Sorosilicates on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Silicate minerals are rock-forming
Silicate minerals are rock-forming  Living organisms also contribute to this geologic cycle. For example, a type of
Living organisms also contribute to this geologic cycle. For example, a type of

 Nesosilicates (from Greek 'island'), or orthosilicates, have the orthosilicate ion, which constitute isolated (insular)
Nesosilicates (from Greek 'island'), or orthosilicates, have the orthosilicate ion, which constitute isolated (insular)
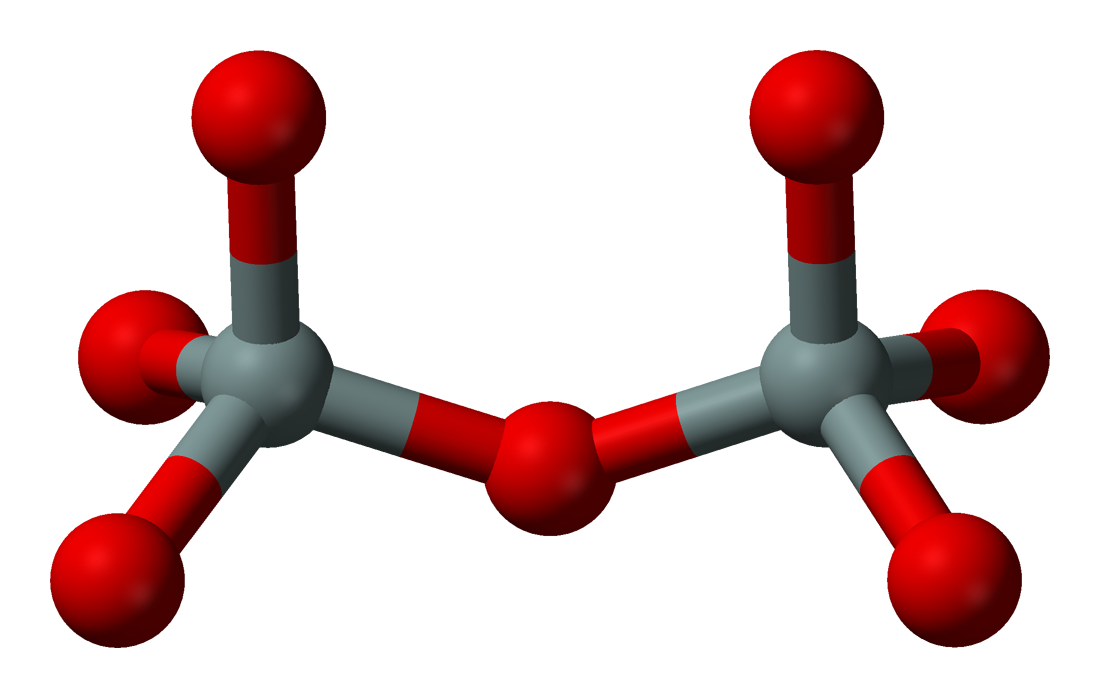
 Sorosilicates (from Greek 'heap, mound') have isolated
Sorosilicates (from Greek 'heap, mound') have isolated


 Cyclosilicates (from Greek 'circle'), or ring silicates, have three or more tetrahedra linked in a ring. The general formula is (Si''x''O3''x'')2''x''−, where one or more silicon atoms can be replaced by other 4-coordinated atom(s). The silicon:oxygen ratio is 1:3. Double rings have the formula (Si2''x''O5''x'')2''x''− or a 2:5 ratio. The Nickel–Strunz classification is 09.C. Possible ring sizes include:
Cyclosilicates (from Greek 'circle'), or ring silicates, have three or more tetrahedra linked in a ring. The general formula is (Si''x''O3''x'')2''x''−, where one or more silicon atoms can be replaced by other 4-coordinated atom(s). The silicon:oxygen ratio is 1:3. Double rings have the formula (Si2''x''O5''x'')2''x''− or a 2:5 ratio. The Nickel–Strunz classification is 09.C. Possible ring sizes include:
File:Beryll.ring.combined.png, 6 units ,
Some example minerals are:
* 3-member single ring
**
File:Pyroxen-chain.png, Inosilicate, pyroxene family, with 2-periodic single chain ,
File:Muskovite.sheet.png, Phyllosilicate, mica group,

 Tectosilicates, or "framework silicates," have a three-dimensional framework of silicate
Tectosilicates, or "framework silicates," have a three-dimensional framework of silicate
–
**Leucite">Coxygen">O3)2">aluminum">Al6silicon.html" ;"title="luminum.html" ;"title="oxygen.html" ;"ti ...
–
**Leucite –
**Nepheline –
**Sodalite –
**Hauyne –
***Lazurite –
*Tectosilicates, scapolite group
**Marialite –
**Meionite –
*Tectosilicates, zeolite family
**Natrolite –
** Erionite –
** Silicate minerals are rock-forming
Silicate minerals are rock-forming mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
s made up of silicate groups. They are the largest and most important class of minerals and make up approximately 90 percent of Earth's crust.
In mineralogy, silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
(silicon dioxide, ) is usually considered a silicate mineral. Silica is found in nature as the mineral quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical ...
, and its polymorphs.
On Earth, a wide variety of silicate minerals occur in an even wider range of combinations as a result of the processes that have been forming and re-working the crust for billions of years. These processes include partial melting
Melting, or fusion, is a physical process that results in the phase transition of a substance from a solid to a liquid. This occurs when the internal energy of the solid increases, typically by the application of heat or pressure, which inc ...
, crystallization, fractionation
Fractionation is a separation process in which a certain quantity of a mixture (of gases, solids, liquids, enzymes, or isotopes, or a suspension) is divided during a phase transition, into a number of smaller quantities (fractions) in which the ...
, metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of ch ...
, weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs ''in situ'' (on site, with little or no movement) ...
, and diagenesis
Diagenesis () is the process that describes physical and chemical changes in sediments first caused by water-rock interactions, microbial activity, and compaction after their deposition. Increased pressure and temperature only start to play a ...
.
 Living organisms also contribute to this geologic cycle. For example, a type of
Living organisms also contribute to this geologic cycle. For example, a type of plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water (or air) that are unable to propel themselves against a current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucia ...
known as diatoms construct their exoskeleton
An exoskeleton (from Greek ''éxō'' "outer" and ''skeletós'' "skeleton") is an external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to an internal skeleton (endoskeleton) in for example, a human. In usage, some of the ...
s ("frustules") from silica extracted from seawater
Seawater, or salt water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has appr ...
. The frustules of dead diatoms are a major constituent of deep ocean
The deep sea is broadly defined as the ocean depth where light begins to fade, at an approximate depth of 200 metres (656 feet) or the point of transition from continental shelves to continental slopes. Conditions within the deep sea are a combin ...
sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sa ...
, and of diatomaceous earth.
General structure
A silicate mineral is generally an inorganic compound consisting of subunits with the formula iO2+nsup>2n-. Although depicted as such, the description of silicates as anions is a simplification. Balancing the charges of the silicate anions are metal cations, Mx+. Typical cations are Mg2+, Fe2+, and Na+. The Si-O-M linkage between the silicates and the metals are strong, polar-covalent bonds. Silicate anions ( iO2+nsup>2n-) are invariably colorless, or when crushed to a fine powder, white. The colors of silicate minerals arise from the metal component, commonly iron. In most silicate minerals, silicon is tetrahedral, being surrounded by four oxides. The coordination number of the oxides is variable except when it bridges two silicon centers, in which case the oxide has a coordination number of two. Some silicon centers may be replaced by atoms of other elements, still bound to the four corner oxygen corners. If the substituted atom is not normally tetravalent, it usually contributes extra charge to the anion, which then requires extra cations. For example, in the mineralorthoclase
Orthoclase, or orthoclase feldspar ( endmember formula K Al Si3 O8), is an important tectosilicate mineral which forms igneous rock. The name is from the Ancient Greek for "straight fracture," because its two cleavage planes are at right angles ...
, the anion is a tridimensional network of tetrahedra in which all oxygen corners are shared. If all tetrahedra had silicon centers, the anion would be just neutral silica . Replacement of one in every four silicon atoms by an aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ha ...
atom results in the anion , whose charge is neutralized by the potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosph ...
cations .
Main groups
In mineralogy, silicate minerals are classified into seven major groups according to the structure of their silicate anion:Hurlbut, Cornelius S.; Klein, Cornelis , , 1985). ''Manual of Mineralogy'', Wiley, (20th edition ed.). Note that tectosilicates can only have additional cations if some of the silicon is replaced by an atom of lower valence such as aluminum. Al for Si substitution is common.Nesosilicates or orthosilicates

 Nesosilicates (from Greek 'island'), or orthosilicates, have the orthosilicate ion, which constitute isolated (insular)
Nesosilicates (from Greek 'island'), or orthosilicates, have the orthosilicate ion, which constitute isolated (insular) tetrahedra
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the o ...
that are connected only by interstitial cations. The Nickel–Strunz classification
Nickel–Strunz classification is a scheme for categorizing minerals based upon their chemical composition, introduced by German mineralogist Karl Hugo Strunz (24 February 1910 – 19 April 2006) in his ''Mineralogische Tabellen'' (1941).
The 4th ...
is 09.A –examples include:
*Phenakite group
**Phenakite
Phenakite or phenacite is a fairly rare nesosilicate mineral consisting of beryllium orthosilicate, Be2 Si O4. Occasionally used as a gemstone, phenakite occurs as isolated crystals, which are rhombohedral with parallel-faced hemihedrism, and are ...
–
**Willemite
Willemite is a zinc silicate mineral () and a minor ore of zinc. It is highly fluorescent (green) under shortwave ultraviolet light. It occurs in a variety of colors in daylight, in fibrous masses and apple-green gemmy masses. Troostite is a vari ...
–
*Olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers quickl ...
group
**Forsterite
Forsterite (Mg2SiO4; commonly abbreviated as Fo; also known as white olivine) is the magnesium-rich end-member of the olivine solid solution series. It is isomorphous with the iron-rich end-member, fayalite. Forsterite crystallizes in the orthorh ...
–
**Fayalite
Fayalite (, commonly abbreviated to Fa) is the iron-rich end-member of the olivine solid-solution series. In common with all minerals in the olivine group, fayalite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system (space group ''Pbnm'') with cell parame ...
–
**Tephroite
Tephroite is the manganese endmember of the olivine group of nesosilicate minerals with the formula Mn2 Si O4. A solid solution series exists between tephroite and its analogues, the group endmembers fayalite and forsterite. Divalent iron or m ...
–
*Garnet
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives.
All species of garnets possess similar physical properties and crystal forms, but differ in chemical composition. The different s ...
group
**Pyrope
The mineral pyrope is a member of the garnet group. Pyrope is the only member of the garnet family to always display red colouration in natural samples, and it is from this characteristic that it gets its name: from the Greek for ''fire'' and ''e ...
–
** Almandine –
** Spessartine –
**Grossular
Grossular is a calcium-aluminium species of the garnet group of minerals. It has the chemical formula of Ca3Al2(SiO4)3 but the calcium may, in part, be replaced by ferrous iron and the aluminium by ferric iron. The name grossular is derived from t ...
