Suebic Kingdom on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Kingdom of the Suebi ( la, Regnum Suevorum), also called the Kingdom of Galicia ( la, Regnum Galicia) or Suebi Kingdom of Galicia ( la, Galicia suevorum regnum), was a Germanic post-Roman kingdom that was one of the first to separate from the
The Kingdom of the Suebi ( la, Regnum Suevorum), also called the Kingdom of Galicia ( la, Regnum Galicia) or Suebi Kingdom of Galicia ( la, Galicia suevorum regnum), was a Germanic post-Roman kingdom that was one of the first to separate from the
 Additionally it has been pointed out that the lack of mention of the Suevi could mean that they were not ''per se'' an older distinct ethnic group, but the result of a recent
Additionally it has been pointed out that the lack of mention of the Suevi could mean that they were not ''per se'' an older distinct ethnic group, but the result of a recent
 The civil war that erupted in the Iberian Peninsula between the forces of Constantine and Gerontius left the passes through the
The civil war that erupted in the Iberian Peninsula between the forces of Constantine and Gerontius left the passes through the
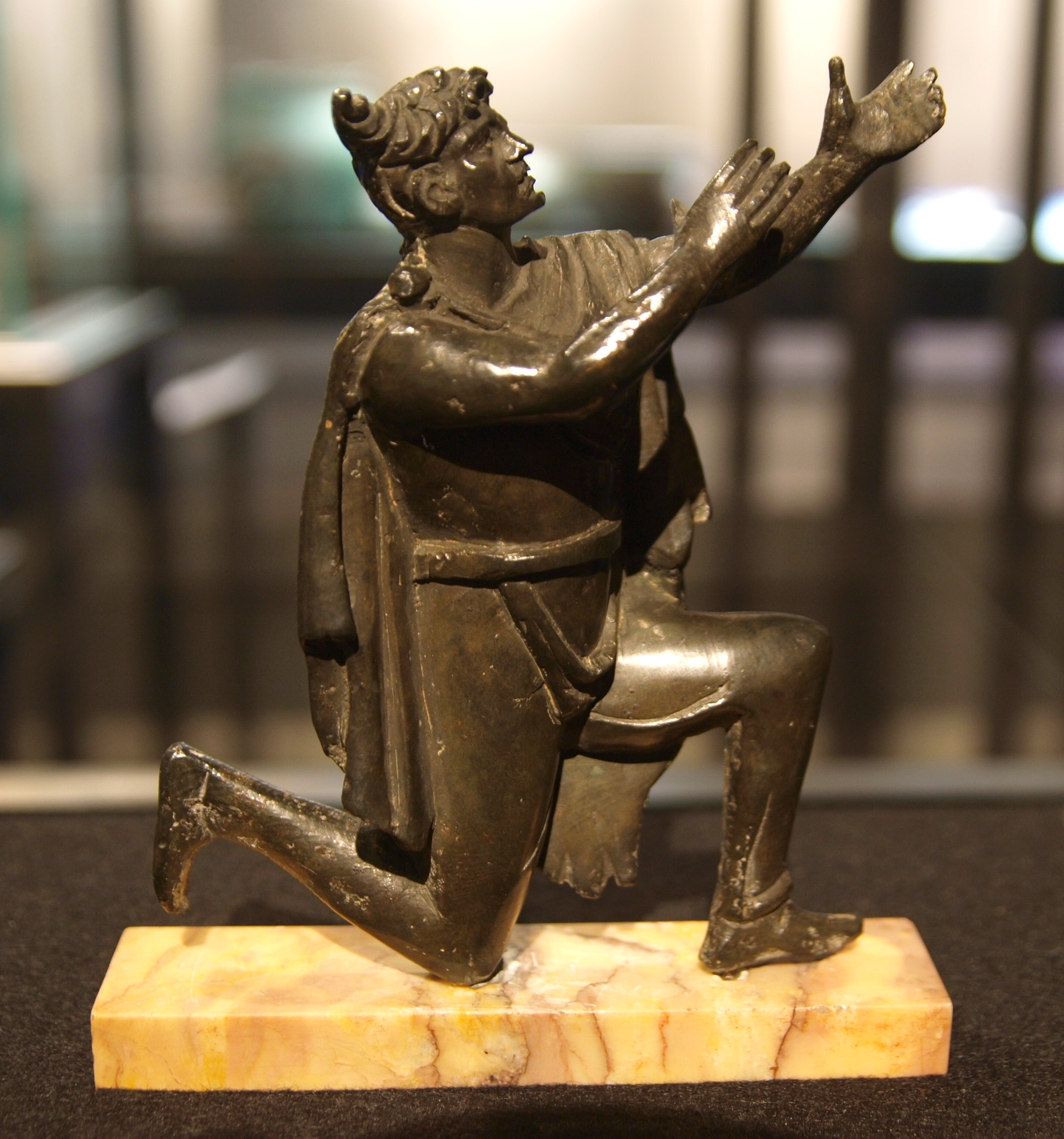
 In 438 Hermeric became ill. Having annexed the entirety of the former Roman province of
In 438 Hermeric became ill. Having annexed the entirety of the former Roman province of
 In 464, Remismund, an ambassador who had travelled between Gallaecia and Gaul on several occasions, became King. Remismund was able to unite the factions of Suevi under his rule, and at the same time restore peace. He was also recognized, perhaps even approved of, by Theodoric, who sent him gifts and weapons along with a wife. Under the leadership of Remismund, the Suevi would again raid the nearby countries, plundering the lands of Lusitania and the
In 464, Remismund, an ambassador who had travelled between Gallaecia and Gaul on several occasions, became King. Remismund was able to unite the factions of Suevi under his rule, and at the same time restore peace. He was also recognized, perhaps even approved of, by Theodoric, who sent him gifts and weapons along with a wife. Under the leadership of Remismund, the Suevi would again raid the nearby countries, plundering the lands of Lusitania and the
 The conversion of the Suebi to Orthodoxy is presented very differently in the primary sources. A contemporary record, the minutes of the
The conversion of the Suebi to Orthodoxy is presented very differently in the primary sources. A contemporary record, the minutes of the  Dahn equated Chararic with Theodemar, even saying that the latter was the name he took upon baptism. It has also been suggested that Theodemar and Ariamir were the same person and the son of Chararic. In the opinion of some historians, Chararic is nothing more than an error on the part of Gregory of Tours and never existed. If, as Gregory relates, Martin of Braga died about the year 580 and had been bishop for about thirty years, then the conversion of Chararic must have occurred around 550 at the latest. Finally, Ferreiro believes the conversion of the Suevi was progressive and stepwise and that Chararic's public conversion was only followed by the lifting of a ban on Orthodox synods in the reign of his successor, which would have been Ariamir; while Theodemar would have been responsible for beginning a persecution of the Arians in his kingdom, to root out their heresy.
Finally, the Suebic conversion is ascribed not to a Suebe, but to a Visigoth, by the chronicler John of Biclarum. He put their conversion alongside that of the Goths, occurring under
Dahn equated Chararic with Theodemar, even saying that the latter was the name he took upon baptism. It has also been suggested that Theodemar and Ariamir were the same person and the son of Chararic. In the opinion of some historians, Chararic is nothing more than an error on the part of Gregory of Tours and never existed. If, as Gregory relates, Martin of Braga died about the year 580 and had been bishop for about thirty years, then the conversion of Chararic must have occurred around 550 at the latest. Finally, Ferreiro believes the conversion of the Suevi was progressive and stepwise and that Chararic's public conversion was only followed by the lifting of a ban on Orthodox synods in the reign of his successor, which would have been Ariamir; while Theodemar would have been responsible for beginning a persecution of the Arians in his kingdom, to root out their heresy.
Finally, the Suebic conversion is ascribed not to a Suebe, but to a Visigoth, by the chronicler John of Biclarum. He put their conversion alongside that of the Goths, occurring under
 Sometime late in the 5th century or early in the sixth century, a group of
Sometime late in the 5th century or early in the sixth century, a group of
 According to John of Biclaro, in 570 Miro succeeded Theodemar as king of the Sueves.Cambridge Ancient History, vol. 14., s.v. "Spain: The Suevic Kingdom" During his time, the Suevic kingdom was challenged again by the Visigoths who, under their king
According to John of Biclaro, in 570 Miro succeeded Theodemar as king of the Sueves.Cambridge Ancient History, vol. 14., s.v. "Spain: The Suevic Kingdom" During his time, the Suevic kingdom was challenged again by the Visigoths who, under their king
 On the death of Miro, his son Eboric, Eburic was made king, but apparently not before sending tokens of appreciation and friendship to Leovigild. Not a year later his brother-in-law, named Andeca, Audeca, accompanied by the army, seized power. He took Eburic into a monastery forced him to Holy orders in the Catholic Church, ordain as a priest, thereby making him ineligible for the throne. Then Audeca married Siseguntia, king Miro's widow, and made himself king. This usurpation and the friendship granted by Eboric gave Leovigild the opportunity to seize the neighboring kingdom. In 585 Leovigild went to war against the Sueves, invading Gallecia. In the words of John of Biclaro: "''King Leovigild devastates Gallaecia and deprives Audeca of the totality of the Kingdom; the nation of the Sueves, their treasure and fatherland are conduced to his own power and turned into a province of the Goths.''" During the campaign, the Franks of king Guntram attacked Septimania, maybe trying to help the Sueves, at the same time sending ships to Gallaecia which were intercepted by Leovigild's troops, who took their cargo and killed or enslaved most of their crews. Thus was the kingdom transferred to the Goths as one of their three administrative regions: Gallaecia, Hispania and Gallia Narbonensis. Audeca, captured, was tonsured and forced to take holy orders, then sent into exile in Beja (Portugal), Beja, in Southern Lusitania.
This same year, 585, a man named Malaric rebelled against the Goths and reclaimed the throne, but he was finally defeated and captured by the generals of Leovigild, who took him in chains to the Visigothic king.
On the death of Miro, his son Eboric, Eburic was made king, but apparently not before sending tokens of appreciation and friendship to Leovigild. Not a year later his brother-in-law, named Andeca, Audeca, accompanied by the army, seized power. He took Eburic into a monastery forced him to Holy orders in the Catholic Church, ordain as a priest, thereby making him ineligible for the throne. Then Audeca married Siseguntia, king Miro's widow, and made himself king. This usurpation and the friendship granted by Eboric gave Leovigild the opportunity to seize the neighboring kingdom. In 585 Leovigild went to war against the Sueves, invading Gallecia. In the words of John of Biclaro: "''King Leovigild devastates Gallaecia and deprives Audeca of the totality of the Kingdom; the nation of the Sueves, their treasure and fatherland are conduced to his own power and turned into a province of the Goths.''" During the campaign, the Franks of king Guntram attacked Septimania, maybe trying to help the Sueves, at the same time sending ships to Gallaecia which were intercepted by Leovigild's troops, who took their cargo and killed or enslaved most of their crews. Thus was the kingdom transferred to the Goths as one of their three administrative regions: Gallaecia, Hispania and Gallia Narbonensis. Audeca, captured, was tonsured and forced to take holy orders, then sent into exile in Beja (Portugal), Beja, in Southern Lusitania.
This same year, 585, a man named Malaric rebelled against the Goths and reclaimed the throne, but he was finally defeated and captured by the generals of Leovigild, who took him in chains to the Visigothic king.
 After the conquest, king Leovigild reintroduced the Arian Church among the Sueves,Thompson 1979, 105 but this was a short-lived institution, because after his death in 586 his son Reccared openly promoted the mass conversion of Visigoths and Sueves to Catholicism. Reccared's plans were opposed by a group of Arian conspirators; its leader, Segga, was exiled to Gallaecia, after his hands were amputated. The conversion occurred during the Third Council of Toledo, with the assistance of seventy-two bishops from Hispania, Gaul and Gallaecia. There, eight bishops renounced their Arianism, among them four Suevi: Argiovittus of Porto, Beccila of Lugo, Gardingus of Tui and Sunnila of Viseu. The mass conversion was celebrated by king Reccared: "Not only the conversion of the Goths is found among the favours that we have received, but also the infinite multitude of the Sueves, whom with divine assistance we have subjected to our realm. Although led into heresy by external fault, with our diligence we have brought them to the origins of truth". He was styled as "King of the Visigoths and of the Suevi" in a letter sent to him by Pope Gregory the Great soon after.
Under the Goths, the administrative apparatus of the Suevi Kingdom was initially maintained —many of the Suevi districts established during the reign of Theodemar are also known as later Visigothic mints— but during the middle years of the seventh century an administrative and ecclesiastical reform led to the disappearance of most of these mints, with the exception of that of the cities of Braga, Lugo and Tui. Also the northern Lusitanian bishoprics of Lamego,
After the conquest, king Leovigild reintroduced the Arian Church among the Sueves,Thompson 1979, 105 but this was a short-lived institution, because after his death in 586 his son Reccared openly promoted the mass conversion of Visigoths and Sueves to Catholicism. Reccared's plans were opposed by a group of Arian conspirators; its leader, Segga, was exiled to Gallaecia, after his hands were amputated. The conversion occurred during the Third Council of Toledo, with the assistance of seventy-two bishops from Hispania, Gaul and Gallaecia. There, eight bishops renounced their Arianism, among them four Suevi: Argiovittus of Porto, Beccila of Lugo, Gardingus of Tui and Sunnila of Viseu. The mass conversion was celebrated by king Reccared: "Not only the conversion of the Goths is found among the favours that we have received, but also the infinite multitude of the Sueves, whom with divine assistance we have subjected to our realm. Although led into heresy by external fault, with our diligence we have brought them to the origins of truth". He was styled as "King of the Visigoths and of the Suevi" in a letter sent to him by Pope Gregory the Great soon after.
