Space Systems Command (SSC) is the
United States Space Force
The United States Space Force (USSF) is the space service branch of the U.S. Armed Forces, one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and the world's only independent space force. Along with its sister branch, the U.S. Air Force, the Space ...
's
space development,
acquisition,
launch, and
logistics
Logistics is generally the detailed organization and implementation of a complex operation. In a general business sense, logistics manages the flow of goods between the point of origin and the point of consumption to meet the requirements of ...
field command. It is headquartered at
Los Angeles Air Force Base,
California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
and manages the United States'
space launch range
A spaceport or cosmodrome is a site for launching or receiving spacecraft, by analogy to a seaport for ships or an airport for aircraft. The word ''spaceport'', and even more so ''cosmodrome'', has traditionally been used for sites capable ...
s.
Space Systems Command is the oldest military space organization in the
United States Armed Forces
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is ...
, first established as the Western Development Division (WDD) on 1 April 1954 under
Air Research and Development Command
The Air Force Systems Command (AFSC) is an inactive United States Air Force Major Command. It was established in April 1951, being split off from Air Materiel Command. The mission of AFSC was Research and Development for new weapons systems.
Ove ...
to manage the U.S. Air Force's
ballistic missile
A ballistic missile is a type of missile that uses projectile motion to deliver warheads on a target. These weapons are guided only during relatively brief periods—most of the flight is unpowered. Short-range ballistic missiles stay within t ...
program. It gained responsibility for
spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, ...
development in 1955 and was renamed the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division (AFBMD) in 1957. As part of Air Research and Development Command's transformation the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division's space and missile responsibilities were split, with the Space Systems Division (SSD) established in 1961. In 1967, the Space Systems Division was reorganized as the Space and Missile Systems Organization (SAMSO), absorbing the Ballistic Systems Division. In 1979, the Space and Missile Systems Organization was renamed the Space Division and divested itself of ballistic missile development. In 1989, the Space Division returned to its historic name of the Space Systems Division and regained its ballistic missile development role in 1990.
With the merger of Air Force Systems Command and
Air Force Logistics Command
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing fo ...
in 1992, the Space Systems Division was redesignated the Space and Missile Systems Center (SMC). In response to the recommendations of the Space Commission, in 2001 it was reassigned to
Air Force Space Command
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for ...
, remaining attached through its redesignation as
Space Operations Command
Space Operations Command (SpOC) is the United States Space Force's space operations, cyber operations, and intelligence field command. It is headquartered at Peterson Space Force Base, Colorado and serves as the U.S. Space Force's service ...
in October 2020. On 22 April 2021, it transferred from a U.S. Air Force unit to a U.S. Space Force unit and was reassigned from Space Operations Command to Headquarters United States Space Force. On 13 August 2021, the Space and Missile Systems Center was renamed Space Systems Command and became a full U.S. Space Force field command.
History
The Military Space Program begins under Air Research and Development Command

Western Development Division
The United States' ballistic missile program was started by the
United States Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
immediately after the end of the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, with the
German Army
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the ''Luftwaf ...
's employment of the
V-2 rocket
The V-2 (german: Vergeltungswaffe 2, lit=Retaliation Weapon 2), with the technical name ''Aggregat 4'' (A-4), was the world’s first long-range guided ballistic missile. The missile, powered by a liquid-propellant rocket engine, was develop ...
demonstrating its viability. However, initial efforts to combine ballistic missiles and
nuclear weapons
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bom ...
was technologically infeasible until the development of
thermonuclear weapons. In the early 1950s, the Soviet Union was outpacing the United States in ballistic missile development, leading
Trevor Gardner
Trevor Gardner (24 August 1915 - 28 September 1963) was Assistant Secretary of the U.S. Air Force for Research and Development during the early 1950s. Together with Bernard Schriever, the Air Staff's Assistant for Development Planning, Gardner was ...
to charter the
Teapot Committee
The Teapot Committee was the codename of the Strategic Missile Evaluation Committee to evaluate strategic missiles of the U.S. Air Force.
Establishment
In October 1953, the Assistant Secretary of the U.S. Air Force for Research and Development ...
to determine why the United States was struggling.
As a direct result of the Committee's recommendation,
Air Research and Development Command
The Air Force Systems Command (AFSC) is an inactive United States Air Force Major Command. It was established in April 1951, being split off from Air Materiel Command. The mission of AFSC was Research and Development for new weapons systems.
Ove ...
established the Western Development Division at
Los Angeles Air Force Station
Los Angeles Air Force Base (LAAFB) is a United States Space Force Base located in El Segundo, California. Los Angeles Air Force Base houses and supports the headquarters of the United States Space Force's Space Systems Command (SSC), which w ...
under Brigadier General
Bernard Schriever
Bernard Adolph Schriever (14 September 1910 – 20 June 2005), also known as Bennie Schriever, was a United States Air Force general who played a major role in the Air Force's space and ballistic missile programs.
Born in Bremen, Germany, Schr ...
on 1 July 1954 to manage the Air Force's ballistic missile program. The Western Development Division's first program was the
Convair
Convair, previously Consolidated Vultee, was an American aircraft manufacturing company that later expanded into rockets and spacecraft. The company was formed in 1943 by the merger of Consolidated Aircraft and Vultee Aircraft. In 1953, i ...
SM-65 Atlas
The SM-65 Atlas was the first operational intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed by the United States and the first member of the Atlas rocket family. It was built for the U.S. Air Force by the Convair Division of General Dy ...
intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapo ...
, however by 1955 it initiated development of the
Martin Martin may refer to:
Places
* Martin City (disambiguation)
* Martin County (disambiguation)
* Martin Township (disambiguation)
Antarctica
* Martin Peninsula, Marie Byrd Land
* Port Martin, Adelie Land
* Point Martin, South Orkney Islands
Austr ...
HGM-25A Titan I ICBM and
Douglas
Douglas may refer to:
People
* Douglas (given name)
* Douglas (surname)
Animals
*Douglas (parrot), macaw that starred as the parrot ''Rosalinda'' in Pippi Longstocking
* Douglas the camel, a camel in the Confederate Army in the American Civil ...
PGM-17 Thor
The PGM-17A Thor was the first operational ballistic missile of the United States Air Force (USAF). Named after the Norse god of thunder, it was deployed in the United Kingdom between 1959 and September 1963 as an intermediate-range ballistic ...
intermediate range ballistic missile. On 10 October 1955, the Western Development Division gained responsibility for
spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, ...
development when the Weapon System 117L satellite, intended to conduct reconnaissance and missile warning, was transferred from the
Wright Air Development Center
The Aeronautical Systems Center (ASC) is an inactivated Air Force product center that designed, developed and delivered weapon systems and capabilities for U.S. Air Force, other U.S. military, allied and coalition-partner warfighters. ASC managed ...
. On 1 June 1957, the Western Development Division was renamed the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division.
Air Force Ballistic Missile Division

On 20 September 1957, the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division conducted the first launch of a Thor missile from
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida.
Headquartered at the nearby Patrick Space Force Base, the statio ...
, Florida and on 17 December 1957, also performed the first launch of an Atlas missile. By 1960, the PGM-17 Thor IRBM was deployed to the United Kingdom and turned over to
Strategic Air Command
Strategic Air Command (SAC) was both a United States Department of Defense Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command responsible for command and control of the strategic bomber and intercontinental ballistic missile ...
and the
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
. The SM-65 Atlas ICBM was turned over SAC by the end of 1962. In 1960, the HGM-25A Titan I ICBM made its first flight and was turned over to Strategic Air Command in 1962, completing the deployment of the first-generation ballistic missiles.
These first-generation ballistic missiles also served as the foundation for the first-generation of
space launch vehicles. The first space launch vehicle developed by the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division was the
Thor-Able, which used a Thor IRBM as the first stage and a
Vanguard
The vanguard (also called the advance guard) is the leading part of an advancing military formation. It has a number of functions, including seeking out the enemy and securing ground in advance of the main force.
History
The vanguard derives f ...
-derived
Able
Able may refer to:
* Able (1920 automobile), a small French cyclecar
* Able (rocket stage), an upper stage for Vanguard, Atlas, and Thor rockets
* Able (surname)
* ABLE account, a savings plan for people with disabilities
* Able UK, British ship ...
. Its first launch was on 11 October 1958. The first satellite launched by the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division was the
Army Signal Corps
The United States Army Signal Corps (USASC) is a branch of the United States Army that creates and manages communications and information systems for the command and control of combined arms forces. It was established in 1860, the brainchild of Ma ...
SCORE
Score or scorer may refer to:
*Test score, the result of an exam or test
Business
* Score Digital, now part of Bauer Radio
* Score Entertainment, a former American trading card design and manufacturing company
* Score Media, a former Canadian ...
using an
Atlas B
The SM-65 Atlas was the first operational intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed by the United States and the first member of the Atlas rocket family. It was built for the U.S. Air Force by the Convair Division of General Dyna ...
. The
Thor
Thor (; from non, Þórr ) is a prominent god in Germanic paganism. In Norse mythology, he is a hammer-wielding god associated with lightning, thunder, storms, sacred groves and trees, strength, the protection of humankind, hallowing, ...
and
Atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geogra ...
rocket families would form the core of the United States' space launch fleet. Following its 1958 establishment,
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
immediately began using the Thor for space launches and in 1959 developed the
Thor-Delta
The Thor-Delta, also known as Delta DM-19 or just Delta was an early American expendable launch system used for 12 orbital launches in the early 1960s. A derivative of the Thor-Able, it was a member of the Thor family of rockets, and the first ...