–
** Andradite –
**Uvarovite
Uvarovite is a chromium-bearing garnet group species with the formula: Ca3 Cr2( Si O4)3. It was discovered in 1832 by Germain Henri Hess who named it after Count Sergei Semenovitch Uvarov (1765–1855), a Russian statesman and amateur mineral ...
–
** Hydrogrossular –
*Zircon group
**Zircon
Zircon () is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. Its chemical name is zirconium(IV) silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is Zr SiO4. An empirical formula showing some of t ...
–
**Thorite
Thorite, (Th,U)SiO4, is a rare nesosilicate of thorium that crystallizes in the tetragonal system and is isomorphous with zircon and hafnon. It is the most common mineral of thorium and is nearly always strongly radioactive. It was named in 1829 to ...
–
**Hafnon
Hafnon is a hafnium nesosilicate mineral, chemical formula or . In natural zircon part of the zirconium is replaced by the very similar hafnium and so natural zircon is never pure . A zircon with 100% hafnium substitution can be made synthetical ...
–
* group
**Andalusite
Andalusite is an aluminium nesosilicate mineral with the chemical formula Al2SiO5. This mineral was called andalousite by Delamétehrie, who thought it came from Andalusia, Spain. It soon became clear that it was a locality error, and that the spe ...
–
**Kyanite
Kyanite is a typically blue aluminosilicate mineral, found in aluminium-rich metamorphic pegmatites and sedimentary rock. It is the high pressure polymorph of andalusite and sillimanite, and the presence of kyanite in metamorphic rocks gener ...
–
**Sillimanite
Sillimanite is an aluminosilicate mineral with the chemical formula Al2SiO5. Sillimanite is named after the American chemist Benjamin Silliman (1779–1864). It was first described in 1824 for an occurrence in Chester, Connecticut.
Occurrence ...
–
**Dumortierite
Dumortierite is a fibrous variably colored aluminium boro-silicate mineral, Al7BO3(SiO4)3O3. Dumortierite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system typically forming fibrous aggregates of slender prismatic crystals. The crystals are vitreous and var ...
–
** Topaz –
** Staurolite –
*Humite
Humite is a mineral found in the volcanically ejected masses of Vesuvius
Mount Vesuvius ( ; it, Vesuvio ; nap, 'O Vesuvio , also or ; la, Vesuvius , also , or ) is a somma-stratovolcano located on the Gulf of Naples in Campania, Ital ...
group –
** Norbergite –
**Chondrodite
Chondrodite is a nesosilicate mineral with formula . Although it is a fairly rare mineral, it is the most frequently encountered member of the humite group of minerals. It is formed in hydrothermal deposits from locally metamorphosed dolomite. I ...
–
**Humite
Humite is a mineral found in the volcanically ejected masses of Vesuvius
Mount Vesuvius ( ; it, Vesuvio ; nap, 'O Vesuvio , also or ; la, Vesuvius , also , or ) is a somma-stratovolcano located on the Gulf of Naples in Campania, Ital ...
–
**Clinohumite
Clinohumite is an uncommon member of the humite group, a magnesium silicate according to the chemical formula ( Mg, Fe)9( Si O4)4( F,O H)2. The formula can be thought of as four olivine (Mg2SiO4), plus one brucite (Mg(OH)2). Indeed, the mineral ...
–
*Datolite
Datolite is a calcium boron hydroxide nesosilicate, Ca B Si O4(O H). It was first observed by Jens Esmark in 1806, and named by him from δατεῖσθαι, "to divide," and λίθος, "stone," in allusion to the granular structure
of the massi ...
–
*Titanite
Titanite, or sphene (from the Greek ''sphenos'' (σφηνώ), meaning wedge), is a calcium titanium nesosilicate mineral, Ca Ti Si O5. Trace impurities of iron and aluminium are typically present. Also commonly present are rare earth metals ...
–
*Chloritoid
Chloritoid is a silicate mineral of Metamorphism, metamorphic origin. It is an iron magnesium manganese alumino-silicate hydroxide with formula . It occurs as greenish grey to black platy micaceous crystals and foliation (geology), foliated masses. ...
–
*Mullite
Mullite or porcelainite is a rare silicate mineral formed during contact metamorphism of clay minerals. It can form two stoichiometric forms: 3 Al2 O32 SiO2 or 2Al2O3 SiO2. Unusually, mullite has no charge-balancing cations present. As a result, th ...
(aka Porcelainite) –
Sorosilicates

 Sorosilicates (from Greek 'heap, mound') have isolated
Sorosilicates (from Greek 'heap, mound') have isolated pyrosilicate
A pyrosilicate is a type of chemical compound; either an ionic compound that contains the pyrosilicate anion , or an organic compound with the hexavalent ≡-O-≡ group. The anion is also called disilicateViktor Renman (2017): "Structural and ...
anions , consisting of double tetrahedra with a shared oxygen vertex—a silicon:oxygen ratio of 2:7. The Nickel–Strunz classification is 09.B. Examples include:
*Thortveitite
Thortveitite is a rare mineral consisting of scandium yttrium silicate (Sc,Y)2Si2O7. It is the primary source of scandium. Occurrence is in granitic pegmatites. It was named after Olaus Thortveit, a Norwegian engineer. It is grayish-green, blac ...
–
*Hemimorphite
Hemimorphite is the chemical compound Zn4( Si2O7)( OH)2 ·H2O, a component of mineral calamine. It is a silicate mineral which, together with smithsonite (ZnCO3), has been historically mined from the upper parts of zinc and lead ores. Both ...
(calamine
Calamine, also known as calamine lotion, is a medication used to treat mild itchiness. This includes from sunburn, insect bites, poison ivy, poison oak, and other mild skin conditions. It may also help dry out skin irritation. It is applie ...
