Solar power in California on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Solar power in California includes utility-scale
 * The Desert Sunlight Solar Farm is a 550 MW solar power plant in Riverside County, that uses thin-film solar CdTe-modules made by First Solar. The plant was completed in December 2014.
* The Imperial Valley Solar Project is a 99 MW power station, located in Imperial County.
* The
* The Desert Sunlight Solar Farm is a 550 MW solar power plant in Riverside County, that uses thin-film solar CdTe-modules made by First Solar. The plant was completed in December 2014.
* The Imperial Valley Solar Project is a 99 MW power station, located in Imperial County.
* The
 California has several large concentrated solar power plants.
The Ivanpah Solar Electric Generating System (392 MW), located southwest of
California has several large concentrated solar power plants.
The Ivanpah Solar Electric Generating System (392 MW), located southwest of
In California’s Mojave Desert, Solar-Thermal Projects Take Off
''Yale Environment 360'', 27 October 2010. The Genesis Solar Energy Project is an operational 250 MW solar thermal power station located in Riverside County, California. It features a
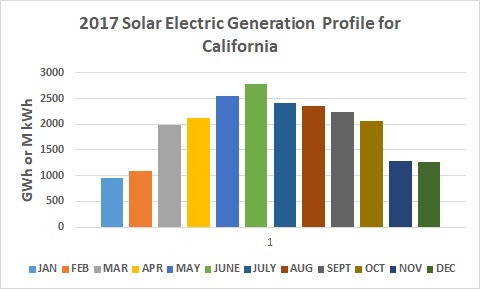
 Beginning with the 2014 data year, the Energy Information Administration has estimated distributed solar photovoltaic generation and distributed solar photovoltaic capacity. These non-utility scale estimates project that, California, generated the following additional solar energy.
Beginning with the 2014 data year, the Energy Information Administration has estimated distributed solar photovoltaic generation and distributed solar photovoltaic capacity. These non-utility scale estimates project that, California, generated the following additional solar energy.
. of new, solar-produced electricity by 2016 — moving the state toward a cleaner energy future and helping lower the cost of solar systems for consumers. The California Solar Initiative has "a total budget of $2.167 billion between 2007 and 2016 and a goal to install approximately 1,940 MW of new solar generation capacity." The California Solar Initiative
According to the CPUC, homeowners, businesses, and local governments installed 158 MW of solar photovoltaics (PV) in 2008, doubling the 78 MW installed in 2007, giving California a cumulative total of 441 MW of distributed solar PV systems, the highest in the country. As of August 2016, 4,216 MW have been installed in 537,647 projects. The average cost of systems less than 10 kW is $5.33/watt and $4.38/watt for systems over 10 kW. Of these, 3,391 MW were rooftop solar in 2015.2016 State of the Interconnection
page 10-14 + 18-23. '' WECC'', 2016
Archive
/ref> The CSI initially offered cash incentives on solar PV systems of up to $2.50 per AC watt. These incentives, combined with federal tax incentives, could cover up to 50% of the total cost of a solar system. The incentive program was designed so that the incentives would reduce in steps based on the amount of solar installed in each of 6 categories. There are separate steps for residential and non-residential customers in the territories of each of the State's 3 investor-owned utilities. As of July 2012, the rebates range from $0.20 to $0.35 per AC watt for residential and commercial systems and from $0.70 to $1.10 for systems for non-profits and government entities. There are many financial incentives to support the use of renewable energy in other US states. CSI provides more than $2 billion worth of incentives to customers for installing photovoltaic, and electricity displacing solar thermal systems in the three California Investor-Owned Utilities service territories. The program was authorized by the California Public Utilities Commission and by the Senate Bill 1 (SB 1): * Decision (D.) 06-01-024, in collaboration with the California Energy Commission, with the goal of installing 3,000 MW of new solar facilities in California's homes and businesses by 2017. * On August 21, 2006, the Governor signed SB1, which directs the CPUC and the CEC to implement the CSI program consistent with specific requirements and budget limits set forth in legislation. Responsibility for administration of the CSI Program is shared by Investor-Owned Utilities: * Pacific Gas and Electric Company – PG&E customers; * Southern California Edison Company – SCE customers; * California Center for Sustainable Energy – SDG&E customers. Residential installation starts in early 2007 fell off sharply in SCE territory because of the disincentives inherent in SB1, requiring time-of-use (TOU) tariffs, with the result that homeowners who install panels may find their electric bill increasing rather than decreasing. The governor and legislature moved quickly to pass AB1714 (June 2007) to delay the implementation of this rule until 2009.
