Stoichiometric coefficient on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A chemical equation is the symbolic representation of a
2HCl + 2Na -> 2NaCl + H2
Given the formulas are fairly simple, this equation could be read as "two H-C-L plus two N-A yields two N-A-C-L and H two." Alternately, and in general for equations involving complex chemicals, the chemical formulas are read using
2HCl(aq) + 2Na(s) -> 2NaCl(aq) + H2(g)
That reaction would have different 2HCl(g) + 2Na(s) -> 2NaCl(s) + H2(g)
Alternately, an arrow without parentheses is used in some cases to indicate formation of a gas ↑ or precipitate ↓. This is especially useful if only one such species is formed. Here is an example indicating that hydrogen gas is formed:
:2HCl + 2Na -> 2 NaCl + H2 ^
 If the reaction requires energy, it is indicated above the arrow. A capital Greek letter delta (Δ) or a triangle (△) is put on the reaction arrow to show that energy in the form of heat is added to the reaction. The expression is used as a symbol for the addition of energy in the form of light. Other symbols are used for other specific types of energy or radiation.
Similarly, if a reaction requires a certain medium with certain specific characteristics, then the name of the acid or base that is used as a medium may be placed on top of the arrow. If no specific acid or base is required, another way of denoting the use of an acidic or basic medium is to write H+ or OH− (or even "acid" or "base") on top of the arrow. Specific conditions of the temperature and pressure, as well as the presence of catalysts, may be indicated in the same way.
If the reaction requires energy, it is indicated above the arrow. A capital Greek letter delta (Δ) or a triangle (△) is put on the reaction arrow to show that energy in the form of heat is added to the reaction. The expression is used as a symbol for the addition of energy in the form of light. Other symbols are used for other specific types of energy or radiation.
Similarly, if a reaction requires a certain medium with certain specific characteristics, then the name of the acid or base that is used as a medium may be placed on top of the arrow. If no specific acid or base is required, another way of denoting the use of an acidic or basic medium is to write H+ or OH− (or even "acid" or "base") on top of the arrow. Specific conditions of the temperature and pressure, as well as the presence of catalysts, may be indicated in the same way.
 The standard notation for chemical equations only permits all reactants on one side, all products on the other, and all stoichiometric coefficients positive. For example, the usual form of the equation for
The standard notation for chemical equations only permits all reactants on one side, all products on the other, and all stoichiometric coefficients positive. For example, the usual form of the equation for 2 CH3OH -> CH3OCH3 + H2O
Sometimes an extension is used, where some substances with their stoichiometric coefficients are moved above or below the arrow, preceded by a plus sign or nothing for a reactant, and by a minus sign for a product. Then the same equation can look like this:
: 2 CH3OH -> overset\ceCH3OCH3
Such notation serves to hide less important substances from the sides of the equation, to make the type of reaction at hand more obvious, and to facilitate chaining of chemical equations. This is very useful in illustrating multi-step reaction mechanisms. Note that the substances above or below the arrows are not 2 CH3OH \;-\; H2O -> CH3OCH3
HCl + Na -> NaCl + 1/2 H2
In some circumstances the fractional coefficients are even inevitable. For example, the reaction corresponding to the standard enthalpy of formation must be written such that one molecule of a single product is formed. This will often require that some reactant coefficients be fractional, as is the case with the formation of Li(s) + 1/2F2(g) -> LiF(s)
 The method of inspection can be outlined as setting the most complex substance's stoichiometric coefficient to 1 and assigning values to other coefficients step by step such that both sides of the equation end up with the same number of atoms for each element. If any fractional coefficients arise during this process, the presence of fractions may be eliminated (at any time) by multiplying all coefficients by their
The method of inspection can be outlined as setting the most complex substance's stoichiometric coefficient to 1 and assigning values to other coefficients step by step such that both sides of the equation end up with the same number of atoms for each element. If any fractional coefficients arise during this process, the presence of fractions may be eliminated (at any time) by multiplying all coefficients by their \mathord\, + \mathord\, -> \mathord\, + \mathord\,
is achieved as follows:
# A coefficient of 1 is placed in front of the most complex formula ( CH4):
#:1 + \mathord\, -> \mathord\, + \mathord\,
# The left-hand side has 1 1 + \mathord\, -> 1 + 2 H2O
# Balancing the 4 1 CH4 + 2 O2 -> 1 CO2 + 2 H2O
# The coefficients equal to 1 are omitted, as they do not need to be specified explicitly:
#:CH4 + 2 O2 -> CO2 + 2 H2O
# It is wise to check that the final equation is balanced, i.e. that for each element there is the same number of atoms on the left- and right-hand side: 1 carbon, 4 hydrogen, and 4 oxygen.
