St. Gallen (canton) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The canton of St. Gallen, also canton of St Gall (german: link=no, Kanton St. Gallen ; rm, Chantun Son Gagl; french: Canton de Saint-Gall; it, Canton San Gallo), is a canton of Switzerland. The capital is
 The canton of St. Gallen is an artificial construct of various historical territories, defined by
The canton of St. Gallen is an artificial construct of various historical territories, defined by
 The canton is located in the north east of Switzerland. It is bounded to the north by Lake Constance (''Bodensee''). To the east lies the Rhine valley. Over the Rhine are
The canton is located in the north east of Switzerland. It is bounded to the north by Lake Constance (''Bodensee''). To the east lies the Rhine valley. Over the Rhine are
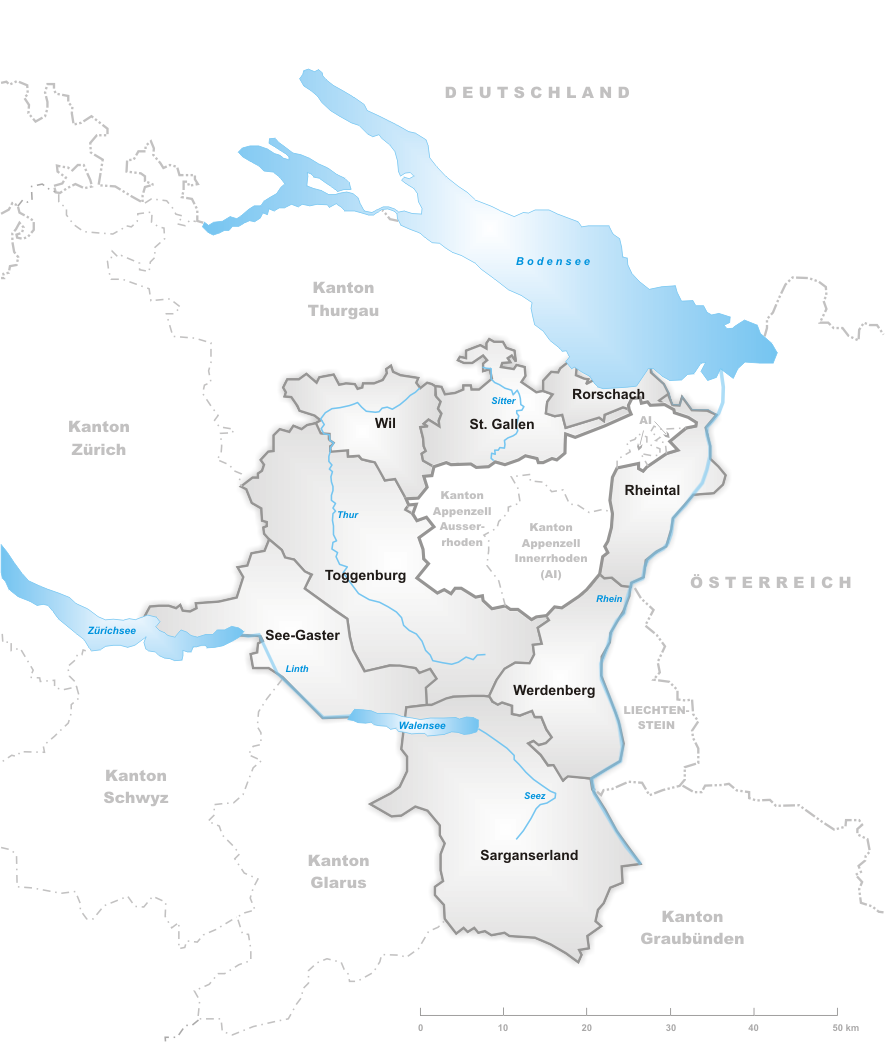 Since 2003 the canton is subdivided into 8
Since 2003 the canton is subdivided into 8
 88% of the population is German-speaking.
The main centres of population are the capital St. Gallen (69,700 inhabitants),
88% of the population is German-speaking.
The main centres of population are the capital St. Gallen (69,700 inhabitants),
Official website
stadt Restaurant st Gallen spitze
{{DEFAULTSORT:St. Gallen Cantons of Switzerland Cantons of the Helvetic Republic 1803 establishments in Switzerland States and territories established in 1803
St. Gallen
, neighboring_municipalities = Eggersriet, Gaiserwald, Gossau, Herisau (AR), Mörschwil, Speicher (AR), Stein (AR), Teufen (AR), Untereggen, Wittenbach
, twintowns = Liberec (Czech Republic)
, website = ...
.
