Soil resistivity on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Soil resistivity is a measure of how much the
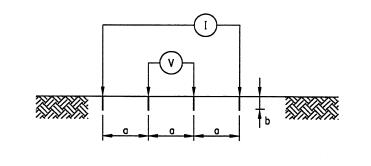 The Wenner four-pin method, as shown in figure above, is the most commonly used technique for soil resistivity measurements.
Using the Wenner method, the apparent soil resistivity value is:
:
where
''ρE'' = measured apparent soil resistivity (Ωm)
''a'' = electrode spacing (m)
''b'' = depth of the electrodes (m)
''RW'' = Wenner resistance measured as "V/I" in Figure (Ω)
If ''b'' is small compared to ''a'', as is the case of probes penetrating the ground only for a short distance (as normally happens), the previous equation can be reduced to:
:
The Wenner four-pin method, as shown in figure above, is the most commonly used technique for soil resistivity measurements.
Using the Wenner method, the apparent soil resistivity value is:
:
where
''ρE'' = measured apparent soil resistivity (Ωm)
''a'' = electrode spacing (m)
''b'' = depth of the electrodes (m)
''RW'' = Wenner resistance measured as "V/I" in Figure (Ω)
If ''b'' is small compared to ''a'', as is the case of probes penetrating the ground only for a short distance (as normally happens), the previous equation can be reduced to:
:
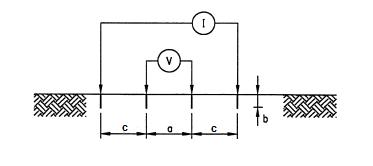 In the Schlumberger method the distance between the voltages probe is ''a'' and the distances from voltages probe and currents probe are ''c'' (see figure above).
Using the Schlumberger method, if ''b'' is small compared to ''a'' and ''c'', and ''c''>''2a'', the apparent soil resistivity value is:
:
where
''ρE'' = measured apparent soil resistance (Ωm)
''a'' = electrode spacing (m)
''b'' = depth of the electrodes (m)
''c'' = electrode spacing (m)
''RS'' = Schlumberger resistance measured as "V/I" in Figure (Ω)
In the Schlumberger method the distance between the voltages probe is ''a'' and the distances from voltages probe and currents probe are ''c'' (see figure above).
Using the Schlumberger method, if ''b'' is small compared to ''a'' and ''c'', and ''c''>''2a'', the apparent soil resistivity value is:
:
where
''ρE'' = measured apparent soil resistance (Ωm)
''a'' = electrode spacing (m)
''b'' = depth of the electrodes (m)
''c'' = electrode spacing (m)
''RS'' = Schlumberger resistance measured as "V/I" in Figure (Ω)
 The conversion between values measured using the Schlumberger and Wenner methods is possible only in an approximate way. In any cases, for both Wenner and Schlumberger methods the electrode spacing between the currents probe corresponds to the depth of soil investigation and the measured apparent soil resistivity is referred to a soil volume as in the figure.
The current tends to flow near the surface for small probe spacing, whereas more current penetrates deeper into the soil for large spacing. The resistivity measured for a given current probe spacing represents, to a first approximation, the apparent resistivity of the soil to a depth equal to that spacing.
If the apparent soil resistivity measured with Schlumberger method ''ρE'' (with the corresponding electrode spacing ''aS'' and ''c'') is given, assuming that the soil resistivity refers to a volume as in the figure with ''a=L/3'' follows:
:
with
:
where:
''RW'' = equivalent Wenner resistance (Ω)
''aW'' = equivalent electrode spacing with Wenner method (m)
''aS'' =
The conversion between values measured using the Schlumberger and Wenner methods is possible only in an approximate way. In any cases, for both Wenner and Schlumberger methods the electrode spacing between the currents probe corresponds to the depth of soil investigation and the measured apparent soil resistivity is referred to a soil volume as in the figure.
The current tends to flow near the surface for small probe spacing, whereas more current penetrates deeper into the soil for large spacing. The resistivity measured for a given current probe spacing represents, to a first approximation, the apparent resistivity of the soil to a depth equal to that spacing.
If the apparent soil resistivity measured with Schlumberger method ''ρE'' (with the corresponding electrode spacing ''aS'' and ''c'') is given, assuming that the soil resistivity refers to a volume as in the figure with ''a=L/3'' follows:
:
with
:
where:
''RW'' = equivalent Wenner resistance (Ω)
''aW'' = equivalent electrode spacing with Wenner method (m)
''aS'' =
soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former ...
resists or conducts electric current. It is a critical factor in design of systems that rely on passing current through the Earth's surface. It is a very important parameter for finding the best location of a transmitter working on low frequiencies (VLF, LF, MF and lower shortwave) as such radio stations usually use ground as counterpole. An understanding of the soil resistivity and how it varies with depth in the soil is necessary to design the grounding system in an electrical substation
A substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, or perform any of several other important functions. Between the generating station and ...