\mathit_1 + \mathit_2 -> \mathit_3 + \mathit_4
All solutions to this system of linear equations are of the following form, where is any CH4 + 2 O2 -> CO2 + 2 H2O
CaCl2 + 2AgNO3 -> Ca(NO3)2 + 2 AgCl(v)
the full ionic equation is:
:Ca^2+ + 2Cl^- + 2Ag+ + 2NO3^- -> Ca^2+ + 2NO3^- + 2AgCl(v)
or, with all physical states included:
:Ca^2+(aq) + 2Cl^(aq) + 2Ag+(aq) + 2NO3^(aq) -> Ca^2+(aq) + 2NO3^(aq) + 2AgCl(v)
In this reaction, the Ca2+ and the NO3− ions remain in solution and are not part of the reaction. That is, these ions are identical on both the reactant and product side of the chemical equation. Because such ions do not participate in the reaction, they are called 2Cl^- + 2Ag+ -> 2AgCl(v)
or, in ''reduced'' balanced form,
:Ag+ + Cl^- -> AgCl(v)
In a neutralization or acid/ base reaction, the net ionic equation will usually be:
:H+ (aq) + OH^(aq) -> H2O(l)
There are a few acid/base reactions that produce a precipitate in addition to the water molecule shown above. An example is the reaction of 3Ba(OH)2 + 2H3PO4 -> 6H2O + Ba3(PO4)2(v)
:
Double displacement reactions that feature a
chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the pos ...
in the form of symbols and chemical formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbol ...
s. The reactant
In chemistry, a reagent ( ) or analytical reagent is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or test if one occurs. The terms ''reactant'' and ''reagent'' are often used interchangeably, but reactant specifies a ...
entities are given on the left-hand side and the product
Product may refer to:
Business
* Product (business), an item that serves as a solution to a specific consumer problem.
* Product (project management), a deliverable or set of deliverables that contribute to a business solution
Mathematics
* Produ ...
entities on the right-hand side with a plus sign between the entities in both the reactants and the products, and an arrow that points towards the products to show the direction of the reaction. The chemical formulas may be symbolic, structural
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such ...
(pictorial diagrams), or intermixed. The coefficients next to the symbols and formulas of entities are the absolute values of the stoichiometric numbers. The first chemical equation was diagrammed by Jean Beguin Jean Beguin (1550–1620) was an iatrochemist noted for his 1610 ''Tyrocinium Chymicum'' (Begin Chemistry)Digital edition, which many consider to be one of the first chemistry textbooks. In the 1615 edition of his textbook, Beguin made the first-e ...
in 1615.
Structure
A chemical equation (see an example below) consists of a list of reactants (the starting substances) on the left-hand side, an arrow symbol, and a list of products (substances formed in the chemical reaction) on the right-hand side. Each substance is specified by itschemical formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbol ...
, optionally preceded by a number called stoichiometric coefficient
A chemical equation is the symbolic representation of a chemical reaction in the form of symbols and chemical formulas. The reactant entities are given on the left-hand side and the product entities on the right-hand side with a plus sign between ...
. The coefficient specifies how many entities (e.g. molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
s) of that substance are involved in the reaction on a molecular basis. If not written explicitly, the coefficient is equal to 1. Multiple substances on any side of the equation are separated from each other by a plus sign.
As an example, the equation for the reaction of hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...
with sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
can be denoted:
:IUPAC nomenclature
A chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
T ...
, which could verbalise this equation as "two hydrochloric acid molecules and two sodium atoms react to form two formula unit
In chemistry, a formula unit is the empirical formula of any ionic or covalent network solid compound used as an independent entity for stoichiometric calculations. It is the lowest whole number ratio of ions represented in an ionic compound. E ...
s of sodium chloride and a hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
gas molecule."
