 plastic scintillator module planes, which in the central part are interleaved with 2.8 cm thick bags fillable of water and thick brass sheets, and in two peripheral regions scintillator modules are sandwiched with lead sheets. By comparison of the amount of interaction between modes with and without water in the bags, it is possible to extract the number of neutrino interactions occurring on the water – the target material inside the far detector Super-Kamiokande.
The size of the entire active P0D volume is around 2.1 m × 2.2 m × 2.4 m (X×Y×Z) and its mass with and without water is 15.8 and 12.9 tons respectively.
The main goal of the Pi-Zero Detector is a measurement of neutral pion
In particle physics, a pion (or a pi meson, denoted with the Greek letter pi: ) is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the lightest mesons and, more gene ...
s production in neutral current
Weak neutral current interactions are one of the ways in which subatomic particles can interact by means of the weak force. These interactions are mediated by the Z boson. The discovery of weak neutral currents was a significant step towa ...
neutrino interactions on water:
: + N → + N’ +
This reaction can mimic electron neutrino interactions because photons from decay can be mis-reconstructed as an electron in the Super-Kamiokande detector, thus this reaction can mimic electron neutrino interactions and constitute an important background in electron neutrino appearance measurement.
Time projection chambers
Three Time Projection Chambers (TPCs) are gas-tight rectangular boxes, with a cathode plane in the centre and readout MicroMegas modules at both sides parallel to the cathode. TPCs are filled withargon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as ...
-based drift gas under atmospheric pressure. Charged particles crossing TPC ionise the gas along their track. The ionisation electrons drift from the cathode to the sides of the TPC, where they are detected by the MicroMegas providing a 3D image of a path of the traversing charged particle. Y and Z coordinates are based on the position of the detected ionisation electrons on the MicroMegas modules, and X coordinate is based on the electrons drift time. In the magnetic field, the curvature of this path allows to determine charge
Charge or charged may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* '' Charge, Zero Emissions/Maximum Speed'', a 2011 documentary
Music
* ''Charge'' (David Ford album)
* ''Charge'' (Machel Montano album)
* ''Charge!!'', an album by The Aqu ...
and momentum of the particle, and the amount of the ionisation electrons per unit distance is used to identify particles based on the Bethe-Bloch formula.
Fine-grained detectors
Two Fine-Grained Detectors (FGDs) are placed after the first and second TPCs. Together the FGDs and TPCs make up the tracker of ND280. The FGDs provide the active target mass for the neutrino interactions and are able to measure the short tracks of proton recoil. The first FGD is composed of scintillator layers only, while the second FGD is composed of alternating layers of scintillator and water. The second FGD is partially composed of water because the Super-Kamiokande detector is water-based. Cross sections on carbon and on the water can be determined from a comparison of neutrino interactions in the two FGDs.Electromagnetic Calorimeter
The Electromagnetic Calorimeter (ECal) surrounds the inner detectors (P0D, TPCs, FGDs) and consists of scintillator layers sandwiched with lead absorber sheets. Its role is to detect neutral particles, especially photons, and measure their energy and direction, as well as to detect charged particles providing additional information relevant for their identification.Side Muon Range Detector
The Side Muon Range Detector (SMRD) consists of scintillator modules which are inserted into the gaps in the magnet. The SMRD records muons escaping the inner parts of the detector at large angles with respect to the beam direction. The remaining types of particles (except for neutrinos) are mostly stopped in the calorimeter. SMRD can also act as a trigger forcosmic rays
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our ow ...
. Finally, it can help identify beam interactions in the surrounding walls and in the magnet itself.
WAGASCI-BabyMIND
 WAGASCI-BabyMIND is a new detector located next to the INGRID and ND280 detectors, devoted to
WAGASCI-BabyMIND is a new detector located next to the INGRID and ND280 detectors, devoted to neutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is a fermion (an elementary particle with spin of ) that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass ...
interaction studies. It provided the first neutrino beam data using a full detector setup during the 2019/2020 winter run.
The WAGASCI-BabyMIND consists of several sub-detectors:
* Two new water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
- scintillator detectors (WAGASCI, WAter-Grid-SCIntillator-Detector) that act as the main water targets and particle trackers. The 3D grid-like structure of scintillator bars creates hollow cavities filled with water.