 California has a favorable net metering law, being one of five states to receive an A in 2007, while five states received an F, in an evaluation of the 38 states plus
California has a favorable net metering law, being one of five states to receive an A in 2007, while five states received an F, in an evaluation of the 38 states plus
Go Solar CaliforniaGo Solar CaliforniaCalifornia Energy CommissionCalifornia Solar Energy Industries AssociationNorthern California Solar Energy AssociationSolar CaliforniaRenewables Portfolio StandardCalifornia's Renewable Energy Law Lives!
(California only)
Google Map of Operating and Under Construction California Utility Scale PVNREL solar insolation map
{{Energy in the USA
solar power plant
A photovoltaic power station, also known as a solar park, solar farm, or solar power plant, is a large-scale grid-connected photovoltaic power system (PV system) designed for the supply of merchant power. They are different from most building- ...
s as well as local distributed generation
Distributed generation, also distributed energy, on-site generation (OSG), or district/decentralized energy, is electrical generation and storage performed by a variety of small, grid-connected or distribution system-connected devices referred to ...
, mostly from rooftop photovoltaics
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially ...
. It has been growing rapidly because of high insolation, community support, declining solar costs, and a Renewable Portfolio Standard which requires that 33% of California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
's electricity come from renewable resource
A renewable resource, also known as a flow resource, is a natural resource which will replenish to replace the portion depleted by usage and consumption, either through natural reproduction or other recurring processes in a finite amount of ti ...
s by 2020, and 60% by 2030. Much of this is expected to come from solar power via photovoltaic facilities or concentrated solar power facilities.
In 2019, the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) reported a total of 27,400 MW of solar capacity installed (3,125 MW in 2019 alone), making up 20% of all electricity produced in the state. In October 2020, California ranked as the highest solar power generating state in the nation, producing enough solar capacity to power 8.4 million homes in the state. In 2020, SEIA estimated that California will increase its solar capacity by over 19,000 MW over the next five years, second behind Texas at 20,000 MW.
History
Over the last 20 years, California has been home to a number of the world's largest solar facilities, many of which are located in theMojave Desert
The Mojave Desert ( ; mov, Hayikwiir Mat'aar; es, Desierto de Mojave) is a desert in the rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada mountains in the Southwestern United States. It is named for the indigenous Mojave people. It is located primarily ...
. In 1991, the 354 MW Solar Energy Generating Systems
Solar Energy Generating Systems (SEGS) is a concentrated solar power plant in California, United States. With the combined capacity from three separate locations at 354 megawatt (MW), it was once the world's second largest solar thermal energy g ...
plant (located in San Bernardino County, California
San Bernardino County (), officially the County of San Bernardino, is a county located in the southern portion of the U.S. state of California, and is located within the Inland Empire area. As of the 2020 U.S. Census, the population was 2,181, ...
) held the title until being bested by the 392 MW Ivanpah Solar Electric Generating System, a solar thermal plant located in San Bernardino County near the Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a state in the Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th-most extensive, ...
border.
The early to mid 2010s saw the sharpest increase in solar development. By the end of 2013, California had 490 MW of concentrated solar power and 5,183 MW of photovoltaics capacity in operation.
In 2014, the 550 MW Topaz Solar Farm became the new "world's largest operational" solar facility and went online in San Luis Obispo County
San Luis Obispo County (), officially the County of San Luis Obispo, is a county on the Central Coast of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 282,424. The county seat is San Luis Obispo.
Junípero Serra founded the Miss ...
, California. A second 550 MW facility, Desert Sunlight Solar Farm, also went online in Riverside County
Riverside County is a county located in the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 2,418,185, making it the fourth-most populous county in California and the 10th-most populous in the Uni ...
in 2014 and was constructed by First Solar
First Solar, Inc. is an American manufacturer of solar panels, and a provider of utility-scale PV power plants and supporting services that include finance, construction, maintenance and end-of-life panel recycling. First Solar uses rigid thi ...
. Both these were superseded, however, by the Solar Star photovoltaic project that went online with 579 MW in June 2015 in Antelope Valley, California, which is located in southern Kern County
Kern County is a county located in the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 909,235. Its county seat is Bakersfield.
Kern County comprises the Bakersfield, California, Metropolitan statistical area. The county sp ...
