Squalicorax on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Squalicorax'', commonly known as the crow shark, is a genus of extinct lamniform
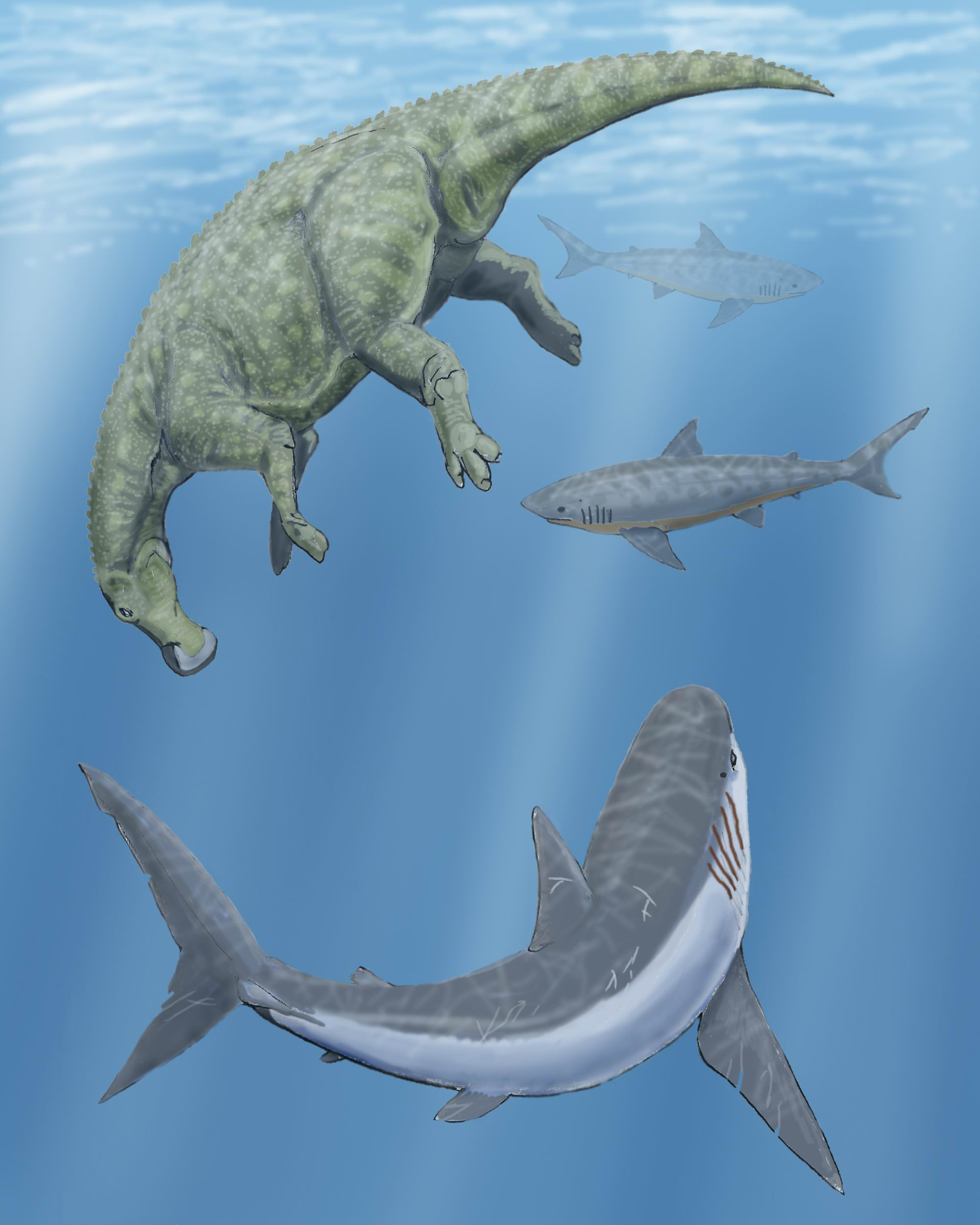


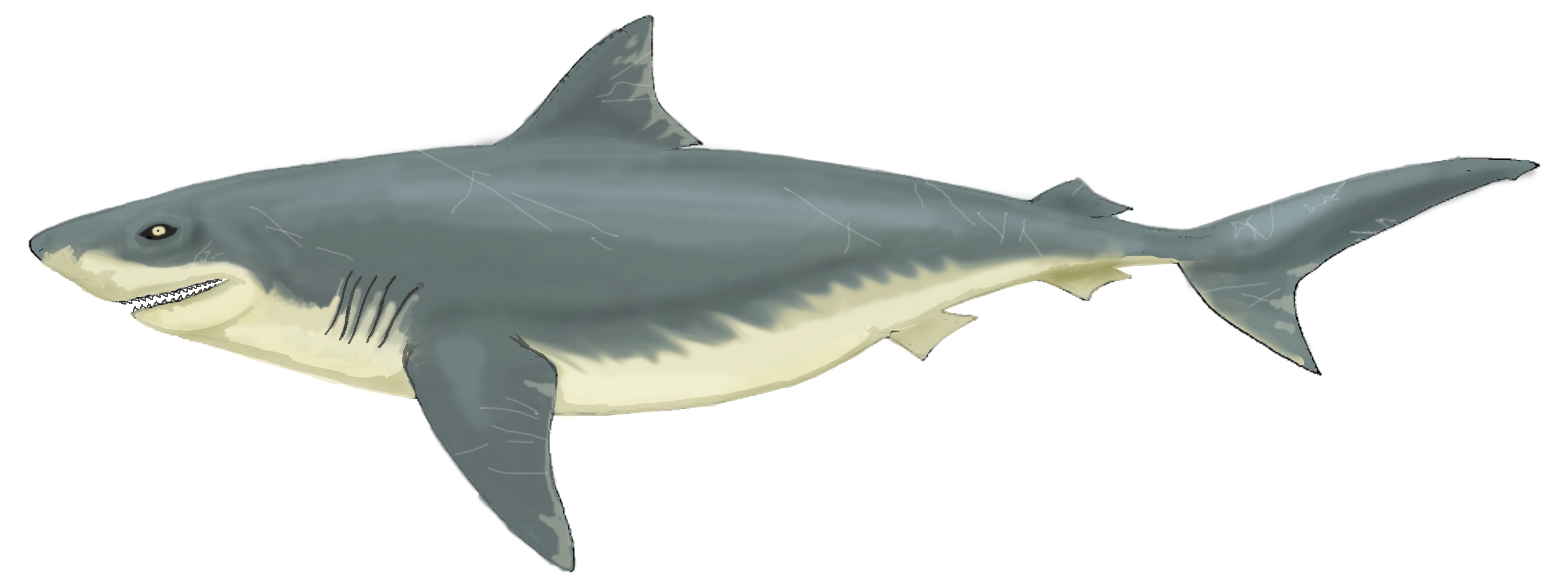

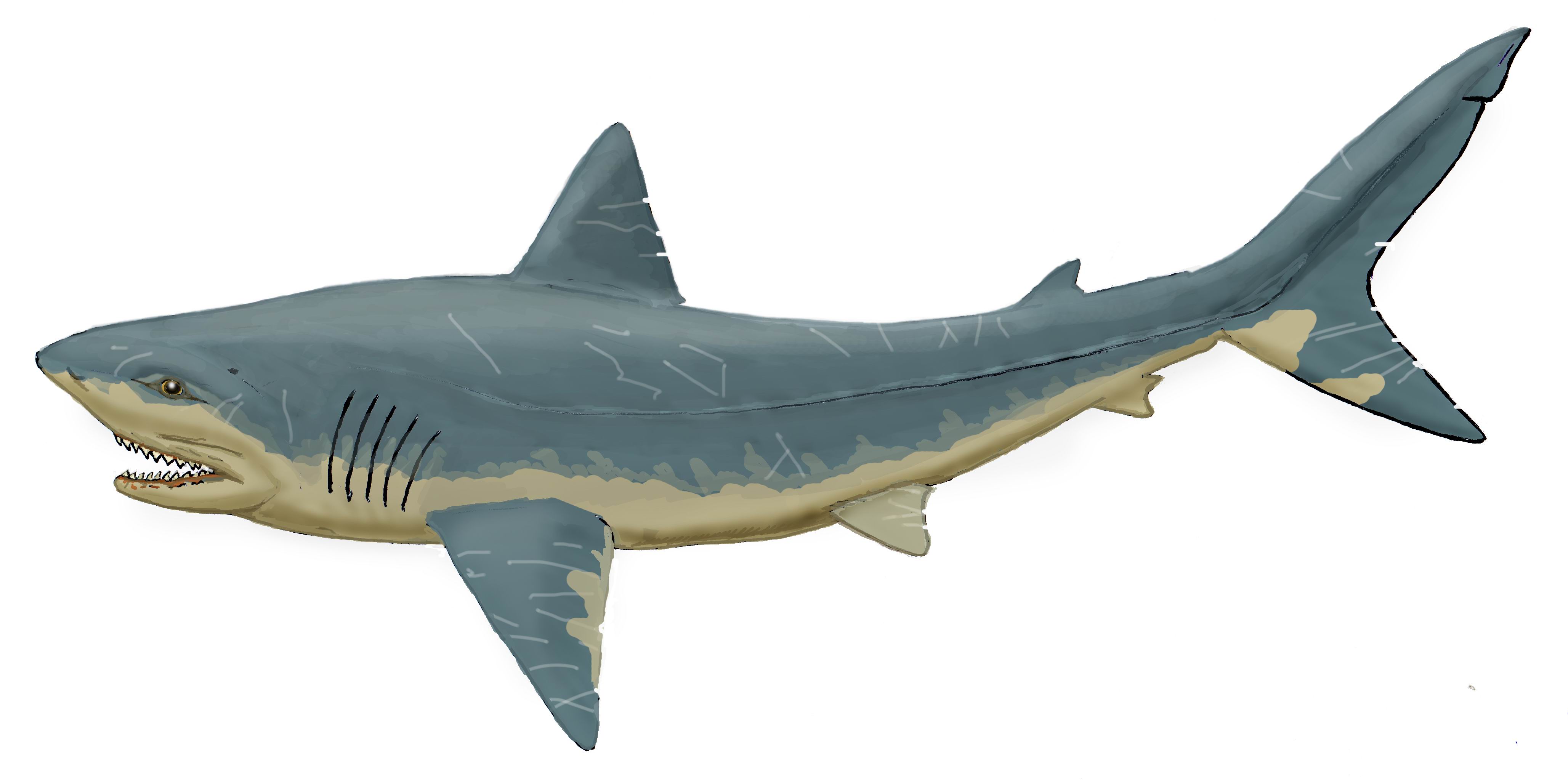 The following are the best studied American species for which relatively complete skeletons are described:
* ''Squalicorax falcatus'' (Agassiz, 1843) – is a medium-sized shark with a broad snout and relatively small teeth. Its length reached almost 3 m. It lived during the Cenomanian to early Santonian (
The following are the best studied American species for which relatively complete skeletons are described:
* ''Squalicorax falcatus'' (Agassiz, 1843) – is a medium-sized shark with a broad snout and relatively small teeth. Its length reached almost 3 m. It lived during the Cenomanian to early Santonian (
Elasmo.com page on Squalicorax
* ttp://www.elasmo-research.org/education/evolution/squalicorax.htm Squalicorax beim ReefQuest Centre for Shark Research {{Taxonbar, from=Q134511 Anacoracidae Cretaceous sharks Late Cretaceous fish of North America Cretaceous fish of Europe Fossil taxa described in 1939 Demopolis Chalk Mooreville Chalk Prehistoric shark genera
shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachi ...