Thanks to such a structure, a high water to scintillator mass ratio was obtained (80% H2O + 20% CH) and the acceptance is high and approximately constant in all directions.
* One Proton Module, the same as in the INGRID
Ingrid may refer to:
* Ingrid (given name)
* Ingrid (record label), and artist collective
* Ingrid Burley, rapper known mononymously as Ingrid
* Tropical Storm Ingrid, various cyclones
* 1026 Ingrid, an asteroid
* InGrid, the grid computing project ...
detector, made of plain plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptab ...
scintillator (CH) bars, that acts as the main CH target and particle tracker.
* Two WallMRD (Wall Muon Range Detector) that are non-magnetized muon spectrometers to detect side going muons. They are made of passive iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
planes intertwined with active scintillator planes.
* One BabyMIND (prototype Magnetized Iron Neutrino Detector) that is a magnetized muon spectrometer to detect forward-going muons. BabyMIND sports an original configuration of scintillation modules intertwined with magnetized ferrite modules like a sandwich. The modules can be rearranged easily to adapt the magnetic field to the particular needs of the experiment. The magnetic field is created only inside the ferrite so it is very power efficient compared to magnets that have to magnetize empty spaces around them like the ND280 one. However, the magnetic field is not homogeneous over the travel volume of the muons, and this poses a still open challenge for momentum reconstruction.
All the active material in the detectors is made up of plastic scintillator and is read as explained in section Signal readout.
The main goal of the WAGASCI-BabyMIND detector is a reduction of the systematic error in the T2K oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
analysis, which will be achieved thanks to its complementarity with respect to the ND280 detector:
* Different target material between ND280 (80% CH + 20% H2O) and SK (pure H2O) forces us to rely on cross-section models to disentangle the H2O cross-section estimate from the CH one. The fraction of water in WAGASCI water-scintillator modules is 80% enabling a measurement of the charged-current neutrino cross-section ratio between water (H2O) and plastic (CH) with 3% accuracy.
* The new detector will provide measurements of various charged-current neutrino interaction channels with high precision, lower momentum threshold and full angular acceptance. These will constrain flux and cross-section models uncertainties for the particles produced at high angles. These assets will also facilitate detection of low momentum hadrons produced in the interaction of the neutrino with bounded states of 2 nucleons or through reinteractions inside the target nucleus of particles produced by the neutrino, and thus better modelling of such interactions in the far detector.
* Location at the same distance of 280 meters from the graphite target as ND280 and INGRID detectors, but at a different off-axis angle of 1.5 degrees, causes that the energy spectrum of the neutrino beam is peaked around different energies for each of the off-axis angles corresponding to the detectors. Combination
In mathematics, a combination is a selection of items from a set that has distinct members, such that the order of selection does not matter (unlike permutations). For example, given three fruits, say an apple, an orange and a pear, there are th ...
of measurements from these detectors will provide an improved constraint on the neutrino cross-sections as a function of their energy.
Super-Kamiokande
 Super-Kamiokande detector is located 1000 m underground in the Mozumi Mine, under Mount Ikeno in the Kamioka area of Hida city. It is a stainless steel cylindrical tank of about 40 m height and diameter, filled with 50,000 tons of
Super-Kamiokande detector is located 1000 m underground in the Mozumi Mine, under Mount Ikeno in the Kamioka area of Hida city. It is a stainless steel cylindrical tank of about 40 m height and diameter, filled with 50,000 tons of water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
and instrumented with around 13,000 photomultiplier tubes (PMT). It detects a cone
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base (frequently, though not necessarily, circular) to a point called the apex or vertex.
A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, or lines con ...
of Cherenkov light emitted by charged particles moving in water faster than light in this medium.
Its goal is to measure muons and electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no ...
s produced in charged current quasielastic interactions (CCQE) of and , respectively. Due to relatively large mass, muons usually do not change their direction and thus produce a well-defined cone of Cherenkov light observed by PMTs as a clear, sharp ring. In contrast, electrons, because of smaller mass, are more susceptible to scattering and almost always produce electromagnetic showers, observed by PMTs as a ring with fuzzy edges. Neutrino energy is calculated based on the direction and energy of a charged lepton produced in the CCQE interaction. In this way, and spectra are determined, leading to the measurement of the oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
parameters relevant for muon neutrino disappearance and electron neutrino appearance.
