''Spirit'', also known as MER-A (Mars Exploration Rover – A) or MER-2, is a
Mars robotic rover, active from 2004 to 2010.
''Spirit'' was operational on Mars for
sols or 3.3 Martian years (
days;
'). It was one of two
rovers of
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
's
Mars Exploration Rover
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover (MER) mission was a robotic space mission involving two Mars rovers, '' Spirit'' and '' Opportunity'', exploring the planet Mars. It began in 2003 with the launch of the two rovers to explore the Martian surface ...
Mission managed by the
Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a federally funded research and development center and NASA field center in the City of La Cañada Flintridge, California, United States.
Founded in the 1930s by Caltech researchers, JPL is owned by NASA an ...
(JPL). Spirit landed successfully within the impact crater
Gusev on
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
at 04:35
Ground UTC on January 4, 2004, three weeks before its twin, ''
Opportunity
Opportunity may refer to:
Places
* Opportunity, Montana, an unincorporated community, United States
* Opportunity, Nebraska, an unincorporated community, United States
* Opportunity, Washington, a former census-designated place, United States
* ...
'' (MER-B), which landed on the other side of the planet. Its name was chosen through a
NASA-sponsored student essay competition. The rover got stuck in a "sand trap" in late 2009 at an angle that hampered recharging of its batteries; its last communication with Earth was on March 22, 2010.
The rover completed its planned 90-
sol mission (slightly less than 92.5 Earth days). Aided by
cleaning event
__NOTOC__
A cleaning event is a phenomenon whereby dust is removed from solar panels, in the context of exploration and science rovers on Mars, supposedly by the action of wind. The term cleaning event is used on several NASA webpages; general ...
s that resulted in more energy from its solar panels, ''Spirit'' went on to function effectively over twenty times longer than NASA planners expected. ''Spirit'' also logged of driving instead of the planned , allowing more extensive geological analysis of Martian rocks and planetary surface features. Initial scientific results from the first phase of the mission (the 90-sol prime mission) were published in a special issue of the journal
''Science''.
On May 1, 2009 (5 years, 3 months, 27 Earth days after landing; 21 times the planned mission duration), ''Spirit'' became stuck in soft sand.
This was not the first of the mission's "embedding events" and for the following eight months NASA carefully analyzed the situation, running Earth-based theoretical and practical simulations, and finally programming the rover to make
extrication
Vehicle extrication is the process of removing a vehicle from around a person who has been involved in a motor vehicle collision, when conventional means of exit are impossible or inadvisable. A delicate approach is needed to minimize injury to th ...
drives in an attempt to free itself. These efforts continued until January 26, 2010, when NASA officials announced that the rover was likely irrecoverably obstructed by its location in soft sand,
though it continued to perform scientific research from its current location.
The rover continued in a stationary science platform role until communication with ''Spirit'' stopped on March 22, 2010 (sol ).
[September 30 – October 5, 2010 Spirit Remains Silent at Troy](_blank)
NASA. October 5, 2010. JPL continued to attempt to regain contact until May 24, 2011, when NASA announced that efforts to communicate with the unresponsive rover had ended, calling the mission complete.
A formal farewell took place at NASA headquarters shortly thereafter.
Mission overview


The primary surface mission for ''Spirit'' was planned to last at least 90
sols. The mission received several extensions and lasted about 2,208 sols. On August 11, 2007, ''Spirit'' obtained the second longest operational duration on the surface of Mars for a lander or rover at 1282 Sols, one sol longer than the
Viking 2 lander. Viking 2 was powered by a nuclear cell whereas ''Spirit'' is powered by solar arrays. Until ''Opportunity'' overtook it on May 19, 2010, the Mars probe with longest operational period was
Viking 1 that lasted for 2245 Sols on the surface of Mars. On March 22, 2010, ''Spirit'' sent its last communication, thus falling just over a month short of surpassing Viking 1's operational record. An archive of weekly updates on the rover's status can be found at the ''Spirit'' Update Archive.
''Spirit's'' total odometry is .
Objectives

The scientific objectives of the Mars Exploration Rover mission were to:
* Search for and characterize a variety of rocks and soils that hold clues to past water activity. In particular, samples sought will include those that have minerals deposited by water-related processes such as
precipitation,
evaporation,
sedimentary cementation or
hydrothermal activity.
* Determine the distribution and composition of minerals, rocks, and soils surrounding the landing sites.
* Determine what
geologic processes have shaped the local terrain and influenced the chemistry. Such processes could include water or wind erosion, sedimentation, hydrothermal mechanisms, volcanism, and cratering.
* Perform calibration and validation of surface observations made by
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' (MRO) is a spacecraft designed to study the geology and climate of Mars, provide reconnaissance of future landing sites, and relay data from surface missions back to Earth. It was launched on August 12, 2005, an ...
instruments. This will help determine the accuracy and effectiveness of various instruments that survey
Martian geology from orbit.
* Search for iron-containing minerals, identify and quantify relative amounts of specific mineral types that contain water or were formed in water, such as iron-bearing carbonates.
* Characterize the
mineralogy and textures of rocks and soils and determine the processes that created them.
* Search for geological clues to the
environmental conditions that existed when liquid water was present.
* Assess whether those environments were conducive to life.
NASA sought evidence of life on Mars, beginning with the question of whether the Martian environment was ever suitable for life. Life forms known to science require water, so the history of
water on Mars
Almost all water on Mars today exists as ice, though it also exists in small quantities as vapor in the atmosphere. What was thought to be low-volume liquid brines in shallow Martian soil, also called recurrent slope lineae, may be grains of ...
is a critical piece of knowledge. Although the Mars Exploration Rovers did not have the ability to detect life directly, they offered very important information on the habitability of the environment during the planet's history.
Design and construction
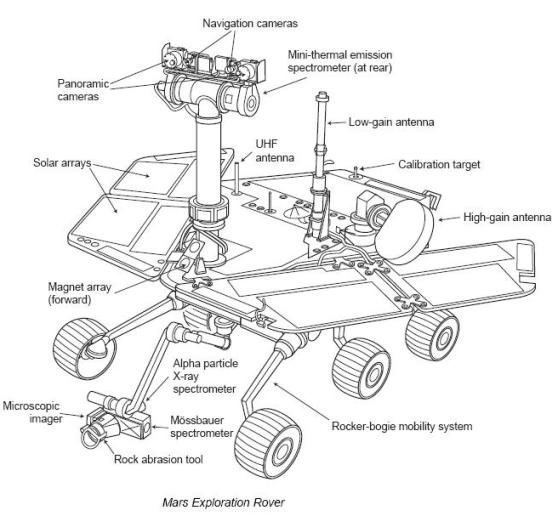

''Spirit'' (and its twin, ''
Opportunity
Opportunity may refer to:
Places
* Opportunity, Montana, an unincorporated community, United States
* Opportunity, Nebraska, an unincorporated community, United States
* Opportunity, Washington, a former census-designated place, United States
* ...
'') are six-wheeled,
solar-powered robots standing high, wide and long and weighing . Six wheels on a
rocker-bogie system enabled mobility over rough terrain. Each wheel had its own motor. The vehicle was steered at front and rear and was designed to operate safely at tilts of up to 30 degrees. The maximum speed was ; , although the average speed was about . Both ''Spirit'' and ''Opportunity'' have pieces of the fallen
World Trade Center's metal on them that were "turned into shields to protect cables on the drilling mechanisms".
The solar arrays generated about 140 watts for up to four hours per Martian day (sol) while rechargeable
lithium ion batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also see ...
stored energy for use at night. ''Spirit's'' onboard computer used a 20 MHz
RAD6000 CPU with 128 MB of DRAM, 3 MB of EEPROM, and 256 MB of flash memory. The rover's
operating temperature ranged from .
Radioisotope heater unit
Radioisotope heater units (RHU) are small devices that provide heat through radioactive decay. They are similar to tiny radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTG) and normally provide about one watt of heat each, derived from the decay of a fe ...
s provided a base level of heating, assisted by electrical heaters when necessary. A gold film and a layer of silica
aerogel provided insulation.