. The Atlas was adopted by NASA in 1959 and
Project Mercury
Project Mercury was the first human spaceflight program of the United States, running from 1958 through 1963. An early highlight of the Space Race, its goal was to put a man into Earth orbit and return him safely, ideally before the Soviet Un ...
used the
Atlas LV-3B for its orbital flights, with the Army's
Mercury-Redstone Launch Vehicle
The Mercury-Redstone Launch Vehicle, designed for NASA's Project Mercury, was the first American crewed space booster. It was used for six sub-orbital Mercury flights from 1960–1961; culminating with the launch of the first, and 11 weeks ...
used only for sub-orbital flights.
Following the launch of
Sputnik 1
Sputnik 1 (; see § Etymology) was the first artificial Earth satellite. It was launched into an elliptical low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on 4 October 1957 as part of the Soviet space program. It sent a radio signal back to Earth for ...
by the Soviet Union, the
Eisenhower administration
Dwight D. Eisenhower's tenure as the 34th president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1953, and ended on January 20, 1961. Eisenhower, a Republican from Kansas, took office following a landslide victory ...
attempted to centralize all military and civil space programs in the
Advanced Research Projects Agency, however responsibility was returned to the military services in September 1959. The
U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cl ...
was designated as the lead service for
communication satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Eart ...
s, the
U.S. Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage o ...
for
navigation satellite
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning. It allows satellite navigation devices to determine their location (longitude, latitude, and altitude/elevation) to high pre ...
s, and the
U.S. Air Force for
reconnaissance and surveillance satellites and
space launch vehicles. This split arrangement lasted until March 1961, when Secretary of Defense
Robert McNamara
Robert Strange McNamara (; June 9, 1916 – July 6, 2009) was an American business executive and the eighth United States Secretary of Defense, serving from 1961 to 1968 under Presidents John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson. He remains the ...
assigned the Air Force a near monopoly on military space development, with the exception of reconnaissance programs, which were passed to the
National Reconnaissance Office
The National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) is a member of the United States Intelligence Community and an agency of the United States Department of Defense which designs, builds, launches, and operates the reconnaissance satellites of the U.S. fe ...
in 1961.
The Weapon System 117L program, initially intending to perform a variety of task under different sub-systems, was broken into three different programs in 1959. The
Discoverer Program, better known as Corona, was a photographic reconnaissance satellite that ejected film for recovery in-atmosphere. The Discoverers were launched using a
Thor-Agena booster, with
Discoverer 1 becoming the first satellite to enter a
polar orbit
A polar orbit is one in which a satellite passes above or nearly above both poles of the body being orbited (usually a planet such as the Earth, but possibly another body such as the Moon or Sun) on each revolution. It has an inclination of about ...
and
Discoverer 2
Discoverer 2 was an American optical reconnaissance satellite launched on 13 April 1959 at 21:18:39 GMT, the second of three test flights of the Corona KH-1 spy satellite series. Discoverer 2 was the first satellite to be stabilized in orbit in ...
was the first to have
three-axis stabilization. In 1960,
Discoverer 13
Discoverer 13 was an American optical reconnaissance satellite launched on 10 Aug 1960 at 20:37:54 GMT. The last of five test flights of the Corona KH-1 spy satellite series, it was the first fully successful flight in the Discoverer series. On ...
was the first to return a capsule when it crashed into the
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
and
Discoverer 14 marked the first successful return of film when it was
recovered in-air by a
6593d Test Squadron
The 6593d Test Squadron is an inactive United States Air Force unit. Its last was assigned to the 6594th Test Group, stationed at Hickam AFB, Hawaii. It was inactivated on 1 July 1972.
Mission
The 6593d Test Squadron's mission was to develop a ...
Fairchild JC-119 Flying Boxcar.
The
Satellite and Missile Observation Program (SAMOS), was intended as a heavier counterpart to Discoverer and used the
Atlas-Agena booster. SAMOS was intended to collect photographic and electromagnetic reconnaissance data, but instead of returning film capsules to earth, SAMOS would electronically transmit the data to ground stations. However, the technology for electro-optical film readout was not mature and it was canceled by
Undersecretary of the Air Force Joseph V. Charyk
Joseph Vincent Charyk (September 9, 1920 – September 28, 2016) was widely credited as the founder of the geosynchronous communications satellite industry. He was born in Canmore, Alberta to a Ukrainian family. Early in his career, Charyk consoli ...
. The
Missile Defense Alarm System (MIDAS) was the third program derived from WS 117L and focused on providing missile warning of ICBMs using infrared sensors. Initial plans called for a constellation of eight spacecraft in polar orbits to monitor the Soviet Union, however due to early satellite failures it remained a test program until 1968.
To control these satellites, in 1958 the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division established an interim satellite control facility at
Lockheed Missile and Space Division. On 6 April 1959, the
6594th Test Wing was established to operate the facility and on 1 March 1960 it transferred operations to
Sunnyvale Air Force Station in California. It also established a global
Air Force Satellite Control Network
The Satellite Control Network (SCN), operated by the United States Space Force's Space Delta 6, provides support for the operation, control, and maintenance of a variety of United States Department of Defense and some non-DoD satellites. This i ...
. On 1 November 1959, the 6592nd Support Group was established to manage
Los Angeles Air Force Station
Los Angeles Air Force Base (LAAFB) is a United States Space Force Base located in El Segundo, California. Los Angeles Air Force Base houses and supports the headquarters of the United States Space Force's Space Systems Command (SSC), which w ...
.
The first space missions launched by the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division were not military, the but scientific
Pioneer lunar probes. First directed by the Advanced Research Projects Agency, they were later turned over to NASA. The Thor-Able rocket was specifically developed by the Air Force Ballistic Missile Agency for these lunar missions, which aimed to enhance scientific knowledge and American global prestige during the
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
. ARPA assigned the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division responsibility for three probes to be launched with the Thor-Able, the
Army Ballistic Missile Agency two probes to be launched with the
Juno II
Juno II was an American space launch vehicle used during the late 1950s and early 1960s. It was derived from the Jupiter missile, which was used as the first stage.
Development
Solid rocket motors derived from the MGM-29 Sergeant were use ...
, and the
Naval Ordnance Test Station to provide the imaging system.
Pioneer 0,
Pioneer 1, and
Pioneer 2 were the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division's lunar probes. While Pioneer 0 and Pioneer 2 suffered launch failures and Pioneer 1 only traveled a third of the way to the Moon, it was world's first
deep space probe and provided information on the extent of the
Van Allen radiation belts.
Space and missile development under Air Force Systems Command

Space Systems Division
On 1 April 1961, Air Research and Development Command was reorganized as
Air Force Systems Command
The Air Force Systems Command (AFSC) is an inactive United States Air Force Major Command. It was established in April 1951, being split off from Air Materiel Command. The mission of AFSC was Research and Development for new weapons systems.
Ov ...
. Space and missile programs had grown to the point where the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division was split on 1 April 1961, with space systems being organized under the Space Systems Division and missile programs under the Ballistic Systems Division.
The Ballistic Systems Division, which moved to
Norton Air Force Base, continued the work of the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division on second-generation ballistic missiles. The first major missile system it worked on was the
LGM-25C Titan II
The Titan II was an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed by the Glenn L. Martin Company from the earlier Titan I missile. Titan II was originally designed and used as an ICBM, but was later adapted as a medium-lift space l ...
ICBM, which was an improvement over the LGM-25A Titan I. It featured storable propellent, an all-inertial guidance system, and could be launched from undergrounds
missile silos
A missile launch facility, also known as an underground missile silo, launch facility (LF), or nuclear silo, is a vertical cylindrical structure constructed underground, for the storage and launching of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs ...
. The first Titan IIs came on alert with Strategic Air Command in June 1963. It also began development of the
LGM-30 Minuteman
The LGM-30 Minuteman is an American land-based intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) in service with the Air Force Global Strike Command. , the LGM-30G Minuteman III version is the only land-based ICBM in service in the United States and ...
ICBM, which was the first Air Force ballistic missile to use solid fuel rather than liquid fuel. The first Minuteman I was launched by the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division on 1 February 1962 and turned over to Strategic Air Command on 11 September 1962. By 1965, the Minuteman I had replaced the Atlas and Titan I ICBMs.
The Space Systems Division, still located at
Los Angeles Air Force Station
Los Angeles Air Force Base (LAAFB) is a United States Space Force Base located in El Segundo, California. Los Angeles Air Force Base houses and supports the headquarters of the United States Space Force's Space Systems Command (SSC), which w ...
, carried on the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division's development of the
Titan III space launch vehicle, which was initiated in 1961 and first flow on 1 September 1964. The
Titan IIIA consisted of a modified Titan II ballistic missile with a
Transtage upper stage. The
Titan IIIC
The Titan IIIC was an expendable launch system used by the United States Air Force from 1965 until 1982. It was the first Titan booster to feature large solid rocket motors and was planned to be used as a launcher for the Dyna-Soar, though the ...
was first launched from
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida.