History
T2K is a successor of the KEK to Kamioka ( K2K) experiment, which ran from 1999 till 2004. In the K2K experiment, an accelerator beam of muon neutrinos was produced at KEK facility inTsukuba
is a city located in Ibaraki Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 244,528 in 108,669 households and a population density of 862 persons per km². The percentage of the population aged over 65 was 20.3%. The total ar ...
( Japan) and sent towards the Super-Kamiokande
Super-Kamiokande (abbreviation of Super-Kamioka Neutrino Detection Experiment, also abbreviated to Super-K or SK; ja, スーパーカミオカンデ) is a Neutrino detector, neutrino observatory located Kamioka Observatory, under Mount Ikeno ...
detector, located 250 km away. The K2K experiment results confirmed at the confidence level of 99.9985% (4.3 σ) the disappearance of the muon neutrino
The muon neutrino is an elementary particle which has the symbol () and zero electric charge. Together with the muon it forms the second generation of leptons, hence the name muon neutrino. It was discovered in 1962 by Leon Lederman, Melvin Schwar ...
s and were consistent with the previous measurements of oscillation parameters measured by the Super-Kamiokande detector for atmospheric neutrinos.
The construction of the neutrino beamline started in 2004 and it was successfully commissioned in 2009. Construction of the entire INGRID detector and majority of the ND280 detector (without barrel part of the electromagnetic calorimeter) was completed in 2009. The missing part of the calorimeter was installed in the fall of 2010. T2K far detector is the large Super-Kamiokande detector, which has been running since 1996 and studying proton lifetime and oscillations of atmospheric, solar and accelerator neutrinos.
T2K experiment started to take neutrino data for a physics analysis in January 2010, initially with an incomplete ND280 detector, and starting from November 2010 with the full setup. The data taking was interrupted for one year by the Great Tohoku Earthquake in March 2011. The proton beam power, and thus the neutrino beam intensity, was constantly growing, reaching by February 2020 the power of 515 kW and a total number of accumulated protons on target of 3.6×1021 protons with 55% of data in neutrino-mode and 45% in antineutrino-mode.
Future plans
The T2K experiment operated in the current form until 2020. In 2021 the first data run withgadolinium
Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. Gadolinium is a silvery-white metal when oxidation is removed. It is only slightly malleable and is a ductile rare-earth element. Gadolinium reacts with atmospheric oxygen ...
loaded into the Super-Kamiokande far detector was taken. In 2021–2022 a major upgrade of the neutrino beamline and the ND280 near detector will be performed. From 2023 till 2026 neutrino data will be taken within the second phase of the T2K experiment (T2K-II). In 2027, the successor of the T2K experiment – the Hyper-Kamiokande (HK) experiment – will be launched with the new, 250,000-ton water Cherenkov far detector – the Hyper-Kamiokande Hyper-Kamiokande is a neutrino observatory being constructed on the site of the Kamioka Observatory, near Kamioka, Japan.
The project started in 2010 as a successor to Super-Kamiokande. It was ranked as among the 28 top priority projects of the J ...
detector. The building of an additional Intermediate Water Cherenkov detector at a distance of around is also considered for the HK experiment.
T2K-II
Phase II of the T2K experiment is expected to start at the beginning of 2023 and last until 2026, following by the commencement of the HK experiment. The physics goals of T2K-II are a measurement of theoscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
parameters ''θ''23 and Δ''m'' with a precision of 1.7° and 1%, respectively, as well as a confirmation at the level of 3 σ or more of the matter-antimatter asymmetry in the neutrino sector in a wide range of possible true values of ''δ''CP – the parameter responsible for the CP (matter-antimatter) asymmetry. Achievement of these goals requires the reduction of statistical and systematic errors. Thus a significant upgrade of the beamline and the ND280 detector, doping of SK water with gadolinium
Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. Gadolinium is a silvery-white metal when oxidation is removed. It is only slightly malleable and is a ductile rare-earth element. Gadolinium reacts with atmospheric oxygen ...
to allow / discrimination in the far detector, as well as improvements in the software and analysis methods will be done.