. While California hosted the three largest photovoltaic facilities in the world (as of July 2015), there are yet several proposals for even larger facilities seeking regulatory approval in California, such as the 2.7 GW Westlands Solar Park
The Westlands Solar Park is large-scale solar power project in Kings County south of Fresno, California. It intends to build many photovoltaic power plants with a capacity totaling upwards of 2,000 megawatts (MW), larger than the world's largest ...
.
In December 2017, the Solar on Multifamily Affordable Housing (SOMAH) program was approved by the California Public Utilities Commission
The California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC or PUC) is a regulatory agency that regulates privately owned public utilities in the state of California, including electric power, telecommunications, natural gas and water companies. In addition ...
. The program will allocate one billion dollars from the state's greenhouse gas cap-and-trade program over the following decade to incentivize owners of affordable, multi-family buildings to install solar, with a goal of adding 300 MW of capacity.
California also leads the nation in the number of homes which have solar panels installed, totaling over 230,000. Many were installed because of the Million Solar Roof
Initiative.
In May 2018, the 5 commissioners of the California Energy Commission
The California Energy Commission, formally the Energy Resources Conservation and Development Commission, is the primary energy policy and planning agency for California.
Created in 1974 and headquartered in Sacramento, the Commission'core respon ...
(CEC) voted unanimously to require that nearly all new homes (both single-family and multi-family) under four stories in the state be built with photovoltaic solar panes. Developers can pursue community solar projects instead of rooftop panel systems for individual properties if they receive approval from the CEC and local utility company. In early 2020, the CEC decided to give developers the option to build new homes that retrieve solar power from rooftop solar panels or from the Sacramento Municipality Utility District (SMUD)'s offsite solar installations.
The size of the systems to be installed is to be somewhat limited and is intended to perform a supplementary role. Builders will be able to decrease the size of the system further if they incorporate power storage into the home. The justification for the smaller size of the systems is due to the high amount of solar power produced by the grid during the daytime, much of which is attributable to California's extensive use of utility grade solar systems. This overlap would devalue a more powerful home solar system, as the energy it would displace from the grid would be largely solar generated.
Housing affordability is also a concern with this measure, an area where California already struggles greatly. According to a 2017 survey conducted by the U.S. Census Bureau, 37.8% of California homeowners with mortgages are "cost-burdened," with housing costs exceeding 30% of the household income, and 16.3% face housing costs exceeding 50% of the household income. The CEC predicts that the requirement of photovoltaic panels will increase the cost of a newly built single-family home by about $40 per month in extra mortgage payments, but eventually save about $80 on electricity costs.'''' The CEC released data showing that the system would more than pay for itself, however charitable organizations such as Habitat for Humanity have expressed their concerns as this will require the organization to receive additional donations in order to pay for the photovoltaic panels that the group would be required to install on every house it builds.
Photovoltaics
In 2011, California's goal to install 3,000 MW of distributed generation by 2016 was expanded to 12,000 MW by 2020. California has more photovoltaics installed than any other federal state, and 48% of the U.S. total in 2010. For the first time in 2008 the installed photovoltaics exceeded the state's 354 MW of solar thermal (CSP). There are plans to build over 15,000 MW of utility scale photovoltaic plants in California. At the end of 2012, small systems of less than 10 kWp were averaging $5.39/W, and large systems of over 500 kWp were averaging $2.77/W. California has the technical potential to install 128.9 GW of rooftop solar panels, which would generate 194,000 GWh/year, about 74% of the total electricity used in California in 2013. This is environmentally desirable because it would conserve large swaths of desert by placing panels atop preexisting structures instead. However, this would supply three to four times peak midday demand, requiring output to be stored or exported on sunny days.Planned
* The Crimson Solar Project is a proposed 350 MW photovoltaic power station to be located southwest ofMesa Verde, California
Mesa Verde (Spanish for "Green Table") is a census-designated place in Riverside County, California. Mesa Verde sits at an elevation of . The 2010 United States census reported Mesa Verde's population was 1,023.
Geography
According to the United ...
and will include an energy storage project. The Bureau of Land Management gave final approval to Sonoran West Solar Holdings to build the installation on May 3, 2021.
* The 400 MW Rexford solar farm in Tulare County
Tulare County ( ) is a county located in the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 473,117. The county seat is Visalia. The county is named for Tulare Lake, once the largest freshwater lake west of the Great Lakes. ...
(with 180MW/540MWh of energy storage) received a 15-year power purchase agreement
A power purchase agreement (PPA), or electricity power agreement, is a contract between two parties, one which generates electricity (the seller) and one which is looking to purchase electricity (the buyer). The PPA defines all of the commercial te ...
in 2020, expected operational by 2023.