Under the Goths, the administrative apparatus of the Suevi Kingdom was initially maintained —many of the Suevi districts established during the reign of Theodemar are also known as later Visigothic mints— but during the middle years of the seventh century an administrative and ecclesiastical reform led to the disappearance of most of these mints, with the exception of that of the cities of Braga, Lugo and Tui. Also the northern Lusitanian bishoprics of Lamego,
 *
*
 Unlike some other barbarian peoples, such as the Vandals, Visigoths, Ostrogoths and Huns, which played an important part in Rome's loss of the western provinces, the Sueves—establishing themselves in Gallaecia and northern Lusitania, which were remote and extra-Mediterranean areas—seldom posed a threat to Rome and to Rome's interests; in fact, at times where we have more detailed knowledge of their history through a diversity of sources, that is precisely when they became a challenge, as it was under the reign of Rechila. Throughout their history as an independent nation, they maintained an important diplomatic activity, most notably with Rome, the Vandals, the Visigoths, and, later, with the
Unlike some other barbarian peoples, such as the Vandals, Visigoths, Ostrogoths and Huns, which played an important part in Rome's loss of the western provinces, the Sueves—establishing themselves in Gallaecia and northern Lusitania, which were remote and extra-Mediterranean areas—seldom posed a threat to Rome and to Rome's interests; in fact, at times where we have more detailed knowledge of their history through a diversity of sources, that is precisely when they became a challenge, as it was under the reign of Rechila. Throughout their history as an independent nation, they maintained an important diplomatic activity, most notably with Rome, the Vandals, the Visigoths, and, later, with the  The conflict of Vandals and Sueves is also narrated by
The conflict of Vandals and Sueves is also narrated by

 As the Suebi quickly adopted the local Vulgar Latin language, few traces were left of their Germanic tongue in the Galician language, Galician and Portuguese languages. Distinguishing between loanwords from Gothic or Suevic is difficult, but there is a series of words, characteristic of Galicia and northern half of Portugal, which are attributed either to the Suebi or to the Goths, although no major Visigothic immigration into Gallaecia is known before the 8th century. These words are rural in nature, relative to animals, agriculture, and country life: ''laverca'' 'lark' (from Proto-Germanic *laiwazikōn 'lark'), ''meixengra'' 'titmouse' (same word as Old Norse ''meisingr'' 'titmouse', from *maisōn 'titmouse'),Kremer 2004: 140 ''lobio'' or ''lóvio'' 'vinegrape' (to *lauban 'foliage'), ''britar'' 'to break' (from *breutanan 'to break'), ''escá'' 'bushel' (from ancient ''scala'' 'bowl', from *skēlō 'bowl'), ''ouva'' 'elf, spirit' (from *albaz 'elf'), ''marco'' 'boundary stone' (from PGmc *markan 'frontier, limit'), ''groba'' 'gully' (from *grōbō 'groove'), ''maga ''
As the Suebi quickly adopted the local Vulgar Latin language, few traces were left of their Germanic tongue in the Galician language, Galician and Portuguese languages. Distinguishing between loanwords from Gothic or Suevic is difficult, but there is a series of words, characteristic of Galicia and northern half of Portugal, which are attributed either to the Suebi or to the Goths, although no major Visigothic immigration into Gallaecia is known before the 8th century. These words are rural in nature, relative to animals, agriculture, and country life: ''laverca'' 'lark' (from Proto-Germanic *laiwazikōn 'lark'), ''meixengra'' 'titmouse' (same word as Old Norse ''meisingr'' 'titmouse', from *maisōn 'titmouse'),Kremer 2004: 140 ''lobio'' or ''lóvio'' 'vinegrape' (to *lauban 'foliage'), ''britar'' 'to break' (from *breutanan 'to break'), ''escá'' 'bushel' (from ancient ''scala'' 'bowl', from *skēlō 'bowl'), ''ouva'' 'elf, spirit' (from *albaz 'elf'), ''marco'' 'boundary stone' (from PGmc *markan 'frontier, limit'), ''groba'' 'gully' (from *grōbō 'groove'), ''maga '''guts of fish' and ''esmagar '''to smash' (from PGmc *magōn 'stomach'), ''bremar '''to yearn' (from PGmc *bremmanan 'to roar'), ''trousa '''snowslide' (from PGmc *dreusanan 'to fall'), brétema 'mist' (from PGmc *breþmaz 'breath, vapour'), ''gabar '''to praise', ''ornear '''to bray' (from PGmc *hurnjanan 'to blow a horn'), ''zapa '''lid, cap' (from PGmc *tappōn 'tap'), ''fita '''ribbon', ''sá '''origin, generation' (from PGmc *salaz 'hall, dwelling'), among others.
Most notable were their contributions to local toponymy and anthroponymy, as Germanic personal names in Galicia#Names used by the Suevi, personal names borne by the Sueves were in use among Galicians up to the Low Middle Ages, while East Germanic languages, East Germanic names in general were most common among locals during the High Middle Ages. From these names is derived also a rich toponymy, found mainly in northern
"Identity and Interaction: The Suevi and the Hispano-Romans."
' University of Virginia: Spring 2007. *Burgess, R. W., ed. (1993). ''The Chronicle of Hydatius''. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, 1993. *Cameron, Averil and others, ed. (2001a). ''Cambridge Ancient History, vol. 13, Late Antiquity: The Late Empire A.D. 337–425''. Cambridge, England: University of Cambridge Press, 2001. *Cameron, Averil and others, ed. (2001b). ''Cambridge Ancient History, vol. 14, Late Antiquity: Empire and Successors A.D. 425–600''. Cambridge, England: University of Cambridge Press, 2001. * DCECH = Coromines, Joan (2012). Diccionario crítico etimológico castellano e hispánico. Madrid: Gredos. . *Donini, Guido and Gordon B. Ford Jr., transl. (1970). ''Isidore of Seville’s History of the Kings of the Goths, Vandals, and Suevi'', 2nd rev. ed. Leiden, Netherlands: E. J. Brill, 1970. *Ferreiro, Alberto (1995).
"Braga and Tours: Some Observations on Gregory's ''De virtutibus sancti Martini''.
' ''Journal of Early Christian Studies''. 3 (1995), p. 195–210. * * * Kremer, Dieter (2004). El elemento germánico y su influencia en la historia lingüística peninsular, in Rafael Cano, Historia de la lengua española. , p. 133-148. *Kulikowski, Michael (2004). ''Late Roman Spain and its Cities.'' Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2004. * * Orel, Vladimir (2003). A Handbook of Germanic Etymology. Leiden: Brill. . * * *Thompson, E. A. (1980). ''The Conversion of the Spanish Suevi to Catholicism.'' ''Visigothic Spain: New Approaches''. ed. Edward James (historian), Edward James. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1980. . *Thompson, E. A. (1982). ''Romans and Barbarians''. Madison, WI: University of Wisconsin Press, 1982. *Williams, Megan: Personal Communication, San Francisco State University History Professor. 16 November 2010.
The Chronicle of Hydatius
is the main source for the history of the suevi in Galicia and Portugal up to 468.
Medieval Galician anthroponomy
in ''Collectio Hispana Gallica Augustodunensis''
- translated by I.W. Raymond {{Authority control Kingdom of the Suebi, Germanic kingdoms, Suebi Former countries on the Iberian Peninsula, Suebi Medieval Portugal Medieval Galicia (Spain) History of Portugal by polity Former countries in Europe, Suebi Former kingdoms, Suebi Former monarchies of Europe, Suebi 5th century in Hispania 6th century in Hispania States and territories established in the 400s States and territories disestablished in the 580s 409 establishments 585 disestablishments Barbarian kingdoms
 The Kingdom of the Suebi ( la, Regnum Suevorum), also called the Kingdom of Galicia ( la, Regnum Galicia) or Suebi Kingdom of Galicia ( la, Galicia suevorum regnum), was a Germanic post-Roman kingdom that was one of the first to separate from the
The Kingdom of the Suebi ( la, Regnum Suevorum), also called the Kingdom of Galicia ( la, Regnum Galicia) or Suebi Kingdom of Galicia ( la, Galicia suevorum regnum), was a Germanic post-Roman kingdom that was one of the first to separate from the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
. Based in the former Roman provinces of Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia (Spain), Galicia, Norte, Portugal, northern Portugal, Asturias and León (province), Leon and the lat ...
and northern Lusitania
Lusitania (; ) was an ancient Iberian Roman province located where modern Portugal (south of the Douro river) and
a portion of western Spain (the present Extremadura and the province of Salamanca) lie. It was named after the Lusitani or Lu ...
, the de facto kingdom was established by the Suebi
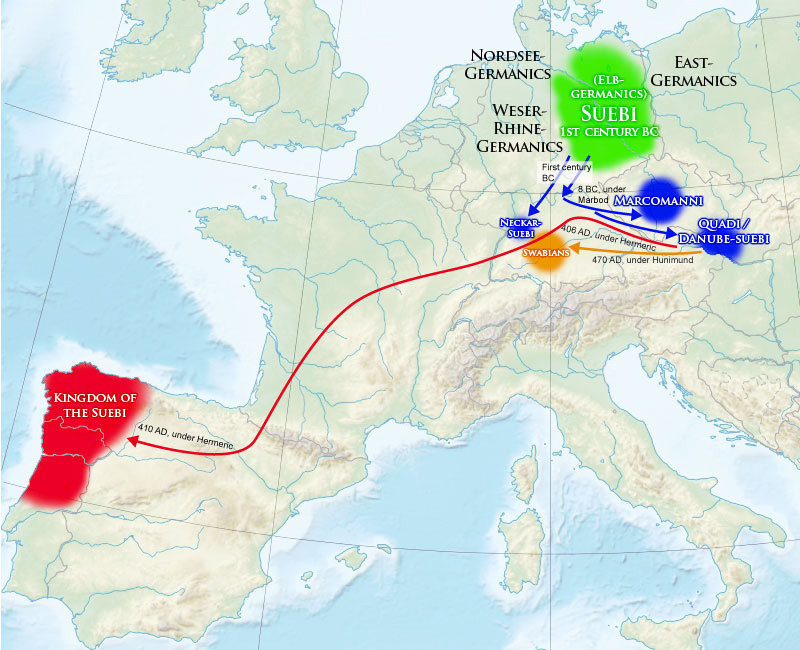
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own name ...
about 409, and during the 6th century it became a formally declared kingdom identifying with Gallaecia. It maintained its independence until 585, when it was annexed by the Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is k ...
, and was turned into the sixth province of the Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of the Goths ( la, Regnum Gothorum), was a kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic successor states to ...
in Hispania.
Origins
Little is known about theSuevi
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own names ...
who crossed the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, source ...
on the night of 31 December 406 AD and entered the Roman Empire. It is speculated that these Suevi are the same group as the Quadi
The Quadi were a Germanic
*
*
*
people who lived approximately in the area of modern Moravia in the time of the Roman Empire. The only surviving contemporary reports about the Germanic tribe are those of the Romans, whose empire had its bord ...
, who are mentioned in early writings as living north of the middle Danube, in what is now lower Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
and western Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the ...
,Thompson, ''Romans and Barbarians'', 152 and who played an important part in the Germanic Wars
This is a chronology of warfare between the Romans and various Germanic peoples between 113 BC and 476. The nature of these wars varied through time between Roman conquest, Germanic uprisings and later Germanic invasions of the Western Roma ...
of the 2nd century, when, allied with the Marcomanni
The Marcomanni were a Germanic people
*
*
*
that established a powerful kingdom north of the Danube, somewhere near modern Bohemia, during the peak of power of the nearby Roman Empire. According to Tacitus and Strabo, they were Suebian.
O ...
, they fought fiercely against the Romans under Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (Latin: áːɾkus̠ auɾέːli.us̠ antɔ́ːni.us̠ English: ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 AD and a Stoic philosopher. He was the last of the rulers known as the Five Good E ...
. The main reason behind the identification of the Suevi and Quadi as the same group comes from a letter written by St. Jerome to Ageruchia, listing the invaders of the 406 crossing into Gaul, in which the Quadi are listed and the Suevi are not. The argument for this theory, however, is based solely on the disappearance of the Quadi in the text and the emergence of the Suevi, which conflicts with the testimony of other contemporary authors, such as Orosius
Paulus Orosius (; born 375/385 – 420 AD), less often Paul Orosius in English, was a Roman priest, historian and theologian, and a student of Augustine of Hippo. It is possible that he was born in ''Bracara Augusta'' (now Braga, Portugal), t ...
, who did indeed cite the Suevi among the peoples traversing the Rhine in 406, and side by side with Quadi, Marcomanni, Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal Kingdom, Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The ...
and Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
in another passage. Sixth century authors identified the Sueves of Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia (Spain), Galicia, Norte, Portugal, northern Portugal, Asturias and León (province), Leon and the lat ...
with the Alamanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into pre ...
, or simply with ''Germans'',Procopius, ''History of the Wars'', III.3 whilst the 4th century Laterculus Veronensis mentions some Suevi side by side with Alamanni, Quadi, Marcomanni and other Germanic peoples.
 Additionally it has been pointed out that the lack of mention of the Suevi could mean that they were not ''per se'' an older distinct ethnic group, but the result of a recent
Additionally it has been pointed out that the lack of mention of the Suevi could mean that they were not ''per se'' an older distinct ethnic group, but the result of a recent ethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis (; ) is "the formation and development of an ethnic group".
This can originate by group self-identification or by outside identification.
The term ''ethnogenesis'' was originally a mid-19th century neologism that was later introd ...
, with many smaller groups—among them part of the Quadi and Marcomanni—coming together during the migration from the Danube valley to the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
. Other groups of Sueves are mentioned by Jordanes
Jordanes (), also written as Jordanis or Jornandes, was a 6th-century Eastern Roman bureaucrat widely believed to be of Gothic descent who became a historian later in life. Late in life he wrote two works, one on Roman history ('' Romana'') an ...
and other historians as residing by the Danube regions during the 5th and 6th centuries.
Although there is no clearly documented reason behind the migration of 405
, a widely accepted theory is that the migration of the various Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
west of the Rhine was due to the westward push of the Huns during the late 4th century, which forced the Germanic peoples westward in response to the threat. This theory has created controversy within the academic community, because of the lack of convincing evidence.
Whether displaced by the Huns or not, the Suevi along with the Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal Kingdom, Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The ...
and Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
crossed the Rhine on the night of 31 December 405. Their entrance into the Roman Empire was at a moment when the Roman West was experiencing a series of invasions and civil wars; between 405 and 406, the Western regions of the empire saw the invasion of Italy by Goths under Radagaisus
Radagaisus (died 23 August 406) was a Gothic king who led an invasion of Roman Italy in late 405 and the first half of 406.Peter Heather, ''The Fall of the Roman Empire: A New History of Rome and the Barbarians'', 2nd ed. 2006:194; A committed ...