Beam upgrade
The beam upgrade plan requires one year long shut down of theJ-PARC
J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex) is a high intensity proton accelerator facility. It is a joint project between KEK and JAEA and is located at the Tokai campus of JAEA. J-PARC aims for the frontier in materials and life scienc ...
Main Ring accelerator in 2021, followed by a constant gradual increase of the proton beam power until the start of the HK experiment. The beam power should reach 750 kW in 2022 and then grow to 1.3 MW by 2029.
In February 2020, the proton beam power reached 515 kW with 2.7x1014 protons per pulse and with 2.48 seconds between pulses (so-called repetition cycle). To reach 750 kW, the repetition cycle will be reduced to 1.32 s with 2.0x1014 protons per pulse, while for 1.3 MW the repetition cycle has to be further decreased to 1.16 s and the number of protons per pulse has to increase to 3.2x1014. In addition to increasing the primary proton beam power, the current in the horns Horns or The Horns may refer to:
* Plural of Horn (instrument), a group of musical instruments all with a horn-shaped bells
* The Horns (Colorado), a summit on Cheyenne Mountain
* ''Horns'' (novel), a dark fantasy novel written in 2010 by Joe Hill ...
focusing secondary particles (pion
In particle physics, a pion (or a pi meson, denoted with the Greek letter pi: ) is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the lightest mesons and, more gene ...
s, kaon
KAON (Karlsruhe ontology) is an ontology infrastructure developed by the University of Karlsruhe and the Research Center for Information Technologies in Karlsruhe.
Its first incarnation was developed in 2002 and supported an enhanced version of ...
s, etc.) with a chosen electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes charged matter to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be ''positive'' or ''negative'' (commonly carried by protons and electrons respe ...
will also be increased from 250 kA to 320 kA. This will increase the amount of right-sign neutrinos (neutrinos in the neutrino mode beam and anti-neutrinos in the anti-neutrino mode beam) by 10%, and reduce the amount of wrong-sign neutrinos (anti-neutrinos in the neutrino-mode beam and neutrinos in the anti-neutrino mode beam) by around 5 - 10%.
Reduction of the repetition cycle will require a series of hardware upgrades, including a major upgrade of the Main Ring power supplies
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a res ...
and a minor upgrade of the focusing horn power supplies, all of which will be installed during the long shutdown in 2021. Increasing the horn current will require using an additional (third) horn power supply. Meanwhile, the higher proton beam power demands enhancement of the cooling
Cooling is removal of heat, usually resulting in a lower temperature and/or phase change. Temperature lowering achieved by any other means may also be called cooling.ASHRAE Terminology, https://www.ashrae.org/technical-resources/free-resources/as ...
capacity of the secondary beamline components such as the graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on lar ...
target, the magnetic horns and the beam dump, as well as disposal of a larger amount of irradiated cooling water.
ND280 Upgrade
 The current design of the ND280 detector is optimized for the detection and reconstruction of forward-going leptons ( muons and
The current design of the ND280 detector is optimized for the detection and reconstruction of forward-going leptons ( muons and electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no ...
s), but it also has a number of limitations, like low reconstruction efficiency of particles produced almost perpendicular and backward with respect to the direction of the interacting neutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is a fermion (an elementary particle with spin of ) that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass ...
, as well as too high momentum threshold to reconstruct a large part of produced pions and knocked-out nucleons (protons and neutrons). In Charged Current Quasi-Elastic (CCQE) interactions, the dominating interaction in the ND280 near detector, kinematics of produced lepton is enough in the reconstruction of the incoming neutrino energy. However, other types of neutrino interactions in which additional particles (pion
In particle physics, a pion (or a pi meson, denoted with the Greek letter pi: ) is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the lightest mesons and, more gene ...
s, kaon
KAON (Karlsruhe ontology) is an ontology infrastructure developed by the University of Karlsruhe and the Research Center for Information Technologies in Karlsruhe.
Its first incarnation was developed in 2002 and supported an enhanced version of ...
s, nucleon
In physics and chemistry, a nucleon is either a proton or a neutron, considered in its role as a component of an atomic nucleus. The number of nucleons in a nucleus defines the atom's mass number (nucleon number).