Located in northeastern Switzerland
Eastern Switzerland (german: Ostschweiz, french: Suisse orientale, rm, Svizra orientala, it, Svizzera orientale) is the common name of the region situated to the east of Glarus Alps, with the cantons of Schaffhausen, Thurgau, St. Gallen, Appenz ...
, the canton has an area of (5% of Switzerland) and a resident population close to half a million as of 2015 (6% of Switzerland). It was formed in 1803 as a conflation of the city of St. Gallen
, neighboring_municipalities = Eggersriet, Gaiserwald, Gossau, Herisau (AR), Mörschwil, Speicher (AR), Stein (AR), Teufen (AR), Untereggen, Wittenbach
, twintowns = Liberec (Czech Republic)
, website = ...
, the territories of the Abbey of St. Gall
The Abbey of Saint Gall (german: Abtei St. Gallen) is a dissolved abbey (747–1805) in a Catholic religious complex in the city of St. Gallen in Switzerland. The Carolingian-era monastery existed from 719, founded by Saint Othmar on the spot ...
and various former subject territories of the Old Swiss Confederacy.
History
 The canton of St. Gallen is an artificial construct of various historical territories, defined by
The canton of St. Gallen is an artificial construct of various historical territories, defined by Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
in the Act of Mediation
The Act of Mediation () was issued by Napoleon Bonaparte, First Consul of the French Republic on 19 February 1803 establishing the Swiss Confederation. The act also abolished the previous Helvetic Republic, which had existed since the invasi ...
in 1803.
About half of the canton's area corresponds to the acquisitions of the abbey of St. Gall
The Abbey of Saint Gall (german: Abtei St. Gallen) is a dissolved abbey (747–1805) in a Catholic religious complex in the city of St. Gallen in Switzerland. The Carolingian-era monastery existed from 719, founded by Saint Othmar on the spot ...
en over centuries.
The city of St. Gallen became independent of the abbey in 1405. At the same time, the abbey lost control of Appenzell. Conversely, the Toggenburg
Toggenburg is a region of Switzerland. It corresponds to the upper valley of the river Thur and that of its main tributary, the Necker. Since 1 January 2003, Toggenburg has been a constituency (''Wahlkreis'') of the canton of St. Gallen ( ...
was acquired by the Abbey in 1468.
Both the city and the abbey were associates (''Zugewandte Orte
The Old Swiss Confederacy or Swiss Confederacy (Modern German: ; historically , after the Reformation also , "Confederation of the Swiss") was a loose confederation of independent small states (, German or In the charters of the 14th century ...
'') of the Old Swiss Confederacy, but unlike Appenzell never joined as full members.
The territories at Lake Zürich
__NOTOC__
Lake Zurich ( Swiss German/ Alemannic: ''Zürisee''; German: ''Zürichsee''; rm, Lai da Turitg) is a lake in Switzerland, extending southeast of the city of Zürich. Depending on the context, Lake Zurich or ''Zürichsee'' can be used ...
, Walensee
The Walensee, also known as ''Lake Walen'' or ''Lake Walenstadt'' from Walenstadt, is one of the larger lakes in Switzerland, with about two thirds of its area in the Canton of St. Gallen and about one third in the Canton of Glarus. Other towns ...
and Rheintal
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, sou ...
remained independent until 1798. In the Helvetic Republic, the northern parts of the modern canton together with Appenzell became the canton of Säntis, while its southern parts together with Glarus
, neighboring_municipalities= Glarus Nord, Glarus Süd, Muotathal (SZ), Innerthal (SZ)
, twintowns= Wiesbaden-Biebrich (Germany)
}
Glarus (; gsw, Glaris; french: Glaris; it, Glarona; rm, Glaruna) is the capital of the canton of Glarus ...
became the canton of Linth.
Before the 1798 French invasion,
the territory of the modern canton consisted of the free city of St. Gallen, the territories of the Abbey of St. Gallen (including Fürstenland
Fürstenland or Alte Landschaft is the name of a historical territory of the Swiss canton of St. Gallen, corresponding to the modern districts of St. Gallen (without the city proper), Wil and Rorschach.
It was a subject territory of the Abbey of ...
and Toggenburg
Toggenburg is a region of Switzerland. It corresponds to the upper valley of the river Thur and that of its main tributary, the Necker. Since 1 January 2003, Toggenburg has been a constituency (''Wahlkreis'') of the canton of St. Gallen ( ...
), the free city of Rapperswil
Rapperswil (Swiss German: or ;Andres Kristol, ''Rapperswil SG (See)'' in: ''Dictionnaire toponymique des communes suisses – Lexikon der schweizerischen Gemeindenamen – Dizionario toponomastico dei comuni svizzeri (DTS, LSG)'', Centre de dial ...