Communications depended on an omnidirectional low-gain antenna communicating at a low data rate and a steerable high-gain antenna, both in direct contact with Earth. A low-gain antenna was also used to relay data to spacecraft orbiting Mars.
Science payload
The science instruments included:
*
Panoramic Camera (Pancam) – examined the texture, color, mineralogy, and structure of the local terrain.
*
Navigation Camera (Navcam) – monochrome with a higher field of view but lower resolution, for navigation and driving.
*
Miniature Thermal Emission Spectrometer (Mini-TES) – identified promising rocks and soils for closer examination, and determined the processes that formed them.
*
Hazcams, two B&W cameras with 120 degree field of view, that provided additional data about the rover's surroundings.
The rover arm held the following instruments:
*
Mössbauer spectrometer (MB)
MIMOS II MIMOS II is the miniaturised Mössbauer spectrometer, developed by Dr. Göstar Klingelhöfer at the Johannes Gutenberg University in Mainz, Germany, that is used on the Mars Exploration Rovers '' Spirit'' and '' Opportunity'' for close-up investiga ...
– used for close-up investigations of the mineralogy of iron-bearing rocks and soils.
*
Alpha particle X-ray spectrometer
:''APXS is also an abbreviation for APache eXtenSion tool, an extension for Apache web servers.''
An alpha particle X-ray spectrometer (APXS) is a spectrometer that analyses the chemical element composition of a sample from scattered alpha part ...
(APXS) – close-up analysis of the abundances of elements that make up rocks and soils.
* Magnets – for collecting magnetic dust particles.
* Microscopic Imager (MI) – obtained close-up, high-resolution images of rocks and soils.
*
Rock Abrasion Tool (RAT) – exposed fresh material for examination by instruments on board.
Mission timeline
2004
The ''Spirit'' Mars rover landed successfully on the surface of Mars on 04:35
SCET on January 4, 2004. This was the start of its 90-sol mission, but solar cell cleaning events would mean it was the start of a much longer mission, lasting until 2010.
Landing site: ''Columbia'' Memorial Station
''Spirit'' was targeted to a site that appears to have been affected by liquid water in the past, the crater
Gusev, a possible former lake in a giant
impact crater
An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact crater ...
about from the center of the target ellipse at .
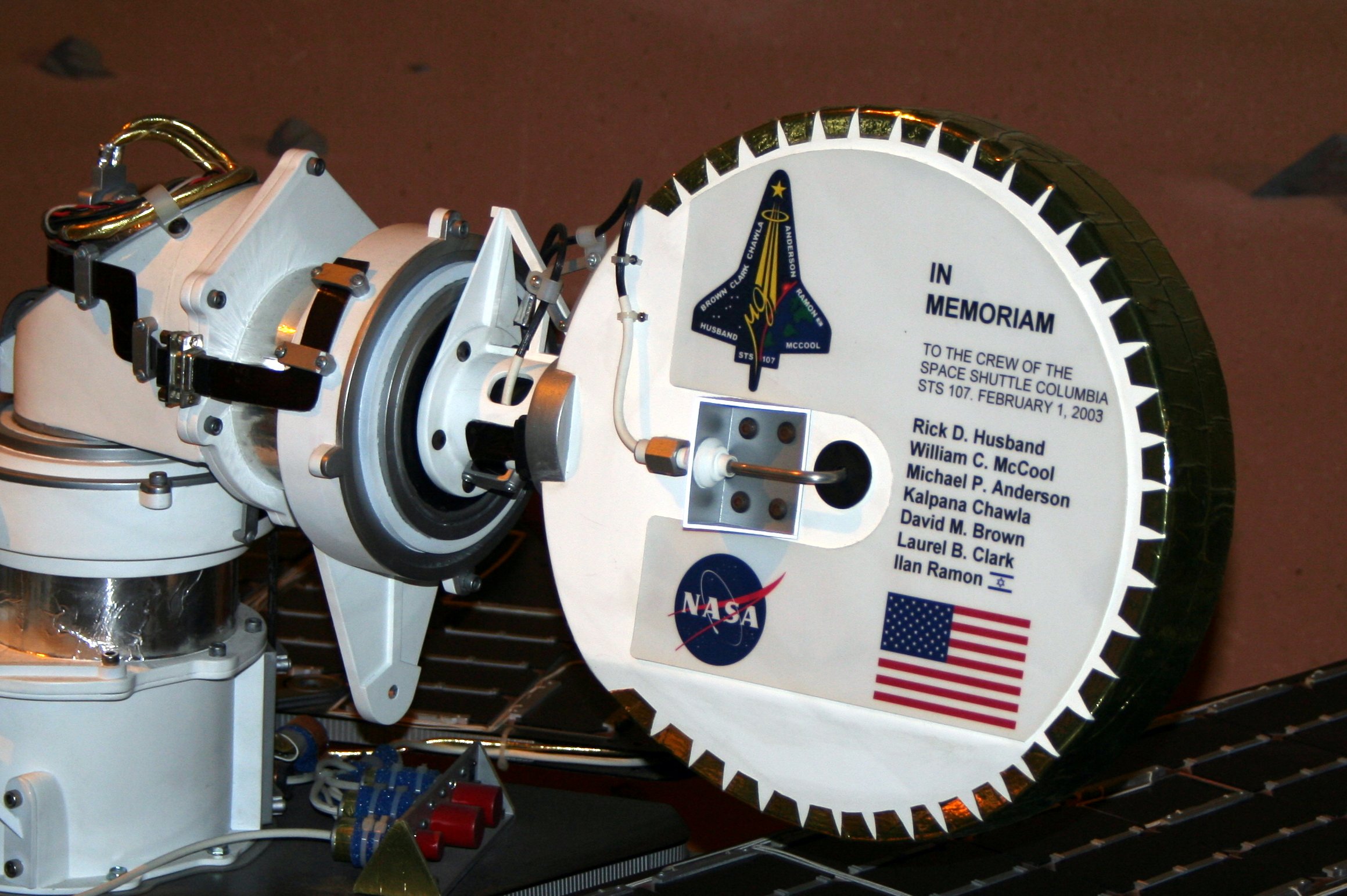
After the airbag-protected landing craft settled onto the surface, the rover rolled out to take panoramic images. These give scientists the information they need to select promising geological targets and drive to those locations to perform on-site scientific investigations. The panoramic image below shows a slightly rolling surface, littered with small rocks, with hills on the horizon up to away. The MER team named the landing site "''Columbia'' Memorial Station," in honor of the seven
astronauts killed in the
Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster.
"Sleepy Hollow," a shallow depression in the Mars ground at the right side of the above picture, was targeted as an early destination when the rover drove off its lander platform. NASA scientists were very interested in this crater. It is across and about north of the lander.
First color image

To the right is the first color image derived from images taken by the panoramic camera on the Mars Exploration Rover ''Spirit''. It was the highest resolution image taken on the surface of another planet. According to the camera designer Jim Bell of
Cornell University
Cornell University is a private statutory land-grant research university based in Ithaca, New York. It is a member of the Ivy League. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White, Cornell was founded with the intention to tea ...
, the panoramic mosaic consists of four pancam images high by three wide. The picture shown originally had a full size of 4,000 by 3,000
pixels
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the sm ...
. However, a complete pancam panorama is even 8 times larger than that, and could be taken in stereo (i.e., two complete pictures, making the resolution twice as large again.) The colors are fairly accurate. (For a technical explanation, se
colors outside the range of the human eye)
The MER pancams are black-and-white instruments. Thirteen rotating filter wheels produce multiple images of the same scene at different wavelengths. Once received on Earth, these images can be combined to produce color images.
