Sussex Downs on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The South Downs are a range of
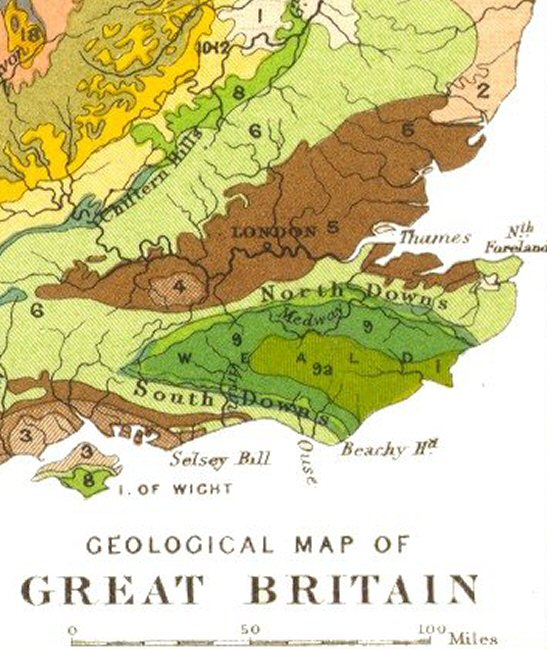
 The South Downs are formed from a thick band of chalk which was deposited during the
The South Downs are formed from a thick band of chalk which was deposited during the

File:Devil's Dyke with storm clouds and rainbow.JPG, Looking east along the Downs towards the
Sussex South Downs Guide
Visit South Downs tourism website
South Downs National Park Trust website
South Downs Discovery walks and tours website
{{Authority control Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty in England Geology of England Hills of East Sussex Hills of Hampshire Hills of West Sussex Natural regions of England Protected areas of East Sussex Protected areas of Hampshire Protected areas of West Sussex
chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. Ch ...
hills that extends for about across the south-eastern coastal counties of England from the Itchen valley of Hampshire in the west to Beachy Head
Beachy Head is a chalk headland in East Sussex, England. It is situated close to Eastbourne, immediately east of the Seven Sisters.
Beachy Head is located within the administrative area of Eastbourne Borough Council which owns the land, formi ...
, in the Eastbourne Downland Estate, East Sussex, in the east. The Downs are bounded on the northern side by a steep escarpment, from whose crest there are extensive views northwards across the Weald. The South Downs National Park
The South Downs National Park is England's newest national park, designated on 31 March 2010. The park, covering an area of in southern England, stretches for from Winchester in the west to Eastbourne in the east through the counties of Hamp ...
forms a much larger area than the chalk range of the South Downs and includes large parts of the Weald.
The South Downs are characterised by rolling chalk downland with close-cropped turf and dry valleys, and are recognised as one of the most important chalk landscapes in England. The range is one of the four main areas of chalk downland
Downland, chalkland, chalk downs or just downs are areas of open chalk hills, such as the North Downs. This term is used to describe the characteristic landscape in southern England where chalk is exposed at the surface. The name "downs" is deriv ...
in southern England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
.
The South Downs are relatively less populated compared to South East England
South East England is one of the nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. It consists of the counties of Buckinghamshire, East Sussex, Hampshire, the Isle of Wight, Kent, Oxfordshire, Berkshi ...
as a whole, although there has been large-scale urban encroachment onto the chalk downland by major seaside resorts, including most notably Brighton and Hove
Brighton and Hove () is a city and unitary authority in East Sussex, England. It consists primarily of the settlements of Brighton and Hove, alongside neighbouring villages.
Often referred to synonymously as Brighton, the City of Brighton and H ...
. The South Downs have been inhabited since ancient times and at periods the area has supported a large population, particularly during Romano-British times. There is a rich heritage of historical features and archaeological remains, including defensive sites, burial mounds and field boundaries. Within the South Downs Environmentally Sensitive Area there are thirty-seven Sites of Special Scientific Interest
A Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in Great Britain or an Area of Special Scientific Interest (ASSI) in the Isle of Man and Northern Ireland is a conservation designation denoting a protected area in the United Kingdom and Isle of ...
, including large areas of chalk grassland.