) –
*Lawsonite
Lawsonite is a hydrous calcium aluminium sorosilicate mineral with formula CaAl2Si2O7(OH)2·H2O. Lawsonite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system in prismatic, often tabular crystals. Crystal twinning is common. It forms transparent to transluc ...
–
*Axinite
Axinite is a brown to violet-brown, or reddish-brown bladed group of minerals composed of calcium aluminium boro-silicate, . Axinite is pyroelectric and piezoelectric.
The axinite group includes:
*Axinite-(Fe) or ferroaxinite, Ca2Fe2+Al2BOSi4O15( ...
–
* Ilvaite –
*Epidote group (has both and groups}
**Epidote
Epidote is a calcium aluminium iron sorosilicate mineral.
Description
Well developed crystals of epidote, Ca2Al2(Fe3+;Al)(SiO4)(Si2O7)O(OH), crystallizing in the monoclinic system, are of frequent occurrence: they are commonly prismatic in hab ...
–
**Zoisite
Zoisite, first known as saualpite, after its type locality, is a calcium aluminium hydroxy sorosilicate belonging to the epidote group of minerals. Its chemical formula is Ca2 Al3( Si O4)(Si2O7)O(O H).
Zoisite occurs as prismatic, orthorho ...
–
***Tanzanite
Tanzanite is the blue and violet variety of the mineral zoisite (a calcium aluminium hydroxyl sorosilicate), caused by small amounts of vanadium. Tanzanite belongs to the epidote mineral group. Tanzanite is only found in Simanjiro District of Ma ...
–
**Clinozoisite
Clinozoisite is a complex calcium aluminium sorosilicate mineral with formula: Ca2Al3(Si2O7)(SiO4)O(OH). It forms a continuous solid solution series with epidote by substitution of iron(III) in the aluminium (m3 site) and is also called ''alumi ...
–
**Allanite
Allanite (also called orthite) is a sorosilicate group of minerals within the broader epidote group that contain a significant amount of rare-earth elements. The mineral occurs mainly in metamorphosed clay-rich sediments and felsic igneous rock ...
–
** Dollaseite-(Ce) –
*Vesuvianite
Vesuvianite, also known as idocrase, is a green, brown, yellow, or blue silicate mineral. Vesuvianite occurs as tetragonal crystals in skarn deposits and limestones that have been subjected to contact metamorphism. It was first discovered within ...
(idocrase
Vesuvianite, also known as idocrase, is a green, brown, yellow, or blue silicate mineral. Vesuvianite occurs as Tetragonal crystal system, tetragonal crystals in skarn deposits and limestones that have been subjected to contact metamorphism. It w ...
) –
Cyclosilicates


 Cyclosilicates (from Greek 'circle'), or ring silicates, have three or more tetrahedra linked in a ring. The general formula is (Si''x''O3''x'')2''x''−, where one or more silicon atoms can be replaced by other 4-coordinated atom(s). The silicon:oxygen ratio is 1:3. Double rings have the formula (Si2''x''O5''x'')2''x''− or a 2:5 ratio. The Nickel–Strunz classification is 09.C. Possible ring sizes include:
Cyclosilicates (from Greek 'circle'), or ring silicates, have three or more tetrahedra linked in a ring. The general formula is (Si''x''O3''x'')2''x''−, where one or more silicon atoms can be replaced by other 4-coordinated atom(s). The silicon:oxygen ratio is 1:3. Double rings have the formula (Si2''x''O5''x'')2''x''− or a 2:5 ratio. The Nickel–Strunz classification is 09.C. Possible ring sizes include:
beryl
Beryl ( ) is a mineral composed of beryllium aluminium silicate with the chemical formula Be3Al2Si6O18. Well-known varieties of beryl include emerald and aquamarine. Naturally occurring, hexagonal crystals of beryl can be up to several ...
(red: Si, blue: O)
File:Benitoid.2200.png, 3 units , benitoite
Benitoite () is a rare blue barium titanium cyclosilicate, found in hydrothermally altered serpentinite. It forms in low temperature, high pressure environments typical of subduction zones at convergent plate boundaries. Benitoite fluoresces ...
File:Papagoite.2200.png, 4 units , papagoite
Papagoite is a rare cyclosilicate mineral. Chemically, it is a calcium copper aluminium silicate hydroxide, found as a secondary mineral on slip surfaces and in altered granodiorite veins, either in massive form or as microscopic crystals that may ...
File:Eudialyte.2200.png, 9 units , eudialyte
Eudialyte, whose name derives from the Greek phrase , , meaning "well decomposable", is a somewhat rare, nine member ring cyclosilicate mineral, which forms in alkaline igneous rocks, such as nepheline syenites. Its name alludes to its ready ...
File:Milarite.png, 6 units, double ring , milarite
Milarite is a rare beryl. It is a member of the osumilite group. Crystals of this mineral typically come in green or yellow. The mineral gets name after Val Milar.
Occurrence
The mineral can be found be found in countries like Switzerland, Bra ...
Benitoite
Benitoite () is a rare blue barium titanium cyclosilicate, found in hydrothermally altered serpentinite. It forms in low temperature, high pressure environments typical of subduction zones at convergent plate boundaries. Benitoite fluoresces ...
–
* 4-member single ring
** Papagoite
Papagoite is a rare cyclosilicate mineral. Chemically, it is a calcium copper aluminium silicate hydroxide, found as a secondary mineral on slip surfaces and in altered granodiorite veins, either in massive form or as microscopic crystals that may ...
– .