Sol flash memory management anomaly
On January 21, 2004 (sol ), ''Spirit'' abruptly ceased communicating with mission control. The next day the rover radioed a 7.8 bit/s beep, confirming that it had received a transmission from Earth but indicating that the craft believed it was in a fault mode. Commands would only be responded to intermittently. This was described as a very serious anomaly, but potentially recoverable if it were a software or memory corruption issue rather than a serious hardware failure. ''Spirit'' was commanded to transmit engineering data, and on January 23 sent several short low-bitrate messages before finally transmitting 73 megabits via
X band to ''
Mars Odyssey
''2001 Mars Odyssey'' is a robotic spacecraft orbiting the planet Mars. The project was developed by NASA, and contracted out to Lockheed Martin, with an expected cost for the entire mission of US$297 million. Its mission is to use spectro ...
''. The readings from the engineering data suggested that the rover was not staying in sleep mode. As such, it was wasting its battery energy and overheating – risk factors that could potentially destroy the rover if not fixed soon. On sol 20, the command team sent it the command SHUTDWN_DMT_TIL ("Shutdown Dammit Until") to try to cause it to suspend itself until a given time. It seemingly ignored the command.
The leading theory at the time was that the rover was stuck in a "reboot loop". The rover was programmed to reboot if there was a fault aboard. However, if there was a fault that occurred during reboot, it would continue to reboot forever. The fact that the problem persisted through reboot suggested that the error was not in RAM, but in either the
flash memory, the
EEPROM, or a hardware fault. The last case would likely doom the rover. Anticipating the potential for errors in the flash memory and EEPROM, the designers had made it so that the rover could be booted without ever touching the flash memory. The radio itself could decode a limited command set – enough to tell the rover to reboot without using flash. Without access to flash memory the reboot cycle was broken.
On January 24, 2004 (sol ) the rover repair team announced that the problem was with ''Spirits flash memory and the software that wrote to it. The flash hardware was believed to be working correctly but the file management module in the software was "not robust enough" for the operations the ''Spirit'' was engaged in when the problem occurred, indicating that the problem was caused by a software bug as opposed to faulty hardware. NASA engineers finally came to the conclusion that there were too many files on the file system, which was a relatively minor problem. Most of these files contained unneeded in-flight data. After realizing what the problem was, the engineers deleted some files, and eventually reformatted the entire flash memory system. On February 6 (sol ), the rover was restored to its original working condition, and science activities resumed.
[Planetary Blog](_blank)
First intentional grinding of a rock on Mars
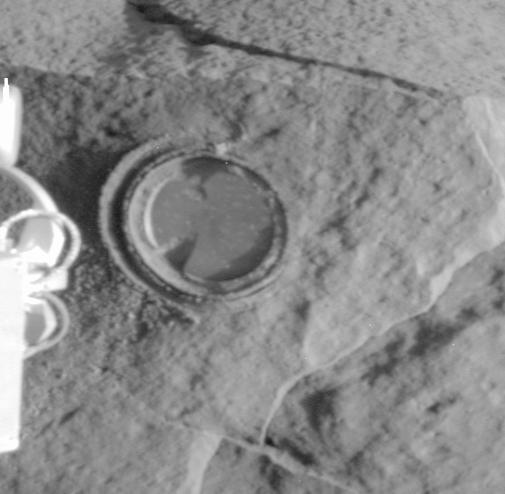

For the first intentional grinding of a rock on Mars, the ''Spirit'' team chose a rock called "
Adirondack". To make the drive there, the rover turned 40 degrees in short arcs totaling . It then turned in place to face the target rock and drove four short moves straightforward totaling . Adirondack was chosen over another rock called "Sashimi", which was closer to the rover, as Adirondack's surface was smoother, making it more suitable for the
Rock Abrasion Tool (aka "RAT").
''Spirit'' made a small depression in the rock, in diameter and deep. Examination of the freshly exposed interior with the rover's microscopic imager and other instruments confirmed that the rock is volcanic basalt.
Humphrey rock
On March 5, 2004, NASA announced that ''Spirit'' had found hints of water history on Mars in a rock dubbed "Humphrey".
Raymond Arvidson, the McDonnell University Professor and chair of Earth and Planetary Sciences at
Washington University in St. Louis, reported during a NASA press conference: "If we found this rock on Earth, we would say it is a volcanic rock that had a little fluid moving through it." In contrast to the rocks found by the twin rover ''Opportunity'', this one was formed from
magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural sa ...
and then acquired bright material in small crevices, which look like crystallized minerals. If this interpretation holds true, the minerals were most likely dissolved in water, which was either carried inside the rock or interacted with it at a later stage, after it formed.
Bonneville crater
On sol March 11, 2004, ''Spirit'' reached
Bonneville crater after a journey. This crater is about across with a floor about
below the surface. JPL decided that it would be a bad idea to send the rover down into the crater, as they saw no targets of interest inside. ''Spirit'' drove along the southern rim and continued to the southwest towards the Columbia Hills.
''Spirit'' reached Missoula crater on sol 105. The crater is roughly across and deep. Missoula crater was not considered a high priority target due to the older rocks it contained. The rover skirted the northern rim, and continued to the southeast.
It then reached Lahontan crater on sol 118, and drove along the rim until sol 120. Lahontan is about across and about deep. A long, snaking sand dune stretches away from its southwestern side, and ''Spirit'' went around it, because loose sand dunes present an unknown risk to the ability of the rover wheels to get traction.
Columbia Hills
''Spirit'' drove from Bonneville crater in a direct line to the Columbia Hills. The route was only directly controlled by the engineers when the terrain was difficult to navigate; otherwise, the rover drove in an autonomous mode. On sol 159, ''Spirit'' reached the first of many targets at the base of the
Columbia Hills called West Spur. Hank's Hollow was studied for 23 sols. Within Hank's Hollow was the strange-looking rock dubbed "
Pot of Gold". Analysing this rock was difficult for ''Spirit'', because it lay in a slippery area. After a detailed analysis with the AXPS-and the Mößbauer instrument it was detected that it contains hematite. This kind of rock can be built in connection with water.
As the produced energy from the solar panels was lowering due to the setting Sun and dust the Deep Sleep Mode was introduced. In this mode the rover was shut down completely during the night in order to save energy, even if the instruments would fail. The route was selected so that the rover's panels were tilted as much as possible towards the winter sunlight.
From here, ''Spirit'' took a northerly path along the base of the hill towards the target Wooly Patch, which was studied from sol 192 to sol 199. By sol 203, ''Spirit'' had driven southward up the hill and arrived at the rock dubbed "Clovis". Clovis was ground and analyzed from sol 210 to sol 225. Following Clovis came the targets of Ebenezer (Sols 226–235), Tetl (sol 270), Uchben and Palinque (Sols 281–295), and Lutefisk (Sols 296–303). From Sols 239 to 262, ''Spirit'' powered down for
solar conjunction, when communications with the Earth are blocked. Slowly, ''Spirit'' made its way around the summit of Husband Hill, and at sol 344 was ready to climb over the newly designated "Cumberland Ridge" and into "
Larry's Lookout" and "Tennessee Valley". ''Spirit'' also did some communication tests with the ESA orbiter ''
Mars Express
''Mars Express'' is a space exploration mission being conducted by the European Space Agency (ESA). The ''Mars Express'' mission is exploring the planet Mars, and is the first planetary mission attempted by the agency. "Express" originally ref ...
'' though most of the communication was usually done with the NASA orbiters ''
Mars Odyssey
''2001 Mars Odyssey'' is a robotic spacecraft orbiting the planet Mars. The project was developed by NASA, and contracted out to Lockheed Martin, with an expected cost for the entire mission of US$297 million. Its mission is to use spectro ...
'' and ''
Mars Global Surveyor
''Mars Global Surveyor'' (MGS) was an American robotic space probe developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and launched November 1996. MGS was a global mapping mission that examined the entire planet, from the ionosphere down through t ...
''.
2005
Driving up to Husband Hill
''Spirit'' had now been on Mars for one Earth year and was driving slowly uphill towards the top of Husband Hill. This was difficult because there were many rocky obstacles and sandy parts. This led frequently to slippage and the route could not be driven as planned. In February, ''Spirits computer received a software update in order to drive more autonomously. On sol 371, ''Spirit'' arrived at a rock named "Peace" near the top of Cumberland Ridge. ''Spirit'' ground ''Peace'' with the RAT on sol 373. By sol 390 (mid-February 2005), ''Spirit'' was advancing towards "Larry's Lookout", by driving up the hill in reverse. The scientists at this time were trying to conserve as much energy as possible for the climb.