Until the 1960s, nucleons were ...
s) were lost, may be mis-reconstructed as CCQE and introduce a bias
Bias is a disproportionate weight ''in favor of'' or ''against'' an idea or thing, usually in a way that is closed-minded, prejudicial, or unfair. Biases can be innate or learned. People may develop biases for or against an individual, a group ...
in the reconstructed neutrino energy spectrum. Thus, it is essential to optimize the detector to be sensitive to additional particles and nuclear effects.
Three main measures need to be taken to address these issues:
* The detector needs to efficiently detect the nucleons in the final state of neutrino interactions. For this, the detection thresholds need to be lowered.
* High-angle and backwards-going tracks must be well-reconstructed. This is achieved by increasing the angular acceptance and the efficiency of the discrimination between backward from forward going tracks using timing information.
* Finally, the total fiducial volume (the mass available for neutrino interactions) of the tracker part of the ND280 detector, characterised with a better reconstruction ability, needs to be enlarged in order to increase the rate of neutrino interactions.
The Upgrade of the ND280 detector (ND280 Upgrade) addresses these requirements by replacing a part of the P0D sub-detector with three types of new sub-detectors. The existing downstream part, consisting of two Fine-Grained scintillation Detectors (FGDs) and three Time Projection Chambers (TPCs), will maintain their sandwiched structure and continue to detect forward going leptons and high momentum hadrons. The upstream part which now hosts the P0D sub-detector will be replaced by three novel sub-detectors: a scintillating 3D target (Super Fine-Grained Detector or SuperFGD), two new TPCs on top and below the SuperFGD (High-Angle TPCs or HATPCs), and six Time-of-Flight (TOF) detectors surrounding the new structure. Each of these sub-detectors is briefly described below. The installation of the new sub-detectors into ND280 will be done in 2022.
=SuperFGD
= The SuperFGD is a detector consisting of approximately 2 million 1 cm3 scintillating polystyrene cubes. The cubes are woven with a series ofoptical fibres
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means t ...
designed to detect the light emitted by the particles produced during the interactions in the target. Unlike the current FGDs, the SuperFGD has a three-fold projective 2D readouts providing a quasi-3D readout. This readout configuration increases the detection of short tracks almost uniformly in all directions. Due to its geometry and coupled with the TOF and the HATPCs, the SuperFGD has the capability to detect fast-neutrons, which could be useful in the reconstruction of the antineutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is a fermion (an elementary particle with spin of ) that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass is ...
energy.
=HATPC
= The High AngleTime Projection Chamber
In physics, a time projection chamber (TPC) is a type of particle detector that uses a combination of electric fields and magnetic fields together with a sensitive volume of gas or liquid to perform a three-dimensional reconstruction of a particl ...
s (HATPCs) will surround the SuperFGD in the plane perpendicular to the incoming neutrino beam. Their design is similar to that of the existing TPCs, as they both use the MicroMegas modules technology for track reconstruction. The main novel feature of the HATPCs, aside from their high angle coverage, is the use of the resistive MicroMegas technology. The latter consists of applying a layer of resistive
The electrical resistance of an object is a measure of its opposition to the flow of electric current. Its reciprocal quantity is , measuring the ease with which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels ...
material to increase the charge-sharing capabilities of the MicroMegas modules. This reduces the number of readout channels and allows for a spatial resolution which is as good as the one in the current TPCs.
=TOF
= The six Time-of-Flight (TOF) detectors surrounding the HATPCs and SuperFGD are a series ofplastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptab ...
scintillator layers designed to identify the particle direction sense through the measurement of the time of flight
Time of flight (ToF) is the measurement of the time taken by an object, particle or wave (be it acoustic, electromagnetic, etc.) to travel a distance through a medium. This information can then be used to measure velocity or path length, or as a w ...
for each crossing track with a timing resolution of the order of 600 ps. The capability to determine track direction sense has been proven in the actual ND280 to be critical to reduce background generated outside the active inner detectors.