Headquartered at the nearby Patrick Space Force Base, the stati ...
on 18 June 1965 and used two large solid rocket booster. The Space Systems Division also developed the
Titan IIIB and provided NASA with
Titan II GLV
The Titan II GLV (Gemini Launch Vehicle) or Gemini-Titan II was an American expendable launch system derived from the Titan II missile, which was used to launch twelve Gemini missions for NASA between 1964 and 1966. Two uncrewed launches foll ...
s for
Project Gemini
Project Gemini () was NASA's second human spaceflight program. Conducted between projects Mercury and Apollo, Gemini started in 1961 and concluded in 1966. The Gemini spacecraft carried a two-astronaut crew. Ten Gemini crews and 16 individual ...
and developed the
Agena target vehicle.
In 1963, the Space Systems Division initiated the
Defense Support Program
The Defense Support Program (DSP) is a program of the United States Space Force that operated the reconnaissance satellites which form the principal component of the ''Satellite Early Warning System'' used by the United States.
DSP satellite ...
, which was intended to succeeded where MIDAS failed and create an orbital constellation of infrared missile warning sensors. It also continued developing the
Vela nuclear detonation detection satellites. The Vela satellite network came out of a Air Force Ballistic Missile Division–
Atomic Energy Commission–NASA agreement in 1960 to develop a high-altitude nuclear detection system to ensure compliance with the
Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty
The Partial Test Ban Treaty (PTBT) is the abbreviated name of the 1963 Treaty Banning Nuclear Weapon Tests in the Atmosphere, in Outer Space and Under Water, which prohibited all test detonations of nuclear weapons except for those conducted ...
. The Atomic Energy Commission flew test detectors on Space Systems Division Discoverer satellites and the first Vela satellites were launched on an Atlas-Agena on 16 October 1963.
The Space Systems Division also began development on the
Defense Meteorological Support Program
The Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) monitors meteorological, oceanographic, and solar-terrestrial physics for the United States Department of Defense. The program is managed by the United States Space Force with on-orbit operat ...
(DMSP). The DMSP Block 1 satellites were launched on a
Scout X-2
Scout X-2 was an American expendable launch system and sounding rocket which was flown twice in 1962. It was a four-stage rocket, based on the earlier Scout X-1, uprated first and third stages. It was a member of the Scout family of rockets.
T ...
rocket in 1962, however the other four launch attempts failed. Further DMSP Block I launches were conducted on the
Thor-Agena and
Thor-Burner
The Thor-Burner was an American expendable launch system, a member of the Thor rocket family. It consisted of a Thor missile, with one or two Burner upper stages. It was used between 1965 and 1976 to orbit a number of satellites, most commonly De ...
boosters. The Thor-Burner also launched the DMSP Block II and DMSP Block III satellites, which provided weather reconnaissance during the
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
. The Block 4 satellites first launched in 1966. The Army Signal Corps' project SCORE, launched by the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division in 1958, was the world's first communications satellite but intended as a proof of concept. The Army Signal Corps followed by launching
Courier 1B on an Air Force Ballistic Missile Division
Thor-Ablestar in 1960, but it failed after 17 days in orbit. The Space Systems Division began development on the
Initial Defense Communications Satellite Program (IDCSP) in 1962, launching constellations from 1966 to 1968. the IDCSP, also known as the Defense Satellite Communications Program Phase I (DSCS I) once operational, transmitted both voice and images to support the United States during the Vietnam War.
Although almost all
crewed spacecraft programs went to NASA after its creation in 1958, the Air Force retained the
Boeing X-20 Dyna-Soar program under the
Wright Air Development Center
The Aeronautical Systems Center (ASC) is an inactivated Air Force product center that designed, developed and delivered weapon systems and capabilities for U.S. Air Force, other U.S. military, allied and coalition-partner warfighters. ASC managed ...
, with the Titan IIIC initially intended as its booster. The program, however, was canceled in 1963 when it was determined that the
Blue Gemini
Blue Gemini was a United States Air Force (USAF) project first proposed in August 1962 for a series of seven flights of Gemini spacecraft to enable the Air Force to gain manned spaceflight experience prior to the launch of the Manned Orbital Deve ...
program would better satisfy its objectives. However, Defense Secretary Robert McNamara announced the
Manned Orbiting Laboratory
The Manned Orbiting Laboratory (MOL) was part of the United States Air Force (USAF) human spaceflight program in the 1960s. The project was developed from early USAF concepts of crewed space stations as reconnaissance satellites, and was a su ...
program, which was assigned to the Space Systems Division by General Bernard Schriever.
Douglas Aircraft Company
The Douglas Aircraft Company was an American aerospace manufacturer based in Southern California. It was founded in 1921 by Donald Wills Douglas Sr. and later merged with McDonnell Aircraft in 1967 to form McDonnell Douglas; it then operated a ...
was responsible for the spacecraft, and the Space Systems Division was developing the
Titan IIIM booster. However, the program only had a single test flight,
OPS 0855, before being canceled in 1969.
The Space Systems Division also was responsible for
anti-satellite weapon
Anti-satellite weapons (ASAT) are space weapons designed to incapacitate or destroy satellites for strategic or tactical
purposes. Several nations possess operational ASAT systems. Although no ASAT system has been utilised in warfare, a few ...
s development. The first United States ASAT system was the Army's
Nike Zeus
Nike Zeus was an anti-ballistic missile (ABM) system developed by the US Army during the late 1950s and early 1960s that was designed to destroy incoming Soviet intercontinental ballistic missile warheads before they could hit their targets. It ...
missiles located at
Kwajalein Missile Range
The Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site, commonly referred to as the Reagan Test Site (formerly Kwajalein Missile Range), is a missile test range in Marshall Islands ( Pacific Ocean). It covers about and includes rocket launch ...
and declared operational in 1963, but shut down in 1964 by the Defense Department, which favored the Air Force's ASAT efforts. The Space Systems Division's
Program 437
Program 437 was the second anti-satellite weapons program of the U.S. military.Peebles, Curtis. "High Frontier: The United States Air Force and the Military Space Program", 1997 The US anti-satellite weapons program began development in the e ...
used Thor boosters and nuclear warheads to destroy a satellite or space-based weapon from
Johnston Atoll
Johnston Atoll is an unincorporated territory of the United States, currently administered by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS). Johnston Atoll is a National Wildlife Refuge and part of the Pacific Remote Islands Marine Nati ...
. The system was declared operational in 1964 and turned over to
Aerospace Defense Command
Aerospace Defense Command was a major command of the United States Air Force, responsible for continental air defense. It was activated in 1968 and disbanded in 1980. Its predecessor, Air Defense Command, was established in 1946, briefly ina ...
, however it was put on standby in 1970 and shut down in 1975. Program 437 also include the Program 437AP configuration, which give it the capability to inspect satellites. The Space Systems Division also managed the
Space Test Program, known as the Space Experiments Support Program until 1971, for the Defense Department since it began in 1965.
In 1965, Space Systems Division replaced the 6594th Aerospace Test Wing with the
Air Force Satellite Control Facility
The United States Air Force's Air Force Satellite Control Facility (AFSCF) was a space command and control unit located at Onizuka AFS, California. It has the distinction of being heavily involved in the world's first reconnaissance satellite pr ...
. Space launches were also conducted by the Space Systems Division, with the
6595th Aerospace Test Wing responsible for
Vandenberg Air Force Base Vandenberg may refer to:
* Vandenberg (surname), including a list of people with the name
* USNS ''General Hoyt S. Vandenberg'' (T-AGM-10), transport ship in the United States Navy, sank as an artificial reef in Key West, Florida
* Vandenberg Sp ...
launches and the
6555th Aerospace Test Wing
The 6555th Aerospace Test Group is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the Eastern Space and Missile Center and stationed at Patrick Air Force Base, Florida. It was inactivated on 1 October 1990.
Prior to the a ...
responsible for launches from
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida.
Headquartered at the nearby Patrick Space Force Base, the statio ...
.
Space and Missile Systems Organization


On 1 July 1967, the Space Systems Division and Ballistic Systems Division were remerged, forming the Space and Missile Systems Office (SAMSO).
This remerger was prompted by economic reasons and SAMSO was located as Los Angeles Air Force Station. SAMSO did not start any new ballistic missile programs, but did oversee the replacement of the Minuteman I with the Minuteman II, which had improved range and guidance, and the Minuteman III, which more penetration aids to counter anti-ballistic missile defense systems and could be equipped with three
multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle
A multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRV) is an exoatmospheric ballistic missile payload containing several warheads, each capable of being aimed to hit a different target. The concept is almost invariably associated with i ...
s.
The Titan III space launch vehicle family was also expanded to include the
Titan IIID and
Titan IIIE
The Titan IIIE or Titan 3E, also known as the Titan III-Centaur, was an American expendable launch system. Launched seven times between 1974 and 1977, it enabled several high-profile NASA missions, including the Voyager and Viking planetary prob ...
, which were used to support NASA's launch of the
Viking program in 1976. The Space and Missile Systems Organization was also the Department of Defense lead for the
Space Transportation System
The Space Transportation System (STS), also known internally to NASA as the Integrated Program Plan (IPP), was a proposed system of reusable crewed space vehicles envisioned in 1969 to support extended operations beyond the Apollo program. ...
, which would be developed into the
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program n ...