''Spirit'' also investigated some targets along the way, including the soil target, "Paso Robles", which contained the highest amount of salt found on the red planet. The soil also contained a high amount of
phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ear ...
in its composition, however not nearly as high as another rock sampled by ''Spirit'', "Wishstone". One of the scientists working with ''Spirit,'' Dr. Steve Squyres, said of the discovery, "We're still trying to work out what this means, but clearly, with this much salt around, water had a hand here".
Image:Pot of gold-Close-med.jpg, Pot of Gold rock
Image:Gusev - Colina Husband.jpg, ''Spirits traverse up Husband Hill
Image:MarsSunset.jpg, Martian sunset by ''Spirit'' at Gusev crater, May 19, 2005.
Dust devils
On March 9, 2005 (probably during the Martian night), the rover's solar panel efficiency jumped from the original ~60% to 93%, followed on March 10, by the sighting of
dust devils
A dust devil is a strong, well-formed, and relatively short-lived whirlwind. Its size ranges from small (half a metre wide and a few metres tall) to large (more than 10 m wide and more than 1 km tall). The primary vertical motion is ...
. NASA scientists speculated a dust devil must have swept the solar panels clean, possibly significantly extending the duration of the mission. This also marked the first time dust devils had been spotted by ''Spirit'' or ''Opportunity''. Dust devils had previously only been photographed by the ''
Pathfinder
Pathfinder may refer to:
Businesses
* Pathfinder Energy Services, a division of Smith International
* Pathfinder Press, a publisher of socialist literature
Computing and information science
* Path Finder, a Macintosh file browser
* Pathfinder ( ...
'' probe.
Mission members monitoring ''Spirit'' on Mars reported on March 12, 2005 (sol ), that a lucky encounter with a dust devil had cleaned the robot's solar panels. Energy levels dramatically increased and daily science work was anticipated to be expanded.

Husband Hill summit
As of August ''Spirit'' was only away from the top. Here it was found that Husband Hill has two summits, with one a little higher than the other. On August 21 (sol ), ''Spirit'' reached the real summit of Husband Hill. The rover was the first spacecraft to climb atop a mountain on another planet. The whole distance driven totaled 4971 meters.
The summit itself was flat. ''Spirit'' took a 360 degree panorama in real color, which included the whole Gusev crater. At night the rover observed the moons
Phobos and
Deimos in order to determine their orbits better.
On sol 656 ''Spirit'' surveyed the Mars sky and the opacity of the atmosphere with its pancam to make a coordinated science campaign with the Hubble Space Telescope in Earth orbit.
From the peak ''Spirit'' spotted a striking formation, which was dubbed "Home Plate". This was an interesting target, but ''Spirit'' would be driven later to the McCool Hill to tilt its solar panels towards the Sun in the coming winter. At the end of October the rover was driven downhill and to Home Plate. On the way down ''Spirit'' reached the rock formation named "Comanche" on sol 690. Scientists used data from all three spectrometers to find out that about one-fourth of the composition of Comanche is magnesium iron carbonate. That concentration is 10 times higher than for any previously identified carbonate in a Martian rock. Carbonates originate in wet, near-neutral conditions but dissolve in acid. The find at Comanche is the first unambiguous evidence from the Mars Exploration Mission rovers for a past Martian environment that may have been more favorable to life than the wet but acidic conditions indicated by the rovers' earlier finds.
2006
Driving to McCool Hill
In 2006 ''Spirit'' drove towards an area dubbed Home Plate, and reached it in February. For events in 2006 by NASA se
NASA Spirit Archive 2006
''Spirit's'' next stop was originally planned to be the north face of
McCool Hill, where ''Spirit'' would receive adequate sunlight during the Martian winter. On March 16, 2006, JPL announced that ''Spirit's'' troublesome front wheel had stopped working altogether. Despite this, ''Spirit'' was still making progress toward McCool Hill because the control team programmed the rover to drive toward McCool Hill backwards, dragging its broken wheel. In late March, ''Spirit'' encountered loose soil that was impeding its progress toward McCool Hill. A decision was made to terminate attempts to reach McCool Hill and instead park on a nearby ridge named Low Ridge Haven.
''Spirit'' arrived at the north west corner of
Home Plate
A baseball field, also called a ball field or baseball diamond, is the field upon which the game of baseball is played. The term can also be used as a metonym for a baseball park. The term sandlot is sometimes used, although this usually refers ...
, a raised and layered outcrop on sol 744 (February 2006) after an effort to maximize driving. Scientific observations were conducted with ''Spirit's'' robotic arm.
Low Ridge Haven

Reaching the ridge on April 9, 2006, and parking on the ridge with an 11° incline to the north, ''Spirit'' spent the next eight months on the ridge, spending that time undertaking observations of changes in the surrounding area. No drives were attempted because of the low energy levels the rover was experiencing during the Martian winter. The rover made its first drive, a short turn to position targets of interest within reach of the robotic arm, in early November 2006, following the shortest days of winter and solar conjunction when communications with Earth were severely limited.
While at Low Ridge, ''Spirit'' imaged two rocks of similar chemical nature to that of ''Opportunitys
Heat Shield Rock
Heat Shield Rock is a basketball-sized iron-nickel meteorite found on the Meridiani Planum plain of Mars by the Mars rover ''Opportunity'' in January 2005.
Informally referred to as "Heat Shield Rock" by the Opportunity research team, the m ...
, a
meteorite on the surface of Mars. Named "Zhong Shan" for
Sun Yat-sen and "Allan Hills" for the
location
In geography, location or place are used to denote a region (point, line, or area) on Earth's surface or elsewhere. The term ''location'' generally implies a higher degree of certainty than ''place'', the latter often indicating an entity with an ...
in
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
where several Martian meteorites have been found, they stood out against the background rocks that were darker. Further spectrographic testing is being done to determine the exact composition of these rocks, which may turn out to also be meteorites.
2007
Software upgrade
On January 4, 2007 (sol ), both rovers received new flight software to the onboard computers. The update was received just in time for the third anniversary of their landing. The new systems let the rovers decide whether or not to transmit an image, and whether or not to extend their arms to examine rocks, which would save much time for scientists as they would not have to sift through hundreds of images to find the one they want, or examine the surroundings to decide to extend the arms and examine the rocks.
Silica Valley

''Spirits dead wheel turned out to have a silver lining. As it was traveling in March 2007, pulling the dead wheel behind, the wheel scraped off the upper layer of the Martian soil, uncovering a patch of ground that scientists say shows evidence of a past environment that would have been perfect for microbial life. It is similar to areas on Earth where water or steam from hot springs came into contact with volcanic rocks. On Earth, these are locations that tend to teem with bacteria, said rover chief scientist
Steve Squyres
Steven Weldon Squyres (born January 9, 1956) is an American geologist and planetary scientist. He was the James A. Weeks Professor of Physical Sciences at Cornell University in Ithaca, New York. His research area is in planetary sciences, with a f ...
. "We're really excited about this," he told a meeting of the American Geophysical Union (AGU). The area is extremely rich in
silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
–the main ingredient of window glass. The researchers have now concluded that the bright material must have been produced in one of two ways. One: hot-spring deposits produced when water dissolved silica at one location and then carried it to another (i.e. a geyser). Two: acidic steam rising through cracks in rocks stripped them of their mineral components, leaving silica behind. "The important thing is that whether it is one hypothesis or the other, the implications for the former habitability of Mars are pretty much the same," Squyres explained to BBC News. Hot water provides an environment in which
microbes can thrive and the precipitation of that silica entombs and preserves them. Squyres added, "You can go to
hot spring
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by c ...
s and you can go to
fumarole
A fumarole (or fumerole) is a vent in the surface of the Earth or other rocky planet from which hot volcanic gases and vapors are emitted, without any accompanying liquids or solids. Fumaroles are characteristic of the late stages of volcani ...
s and at either place on Earth it is teeming with life –
microbial life
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
."