, as well as a steady stream of usurpers. This allowed the invading barbarians to enter Gaul with little resistance, consequently allowing for the barbarians to cause considerable damage to the northern provinces of Germania Inferior
Germania Inferior ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed Germania Secunda in the fourth century, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Agripp ...
, Belgica Prima
Gallia Belgica ("Belgic Gaul") was a province of the Roman Empire located in the north-eastern part of Roman Gaul, in what is today primarily northern France, Belgium, and Luxembourg, along with parts of the Netherlands and Germany.
In 50 BC, ...
, and Belgica Secunda
Gallia Belgica ("Belgic Gaul") was a province of the Roman Empire located in the north-eastern part of Roman Gaul, in what is today primarily northern France, Belgium, and Luxembourg, along with parts of the Netherlands and Germany.
In 50 BC, ...
before the empire saw them as a threat. In response to the barbarian invasion of Gaul, the usurper Constantine III Constantine III may refer to:
* Constantine III (Western Roman Emperor), self-proclaimed western Roman Emperor 407–411
* Heraclius Constantine, Byzantine Emperor in 641
* Constans II, Byzantine emperor 641–668, sometimes referred to under this ...
halted the masses of Vandals, Alans, and Sueves, confining them to northern Gaul. But in the spring of 409, Gerontius led a revolt in Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hi ...
and set up his own emperor, Maximus. Constantine, who had recently been elevated to the title of Augustus, set off to Hispania to deal with the rebellion. Gerontius responded by stirring up the barbarians in Gaul against Constantine, convincing them to mobilize again, and, in the summer of 409, the Vandals, Alans, and Suevi began pushing south towards Hispania.
Settlement and integration
 The civil war that erupted in the Iberian Peninsula between the forces of Constantine and Gerontius left the passes through the
The civil war that erupted in the Iberian Peninsula between the forces of Constantine and Gerontius left the passes through the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
either purposely or inadvertently neglected, leaving southern Gaul and the Iberian Peninsula vulnerable to barbarian attack. Hydatius
Hydatius, also spelled Idacius (c. 400 – c. 469) was a late Western Roman writer and clergyman. The bishop of Aquae Flaviae in the Roman province of Gallaecia (almost certainly the modern Chaves, Portugal, in the modern district of Vila Real), he ...
documents that the crossing into the Iberian Peninsula by the Vandals, Alans, and Suevi took place on either 28 September or 12 October 409. Some scholars take the two dates as the beginning and the end of the crossing of the formidable Pyrenees by scores of thousands, since this could not have been accomplished in one day. Hydatius writes that upon entering Hispania, the barbarian peoples, and even the Roman soldiers, spent 409–410 in a frenzy, plundering food and goods from the cities and countryside, which caused a famine that, according to Hydatius, forced the locals to resort to cannibalism: "riven
''Riven'' is a puzzle adventure video game. It is the sequel to '' Myst'' and second in the ''Myst'' series of games. Developed by Cyan Worlds, it was initially published by Red Orb Entertainment, a division of Broderbund. ''Riven'' was distri ...
by hunger human beings devoured human flesh; mothers too feasted upon the bodies of their own children whom they had killed and cooked with their own hands." In 411 the various barbarian groups brokered a peace and divided the provinces of Hispania among themselves ''sorte'', "by lot". Many scholars believe that the reference to "lot" may be to the ''sortes'', "allotments," which barbarian federates received from the Roman government, which suggests that the Suevi and the other invaders had signed a treaty with Maximus. There is, however, no concrete evidence of any treaties between the Romans and the barbarians: Hydatius never mentions any treaty, and states that the peace in 411 was brought about by the compassion of the Lord,Burgess, ''The Chronicle of Hydatius'', 83 while Orosius asserts that the kings of the Vandals, Alans and Sueves were actively pursuing a pact similar to that of the Visigoths at a later date. The division of the land among the four barbarian groups went as such: the Siling Vandals settled in Hispania Baetica
Hispania Baetica, often abbreviated Baetica, was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula). Baetica was bordered to the west by Lusitania, and to the northeast by Hispania Tarraconensis. Baetica remained one of the basic di ...
, the Alans were allotted the provinces of Lusitania
Lusitania (; ) was an ancient Iberian Roman province located where modern Portugal (south of the Douro river) and
a portion of western Spain (the present Extremadura and the province of Salamanca) lie. It was named after the Lusitani or Lu ...
and Hispania Carthaginensis
Hispania Carthaginensis was a Roman province segregated from Hispania Tarraconensis in the new division of Hispania by emperor Diocletian in 298.
The capital of the new province was settled in Carthago Nova, now Cartagena.
It encompassed the ...
, and the Hasding Vandals and the Suevi shared the northwestern province of Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia (Spain), Galicia, Norte, Portugal, northern Portugal, Asturias and León (province), Leon and the lat ...
.
The division of Gallaecia between the Suevi and the Hasding Vandals placed the Suevi in the west of the province, by the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
shores, most probably in lands now between the cities of Porto
Porto or Oporto () is the second-largest city in Portugal, the capital of the Porto District, and one of the Iberian Peninsula's major urban areas. Porto city proper, which is the entire municipality of Porto, is small compared to its metropo ...
in Portugal, in the south, and Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the '' Comarca'' (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality wh ...
in Galicia, in the north. Soon Braga
Braga ( , ; cel-x-proto, Bracara) is a city and a municipality, capital of the northwestern Portuguese district of Braga and of the historical and cultural Minho Province. Braga Municipality has a resident population of 193,333 inhabitants (in ...
would become their capital, and their domain later expanded into Astorga, and in the region of Lugo
Lugo (, ; la, Lucus Augusti) is a city in northwestern Spain in the autonomous community of Galicia. It is the capital of the province of Lugo. The municipality had a population of 98,025 in 2018, making it the fourth most populous city in Ga ...
and in the valley of the Minho river
The Minho ( , ) or Miño ( , , ; cel-x-proto, Miniu) is the longest river in Galicia, sharing the border with Portugal, with a length of . By discharge, it is the fourth river of the Iberian peninsula, after the Douro, Ebro, and Tagus.
The Min ...
, with no evidence suggesting that the Suevi inhabited any other cities in the province prior to 438. The initial relation between Gallaeci and Suevi were not as calamitous as sometimes suggested,Donini and Ford, ''Isidore'',40 as Hydatius mentions no conflict among the locals between 411 and 430. Furthermore, Orosius affirmed that the newcomers "turned their swords into ploughs" once they received their new lands.
The Suebi spoke a Germanic language
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, E ...
and classical sources refer to a Suebian language. In particular, the Suebi are associated with the concept of an "Elbe Germanic" group of early dialects spoken by the Irminones
The Irminones, also referred to as Herminones or Hermiones ( grc, Ἑρμίονες), were a large group of early Germanic tribes settling in the Elbe watershed and by the first century AD expanding into Bavaria, Swabia and Bohemia. Notably this ...
, entering Germany from the east, and originating on the Baltic. In late classical times, these dialects, by now situated to the south of the Elbe, and stretching across the Danube into the Roman empire, experienced the High German consonant shift
In historical linguistics, the High German consonant shift or second Germanic consonant shift is a phonological development ( sound change) that took place in the southern parts of the West Germanic dialect continuum in several phases. It probabl ...
that defines modern High German languages
The High German dialects (german: hochdeutsche Mundarten), or simply High German (); not to be confused with Standard High German which is commonly also called ''High German'', comprise the varieties of German spoken south of the Benrath and ...
, and in its most extreme form, Upper German
Upper German (german: Oberdeutsch ) is a family of High German dialects spoken primarily in the southern German-speaking area ().
History
In the Old High German time, only Alemannic and Bairisch are grouped as Upper German. In the Middle High ...
. pages 194-5.
Based on some toponymical data, another Germanic group accompanied the Suebi and settled in Portugal, the Buri in the region between the rivers Cávado and Homem, the area known as Terras de Bouro (Lands of the Buri), named ''Burio'' until the High Middle Ages.
The kingdom during the 5th century
King Hermeric
In 416, the Visigoths entered the Iberian Peninsula, sent by the emperor of the West to fight off the barbarians arriving in 409. By 418, the Visigoths, led by their king,Wallia
Wallia or Walha ( Spanish: ''Walia'', Portuguese ''Vália''), ( 385 – 418) was king of the Visigoths from 415 to 418, earning a reputation as a great warrior and prudent ruler. He was elected to the throne after Athaulf and then Sigeric were ...
, had devastated both the Siling Vandals and Alans, leaving the Hasding Vandals and the Suevi, undisturbed by Wallia's campaign, as the two remaining forces in the Iberian Peninsula. In 419, after the departure of the Visigoths to their new lands in Aquitania
Gallia Aquitania ( , ), also known as Aquitaine or Aquitaine Gaul, was a province of the Roman Empire. It lies in present-day southwest France, where it gives its name to the modern region of Aquitaine. It was bordered by the provinces of Gal ...
, a conflict arose between the Vandals under Gunderic
Gunderic ( la, Gundericus; 379–428), King of Hasding Vandals (407-418), then King of Vandals and Alans (418–428), led the Hasding Vandals, a Germanic tribe originally residing near the Oder River, to take part in the barbarian invasions of ...
, and the Suevi, led by king Hermeric
Hermeric (died 441) was the king of the Suevi from at least 419 and possibly as early as 406 until his abdication in 438.
Biography
Before 419
Nothing is known for sure about Hermeric before 419, the year in which he is first mentioned; ...
. Both armies met in the Battle of the Nerbasius mountains, but the intervention of Roman forces commanded by the ''comes Hispaniarum'' Asterius ended the conflict by attacking the Vandals and forcing them to move to Baetica, in modern Andalusia, leaving the Suevi in virtually sole possession of the whole province.
In 429, as the Vandals were preparing their departure to Africa, a Swabian warlord named Heremigarius moved to Lusitania to plunder it, but was confronted by the new Vandal king Gaiseric
Gaiseric ( – 25 January 477), also known as Geiseric or Genseric ( la, Gaisericus, Geisericus; reconstructed Vandalic: ) was King of the Vandals and Alans (428–477), ruling a kingdom he established, and was one of the key players in the dif ...
. Heremigarius drowned in the river Guadiana
The Guadiana River (, also , , ), or Odiana, is an international river defining a long stretch of the Portugal-Spain border, separating Extremadura and Andalusia (Spain) from Alentejo and Algarve (Portugal). The river's basin extends from the e ...
while retreating; this is the first instance of an armed Suebi action outside the provincial limits of Gallaecia. Then, after the Vandals left for Africa, the Swabians were the only barbarian entity left in Hispania.
King Hermeric spent the remainder of his years solidifying Suevic rule over the entire province of Gallaecia. In 430 he broke the old peace maintained with the locals, sacking central Gallaecia, although the barely romanised Gallaeci, who were reoccupying old Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ...
hill fort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roma ...
s, managed to force a new peace, which was sealed with the interchange of prisoners. However, new hostilities broke out in 431 and 433. In 433 king Hermeric
Hermeric (died 441) was the king of the Suevi from at least 419 and possibly as early as 406 until his abdication in 438.
Biography
Before 419
Nothing is known for sure about Hermeric before 419, the year in which he is first mentioned; ...
sent a local bishop, Synphosius, as ambassador, this being the first evidence for collaboration between Sueves and locals. However, it was not until 438 that an enduring peace, which would last for twenty years, was reached in the province.