, or for lightning conductors. It is needed for design of grounding (earthing) electrodes for substations and High-voltage direct current
A high-voltage direct current (HVDC) electric power transmission system (also called a power superhighway or an electrical superhighway) uses direct current (DC) for electric power transmission, in contrast with the more common alternating cur ...
transmission systems. It was formerly important in earth-return telegraphy. It can also be a useful measure in agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
as a proxy measurement for moisture content.
In most substations the earth is used to conduct fault current when there are ground faults on the system. In single wire earth return
Single-wire earth return (SWER) or single-wire ground return is a single-wire transmission line which supplies single-phase electric power from an electrical grid to remote areas at lowest cost. Its distinguishing feature is that the earth (or ...
power transmission systems, the earth itself is used as the path of conduction from the end customers (the power consumers) back to the transmission facility.
In general there is some value above which the impedance of the earth connection must not rise, and some maximum step voltage which must not be exceeded to avoid endangering people and livestock.
The soil resistivity value is subject to great variation, due to moisture, temperature and chemical content. Typical values are:
* Usual values: from 10 up to 1000 (Ω-m)
* Exceptional values: from 1000 up to 10000 (Ω-m)
The SI unit of resistivity is the Ohm-meter (Ω-m); in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
the Ohm-centimeter (Ω-cm) is often used instead. One Ω-m is 100 Ω-cm. Sometimes the conductivity
Conductivity may refer to:
*Electrical conductivity, a measure of a material's ability to conduct an electric current
**Conductivity (electrolytic), the electrical conductivity of an electrolyte in solution
** Ionic conductivity (solid state), ele ...
, the reciprocal of the resistivity, is quoted instead.
A wide range of typical soil resistivity
Electrical resistivity (also called specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity) is a fundamental property of a material that measures how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows ...
values can be found in literature. Military Handbook 419 (MIL-HDBK-419A) contains reference tables and formulae for the resistance of various patterns of rods and wires buried in soil of known resistivity. Being copyright free, these numbers are widely copied, sometimes without acknowledgement.
Measurement
Because soil quality may vary greatly with depth and over a wide lateral area, estimation of soil resistivity based on soil classification provide only a rough approximation. Actual resistivity measurements are required to fully qualify the resistivity and its effects on the overall transmission system. Several methods of resistivity measurement are frequently employed: For measurement the user can use Grounding resistance tester.Wenner method
 The Wenner four-pin method, as shown in figure above, is the most commonly used technique for soil resistivity measurements.
Using the Wenner method, the apparent soil resistivity value is:
:
where
''ρE'' = measured apparent soil resistivity (Ωm)
''a'' = electrode spacing (m)
''b'' = depth of the electrodes (m)
''RW'' = Wenner resistance measured as "V/I" in Figure (Ω)
If ''b'' is small compared to ''a'', as is the case of probes penetrating the ground only for a short distance (as normally happens), the previous equation can be reduced to:
:
The Wenner four-pin method, as shown in figure above, is the most commonly used technique for soil resistivity measurements.
Using the Wenner method, the apparent soil resistivity value is:
:
where
''ρE'' = measured apparent soil resistivity (Ωm)
''a'' = electrode spacing (m)
''b'' = depth of the electrodes (m)
''RW'' = Wenner resistance measured as "V/I" in Figure (Ω)
If ''b'' is small compared to ''a'', as is the case of probes penetrating the ground only for a short distance (as normally happens), the previous equation can be reduced to:
:
Schlumberger method
 In the Schlumberger method the distance between the voltages probe is ''a'' and the distances from voltages probe and currents probe are ''c'' (see figure above).
Using the Schlumberger method, if ''b'' is small compared to ''a'' and ''c'', and ''c''>''2a'', the apparent soil resistivity value is:
:
where
''ρE'' = measured apparent soil resistance (Ωm)
''a'' = electrode spacing (m)
''b'' = depth of the electrodes (m)
''c'' = electrode spacing (m)
''RS'' = Schlumberger resistance measured as "V/I" in Figure (Ω)
In the Schlumberger method the distance between the voltages probe is ''a'' and the distances from voltages probe and currents probe are ''c'' (see figure above).