Global dust storm and Home Plate
During 2007, ''Spirit'' spent several months near the base of the Home Plate plateau. On sol 1306 ''Spirit'' climbed onto the eastern edge of the plateau. In September and October it examined rocks and soils at several locations on the southern half of the plateau. On November 6, ''Spirit'' had reached the western edge of Home Plate, and started taking pictures for a panoramic overview of the western valley, with Grissom Hill and Husband Hill visible. The panorama image was published on NASA's website on January 3, 2008, to little attention, until January 23, when an independent website published a magnified detail of the image that showed a rock feature a few centimeters high resembling a humanoid figure seen from the side with its right arm partially raised.
Towards the end of June 2007, a series of dust storms began clouding the Martian atmosphere with dust. The storms intensified and by July 20, both ''Spirit'' and ''Opportunity'' were facing the real possibility of system failure due to lack of energy. NASA released a statement to the press that said (in part) "We're rooting for our rovers to survive these storms, but they were never designed for conditions this intense". The key problem caused by the dust storms was a dramatic reduction in solar energy caused by there being so much dust in the atmosphere that it was blocking 99 percent of direct sunlight to ''Opportunity'', and slightly more to ''Spirit''.
Normally the solar arrays on the rovers are able to generate up to of energy per
Martian day. After the storms, the amount of energy generated was greatly reduced to . If the rovers generate less than per day they must start draining their batteries to run survival heaters. If the batteries run dry, key electrical elements are likely to fail due to the intense cold. Both rovers were put into the lowest-power setting in order to wait out the storms. In early August the storms began to clear slightly, allowing the rovers to successfully charge their batteries. They were kept in hibernation in order to wait out the remainder of the storm.
2008
Hibernating
The main concern was the energy level for ''Spirit''. To increase the amount of light hitting the solar panels, the rover was parked in the northern part of Home Plate on as steep a slope as possible. It was expected that the level of dust cover on the solar panels would increase by 70 percent and that a slope of 30 degrees would be necessary to survive the winter. In February, a tilt of 29.9 degrees was achieved. Extra energy was available at times, and a high definition panorama named ''Bonestell'' was produced. At other times when there was only enough solar energy to recharge the batteries, communication with Earth was minimized and all unnecessary instruments were switched off. At winter solstice the energy production declined to 235 watt hours per sol.
Winter dust storm
On November 10, 2008, a large dust storm further reduced the output of the solar panels to per day—a critically low level. NASA officials were hopeful that ''Spirit'' would survive the storm, and that the energy level would rise once the storm had passed and the skies started clearing. They attempted to conserve energy by shutting down systems for extended periods of time, including the heaters. On November 13, 2008, the rover awoke and communicated with mission control as scheduled.
From November 14, 2008, to November 20, 2008 (sols to ), ''Spirit'' averaged per day. The heaters for the thermal emission spectrometer, which used about per day, were disabled on November 11, 2008. Tests on the thermal emission spectrometer indicate that it was undamaged, and the heaters would be enabled with sufficient energy. The
solar conjunction, where the Sun is between Earth and Mars, started on November 29, 2008, and communication with the rovers was not possible until December 13, 2008.
2009
Increased energy
On February 6, 2009, a beneficial wind blew off some of the dust accumulated on the panels. This led to an increase in energy output to per day. NASA officials stated that this increase in energy was to be used predominantly for driving.
On April 18, 2009 (sol ) and April 28, 2009 (sol ) energy output of the solar arrays were increased by cleaning events.
The energy output of ''Spirit's'' solar arrays climbed from per day on March 31, 2009, to per day on April 29, 2009.
Sand trap

On May 1, 2009 (sol ), the rover became stuck in soft sand, the machine resting upon a cache of
iron(III) sulfate
Iron(III) sulfate (or ferric sulfate), is a family of inorganic compounds with the formula Fe2(SO4)3(H2O)n. A variety of hydrates are known, including the most commonly encountered form of "ferric sulfate". Solutions are used in dyeing as a morda ...
(
jarosite) hidden under a veneer of normal-looking soil. Iron sulfate has very little cohesion, making it difficult for the rover's wheels to gain traction.
JPL team members simulated the situation by means of a rover mock-up and computer models in an attempt to get the rover back on track. To reproduce the same
soil mechanical conditions on Earth as those prevailing on Mars under low
gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stro ...
and under very weak atmospheric pressure, tests with a lighter version of a mock-up of ''Spirit'' were conducted at JPL in a special sandbox to attempt to simulate the
cohesion behavior of
poorly consolidated soils under low gravity.
Preliminary extrication drives began on November 17, 2009.
On December 17, 2009 (sol ), the right-front wheel suddenly began to operate normally for the first three out of four rotations attempts. It was unknown what effect it would have on freeing the rover if the wheel became fully operational again. The right rear wheel had also stalled on November 28 (sol ) and remained inoperable for the remainder of the mission. This left the rover with only four fully operational wheels. If the team could not gain movement and adjust the tilt of the solar panels, or gain a beneficial wind to clean the panels, the rover would only be able to sustain operations until May 2010.
2010
Mars winter at Troy
On January 26, 2010 (sol ), after several months attempting to free the rover, NASA decided to redefine the mobile robot mission by calling it a stationary research platform. Efforts were directed in preparing a more suitable orientation of the platform in relation to the Sun in an attempt to allow a more efficient recharge of the platform's batteries. This was needed to keep some systems operational during the Martian winter. On March 30, 2010, Spirit skipped a planned communication session and as anticipated from recent power-supply projections, had probably entered a low-power hibernation mode.

The last communication with the rover was March 22, 2010 (sol ) and there is a strong possibility the rover's batteries lost so much energy at some point that the mission clock stopped. In previous winters the rover was able to park on a Sun-facing slope and keep its internal temperature above , but since the rover was stuck on flat ground it is estimated that its internal temperature dropped to . If ''Spirit'' had survived these conditions and there had been a cleaning event, there was a possibility that with the southern summer solstice in March 2011, solar energy would increase to a level that would wake up the rover.
Communication attempts
''Spirit'' remains silent at its location, called "Troy," on the west side of Home Plate. There was no communication with the rover after March 22, 2010 (sol ).
It is likely that ''Spirit'' experienced a low-power fault and had turned off all sub-systems, including communication, and gone into a deep sleep, trying to recharge its batteries. It is also possible that the rover had experienced a mission clock fault. If that had happened, the rover would have lost track of time and tried to remain asleep until enough sunlight struck the solar arrays to wake it. This state is called "Solar Groovy." If the rover woke up from a mission clock fault, it would only listen. Starting on July 26, 2010 (sol ), a new procedure to address the possible mission clock fault was implemented.
Each sol, the Deep Space Network mission controllers sent a set of X-band "Sweep & Beep" commands. If the rover had experienced a mission clock fault and then had been awoken during the day, it would have listened during brief, 20-minute intervals during each hour awake. Due to the possible clock fault, the timing of these 20-minute listening intervals was not known, so multiple "Sweep & Beep" commands were sent. If the rover heard one of these commands, it would have responded with an X-band beep signal, updating the mission controllers on its status and allowing them to investigate the state of the rover further. But even with this new strategy, there was no response from the rover.
The rover had driven until it became immobile.
2011
Mission end
JPL continued attempts to regain contact with ''Spirit'' until May 25, 2011, when NASA announced the end of contact efforts and the completion of the mission.
According to NASA, the rover likely experienced excessively cold "internal temperatures" due to "inadequate energy to run its survival heaters" that, in turn, was a result of "a stressful Martian winter without much sunlight." Many critical components and connections would have been "susceptible to damage from the cold."
Assets that had been needed to support ''Spirit'' were transitioned to support ''Spirit's'' then still-active
''Opportunity'' rover,
and Mars rover ''
Curiosity'' which is exploring Gale Crater and has been doing so for more than six years.