King Rechila
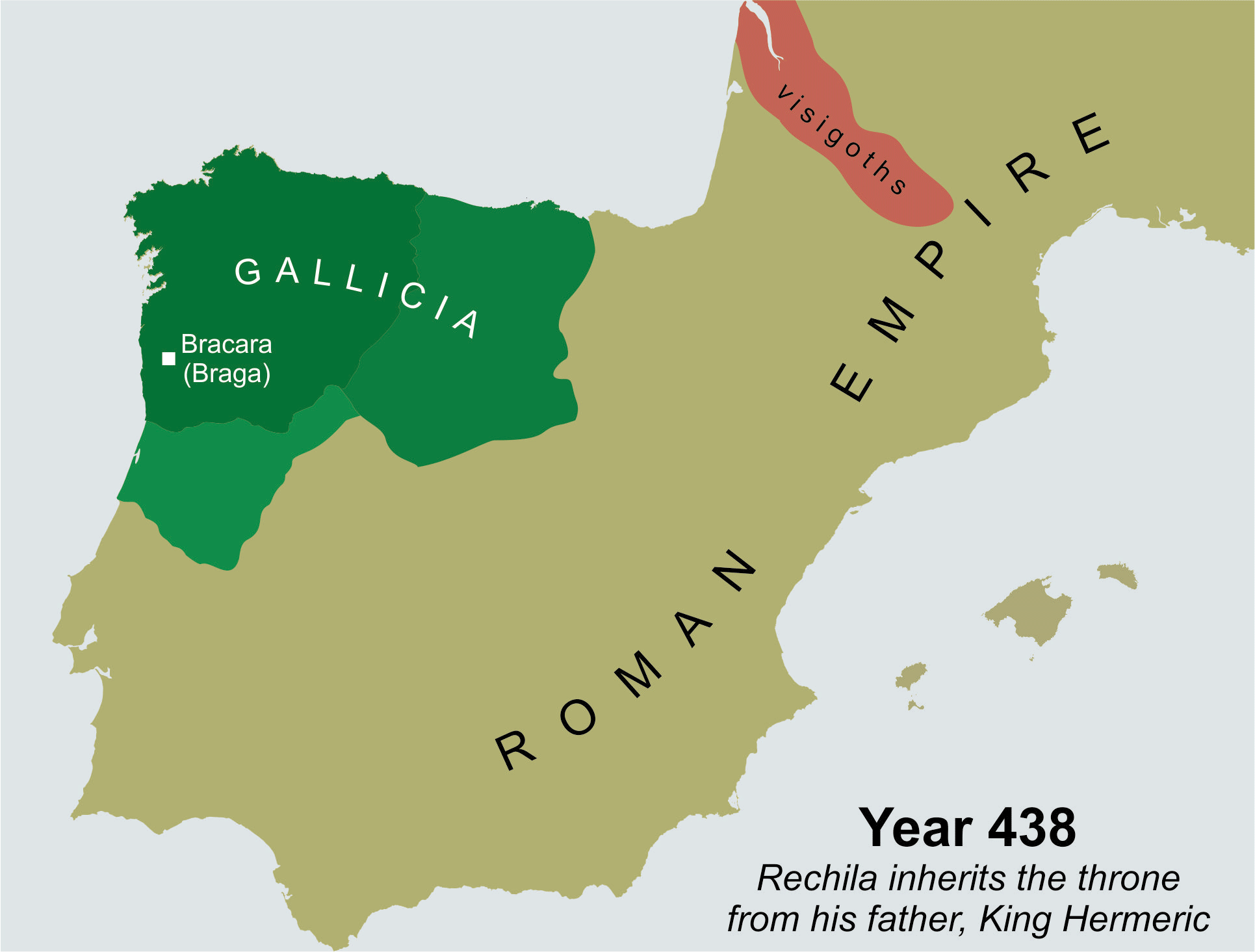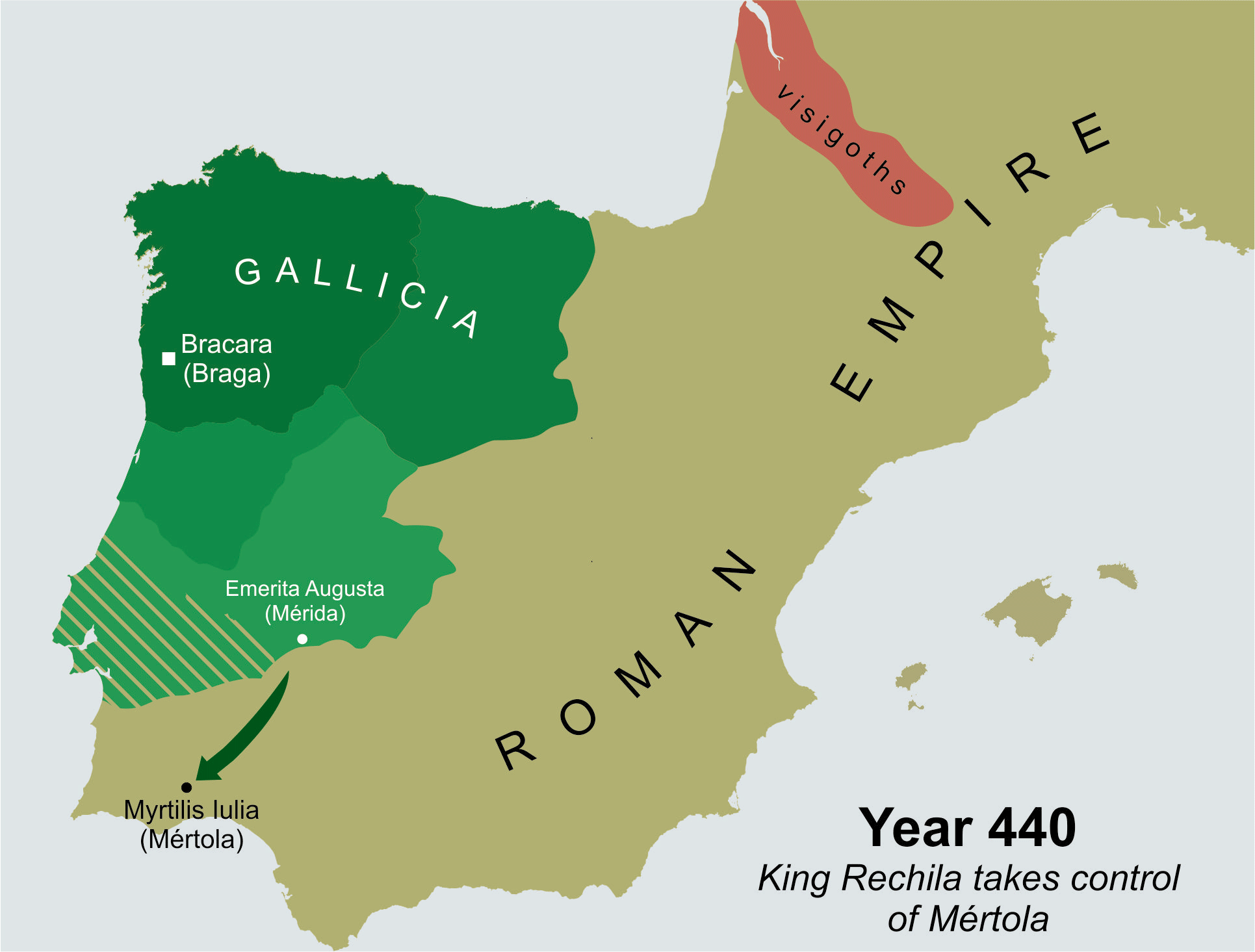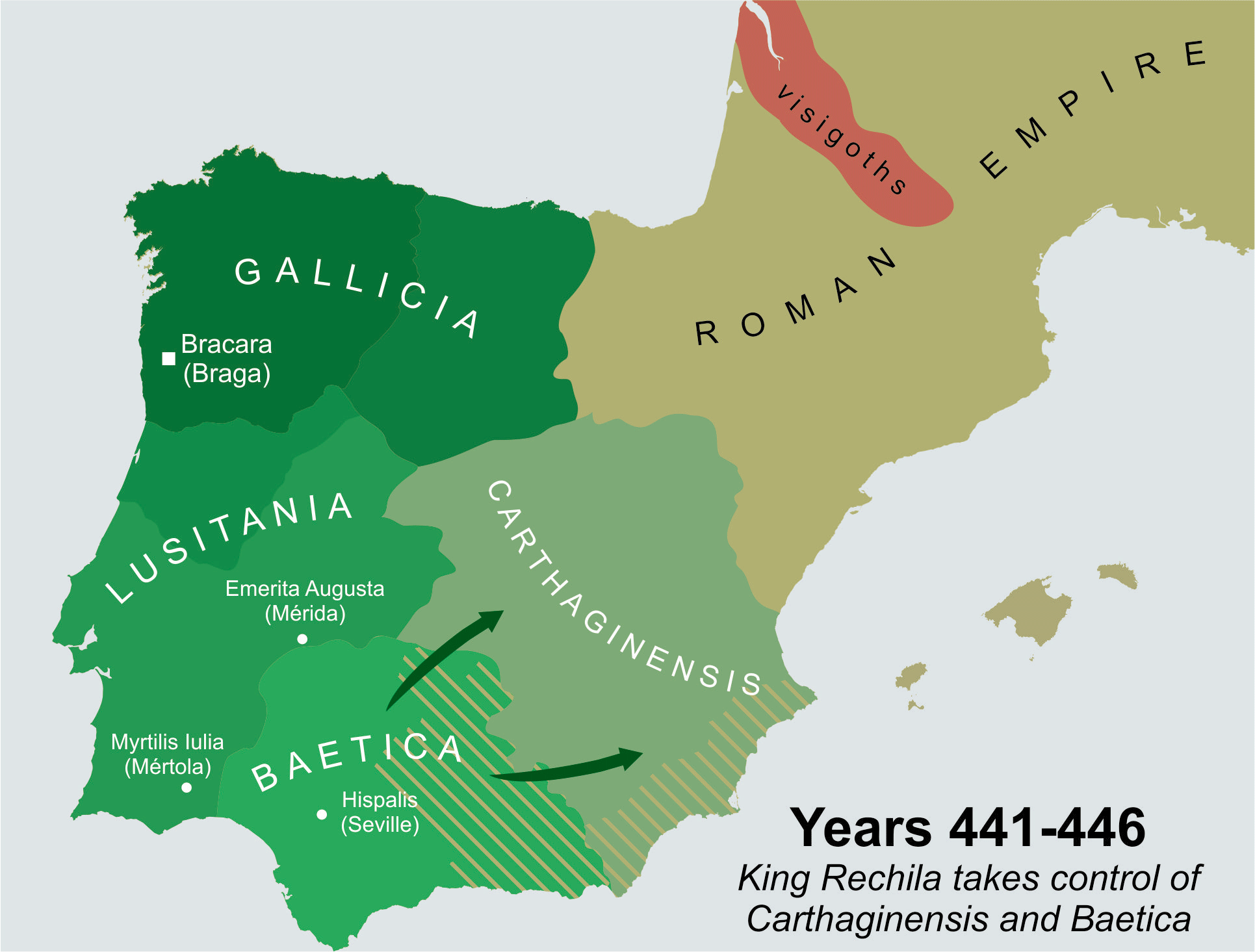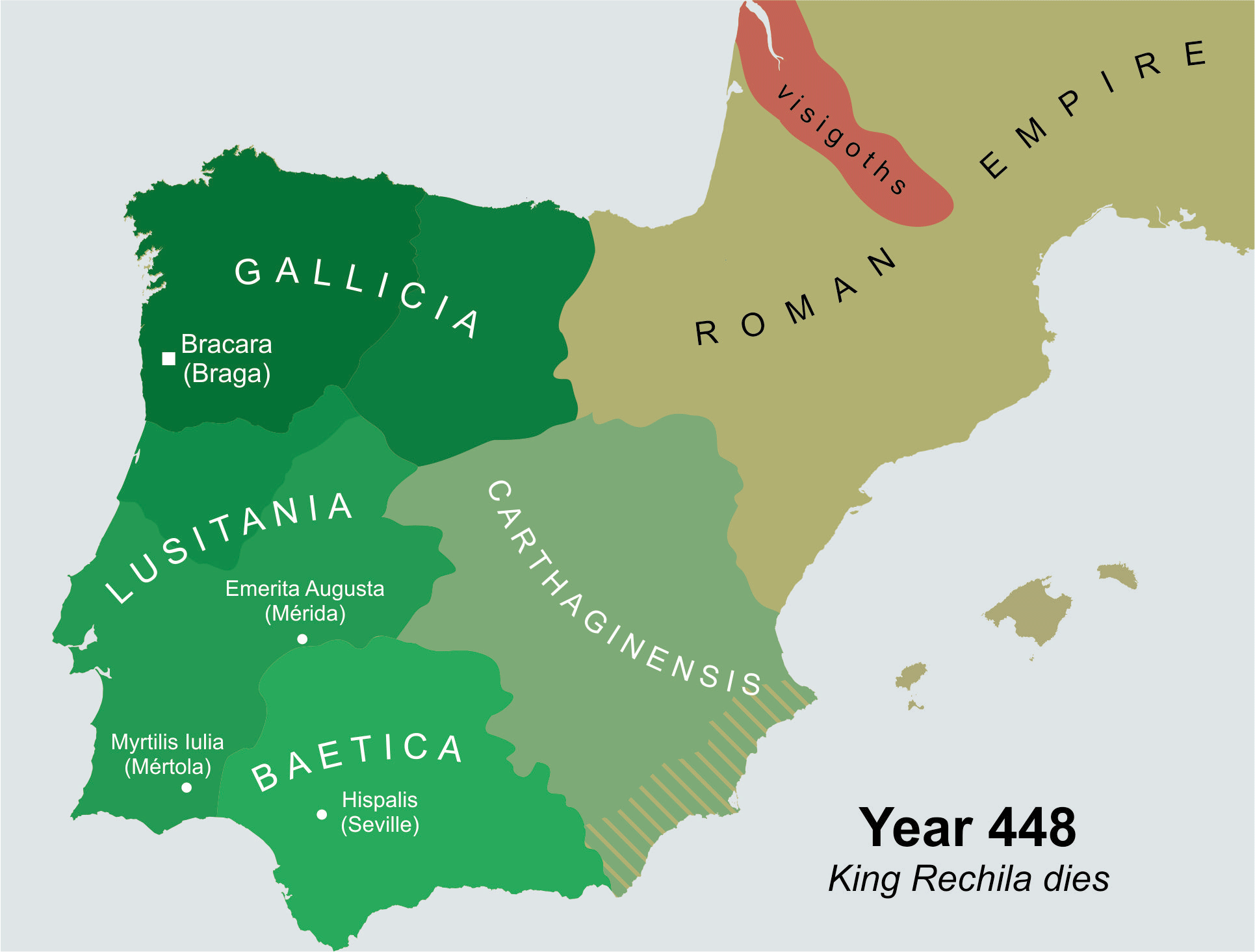
 In 438 Hermeric became ill. Having annexed the entirety of the former Roman province of
In 438 Hermeric became ill. Having annexed the entirety of the former Roman province of Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia (Spain), Galicia, Norte, Portugal, northern Portugal, Asturias and León (province), Leon and the lat ...
, he made peace with the local population, and retired, leaving his son Rechila
Rechila (died 448) was the Suevic king of Galicia from 438 until his death. There are few primary sources for his life, but Hydatius was a contemporary Christian (non-Arian) chronicler in Galicia.
When his father, Hermeric, turned ill in 438, ...
as king of the Sueves. Rechila saw an opportunity for expansion and began pushing to other areas of the Iberian Peninsula. In the same year he campaigned in Baetica, defeating in open battle the ''Romanae militiae dux'' Andevotus by the banks of the Genil
The Genil River is the main (left) tributary of the river Guadalquivir in Andalusia, Spain. The Roman ''Singilis'', its modern name derives from the Moorish rendering of the Roman name: ''Sinyil, Sannil'', and ''Sinnil''.
Route
The source of th ...
river, capturing a large treasure. A year later, in 439, the Sueves invaded Lusitania and entered into its capital, Mérida, which briefly became the new capital of their kingdom. Rechila continued with the expansion of the kingdom, and by 440 he fruitfully besieged and forced the surrender of a Roman official, count Censorius, in the strategic city of Mértola
Mértola () is a municipality in southeastern Portuguese Alentejo near the Spanish border. In 2011, the population was 7,274, in an area of approximately : it is the sixth-largest municipality in Portugal. Meanwhile, it is the second-lowest popula ...
. Next year, in 441, the armies of Rechila
Rechila (died 448) was the Suevic king of Galicia from 438 until his death. There are few primary sources for his life, but Hydatius was a contemporary Christian (non-Arian) chronicler in Galicia.
When his father, Hermeric, turned ill in 438, ...
conquered Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Penins ...
, just months after the death of the old king Hermeric
Hermeric (died 441) was the king of the Suevi from at least 419 and possibly as early as 406 until his abdication in 438.
Biography
Before 419
Nothing is known for sure about Hermeric before 419, the year in which he is first mentioned; ...
, who had ruled his people for more than thirty years. With the conquest of Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Penins ...
, capital of Baetica
Hispania Baetica, often abbreviated Baetica, was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula). Baetica was bordered to the west by Lusitania, and to the northeast by Hispania Tarraconensis. Baetica remained one of the basi ...