The grazing of sheep on the thin, well-drained chalk soils of the Downs over many centuries and browsing by rabbits resulted in the fine, short, springy turf, known as ''old chalk grassland'', that has come to epitomise the South Downs today. Until the middle of the 20th century, an agricultural system operated by downland farmers known as 'sheep-and-corn farming' underpinned this: the sheep (most famously the Southdown breed) of villagers would be systematically confined to certain corn fields to improve their fertility with their droppings and then they would be let out onto the downland to graze. However, starting in 1940 with government measures during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
to increase domestic food production and continuing into the 1950s, much grassland was ploughed up for arable farming, fundamentally changing the landscape and ecology, with the loss of much biodiversity. As a result, while old chalk grassland accounted for 40-50% of the eastern Downs before the war, only 3-4% survives. This and development pressures from the surrounding population centres ultimately led to the decision to create the South Downs National Park
The South Downs National Park is England's newest national park, designated on 31 March 2010. The park, covering an area of in southern England, stretches for from Winchester in the west to Eastbourne in the east through the counties of Hamp ...
, which came into full operation on 1 April 2011, to protect and restore the Downs.
The South Downs have also been designated as a National Character Area (NCA 125) by Natural England
Natural England is a non-departmental public body in the United Kingdom sponsored by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. It is responsible for ensuring that England's natural environment, including its land, flora and fauna, ...
. It is bordered by the Hampshire Downs
The Hampshire Downs form a large area of downland in central southern England, mainly in the county of Hampshire but with parts in Berkshire and Wiltshire. They are part of a belt of chalk downland that extends from the South Downs in the southe ...
, the Wealden Greensand, the Low Weald and the Pevensey Levels
Pevensey Levels is a biological Site of Special Scientific Interest between Bexhill-on-Sea and Hailsham in East Sussex. It is a Nature Conservation Review site, Grade I, a Ramsar site and a Special Area of Conservation. An area of is a nati ...
to the north and the South Hampshire Lowlands and South Coast Plain to the south.
The downland is a highly popular recreational destination, particularly for walkers, horseriders and mountain bikers. A long distance footpath and bridleway, the South Downs Way
The South Downs Way is a long distance footpath and bridleway running along the South Downs in southern England. It is one of 16 National Trails in England and Wales. The trail runs for from Winchester in Hampshire to Eastbourne in East Susse ...
, follows the entire length of the chalk ridge from Winchester to Eastbourne, complemented by many interconnecting public footpaths and bridleways.
Toponymy
The term 'downs' is fromOld English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ...
''dūn'', meaning 'hill'. The word acquired the sense of 'elevated rolling grassland' around the fourteenth century. These hills are prefixed 'south' to distinguish them from another chalk escarpment, the North Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. Much of the North Downs comprises two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONBs): the Surrey Hills a ...
, which runs roughly parallel to them about away on the northern edge of the Weald.
Geology

Cretaceous Period
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of t ...
between 100 and 66 million years ago within a shallow sea which extended across much of northwest Europe. The rock is composed of the microscopic skeletons of plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water (or air) that are unable to propel themselves against a current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucia ...
which lived in the sea, hence its colour. The chalk has many fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s, and bands of flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and sta ...
occur throughout the formation. The Chalk is divided into the Lower, Middle and Upper Chalk, a thin band of cream-coloured nodular chalk known as the Melbourn Rock marking the boundary between the Lower and Middle units.
The strata of southeast England, including the Chalk, were gently folded during a phase of the Alpine Orogeny to produce the Weald-Artois Anticline, a dome-like structure with a long east-west axis. Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
has removed the central part of the dome, leaving the north-facing escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''esca ...
of the South Downs along its southern margin with the south-facing chalk escarpment of the North Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. Much of the North Downs comprises two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONBs): the Surrey Hills a ...
as its counterpart on the northern side, as shown on the diagram. Between these two escarpments the anticline has been subject to differential erosion so that geologically distinct areas of hills and vales lie in roughly concentric circles towards the centre; these comprise the Greensand Ridge, most prominent on the north side of the Weald, where it includes Leith Hill
Leith Hill in southern England is the highest summit of the Greensand Ridge, approximately southwest of Dorking, Surrey and southwest of central London. It reaches above sea level, and is the second highest point in southeast England, after ...
, the highest hill in south-east England, the low-lying clay vales of the Low Weald, formed of less resistant Weald Clay, and finally the more highly resistant sandstones of the High Weald at the centre of the anticline, whose elevated forest ridge includes most notably Ashdown Forest.