Reaction types
Different variants of the arrow symbol are used to denote the type of a reaction: :State of matter
To indicatephysical state
In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many intermediate states are known to exist, such as liquid crystal, ...
of a chemical, a symbol in parentheses may be appended to its formula: (s) for a solid, (l) for a liquid, (g) for a gas, and (aq) for an aqueous solution. This is especially done when one wishes to emphasize the states or changes thereof. For example, the reaction of aqueous hydrochloric acid with solid (metallic) sodium to form aqueous sodium chloride and hydrogen gas would be written like this:
:thermodynamic
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws of the ...
and kinetic properties if gaseous hydrogen chloride
The compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colourless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hydrogen chloride ga ...
were to replace the hydrochloric acid as a reactant:
:Catalysis and other conditions
Notation variants
 The standard notation for chemical equations only permits all reactants on one side, all products on the other, and all stoichiometric coefficients positive. For example, the usual form of the equation for
The standard notation for chemical equations only permits all reactants on one side, all products on the other, and all stoichiometric coefficients positive. For example, the usual form of the equation for dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water, with an accompanying disruption of metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds free water intake, usually due to exercise, disease, or high environmental temperature. Mil ...
of methanol to dimethylether
Dimethyl ether (DME; also known as methoxymethane) is the organic compound with the formula CH3OCH3,
(sometimes ambiguously simplified to C2H6O as it is an isomer of ethanol). The simplest ether, it is a colorless gas that is a useful precursor ...
is:
: catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
s in this case, because they are consumed or produced in the reaction like ordinary reactants or products.
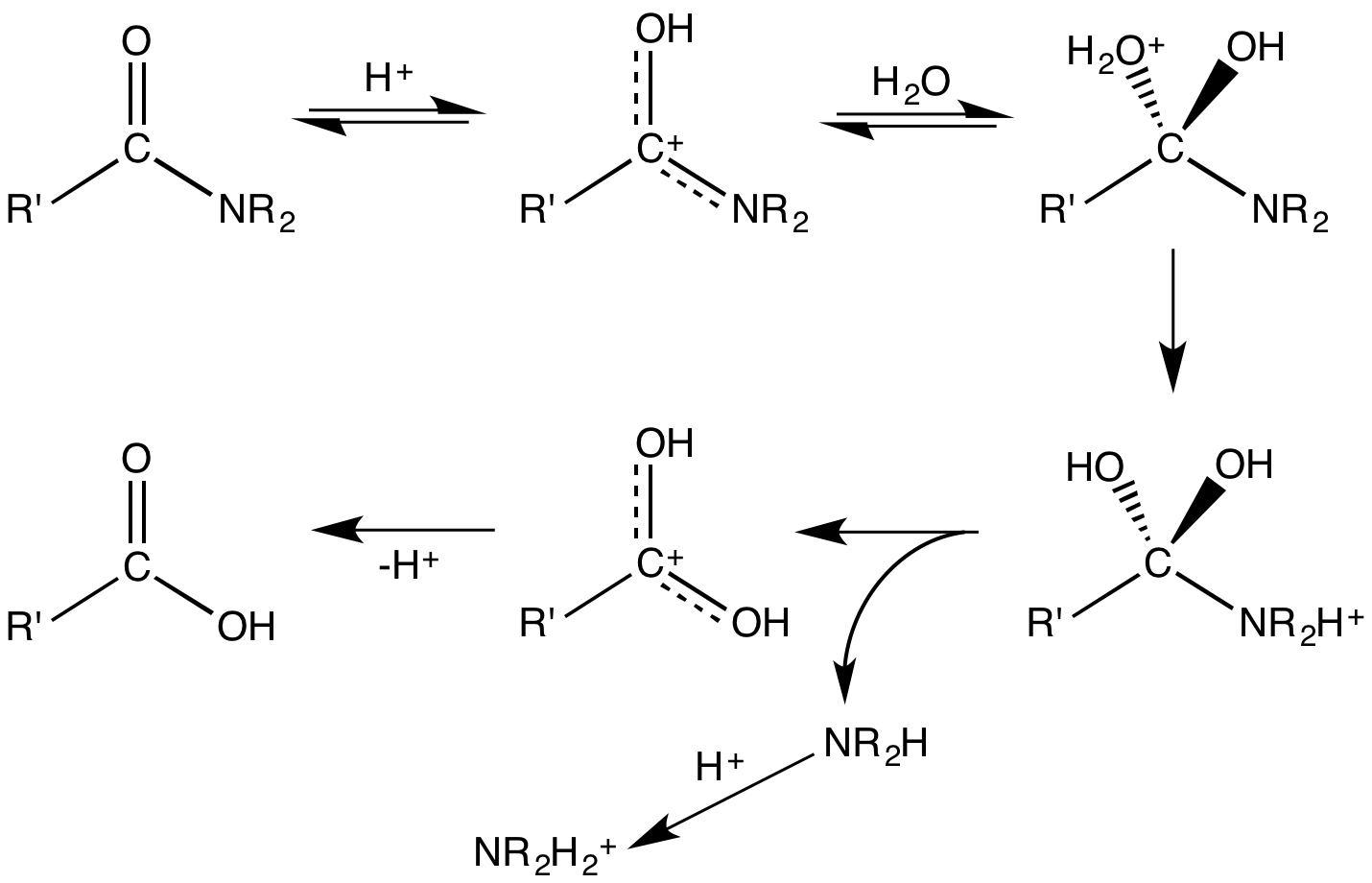
Another extension used in reaction mechanisms moves some substances to branches of the arrow. Both extensions are used in the example illustration of a mechanism.