, the Suevi managed to control Baetica and Carthaginensis. It has been said, however, that the Suevi conquest of Baetica and Carthaginensis was limited to raids, and Suevi presence, if any, was minute.
In 446, the Romans dispatched to the provinces of Baetica and Carthaginensis the magister utriusque militiae
(Latin for "master of soldiers", plural ) was a top-level military command used in the later Roman Empire, dating from the reign of Constantine the Great. The term referred to the senior military officer (equivalent to a war theatre commander, ...
Vitus, who, assisted by a large number of Goths, attempted to subdue the Suevi and restore imperial administration in Hispania. Rechila marched to meet the Romans, and after defeating the Goths, Vitus fled in disgrace; no more imperial attempts were made to retake Hispania.Cambridge Ancient History, col. 14., s.v. "Spain: The Suevic Kingdom" In 448, Rechila died as a pagan
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judaism. I ...
, leaving the crown to his son, Rechiar.
King Rechiar
Rechiar
Rechiar or Flavius Rechiarius (after 415 – December 456) was the third Suevic king of Gallaecia, from 448 until his death, and also the first one to be born in Gallaecia. He was one of the most innovative and belligerent of the Suevi monarch ...
, a Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
Christian, succeeded his father in 448, being one of the first Catholic Christian kings among the Germanic peoples, and the first one to mint coins in his own name. Some believe minting the coins was a sign of Suevi autonomy, due to the use of minting in the late empire as a declaration of independence. Hoping to follow the successful careers of his father and his grandfather, Rechiar made a series of bold political moves throughout his reign. The first one was his marriage to the daughter of the Gothic king Theodoric I
Theodoric I ( got, Þiudarīks; la, Theodericus; 390 or 393 – 20 or 24 June 451) was the King of the Visigoths from 418 to 451. Theodoric is famous for his part in stopping Attila (the Hun) at the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains in 451, where ...
in 448, so improving the relationship between the two peoples. He also led a number of successful plundering campaigns to Vasconia
The Duchy of Gascony or Duchy of Vasconia ( eu, Baskoniako dukerria; oc, ducat de Gasconha; french: duché de Gascogne, duché de Vasconie) was a duchy located in present-day southwestern France and northeastern Spain, an area encompassing the ...
, Saragossa
Zaragoza, also known in English as Saragossa,''Encyclopædia Britannica'"Zaragoza (conventional Saragossa)" is the capital city of the Zaragoza Province and of the autonomous community of Aragon, Spain. It lies by the Ebro river and its tributar ...
and Lleida
Lleida (, ; Spanish: Lérida ) is a city in the west of Catalonia, Spain. It is the capital city of the province of Lleida.
Geographically, it is located in the Catalan Central Depression. It is also the capital city of the Segrià comarca, a ...
, in Hispania Tarraconensis
Hispania Tarraconensis was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania. It encompassed much of the northern, eastern and central territories of modern Spain along with modern northern Portugal. Southern Spain, the region now called Andalusia was the ...
(then the northeastern quarter of the peninsula, stretching from the Mediterranean to the Gulf of Biscay
The Bay of Biscay (), known in Spain as the Gulf of Biscay ( es, Golfo de Vizcaya, eu, Bizkaiko Golkoa), and in France and some border regions as the Gulf of Gascony (french: Golfe de Gascogne, oc, Golf de Gasconha, br, Pleg-mor Gwaskogn), ...
, which was still under Roman rule) sometimes acting in coalition with local bagaudae
Bagaudae (also spelled bacaudae) were groups of peasant insurgents in the later Roman Empire who arose during the Crisis of the Third Century, and persisted until the very end of the Western Empire, particularly in the less-Romanised areas of G ...
(local Hispano-Roman insurgents). In Lleida
Lleida (, ; Spanish: Lérida ) is a city in the west of Catalonia, Spain. It is the capital city of the province of Lleida.
Geographically, it is located in the Catalan Central Depression. It is also the capital city of the Segrià comarca, a ...
he also captured prisoners, who were taken as serfs back to the Sueves' lands in Gallaecia and Lusitania. Rome then sent an ambassador to the Sueves, obtaining some concessions, but in 455 the Sueves plundered lands in Carthaginensis which had been previously returned to Rome. In response, the new emperor Avitus and the Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is k ...
sent a joint embassy, remembering that the peace established with Rome was also granted by the Goths. But Rechiar launched two new campaigns in Tarraconensis, in 455 and 456, returning to Galicia with large numbers of prisoners.
The emperor Avitus finally responded to Rechiar's defiance in the autumn of 456, sending the Visigoth king Theodoric II over the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
and into Gallaecia, at the head of a large army of foederati
''Foederati'' (, singular: ''foederatus'' ) were peoples and cities bound by a treaty, known as ''foedus'', with Rome. During the Roman Republic, the term identified the ''socii'', but during the Roman Empire, it was used to describe foreign stat ...
which also included the Burgundian kings Gundioc and Hilperic. The Suevi mobilized and both armies met on 5 October, by the river Órbigo near Astorga. Theoderic II's Goths, on the right wing, defeated the Suevi. While many Sueves were killed in the battle, and many others were captured, most managed to flee. King Rechiar fled wounded in the direction of the coast, pursued by the Gothic army, which entered and plundered Braga
Braga ( , ; cel-x-proto, Bracara) is a city and a municipality, capital of the northwestern Portuguese district of Braga and of the historical and cultural Minho Province. Braga Municipality has a resident population of 193,333 inhabitants (in ...
on 28 October. King Rechiar was later captured in Porto
Porto or Oporto () is the second-largest city in Portugal, the capital of the Porto District, and one of the Iberian Peninsula's major urban areas. Porto city proper, which is the entire municipality of Porto, is small compared to its metropo ...
while trying to embark, and was executed in December. Theodoric continued his war on the Suevi for three months, but in April 459 he returned to Gaul, alarmed by the political and military movements of the new emperor, Majorian
Majorian ( la, Iulius Valerius Maiorianus; died 7 August 461) was the western Roman emperor from 457 to 461. A prominent general of the Roman army, Majorian deposed Emperor Avitus in 457 and succeeded him. Majorian was the last emperor to make ...
, and of the ''magister militum'' Ricimer
Flavius Ricimer ( , ; – 18/19 August 472) was a Romanized Germanic general who effectively ruled the remaining territory of the Western Roman Empire from 461 until his death in 472, with a brief interlude in which he contested power with An ...
—a half-Sueve, maybe a kinsman of Rechiar—while his allies and the rest of the Goths sacked Astorga, Palencia and other places, on their way back to the Pyrenees.
Competing kings
When the Visigoths disposed of Rechiar, the royal bloodline of Hermeric vanished and the conventional mechanism for Suevi leadership died with it. In 456, oneAioulf Aioulf or Ag(r)iwulf (died June 457) was an obscure king of Galicia from 456. In 448, after eight years in captivity, the Roman ambassador Censorius was executed by one Agiulf at Seville (''Hispalis''). This Agiulf has sometimes been identified wi ...
took over the leadership of the Sueves. The origins behind Aioulf's ascension are not clear: Hydatius wrote that Aioulf was a Goth deserter, while the historian Jordanes
Jordanes (), also written as Jordanis or Jornandes, was a 6th-century Eastern Roman bureaucrat widely believed to be of Gothic descent who became a historian later in life. Late in life he wrote two works, one on Roman history ('' Romana'') an ...
wrote that he was a Warni
The Varini, Warni or Warini were one or more Germanic peoples who originally lived in what is now northeastern Germany, near the Baltic sea.
They are first named in the Roman era, and appear to have survived into the Middle Ages. It is proposed ...
appointed by Theodoric to govern Gallaecia, and that he was persuaded by the Suevi into this adventure. Either way, he was killed in Porto
Porto or Oporto () is the second-largest city in Portugal, the capital of the Porto District, and one of the Iberian Peninsula's major urban areas. Porto city proper, which is the entire municipality of Porto, is small compared to its metropo ...
in June 457, but his rebellion, together with the armed actions of Majorian against the Visigoths, eased the pressure on the Suevi.
In 456, the same year as the execution of Rechiar, Hydatius stated that "the Sueves set up Maldras as their king." This statement suggests that the Suevi as a people may have had a voice in the selection of a new ruler. The election of Maldras Maldras (or Masdras) (died February 460) was the Suevic king of Galicia from 456 until his death. After the execution of Rechiar by the victorious Visigoths, the Suevi are said to have established Maldras on the throne. During his reign the Suevi ...
would lead to a schism among the Suevi, as some followed another king, named Framta Framta, Framtan or Framtane ( Latin: ''Framtanus'', Spanish: ''Frantán''; died 457) was one of the kings of the Suevi in Galicia in 457.
After the death of the Suevic king Rechiar, executed by the conquering Visigoths, and the Warnic king Aiou ...
, who died just a year later. Both factions then sought peace with the local Gallaeci.
In 458 the Goths again sent an army into Hispania, which arrived in Baetica
Hispania Baetica, often abbreviated Baetica, was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula). Baetica was bordered to the west by Lusitania, and to the northeast by Hispania Tarraconensis. Baetica remained one of the basi ...
in July, thereby depriving the Sueves of this province. This field army stayed in Iberia for several years.
In 460 Maldras was killed, after a reign of four years during which he plundered Sueves and Romans alike, in Lusitania and in the south of Gallaecia past the valley of the Douro
The Douro (, , ; es, Duero ; la, Durius) is the highest-flow river of the Iberian Peninsula. It rises near Duruelo de la Sierra in Soria Province, central Spain, meanders south briefly then flows generally west through the north-west part o ...
river. Meanwhile, the Sueves in the north chose another leader, Rechimund Richimund or Rechimund was a Suevic leader in Galicia from 457 until about 464. He was not recorded as a king (''rex''), though Hydatius wrote that ''inter Frumarium et Rechimundum oritur de regni potestate dissensio'' ("between Frumar and Rechimund ...
, who plundered Gallaecia in 459 and 460. This same year they captured the walled city of Lugo
Lugo (, ; la, Lucus Augusti) is a city in northwestern Spain in the autonomous community of Galicia. It is the capital of the province of Lugo. The municipality had a population of 98,025 in 2018, making it the fourth most populous city in Ga ...
, which was still under the authority of a Roman official. As a response, the Goths sent their army to punish the Suevi who dwelt in the outskirts of the city and nearby regions, but their campaign was revealed by some locals, whom Hydatius considered traitors. From that very moment Lugo became an important centre for the Sueves, and was used as capital by Rechimund.
In the south Frumar Frumar (or Frumarius) (died 464) was a Suevic warlord who succeeded Maldras (who was assassinated in February 460), as leader of the Suevic group then raiding Lusitania.Thompson, 167. Hydatius wrote: ''Inter Frumarium et Rechimundum oritur de regni ...
succeeded Maldras and his faction, but his death in 464 closed a period of internal dissent among the Sueves, and permanent conflict with the native Gallaecian population.
King Remismund
 In 464, Remismund, an ambassador who had travelled between Gallaecia and Gaul on several occasions, became King. Remismund was able to unite the factions of Suevi under his rule, and at the same time restore peace. He was also recognized, perhaps even approved of, by Theodoric, who sent him gifts and weapons along with a wife. Under the leadership of Remismund, the Suevi would again raid the nearby countries, plundering the lands of Lusitania and the
In 464, Remismund, an ambassador who had travelled between Gallaecia and Gaul on several occasions, became King. Remismund was able to unite the factions of Suevi under his rule, and at the same time restore peace. He was also recognized, perhaps even approved of, by Theodoric, who sent him gifts and weapons along with a wife. Under the leadership of Remismund, the Suevi would again raid the nearby countries, plundering the lands of Lusitania and the Conventus Asturicense
In Ancient Rome territorial organization, a ''conventus iuridicus'' was the capital city of a subdivision of some provinces (Dalmatia, Hispania, Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either cons ...
, whilst still fighting Gallaeci tribes like the Aunonenses, who refused to submit to Remismund. In 468 they managed to destroy part of the walls of Conimbriga, in Lusitania, which was sacked and then mostly abandoned after the inhabitants fled or were taken back to the north as slaves. The next year they captured Lisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administrative limits w ...
, which was surrendered by its leader, Lusidio. He later became ambassador of the Suevi to the Emperor. The end of the chronicle of Hydatius in 468 doesn't let us know the later fate of Remismund.
The Suevi probably remained mostly pagan until an Arian
Arianism ( grc-x-koine, Ἀρειανισμός, ) is a Christological doctrine first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter from Alexandria, Egypt. Arian theology holds that Jesus Christ is the Son of God, who was begotten by God ...
missionary named Ajax
Ajax may refer to:
Greek mythology and tragedy
* Ajax the Great, a Greek mythological hero, son of King Telamon and Periboea
* Ajax the Lesser, a Greek mythological hero, son of Oileus, the king of Locris
* ''Ajax'' (play), by the ancient Gree ...
, sent by the Visigothic king Theodoric II at the request of the Suebic unifier Remismund, converted them in 466 and established a lasting Arian church which dominated the people until their conversion to Catholicism in the 560s.
The Arian period
Little is known of the period between 470 and 550, beyond the testimony of Isidore of Seville, who in the 7th century wrote that many kings reign during this time, all of them Arians. A medieval document named ''Divisio Wambae'' mentions one king named Theodemund, otherwise unknown. Other less reliable and very posterior chronicles mention the reign of several kings under the names of Hermeneric II, Rechila II and Rechiar II. More trustworthy is a stone inscription found in VairãoPortugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of th ...
, recording the foundation of a church by a Benedictine nun, in 535, under the rule of one Veremund who is addressed as ''the most serene king Veremund'', although this inscription has also been attributed to king Bermudo II of León. Also, thanks to a letter sent by Pope Vigilius
Pope Vigilius (died 7 June 555) was the bishop of Rome from 29 March 537 to his death. He is considered the first pope of the Byzantine papacy. Born into Roman aristocracy, Vigilius served as a deacon and papal ''apocrisiarius'' in Constantino ...
to the bishop Profuturus of Braga ''circa'' 540, it is known that a certain number of Catholic Orthodox had converted to Arianism, and that some Catholic Orthodox churches had been demolished in the past in unspecified circumstances.