The chalk, being porous, allows water to soak through; as a result there are many winterbournes along the northern edge.
Geography
The South Downs are a long chalkescarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''esca ...
that stretches for over , rising from the valley of the River Itchen near Winchester, Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English cities on its south coast, Southampton and Portsmouth, Hampshire ...
, in the west to Beachy Head
Beachy Head is a chalk headland in East Sussex, England. It is situated close to Eastbourne, immediately east of the Seven Sisters.
Beachy Head is located within the administrative area of Eastbourne Borough Council which owns the land, formi ...
near Eastbourne
Eastbourne () is a town and seaside resort in East Sussex, on the south coast of England, east of Brighton and south of London. Eastbourne is immediately east of Beachy Head, the highest chalk sea cliff in Great Britain and part of the la ...
, East Sussex, in the east. Behind the steep north-facing scarp slope, the gently inclined dip slope
A dip slope is a topographic (geomorphic) surface which slopes in the same direction, and often by the same amount, as the true dip or apparent dip of the underlying strata.Jackson, JA, J Mehl and K Neuendorf (2005) ''Glossary of Geology.'' Amer ...
of undulating chalk downland extends for a distance of up to southwards. Viewed from high points further north in the High Weald and on the North Downs, the scarp of the South Downs presents itself as a steep wall that bounds the horizon, with its grassland heights punctuated with clumps of trees (such as Chanctonbury Ring
Chanctonbury Ring is a prehistoric hill fort atop Chanctonbury Hill on the South Downs, on the border of the civil parishes of Washington and Wiston in the English county of West Sussex. A ridgeway, now part of the South Downs Way, runs along ...
).
In the west, the chalk ridge of the South Downs merges with the North Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. Much of the North Downs comprises two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONBs): the Surrey Hills a ...
to form the Hampshire Downs
The Hampshire Downs form a large area of downland in central southern England, mainly in the county of Hampshire but with parts in Berkshire and Wiltshire. They are part of a belt of chalk downland that extends from the South Downs in the southe ...
. In the east, the escarpment terminates at the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
coast between Seaford and Eastbourne
Eastbourne () is a town and seaside resort in East Sussex, on the south coast of England, east of Brighton and south of London. Eastbourne is immediately east of Beachy Head, the highest chalk sea cliff in Great Britain and part of the la ...
, where it produces the spectacular white cliffs of Seaford Head, the cross-section of dry valleys known as the Seven Sisters and Beachy Head
Beachy Head is a chalk headland in East Sussex, England. It is situated close to Eastbourne, immediately east of the Seven Sisters.
Beachy Head is located within the administrative area of Eastbourne Borough Council which owns the land, formi ...
, the highest chalk sea cliff in Britain at above sea level.
The South Downs may be said to have three main component parts: the East Hampshire Downs, the Western Downs and the Eastern Downs, together with the river valleys that cut across them and the land immediately below them, the ''scarpfoot''. The Western and Eastern Downs are often collectively referred to as the ''Sussex Downs''. The Western Downs, lying west of the River Arun
The River Arun () is a river in the English county of West Sussex. At long, it is the longest river entirely in Sussex and one of the longest starting in Sussex after the River Medway, River Wey and River Mole. From the series of small strea ...
, are much more wooded, particularly on the scarp face, than the Eastern Downs. The bare Eastern Downs – the only part of the chalk escarpment to which, until the late 19th century, the term "South Downs" was usually applied – have come to epitomise, in literature and art, the South Downs as a whole and which have been the subject matter of such celebrated writers and artists as Rudyard Kipling
Joseph Rudyard Kipling ( ; 30 December 1865 – 18 January 1936)''The Times'', (London) 18 January 1936, p. 12. was an English novelist, short-story writer, poet, and journalist. He was born in British India, which inspired much of his work.
...
(the "blunt, bow-headed, whale-backed downs") and Eric Ravilious.
Four river valleys cut through the South Downs, namely those of the rivers Arun, Adur, Ouse and Cuckmere, providing a contrasting landscape. Chalk aquifers and to a lesser extent winterbourne streams supply much of the water required by the surrounding settlements. Dew pond
A dew pond is an artificial pond usually sited on the top of a hill, intended for watering livestock. Dew ponds are used in areas where a natural supply of surface water may not be readily available. The name dew pond (sometimes cloud pond or mist ...
s, artificial ponds for watering livestock, are a characteristic feature on the downland.
