Stalagmitic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
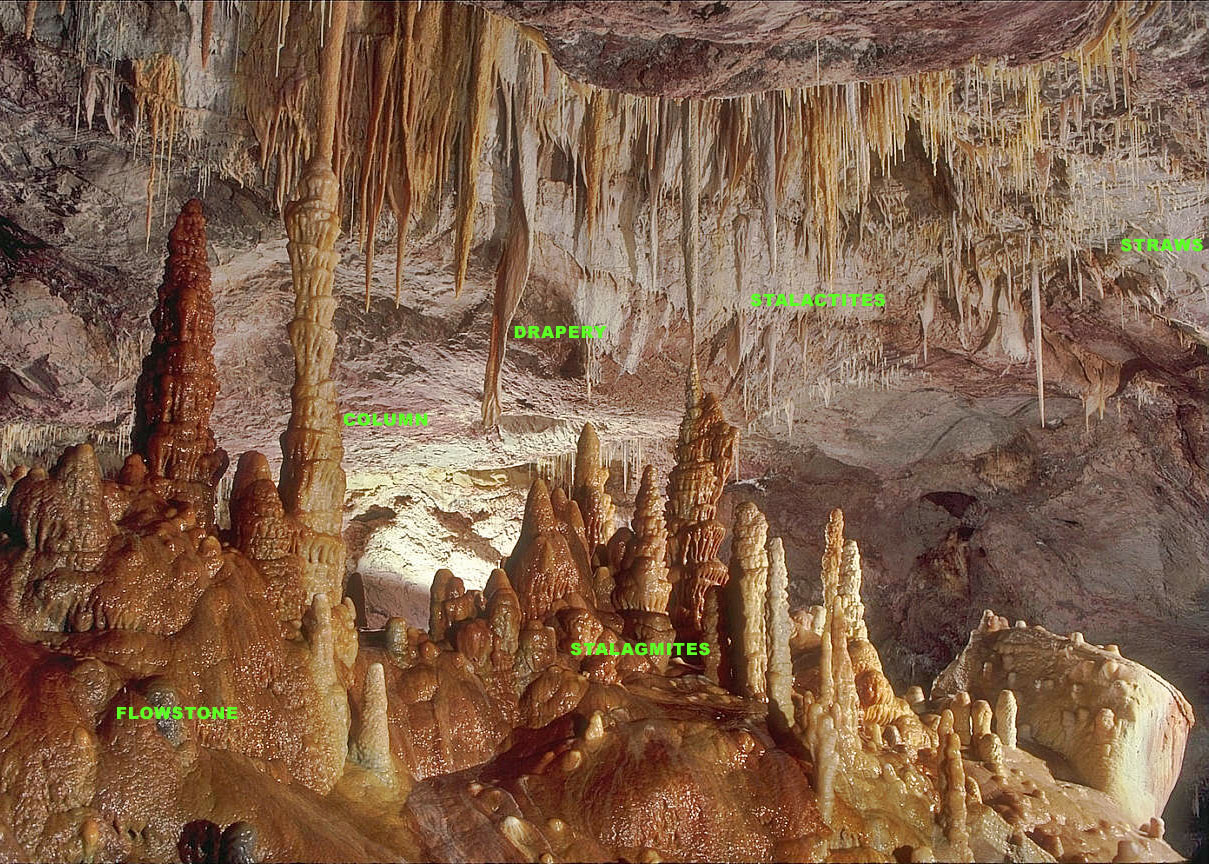
 A stalagmite (, ; from the
A stalagmite (, ; from the
 Stalactites and stalagmites can also form on
Stalactites and stalagmites can also form on
Image:Coves_d'Artà_05.jpg , Coves d’Artà, Mallorca, Spain
File:Seven stars cave.JPG ,

 A stalagmite (, ; from the
A stalagmite (, ; from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, from , "dropping, trickling")
is a type of rock formation that rises from the floor of a cave
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea ...
due to the accumulation of material deposited on the floor from ceiling drippings. Stalagmites are typically composed of calcium carbonate, but may consist of lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
, mud, peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and is the most efficient ...
, pitch, sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class o ...
, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rat
A pack rat or packrat, also called a woodrat or trade rat, are any species in the North and Central American rodent genus ''Neotoma''. Pack rats have a rat-like appearance, with long tails, large ears, and large, black eyes. Pack rats are notice ...
s).
The corresponding formation hanging down from the ceiling of a cave is a stalactite. Mnemonic
A mnemonic ( ) device, or memory device, is any learning technique that aids information retention or retrieval (remembering) in the human memory for better understanding.