known to have lived during the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
period. The genus had a global distribution in the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', ...
epoch. Multiple species within this genus are considered to be wastebasket taxon
Wastebasket taxon (also called a wastebin taxon, dustbin taxon or catch-all taxon) is a term used by some taxonomists to refer to a taxon that has the sole purpose of classifying organisms that do not fit anywhere else. They are typically defined ...
due to morphological similarities in the teeth.
Etymology
The name ''Squalicorax'' is derived from theLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''squalus'' for shark and the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
κόραξ, "''korax''" for raven.
Description
These sharks are of medium size, up to 5 m (usually around 2 m) in length. Their bodies were similar to the modern gray reef sharks, but the shape of the teeth is strikingly similar to that of a tiger shark. The teeth are numerous, relatively small, with a curved crown and serrated, up to 2.5 – 3 cm in height. Large numbers of fossilteeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, t ...
have been found in Europe, North Africa, and North America. Squalicorax is one of three Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
lamniformes
The Lamniformes (, from Greek ''lamna'' "fish of prey") are an order of sharks commonly known as mackerel sharks (which may also refer specifically to the family Lamnidae). It includes some of the most familiar species of sharks, such as the grea ...
to garner serrations along with '' Pseudocorax'' and '' Galeocorax''.
''Squalicorax'' was a coastal predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill th ...
, but also scavenged as evidenced by a ''Squalicorax'' tooth found embedded in the metatarsal
The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the me ...
(foot) bone of a terrestrial hadrosaurid dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
that most likely died on land and ended up in the water. Other food sources included turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked t ...
s, mosasaur
Mosasaurs (from Latin ''Mosa'' meaning the 'Meuse', and Greek ' meaning 'lizard') comprise a group of extinct, large marine reptiles from the Late Cretaceous. Their first fossil remains were discovered in a limestone quarry at Maastricht on ...
s, ichthyodectids, and other bony fishes and sea creatures. Tooth marks from this shark have also been found on the bones of '' Pteranodon'', but whether the shark actively snatched such large pterosaurs out of the air, attacked them as they dove after prey, or was simply scavenging is not known.