Under construction
* The Blythe Solar Power Project is a partially completed 485 MW (235 active as of 2020) photovoltaic power station which is located in eastern Riverside County. *The San Pablo Raceway Solar Plant is a 100 MW photovoltaic facility located in Los Angeles County that is in the beginning stages of construction.Operational
 * The Desert Sunlight Solar Farm is a 550 MW solar power plant in Riverside County, that uses thin-film solar CdTe-modules made by First Solar. The plant was completed in December 2014.
* The Imperial Valley Solar Project is a 99 MW power station, located in Imperial County.
* The
* The Desert Sunlight Solar Farm is a 550 MW solar power plant in Riverside County, that uses thin-film solar CdTe-modules made by First Solar. The plant was completed in December 2014.
* The Imperial Valley Solar Project is a 99 MW power station, located in Imperial County.
* The California Valley Solar Ranch
The California Valley Solar Ranch (CVSR) is a 250 megawatt (MW AC) photovoltaic power plant in the Carrizo Plain, northeast of California Valley. The project is owned by NRG Energy, and SunPower is the EPC contractor and technology provider ...
(CVSR) is a 250 MW solar photovoltaic power plant, built by SunPower
SunPower is an American provider of photovoltaic solar energy generation systems and battery energy storage products, primarily for residential customers. The company, headquartered in San Jose, California, was founded in 1985 by Richard Swa ...
in the Carrizo Plain, northeast of California Valley.
* The Mount Signal Solar project was completed near the Mexican border in May 2014. The installed PV capacity of the solar farm amounts to 265.7 MW (206 MWAC).
* The Topaz Solar Farm is a 550 MW power station located in San Luis Obispo County. It was completed in November 2014 and was the world's largest PV power plant at the time.
* The Desert Stateline Solar Facility is a 300 MW power plant near the Nevada border in San Bernardino County.
* The Redwood Solar Cluster is a group of 4 smaller solar generating stations that amount to 100 MW located in Kern County. The final phase was completed in March 2018.
* The California Flats Solar Project
The California Flats Solar Project is a 280 megawatt (MW AC) photovoltaic power station on Hearst Communications' Jack Ranch in the Cholame Hills area of southeastern Monterey County, California, near the San Luis Obispo, Kings, and Fresno C ...
is a 280 MW photovoltaic power plant located in Monterey County, which was opened in May 2019.
*The Blythe Mesa Solar Power Project.
*The Maverick Solar Cluster is a group of 4 operational single-axis tracker photovoltaic power plants. The first part opened in Riverside County
Riverside County is a county located in the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 2,418,185, making it the fourth-most populous county in California and the 10th-most populous in the Uni ...
in January, 2021. The group was completed in August 2022 at 620 MW dc and 457 MW ac, with a 50MW/200MWh battery energy storage system (BESS). They are part of the larger Palen Solar Project.
Solar thermal power
 California has several large concentrated solar power plants.
The Ivanpah Solar Electric Generating System (392 MW), located southwest of
California has several large concentrated solar power plants.
The Ivanpah Solar Electric Generating System (392 MW), located southwest of Las Vegas
Las Vegas (; Spanish for "The Meadows"), often known simply as Vegas, is the 25th-most populous city in the United States, the most populous city in the state of Nevada, and the county seat of Clark County. The city anchors the Las Vegas ...
and developed by BrightSource Energy
BrightSource Energy, Inc. is an Oakland, California based, corporation that designs, builds, finances, and operates utility-scale solar power plants.
Greentech Media ranked BrightSource as one of the top 10 greentech startups in the world in 200 ...
and Bechtel, is the world's largest solar thermal power project.
The project has received a $1.375 billion loan guarantee from the United States Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and manages the research and development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons in the United Stat ...
.
It deploys 347,000 heliostat mirrors focusing solar energy on boilers located on centralized solar power towers.Todd WoodyIn California’s Mojave Desert, Solar-Thermal Projects Take Off
''Yale Environment 360'', 27 October 2010. The Genesis Solar Energy Project is an operational 250 MW solar thermal power station located in Riverside County, California. It features a
parabolic trough
A parabolic trough is a type of solar thermal collector that is straight in one dimension and curved as a parabola in the other two, lined with a polished metal mirror. The sunlight which enters the mirror parallel to its plane of symmetry is foc ...
design and is run by NextEra Energy Resources
NextEra Energy Resources, LLC (NEER) is a wholesale electricity supplier based in Juno Beach, Florida. NEER is a subsidiary of NextEra Energy (), a Fortune 200 company. Prior to 2009, NextEra Energy Resources was known as FPL Energy.