=Impact on Neutrino Oscillation Physics
= The impact the ND280 Upgrade will have on the analyses at T2K is two-fold. Firstly, an increase in statistics thanks to the 2 ton SuperFGD target will allow to nearly double the amount of data in certain samples. Secondly and more relevant, the new configuration will allow for better detection of additional final state particles: high angle particles thanks to the increased angular acceptance, and less energetic particles because of lower detection thresholds. This detector acceptance improvement is important to cover almost the same phase space available at the far detector (SK). In addition, final state particles will allow probing nuclear effects which are essential for constraining the systematic effects of the oscillation analysis. It is an important step as well in the transition to using semi-inclusive or exclusive models in neutrino oscillation physics, as opposed to current inclusive models which use only the final state lepton in their predictions.SK-Gd
The third element to be improved within T2K – phase II is the introduction ofgadolinium
Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. Gadolinium is a silvery-white metal when oxidation is removed. It is only slightly malleable and is a ductile rare-earth element. Gadolinium reacts with atmospheric oxygen ...
into the Super-Kamiokande
Super-Kamiokande (abbreviation of Super-Kamioka Neutrino Detection Experiment, also abbreviated to Super-K or SK; ja, スーパーカミオカンデ) is a Neutrino detector, neutrino observatory located Kamioka Observatory, under Mount Ikeno ...
, which so far was filled with ultra-pure water. SK is not able to measure the charge
Charge or charged may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* '' Charge, Zero Emissions/Maximum Speed'', a 2011 documentary
Music
* ''Charge'' (David Ford album)
* ''Charge'' (Machel Montano album)
* ''Charge!!'', an album by The Aqu ...
of the registered particle. That means it is not possible to distinguish neutrino from antineutrino interaction based on a charge of produced lepton (e.g. is produced by while by ). In (anti)neutrino-nucleus interactions, apart from a charged lepton production, a nucleon
In physics and chemistry, a nucleon is either a proton or a neutron, considered in its role as a component of an atomic nucleus. The number of nucleons in a nucleus defines the atom's mass number (nucleon number).
Until the 1960s, nucleons were ...
is usually realised from the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
* Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
. Because of charge conservation
In physics, charge conservation is the principle that the total electric charge in an isolated system never changes. The net quantity of electric charge, the amount of positive charge minus the amount of negative charge in the universe, is alwa ...
, for neutrinos it is mostly a proton and for antineutrinos – a neutron:
: + → +
: + → + .
Cherenkov energy threshold (minimal total energy of a charged particle to produce Cherenkov light) is proportional to the particle mass, and in water it equals 0.8 MeV for electrons, 160 MeV for muons and 1400 MeV for protons. Thus, protons released in neutrino interactions often fall below the threshold and remain undetected. Neutron, as a neutral particle, does not produce Cherenkov light. However, it can be absorbed by another nucleus, which goes into an excited state and during deexcitation produced gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically ...
s. High energy photons (for gadolinium their total energy is about 8 MeV) scatter electrons from an atom and/or produce electron-positron pairs, which then produce Cherenkov light. Gadolinium is a naturally occurring element with the highest cross-section on the capture of neutrons at thermal
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example ...
energy. For 25 meV neutrons, the cross-section for gadolinium is about 105 times higher than for hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
. The fraction of neutrons that will be captured in SK is 50% for 0.01% Gd concentration and 90% for 0.1% concentration – the planned final Gd concentration in SK. The signal from neutron capture is delayed by a fraction of a millisecond (the time the neutron travels across the water before the capture plus the time when Gd remains in the excited state) with respect to the charged lepton signal and usually appears within a distance of 50 cm (the distance travelled by the neutron before the capture) from the neutrino interaction point. Such a double flash event (the first flash from the charged lepton, the second flash from the Gd deexcitation photons) is a signature of an antineutrino interaction.
The first loading of 13 tons of Gd2(SO4)3·8 ( gadolinium(III) sulfate octahydrate) into SK water was done in July–August 2020 and lead to a 0.011% concentration of Gd. T2K collected its first data with Gd in SK in March–April 2021. Usage of gadolinium-doped water will allow studying remote supernova neutrinos, for which 's are the most reactive in SK but were yet indistinguishable from neutrinos from other sources. It will also improve the detector performance for supernova explosions in our galaxy and study better matter-antimatter differences in accelerator neutrino
An accelerator neutrino is a human-generated neutrino or antineutrino obtained using particle accelerators, in which beam of protons is accelerated and collided with a fixed target, producing mesons (mainly pions) which then decay into neutrinos. ...
oscillations.