Mnemonics make use of elaborative encoding, retrieval cues, and imag ...
s have been developed for which word refers to which type of formation; one is that ''stalactite'' has a C for "ceiling", and ''stalagmite'' has a G for "ground", another is that, as with ants in the pants, the mites go up and the tights (tites) come down.
Formation and type
Limestone stalagmites
The most common stalagmites arespeleothem
A speleothem (; ) is a geological formation by mineral deposits that accumulate over time in natural caves. Speleothems most commonly form in calcareous caves due to carbonate dissolution reactions. They can take a variety of forms, depending ...
s, which usually form in limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
caves. Stalagmite formation occurs only under certain pH conditions within the cavern. They form through deposition of calcium carbonate and other minerals, which is precipitate
In an aqueous solution, precipitation is the process of transforming a dissolved substance into an insoluble solid from a super-saturated solution. The solid formed is called the precipitate. In case of an inorganic chemical reaction leading ...
d from mineralized water solutions. Limestone is the chief form of calcium carbonate rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales ...
, which is dissolved by water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
that contains carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
, forming a calcium bicarbonate
Calcium bicarbonate, also called calcium hydrogencarbonate, has the chemical formula Ca(HCO3)2. The term does not refer to a known solid compound; it exists only in aqueous solution containing calcium (Ca2+), bicarbonate (), and carbonate () ions ...
solution in caverns. The partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the water must be greater than the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the cave chamber for conventional stalagmite growth.
If stalactites – the ceiling formations – grow long enough to connect with stalagmites on the floor, they form a column.
Stalagmites should normally not be touched, since the rock buildup is formed by minerals precipitating out of the water solution onto the existing surface; skin oils can alter the surface tension where the mineral water clings or flows, thus affecting the growth of the formation. Oils and dirt (mud, clay) from human contact can also stain the formation and change its color permanently.
Lava stalagmites
Another type of stalagmite is formed in lava tubes while molten and fluidlava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
is still active inside. Their mineralogical composition, close to that of siliceous
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one ...
minerals commonly found in basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
(for example, obsidian), the main constituent of volcanic glass
Volcanic glass is the amorphous solid, amorphous (uncrystallized) product of rapidly cooling magma. Like all types of glass, it is a state of matter intermediate between the closely packed, highly ordered array of a crystal and the highly disorde ...
, is different. Their mechanism of formation/crystallization is also notably different from that of limestone stalagmites () but the common point is that it remains driven by gravity. Drops of molten lava (siliceous material, ) solidify onto the floor of the already emptied lava tube, when the lava temperature sufficiently decreases after the passage and the complete purge of the main lava flow. Essentially, it is still the gravity deposition of material onto the floor of a cave (or a void).
However the difference from calcareous stalagmites is that the transport of siliceous material occurs in the molten state and not dissolved in aqueous solution; degassing does not play any significant role. With lava stalagmites, their formation also happens very quickly in only a matter of hours, days, or weeks, whereas limestone stalagmites may take up to thousands or hundred thousands of years. A key difference with lava stalagmites is that once the molten lava has ceased flowing, so too will the stalagmites cease to grow. This means that if the lava stalagmites were to be broken, they would never grow back. Stalagmites in lava tubes are rarer than their stalactite counterparts because during their formation, the dripping molten material most often falls onto still-moving lava flow which absorbs or carries the material away.
The generic term "lavacicle" has been applied to lava stalactites and stalagmites indiscriminately, and evolved from the word "icicle".
Ice stalagmites
A common stalagmite foundseason
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and ...
ally or year round in many caves is the ice stalagmite, commonly referred to as icicle
An icicle is a spike of ice formed when water falling from an object freezes.
Formation and dynamics
Icicles can form during bright, sunny, but subfreezing weather, when ice or snow melted by sunlight or some other heat source (such a ...
s, especially in above-ground contexts. Water seep
A seep or flush is a moist or wet place where water, usually groundwater, reaches the earth's surface from an underground aquifer.
Description
Seeps are usually not of sufficient volume to be flowing beyond their immediate above-ground location. ...
age from the surface
A surface, as the term is most generally used, is the outermost or uppermost layer of a physical object or space. It is the portion or region of the object that can first be perceived by an observer using the senses of sight and touch, and is ...
will penetrate into a cave and if temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various Conversion of units of temperature, temp ...
s are below freezing
Freezing is a phase transition where a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point. In accordance with the internationally established definition, freezing means the solidification phase change of a liquid ...
temperature, the water will collect on the floor into stalagmites. Deposition may also occur directly from the freezing of water vapor
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous p ...