Using the Schlumberger method, if ''b'' is small compared to ''a'' and ''c'', and ''c''>''2a'', the apparent soil resistivity value is:
:
where
''ρE'' = measured apparent soil resistance (Ωm)
''a'' = electrode spacing (m)
''b'' = depth of the electrodes (m)
''c'' = electrode spacing (m)
''RS'' = Schlumberger resistance measured as "V/I" in Figure (Ω)
Conversion
 The conversion between values measured using the Schlumberger and Wenner methods is possible only in an approximate way. In any cases, for both Wenner and Schlumberger methods the electrode spacing between the currents probe corresponds to the depth of soil investigation and the measured apparent soil resistivity is referred to a soil volume as in the figure.
The current tends to flow near the surface for small probe spacing, whereas more current penetrates deeper into the soil for large spacing. The resistivity measured for a given current probe spacing represents, to a first approximation, the apparent resistivity of the soil to a depth equal to that spacing.
If the apparent soil resistivity measured with Schlumberger method ''ρE'' (with the corresponding electrode spacing ''aS'' and ''c'') is given, assuming that the soil resistivity refers to a volume as in the figure with ''a=L/3'' follows:
:
with
:
where:
''RW'' = equivalent Wenner resistance (Ω)
''aW'' = equivalent electrode spacing with Wenner method (m)
''aS'' =
The conversion between values measured using the Schlumberger and Wenner methods is possible only in an approximate way. In any cases, for both Wenner and Schlumberger methods the electrode spacing between the currents probe corresponds to the depth of soil investigation and the measured apparent soil resistivity is referred to a soil volume as in the figure.
The current tends to flow near the surface for small probe spacing, whereas more current penetrates deeper into the soil for large spacing. The resistivity measured for a given current probe spacing represents, to a first approximation, the apparent resistivity of the soil to a depth equal to that spacing.
If the apparent soil resistivity measured with Schlumberger method ''ρE'' (with the corresponding electrode spacing ''aS'' and ''c'') is given, assuming that the soil resistivity refers to a volume as in the figure with ''a=L/3'' follows:
:
with
:
where:
''RW'' = equivalent Wenner resistance (Ω)
''aW'' = equivalent electrode spacing with Wenner method (m)
''aS'' = electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials ...
spacing between voltages probe with Schlumberger method (m)
''c'' = electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials ...
spacing between voltages and currents probe with Schlumberger method (m)
If the measured Schlumberger resistance is given, before calculating the apparent soil resistivity
Electrical resistivity (also called specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity) is a fundamental property of a material that measures how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows ...
the following factor must be calculated:
:
The Wenner method is the most widely used method for measuring soil resistivity for electrical grounding (earthing) purposes. The Schlumberger method was developed to increase the voltage signal for the earlier, less sensitive instruments, by placing the potential probes closer to the current probes.
The soil resistivity
Electrical resistivity (also called specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity) is a fundamental property of a material that measures how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows ...
measurements will be affected by existing nearby grounded electrodes. Buried conductive objects in contact with the soil can invalidate readings made by the methods described if they are close enough to alter the test current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
flow pattern. This is particularly true for large or long objects.
Variability
Electrical conduction in soil is essentially electrolytic and for this reason the soil resistivity depends on: * moisture content * salt content * temperature (above the freezing point 0 °C) Because of the variability of soil resistivity,IEC
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; in French: ''Commission électrotechnique internationale'') is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and r ...
standards require that the seasonal variation in resistivity be accounted for in transmission system design. Soil resistivity can increase by a factor of 10 or more in very cold temperatures.IEEE Recommended Practice for Grounding of Industrial and Commercial Power Systems, IEEE Std. 142-1982'', table 7, page 122
Corrosion
Soil resistivity is one of the driving factors determining the corrosiveness of soil. The soil corrosiveness is classified based on soil electricalresistivity
Electrical resistivity (also called specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity) is a fundamental property of a material that measures how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows ...
by the British Standard
British Standards (BS) are the standards produced by the BSI Group which is incorporated under a royal charter and which is formally designated as the national standards body (NSB) for the UK. The BSI Group produces British Standards under the ...
BS-1377 as follow:
* ''ρE'' > 100 Ωm: slightly corrosive
* 50 < ''ρE'' < 100 Ωm: moderately corrosive
* 10 < ''ρE'' < 50 Ωm: corrosive
* ''ρE'' < 10 Ωm: severe
References
Further reading
* {{Authority control Electric power distribution Electrical resistance and conductance Electrical safety