. As part of its contribution, it built a Space Shuttle launch and recovery site at
Vandenberg Air Force Base Vandenberg may refer to:
* Vandenberg (surname), including a list of people with the name
* USNS ''General Hoyt S. Vandenberg'' (T-AGM-10), transport ship in the United States Navy, sank as an artificial reef in Key West, Florida
* Vandenberg Sp ...
for polar launches and also developed the
Inertial Upper Stage
The Inertial Upper Stage (IUS), originally designated the Interim Upper Stage, was a two-stage, solid-fueled space launch system developed by Boeing for the United States Air Force beginning in 1976 for raising payloads from low Earth orbit to ...
.
The Space and Missile Systems Organization also oversaw the first launch of the Defense Support Program in 1970 on a Titan IIIC and the development and launch of the Advanced Vela satellites on Titan IIICs in 1967, 1969, and 1970. Three Defense Meteorological Support Program Block 5A, Block 5B, Block 5C, and Block 5D-1 satellites were also launched in the 1970s.
Although not an Air Force program, the Navy's
Transit
Transit may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Transit'' (1979 film), a 1979 Israeli film
* ''Transit'' (2005 film), a film produced by MTV and Staying-Alive about four people in countries in the world
* ''Transit'' (2006 film), a 2006 ...
satellite system was the world's first
satellite navigation
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning. It allows satellite navigation devices to determine their location ( longitude, latitude, and altitude/ elevation) to hig ...
constellation and started development in 1958. It was first launched on an Air Force Ballistic Missile Division booster in 1960 and achieved initial operational capability in 1964 and full operational capability in 1968. Transit used three operational satellites to enable users on ships and submarines to calculate their location in two dimensions and continued to operate until 1996. The Navy and Air Force both began follow on programs, with the Space and Missile Systems Organization developing
Project 621B
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
, envisioning a constellation of 20 satellites in synchronous inclined orbits. The Navy's
Timation program instead envisioned a constellation of 21 to 27 satellites in medium altitude orbits. In 1973,
Deputy Secretary of Defense
The deputy secretary of defense (acronym: DepSecDef) is a statutory office () and the second-highest-ranking official in the Department of Defense of the United States of America.
The deputy secretary is the principal civilian deputy to the sec ...
William P. Clements
William Perry Clements Jr. (April 13, 1917 – May 29, 2011) was an American businessman and Republican Party politician who served two non-consecutive terms as the governor of Texas between 1979 and 1991. His terms bookended the sole ...
directed the two programs merge into the Space and Missile Systems Organization's
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite ...
, which used Program 621B's signal structure and frequencies and the
medium earth orbit
A medium Earth orbit (MEO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an altitude above a low Earth orbit (LEO) and below a high Earth orbit (HEO) – between above sea level. s of Timation.
The Space and Missile Systems Organization also led the development of the
Defense Satellite Communications System Phase II
The Defense Satellite Communications System (DSCS) is a United States Space Force satellite constellation that provides the United States with military communications to support globally distributed military users. Beginning in 2007, DSCS is b ...
(DSCS II). DSCS II had increased communications
capacity, greater transmission strength, and longer lifetimes. As well, they also had steerable antennas. The first developmental contract was issued in 1969 and the first launch to
geosynchronous orbit
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds (one sidereal day). The synchronization of rotation and orbita ...
occurred in 1971, with the full constellation being formed in 1979. SAMSO also operationalized the
Lincoln Experimental Satellites and Tactical Communications Satellite, building the
Fleet Satellite Communications System
FLTSATCOM (also FLTSAT) is a satellite communication system of the U.S. Space Force which was used for UHF radio communications between ships, submarines, airplanes and ground stations of the Navy.
Most of the transponders on these satellites ...
(FLTSATCOM). Although the FLTSATCOM program was owned by the Navy, SAMSO managed the satellite acquisition, which started in 1971. It also managed the
Air Force Satellite Communications
The United States military's Air Force Satellite Communications (AFSATCOM) is a network of ground and space systems to allow rapid dissemination of communications to a worldwide audience. AFSATCOM's creation was during the height of the Cold War ...
system which became operational in 1978 and relied on transponders on FLTSATCOM and enabled the Air Force control over its strategic forces. SAMSO also managed the acquisition and launch of
Skynet 1, which was launched on behalf of the
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
in 1969 and 1970. SAMSO also assisted the United Kingdom with the development of Skynet 2, which launched in 1974 and was turned over to the Royal Air Force in 1975. SAMSO also acquired and launched the NATO II and NATO III satellites. DSCS II, Skynet, and the NATO satellites were designed to be compatible with each other.
During the 1970s, the Space and Missile Systems Organization began a follow-on ASAT program to Program 437 that did not use nuclear warheads. The first, Project Spike, used a two-staged missile launched from a
Convair F-106 Delta Dart
The Convair F-106 Delta Dart was the primary all-weather interceptor aircraft of the United States Air Force from the 1960s through to the 1980s. Designed as the so-called "Ultimate Interceptor", it proved to be the last specialist interceptor i ...
. Project Spike did not enter development, however it served as a proof of concept for the
Air-launched ASAT, which entered development in 1976.
In 1970, SAMSO's 6555th Aerospace Test Wing at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station became the
6555th Aerospace Test Group
The 6555th Aerospace Test Group is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the Eastern Space and Missile Center and stationed at Patrick Air Force Base, Florida. It was inactivated on 1 October 1990.
Prior to the a ...
and realigned under its
6595th Aerospace Test Wing at Vandenberg Air Force Base. The
6595th Aerospace Test Wing was then realigned under SAMSO's new Space and Missile Test Center (SAMTEC), which oversaw launches at both Vandenberg Air Force Base and Cape Canaveral Space Force Station and operated the
Western Test Range
The Western Range (WR) is the space launch range that supports the major launch head at Vandenberg Space Force Base. Managed by the Space Launch Delta 30, the WR extends from the West Coast of the United States to 90° East longitude in the ...
. In 1977, it gained the
Eastern Test Range
The Eastern Range (ER) is an American rocket range ( Spaceport) that supports missile and rocket launches from the two major launch heads located at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station and the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida. The range h ...
. On 1 August 1971, the 6592nd Support Group for Los Angeles Air Force Station was redesignated the 6592nd Air Base Group.
Space Division

On 1 October 1979, the Space and Missile Systems Organization was redesignated as the Space Division and split off its ballistic missile functions into the Ballistic Missile Office due to growth in both mission areas.
Starting in 1982, the Ballistic Missile Office assisted Strategic Air Command in deactivating the remaining Titan II missiles and placing them into storage for possible conversion into space launch vehicles. Under the
Strategic Arms Limitation Talks
The Strategic Arms Limitation Talks (SALT) were two rounds of bilateral conferences and corresponding international treaties involving the United States and the Soviet Union. The Cold War superpowers dealt with arms control in two rounds of ...
, both the United States and Soviet Union were limited in the number of missiles they could deploy. This shifted the focus to quality. In 1973, the Space and Missile Systems Organization started the MX program, which looked at traditionally silo-based, ground-mobile, and
air-launched ballistic missile
An air-launched ballistic missile or ALBM is a ballistic missile launched from an aircraft. An ALBM allows the launch aircraft to stand off at long distances from its target, keeping it well outside the range of defensive weapons like anti-aircr ...
options. In 1982, it was named the
LGM-118 Peacekeeper ICBM by President
Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
and was capable of launching ten reentry vehicles at different targets more than 6,000 miles away. In 1983, the Peacekeeper had its first test launch from
Vandenberg Air Force Base Vandenberg may refer to:
* Vandenberg (surname), including a list of people with the name
* USNS ''General Hoyt S. Vandenberg'' (T-AGM-10), transport ship in the United States Navy, sank as an artificial reef in Key West, Florida
* Vandenberg Sp ...
to a target in the
Kwajalein Missile Range
The Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site, commonly referred to as the Reagan Test Site (formerly Kwajalein Missile Range), is a missile test range in Marshall Islands ( Pacific Ocean). It covers about and includes rocket launch ...
and the first went on alert with Strategic Air Command in 1986, being fully deployed in 1988. The permanent basing construct including making the Peacekeeper rail-mobile on trains, but with the end of the Cold War those plans were canceled by President
George H. W. Bush in 1991. The Ballistic Missile Office also started development on the
MGM-134 Midgetman
The MGM-134A Midgetman, also known as the Small Intercontinental Ballistic Missile, was an intercontinental ballistic missile developed by the United States Air Force. The system was mobile and could be set up rapidly, allowing it to move to a ne ...
ICBM in 1986, also known as the Small ICBM, which would be held in road-mobile launchers. Its first test flight occurred in 1991 from
Vandenberg Air Force Base Vandenberg may refer to:
* Vandenberg (surname), including a list of people with the name
* USNS ''General Hoyt S. Vandenberg'' (T-AGM-10), transport ship in the United States Navy, sank as an artificial reef in Key West, Florida
* Vandenberg Sp ...
to a target in the
Kwajalein Missile Range
The Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site, commonly referred to as the Reagan Test Site (formerly Kwajalein Missile Range), is a missile test range in Marshall Islands ( Pacific Ocean). It covers about and includes rocket launch ...
, but was canceled in 1992 due to the end of the Cold War.