* 6-member single ring
**Beryl
Beryl ( ) is a mineral composed of beryllium aluminium silicate with the chemical formula Be3Al2Si6O18. Well-known varieties of beryl include emerald and aquamarine. Naturally occurring, hexagonal crystals of beryl can be up to several ...
–
** Bazzite –
**Sugilite
Sugilite ( ) is a relatively rare pink to purple cyclosilicate mineral with the complex chemical formula K Na2( Fe, Mn, Al)2 Li3 Si12 O30. Sugilite crystallizes in the hexagonal system with prismatic crystals. The crystals are rarely found and ...
–
**Tourmaline
Tourmaline ( ) is a crystalline silicate mineral group in which boron is compounded with elements such as aluminium, iron, magnesium, sodium, lithium, or potassium. Tourmaline is a gemstone and can be found in a wide variety of colors.
The te ...
–
**Pezzottaite
Pezzottaite, marketed under the name raspberyl or raspberry beryl, is a mineral species first recognized by the International Mineralogical Association in September 2003. Pezzottaite is a caesium analogue of beryl, a silicate of caesium, ber ...
–
**Osumilite
Osumilite is a very rare potassium-sodium-iron-magnesium-aluminium silicate mineral. Osumilite is part of the milarite group (also known as the milarite-osumilite group) of cyclosilicates.
Characteristics
Osumilite chemical formula is .Don S. ...
–
**Cordierite
Cordierite (mineralogy) or iolite (gemology) is a magnesium iron aluminium cyclosilicate. Iron is almost always present and a solid solution exists between Mg-rich cordierite and Fe-rich sekaninaite with a series formula: to . A high-temperat ...
–
**Sekaninaite
Sekaninaite ((Fe+2,Mg)2Al4Si5O18) is a silicate mineral, the iron-rich analogue of cordierite.
It was first described in 1968 for an occurrence in Dolní Bory, Vysočina Region, Moravia, Czech Republic, and is now known also from Ireland, Japan, ...
–
* 9-member single ring
** Eudialyte
Eudialyte, whose name derives from the Greek phrase , , meaning "well decomposable", is a somewhat rare, nine member ring cyclosilicate mineral, which forms in alkaline igneous rocks, such as nepheline syenites. Its name alludes to its ready ...
–
* 6-member double ring
**Milarite
Milarite is a rare beryl. It is a member of the osumilite group. Crystals of this mineral typically come in green or yellow. The mineral gets name after Val Milar.
Occurrence
The mineral can be found be found in countries like Switzerland, Bra ...
–
Note that the ring in axinite
Axinite is a brown to violet-brown, or reddish-brown bladed group of minerals composed of calcium aluminium boro-silicate, . Axinite is pyroelectric and piezoelectric.
The axinite group includes:
*Axinite-(Fe) or ferroaxinite, Ca2Fe2+Al2BOSi4O15( ...
contains two B and four Si tetrahedra and is highly distorted compared to the other 6-member ring cyclosilicates.
Inosilicates
Inosilicates (from Greek enitive: 'fibre'), or chain silicates, have interlocking chains of silicatetetrahedra
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the o ...
with either , 1:3 ratio, for single chains or , 4:11 ratio, for double chains. The Nickel–Strunz classification is 09.D – examples include:
Single chain inosilicates
* Pyroxene group **Enstatite – orthoferrosilite series *** Enstatite – *** Ferrosilite – **Pigeonite
Pigeonite is a mineral in the clinopyroxene subgroup of the pyroxene group. It has a general formula of . The calcium cation fraction can vary from 5% to 25%, with iron and magnesium making up the rest of the cations.
Pigeonite crystallizes in th ...
–
**Diopside – hedenbergite series
***Diopside
Diopside is a monoclinic pyroxene mineral with composition . It forms complete solid solution series with hedenbergite () and augite, and partial solid solutions with orthopyroxene and pigeonite. It forms variably colored, but typically dull ...
–
***Hedenbergite
Hedenbergite, Ca Fe Si2 O6, is the iron rich end member of the pyroxene group having a monoclinic crystal system. The mineral is extremely rarely found as a pure substance, and usually has to be synthesized in a lab. It was named in 1819 after M ...
–
*** Augite –
**Sodium pyroxene series
*** Jadeite –
***Aegirine
Aegirine is a member of the clino pyroxene group of inosilicate minerals. Aegirine is the sodium endmember of the aegirine-augite series. Aegirine has the chemical formula Na Fe Si2 O6 in which the iron is present as Fe3+. In the aegirine-augit ...
(or acmite) –
**Spodumene
Spodumene is a pyroxene mineral consisting of lithium aluminium inosilicate, Li Al( Si O3)2, and is a source of lithium. It occurs as colorless to yellowish, purplish, or lilac kunzite (see below), yellowish-green or emerald-green hiddenite, pr ...
–
** Pyroxferroite -
*Pyroxenoid group
**Wollastonite
Wollastonite is a calcium inosilicate mineral ( Ca Si O3) that may contain small amounts of iron, magnesium, and manganese substituting for calcium. It is usually white. It forms when impure limestone or dolomite is subjected to high temperature ...
–
**Rhodonite
Rhodonite is a manganese inosilicate, (Mn, Fe, Mg, Ca)SiO3 and member of the pyroxenoid group of minerals, crystallizing in the triclinic system. It commonly occurs as cleavable to compact masses with a rose-red color (the name comes from the G ...
–
**Pectolite
Pectolite is a white to gray mineral, Na Ca2 Si3 O8(O H), sodium calcium hydroxide inosilicate. It crystallizes in the triclinic system typically occurring in radiated or fibrous crystalline masses. It has a Mohs hardness of 4.5 to 5 and a specif ...