, Pfäfers Abbey
Pfäfers Abbey (german: Kloster Pfäfers), also known as St. Pirminsberg from its position on a mountain, was a Benedictine monastery in Pfäfers near Bad Ragaz, in the canton of St. Gallen, Switzerland.
Situated at the junction of the Tamina an ...
, Sargans
Sargans is a municipality in the ''Wahlkreis'' (constituency) of Sarganserland in the canton of St. Gallen in Switzerland.
Sargans is known for its castle, which dates from before the founding of the Swiss Confederation in 1291. Sargans was al ...
and the independent lordships (bailiwicks) of Rheintal
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, sou ...
, Sax-Forstegg
The Lordship of Sax-Forstegg was a territory in the Alpine Rhine Valley, including the settlements of Sennwald and Altstätten, now part of the canton of St. Gallen, Switzerland.
It was named for the baronial family of Sax and their castle Forst ...
, Hohensax
The noble family von Sax (originally ''de Sacco'') were a medieval noble family in eastern Switzerland. They owned estates and castles on both sides of the Alps in the modern cantons of St. Gallen, Graubünden and Ticino. The origin of the fami ...
, Werdenberg, Windegg and Uznach
Uznach is a municipality in the ''Wahlkreis'' (constituency) of See-Gaster in the canton of St. Gallen in Switzerland.
History
Uznach is first mentioned in 741 as ''Uzinaa'' in a grant from a noble lady at Benken Abbey to the Abbey of Saint G ...
.
In April 1798, the territories of the later canton of St. Gallen
were divided between the cantons of Säntis
At above sea level, Säntis is the highest mountain in the Alpstein massif of northeastern Switzerland. It is also the culminating point of the whole Appenzell Alps, between Lake Walen and Lake Constance. Shared by three cantons, the mounta ...
and Linth
The Linth (pronounced "lint") is a Swiss river that rises near the village of Linthal in the mountains of the canton of Glarus, and eventually flows into the Obersee section of Lake Zurich. It is about in length.
The water power of the Lin ...
of the Helvetic Republic (along with Appenzell, Glarus
, neighboring_municipalities= Glarus Nord, Glarus Süd, Muotathal (SZ), Innerthal (SZ)
, twintowns= Wiesbaden-Biebrich (Germany)
}
Glarus (; gsw, Glaris; french: Glaris; it, Glarona; rm, Glaruna) is the capital of the canton of Glarus ...
and parts of Schwyz
The town of Schwyz (; french: Schwytz; it, Svitto) is the capital of the canton of Schwyz in Switzerland.
The Federal Charter of 1291 or ''Bundesbrief'', the charter that eventually led to the foundation of Switzerland, can be seen at the ' ...
.
However, the two new Cantons had immediate financial problems and were forced to institute a number of unpopular taxes and laws. The Abbey was secularized on 17 September 1798 and the Prince-Abbot Pankraz Vorster fled to Vienna. The unpopular laws and the closing of the Abbey caused unrest throughout the area. When the War of the Second Coalition
The War of the Second Coalition (1798/9 – 1801/2, depending on periodisation) was the second war on revolutionary France by most of the European monarchies, led by Britain, Austria and Russia, and including the Ottoman Empire, Portugal, N ...
broke out in 1799, an Austrian army marched into eastern Switzerland and returned the Prince-Abbot to his throne at the Abbey. However, his victory was short-lived. The Austrian and Russian armies were defeated outside Zürich and the French Army returned to St. Gallen driving the Prince-Abbot out.
In 1803, as part of the Act of Mediation
The Act of Mediation () was issued by Napoleon Bonaparte, First Consul of the French Republic on 19 February 1803 establishing the Swiss Confederation. The act also abolished the previous Helvetic Republic, which had existed since the invasi ...
, the area joined the Swiss Confederation as the Canton of St. Gallen.
The cantonal constitution of 1803 was revised in 1814. Because of the confessional heterogeneity of the canton's population, the 1814 constitution did unusually organise matters of religion, marriage and education not on a cantonal level but introduced a twofold division (confessional dualism), with separate Protestant and a Catholic assemblies subordinate to the legislative cantonal assembly (Grosser Rat).
The constitution was revised again in 1831, introducing elements of direct democracy. The constitution of 1831 divided the canton into 15 districts (''Bezirke''),
reduced to 14 in 1918 (fusion of Tablat district with St. Gallen district).
Due to continuing confessional squabbles over the organisation of schools, the canton eventually placed education under its authority in 1861.