The Space Division continued the Space and Missile Systems Organization's military development of the
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program n ...
alongside NASA, however in 1986 the
Space Shuttle ''Challenger'' exploded during launch, forcing NASA to suspend all launches until 1988. Not only did it suspend the development of Shuttle launch and recovery facilities at Vandenberg Air Force Base, but also delayed all military payloads that were scheduled to be launched on the shuttle. The Space Division had been developing the
Titan 34D as a backup in the event that there were any issues with the Shuttle program and after two launch failures in 1985 and 1986 suspended Titan 34 Launches, they resumed in 1987, restoring the only launch alternative to the Space Shuttle for large payloads. The
Titan IV
Titan IV was a family of heavy-lift space launch vehicles developed by Martin Marietta and operated by the United States Air Force from 1989 to 2005. Launches were conducted from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida and Vandenberg Air Forc ...
had already started development in 1985, but the ''Challenger'' disaster reinforced the need to have a diverse fleet of space launch vehicles. The Titan IV had its first launch in 1989 and could use either the
Inertial Upper Stage
The Inertial Upper Stage (IUS), originally designated the Interim Upper Stage, was a two-stage, solid-fueled space launch system developed by Boeing for the United States Air Force beginning in 1976 for raising payloads from low Earth orbit to ...
or an upgraded
Centaur
A centaur ( ; grc, κένταυρος, kéntauros; ), or occasionally hippocentaur, is a creature from Greek mythology with the upper body of a human and the lower body and legs of a horse.
Centaurs are thought of in many Greek myths as bein ...
stage. It also began the development of two new medium launch vehicles, with the
Delta II
Delta II was an expendable launch system, originally designed and built by McDonnell Douglas. Delta II was part of the Delta rocket family and entered service in 1989. Delta II vehicles included the Delta 6000, and the two later Delta 7000 va ...
intended to launch the
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite ...
and the
Atlas II
Atlas II was a member of the Atlas family of launch vehicles, which evolved from the successful Atlas missile program of the 1950s. The Atlas II was a direct evolution of the Atlas I, featuring longer first stage tanks, higher-performing engine ...
intended to launch the
Defense Satellite Communications System.
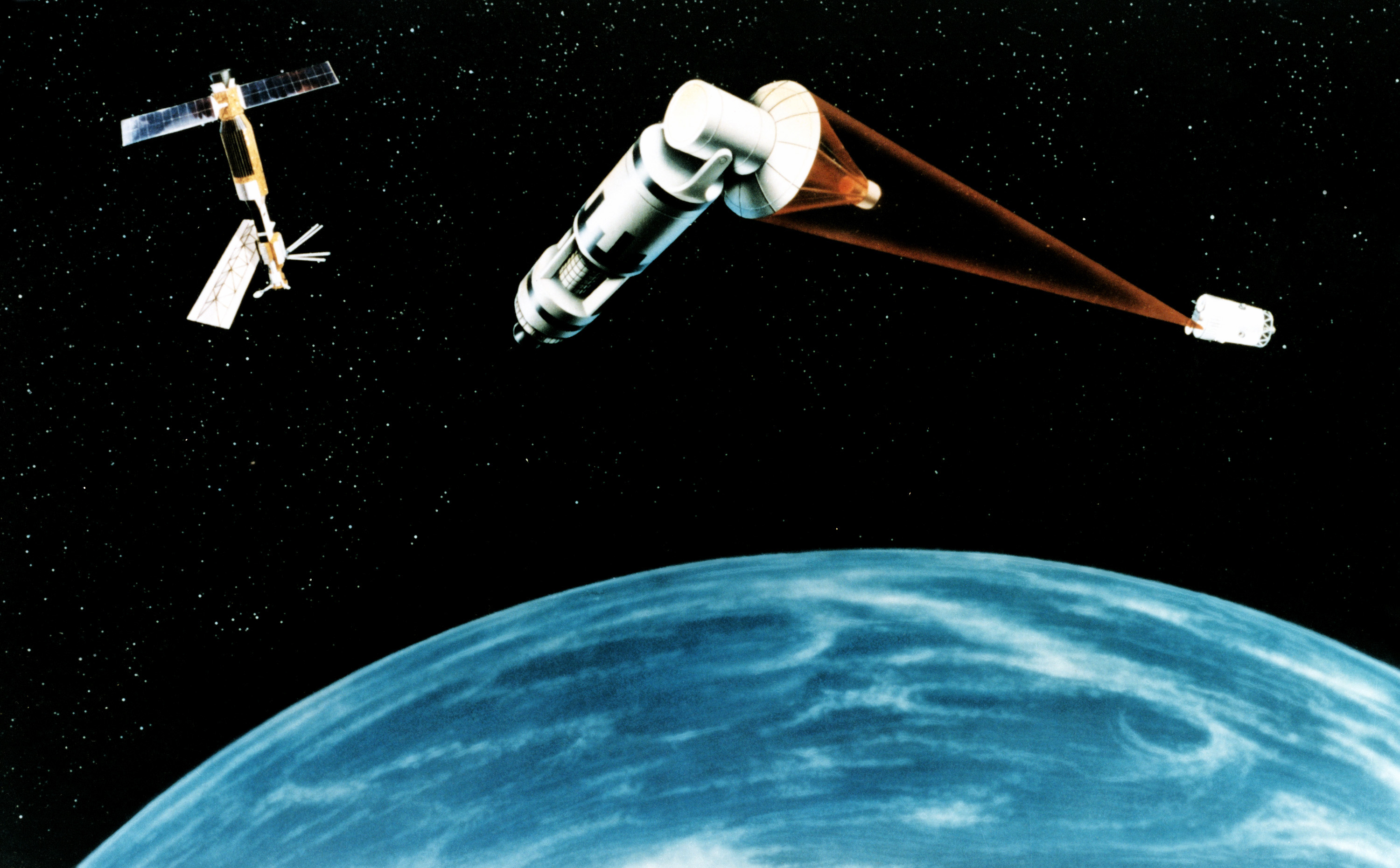
The Space Division launched the first Defense Meteorological Support Program Block 5D-2s and started the procurement process for DMSP Block 5D-3s, as well as starting the deployment of the Global Positioning System constellation. It also continued the
Defense Satellite Communications System Phase III
The Defense Satellite Communications System (DSCS) is a United States Space Force satellite constellation that provides the United States with military communications to support globally distributed military users. Beginning in 2007, DSCS is b ...
deployment, launching the first in 1982 and the full constellation was completed in 1993. The
Military Strategic and Tactical Relay, or Milstar, strategic satellite communication program was started in 1982.
The Space Division initiated the largest change to the
Air Force Satellite Control Network
The Satellite Control Network (SCN), operated by the United States Space Force's Space Delta 6, provides support for the operation, control, and maintenance of a variety of United States Department of Defense and some non-DoD satellites. This i ...
since its inception, with Secretary of Defense
Harold Brown authorizing the construction of a Consolidated Space Operations Center at
Falcon Air Force Base
Schriever Space Force Base, previously Schriever Air Force Base, Falcon Air Force Base, and Falcon Air Force Station, is a base of the United States Space Force located approximately east of Peterson Space Force Base near Colorado Springs in ...
in 1979. It was intended to comprise two parts, a Satellite Operations Complex to replace
Onizuka Air Force Base
Onizuka Air Force Station or Onizuka AFS was a United States Air Force installation in Sunnyvale, California, at the intersection of State Route 237 and North Mathilda Avenue. It was operational from 1960 to 2010.
Its distinguishing feature was ...
and a Shuttle Operations and Planning Center to replace
Johnson Space Center
The Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center (JSC) is NASA's center for human spaceflight (originally named the Manned Spacecraft Center), where human spaceflight training, research, and flight control are conducted. It was renamed in honor of the late ...
for military missions. The Shuttle Operation and Planning Center was canceled in 1987, while the Consolidated Space Operations Center gradually came online in 1989 and was fully transferred to
Air Force Space Command
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for ...
in 1993.
The Space Division also continued the air-launched ASAT program that SAMSO started in 1976, culminating in the development of the
ASM-135 ASAT. Its first test was on 21 January 1984 and on 13 September 1985, it was launched from a
McDonnell Douglas F-15A Eagle
The McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle is an American twin-engine, all-weather tactical fighter aircraft designed by McDonnell Douglas (now part of Boeing). Following reviews of proposals, the United States Air Force selected McDonnell Douglas's ...
to destroy the
Solwind research satellite. The program was terminated in 1988 due to budgetary and congressional restrictions. Starting in 1983, the Department of Defense announced the
Strategic Defense Initiative
The Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI), derisively nicknamed the "''Star Wars'' program", was a proposed missile defense system intended to protect the United States from attack by ballistic strategic nuclear weapons ( intercontinental ballist ...
to provide missile defense, with the Space Division responsible for its space-based and Air Force components. In 1987, the Strategic Defense Initiative Organization selected the Space Division's
Boost Surveillance and Tracking System
The Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI), derisively nicknamed the "''Star Wars'' program", was a proposed missile defense system intended to protect the United States from attack by ballistic strategic nuclear weapons ( intercontinental ballist ...
,
Space Surveillance and Tracking System
The Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI), derisively nicknamed the "''Star Wars'' program", was a proposed missile defense system intended to protect the United States from attack by ballistic strategic nuclear weapons ( intercontinental ballist ...