Conversion to Catholic Orthodoxy
 The conversion of the Suebi to Orthodoxy is presented very differently in the primary sources. A contemporary record, the minutes of the
The conversion of the Suebi to Orthodoxy is presented very differently in the primary sources. A contemporary record, the minutes of the First Council of Braga
In the First Council of Braga of 561, eight bishops took part, and twenty-two decrees were promulgated. In a number of canons, the council took aim directly at doctrines of Priscillianism.
Those decrees included the following: that in the service ...
—which met on 1 May 561—state explicitly that the synod was held at the orders of a king named Ariamir
Ariamir (died before 566) was the Suevic King of Galicia, with his capital at Bracara, from 558/9. The bishops of the First Council of Braga recorded Ariamir as the king who summoned them and under whose auspices they deliberated. Because the bis ...
. While his Orthodoxy is not in doubt, that he was the first Orthodox monarch of the Suebes since Rechiar has been contested on the grounds that he is not explicitly stated to have been.Thompson, 86. He was, however, the first to hold an Orthodox synod. On the other hand, the ''Historia Suevorum
The ''Historia de regibus Gothorum, Vandalorum et Suevorum'' ("History of the Kings of the Goths, Vandals and Suevi") is a Latin history of the Goths from 265 to 624, written by Isidore of Seville. It is a condensed account and, due to its diver ...
'' of Isidore of Seville
Isidore of Seville ( la, Isidorus Hispalensis; c. 560 – 4 April 636) was a Spanish scholar, theologian, and archbishop of Seville. He is widely regarded, in the words of 19th-century historian Montalembert, as "the last scholar of ...
states that it was Theodemar who brought about the conversion of his people from Arianism with the help of the missionary Martin of Braga
Martin of Braga (in Latin ''Martinus Bracarensis'', in Portuguese, known as ''Martinho de Dume'' 520–580 AD) was an archbishop of Bracara Augusta in Gallaecia (now Braga in Portugal), a missionary, a monastic founder, and an ecclesiastical ...
. And finally, according to the Frankish historian Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours (30 November 538 – 17 November 594 AD) was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours, which made him a leading prelate of the area that had been previously referred to as Gaul by the Romans. He was born Georgius Floren ...
, an otherwise unknown sovereign named Chararic, having heard of Martin of Tours
Martin of Tours ( la, Sanctus Martinus Turonensis; 316/336 – 8 November 397), also known as Martin the Merciful, was the third bishop of Tours. He has become one of the most familiar and recognizable Christian saints in France, heralded as the ...
, promised to accept the beliefs of the saint if only his son was cured of leprosy. Through the relics and intercession of Saint Martin the son was healed; Chararic and the entire royal household converted to the Nicene faith.Thompson, 83. As the coming of the relics of Saint Martin of Tours
Martin of Tours ( la, Sanctus Martinus Turonensis; 316/336 – 8 November 397), also known as Martin the Merciful, was the third bishop of Tours. He has become one of the most familiar and recognizable Christian saints in France, heralded as the ...
and the conversion of Chararic are made to coincide in the narration with the arrival of Martin of Braga
Martin of Braga (in Latin ''Martinus Bracarensis'', in Portuguese, known as ''Martinho de Dume'' 520–580 AD) was an archbishop of Bracara Augusta in Gallaecia (now Braga in Portugal), a missionary, a monastic founder, and an ecclesiastical ...
, ''circa'' 550, this legend has been interpreted as an allegory of the pastoral work of Saint Martin of Braga, and of his devotion to Saint Martin of Tours.
Most scholars have attempted to meld these stories. It has been alleged that Chararic and Theodemar must have been successors of Ariamir, since Ariamir was the first Suebic monarch to lift the ban on Orthodox synods; Isidore therefore gets the chronology wrong. Reinhart suggested that Chararic was converted first through the relics
In religion, a relic is an object or article of religious significance from the past. It usually consists of the physical remains of a saint or the personal effects of the saint or venerated person preserved for purposes of veneration as a tangi ...
of Saint Martin and that Theodemar was converted later through the preaching of Martin of Braga.
 Dahn equated Chararic with Theodemar, even saying that the latter was the name he took upon baptism. It has also been suggested that Theodemar and Ariamir were the same person and the son of Chararic. In the opinion of some historians, Chararic is nothing more than an error on the part of Gregory of Tours and never existed. If, as Gregory relates, Martin of Braga died about the year 580 and had been bishop for about thirty years, then the conversion of Chararic must have occurred around 550 at the latest. Finally, Ferreiro believes the conversion of the Suevi was progressive and stepwise and that Chararic's public conversion was only followed by the lifting of a ban on Orthodox synods in the reign of his successor, which would have been Ariamir; while Theodemar would have been responsible for beginning a persecution of the Arians in his kingdom, to root out their heresy.
Finally, the Suebic conversion is ascribed not to a Suebe, but to a Visigoth, by the chronicler John of Biclarum. He put their conversion alongside that of the Goths, occurring under
Dahn equated Chararic with Theodemar, even saying that the latter was the name he took upon baptism. It has also been suggested that Theodemar and Ariamir were the same person and the son of Chararic. In the opinion of some historians, Chararic is nothing more than an error on the part of Gregory of Tours and never existed. If, as Gregory relates, Martin of Braga died about the year 580 and had been bishop for about thirty years, then the conversion of Chararic must have occurred around 550 at the latest. Finally, Ferreiro believes the conversion of the Suevi was progressive and stepwise and that Chararic's public conversion was only followed by the lifting of a ban on Orthodox synods in the reign of his successor, which would have been Ariamir; while Theodemar would have been responsible for beginning a persecution of the Arians in his kingdom, to root out their heresy.
Finally, the Suebic conversion is ascribed not to a Suebe, but to a Visigoth, by the chronicler John of Biclarum. He put their conversion alongside that of the Goths, occurring under Reccared I
Reccared I (or Recared; la, Flavius Reccaredus; es, Flavio Recaredo; 559 – December 601; reigned 586–601) was Visigothic King of Hispania and Septimania. His reign marked a climactic shift in history, with the king's renunciation of Arianis ...
in 587–589, but, as such, this corresponds to a later time, when the kingdom was undergoing its integration with the Visigothic kingdom.
6th century and annexation
Britons
 Sometime late in the 5th century or early in the sixth century, a group of
Sometime late in the 5th century or early in the sixth century, a group of Romano-Britons
The Romano-British culture arose in Britain under the Roman Empire following the Roman conquest in AD 43 and the creation of the province of Britannia. It arose as a fusion of the imported Roman culture with that of the indigenous Britons, a ...
escaping the Anglo-Saxons settled in the north of the Suebi
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own name ...
Kingdom of Gallæcia in lands which subsequently acquired the name Britonia
Britonia (which became Bretoña in Galician and Spanish) is the historical, apparently Latinized name of a Celtic settlement by Romano-Britons on the Iberian peninsula following the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. The area is roughly analogous ...
.Koch, John T. (2006). "Britonia". In John T. Koch, ''Celtic Culture: A Historical Encyclopedia''. Santa Barbara: ABC-CLIO, p. 291. Most of what is known about the settlement comes from ecclesiastical sources; records from the 572 Second Council of Braga The Second Council of Braga, held in 572, presided over by Martin of Braga, was held to increase the number of bishops in Galaecia. Twelve bishops assisted at this council, and ten decrees were promulgated: (1) that the bishops should in their vis ...
refer to a diocese
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associ ...
called the ''Britonensis ecclesia'' ("British church") and an episcopal see
An episcopal see is, in a practical use of the phrase, the area of a bishop's ecclesiastical jurisdiction.
Phrases concerning actions occurring within or outside an episcopal see are indicative of the geographical significance of the term, mak ...
called the ''sedes Britonarum'' ("See of the Britons"), while the administrative and ecclesiastical document usually known as Divisio Theodemiri
Division is a taxonomic rank in biological classification that is used differently in zoology and in botany.
In botany and mycology, ''division'' refers to a rank equivalent to phylum. The use of either term is allowed under the Internationa ...
or ''Parochiale suevorum'', attribute to them their own churches and the monastery ''Maximi'', likely the monastery of Santa Maria de Bretoña. The bishop representing this diocese at the II Council of Braga bore the Brythonic
Brittonic or Brythonic may refer to:
*Common Brittonic, or Brythonic, the Celtic language anciently spoken in Great Britain
*Brittonic languages, a branch of the Celtic languages descended from Common Brittonic
*Britons (Celtic people)
The Br ...
name Mailoc
__NOTOC__
Mailoc or Maeloc was a 6th-century bishop of Britonia, a settlement founded by expatriate Britons in Galicia, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, nat ...
. The see continued to be represented at several councils through the 7th century.
King Ariamir and king Theodemar
On 1 May 561, kingAriamir
Ariamir (died before 566) was the Suevic King of Galicia, with his capital at Bracara, from 558/9. The bishops of the First Council of Braga recorded Ariamir as the king who summoned them and under whose auspices they deliberated. Because the bis ...
, who was in the third year of his reign, called the First Council of Braga
In the First Council of Braga of 561, eight bishops took part, and twenty-two decrees were promulgated. In a number of canons, the council took aim directly at doctrines of Priscillianism.
Those decrees included the following: that in the service ...
, being styled ''The most glorious king Ariamir'' in the acts. The first Orthodox Council held in the Kingdom, it was almost entirely devoted to the condemnation of Priscillianism
Priscillianism was a Christian sect developed in the Iberian Peninsula under the Roman Empire in the 4th century by Priscillian. It is derived from the Gnostic doctrines taught by Marcus, an Egyptian from Memphis. Priscillianism was later con ...
, making no mention at all of Arianism
Arianism ( grc-x-koine, Ἀρειανισμός, ) is a Christological doctrine first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter from Alexandria, Egypt. Arian theology holds that Jesus Christ is the Son of God, who was begotten by God ...
, and only once reproving clerics for adorning his clothes and for wearing ''granos'', a Germanic word implying either pigtails, long beard, moustache, or a Suebian knot
The Suebian knot (german: Suebenknoten) is a historical male hairstyle ascribed to the tribe of the Germanic Suebi. The knot is attested by Tacitus in his 1st century AD work ''Germania'', found on contemporary depictions of Germanic peoples, t ...
, a custom declared pagan. Of the eight assistant bishops only one bore a Germanic name, bishop ''Ilderic''.
Later, on 1 January 569, Ariamir's successor, Theodemar, held a council in Lugo, which dealt with the administrative and ecclesiastical organization of the Kingdom. At his request, the Kingdom of Gallaecia
The Kingdom of the Suebi ( la, Regnum Suevorum), also called the Kingdom of Galicia ( la, Regnum Galicia) or Suebi Kingdom of Galicia ( la, Galicia suevorum regnum), was a Germanic post-Roman kingdom that was one of the first to separate from ...
was divided in two provinces or synods, under the obedience of the metropolitans Braga and Lugo, and thirteen episcopal sees, some of them new, for which new bishops were ordered, others old: Iria Flavia
Iria Flavia or simply Iria in Galicia, northwestern Spain, is an Ancient settlement and former bishopric in the modern municipality of Padrón, which remains a Catholic titular see.
History
Located at the confluence of the Sar and Ulla rive ...
, Britonia
Britonia (which became Bretoña in Galician and Spanish) is the historical, apparently Latinized name of a Celtic settlement by Romano-Britons on the Iberian peninsula following the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. The area is roughly analogous ...
, Astorga, Ourense
Ourense (; es, Orense ) is a city and capital of the province of Ourense, located in the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Galicia (Spain), Galicia, northwestern Spain. It is on the Camino Sanabrés path of the Way of St ...
and Tui in the north, under the obedience of Lugo
Lugo (, ; la, Lucus Augusti) is a city in northwestern Spain in the autonomous community of Galicia. It is the capital of the province of Lugo. The municipality had a population of 98,025 in 2018, making it the fourth most populous city in Ga ...
; and Dume, Porto
Porto or Oporto () is the second-largest city in Portugal, the capital of the Porto District, and one of the Iberian Peninsula's major urban areas. Porto city proper, which is the entire municipality of Porto, is small compared to its metropo ...
, Viseu
Viseu () is a city and municipality in the Centro Region of Portugal and the capital of the district of the same name, with a population of 100,000 inhabitants, and center of the Viseu Dão Lafões intermunipical community, with 267,633 inhabi ...
, Lamego, Coimbra
Coimbra (, also , , or ) is a city and a municipality in Portugal. The population of the municipality at the 2011 census was 143,397, in an area of .
The fourth-largest urban area in Portugal after Lisbon, Porto, and Braga, it is the largest cit ...
and Idanha-a-Velha in the south, dependent of Braga
Braga ( , ; cel-x-proto, Bracara) is a city and a municipality, capital of the northwestern Portuguese district of Braga and of the historical and cultural Minho Province. Braga Municipality has a resident population of 193,333 inhabitants (in ...
. Each see was then further divided into smaller territories, named ''ecclesiae'' and ''pagi''. The election of Lugo as metropolitan of the north was due to its central situation in relation to its dependant sees and that city.
King Miro
 According to John of Biclaro, in 570 Miro succeeded Theodemar as king of the Sueves.Cambridge Ancient History, vol. 14., s.v. "Spain: The Suevic Kingdom" During his time, the Suevic kingdom was challenged again by the Visigoths who, under their king
According to John of Biclaro, in 570 Miro succeeded Theodemar as king of the Sueves.Cambridge Ancient History, vol. 14., s.v. "Spain: The Suevic Kingdom" During his time, the Suevic kingdom was challenged again by the Visigoths who, under their king Leovigild
Liuvigild, Leuvigild, Leovigild, or ''Leovigildo'' (Spanish and Portuguese), ( 519 – 586) was a Visigothic King of Hispania and Septimania from 568 to 586. Known for his Codex Revisus or Code of Leovigild, a law allowing equal rights between th ...
, were reconstituting their kingdom, reduced and mostly ruled by foreigners since their defeat by the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools ...
in the Battle of Vouillé
The Battle of Vouillé (from Latin ''Campus Vogladensis'') was fought in the northern marches of Visigothic territory, at Vouillé, near Poitiers (Gaul), in the spring of 507 between the Franks, commanded by Clovis, and the Visigoths, comman ...
.