–
Double chain inosilicates
* Amphibole group **Anthophyllite
Anthophyllite is an orthorhombic amphibole mineral: ☐Mg2Mg5Si8O22(OH)2 (☐ is for a vacancy, a point defect in the crystal structure), magnesium iron inosilicate hydroxide. Anthophyllite is polymorphic with cummingtonite. Some forms of antho ...
–
**Cummingtonite series
***Cummingtonite
Cummingtonite ( ) is a metamorphic amphibole with the chemical composition , magnesium iron silicate hydroxide.
Monoclinic cummingtonite is compositionally similar and polymorphic with orthorhombic anthophyllite, which is a much more common ...
–
***Grunerite
Grunerite is a mineral of the amphibole group of minerals with formula Fe7 Si8 O22( OH)2. It is the iron endmember of the grunerite-cummingtonite series. It forms as fibrous, columnar or massive aggregates of crystals. The crystals are monoclini ...
–
**Tremolite series
***Tremolite
Tremolite is a member of the amphibole group of silicate minerals with composition: Ca2(Mg5.0-4.5Fe2+0.0-0.5)Si8O22(OH)2. Tremolite forms by metamorphism of sediments rich in dolomite and quartz. Tremolite forms a series with actinolite and fe ...
–
***Actinolite
Actinolite is an amphibole silicate mineral with the chemical formula .
Etymology
The name ''actinolite'' is derived from the Greek word ''aktis'' (), meaning "beam" or "ray", because of the mineral's fibrous nature.
Mineralogy
Actinolite is ...
–
**Hornblende
Hornblende is a complex inosilicate series of minerals. It is not a recognized mineral in its own right, but the name is used as a general or field term, to refer to a dark amphibole. Hornblende minerals are common in igneous and metamorphic rock ...
–
**Sodium amphibole group
***Glaucophane
Glaucophane is the name of a mineral and a mineral group belonging to the sodic amphibole supergroup of the double chain inosilicates, with the chemical formula ☐Na2(Mg3Al2)Si8O22(OH)2.
Glaucophane crystallizes in the monoclinic system.
Name
G ...
–
***Riebeckite
Riebeckite is a sodium-rich member of the amphibole group of silicate minerals, chemical formula Na2(Fe2+3Fe3+2)Si8O22(OH)2. It forms a solid solution series with magnesioriebeckite. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system, usually as long prisma ...
( asbestos) –
***Arfvedsonite
Arfvedsonite () is a sodium amphibole mineral with composition: aNa2] Fe2+)4Fe3+(OH)2, Si8O22]. It crystallizes in the monoclinic prismatic crystal system and typically occurs as greenish black to bluish grey fibrous to radiating or stellate pr ...
–
diopside
Diopside is a monoclinic pyroxene mineral with composition . It forms complete solid solution series with hedenbergite () and augite, and partial solid solutions with orthopyroxene and pigeonite. It forms variably colored, but typically dull ...
File:Tremolite-chain.png, Inosilicate, clinoamphibole, with 2-periodic double chains , tremolite
Tremolite is a member of the amphibole group of silicate minerals with composition: Ca2(Mg5.0-4.5Fe2+0.0-0.5)Si8O22(OH)2. Tremolite forms by metamorphism of sediments rich in dolomite and quartz. Tremolite forms a series with actinolite and fe ...
File:Wollastonite-chain.png, Inosilicate, unbranched 3-periodic single chain of wollastonite
Wollastonite is a calcium inosilicate mineral ( Ca Si O3) that may contain small amounts of iron, magnesium, and manganese substituting for calcium. It is usually white. It forms when impure limestone or dolomite is subjected to high temperature ...
File:Rhodonite-chain.png, Inosilicate with 5-periodic single chain, rhodonite
Rhodonite is a manganese inosilicate, (Mn, Fe, Mg, Ca)SiO3 and member of the pyroxenoid group of minerals, crystallizing in the triclinic system. It commonly occurs as cleavable to compact masses with a rose-red color (the name comes from the G ...
File:Pellyite-chain.png, Inosilicate with cyclic branched 8-periodic chain, pellyite
Phyllosilicates
Phyllosilicates (from Greek 'leaf'), or sheet silicates, form parallel sheets of silicate tetrahedra with or a 2:5 ratio. The Nickel–Strunz classification is 09.E. All phyllosilicate minerals are hydrated, with eitherwater
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
or hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydro ...
groups attached.
Examples include:
*Serpentine subgroup
Serpentine subgroup (part of the kaolinite-serpentine group in the category of phyllosilicates) are greenish, brownish, or spotted minerals commonly found in serpentinite. They are used as a source of magnesium and asbestos, and as decorative ...
**Antigorite
Antigorite is a lamellated, monoclinic mineral in the phylosilicate serpentine subgroup with the ideal chemical formula of (Mg,Fe2+)3Si2O5(OH)4. It is the high-pressure polymorph of serpentine and is commonly found in metamorphosed serpentinite ...
–
**Chrysotile
Chrysotile or white asbestos is the most commonly encountered form of asbestos, accounting for approximately 95% of the asbestos in the United StatesOccupational Safety and Health Administration, U.S. Department of Labor (2007)29 C.F.R.&nb ...
–
** Lizardite –
* Clay minerals group
**1:1 clay minerals (TO)
***Halloysite
Halloysite is an aluminosilicate clay mineral with the empirical formula Al2Si2O5(OH)4. Its main constituents are oxygen (55.78%), silicon (21.76%), aluminium (20.90%), and hydrogen (1.56%). Halloysite typically forms by hydrothermal alteration ...
–
*** Kaolinite –
**2:1 clay minerals (TOT)
***Pyrophyllite
Pyrophyllite is a phyllosilicate mineral composed of aluminium silicate hydroxide: Al2Si4O10(OH)2. It occurs in two forms (habits): crystalline folia and compact masses; distinct crystals are not known.