Description of selected species




 The following are the best studied American species for which relatively complete skeletons are described:
* ''Squalicorax falcatus'' (Agassiz, 1843) – is a medium-sized shark with a broad snout and relatively small teeth. Its length reached almost 3 m. It lived during the Cenomanian to early Santonian (
The following are the best studied American species for which relatively complete skeletons are described:
* ''Squalicorax falcatus'' (Agassiz, 1843) – is a medium-sized shark with a broad snout and relatively small teeth. Its length reached almost 3 m. It lived during the Cenomanian to early Santonian (Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campani ...
). Complete skeletons are known from sediments of the Western Inland Sea of the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
in Kansas, South Dakota, and Wyoming, all in the USA. The teeth are also found in France, the Czech Republic, Canada, and Morocco. Given the small teeth, this species is considered a hunter of small prey. However, teeth marks on the bones of marine reptiles are evidence that these shark also fed on carrion. The body shape and structure of the trunk placoid scale
A fish scale is a small rigid plate that grows out of the skin of a fish. The skin of most jawed fishes is covered with these protective scales, which can also provide effective camouflage through the use of reflection and colouration, as ...
s indicate the ability to swim quickly. A fully articulated 1.9-m long fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
skeleton of ''Squalicorax falcatus'' has been found in Kansas, evidence of its presence in the Western Interior Seaway
The Western Interior Seaway (also called the Cretaceous Seaway, the Niobraran Sea, the North American Inland Sea, and the Western Interior Sea) was a large inland sea that split the continent of North America into two landmasses. The ancient sea ...
.
* ''Squalicorax kaupi'' (Agassiz, 1843) is from the late Santonian to the late Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the interval ...
of North America, New Zealand, Japan, Africa, Europe, Kazakhstan, Jordan. and other places. It was slightly larger than the preceding species, of which it was probably an ancestor.
* ''Squalicorax pristodontus'' (Agassiz, 1843) is the largest species, more than 5 m long. From the size of its largest known teeth, it can be estimated that ''S. pristodontus'' grew to 5 m (16.5 ft) in length. It lived during the late Campanian to early Maastrichtian of North America, France, the Netherlands, Egypt, Morocco, and Madagascar. The relatively complete remains (vertebrae and fragments of jaws) have been found in marine sediments in North America. It is the species with the largest teeth, these teeth being loosely spaced and relatively very large in comparison with other species. In this genus of sharks, studies have shown no precise correlation between the size of the teeth and the length of the body. They could eat relatively large prey and carrion.
* ''Squalicorax volgensis'' - the oldest species of the genus, from the Early Cretaceous of the Volga – has been described by L. Glickman ''et al.'' in 1971. The teeth of this species had virtually no serration. They are known from the Albian
The Albian is both an age of the geologic timescale and a stage in the stratigraphic column. It is the youngest or uppermost subdivision of the Early/Lower Cretaceous Epoch/ Series. Its approximate time range is 113.0 ± 1.0 Ma to 100.5 ± 0 ...
to the Turonian
The Turonian is, in the ICS' geologic timescale, the second age in the Late Cretaceous Epoch, or a stage in the Upper Cretaceous Series. It spans the time between 93.9 ± 0.8 Ma and 89.8 ± 1 Ma (million years ago). The Turonian is preceded b ...
Age in Eastern and Western Europe, as well as Texas.
The world's largest and most complete semiarticulated fossil of ''Squalicorax'' was found in 2014 in stores of the Canadian Fossil Discovery Centre in Morden, Manitoba
Morden is a city located in the Pembina Valley region of southern Manitoba, Canada near the United States border. It is about west of the neighbouring city of Winkler, Manitoba, Winkler; together Morden and Winkler are often referred to as Manito ...
, in Canada, where it is now displayed. It measures more than 3 m in length.
References
Sources
* H. Cappetta, ''Handbook of Paleoichthyology'' (Gustav Fischer, 1987)External links
Elasmo.com page on Squalicorax
* ttp://www.elasmo-research.org/education/evolution/squalicorax.htm Squalicorax beim ReefQuest Centre for Shark Research {{Taxonbar, from=Q134511 Anacoracidae Cretaceous sharks Late Cretaceous fish of North America Cretaceous fish of Europe Fossil taxa described in 1939 Demopolis Chalk Mooreville Chalk Prehistoric shark genera