In 572 Miro ordered the celebration of the Second Council of Braga The Second Council of Braga, held in 572, presided over by Martin of Braga, was held to increase the number of bishops in Galaecia. Twelve bishops assisted at this council, and ten decrees were promulgated: (1) that the bishops should in their vis ...
, which was presided over by the Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now west ...
n Saint Martin of Braga as archbishop of the Suevi kingdom’s capital. Martin was a cultivated man, praised by Isidore of Seville
Isidore of Seville ( la, Isidorus Hispalensis; c. 560 – 4 April 636) was a Spanish scholar, theologian, and archbishop of Seville. He is widely regarded, in the words of 19th-century historian Montalembert, as "the last scholar of ...
, Venantius Fortunatus
Venantius Honorius Clementianus Fortunatus ( 530 600/609 AD; french: Venance Fortunat), known as Saint Venantius Fortunatus (, ), was a Latin poet and hymnographer in the Merovingian Court, and a bishop of the Early Church who has been venerate ...
and Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours (30 November 538 – 17 November 594 AD) was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours, which made him a leading prelate of the area that had been previously referred to as Gaul by the Romans. He was born Georgius Floren ...
, who led the Sueves to Catholicism and who promoted the cultural and political renaissance of the kingdom. In the acts of the Council, Martin declared the unity and purity of the Catholic faith in Gallaecia and, for the first time, Arius
Arius (; grc-koi, Ἄρειος, ; 250 or 256 – 336) was a Cyrenaic presbyter, ascetic, and priest best known for the doctrine of Arianism. His teachings about the nature of the Godhead in Christianity, which emphasized God the Father's ...
was discredited. Notably, of the twelve assistant bishops, five were Sueves (Nitigius Nitigius (? - 570-585 - ?) was a medieval Galician clergyman.
References
* Consello da Cultura Galega (ed.), ''Documentos da Catedral de Lugo'', (Santiago de Compostela, 1998)
6th-century Galician bishops
{{Spain-RC-bishop-stub ...
of Lugo
Lugo (, ; la, Lucus Augusti) is a city in northwestern Spain in the autonomous community of Galicia. It is the capital of the province of Lugo. The municipality had a population of 98,025 in 2018, making it the fourth most populous city in Ga ...
, Wittimer of Ourense
Ourense (; es, Orense ) is a city and capital of the province of Ourense, located in the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Galicia (Spain), Galicia, northwestern Spain. It is on the Camino Sanabrés path of the Way of St ...
, Anila
Anila or Anil (Sanskrit: अनिल ' "wind") is one of the Vasus in Hinduism, gods of the elements of the cosmos. He is equated with the wind god Vāyu
Vayu (, sa, वायु, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of th ...
of Tui, Remisol of Viseu
Viseu () is a city and municipality in the Centro Region of Portugal and the capital of the district of the same name, with a population of 100,000 inhabitants, and center of the Viseu Dão Lafões intermunipical community, with 267,633 inhabi ...
, Adoric of Idanha-a-Velha), and one was a Briton, Mailoc
__NOTOC__
Mailoc or Maeloc was a 6th-century bishop of Britonia, a settlement founded by expatriate Britons in Galicia, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, nat ...
.
This same year of 572 Miro led an expedition against the Runcones The Ruccones (also called Rucones, Runcones, or Roccones) were a tribal group, probably related to the Astures or the Basques, who lived semi-autonomously in northern Hispania from the fifth through to the seventh centuries. Their population area ...
, when the Visigoth king Leovigild was conducting successful military activity in the south: he had recovered for the Visigoths the cities of Cordova, Spain, Cordova and Medina-Sidonia, and had led a successful assault on the region around the city of Málaga. But from 573 on his campaigns got closer to Suevic lands, first occupying Sabaria, later the Aregenses mountains and Cantabria, where he expelled some invaders. Finally, in 576, he entered Gallaecia itself, disturbing the boundaries of the kingdom, but Miro sent ambassadors and obtained from Leovigild a temporary peace. It was probably during this period that the Suevi also sent some ambassadors to the Frankish king Gontram, who were intercepted by Chilperic I near Poitiers, and imprisoned for a year, as recorded by Gregory of Tours.
Later, in 579, Leovigild's son, prince Hermenegild, rebelled against his father, proclaiming himself king. He, while residing in Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Penins ...
, had converted to Catholicism under the influence of his wife, the Frankish princess Ingund (wife of Hermenegild), Ingundis, and of Leander of Seville, in open opposition to the Arianism of his father. But it was not until 582 that Leovigild gathered his armies to attack his son: first, he took Mérida; then, in 583, he marched to Seville. Under siege, Hermenegild's rebellion became dependent on the support offered by the Eastern Roman Empire, which controlled much of the southern coastal regions of Hispania since Justinian I, and by the Sueves. This same year Miro, ''king of the Gallaecians'', marched south with his army, with the intention of breaking through the blockade, but, while camped, he found himself besieged by Leovigild, and was then forced to sign a treaty of fidelity with the Visigothic king. After exchanging presents, Miro returned to Gallaecia, where he was laid to bed some days later, dying soon after, due to "the bad waters of Spain", according to Gregory of Tours. Hermenegild's rebellion ended in 584, as Leovigild bribed the Byzantines with 30,000 solidi, thereby depriving his son of their support.
Last kings
 On the death of Miro, his son Eboric, Eburic was made king, but apparently not before sending tokens of appreciation and friendship to Leovigild. Not a year later his brother-in-law, named Andeca, Audeca, accompanied by the army, seized power. He took Eburic into a monastery forced him to Holy orders in the Catholic Church, ordain as a priest, thereby making him ineligible for the throne. Then Audeca married Siseguntia, king Miro's widow, and made himself king. This usurpation and the friendship granted by Eboric gave Leovigild the opportunity to seize the neighboring kingdom. In 585 Leovigild went to war against the Sueves, invading Gallecia. In the words of John of Biclaro: "''King Leovigild devastates Gallaecia and deprives Audeca of the totality of the Kingdom; the nation of the Sueves, their treasure and fatherland are conduced to his own power and turned into a province of the Goths.''" During the campaign, the Franks of king Guntram attacked Septimania, maybe trying to help the Sueves, at the same time sending ships to Gallaecia which were intercepted by Leovigild's troops, who took their cargo and killed or enslaved most of their crews. Thus was the kingdom transferred to the Goths as one of their three administrative regions: Gallaecia, Hispania and Gallia Narbonensis. Audeca, captured, was tonsured and forced to take holy orders, then sent into exile in Beja (Portugal), Beja, in Southern Lusitania.
This same year, 585, a man named Malaric rebelled against the Goths and reclaimed the throne, but he was finally defeated and captured by the generals of Leovigild, who took him in chains to the Visigothic king.
On the death of Miro, his son Eboric, Eburic was made king, but apparently not before sending tokens of appreciation and friendship to Leovigild. Not a year later his brother-in-law, named Andeca, Audeca, accompanied by the army, seized power. He took Eburic into a monastery forced him to Holy orders in the Catholic Church, ordain as a priest, thereby making him ineligible for the throne. Then Audeca married Siseguntia, king Miro's widow, and made himself king. This usurpation and the friendship granted by Eboric gave Leovigild the opportunity to seize the neighboring kingdom. In 585 Leovigild went to war against the Sueves, invading Gallecia. In the words of John of Biclaro: "''King Leovigild devastates Gallaecia and deprives Audeca of the totality of the Kingdom; the nation of the Sueves, their treasure and fatherland are conduced to his own power and turned into a province of the Goths.''" During the campaign, the Franks of king Guntram attacked Septimania, maybe trying to help the Sueves, at the same time sending ships to Gallaecia which were intercepted by Leovigild's troops, who took their cargo and killed or enslaved most of their crews. Thus was the kingdom transferred to the Goths as one of their three administrative regions: Gallaecia, Hispania and Gallia Narbonensis. Audeca, captured, was tonsured and forced to take holy orders, then sent into exile in Beja (Portugal), Beja, in Southern Lusitania.
This same year, 585, a man named Malaric rebelled against the Goths and reclaimed the throne, but he was finally defeated and captured by the generals of Leovigild, who took him in chains to the Visigothic king.
Annexation
Viseu
Viseu () is a city and municipality in the Centro Region of Portugal and the capital of the district of the same name, with a population of 100,000 inhabitants, and center of the Viseu Dão Lafões intermunipical community, with 267,633 inhabi ...
, Coimbra
Coimbra (, also , , or ) is a city and a municipality in Portugal. The population of the municipality at the 2011 census was 143,397, in an area of .
The fourth-largest urban area in Portugal after Lisbon, Porto, and Braga, it is the largest cit ...
and Idanha-a-Velha, in lands which had been annexed to Gallaecia in the fifth century, were returned to the obedience of Mérida. It has been also pointed out that no visible Gothic immigration took place during the 6th and the 7th century into Gallaecia."The small proprietors in contrast were men of overwhelmingly Celtic, Roman and Suevic stock, not Visigoths, for in the century since Leovigild's conquest of the Suevic kingdom in 585 there had been no perceptible Visigothic migration to the northwest.",
The last mention of the Sueves as a separate people dates to a 10th-century gloss in a Spanish codex: "hanc arbor romani pruni vocant, spani nixum, uuandali et goti et suebi et celtiberi ceruleum dicunt" ("This tree is called plum-tree by the Romans; ''nixum'' by the Spaniards; the Vandals, the Sueves, the Goths, and the Celtiberians call it ''ceruleum''"), but in this context ''Suebi'' probably meant simply ''Gallaeci''.
List of Galician Suebic monarchs
 *
*Hermeric
Hermeric (died 441) was the king of the Suevi from at least 419 and possibly as early as 406 until his abdication in 438.
Biography
Before 419
Nothing is known for sure about Hermeric before 419, the year in which he is first mentioned; ...
, c. 409–438
* Heremigarius, 427–429, leader in Lusitania
Lusitania (; ) was an ancient Iberian Roman province located where modern Portugal (south of the Douro river) and
a portion of western Spain (the present Extremadura and the province of Salamanca) lie. It was named after the Lusitani or Lu ...
*Rechila
Rechila (died 448) was the Suevic king of Galicia from 438 until his death. There are few primary sources for his life, but Hydatius was a contemporary Christian (non-Arian) chronicler in Galicia.
When his father, Hermeric, turned ill in 438, ...
, 438–448
*Rechiar
Rechiar or Flavius Rechiarius (after 415 – December 456) was the third Suevic king of Gallaecia, from 448 until his death, and also the first one to be born in Gallaecia. He was one of the most innovative and belligerent of the Suevi monarch ...
, 448–456
*Aioulf Aioulf or Ag(r)iwulf (died June 457) was an obscure king of Galicia from 456. In 448, after eight years in captivity, the Roman ambassador Censorius was executed by one Agiulf at Seville (''Hispalis''). This Agiulf has sometimes been identified wi ...
, 456–457, foreigner, possibly appointee of the Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is k ...
*Maldras Maldras (or Masdras) (died February 460) was the Suevic king of Galicia from 456 until his death. After the execution of Rechiar by the victorious Visigoths, the Suevi are said to have established Maldras on the throne. During his reign the Suevi ...
, 456–460, in opposition to Framta after 457
*Framta Framta, Framtan or Framtane ( Latin: ''Framtanus'', Spanish: ''Frantán''; died 457) was one of the kings of the Suevi in Galicia in 457.
After the death of the Suevic king Rechiar, executed by the conquering Visigoths, and the Warnic king Aiou ...
, 457, in opposition to Maldras
*Richimund, 457–464, successor of Framta
*Frumar Frumar (or Frumarius) (died 464) was a Suevic warlord who succeeded Maldras (who was assassinated in February 460), as leader of the Suevic group then raiding Lusitania.Thompson, 167. Hydatius wrote: ''Inter Frumarium et Rechimundum oritur de regni ...
, 460–464, successor of Maldras
* Remismund, 464–469, succeeded Frumar, reunited the Suebi
*''Period of obscurity''
**Hermeneric fl. c. 485
**Veremund fl. 535
**Theodemund fl. 6th century
*Chararic (Suebian king), Chararic, after c.550–558/559, existence sometimes doubted
*Ariamir
Ariamir (died before 566) was the Suevic King of Galicia, with his capital at Bracara, from 558/9. The bishops of the First Council of Braga recorded Ariamir as the king who summoned them and under whose auspices they deliberated. Because the bis ...
, 558/559–561/566
* Theodemar, 561/566–570
*Miro of Gallaecia, Miro, 570–583
*Eboric, 583–584, deposed and put in a monastery by Andeca.
*Andeca, 584–585, deposed and put in a monastery by Leovigild
Liuvigild, Leuvigild, Leovigild, or ''Leovigildo'' (Spanish and Portuguese), ( 519 – 586) was a Visigothic King of Hispania and Septimania from 568 to 586. Known for his Codex Revisus or Code of Leovigild, a law allowing equal rights between th ...
.
*Malaric, 585, opposed Leovigild
Liuvigild, Leuvigild, Leovigild, or ''Leovigildo'' (Spanish and Portuguese), ( 519 – 586) was a Visigothic King of Hispania and Septimania from 568 to 586. Known for his Codex Revisus or Code of Leovigild, a law allowing equal rights between th ...
and was defeated.
Sources and controversies
 Unlike some other barbarian peoples, such as the Vandals, Visigoths, Ostrogoths and Huns, which played an important part in Rome's loss of the western provinces, the Sueves—establishing themselves in Gallaecia and northern Lusitania, which were remote and extra-Mediterranean areas—seldom posed a threat to Rome and to Rome's interests; in fact, at times where we have more detailed knowledge of their history through a diversity of sources, that is precisely when they became a challenge, as it was under the reign of Rechila. Throughout their history as an independent nation, they maintained an important diplomatic activity, most notably with Rome, the Vandals, the Visigoths, and, later, with the
Unlike some other barbarian peoples, such as the Vandals, Visigoths, Ostrogoths and Huns, which played an important part in Rome's loss of the western provinces, the Sueves—establishing themselves in Gallaecia and northern Lusitania, which were remote and extra-Mediterranean areas—seldom posed a threat to Rome and to Rome's interests; in fact, at times where we have more detailed knowledge of their history through a diversity of sources, that is precisely when they became a challenge, as it was under the reign of Rechila. Throughout their history as an independent nation, they maintained an important diplomatic activity, most notably with Rome, the Vandals, the Visigoths, and, later, with the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools ...