The constitution was yet again revised in 1890, with a stronger emphasis on direct democracy.
The 1890 constitution remained in effect, with numerous later changes, until 2001, the date of the latest revision of the cantonal constitution.
In the 2001 constitution, the division into districts was replaced by a division into eight constituencies (''Wahlkreise''), effective on 1 January 2003.
Geography
 The canton is located in the north east of Switzerland. It is bounded to the north by Lake Constance (''Bodensee''). To the east lies the Rhine valley. Over the Rhine are
The canton is located in the north east of Switzerland. It is bounded to the north by Lake Constance (''Bodensee''). To the east lies the Rhine valley. Over the Rhine are Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
(state of Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( , ; gsw, label= Vorarlbergisch, Vorarlbearg, , or ) is the westernmost state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with the ...
) and Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein (german: link=no, Fürstentum Liechtenstein), is a German-speaking microstate located in the Alps between Austria and Switzerland. Liechtenstein is a semi-constitutional monarch ...
. To the south, the canton of St. Gallen is bounded by the cantons of Graubünden, Glarus
, neighboring_municipalities= Glarus Nord, Glarus Süd, Muotathal (SZ), Innerthal (SZ)
, twintowns= Wiesbaden-Biebrich (Germany)
}
Glarus (; gsw, Glaris; french: Glaris; it, Glarona; rm, Glaruna) is the capital of the canton of Glarus ...
and Schwyz
The town of Schwyz (; french: Schwytz; it, Svitto) is the capital of the canton of Schwyz in Switzerland.
The Federal Charter of 1291 or ''Bundesbrief'', the charter that eventually led to the foundation of Switzerland, can be seen at the ' ...
. To the west lie the cantons of Zürich and Thurgau
Thurgau (; french: Thurgovie; it, Turgovia), anglicized as Thurgovia, more formally the Canton of Thurgau, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of five districts and its capital is Frauenfeld.
Thurgau is par ...
.
The two half cantons Appenzell Innerrhoden and Appenzell Ausserrhoden are completely surrounded by lands of the canton of St. Gallen.
The main rivers of the canton are the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
, Thur, Linth
The Linth (pronounced "lint") is a Swiss river that rises near the village of Linthal in the mountains of the canton of Glarus, and eventually flows into the Obersee section of Lake Zurich. It is about in length.
The water power of the Lin ...
and Seez. The topography changes from the plains, near river Rhine and Lake Constance, towards the mountainous areas of the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Swi ...
in the south (Appenzell Alps
The Appenzell Alps (german: Appenzeller Alpen) are a mountain range in Switzerland on the northern edge of the Alps. They extend into the cantons of Appenzell Ausserrhoden, Appenzell Innerrhoden and St. Gallen and are bordered by the Glarus Alps ...
and Glarus Alps
The Glarus Alps (german: Glarner Alpen) are a mountain range in central Switzerland. They are bordered by the Uri Alps and the Schwyz Alps to the west, the Lepontine Alps to the south, the Appenzell Alps to the northeast. The eastern part of ...
). About one third () of the canton is wooded, while nearly half is is used for farming. of the farm land is alpine pastures. Of the rest of the canton, is considered unproductive while is filled with housing or roads.
The altitude above the sea-level varies from (the lake of Constance) to (the Ringelspitz). The canton includes portions of the lake of Constance (), of the Walensee (rather over ), and of the lake of Zürich (), and several small lakes wholly within its limits.
The mountains of the canton include part of a thrust fault that was declared a geologic UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
, under the name Swiss Tectonic Arena Sardona, in 2008.
Political subdivisions
Constituencies
 Since 2003 the canton is subdivided into 8
Since 2003 the canton is subdivided into 8 constituencies
An electoral district, also known as an election district, legislative district, voting district, constituency, riding, ward, division, or (election) precinct is a subdivision of a larger state (a country, administrative region, or other polity ...
(''Wahlkreise'') replacing the districts (''Bezirke'').
*Rheintal
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, sou ...
with capital Altstätten
, neighboring_municipalities= Eichberg, Feldkirch (AT-8), Gais (AR), Marbach, Oberegg (AI), Oberriet, Ruggell (LI), Rüte (AI), Rüthi, Sennwald, Trogen (AR)
, twintowns =
Altstätten is a small historic rural town and a municipality in ...
* Rorschach with capital Rorschach
*Sarganserland
The Sarganserland is a constituency (''Wahlkreis'') of the canton of St. Gallen, Switzerland, with a population of 36,892 ().
The constituency corresponds to the historical county of Sargans (13th to 15th century) and the later '' Landvogtei'' Sa ...
with capital Sargans
Sargans is a municipality in the ''Wahlkreis'' (constituency) of Sarganserland in the canton of St. Gallen in Switzerland.