NextEra ...
.
Operational
* TheSolar Energy Generating Systems
Solar Energy Generating Systems (SEGS) is a concentrated solar power plant in California, United States. With the combined capacity from three separate locations at 354 megawatt (MW), it was once the world's second largest solar thermal energy g ...
, is a 361 MW (was 394 MW until 2014) parabolic trough concentrated solar power station located in the Mojave Desert completed in 1990.
* The Genesis Solar Energy Project, is a 280 MW parabolic trough concentrated solar power station located in the Mojave Desert completed in 2013.
* The Ivanpah Solar Power Facility, is a 392 MW solar power tower concentrated solar power station located in the Mojave Desert completed in 2014.
* The Mojave Solar Project
The Mojave Solar Project (MSP) is a concentrated solar power (CSP) facility in the Mojave Desert in California, about northwest of Barstow. Surrounding the hamlet of Lockhart, Mojave Solar is adjacent to Harper Lake and the SEGS VIII–IX solar ...
, is a 280 MW parabolic trough concentrated solar power station located in the Mojave Desert completed in 2014.
Total operational installed gross power is 1,313 MW (1346 MW until 2014). Production in 2015 was 2,309 GWh, 71.2% of U.S. total solar thermal generation.
Planned
South Belridge Oil Field, near Bakersfield, California, a solar EOR facility that is projected to eliminate 376,000 metric tons of carbon emissions. It was announced in November 2017 as a joint venture between GlassPoint Solar and Aera Energy. In 2012, the Bureau of Land Management gave priority status to 5 solar project proposals in California. The 750 MW McCoy Solar Energy Project was proposed by NextEra, though only 1/3 of that wattage was ever installed. The remaining development of the project is currently on hold. The 100 MW Desert Harvest project has been proposed by enXco. The 664 MW Calico Solar Energy Project was redesigned by K Power but later abandoned.Generation

 Beginning with the 2014 data year, the Energy Information Administration has estimated distributed solar photovoltaic generation and distributed solar photovoltaic capacity. These non-utility scale estimates project that, California, generated the following additional solar energy.
Beginning with the 2014 data year, the Energy Information Administration has estimated distributed solar photovoltaic generation and distributed solar photovoltaic capacity. These non-utility scale estimates project that, California, generated the following additional solar energy.
Milestones
On May 13, 2017, theCalifornia Independent System Operator
The California Independent System Operator (CAISO) is a non-profit Independent System Operator (ISO) serving California. It oversees the operation of California's bulk electric power system, transmission lines, and electricity market generated a ...
(CAISO) reported that the state had broken a new renewable energy record, with non-hydro renewables providing 67.2% of the total electricity on the ISO's grid, with another 13.5% being provided by hydro. The ISO reported that solar was providing approximately 17.2% of the total electricity.
On March 5, 2018, at around 1 PM, utility grade solar energy met 50% of California's total electrical power demand for the first time.
On May 2, 2022, CAISO reported that California's electrical demands were met 100% by renewable energy sources for the first time. This was maintained for nearly 15 minutes. During this period, 12,391 of the 18,000 megawatts (68.8%) of statewide electrical demand were generated by PV systems alone.
Government support
Renewable Portfolio Standard
Solar power in California has been growing rapidly. The most recent Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS), SB 100 effective January 1, 2019, requires that 60% of California's electricity come fromrenewable resource
A renewable resource, also known as a flow resource, is a natural resource which will replenish to replace the portion depleted by usage and consumption, either through natural reproduction or other recurring processes in a finite amount of ti ...
s by 2030, and 100% of its electricity from carbon-free sources by 2045. Much of this is expected to come from solar power.
According to a recent report by the California Public Utilities Commission, California failed to meet the 20% renewables by 2010 target. Pacific Gas and Electric Company and Southern California Edison
Southern California Edison (or SCE Corp), the largest subsidiary of Edison International, is the primary electricity supply company for much of Southern California. It provides 15 million people with electricity across a service territory of ap ...
were the closest to meeting the goal. PG&E generated 17.7% of the electricity it sold in 2010 from renewable sources while SCE was the closest to hitting the RPS goal by producing 19.4% of its electricity from renewable sources in 2010. San Diego Gas & Electric
San Diego Gas & Electric (SDG&E) provides natural gas and electricity to San Diego County and southern Orange County in southwestern California, United States. It is owned by Sempra, a Fortune 500 energy services holding company based in San Di ...