. Similar to lava stalagmites, ice stalagmites form very quickly within hours or days. Unlike lava stalagmites however, they may grow back as long as water and temperatures are suitable. Ice stalagmites are more common than their stalactite counterparts because warmer air rises to the ceilings of caves and may raise temperatures to above freezing.
Ice stalactites may also form corresponding stalagmites below them, and given time, may grow together to form an ice column.
Concrete derived stalagmites
 Stalactites and stalagmites can also form on
Stalactites and stalagmites can also form on concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most wid ...
ceilings and floors, although they form much more rapidly there than in the natural cave environment.Hill, C A, and Forti, P, (1997). Cave Minerals of the World, 2nd editions. pp. 217 & 225 untsville, Alabama: National Speleological Society Inc./ref>Smith, G K. (2016). "Calcite straw stalactites growing from concrete structures". Cave and Karst Science, 43(1), 4–10.
The secondary deposits derived from concrete are the result of concrete degradation, where calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
ions
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conven ...
are leached out of the concrete in solution and redeposited on the underside of a concrete structure to form stalactites and stalagmites. Calcium carbonate deposition as a stalagmite occurs when the solution carries the calcium laden leachate solution to the ground under the concrete structure. Carbon dioxide is absorbed into the alkaline leachate solution, which facilitates the chemical reactions to deposit calcium carbonate as a stalagmite. These stalagmites rarely grow taller than a few centimetres.Smith, G K., (2015). "Calcite Straw Stalactites Growing From Concrete Structures". Proceedings of the 30th 'Australian Speleological Federation' conference, Exmouth, Western Australia, edited by Moulds, T. pp. 93–108.
Secondary deposits, which create stalagmites, stalactites, flowstone etc., outside the natural cave
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea ...
environment, are referred to as "calthemite
Calthemite is a secondary deposit, derived from concrete, lime, mortar or other calcareous material outside the cave environment.Smith, G.K. (2016). "Calcite straw stalactites growing from concrete structures", Cave and Karst Science 43(1), 4 ...
s". These concrete derived secondary deposits cannot be referred to as "speleothem
A speleothem (; ) is a geological formation by mineral deposits that accumulate over time in natural caves. Speleothems most commonly form in calcareous caves due to carbonate dissolution reactions. They can take a variety of forms, depending ...
s" due to the definition of the word.
Records
The largest known stalagmite in the world exceeds in height and is in Sơn Đoòng Cave,Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
.
In the Zagros Mountains
The Zagros Mountains ( ar, جبال زاغروس, translit=Jibal Zaghrus; fa, کوههای زاگرس, Kuh hā-ye Zāgros; ku, چیاکانی زاگرۆس, translit=Çiyakani Zagros; Turkish: ''Zagros Dağları''; Luri: ''Kuh hā-ye Zāgr ...
of south Iran, approximately from the ancient city of Bishapur
Bishapur (Middle Persian: ''Bay-Šāpūr''; fa, بیشاپور}, ''Bishâpûr'') was an ancient city in Sasanid Persia (Iran) on the ancient road between Persis and Elam. The road linked the Sassanid capitals Estakhr (very close to Persepolis ...
, in the Shapur cave on the fourth of five terraces stands the 3rd-century colossal statue of Shapur I, second ruler of the Sassanid Empire. The statue, carved from one stalagmite, is nearly high.
Photo gallery
Seven-star Cave
Seven-star Cave () is an extensive limestone cave complex in Seven-star Park, both of which are popular tourist attractions in the city of Guilin in Guangxi Autonomous Region in China. The name derives from the fact the main karst limestone pe ...
, Guilin, China
File:Crayfish_back.JPG , A “crayfish back”, Jenolan Caves
The Jenolan Caves ( Tharawal: ''Binoomea'', ''Bindo'', ''Binda'') are limestone caves located within the Jenolan Karst Conservation Reserve in the Central Tablelands region, west of the Blue Mountains, in Jenolan, Oberon Council, New South Wa ...
, New South Wales, Australia
File:Herault_stalagmite2.JPG , Hérault
Hérault (; oc, Erau, ) is a department of the region of Occitania, Southern France. Named after the Hérault River, its prefecture is Montpellier. It had a population of 1,175,623 in 2019.Castellana Grotte, Apulia, Italy
The Virtual Cave: Stalagmites
{{Authority control Speleothems
References
External links
The Virtual Cave: Stalagmites
{{Authority control Speleothems