Sargans is known for its castle, which dates from before the founding of the Swiss Confederation in 1291. Sargans was al ...
* See-Gaster with capital Rapperswil-Jona
Rapperswil-Jona is a municipality in the ''Wahlkreis'' (constituency) of See-Gaster in the canton of St. Gallen in Switzerland.
Besides Rapperswil and Jona, which were separate municipalities until 2006, the municipality includes Bollingen, B ...
*St. Gallen
, neighboring_municipalities = Eggersriet, Gaiserwald, Gossau, Herisau (AR), Mörschwil, Speicher (AR), Stein (AR), Teufen (AR), Untereggen, Wittenbach
, twintowns = Liberec (Czech Republic)
, website = ...
with capital St. Gallen
, neighboring_municipalities = Eggersriet, Gaiserwald, Gossau, Herisau (AR), Mörschwil, Speicher (AR), Stein (AR), Teufen (AR), Untereggen, Wittenbach
, twintowns = Liberec (Czech Republic)
, website = ...
*Toggenburg
Toggenburg is a region of Switzerland. It corresponds to the upper valley of the river Thur and that of its main tributary, the Necker. Since 1 January 2003, Toggenburg has been a constituency (''Wahlkreis'') of the canton of St. Gallen ( ...
with capital Lichtensteig
Lichtensteig is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the ''Wahlkreis'' (constituency) of Toggenburg (Wahlkreis), Toggenburg in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of St. Gallen (canton), St. Gallen in Switzerland.
History
Lichtensteig w ...
* Werdenberg with capital Buchs
*Wil
Wil () is the capital of the ''Wahlkreis'' (constituency) of Wil in the canton of St. Gallen in Switzerland.
Wil is the third largest city in the Canton of St. Gallen, after the city of St. Gallen and Rapperswil-Jona, a twin city that merged in ...
with capital Wil
Wil () is the capital of the ''Wahlkreis'' (constituency) of Wil in the canton of St. Gallen in Switzerland.
Wil is the third largest city in the Canton of St. Gallen, after the city of St. Gallen and Rapperswil-Jona, a twin city that merged in ...
Municipalities
There are 77 municipalities in the canton ().Politics
Federal election results
: FDP before 2009, FDP.The Liberals after 2009 : "*" indicates that the party was not on the ballot in this canton. : Part of the GPSDemographics
 88% of the population is German-speaking.
The main centres of population are the capital St. Gallen (69,700 inhabitants),
88% of the population is German-speaking.
The main centres of population are the capital St. Gallen (69,700 inhabitants), Rapperswil-Jona
Rapperswil-Jona is a municipality in the ''Wahlkreis'' (constituency) of See-Gaster in the canton of St. Gallen in Switzerland.
Besides Rapperswil and Jona, which were separate municipalities until 2006, the municipality includes Bollingen, B ...
(27,000), Wil
Wil () is the capital of the ''Wahlkreis'' (constituency) of Wil in the canton of St. Gallen in Switzerland.
Wil is the third largest city in the Canton of St. Gallen, after the city of St. Gallen and Rapperswil-Jona, a twin city that merged in ...
(17,500) and Gossau (17,000).
, the population included 97,461 foreigners, or about 20.9% of the total population.
The majority of the population () is Roman Catholic (52%) while a large minority is Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
(28%).
Historical population
The historical population is given in the following table:Economy
Agricultural activity consists predominantly ofdairy farming
Dairy farming is a class of agriculture for long-term production of milk, which is processed (either on the farm or at a dairy plant, either of which may be called a dairy) for eventual sale of a dairy product. Dairy farming has a history th ...
and cattle breeding in the mountainous areas. In the plains fruit and wine production are important, but there is also mixed farming.
Industries of the canton include optical goods, pyrotechnics, chemicals and pharmaceuticals. Tourism plays an important role in the many resorts. There is a thermal spa in Bad Ragaz and another in St. Margrethen and a great number of winter sports facilities.
Education
Higher educational institutions include theHochschule für Technik Rapperswil
HSR (german: Hochschule für Technik Rapperswil) or University of Applied Sciences Rapperswil is a technical university in Rapperswil, a locality of the city of Rapperswil-Jona, Switzerland. HSR is part of the University of Applied Sciences of ...
and the University of St. Gallen
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, t ...
.
Notes and references
External links
Official website
stadt Restaurant st Gallen spitze
{{DEFAULTSORT:St. Gallen Cantons of Switzerland Cantons of the Helvetic Republic 1803 establishments in Switzerland States and territories established in 1803