, on the other hand, generated only 11.9% of its electricity from renewable sources in 2010.
As of October 2020, California had 31,288 MW of solar and 5,830 MW of wind farms. California adopted feed-in tariffs, a tool similar to what Europe has been using, to encourage the solar power industry. Proposals were raised aiming to create a small-scale solar market in California that brings the benefits of the German market, such as distributed generation
Distributed generation, also distributed energy, on-site generation (OSG), or district/decentralized energy, is electrical generation and storage performed by a variety of small, grid-connected or distribution system-connected devices referred to ...
, which avoids the need for transmission because power is generated close to where it is used, and avoid the drawbacks such as excessively high payments that could become a burden on utility customers.
California Solar Initiative
The California Solar Initiative is a 2006 initiative to install 3,000 MW of additional solar power by 2016. Included in it is the Million Solar Roof Initiative. In 2011, this goal was expanded to 12,000 MW by 2020. As part of Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger's Million Solar Roofs Program, California has set a goal to create 1,940 megawattsAbout the California Solar Initiative. of new, solar-produced electricity by 2016 — moving the state toward a cleaner energy future and helping lower the cost of solar systems for consumers. The California Solar Initiative has "a total budget of $2.167 billion between 2007 and 2016 and a goal to install approximately 1,940 MW of new solar generation capacity." The California Solar Initiative
According to the CPUC, homeowners, businesses, and local governments installed 158 MW of solar photovoltaics (PV) in 2008, doubling the 78 MW installed in 2007, giving California a cumulative total of 441 MW of distributed solar PV systems, the highest in the country. As of August 2016, 4,216 MW have been installed in 537,647 projects. The average cost of systems less than 10 kW is $5.33/watt and $4.38/watt for systems over 10 kW. Of these, 3,391 MW were rooftop solar in 2015.2016 State of the Interconnection
page 10-14 + 18-23. '' WECC'', 2016
Archive
/ref> The CSI initially offered cash incentives on solar PV systems of up to $2.50 per AC watt. These incentives, combined with federal tax incentives, could cover up to 50% of the total cost of a solar system. The incentive program was designed so that the incentives would reduce in steps based on the amount of solar installed in each of 6 categories. There are separate steps for residential and non-residential customers in the territories of each of the State's 3 investor-owned utilities. As of July 2012, the rebates range from $0.20 to $0.35 per AC watt for residential and commercial systems and from $0.70 to $1.10 for systems for non-profits and government entities. There are many financial incentives to support the use of renewable energy in other US states. CSI provides more than $2 billion worth of incentives to customers for installing photovoltaic, and electricity displacing solar thermal systems in the three California Investor-Owned Utilities service territories. The program was authorized by the California Public Utilities Commission and by the Senate Bill 1 (SB 1): * Decision (D.) 06-01-024, in collaboration with the California Energy Commission, with the goal of installing 3,000 MW of new solar facilities in California's homes and businesses by 2017. * On August 21, 2006, the Governor signed SB1, which directs the CPUC and the CEC to implement the CSI program consistent with specific requirements and budget limits set forth in legislation. Responsibility for administration of the CSI Program is shared by Investor-Owned Utilities: * Pacific Gas and Electric Company – PG&E customers; * Southern California Edison Company – SCE customers; * California Center for Sustainable Energy – SDG&E customers. Residential installation starts in early 2007 fell off sharply in SCE territory because of the disincentives inherent in SB1, requiring time-of-use (TOU) tariffs, with the result that homeowners who install panels may find their electric bill increasing rather than decreasing. The governor and legislature moved quickly to pass AB1714 (June 2007) to delay the implementation of this rule until 2009.
Net metering
 California has a favorable net metering law, being one of five states to receive an A in 2007, while five states received an F, in an evaluation of the 38 states plus
California has a favorable net metering law, being one of five states to receive an A in 2007, while five states received an F, in an evaluation of the 38 states plus Washington D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, Na ...
with net metering. IREC best practices, based on experience, recommends no limits to net metering, individual or aggregate, and perpetual roll over of kWh credits. As California was rapidly approaching the 5% aggregate limit, a May 24, 2012 ruling by the CPUC clarified the calculation of the limit, and requested a report on the cost of net metering. California subsequently uncapped the net metering program. Typically states have raised or eliminated their aggregate limits before they were reached. By 2011, 16 states including California received an A for net metering.