Discoveries
The rocks on the plains of Gusev are a type of
basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
. They contain the minerals
olivine,
pyroxene,
plagioclase
Plagioclase is a series of tectosilicate (framework silicate) minerals within the feldspar group. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a continuous solid solution series, more pro ...
and magnetite. They look like volcanic basalt, as they are fine-grained with irregular holes (geologists would say they have vesicles and vugs).
Much of the soil on the plains came from the breakdown of the local rocks. Fairly high levels of nickel were found in some soils; probably from
meteorites.
Analysis shows that the rocks have been slightly altered by tiny amounts of water. Outside coatings and cracks inside the rocks suggest water deposited minerals, maybe
bromine compounds. All the rocks contain a fine coating of dust and one or more harder rinds of material. One type can be brushed off, while another needed to be ground off by the
Rock Abrasion Tool (RAT).
There are a variety of rocks in the
Columbia Hills, some of which have been altered by water, but not by very much water.
The dust in Gusev Crater is the same as dust all around the planet. All the dust was found to be magnetic. Moreover, ''Spirit'' found the
magnetism was caused by the mineral
magnetite, especially magnetite that contained the element
titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resista ...
. One magnet was able to completely divert all dust, hence all Martian dust is thought to be magnetic. The spectra of the dust was similar to spectra of bright, low thermal inertia regions like
Tharsis and Arabia that have been detected by orbiting satellites. A thin layer of dust, maybe less than one millimeter thick, covers all surfaces. Something in it contains a small amount of chemically bound water.
[Bell, J (ed.) The Martian Surface. 2008. Cambridge University Press. ]
Plains
Observations of rocks on the plains show they contain the minerals pyroxene, olivine, plagioclase, and magnetite. These rocks can be classified in different ways. The amounts and types of minerals make the rocks primitive basalts—also called picritic basalts. The rocks are similar to ancient terrestrial rocks called basaltic
komatiites.
Rocks of the plains also resemble the basaltic
shergottite
A Martian meteorite is a rock that formed on Mars, was ejected from the planet by an impact event, and traversed interplanetary space before landing on Earth as a meteorite. , 277 meteorites had been classified as Martian, less than half a percen ...
s, meteorites that came from Mars. One classification system compares the amount of alkali elements to the amount of silica on a graph; in this system, Gusev plains rocks lie near the junction of basalt,
picrobasalt, and
tephrite
Tephrite is an igneous, volcanic (extrusive) rock, with aphanitic to porphyritic texture. Mineral content is usually abundant feldspathoids (leucite or nepheline), plagioclase, and lesser alkali feldspar. Pyroxenes (clinopyroxenes) are common ...
. The Irvine-Barager classification calls them basalts.
Plains rocks have been very slightly altered, probably by thin films of water because they are softer and contain veins of light colored material that may be bromine compounds, as well as coatings or rinds. It is thought that small amounts of water may have gotten into cracks inducing mineralization processes).
Coatings on the rocks may have occurred when rocks were buried and interacted with thin films of water and dust.
One sign that they were altered was that it was easier to grind these rocks compared to the same types of rocks found on Earth.
Image:Rockgusev.jpg, Cross-sectional drawing of a typical rock from the plains of Gusev crater. Most rocks contain a coating of dust and one or more harder coatings. Veins of water-deposited minerals are visible, along with crystals of olivine. Veins may contain bromine salts.
Columbia Hills
Scientists found a variety of rock types in the Columbia Hills, and they placed them into six different categories. The six are: Clovis, Wishbone, Peace, Watchtower, Backstay, and Independence. They are named after a prominent rock in each group. Their chemical compositions, as measured by APXS, are significantly different from each other. Most importantly, all of the rocks in Columbia Hills show various degrees of alteration due to aqueous fluids.
They are enriched in the elements phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, and bromine—all of which can be carried around in water solutions. The Columbia Hills' rocks contain basaltic glass, along with varying amounts of olivine and
sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
s.
The olivine abundance varies inversely with the amount of sulfates. This is exactly what is expected because water destroys olivine but helps to produce sulfates.
Acid fog is believed to have changed some of the Watchtower rocks. This was in a long section of Cumberland Ridge and the Husband Hill summit. Certain places became less crystalline and more amorphous. Acidic water vapor from volcanoes dissolved some minerals forming a gel. When water evaporated a cement formed and produced small bumps. This type of process has been observed in the lab when basalt rocks are exposed to sulfuric and hydrochloric acids.
The Clovis group is especially interesting because the
Mössbauer spectrometer (MB) detected
goethite
Goethite (, ) is a mineral of the diaspore group, consisting of iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, specifically the "α" polymorph. It is found in soil and other low-temperature environments such as sediment. Goethite has been well known since ancient t ...
in it. Goethite forms only in the presence of water, so its discovery is the first direct evidence of past water in the Columbia Hills's rocks. In addition, the MB spectra of rocks and outcrops displayed a strong decline in olivine presence,
although the rocks probably once contained much olivine. Olivine is a marker for the lack of water because it easily decomposes in the presence of water. Sulfate was found, and it needs water to form.
Wishstone contained a great deal of plagioclase, some olivine, and
anhydrate (a sulfate). Peace rocks showed
sulfur and strong evidence for bound water, so hydrated sulfates are suspected. Watchtower class rocks lack olivine consequently they may have been altered by water. The Independence class showed some signs of clay (perhaps montmorillonite a member of the smectite group). Clays require fairly long term exposure to water to form.
One type of soil, called Paso Robles, from the Columbia Hills, may be an evaporate deposit because it contains large amounts of sulfur,
phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ear ...
,
calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
, and iron.
Also, MB found that much of the iron in Paso Robles soil was of the oxidized, Fe
3+ form, which would happen if water had been present.
Towards the middle of the six-year mission (a mission that was supposed to last only 90 days), large amounts of pure
silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
were found in the soil.
The silica could have come from the interaction of soil with acid vapors produced by volcanic activity in the presence of water or from water in a hot spring environment.
After ''Spirit'' stopped working scientists studied old data from the Miniature Thermal Emission Spectrometer, or
Mini-TES and confirmed the presence of large amounts of
carbonate-rich rocks, which means that regions of the planet may have once harbored water. The carbonates were discovered in an outcrop of rocks called "Comanche."
In summary, ''Spirit'' found evidence of slight weathering on the plains of Gusev, but no evidence that a lake was there. However, in the Columbia Hills there was clear evidence for a moderate amount of aqueous weathering. The evidence included sulfates and the minerals goethite and carbonates that only form in the presence of water. It is believed that Gusev crater may have held a lake long ago, but it has since been covered by igneous materials. All the dust contains a magnetic component that was identified as magnetite with some titanium. Furthermore, the thin coating of dust that covers everything on Mars is the same in all parts of Mars.
Astronomy
''Spirit'' pointed its cameras towards the sky and observed a
transit of the
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
by Mars'
moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
Deimos (see
Transit of Deimos from Mars). It also took the
first photo of Earth from the surface of another planet in early March 2004.
In late 2005, ''Spirit'' took advantage of a favorable energy situation to make multiple nighttime observations of both of Mars' moons
Phobos and
Deimos.
[Jim Bell (Cornell University) et al]
Pancam Projects: Spirit Night-time Imaging
Retrieved October 21, 2008 These observations included a "
lunar" (or rather phobian)
eclipse as ''Spirit'' watched Phobos disappear into Mars' shadow. Some of ''Spirits star gazing was designed to look for a predicted
meteor shower caused by
Halley's Comet
Halley's Comet or Comet Halley, officially designated 1P/Halley, is a short-period comet visible from Earth every 75–79 years. Halley is the only known short-period comet that is regularly visible to the naked eye from Earth, and thus the on ...
, and although at least four imaged streaks were suspect meteors, they could not be unambiguously differentiated from those caused by cosmic rays.