, and
Space-Based Interceptor
The Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI), derisively nicknamed the "''Star Wars'' program", was a proposed missile defense system intended to protect the United States from attack by ballistic strategic nuclear weapons ( intercontinental ballist ...
for demonstration.
Immediately following the establishment of the Space Division on 1 October 1979, the Space and Missile Test Center was redesignated as the Space and Missile Test Organization, comprising the
Eastern Space and Missile Center
The Space Launch Delta 45 (SLD 45) is a unit of the United States Space Force. The Space Launch Delta 45 is assigned to Space Systems Command and headquartered at Patrick Space Force Base, Florida. The wing also controls Cape Canaveral Space Fo ...
at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and the
Western Space and Missile Center
Space Launch Delta 30 (SLD 30) is a United States Space Force space launch delta assigned to Space Systems Command and headquartered at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California. The Space Launch Delta 30 is responsible for all space launch opera ...
at Vandenberg Air Force Base. On 1 September 1982,
Air Force Space Command
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for ...
was activated as the Air Force's first major command for space and on 1 October 1987 the
Air Force Satellite Control Facility
The United States Air Force's Air Force Satellite Control Facility (AFSCF) was a space command and control unit located at Onizuka AFS, California. It has the distinction of being heavily involved in the world's first reconnaissance satellite pr ...
was inactivated, with its functions being replaced by Air Force Space Command's wings. The Space and Missile Test Organization was inactivated on 1 October 1989, and on 1 October 1990 the Eastern Space and Missile Center and Western Space and Missile Center were transferred to Air Force Space Command's
9th Space Division
The 9th Space Division (9th SD) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with Air Force Space Command, being stationed at Patrick Air Force Base, Florida. It was inactivated on 1 October 1991.
History Tactical ...
, making it responsible for space launch.
However, the Space Division did gain responsibility for some research and development functions, gaining the
Air Force Space Technology Center
Phillips Laboratory was a research and development organization operated by the United States Air Force Materiel Command. In 1997, the Laboratory was merged into the Air Force Research Laboratory as the Space Vehicles and Directed Energy Director ...
at
Kirtland Air Force Base
Kirtland Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base located in the southeast quadrant of the Albuquerque, New Mexico urban area, adjacent to the Albuquerque International Sunport. The base was named for the early Army aviator Col. Ro ...
in October 1982. The Air Force Space Technology Center consisted of the
Air Force Weapons Laboratory
The Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) is a scientific research organization operated by the United States Air Force Materiel Command dedicated to leading the discovery, development, and integration of aerospace warfighting technologies, pl ...
, Air Force Geophysics Laboratory, and
Air Force Rocket Propulsion Laboratory. In 1990, the Air Force Space Technology Center was renamed the
Phillips Laboratory and its three sub-laboratories were directly incorporated into it.
On 15 March 1989, the Space Division reassumed its historical name of the Space Systems Division and the Ballistic Missile Office also was renamed the Ballistic Systems Division. Due to cutbacks in the ballistic missile program due to the end of the Cold War, the Ballistic Systems Division was renamed the Ballistic Missile Organization and realigned under the Space Systems Division on 5 May 1990.
Realignment under Air Force Space Command


As part of the Air Force's restructuring in the early 1990s, Air Force Systems Command merged with
Air Force Logistics Command
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing fo ...
to form
Air Force Materiel Command
Air Force Materiel Command (AFMC) is a major command ( MAJCOM) of the United States Air Force (USAF). AFMC was created on July 1, 1992, through the amalgamation of the former Air Force Logistics Command (AFLC) and the former Air Force Systems Co ...
on 1 July 1992. As part of this merger, the Space Systems Division was redesignated as the Space and Missile Systems Center on the same date.
On 1 October 1993, the 6592nd Air Base Group was redesignated the 655th Air Base Squadron as part of an Air Force-wide restructuring of support groups. In January 1993,
Kirtland Air Force Base
Kirtland Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base located in the southeast quadrant of the Albuquerque, New Mexico urban area, adjacent to the Albuquerque International Sunport. The base was named for the early Army aviator Col. Ro ...
and the
377th Air Base Wing
The 377th Air Base Wing is a wing of the United States Air Force based at Kirtland Air Force Base, New Mexico. The wing has been the host unit at Kirtland since January 1993. It was activated on 1 January 1993, when Air Force Materiel Command a ...
were directly assigned to the Space and Missile Systems Center and the
61st Air Base Group at
Los Angeles Air Force Base was activated on 1 October 1994, replacing the 655th Air Base Squadron. On 8 April 1997, the Philips Laboratory was merged with other Air Force laboratories to form the
Air Force Research Laboratory
The Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) is a scientific research organization operated by the United States Air Force Materiel Command dedicated to leading the discovery, development, and integration of aerospace warfighting technologies, pl ...
and Kirtland Air Force Base and its 377th Air Base Wing was transferred to the
Air Armament Center
The Air Armament Center (AAC) was an Air Force Materiel Command (AFMC) center at Eglin Air Force Base, Florida, responsible for development, acquisition, testing, and deployment of all air-delivered weapons for the U.S. Air Force. Weapon systems ...
on 1 October 1998. The remaining space functions at Kirtland AFB, including test and evaluation, launch of experimental payloads, and Space Shuttle Operations were consolidated into Detachment 12 which activated on 29 June 2001.
The
START I
START I (Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty) was a bilateral treaty between the United States and the Soviet Union on the reduction and the limitation of strategic offensive arms. The treaty was signed on 31 July 1991 and entered into force on 5 De ...
treaty of 1991 and
START II
START II (Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty) was a bilateral treaty between the United States and Russia on the Reduction and Limitation of Strategic Offensive Arms. It was signed by US President George H. W. Bush and Russian President Boris Ye ...
treaty of 1993 between the United States and the Soviet Union and its successor, the Russian Federation, dramatically reduced the amount of nuclear warheads in each superpower's arsenal. This resulted in the U.S. Air Force reducing the amount of Minuteman missiles, reconfiguring its missiles to have only one warhead, and scrapping the Pershing missiles. Due to the dramatic reduction in ballistic missiles, the Space and Missile Systems Center's Ballistic Missile Organization was officially inactivated in September 1993.
The Space and Missile Systems Center followed up on the Space Division's development of the
Delta II
Delta II was an expendable launch system, originally designed and built by McDonnell Douglas. Delta II was part of the Delta rocket family and entered service in 1989. Delta II vehicles included the Delta 6000, and the two later Delta 7000 va ...
and
Atlas II
Atlas II was a member of the Atlas family of launch vehicles, which evolved from the successful Atlas missile program of the 1950s. The Atlas II was a direct evolution of the Atlas I, featuring longer first stage tanks, higher-performing engine ...
space launch vehicles, procuring launches using the upgraded
Atlas III
The Atlas III (known as the Atlas II-AR (R for Russian) early in development ) was an American orbital launch vehicle, used in the years between 2000 and 2005. It was developed from the highly successful Atlas II rocket and shared many compone ...
, which used the Russian
RD-180
The RD-180 ( rus, РД-180, Ракетный Двигатель-180, Raketnyy Dvigatel-180) is a rocket engine designed and built in Russia. It features a dual combustion chamber, dual- nozzle design and is fueled by a RP-1/ LOX mixture. The RD ...
engine. Following six launch failures from April 1998 to May 1999 the Department of Defense started the Launch Broad Area Review, releasing its report in November 1999 and recommending that the Space and Missile Systems Center have broadened responsibility for all Department of Defense launches, from acquisition to deliver of spacecraft on-orbit.
In August 1994, President Bill Clinton signed a National Transportation Space Policy, assigning responsibility for expendable launch vehicles to the Defense Department and directed it to develop improved variants of current vehicles. In response, the Space and Missile Systems Center built the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle program and awarded the first contracts in 1995. One went to McDonnell Douglas for the Delta IV and Delta IV Heavy, while the other went to Lockheed Martin for the Atlas V.
In 2006, the two launch providers merged to form United Launch Alliance. In 2016, SpaceX was awarded its first military launch under the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle program, using its Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy boosters. In 2019, in part due to SpaceX's success with reusable rockets, the program's name was changed to National Security Space Launch.
In 1994, the Space and Missile Systems Center had started the Space-Based Infrared System (SBIRS) program to replace the
Defense Support Program
The Defense Support Program (DSP) is a program of the United States Space Force that operated the reconnaissance satellites which form the principal component of the ''Satellite Early Warning System'' used by the United States.
DSP satellite ...
. SBIRS was built upon technology tested for the
Strategic Defense Initiative
The Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI), derisively nicknamed the "''Star Wars'' program", was a proposed missile defense system intended to protect the United States from attack by ballistic strategic nuclear weapons ( intercontinental ballist ...
, launching its first satellite in 2011. Since the 1970s, proposals were made to merge the military and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) weather satellites. In 1994, President Clinton directed that the programs eventually be merged. In 1995, the Air Force, NASA, and NOAA started the National Polar-orbiting Operational Environmental Satellite System which was intended to replace the Defense Metrological Support Program and be operated by NOAA, but the program collapsed due to cost overruns in 2010 and a full merging of the programs has not occurred. A second Defense Department-only effort, the Defense Weather Satellite System, was canceled by Congress in 2012.