The folia have a pronounced pearly luste ...
–
***Talc
Talc, or talcum, is a clay mineral, composed of hydrated magnesium silicate with the chemical formula Mg3Si4O10(OH)2. Talc in powdered form, often combined with corn starch, is used as baby powder. This mineral is used as a thickening agent a ...
–
***Illite
Illite is a group of closely related non-expanding clay minerals. Illite is a secondary mineral precipitate, and an example of a phyllosilicate, or layered alumino-silicate. Its structure is a 2:1 sandwich of silica tetrahedron (T) – alumina ...
–
***Montmorillonite
Montmorillonite is a very soft phyllosilicate group of minerals that form when they precipitate from water solution as microscopic crystals, known as clay. It is named after Montmorillon in France. Montmorillonite, a member of the smectite gro ...
(smectite) –
*** Chlorite –
***Vermiculite
Vermiculite is a hydrous phyllosilicate mineral which undergoes significant expansion when heated. Exfoliation occurs when the mineral is heated sufficiently, and commercial furnaces can routinely produce this effect. Vermiculite forms by the we ...
–
**Other clay minerals
***Sepiolite
Sepiolite, also known in English by the German name meerschaum ( , ; ; meaning "sea foam"), is a soft white clay mineral, often used to make tobacco pipes (known as meerschaum pipes). A complex magnesium silicate, a typical chemical formula f ...
–
***Palygorskite
Palygorskite or attapulgite is a magnesium aluminium phyllosilicate with the chemical formula ) that occurs in a type of clay soil common to the Southeastern United States. It is one of the types of fuller's earth. Some smaller deposits of thi ...
(or attapulgite) –
* Mica group
** Biotite –
** Fuchsite –
**Muscovite
Muscovite (also known as common mica, isinglass, or potash mica) is a hydrated phyllosilicate mineral of aluminium and potassium with formula K Al2(Al Si3 O10)( F,O H)2, or ( KF)2( Al2O3)3( SiO2)6( H2O). It has a highly perfect basal cleavag ...
–
**Phlogopite
Phlogopite is a yellow, greenish, or reddish-brown member of the mica family of phyllosilicates. It is also known as magnesium mica.
Phlogopite is the magnesium endmember of the biotite solid solution series, with the chemical formula KMg3AlSi3O ...
–
**Lepidolite
Lepidolite is a lilac-gray or rose-colored member of the mica group of minerals with chemical formula . It is the most abundant lithium-bearing mineral and is a secondary source of this metal. It is the major source of the alkali metal rubidi ...
–
**Margarite
Margarite is a calcium rich member of the mica group of the phyllosilicates with formula: Ca Al2(Al2 Si2) O10(O H)2. It forms white to pinkish or yellowish gray masses or thin laminae. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system. It typical ...
–
**Glauconite
Glauconite is an iron potassium phyllosilicate ( mica group) mineral of characteristic green color which is very friable and has very low weathering resistance.
It crystallizes with a monoclinic geometry. Its name is derived from the Gre ...
–
muscovite
Muscovite (also known as common mica, isinglass, or potash mica) is a hydrated phyllosilicate mineral of aluminium and potassium with formula K Al2(Al Si3 O10)( F,O H)2, or ( KF)2( Al2O3)3( SiO2)6( H2O). It has a highly perfect basal cleavag ...
(red: Si, blue: O)
File:Apophyllite.sheet.png, Phyllosilicate, single net of tetrahedra with 4-membered rings, apophyllite
The name apophyllite refers to a specific group of phyllosilicates, a class of minerals. Originally, the group name referred to a specific mineral, but was redefined in 1978 to stand for a class of minerals of similar chemical makeup that compris ...
-(KF)-apophyllite-(KOH) series
File:Pyrosmalite.sheet.png, Phyllosilicate, single tetrahedral nets of 6-membered rings, pyrosmalite-(Fe)-pyrosmalite-(Mn) series
File:Zeophyllite.sheet.png, Phyllosilicate, single tetrahedral nets of 6-membered rings, zeophyllite
File:Carletonite.sheet.png, Phyllosilicate, double nets with 4- and 6-membered rings, carletonite
Tectosilicates

 Tectosilicates, or "framework silicates," have a three-dimensional framework of silicate
Tectosilicates, or "framework silicates," have a three-dimensional framework of silicate tetrahedra
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the o ...
with in a 1:2 ratio. This group comprises nearly 75% of the crust of the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
. Tectosilicates, with the exception of the quartz group, are aluminosilicate
Aluminosilicate minerals ( IMA symbol: Als) are minerals composed of aluminium, silicon, and oxygen, plus countercations. They are a major component of kaolin and other clay minerals.
Andalusite, kyanite, and sillimanite are naturall ...
s. The Nickel–Strunz classifications are 09.F and 09.G, 04.DA (Quartz/ silica family). Examples include:
*3D-Silicates, quartz family
**Quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical ...
–
**Tridymite
Tridymite is a high-temperature polymorph of silica and usually occurs as minute tabular white or colorless pseudo-hexagonal crystals, or scales, in cavities in felsic volcanic rocks. Its chemical formula is Si O2. Tridymite was first describe ...
–
**Cristobalite
Cristobalite is a mineral polymorph of silica that is formed at very high temperatures. It has the same chemical formula as quartz, SiO2, but a distinct crystal structure. Both quartz and cristobalite are polymorphs with all the members of the ...
–
**Coesite
Coesite is a form ( polymorph) of silicon dioxide Si O2 that is formed when very high pressure (2–3 gigapascals), and moderately high temperature (), are applied to quartz. Coesite was first synthesized by Loring Coes Jr., a chemist at the ...