A
transit of Mercury from Mars
frameless, upright=0.5
A transit of Mercury across the Sun as seen from Mars takes place when the planet Mercury passes directly between the Sun and Mars, obscuring a small part of the Sun's disc for an observer on Mars. During a transit, Mercur ...
took place on January 12, 2005, from about 14:45
UTC to 23:05 UTC. Theoretically, this could have been observed by both ''Spirit'' and ''
Opportunity
Opportunity may refer to:
Places
* Opportunity, Montana, an unincorporated community, United States
* Opportunity, Nebraska, an unincorporated community, United States
* Opportunity, Washington, a former census-designated place, United States
* ...
''; however, camera resolution did not permit seeing Mercury's
6.1" angular diameter. They were able to observe transits of
Deimos across the Sun, but at
2' angular diameter, Deimos is about 20 times larger than Mercury's 6.1" angular diameter. Ephemeris data generated by
JPL Horizons
JPL Horizons On-Line Ephemeris System provides access to key Solar System data and flexible production of highly accurate ephemerides for Solar System objects.
Osculating elements at a given epoch (such as produced by the JPL Small-Body Databas ...
indicates that ''Opportunity'' would have been able to observe the transit from the start until local sunset at about 19:23 UTC Earth time, while ''Spirit'' would have been able to observe it from local sunrise at about 19:38 UTC until the end of the transit.
Equipment wear and failures
Both rovers passed their original mission time of 90 sols many times over. The extended time on the surface, and therefore additional stress on components, resulted in some issues developing.
On March 13, 2006 (sol ), the right front wheel ceased working after having covered on Mars. Engineers began driving the rover backwards, dragging the dead wheel. Although this resulted in changes to driving techniques, the dragging effect became a useful tool, partially clearing away soil on the surface as the rover traveled, thus allowing areas to be imaged that would normally be inaccessible. However, in mid-December 2009, to the surprise of the engineers, the right front wheel showed slight movement in a wheel-test on sol 2113 and clearly rotated with normal resistance on three of four wheel-tests on sol 2117, but stalled on the fourth. On November 29, 2009 (sol ), the right rear wheel also stalled and remained inoperable for the remainder of the mission.
Scientific instruments also experienced degradation as a result of exposure to the harsh Martian environment and use over a far longer period than had been anticipated by the mission planners. Over time, the diamond in the resin grinding surface of the
Rock Abrasion Tool wore down, after that the device could only be used to brush targets. All of the other science instruments and engineering cameras continued to function until contact was lost; however, towards the end of ''Spirits life, the
MIMOS II MIMOS II is the miniaturised Mössbauer spectrometer, developed by Dr. Göstar Klingelhöfer at the Johannes Gutenberg University in Mainz, Germany, that is used on the Mars Exploration Rovers '' Spirit'' and '' Opportunity'' for close-up investiga ...
Mössbauer spectrometer took much longer to produce results than it did earlier in the mission because of the decay of its
cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, p ...
-57 gamma ray source that has a half life of 271 days.
Honors

To rover
To commemorate ''Spirits great contribution to the
exploration of Mars
The planet Mars has been explored remotely by spacecraft. Probes sent from Earth, beginning in the late 20th century, have yielded a large increase in knowledge about the Martian system, focused primarily on understanding its geology and habi ...
, the
asteroid 37452 Spirit
37452 Spirit, provisional designation , is a dark Hildian asteroid from the outermost region of the asteroid belt, approximately 9 kilometers in diameter.
The asteroid was discovered on 24 September 1960, by Dutch astronomers Ingrid and Cornelis ...
has been named after it. The name was proposed by
Ingrid van Houten-Groeneveld who along with
Cornelis Johannes van Houten
Cornelis Johannes van Houten (18 February 1920 – 24 August 2002) was a Dutch astronomer, sometimes referred to as Kees van Houten.
Early life and education
Born in The Hague, he spent his entire career at Leiden University except for a brief pe ...
and
Tom Gehrels discovered the asteroid on September 24, 1960.
Reuben H. Fleet Science Center
The Fleet Science Center (previously the 'Reuben H. Fleet Science Center') is a science museum and planetarium in Balboa Park, located in San Diego, California. It is at the east end of the El Prado Drive walkway, next to the Bea Evenson Fountain ...
and the
Liberty Science Center
Liberty Science Center is an interactive science museum and learning center located in Liberty State Park in Jersey City, New Jersey, United States. At its opening it was the largest such planetarium in the Western Hemisphere and the world's ...
also have an IMAX show called ''Roving Mars'' that documents the journey of both ''Spirit'' and ''Opportunity'', using both CG and actual imagery.
January 4, 2014, was celebrated as the tenth anniversary of its landing on many news sites, despite nearly four years since loss of communications.
To honor the rover, the JPL team named an area near
Endeavour Crater
Endeavour is an impact crater located in the Meridiani Planum extraterrestrial plain within the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) region of the planet Mars. Endeavour is about in diameter. Using ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' data, phy ...
explored by the
''Opportunity'' rover, 'Spirit Point'.
From rover
On January 27, 2004 (sol ) NASA memorialized the crew of
Apollo 1 by naming three hills to the north of "''Columbia'' Memorial Station" as the
Apollo 1 Hills. On February 2, 2004 (sol ) the astronauts on Space Shuttle ''Columbia''s
final mission were further memorialized when NASA named a set of hills to the east of the landing site the
Columbia Hills Complex, denoting seven peaks in that area as "Anderson", "Brown", "Chawla", "Clark", "Husband", "McCool", and "Ramon" in honour of the crew; NASA has submitted these geographical feature names to the
IAU for approval.
Gallery
The rover could take pictures with its different cameras, but only the PanCam camera had the ability to photograph a scene with different color filters. The panorama views were usually built up from PanCam images. ''Spirit'' transferred 128,224 pictures in its lifetime.
Views
File:Bonneville Crater look back.jpg, Looking back from Bonneville crater to the landing site
File:Mars rock Mimi by Spirit rover.jpg, False color image of "Mimi".
Panoramas
Microscopic images
File:Spirit Rat Mazatzal.jpg, Close-up of the rock ''Mazatzal'', which was ground with the Rock Abrasion Tool on sol 82
File:GongGong.jpg, Erosive effect of winds on hardened lava.
From orbit
File:Spirit tracks.gif, Rover tracks up to sol 85 from ''Mars Global Surveyor
''Mars Global Surveyor'' (MGS) was an American robotic space probe developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and launched November 1996. MGS was a global mapping mission that examined the entire planet, from the ionosphere down through t ...
''
File:Spirit MRO.jpg, ''Spirit'' on September 29, 2006, beside Home Plate
Maps

See also
References
External links
JPL, MSSS, and NASA links
JPL's Mars Exploration Rover Mission home page(obsolete JPL Mars Exploration Rover home page)''Spirit'' Mission Profileb
NASA's Solar System ExplorationPlanetary Photojournal NASA JPL's Planetary Photojournal for ''Spirit''
for MER News Briefings at JPL
*
Wikisource:NASA MER press briefings
Finding ''Spirit'': high resolution images of landing site (''Mars Global Surveyor'' – Mars Orbiter Camera)JPL's site devoted to the efforts to free ''Spirit''MER Analyst's Notebook Interactive access to mission data and documentation
Other links
Status Page last updated May 2004
Marsbase.net a site that tracks time on Mars.
MAESTRO – public version of rover simulation software(requires download, last update October 25, 2004)
Cornell's rover site: Athenalast update 2006
(not working as of June 4, 2008)
*
ttp://www.google.com/mars/#lat=-14.569960&lon=175.469512&zoom=12&map=infrared&q=spacecraft Google map with ''Spirit'' landing site marked(AXCH) 2004 Mars Exploration Rovers Highlights– News, status, technical info, history, and more.
''New Scientist'' on ''Spirit'' Dust Devils, March 15, 2005
April 3, 2006
Unmanned Spaceflight.com discussion on ''Spirit''as of 2008-06-04 last updated 2008-06-04 nasatech.net, Nov 23 to December 5, 2005 (long download, uses Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mos ...
)Full-page, High-res spherical panorama of ''Spirit'' at the summit of Husband Hill nasatech.net, Nov 23 to December 5, 2005 (long download, uses Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mos ...