The
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite ...
constellation became fully completed in 1994 and achieved initial operational capability in 1995. Milstar had its first launch in 1995 and the Space and Missile Systems Center started development on the Wideband Global SATCOM system to replace the
Defense Satellite Communications System and the Advanced Extremely High Frequency to replace Milstar. The Brilliant Pebbles space-based anti-missile interceptor was transferred to the Space and Missile Systems Center in 1993 from the Ballistic Missile Defense Organization, but was terminated in 1994.
In 2001, the Space Commission came out with its report on national security space. A major recommendation was realigning the Space and Missile Systems Center from Air Force Materiel Command to
Air Force Space Command
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for ...
to consolidate management of space programs to one major command. This occurred on 1 October 2001.

On 1 August 2006, the Space and Missile Systems Center reorganized itself along a traditional Air Force wing and group construct. These included the Military Satellite Communications Systems Wing which replaced the MILSATCOM Joint System Program Office (JPO), the Launch and Range Systems Wing, which replaced the Launch and Ranges JPO, the Global Positioning Systems Wing, which replaced the Navstar GPS JPO, the Space-Based Infrared Systems Wing, which replaced the SBIRS System Program Office (SPO), the Space Superiority Systems Wing, the Space Development and Test Wing at Kirtland Air Force Base, which included the former SMC Detachment 12, the 61st Air Base Wing, which replaced the 61st Air Base Group, the Satellite Control and Network Systems Group, which replaced the Air Force Satellite Control Network SPO, the Space Logistics Group, which replaced the SMC Logistics Support Squadron, and the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program Systems Group, which replaced the DMSP SPO. On 31 March 2008, the Missile Defense Systems Group was activated.
However, in response to the lead of Air Force Materiel Command, on 10 November 2010 the wings and groups redesignated as directorates and divisions as part of an Air Force acquisitions wide effort. This resulted in the 61st Air Base Wing being inactivated and replaced with the 61st Air Base Group, the GPS Wing becoming the Global Positioning Systems Directorate, the Launch and Range Systems Wing becoming the Launch Enterprise Directorate, the MILSATCOM Wing becoming the Military Satellite Communications Directorate, the Space Superiority Systems Wing becoming the Space Superiority Systems Directorate, the SIBRS Wing becoming the Infrared Space Systems Directorate, the Space Development and Test Wing becoming the Space Development and Test Directorate, the Space Logistics Group becoming the Space Logistics Directorate, the DMSP Group becoming the Defense Weather Systems Directorate, the Missile Defense Systems Group becoming the Missile Defense Systems Division, and the Satellite Control and Network Systems Group becoming the Satellite Control and Network Systems Division
In 2014, the Space and Missile Systems Center combined its Developmental Planning Directorate and the Space Development and Test Directorate to form the Advanced Systems and Development Directorate. The Range and Network Systems Division was eventually stood up to replace the functions of the Satellite Control and Network Systems Division and in 2015 the Defense Weather Systems Directorate and Infrared Space Systems Directorate were combined into the Remote Sensing Systems Directorate. In 2019, these directorates were all replaced as part of the SMC 2.0 reorganization, which instead established the Development Corps, which was responsible for innovation and prototyping, a Production Corps, an Enterprise Corps, which conducted support for products and launch, and an Atlas Corps which provided personnel management.
Redesignation as Space Systems Command and transfer to the Space Force

When the United States Space Force was established as an independent service on 20 December 2019, Air Force Space Command was redesignated as United States Space Force, but functionally remained a major command within the Air Force. The Space and Missile Systems Center remained a part of United States Space Force as it was redesignated as
Space Operations Command
Space Operations Command (SpOC) is the United States Space Force's space operations, cyber operations, and intelligence field command. It is headquartered at Peterson Space Force Base, Colorado and serves as the U.S. Space Force's service ...
, until it was reassigned to Headquarters Space Force on 22 April 2021 and officially transferred from the U.S. Air Force center to a U.S. Space Force field command, although it continued to use the Space and Missile Systems Center name.
On 13 August 2021, the Space and Missile Systems Center was redesignated as Space Systems Command on 13 August 2021. The commander is a Space Force lieutenant general, while the deputy command is a Space Force major general and is also responsible for space launch. In addition to Space and Missile Systems Center units realigning, the 61st Air Base Group was redesignated the Los Angeles Garrison. Space Systems Command also gained Space Launch Delta 30 and Space Launch Delta 45, which they had given up to Air Force Space Command in 1990. The commander of Space Launch Delta 45, a brigadier general, is the Space Systems Command operations director and range acquisitions lead.
Air Force Research Laboratory
The Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) is a scientific research organization operated by the United States Air Force Materiel Command dedicated to leading the discovery, development, and integration of aerospace warfighting technologies, pl ...
space units, such as the Space Vehicles Directorate, Space Electro-Optical Division, Rocket Propulsion Division, and Space Systems Technology Division, administratively report to Space Systems Command, while remaining under the aligned under Air Force Research Labs. The Air Force Life Cycle Management Center's Strategic Warning and Surveillance Systems Division, responsible for ground-based radars, missile warning, space domain awareness, missile defense systems, and shared early warning capabilities, transferred to Space Systems Command.
Space Systems Command also provides support to the Space Rapid Capabilities Office and Space Development Agency (to be transferred in 2022), which are direct reporting units to the Chief of Space Operations.
In July 2021, President Joe Biden, Biden nominated Deputy Director of the
National Reconnaissance Office
The National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) is a member of the United States Intelligence Community and an agency of the United States Department of Defense which designs, builds, launches, and operates the reconnaissance satellites of the U.S. fe ...
Major general (United States), Maj Gen Michael Guetlein to lead Space Systems Command. He was List of positions filled by presidential appointment with Senate confirmation, confirmed with a promotion to Lieutenant general (United States), lieutenant general on 29 July 2021 which became effective on 13 August 2021.
Symbolism
Space Systems Command emblem and color
At the top of the design, rising into space, is a delta riding on an ignition plume. The delta and plume represent the space launch vehicle, launch vehicles need to place Space Force assets into orbit and signifies launch operations from Western Range (USSF), West and Eastern Range, East coast ranges. The constellation Aquila (constellation), Aquila symbolizes the space environment, reflecting Space Systems Command's developing and fielding of space warfighting capabilities. The primary star represents the Space Force's on-orbit capabilities. The sweeping orbit and thunderbolt represent the Space Force's space assets safeguarding the Earth.
Gold (color), Gold is Space Systems Command's distinguishing color and signifying the excellence and intelligence required to identify, prototype, and field innovative space capabilities.
The Space Systems Command emblem and flag were unveiled on 13 April 2021, replacing the Space and Missile Systems Center emblem.
Post–2002 Space and Missile Systems Center emblem
After space and missiles functions were reunited under the Space and Missile Systems Center, it continued to use the old Space and Missile Systems Organization emblem for 10 years. However, when the Space and Missile Systems Center transferred from Air Force Materiel Command to Air Force Space Command it adopted a new emblem on 2 August 2002 to better express its mission and allegiance to Air Force Space Command.
Blue and yellow are the Air Force colors. Blue alludes to the sky, the primary theater of Air Force operations. Yellow refers to the sun and the excellence required of Air Force personnel. The globe represents the night and day missions that the satellite and missile systems must perform. The four pole stars symbolize the communications satellite, communication, Global Positioning System, navigation, spy satellite, surveillance and weather satellites utilized by the Center. The flight symbol stands for deployed intercontinental ballistic missile, missile systems.
Pre–2002 Space and Missile Systems Center, Space Division, and Space and Missile Systems Organization emblem
When the Space and Missile Systems Organization was activated in 1967, it determined it needed a new emblem to represent its space and missile missions. The SAMSO emblem was first approved on 22 May 1968. When the Space Division was established in 1979, it continued to use the SAMSO emblem but reinterpreted it. When the Space and Missile Systems Center was established in 1992, the dual space and missile symbiology was restored. The emblem was replaced in 2002 when the Space and Missile Systems Center transferred to Air Force Space Command.
The Space and Missile Systems Center Organizational emblem represents the cooperation of science, industry, and the military in advancing the defense technology of the United States, and the role of SMC in unifying and directing this effort. It also symbolizes the two major elements of the Organization's mission-- ballistic missile, missile and space launch vehicle, space booster power and satellites in orbit.
In the first symbolism, the diagonal lines represent the role of science, industry, and the military, respectively, in advancing defense technology; and the triangle depicts the function of SMC in directing and managing the work of these elements in the pursuit of desired military objectives. The circle surrounding the diagonal lines represents the total integrating role of SMC in planning, developing and testing military systems and in acquiring them for the national defense.
In the second symbolism, the triangle joined by the three lines symbolizes rocket booster power for payloads as the basis for both ballistic missile and space systems, while the circle represents both satellites and their orbital traces.
Air Force Ballistic Missile Division, Space Systems Division, and Ballistic Systems Division
When the Western Development Division was first established in 1954, it used the emblem of its major command,
Air Research and Development Command
The Air Force Systems Command (AFSC) is an inactive United States Air Force Major Command. It was established in April 1951, being split off from Air Materiel Command. The mission of AFSC was Research and Development for new weapons systems.
Ove ...
. This was carried over by the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division until it created its own emblem on 2 November 1960, which was based on Air Research and Development Command's. However, with the activation of Air Force Systems Command in 1961, the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division was split.