The highest point on the South Downs is Butser Hill, whose summit is above sea level. The plateau-like top of this irregularly shaped hill, which lies just south of Petersfield, Hampshire
Petersfield is a market town and civil parish in the East Hampshire district of Hampshire, England. It is north of Portsmouth. The town has its own railway station on the Portsmouth Direct line, the mainline rail link connecting Portsmouth a ...
, was in regular use through prehistory. It has been designated as a national nature reserve.
Within the boundary of the South Downs National Park, which includes parts of the western Weald to the north of the South Downs, the highest point is Blackdown, West Sussex, which rises to above sea level. However, Blackdown geologically is not part of the South Downs but instead forms part of the Greensand Ridge on the Weald's western margins.
A list of those points on the South Downs above , going from west to east, is given below.
History
Archaeological evidence has revealed that the Downs have been inhabited and utilised for thousands of years.Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
flint mines such as Cissbury
Cissbury Ring is an biological Site of Special Scientific Interest north of Worthing in West Sussex. It is owned by the National Trust and is designated a Scheduled monument for its Neolithic flint mine and Iron Age hillfort.
Cissbury R ...
, burial mounds
A tumulus (plural tumuli) is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds or ''kurgans'', and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a mound of stones built ...
such as the Devil's Jumps and Devil's Humps
The Devil's Humps (also known as the Kings' Graves) are four Bronze Age barrows situated on Bow Hill on the South Downs near Stoughton, West Sussex. They are situated on a downland ridgeway crossed by an ancient trackway, above Kingley Vale.Dy ...
, and hill forts
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Rom ...
like Chanctonbury Ring
Chanctonbury Ring is a prehistoric hill fort atop Chanctonbury Hill on the South Downs, on the border of the civil parishes of Washington and Wiston in the English county of West Sussex. A ridgeway, now part of the South Downs Way, runs along ...
are strong features in the landscape.
It has been estimated that the tree cover of the Downs was cleared over 3000 years ago, and the present closely grazed turf is the result of continual grazing by sheep.
National park
Proposals to create a national park for the South Downs date back to the 1940s. However, it was not until 1999 that the idea received firm government support. After a public enquiry that took place between 2003 and 2009, the government announced its decision to make the South Downs a national park on 31 March 2009. TheSouth Downs National Park
The South Downs National Park is England's newest national park, designated on 31 March 2010. The park, covering an area of in southern England, stretches for from Winchester in the west to Eastbourne in the east through the counties of Hamp ...
finally came into operation on 1 April 2011. Within its boundary are included not only the South Downs proper but also part of the western Weald, a geologically and ecologically quite different district.
The South Downs National Park has replaced two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB)s: East Hampshire AONB
East Hampshire Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB) in England was designated in 1962. The designation was revoked in March 2010, together with the neighbouring Sussex Downs AONB, upon the establishment of the South Downs National Park. T ...
and Sussex Downs AONB
Sussex Downs Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty in England was designated in 1966. The designation was revoked in March 2010, together with the neighbouring East Hampshire AONB, upon the establishment of the South Downs National Park.
The area ...
. During the enquiry process a number of boundary questions were considered, so that the National Park contains areas not in the former AONBs, and vice versa.
National nature reserves
The South Downs contain a number of national nature reserves (NNRs). The NNRs on the Sussex Downs comprise Kingley Vale, nearChichester
Chichester () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and civil parish in West Sussex, England.OS Explorer map 120: Chichester, South Harting and Selsey Scale: 1:25 000. Publisher:Ordnance Survey – Southampton B2 edition. Publi ...
, said by Natural England
Natural England is a non-departmental public body in the United Kingdom sponsored by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. It is responsible for ensuring that England's natural environment, including its land, flora and fauna, ...
to contain one of the finest yew forests in Europe, including a grove of ancient trees which are among the oldest living things in Britain (the reserve is also one of the most important archaeological sites in southern England, with 14 scheduled monument
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a nationally important archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorised change.