The California solar deployment has increased its duck curve
The duck curve is a graph of power production over the course of a day that shows the timing imbalance between peak demand and renewable energy production. Used in utility-scale electricity generation, the term was coined in 2012 by the Cali ...
(power demand for traditional power plants) to the point where large power plants are turned down to minimum during the day, while requiring large and fast power ramp
In telecommunications, power ramp is the way in which the signal increases ("power-on ramp") or falls off ("power-down ramp"), which may result in spectral splatter.
See also
* Soft start
* Power gating
* Voltage scaling
Dynamic voltage scalin ...
ing by load following
A load-following power plant, regarded as producing mid-merit or mid-priced electricity, is a power plant that adjusts its power output as demand for electricity fluctuates throughout the day. Load-following plants are typically in between base l ...
and peaker plants to supply peak demand
Peak demand on an electrical grid is simply the highest electrical power demand that has occurred over a specified time period (Gönen 2008). Peak demand is typically characterized as annual, daily or seasonal and has the unit of power.
Peak dem ...
in the evening when the sun has gone down. Several methods are being developed to cope with the change. Time-of-use pricing is being rolled out, and has been effective in Hawaii.
Mandatory solar power in new homes
In March 2008, Culver City established the first in the nation mandatory solar photovoltaic requirement, which requires an installation of 1 KW of solar photovoltaic power per of new or major remodeled commercial building area. In March 2013,Lancaster, California
Lancaster is a charter city in northern Los Angeles County, in the Antelope Valley of the western Mojave Desert in Southern California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 173,516, making Lancaster the 153rd largest city in the United ...
became the first U.S. city to mandate the inclusion of solar panels on new homes, requiring that "every new housing development must average 1 kilowatt per house."
In May 2013, Sebastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
followed suit, requiring new buildings include either 2 W/sq ft (21.7 W/m2) of insulated building space of photovoltaics, or enough to provide 75% of the expected annual electricity use.
Since January 1, 2014 California law requires all new buildings less than ten stories tall be "solar ready".
In April 2016, San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17th ...
mandated that all new buildings less than ten stories tall include solar panels or solar water heating covering at least 15% of the roof, beginning January 1, 2017.
In 2018, the State of California Building Standards Commission approved solar installation requirements for all new residential buildings with three stories or fewer. This requirement took effect in 2020.
Streamlined permitting
California governorJerry Brown
Edmund Gerald Brown Jr. (born April 7, 1938) is an American lawyer, author, and politician who served as the 34th and 39th governor of California from 1975 to 1983 and 2011 to 2019. A member of the Democratic Party, he was elected Secretary of ...
signed a streamlined permitting bill (AB 2188) for residential solar systems on September 22, 2014. AB 2188 has four major provisions designed to reduce red-tape associated with local solar permits and requires that, by the end of September 2015, all California cities and counties must "adopt an ordinance that creates an expedited, streamlined permitting process for residential rooftop solar energy systems of less than 10 kilowatts in size."
Research and industry reports project the bill could reduce the cost of installing a typical residential solar system in the state by over $1,000.
Alameda County solar financing
Using a 20-year property assessment known as PACE financing, the city of Berkeley had a successful pilot program from 2008 to 2009 as the first city in the country to allow residents to obtain solar power without any initial payment. In the plan, property owners paid as much in increased property taxes as they save in energy costs, allowing them to install the panels for free at no cost to the city. Thirty eight projects are being installed for the pilot stage of the program. PACE financing has spread to 28 states, but is on hold in many due to objections byFreddie Mac
The Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation (FHLMC), commonly known as Freddie Mac, is a publicly traded, government-sponsored enterprise (GSE), headquartered in Tysons Corner, Virginia.Fannie Mae
The Federal National Mortgage Association (FNMA), commonly known as Fannie Mae, is a United States government-sponsored enterprise (GSE) and, since 1968, a publicly traded company. Founded in 1938 during the Great Depression as part of the N ...
, including in Berkeley (which has not continued the pilot as a result). Legislation has been introduced to require acceptance of PACE financing.
City of Los Angeles feed-in tariff
The City of Los Angeles Department of Water and Power initiated a program on January 11, 2013, to pay up to 17 cents/kWh for electricity generated by up to 100 MW of solar power in afeed-in tariff
A feed-in tariff (FIT, FiT, standard offer contract,Couture, T., Cory, K., Kreycik, C., Williams, E., (2010)Policymaker's Guide to Feed-in Tariff Policy Design National Renewable Energy Laboratory, U.S. Dept. of Energy advanced renewable tariff, ...
program.