Use of negative stoichiometric coefficients at either side of the equation (like in the example below) is not widely adopted and is often discouraged.
: Balancing chemical equations
Because nonuclear reaction
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is a process in which two nuclei, or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle, collide to produce one or more new nuclides. Thus, a nuclear reaction must cause a transformatio ...
s take place in a chemical reaction, the chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
s pass through the reaction unchanged. Thus, each side of the chemical equation must represent the same number of atoms of any particular element (or nuclide, if different isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numb ...
s are taken into account). The same holds for the total electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes charged matter to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be ''positive'' or ''negative'' (commonly carried by protons and electrons respe ...
, as stated by the charge conservation
In physics, charge conservation is the principle that the total electric charge in an isolated system never changes. The net quantity of electric charge, the amount of positive charge minus the amount of negative charge in the universe, is alwa ...
law. An equation adhering to these requirements is said to be balanced.
A chemical equation is balanced by assigning suitable values to the stoichiometric coefficients. Simple equations can be balanced by inspection, that is, by trial and error. Another technique involves solving a system of linear equations.
Balanced equations are usually written with smallest natural-number coefficients. Yet sometimes it may be advantageous to accept a fractional coefficient, if it simplifies the other coefficients. The introductory example can thus be rewritten as
:lithium fluoride
Lithium fluoride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula LiF. It is a colorless solid, that transitions to white with decreasing crystal size. Although odorless, lithium fluoride has a bitter-saline taste. Its structure is analogous to ...
:
:Inspection method
 The method of inspection can be outlined as setting the most complex substance's stoichiometric coefficient to 1 and assigning values to other coefficients step by step such that both sides of the equation end up with the same number of atoms for each element. If any fractional coefficients arise during this process, the presence of fractions may be eliminated (at any time) by multiplying all coefficients by their
The method of inspection can be outlined as setting the most complex substance's stoichiometric coefficient to 1 and assigning values to other coefficients step by step such that both sides of the equation end up with the same number of atoms for each element. If any fractional coefficients arise during this process, the presence of fractions may be eliminated (at any time) by multiplying all coefficients by their lowest common denominator
In mathematics, the lowest common denominator or least common denominator (abbreviated LCD) is the lowest common multiple of the denominators of a set of fractions. It simplifies adding, subtracting, and comparing fractions.
Description
The low ...
.
; Example
Balancing of the chemical equation for the complete combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combus ...
of methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Ea ...
:::carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon mak ...
atom, so 1 molecule of CO2 will balance it. The left-hand side also has 4 hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
atoms, which will be balanced by 2 molecules of H2O:
#:oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
atoms of the right-hand side by 2 molecules of O2 yields the equation
#:System of linear equations
For each chemical element (or nuclide or unchangedmoiety
Moiety may refer to:
Chemistry
* Moiety (chemistry), a part or functional group of a molecule
** Moiety conservation, conservation of a subgroup in a chemical species
Anthropology
* Moiety (kinship), either of two groups into which a society is ...
or charge) , its conservation requirement can be expressed by the mathematical equation
:
where
: is the number of atoms of element in a molecule of substance (per formula in the chemical equation), and
: is the stoichiometric coefficient for the substance .
This results in a homogeneous system of linear equations
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts often used in the sciences and statistics relating to the uniformity of a substance or organism. A material or image that is homogeneous is uniform in composition or character (i.e. color, shape, s ...
, which are readily solved using mathematical methods. Such system always has the all-zeros trivial solution In mathematics, the adjective trivial is often used to refer to a claim or a case which can be readily obtained from context, or an object which possesses a simple structure (e.g., groups, topological spaces). The noun triviality usually refers to a ...
, which we are not interested in, but if there are any additional solutions, there will be infinite number of them. Any non-trivial solution will balance the chemical equation. A "preferred" solution is one with whole-number, mostly positive stoichiometric coefficients with greatest common divisor
In mathematics, the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two or more integers, which are not all zero, is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers. For two integers ''x'', ''y'', the greatest common divisor of ''x'' and ''y'' is ...
equal to one.