The various pieces of legislation that legally protect heritage assets from damage and d ...
s); Castle Hill, between Brighton and Lewes, an important example of ancient, traditionally managed grassland; Lewes Downs ( Mount Caburn), a traditionally managed chalk downland (and also an important archaeological site); and Lullington Heath, on the northern fringe of Friston Forest north-west of Eastbourne, one of the largest areas of chalk heath in Britain.
The NNRs on the East Hampshire Downs comprise Butser Hill, near Petersfield, a large area of chalk grassland on the highest point in the South Downs (a large area is also designated as a scheduled monument reflecting its historical significance, particularly in the Bronze and Iron Ages); Old Winchester Hill
{{Infobox SSSI
, image= OldWinchesterHill.JPG
, image_caption =
, name= Old Winchester Hill
, aos= Hampshire
, interest=Biological
, gridref={{gbmappingsmall, SU 642 208
, area= {{convert, 66.2, ha, acre, abbr=off
, notifyda ...
, a lowland grassland on the west and south facing scarp slopes of the Meon valley; and Beacon Hill, a high quality chalk grassland 5 km west of Old Winchester Hill.
Tourism, leisure and sport
In 1923 the Society of Sussex Downsmen (now the South Downs Society) was formed with the aim of protecting the area's unique landscape. The South Downs are a popular area for ramblers with a network of over of well-managed, well-signed and easily accessible trails. The principal bridleway, and longest of them, is theSouth Downs Way
The South Downs Way is a long distance footpath and bridleway running along the South Downs in southern England. It is one of 16 National Trails in England and Wales. The trail runs for from Winchester in Hampshire to Eastbourne in East Susse ...
. The Monarch's Way
The Monarch's Way is a long-distance footpath in England that approximates the escape route taken by King Charles II in 1651 after being defeated in the Battle of Worcester. It runs from Worcester via Bristol and Yeovil to Shoreham, West Su ...
, having originated at Worcester, crosses the South Downs and ends at Shoreham-by-Sea.
Sports undertaken on the Downs include paragliding
Paragliding is the recreational and competitive adventure sport of flying paragliders: lightweight, free-flying, foot-launched glider aircraft with no rigid primary structure. The pilot sits in a harness or lies supine in a cocoon-like 'p ...
, mountain-biking, horse riding
Equestrianism (from Latin , , , 'horseman', 'horse'), commonly known as horse riding (Commonwealth English) or horseback riding (American English), includes the disciplines of riding, driving, and vaulting. This broad description includes the ...
and walking
Walking (also known as ambulation) is one of the main gaits of terrestrial locomotion among legged animals. Walking is typically slower than running and other gaits. Walking is defined by an ' inverted pendulum' gait in which the body vaults ...
. The popular ''Beachy Head Marathon'' (formerly ''Seven Sisters Marathon''), a hilly cross-country marathon, takes place each autumn on the eastern Downs, starting and finishing in Eastbourne. The South Downs Trail Marathon starts in the village of Slindon (near Arundel) and ends at the Queen Elizabeth Country Park (to the south of Petersfield.)
Longer events that take in the South Downs Way include a 100-mile running 'ultramarathon' and mountain biking 75 mile night time race from Beachy Head to Queen Elizabeth Country Park.
Landmarks
Three of the landmarks on the Downs are the Long Man of Wilmington and the Litlington White Horse being chalk carvedhill figure
A hill figure is a large visual representation created by cutting into a steep hillside and revealing the underlying geology. It is a type of geoglyph usually designed to be seen from afar rather than above. In some cases trenches are dug and ...
s, and Clayton Windmills. There is also a war memorial
A war memorial is a building, monument, statue, or other edifice to celebrate a war or victory, or (predominating in modern times) to commemorate those who died or were injured in a war.
Symbolism
Historical usage
It has ...
, The Chattri, dedicated to Indian soldiers who died in the Brighton area, having been brought there for treatment after being injured fighting on the Western Front in the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
.

South Downs in literature
Rudyard Kipling
Joseph Rudyard Kipling ( ; 30 December 1865 – 18 January 1936)''The Times'', (London) 18 January 1936, p. 12. was an English novelist, short-story writer, poet, and journalist. He was born in British India, which inspired much of his work.
...
who lived at Rottingdean
Rottingdean is a village in the city of Brighton and Hove, on the south coast of England. It borders the villages of Saltdean, Ovingdean and Woodingdean, and has a historic centre, often the subject of picture postcards.