20 MW is reserved for small projects of less than 150 kW each. The program could be expanded to 150 MW in March.
State challenges with solar power
Energy storage is becoming a more prominent issue because photovoltaic solar panels can only generate electricity during daylight hours and thermal solar installations can only store energy for up to 10 hours, leaving a window in which the state's energy production must be generated from other sources (natural gas, wind, coal, or nuclear). To remedy this, different sorts of power storage solutions have been proposed such as batteries, compressed air, and ice generation. In April 2018,The San Diego Union Tribune
''The San Diego Union-Tribune'' is a metropolitan daily newspaper published in San Diego, California, that has run since 1868.
Its name derives from a 1992 merger between the two major daily newspapers at the time, ''The San Diego Union'' and ...
reported that Recurrent Energy (a subsidiary of Canadian Solar
Canadian Solar Inc. is a publicly traded company that manufactures solar PV modules and runs large scale solar projects.
History
Founded in 2001 in Guelph, Ontario, Canada by Shawn Qu, Canadian Solar (NASDAQ: CSIQ) has subsidiaries in over 2 ...
) had proposed a large battery, a 350 MW system, to be installed alongside the proposed Crimson Solar Project. The battery will match the proposed facility's nameplate capacity, and is several times larger than the 130 MW Hornsdale Power Reserve
Hornsdale Power Reserve is a 150 MW (194 MWh) grid-connected energy storage system owned by Neoen co-located with the Hornsdale Wind Farm in the Mid North region of South Australia, also owned by Neoen.
The original installation in 2017 was the ...
, the largest lithium battery in existence, which was created by Tesla and is located in South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ...
.
Another issue is overproduction which is most common during the summer months. California's solar production was so vast that by 2017, California had to pay Arizona and other states in the region to accept some of its electricity during peak production hours in order to provide relief to its grid.
California also has aggressive goals when it comes to zero emissions vehicles (ZEVs), and the most prominent type is the electric car, which relies on grid power to charge its battery. Plug-in hybrid cars are also very popular in the state. These types of vehicles add to the demand and burden placed on the electrical grid, which was not designed to support the larger electrical loads required by electric vehicles. One potential solution is to bypass most of the grid with the installation of rooftop solar panels for daytime charging and making use of home energy storage at night. Some electric companies will also provide discounted rates for car owners who charge their vehicles at night when demand is lower. Some cars can be programmed to stagger their charging cycle thought the night. This leads to a steady rate of charging instead of a large spike in the early evening when most commuters return home.
Public opinion
The majority of Californians in desert country support large-scale solar development, according to a 2012 survey conducted on behalf ofBrightSource Energy
BrightSource Energy, Inc. is an Oakland, California based, corporation that designs, builds, finances, and operates utility-scale solar power plants.
Greentech Media ranked BrightSource as one of the top 10 greentech startups in the world in 200 ...
. The survey of more than 1,000 people was conducted throughout Imperial, Inyo, Kern, Riverside, San Bernardino counties in California, where many utility-scale solar projects are underway or planned. Survey results showed that nearly four out of five (almost 80 percent) of people strongly supported development of solar power in their communities. The survey also found that the majority of people were concerned with climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
. It also found that two-thirds of respondents think renewable energy is important to California's future and that the state and federal government should help provide incentives for renewable energy projects.
See also
* Wind power in California *Solar power plants in the Mojave Desert
There are several solar power plants in the Mojave Desert which supply power to the electricity grid. Insolation (solar radiation) in the Mojave Desert is among the best available in the United States, and some significant population centers ar ...
*Solar power in the United States
Solar power includes solar farms as well as local distributed generation, mostly on rooftops and increasingly from community solar arrays. In 2021, utility-scale solar power generated 115 terawatt-hours (TWh), or 2.8% of electricity i ...
*Renewable energy in the United States
According to preliminary data from the US Energy Information Administration, renewable energy accounted for about 12.6% of total primary energy consumption and about 19.8% of the domestically produced electricity in the United States in 202 ...
*Solar Cookers International
Solar Cookers International (SCI) is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit, non-governmental organization that works to improve human and environmental health by supporting the expansion of effective carbon-free solar cooking in world regions of greatest need. ...
References
External links
Go Solar California
(California only)
{{Energy in the USA
California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
Energy in California