–
** Stishovite –
** Moganite –
**Chalcedony
Chalcedony ( , or ) is a cryptocrystalline form of silica, composed of very fine intergrowths of quartz and moganite. These are both silica minerals, but they differ in that quartz has a trigonal crystal structure, while moganite is monocli ...
–
*Tectosilicates, feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) felds ...
group
**Alkali feldspars (potassium feldspars)
***Microcline
Microcline (KAlSi3O8) is an important igneous rock-forming tectosilicate mineral. It is a potassium-rich alkali feldspar. Microcline typically contains minor amounts of sodium. It is common in granite and pegmatites. Microcline forms during slo ...
–
***Orthoclase
Orthoclase, or orthoclase feldspar ( endmember formula K Al Si3 O8), is an important tectosilicate mineral which forms igneous rock. The name is from the Ancient Greek for "straight fracture," because its two cleavage planes are at right angles ...
–
***Anorthoclase
The mineral anorthoclase ((Na,K)AlSi3O8) is a crystalline solid solution in the alkali feldspar series, in which the sodium-aluminium silicate member exists in larger proportion. It typically consists of between 10 and 36 percent of KAlSi3O8 and ...
–
***Sanidine
Sanidine is the high temperature form of potassium feldspar with a general formula K(AlSi3O8). Sanidine is found most typically in felsic volcanic rocks such as obsidian, rhyolite and trachyte. Sanidine crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal sys ...
–
**Plagioclase
Plagioclase is a series of tectosilicate (framework silicate) minerals within the feldspar group. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a continuous solid solution series, more pro ...
feldspars
***Albite
Albite is a plagioclase feldspar mineral. It is the sodium endmember of the plagioclase solid solution series. It represents a plagioclase with less than 10% anorthite content. The pure albite endmember has the formula . It is a tectosilicate ...
–
***Oligoclase
Oligoclase is a rock-forming mineral belonging to the plagioclase feldspars. In chemical composition and in its crystallographic and physical characters it is intermediate between albite ( Na Al Si3 O8) and anorthite ( CaAl2Si2O8). The albite ...
– (Na:Ca 4:1)
***Andesine
Andesine is a silicate mineral, a member of the plagioclase feldspar solid solution series. Its chemical formula is ( Ca, Na)( Al, Si)4 O8, where Ca/(Ca + Na) (% anorthite) is between 30–50%. The formula may be written as Na0.7-0.5Ca0.3-0.5Al ...
– (Na:Ca 3:2)
***Labradorite
Labradorite (( Ca, Na)( Al, Si)4 O8) is a calcium-enriched feldspar mineral first identified in Labrador, Canada, which can display an iridescent effect (schiller).
Labradorite is an intermediate to calcic member of the plagioclase series. It ...
– (Na:Ca 2:3)
*** Bytownite – (Na:Ca 1:4)
*** Anorthite –
*Tectosilicates, feldspathoid
The feldspathoids are a group of tectosilicate minerals which resemble feldspars but have a different structure and much lower silica content. They occur in rare and unusual types of igneous rocks, and are usually not found in rocks containing prim ...
family
**Nosean
Nosean, also known as noselite, is a mineral of the feldspathoid group with formula: Na8 Al6 Si6 O24( SO4). H2O. It forms isometric crystals of variable color: white, grey, blue, green, to brown. It has a Mohs hardness of 5.5 to 6 and a specific ...
–
**Cancrinite
Cancrinite is a complex carbonate and silicate of sodium, calcium and aluminium with the formula Na6 Ca2 O3)2.html" ;"title="carbon">C Coxygen">O3)2"> O3)2">aluminum">Al6silicon.html"_;"title="luminum.html"_;"title="oxygen.html"_;"ti_...
_–
**Leucite.html" ;"title="Coxygen">O3)2">aluminum">Al6silicon.html" ;"title="luminum.html" ;"title="oxygen.html" ;"ti ...Chabazite
Chabazite ()The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) - p. 300 "chabazite /'kabəzʌɪt/ noun "A colourless, pink or yellow zeolite mineral, typically occurring as rhombohedral crystals.". is a tectosilicate mineral of the zeolite group, clos ...
–
**Heulandite
Heulandite is the name of a series of tecto-silicate minerals of the zeolite group. Prior to 1997, heulandite was recognized as a mineral species, but a reclassification in 1997 by the International Mineralogical Association changed it to a ser ...
–
**Stilbite
Stilbite is the name of a series of tectosilicate minerals of the zeolite group. Prior to 1997, stilbite was recognized as a mineral species, but a reclassification in 1997 by the International Mineralogical Association changed it to a series na ...
–
**Scolecite
Scolecite is a tectosilicate mineral belonging to the zeolite group; it is a hydrated calcium silicate, Ca Al2 Si3 O10· 3H2O. Only minor amounts of sodium and traces of potassium substitute for calcium. There is an absence of barium, stron ...
–
**Mordenite
Mordenite is a zeolite mineral with the chemical formula, ( Ca, Na2, K2) Al2 Si10 O24·7 H2O. and it is one of the six most abundant zeolites and is used commercially.
It was first described in 1864 by Henry How. He named it after the small co ...
–
**Analcime
Analcime (; ) or analcite is a white, gray, or colorless tectosilicate mineral. Analcime consists of hydrated sodium aluminium silicate in cubic crystalline form. Its chemical formula is Na Al Si2 O6· H2O. Minor amounts of potassium and calci ...
–
See also
* * *References
External links
Mindat.org, Dana classification
Webmineral : Dana's New Silicate Classification
{{Authority control ja:ケイ酸塩鉱物 pl:Krzemiany