The Space Systems Division was established in 1961 and modified the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division's emblem to form its own, was used from 5 July 1962 until the Space and Missile Systems Organization was formed in 1967. The Ballistic Systems Division also modified elements of the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division, having its emblem approved on 14 February 1962. The Ballistic Systems Division's emblem was retired following the Space and Missile Systems Organization's establishment in 1967, but the Ballistic Missile Office received authorization to use it starting in 1 December 1980, and it was continuously used by the Ballistic Systems Division and Ballistic Missile Organization until it was inactivated on 2 September 1993.
Structure
List of commanders
See also
U.S. Armed Forces systems commands
* United States Army Materiel Command, Army Materiel Command
* Marine Corps Systems Command
* United States Navy systems commands
** Naval Sea Systems Command
** Naval Air Systems Command
** Naval Information Warfare Systems Command
** Naval Facilities Engineering Systems Command
** Naval Supply Systems Command
*
Air Force Materiel Command
Air Force Materiel Command (AFMC) is a major command ( MAJCOM) of the United States Air Force (USAF). AFMC was created on July 1, 1992, through the amalgamation of the former Air Force Logistics Command (AFLC) and the former Air Force Systems Co ...
References
Sources
{{DEFAULTSORT:Space And Missile Systems Center
Units and formations of the United States Space Force
El Segundo, California
Military units and formations in California
Military units and formations established in 1954
1954 establishments in California
Science and technology in Greater Los Angeles
Field commands of the United States Space Force
Satellite operators

 On 20 September 1957, the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division conducted the first launch of a Thor missile from
On 20 September 1957, the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division conducted the first launch of a Thor missile from 

 On 1 July 1967, the Space Systems Division and Ballistic Systems Division were remerged, forming the Space and Missile Systems Office (SAMSO). This remerger was prompted by economic reasons and SAMSO was located as Los Angeles Air Force Station. SAMSO did not start any new ballistic missile programs, but did oversee the replacement of the Minuteman I with the Minuteman II, which had improved range and guidance, and the Minuteman III, which more penetration aids to counter anti-ballistic missile defense systems and could be equipped with three
On 1 July 1967, the Space Systems Division and Ballistic Systems Division were remerged, forming the Space and Missile Systems Office (SAMSO). This remerger was prompted by economic reasons and SAMSO was located as Los Angeles Air Force Station. SAMSO did not start any new ballistic missile programs, but did oversee the replacement of the Minuteman I with the Minuteman II, which had improved range and guidance, and the Minuteman III, which more penetration aids to counter anti-ballistic missile defense systems and could be equipped with three  On 1 October 1979, the Space and Missile Systems Organization was redesignated as the Space Division and split off its ballistic missile functions into the Ballistic Missile Office due to growth in both mission areas.
Starting in 1982, the Ballistic Missile Office assisted Strategic Air Command in deactivating the remaining Titan II missiles and placing them into storage for possible conversion into space launch vehicles. Under the
On 1 October 1979, the Space and Missile Systems Organization was redesignated as the Space Division and split off its ballistic missile functions into the Ballistic Missile Office due to growth in both mission areas.
Starting in 1982, the Ballistic Missile Office assisted Strategic Air Command in deactivating the remaining Titan II missiles and placing them into storage for possible conversion into space launch vehicles. Under the  The Space Division launched the first Defense Meteorological Support Program Block 5D-2s and started the procurement process for DMSP Block 5D-3s, as well as starting the deployment of the Global Positioning System constellation. It also continued the
The Space Division launched the first Defense Meteorological Support Program Block 5D-2s and started the procurement process for DMSP Block 5D-3s, as well as starting the deployment of the Global Positioning System constellation. It also continued the 
 As part of the Air Force's restructuring in the early 1990s, Air Force Systems Command merged with
As part of the Air Force's restructuring in the early 1990s, Air Force Systems Command merged with  On 1 August 2006, the Space and Missile Systems Center reorganized itself along a traditional Air Force wing and group construct. These included the Military Satellite Communications Systems Wing which replaced the MILSATCOM Joint System Program Office (JPO), the Launch and Range Systems Wing, which replaced the Launch and Ranges JPO, the Global Positioning Systems Wing, which replaced the Navstar GPS JPO, the Space-Based Infrared Systems Wing, which replaced the SBIRS System Program Office (SPO), the Space Superiority Systems Wing, the Space Development and Test Wing at Kirtland Air Force Base, which included the former SMC Detachment 12, the 61st Air Base Wing, which replaced the 61st Air Base Group, the Satellite Control and Network Systems Group, which replaced the Air Force Satellite Control Network SPO, the Space Logistics Group, which replaced the SMC Logistics Support Squadron, and the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program Systems Group, which replaced the DMSP SPO. On 31 March 2008, the Missile Defense Systems Group was activated.
However, in response to the lead of Air Force Materiel Command, on 10 November 2010 the wings and groups redesignated as directorates and divisions as part of an Air Force acquisitions wide effort. This resulted in the 61st Air Base Wing being inactivated and replaced with the 61st Air Base Group, the GPS Wing becoming the Global Positioning Systems Directorate, the Launch and Range Systems Wing becoming the Launch Enterprise Directorate, the MILSATCOM Wing becoming the Military Satellite Communications Directorate, the Space Superiority Systems Wing becoming the Space Superiority Systems Directorate, the SIBRS Wing becoming the Infrared Space Systems Directorate, the Space Development and Test Wing becoming the Space Development and Test Directorate, the Space Logistics Group becoming the Space Logistics Directorate, the DMSP Group becoming the Defense Weather Systems Directorate, the Missile Defense Systems Group becoming the Missile Defense Systems Division, and the Satellite Control and Network Systems Group becoming the Satellite Control and Network Systems Division
In 2014, the Space and Missile Systems Center combined its Developmental Planning Directorate and the Space Development and Test Directorate to form the Advanced Systems and Development Directorate. The Range and Network Systems Division was eventually stood up to replace the functions of the Satellite Control and Network Systems Division and in 2015 the Defense Weather Systems Directorate and Infrared Space Systems Directorate were combined into the Remote Sensing Systems Directorate. In 2019, these directorates were all replaced as part of the SMC 2.0 reorganization, which instead established the Development Corps, which was responsible for innovation and prototyping, a Production Corps, an Enterprise Corps, which conducted support for products and launch, and an Atlas Corps which provided personnel management.
On 1 August 2006, the Space and Missile Systems Center reorganized itself along a traditional Air Force wing and group construct. These included the Military Satellite Communications Systems Wing which replaced the MILSATCOM Joint System Program Office (JPO), the Launch and Range Systems Wing, which replaced the Launch and Ranges JPO, the Global Positioning Systems Wing, which replaced the Navstar GPS JPO, the Space-Based Infrared Systems Wing, which replaced the SBIRS System Program Office (SPO), the Space Superiority Systems Wing, the Space Development and Test Wing at Kirtland Air Force Base, which included the former SMC Detachment 12, the 61st Air Base Wing, which replaced the 61st Air Base Group, the Satellite Control and Network Systems Group, which replaced the Air Force Satellite Control Network SPO, the Space Logistics Group, which replaced the SMC Logistics Support Squadron, and the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program Systems Group, which replaced the DMSP SPO. On 31 March 2008, the Missile Defense Systems Group was activated.
However, in response to the lead of Air Force Materiel Command, on 10 November 2010 the wings and groups redesignated as directorates and divisions as part of an Air Force acquisitions wide effort. This resulted in the 61st Air Base Wing being inactivated and replaced with the 61st Air Base Group, the GPS Wing becoming the Global Positioning Systems Directorate, the Launch and Range Systems Wing becoming the Launch Enterprise Directorate, the MILSATCOM Wing becoming the Military Satellite Communications Directorate, the Space Superiority Systems Wing becoming the Space Superiority Systems Directorate, the SIBRS Wing becoming the Infrared Space Systems Directorate, the Space Development and Test Wing becoming the Space Development and Test Directorate, the Space Logistics Group becoming the Space Logistics Directorate, the DMSP Group becoming the Defense Weather Systems Directorate, the Missile Defense Systems Group becoming the Missile Defense Systems Division, and the Satellite Control and Network Systems Group becoming the Satellite Control and Network Systems Division
In 2014, the Space and Missile Systems Center combined its Developmental Planning Directorate and the Space Development and Test Directorate to form the Advanced Systems and Development Directorate. The Range and Network Systems Division was eventually stood up to replace the functions of the Satellite Control and Network Systems Division and in 2015 the Defense Weather Systems Directorate and Infrared Space Systems Directorate were combined into the Remote Sensing Systems Directorate. In 2019, these directorates were all replaced as part of the SMC 2.0 reorganization, which instead established the Development Corps, which was responsible for innovation and prototyping, a Production Corps, an Enterprise Corps, which conducted support for products and launch, and an Atlas Corps which provided personnel management.
 When the United States Space Force was established as an independent service on 20 December 2019, Air Force Space Command was redesignated as United States Space Force, but functionally remained a major command within the Air Force. The Space and Missile Systems Center remained a part of United States Space Force as it was redesignated as
When the United States Space Force was established as an independent service on 20 December 2019, Air Force Space Command was redesignated as United States Space Force, but functionally remained a major command within the Air Force. The Space and Missile Systems Center remained a part of United States Space Force as it was redesignated as