)
XKCD cartoon on ''Spirit''High-resolution videoby Seán Doran that zooms in on ''Spirit''s final location
Archiveof MER progress reports by A.J.S. Rayl at planetary.org
{{DEFAULTSORT:Spirit Rover
Space probes launched in 2003
2003 robots
Aeolis quadrangle
Derelict landers (spacecraft)
*
Missions to Mars
Mars rovers
Robots of the United States
Six-wheeled robots
Solar-powered robots
Spacecraft launched by Delta II rockets
Spacecraft decommissioned in 2011
Soft landings on Mars
2004 on Mars
Mars robots

 The primary surface mission for ''Spirit'' was planned to last at least 90 sols. The mission received several extensions and lasted about 2,208 sols. On August 11, 2007, ''Spirit'' obtained the second longest operational duration on the surface of Mars for a lander or rover at 1282 Sols, one sol longer than the Viking 2 lander. Viking 2 was powered by a nuclear cell whereas ''Spirit'' is powered by solar arrays. Until ''Opportunity'' overtook it on May 19, 2010, the Mars probe with longest operational period was Viking 1 that lasted for 2245 Sols on the surface of Mars. On March 22, 2010, ''Spirit'' sent its last communication, thus falling just over a month short of surpassing Viking 1's operational record. An archive of weekly updates on the rover's status can be found at the ''Spirit'' Update Archive.
''Spirit's'' total odometry is .
The primary surface mission for ''Spirit'' was planned to last at least 90 sols. The mission received several extensions and lasted about 2,208 sols. On August 11, 2007, ''Spirit'' obtained the second longest operational duration on the surface of Mars for a lander or rover at 1282 Sols, one sol longer than the Viking 2 lander. Viking 2 was powered by a nuclear cell whereas ''Spirit'' is powered by solar arrays. Until ''Opportunity'' overtook it on May 19, 2010, the Mars probe with longest operational period was Viking 1 that lasted for 2245 Sols on the surface of Mars. On March 22, 2010, ''Spirit'' sent its last communication, thus falling just over a month short of surpassing Viking 1's operational record. An archive of weekly updates on the rover's status can be found at the ''Spirit'' Update Archive.
''Spirit's'' total odometry is .
 The scientific objectives of the Mars Exploration Rover mission were to:
* Search for and characterize a variety of rocks and soils that hold clues to past water activity. In particular, samples sought will include those that have minerals deposited by water-related processes such as precipitation, evaporation, sedimentary cementation or hydrothermal activity.
* Determine the distribution and composition of minerals, rocks, and soils surrounding the landing sites.
* Determine what geologic processes have shaped the local terrain and influenced the chemistry. Such processes could include water or wind erosion, sedimentation, hydrothermal mechanisms, volcanism, and cratering.
* Perform calibration and validation of surface observations made by
The scientific objectives of the Mars Exploration Rover mission were to:
* Search for and characterize a variety of rocks and soils that hold clues to past water activity. In particular, samples sought will include those that have minerals deposited by water-related processes such as precipitation, evaporation, sedimentary cementation or hydrothermal activity.
* Determine the distribution and composition of minerals, rocks, and soils surrounding the landing sites.
* Determine what geologic processes have shaped the local terrain and influenced the chemistry. Such processes could include water or wind erosion, sedimentation, hydrothermal mechanisms, volcanism, and cratering.
* Perform calibration and validation of surface observations made by 
 ''Spirit'' (and its twin, ''
''Spirit'' (and its twin, '' To the right is the first color image derived from images taken by the panoramic camera on the Mars Exploration Rover ''Spirit''. It was the highest resolution image taken on the surface of another planet. According to the camera designer Jim Bell of
To the right is the first color image derived from images taken by the panoramic camera on the Mars Exploration Rover ''Spirit''. It was the highest resolution image taken on the surface of another planet. According to the camera designer Jim Bell of  For the first intentional grinding of a rock on Mars, the ''Spirit'' team chose a rock called " Adirondack". To make the drive there, the rover turned 40 degrees in short arcs totaling . It then turned in place to face the target rock and drove four short moves straightforward totaling . Adirondack was chosen over another rock called "Sashimi", which was closer to the rover, as Adirondack's surface was smoother, making it more suitable for the Rock Abrasion Tool (aka "RAT").
''Spirit'' made a small depression in the rock, in diameter and deep. Examination of the freshly exposed interior with the rover's microscopic imager and other instruments confirmed that the rock is volcanic basalt.
For the first intentional grinding of a rock on Mars, the ''Spirit'' team chose a rock called " Adirondack". To make the drive there, the rover turned 40 degrees in short arcs totaling . It then turned in place to face the target rock and drove four short moves straightforward totaling . Adirondack was chosen over another rock called "Sashimi", which was closer to the rover, as Adirondack's surface was smoother, making it more suitable for the Rock Abrasion Tool (aka "RAT").
''Spirit'' made a small depression in the rock, in diameter and deep. Examination of the freshly exposed interior with the rover's microscopic imager and other instruments confirmed that the rock is volcanic basalt.

 Reaching the ridge on April 9, 2006, and parking on the ridge with an 11° incline to the north, ''Spirit'' spent the next eight months on the ridge, spending that time undertaking observations of changes in the surrounding area. No drives were attempted because of the low energy levels the rover was experiencing during the Martian winter. The rover made its first drive, a short turn to position targets of interest within reach of the robotic arm, in early November 2006, following the shortest days of winter and solar conjunction when communications with Earth were severely limited.
While at Low Ridge, ''Spirit'' imaged two rocks of similar chemical nature to that of ''Opportunitys
Reaching the ridge on April 9, 2006, and parking on the ridge with an 11° incline to the north, ''Spirit'' spent the next eight months on the ridge, spending that time undertaking observations of changes in the surrounding area. No drives were attempted because of the low energy levels the rover was experiencing during the Martian winter. The rover made its first drive, a short turn to position targets of interest within reach of the robotic arm, in early November 2006, following the shortest days of winter and solar conjunction when communications with Earth were severely limited.
While at Low Ridge, ''Spirit'' imaged two rocks of similar chemical nature to that of ''Opportunitys  ''Spirits dead wheel turned out to have a silver lining. As it was traveling in March 2007, pulling the dead wheel behind, the wheel scraped off the upper layer of the Martian soil, uncovering a patch of ground that scientists say shows evidence of a past environment that would have been perfect for microbial life. It is similar to areas on Earth where water or steam from hot springs came into contact with volcanic rocks. On Earth, these are locations that tend to teem with bacteria, said rover chief scientist
''Spirits dead wheel turned out to have a silver lining. As it was traveling in March 2007, pulling the dead wheel behind, the wheel scraped off the upper layer of the Martian soil, uncovering a patch of ground that scientists say shows evidence of a past environment that would have been perfect for microbial life. It is similar to areas on Earth where water or steam from hot springs came into contact with volcanic rocks. On Earth, these are locations that tend to teem with bacteria, said rover chief scientist  On May 1, 2009 (sol ), the rover became stuck in soft sand, the machine resting upon a cache of
On May 1, 2009 (sol ), the rover became stuck in soft sand, the machine resting upon a cache of  The last communication with the rover was March 22, 2010 (sol ) and there is a strong possibility the rover's batteries lost so much energy at some point that the mission clock stopped. In previous winters the rover was able to park on a Sun-facing slope and keep its internal temperature above , but since the rover was stuck on flat ground it is estimated that its internal temperature dropped to . If ''Spirit'' had survived these conditions and there had been a cleaning event, there was a possibility that with the southern summer solstice in March 2011, solar energy would increase to a level that would wake up the rover.
The last communication with the rover was March 22, 2010 (sol ) and there is a strong possibility the rover's batteries lost so much energy at some point that the mission clock stopped. In previous winters the rover was able to park on a Sun-facing slope and keep its internal temperature above , but since the rover was stuck on flat ground it is estimated that its internal temperature dropped to . If ''Spirit'' had survived these conditions and there had been a cleaning event, there was a possibility that with the southern summer solstice in March 2011, solar energy would increase to a level that would wake up the rover.

