Stellar association on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 A stellar association is a very loose
A stellar association is a very loose
Stellar kinematic groups, Superclusters, Moving Groups
- D. Montes, UCM
- D. Montes, UCM {{Portal bar, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System Star clusters

 A stellar association is a very loose
A stellar association is a very loose star cluster
Star clusters are large groups of stars. Two main types of star clusters can be distinguished: globular clusters are tight groups of ten thousand to millions of old stars which are gravitationally bound, while open clusters are more loosely cl ...
, looser than both open cluster
An open cluster is a type of star cluster made of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way galaxy, an ...
s and globular clusters. Stellar associations will normally contain from 10 to 100 or more stars. The stars share a common origin, but have become gravitationally unbound and are still moving together through space. Associations are primarily identified by their common movement vectors and ages. Identification by chemical composition is also used to factor in association memberships.
Stellar associations were first discovered by the Soviet Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
n astronomer Victor Ambartsumian in 1947. The conventional name for an association uses the names or abbreviations of the constellation (or constellations) in which they are located; the association type, and, sometimes, a numerical identifier.
Types
Victor Ambartsumian first categorized stellar associations into two groups, OB and T, based on the properties of their stars. A third category, R, was later suggested bySidney van den Bergh
Sidney Van den Bergh, OC, FRS (born 20 May 1929 in Wassenaar) is a retired Dutch-Canadian astronomer.
He showed an interest in science from an early age, learning to read with books on astronomy. In addition to being interested in astronomy. ...
for associations that illuminate reflection nebulae.
The OB, T, and R associations form a continuum of young stellar groupings. But it is currently uncertain whether they are an evolutionary sequence, or represent some other factor at work. Some groups also display properties of both OB and T associations, so the categorization is not always clear-cut.
OB associations
Young associations will contain 10–100 massive stars of spectral class O and B, and are known as ''OB associations''. These are believed to form within the same small volume inside a giant molecular cloud. Once the surrounding dust and gas is blown away, the remaining stars become unbound and begin to drift apart. It is believed that the majority of all stars in the Milky Way were formed in OB associations. O class stars are short-lived, and will expire assupernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or whe ...
e after roughly one to fifteen million years, depending on the mass of the star. As a result, OB associations are generally only a few million years in age or less. The O-B stars in the association will have burned all their fuel within
10 million years. (Compare this to the current age of the Sun at about 5 billion years.)
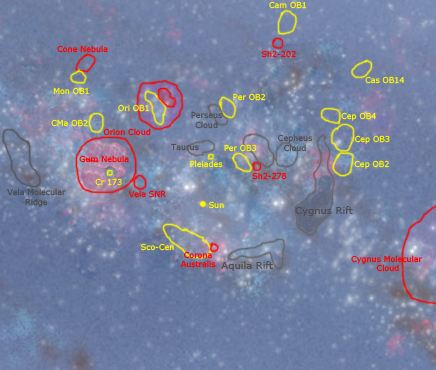
The Hipparcos satellite provided measurements that located a dozen OB associations within 650 parsecs of the Sun. The nearest OB association is the Scorpius–Centaurus association, located about 400 light-years from the Sun.
OB associations have also been found in the Large Magellanic Cloud and the Andromeda Galaxy. These associations can be quite sparse, spanning 1,500 light-years in diameter.
T associations
Young stellar groups can contain a number of infant T Tauri stars that are still in the process of entering the main sequence. These sparse populations of up to a thousand T Tauri stars are known as ''T associations''. The nearest example is the Taurus-Auriga T association (Tau-Aur T association), located at a distance of 140 parsecs from the Sun. Other examples of T associations include the R Corona Australis T association, the Lupus T association, the Chamaeleon T association and the Velorum T association. T associations are often found in the vicinity of the molecular cloud from which they formed. Some, but not all, include O-B class stars. To summarize the characteristics of Moving groups members: they have the same age and origin, the same chemical composition and they have the same amplitude and direction in their vector of velocity.R associations
Associations of stars that illuminate reflection nebulae are called ''R associations'', a name suggested by Sidney van den Bergh after he discovered that the stars in these nebulae had a non-uniform distribution. These young stellar groupings contain main sequence stars that are not sufficiently massive to disperse the interstellar clouds in which they formed. This allows the properties of the surrounding dark cloud to be examined by astronomers. Because R-associations are more plentiful than OB associations, they can be used to trace out the structure of the galactic spiral arms. An example of an R-association is Monoceros R2, located 830 ± 50 parsecs from the Sun.Known associations
The Ursa Major Moving Group is one example of a stellar association. (Except for α Ursae Majoris and η Ursae Majoris, all the stars in the Plough/Big Dipper are part of that group.) Other young moving groups include: * Local Association (Pleiades
The Pleiades (), also known as The Seven Sisters, Messier 45 and other names by different cultures, is an asterism and an open star cluster containing middle-aged, hot B-type stars in the north-west of the constellation Taurus. At a distance ...
moving group)
* Hyades Stream
The Hyades Stream (or Hyades moving group) is a large collection of scattered stars that also share a similar trajectory with the Hyades Cluster. In 1869, Richard A. Proctor observed that numerous stars at large distances from the Hyades share a ...
* IC 2391
IC 2391 (also known as the Omicron Velorum Cluster or Caldwell 85) is an open cluster in the constellation Vela. The Persian astronomer Al Sufi may have first described it about 964. It was found by Abbe Lacaille and cataloged as Lac II 5.
T ...
supercluster
* Beta Pictoris moving group
The Beta Pictoris Moving Group is a young moving group of stars located relatively near Earth. A moving group, in astronomy, is a group of stars that share a common motion through space as well as a common origin. This moving group is named for B ...
* Castor moving group
* AB Doradus moving group AB Doradus Moving Group is a group of about 30 associated stars that are moving through space together with the star AB Doradus. A moving group is distinguished by its members having about the same age, composition (or metallicity) and motion throug ...
* Zeta Herculis
Zeta Herculis, Latinized from ζ Herculis, is a multiple star system in the constellation Hercules. It has a combined apparent visual magnitude of 2.81, which is readily visible to the naked eye. Parallax measurements put it at a dista ...
moving group
* Alpha Persei moving cluster
* Cameleopardis OB1 association
See also
* OB star * Moving groups *Open clusters
An open cluster is a type of star cluster made of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way galaxy, ...
* List of nearby stellar associations and moving groups
References
External links
Stellar kinematic groups, Superclusters, Moving Groups
- D. Montes, UCM
- D. Montes, UCM {{Portal bar, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System Star clusters