Example
Let us assign variables to stoichiometric coefficients of the chemical equation from the previous section and write the corresponding linear equations: :real number
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a ''continuous'' one-dimensional quantity such as a distance, duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that values can have arbitrarily small variations. Every ...
:
:
The choice of yields the preferred solution,
:
which corresponds to the balanced chemical equation:
:Matrix method
The system of linear equations introduced in the previous section can also be written using an efficientmatrix
Matrix most commonly refers to:
* ''The Matrix'' (franchise), an American media franchise
** ''The Matrix'', a 1999 science-fiction action film
** "The Matrix", a fictional setting, a virtual reality environment, within ''The Matrix'' (franchis ...
formalism. First, to unify the reactant and product stoichiometric coefficients , let us introduce the quantity
:
called stoichiometric number, which simplifies the linear equations to
:
where is the total number of reactant and product substances (formulas) in the chemical equation.
Placement of the values at row and column of the composition matrix
:
and arrangement of the stoichiometric numbers into the stoichiometric vector
:
allows the system of equations to be expressed as a single matrix equation
In mathematics, a matrix (plural matrices) is a rectangular array or table of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns, which is used to represent a mathematical object or a property of such an object.
For example,
\begi ...
:
:
Like previously, any nonzero stoichiometric vector , which solves the matrix equation, will balance the chemical equation.
The set of solutions to the matrix equation is a linear space
In mathematics and physics, a vector space (also called a linear space) is a set whose elements, often called ''vectors'', may be added together and multiplied ("scaled") by numbers called ''scalars''. Scalars are often real numbers, but can ...
called the kernel
Kernel may refer to:
Computing
* Kernel (operating system), the central component of most operating systems
* Kernel (image processing), a matrix used for image convolution
* Compute kernel, in GPGPU programming
* Kernel method, in machine learn ...
of the matrix . For this space to contain nonzero vectors , i.e. to have a positive dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus, a line has a dimension of one (1D) because only one coor ...
N, the columns of the composition matrix must not be linearly independent
In the theory of vector spaces, a set of vectors is said to be if there is a nontrivial linear combination of the vectors that equals the zero vector. If no such linear combination exists, then the vectors are said to be . These concepts are ...
. The problem of balancing a chemical equation then becomes the problem of determining the N-dimensional kernel of the composition matrix. It is important to note that only for N = 1 will there be a unique preferred solution to the balancing problem. For N > 1 there will be an infinite number of preferred solutions with N of them linearly independent. If N = 0, there will be only the unusable trivial solution, the zero vector.
Techniques have been developed to quickly calculate a set of N independent solutions to the balancing problem, which are superior to the inspection and in that they are determinative and yield all solutions to the balancing problem.
; Example
Let us take the same chemical equation again and write the corresponding matrix equation:
\mathit_1 + \mathit_2 -> \mathit_3 + \mathit_4
Ionic equations
An ionic equation is a chemical equation in which electrolytes are written as dissociatedion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
s. Ionic equations are used for single and double displacement reaction
A salt metathesis reaction, sometimes called a double displacement reaction, is a chemical process involving the exchange of bonds between two reacting chemical species which results in the creation of products with similar or identical bonding a ...
s that occur in aqueous solutions.
For example, in the following precipitation reaction:
:spectator ion
A spectator ion is an ion that exists as a reactant and a product in a chemical equation. A spectator ion can, therefore, be observed in the reaction of aqueous solutions of sodium carbonate and copper(II) sulfate but does not affect the equilibr ...
s. A ''net ionic'' equation is the full ionic equation from which the spectator ions have been removed. The net ionic equation of the proceeding reactions is:
:barium hydroxide
Barium hydroxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula Ba(OH)2. The monohydrate (''x'' = 1), known as baryta or baryta-water, is one of the principal compounds of barium. This white granular monohydrate is the usual commercial form.
...
with phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid (orthophosphoric acid, monophosphoric acid or phosphoric(V) acid) is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, w ...
, which produces not only water but also the insoluble salt barium phosphate. In this reaction, there are no spectator ions, so the net ionic equation is the same as the full ionic equation.
:carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate ...
reacting with an acid have the net ionic equation:
:
If every ion is a "spectator ion" then there was no reaction, and the net ionic equation is null.
Generally, if ''zj'' is the multiple of elementary charge on the ''j-th'' molecule, charge neutrality may be written as:
:
where the ''νj'' are the stoichiometric coefficients described above. The ''zj'' may be incorporated
as an additional row in the ''aij'' matrix described above, and a properly balanced ionic equation will then also obey:
:
History
Typesetting
Notes
References
{{Authority control Stoichiometry Equations Chemistry