Hyper-Kamiokande experiment
The successor of the T2K experiment, theHyper-Kamiokande Hyper-Kamiokande is a neutrino observatory being constructed on the site of the Kamioka Observatory, near Kamioka, Japan.
The project started in 2010 as a successor to Super-Kamiokande. It was ranked as among the 28 top priority projects of the J ...
(HK) experiment, will use the upgraded system of the currently used accelerator and neutrino beamline and upgraded set of the near detector. Apart from that, a new far detector, the Hyper-Kamiokande detector, and possibly also a new intermediate detector will be built. Part of the beam related upgrade works and the upgrade of the ND280 detector will be performed yet before the start of phase II of the T2K experiment. The HK experiment is expected to start operation around the year 2027.
Hyper-Kamiokande detector
The Hyper-Kamiokande detector will be awater
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
Cherenkov detector, 5 times larger (258 kton of water) than the Super-Kamiokande
Super-Kamiokande (abbreviation of Super-Kamioka Neutrino Detection Experiment, also abbreviated to Super-K or SK; ja, スーパーカミオカンデ) is a Neutrino detector, neutrino observatory located Kamioka Observatory, under Mount Ikeno ...
detector. It will be a cylinder
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infin ...
of diameter and height with 40000 photomultiplier A photomultiplier is a device that converts incident photons into an electrical signal.
Kinds of photomultiplier include:
* Photomultiplier tube, a vacuum tube converting incident photons into an electric signal. Photomultiplier tubes (PMTs for sh ...
tubes of diameter and 6700 photomultiplier tubes of diameter. It will be located south from the Super-Kamiokande detector in the Tochibora mine, under the peak of Nijuugo Mountain, at the same off-axis angle (2.5°) to the neutrino beam centre and in the same distance () from the beam production place at J-PARC
J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex) is a high intensity proton accelerator facility. It is a joint project between KEK and JAEA and is located at the Tokai campus of JAEA. J-PARC aims for the frontier in materials and life scienc ...
. The HK detector construction began in 2020 and the start of data collection is expected in 2027.
Intermediate Water Cherenkov
The Intermediate Water Cherenkov Detector (IWCD) will be located at a distance of from the neutrino production place. It would be a cylinder filled with water of diameter and height with a tall structure instrumented with around 3000 photomultiplier tubes of a diameter. The structure will be moved in a vertical direction by a crane system, providing measurements of neutrino interactions at different off-axis angles, spanning from 1° to 4°, and thus for different energy spectra. Combining the results from different off-axis angles it is possible to extract the results for nearly monochromatic neutrino spectrum without relying on theoretical models of neutrino interactions to reconstruct neutrino energy. Usage of the same type of detector as the far detector with almost the same angular and momentum acceptance allows comparing results from these two detectors without relying on detectors response simulations. These two facts, independence from the neutrino interaction and detector response models, will enable to minimise systematic error in the oscillation analysis. Additional advantages of such a design of the detector is a possibility to search for sterileoscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
pattern for different off-axis angles and to obtain a cleaner sample of electron neutrino
The electron neutrino () is an elementary particle which has zero electric charge and a spin of . Together with the electron, it forms the first generation of leptons, hence the name electron neutrino. It was first hypothesized by Wolfgang Pauli ...
interaction, whose fraction is larger for the larger off-axis angle.
It is planned that the IWCD will be finalised in 2024 and will start to take data from 2025, yet before launching the HK experiment.
See also
*Kamioka Observatory
The is a neutrino and gravitational waves laboratory located underground in the Mozumi mine of the Kamioka Mining and Smelting Co. near the Kamioka section of the city of Hida in Gifu Prefecture, Japan. A set of groundbreaking neutrino experim ...
Notes
References
External links
T2K Experiment Official Website
Super-Kamiokande Realtime Monitor
Neutrino physics – The T2K experiment – YouTube
Inside Japan's Big Physics , Part one: Super Kamiokande – YouTube
{{Neutrino detectors Accelerator neutrino experiments Science and technology in Japan CERN experiments Fixed-target experiments