Name
The name Rotting ...
described the South Downs as "Our blunt, bow-headed whale-backed Downs". Writing in 1920 in his poem ''The South Country'', poet Hilaire Belloc
Joseph Hilaire Pierre René Belloc (, ; 27 July 187016 July 1953) was a Franco-English writer and historian of the early twentieth century. Belloc was also an orator, poet, sailor, satirist, writer of letters, soldier, and political activist. H ...
describes the South Downs as "the great hills of the South Country". In ''On The South Coast'', poet Algernon Charles Swinburne describes the South Downs as "the green smooth-swelling unending downs".
The naturalist-writer William Henry Hudson wrote that "during the whole fifty-three mile length from Beachy Head to Harting the ground never rises above a height of 850 feet, but we feel on top of the world".
Poet Francis William Bourdillon also wrote a poem "On the South Downs".. The South Downs have been home to several writers including Jane Austen who lived at Chawton
Chawton is a village and civil parish in the East Hampshire district of Hampshire, England. The village lies within the South Downs National Park and is famous as the home of Jane Austen for the last eight years of her life.
History
Chawton's re ...
on the edge of the Downs in Hampshire. The Bloomsbury Group often visited Monk's House in Rodmell, the home of Virginia Woolf
Adeline Virginia Woolf (; ; 25 January 1882 28 March 1941) was an English writer, considered one of the most important modernist 20th-century authors and a pioneer in the use of stream of consciousness as a narrative device.
Woolf was born i ...
in the Ouse valley. Alfred, Lord Tennyson
Alfred Tennyson, 1st Baron Tennyson (6 August 1809 – 6 October 1892) was an English poet. He was the Poet Laureate during much of Queen Victoria's reign. In 1829, Tennyson was awarded the Chancellor's Gold Medal at Cambridge for one of his ...
had a second home at Aldworth, on Blackdown; geologically part of the Weald, Blackdown lies north of the South Downs but is included in the South Downs National Park.
In the introduction to Arthur Conan Doyle's short story collection "His Last Bow", Dr. Watson states that Sherlock Holmes has retired to a small farm upon the Downs near Eastbourne. In "His Last Bow" itself, Holmes states that he "lives and keeps bees upon the South Downs". Furthermore, the short story " The Lion's Mane" is about a case which Holmes solves whilst living there.
The author Graham Greene
Henry Graham Greene (2 October 1904 – 3 April 1991) was an English writer and journalist regarded by many as one of the leading English novelists of the 20th century. Combining literary acclaim with widespread popularity, Greene acquir ...
's, first published novel, ' The Man Within' (1929) is set largely on and around the South Downs. The book's principal character, 'Andrews', travels by foot across the Downs to reach Lewes and attend the Assizes. Greene provides a detailed description of both the landscape and its 'feel'.
The author H. G. Wells published a book called “The Invisible Man” in 1898 and it says “He fled to South Down”.
Gallery
Devil's Dyke, Sussex
Devil's Dyke is a 100 metre deep V-shaped dry valley on the South Downs in Sussex in southern England, north-west of Brighton. It is managed by the National Trust, and is also part of the Beeding Hill to Newtimber Hill Site of Special Scienti ...
File:Uk south seven sisters.jpg, South Downs close to Beachy Head
Beachy Head is a chalk headland in East Sussex, England. It is situated close to Eastbourne, immediately east of the Seven Sisters.
Beachy Head is located within the administrative area of Eastbourne Borough Council which owns the land, formi ...
File:Trig Point Kithurst Hill.jpg, Trig Point on Kithurst Hill West Sussex. Located on the South Downs Way above the village of Storrington. 699 ft high at the summit.
File:Treyford Hill South Downs.jpg, Typical topography (Treyford Hill): steep wooded northern slope (left), gently sloping southern slope of pasture and woodland.
File:The South Downs from Lewes.jpg, Photo taken near Lewes, East Sussex
Notes
References
*.Further reading
* .External links
Sussex South Downs Guide
Visit South Downs tourism website
South Downs National Park Trust website
South Downs Discovery walks and tours website
{{Authority control Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty in England Geology of England Hills of East Sussex Hills of Hampshire Hills of West Sussex Natural regions of England Protected areas of East Sussex Protected areas of Hampshire Protected areas of West Sussex