. Again, they become important players during the reign of Miro, in the last third of the 6th century, when they allied with other Catholic powers—the Franks and the Eastern Romans—in support of Hermenegild, and against the Visigothic king Leovigild. Because of their relative isolation and remoteness, sources about the Suevi people are limited, with the number translated into English even fewer.
The most important source for the history of the Suevi during the 5th century is the chronicle written by the native bishop Hydatius
Hydatius, also spelled Idacius (c. 400 – c. 469) was a late Western Roman writer and clergyman. The bishop of Aquae Flaviae in the Roman province of Gallaecia (almost certainly the modern Chaves, Portugal, in the modern district of Vila Real), he ...
in 470, as a continuation of the Chronicle of Saint Jerome. Hydatius was born ''circa'' 400, in the city of the Limici, straddling the southern borders of modern-day Galicia and Portugal, on the valley of the Lima River. He witnessed the 409 settlement of the Suevi peoples in the Iberian Peninsula, and Galicia's transformation from Roman province into an independent barbarian kingdom. Through much of his life he was forced to stay in isolated Roman communities, constantly threatened by the Suevi and Vandals, though we also know that he travelled on several occasions outside of Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hi ...
, for learning or as ambassador, and that he maintained correspondence with other bishops. In 460 he was captured by the Suevic warlord Frumarius, accused of treason by other local men. After being held captive for three months, as the Suevi ravaged the region of Chaves, Portugal, Chaves, he was then released unharmed, against the will of the men who had accused him. Hydatius' chronicle, whilst purporting to be universal, slowly turns into a local history. Following the barbarian settlements, he relates the conflict among the diverse nations; later, he also narrates the frequent conflict of the Sueves with the local, barely romanized, Galicians; the decline of the Roman powers in Hispania; the expansion of the Suevi into the south and the east; their defeat at the hands of Visigoths and other Roman foederati forces; and the posterior reconstitution of their kingdom under Remismund, together with their conversion to Arianism. While he is considered a great historian, his portraits are usually obscure, without any real reason or direction given to the decisions or movement of the Suevi, by mentioning what the Suevi did, but rarely what they said, or what they pretended. So Hydatius's image of the Suevi is from the outside, as lawless marauders. This description of the Suevi has bled into secondary sources: E.A. Thomson, an expert who has written many pieces on the subject, stated, "they just lash out blindly from year to year at any place that they suspected would supply them with food, valuables or money."
Another important source for the history of the Sueves during the initial settlement phase is the ''Seven Books of History Against the Pagans'', by Orosius
Paulus Orosius (; born 375/385 – 420 AD), less often Paul Orosius in English, was a Roman priest, historian and theologian, and a student of Augustine of Hippo. It is possible that he was born in ''Bracara Augusta'' (now Braga, Portugal), t ...
, another local historian. He painted a very different picture of the initial settlement of Sueves and Vandals, less catastrophic than that narrated by Hydatius. In his narration, Sueves and Vandals, after a violent entrance into Hispania, resume a pacific life, while many poor locals joined them, fleeing from Roman taxes and impositions. However, as has been pointed out, his narration is also biased by his agenda, as he was trying to exculpate Christianity for the fall and decadence of Rome.
 The conflict of Vandals and Sueves is also narrated by
The conflict of Vandals and Sueves is also narrated by Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours (30 November 538 – 17 November 594 AD) was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours, which made him a leading prelate of the area that had been previously referred to as Gaul by the Romans. He was born Georgius Floren ...
, who in the 6th century narrated the blockade, the death of Gunderic under unknown circumstances, and the resolution of the conflict in a champions' fight, with the defeated Vandals forced to leave Galicia. A somewhat different history apparently was told among the Vandals, as Procopius wrote that in their traditions king Gunderic was captured and impaled by ''Germans'' in Spain.
For the mid-fifth century we have also chapter 44 of Jordanes
Jordanes (), also written as Jordanis or Jornandes, was a 6th-century Eastern Roman bureaucrat widely believed to be of Gothic descent who became a historian later in life. Late in life he wrote two works, one on Roman history ('' Romana'') an ...
' Getica, which narrates the defeat of the Suevi king Rechiar at the hands of the Roman foederati troops commanded by the Visigoths. It is a vivid, if brief, narration, where Rechiar, a defiant man, has a purpose, a mood, and emotions, as do the rest of the protagonists.
The ending of the Chronicle of Hydatius, in 469, marks the beginning of a period of obscurity in the history of the Sueves, who don't re-emerge into historical light until the mid-sixth century, when we have plenty of sources. Among these, the most notable are the works of the Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now west ...
n Martin of Braga
Martin of Braga (in Latin ''Martinus Bracarensis'', in Portuguese, known as ''Martinho de Dume'' 520–580 AD) was an archbishop of Bracara Augusta in Gallaecia (now Braga in Portugal), a missionary, a monastic founder, and an ecclesiastical ...
, sometimes called the apostle of the Sueves, as well as the accounts of Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours (30 November 538 – 17 November 594 AD) was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours, which made him a leading prelate of the area that had been previously referred to as Gaul by the Romans. He was born Georgius Floren ...
. In the ''Miracles of Saint Martin'', Gregory narrated, and attributed to a miracle of Saint Martin of Tours, the conversion of king Chararic to Catholicism, while in the ''History of the Franks'' he dedicated several chapters to the relations of Sueves, Visigoths and Franks, and to the end of the independence of the Suevi, annexed by the Visigoths in 585. On the other hand, Martin of Braga, a monk who arrived in Galicia circa 550, became a true transformative power: as founder of monasteries and as bishop and abbot of Dume he promoted the conversion of the Sueves, and later as archbishop of Braga and maximum religious authority of the kingdom he participated in the reformation of the Church and of the local administration. Several of his works have been preserved, among them a ''Formula for an Honest life'' dedicated to King Miro; a treatise against the superstitions of the country inhabitants; and several other minor treatises. He was also present in the Councils of Braga, with the deliberations of the second one being led by him, as archbishop of the capital, Braga. The acts of these Councils, together with the ''Divisio Theodemiri'', are the most precious sources on the inner political and religious life of the kingdom.
Of paramount importance is also the chronicle written by John of Biclaro, a Visigoth, ''circa'' 590. While probably partial, his accounts are precious for the last 15 years of independence of the Sueves, as well as for the first years of the Sueves under Visigothic rule.
Finally, of great interest is also a history written by Isidore of Seville
Isidore of Seville ( la, Isidorus Hispalensis; c. 560 – 4 April 636) was a Spanish scholar, theologian, and archbishop of Seville. He is widely regarded, in the words of 19th-century historian Montalembert, as "the last scholar of ...
. He used Hydatius's accounts, together with the Chronicle of John of Biclaro, to form an abridged history of the Suevi in Hispania. The controversy around Isidore's historiography is centered on his omissions and additions, which many historians and scholars consider too numerous to all be simply mistakes. Throughout Isidore's ''History of the Kings of the Goths, Vandals, and Sueves'' certain details from Hydatius are altered. Many scholars attribute these changes to the fact that Isidore may have had sources other than Hydatius at his disposal.
It has been said that the history and relevance of Suevic Galicia was long marginalised and obscured inside Spain, mainly for political reasons. It was left to a German scholar, Wilhem Reinhart, to write the first connected history of the Suebi in Galicia, or more accurately Gallaecia as the official separation between Galicia and Portugal would only take place in 1095 AD.
Cultural legacy
 As the Suebi quickly adopted the local Vulgar Latin language, few traces were left of their Germanic tongue in the Galician language, Galician and Portuguese languages. Distinguishing between loanwords from Gothic or Suevic is difficult, but there is a series of words, characteristic of Galicia and northern half of Portugal, which are attributed either to the Suebi or to the Goths, although no major Visigothic immigration into Gallaecia is known before the 8th century. These words are rural in nature, relative to animals, agriculture, and country life: ''laverca'' 'lark' (from Proto-Germanic *laiwazikōn 'lark'), ''meixengra'' 'titmouse' (same word as Old Norse ''meisingr'' 'titmouse', from *maisōn 'titmouse'),Kremer 2004: 140 ''lobio'' or ''lóvio'' 'vinegrape' (to *lauban 'foliage'), ''britar'' 'to break' (from *breutanan 'to break'), ''escá'' 'bushel' (from ancient ''scala'' 'bowl', from *skēlō 'bowl'), ''ouva'' 'elf, spirit' (from *albaz 'elf'), ''marco'' 'boundary stone' (from PGmc *markan 'frontier, limit'), ''groba'' 'gully' (from *grōbō 'groove'), ''maga ''
As the Suebi quickly adopted the local Vulgar Latin language, few traces were left of their Germanic tongue in the Galician language, Galician and Portuguese languages. Distinguishing between loanwords from Gothic or Suevic is difficult, but there is a series of words, characteristic of Galicia and northern half of Portugal, which are attributed either to the Suebi or to the Goths, although no major Visigothic immigration into Gallaecia is known before the 8th century. These words are rural in nature, relative to animals, agriculture, and country life: ''laverca'' 'lark' (from Proto-Germanic *laiwazikōn 'lark'), ''meixengra'' 'titmouse' (same word as Old Norse ''meisingr'' 'titmouse', from *maisōn 'titmouse'),Kremer 2004: 140 ''lobio'' or ''lóvio'' 'vinegrape' (to *lauban 'foliage'), ''britar'' 'to break' (from *breutanan 'to break'), ''escá'' 'bushel' (from ancient ''scala'' 'bowl', from *skēlō 'bowl'), ''ouva'' 'elf, spirit' (from *albaz 'elf'), ''marco'' 'boundary stone' (from PGmc *markan 'frontier, limit'), ''groba'' 'gully' (from *grōbō 'groove'), ''maga ''Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of th ...
and Galicia, and made up of several thousand place names derived directly from Germanic personal names, expressed as Germanic or Latin genitives: Sandiás, medieval ''Sindilanes'', Germanic genitive form of the name Sindila; Mondariz from the Latin genitive form Munderici ''Munderic's''; Gondomar, Pontevedra, Gondomar from ''Gundemari'' and Baltar, Ourense, Baltar from ''Baltarii'', both in Portugal and Galicia; Guitiriz to ''Witterici''. Another group of toponyms which point to old Germanic settlements are the places named ''Sa'', ''Saa'', ''Sas'', in Galicia, or ''Sá'' in Portugal, all derived from the Germanic word *sal- 'house, hall', and distributed mostly around Braga
Braga ( , ; cel-x-proto, Bracara) is a city and a municipality, capital of the northwestern Portuguese district of Braga and of the historical and cultural Minho Province. Braga Municipality has a resident population of 193,333 inhabitants (in ...
, Porto
Porto or Oporto () is the second-largest city in Portugal, the capital of the Porto District, and one of the Iberian Peninsula's major urban areas. Porto city proper, which is the entire municipality of Porto, is small compared to its metropo ...
and in the Minho river
The Minho ( , ) or Miño ( , , ; cel-x-proto, Miniu) is the longest river in Galicia, sharing the border with Portugal, with a length of . By discharge, it is the fourth river of the Iberian peninsula, after the Douro, Ebro, and Tagus.
The Min ...
valley in Portugal, and around Lugo
Lugo (, ; la, Lucus Augusti) is a city in northwestern Spain in the autonomous community of Galicia. It is the capital of the province of Lugo. The municipality had a population of 98,025 in 2018, making it the fourth most populous city in Ga ...
in Galicia, totalling a few hundred.
In modern Galicia (Spain), Galicia, four parishes and six towns and villages are still named ''Suevos'' or ''Suegos'', from the medieval form ''Suevos'', all of them from the Latin ''Sueuos'' 'Sueves', and referring to old Suevi settlements.
Notes
Bibliography
* *Arias, Jorge C. (2007)."Identity and Interaction: The Suevi and the Hispano-Romans."
' University of Virginia: Spring 2007. *Burgess, R. W., ed. (1993). ''The Chronicle of Hydatius''. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, 1993. *Cameron, Averil and others, ed. (2001a). ''Cambridge Ancient History, vol. 13, Late Antiquity: The Late Empire A.D. 337–425''. Cambridge, England: University of Cambridge Press, 2001. *Cameron, Averil and others, ed. (2001b). ''Cambridge Ancient History, vol. 14, Late Antiquity: Empire and Successors A.D. 425–600''. Cambridge, England: University of Cambridge Press, 2001. * DCECH = Coromines, Joan (2012). Diccionario crítico etimológico castellano e hispánico. Madrid: Gredos. . *Donini, Guido and Gordon B. Ford Jr., transl. (1970). ''Isidore of Seville’s History of the Kings of the Goths, Vandals, and Suevi'', 2nd rev. ed. Leiden, Netherlands: E. J. Brill, 1970. *Ferreiro, Alberto (1995).
"Braga and Tours: Some Observations on Gregory's ''De virtutibus sancti Martini''.
' ''Journal of Early Christian Studies''. 3 (1995), p. 195–210. * * * Kremer, Dieter (2004). El elemento germánico y su influencia en la historia lingüística peninsular, in Rafael Cano, Historia de la lengua española. , p. 133-148. *Kulikowski, Michael (2004). ''Late Roman Spain and its Cities.'' Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2004. * * Orel, Vladimir (2003). A Handbook of Germanic Etymology. Leiden: Brill. . * * *Thompson, E. A. (1980). ''The Conversion of the Spanish Suevi to Catholicism.'' ''Visigothic Spain: New Approaches''. ed. Edward James (historian), Edward James. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1980. . *Thompson, E. A. (1982). ''Romans and Barbarians''. Madison, WI: University of Wisconsin Press, 1982. *Williams, Megan: Personal Communication, San Francisco State University History Professor. 16 November 2010.
External links
The Chronicle of Hydatius
is the main source for the history of the suevi in Galicia and Portugal up to 468.
Medieval Galician anthroponomy
in ''Collectio Hispana Gallica Augustodunensis''
- translated by I.W. Raymond {{Authority control Kingdom of the Suebi, Germanic kingdoms, Suebi Former countries on the Iberian Peninsula, Suebi Medieval Portugal Medieval Galicia (Spain) History of Portugal by polity Former countries in Europe, Suebi Former kingdoms, Suebi Former monarchies of Europe, Suebi 5th century in Hispania 6th century in Hispania States and territories established in the 400s States and territories disestablished in the 580s 409 establishments 585 disestablishments Barbarian kingdoms