Skew-T log-P diagram on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
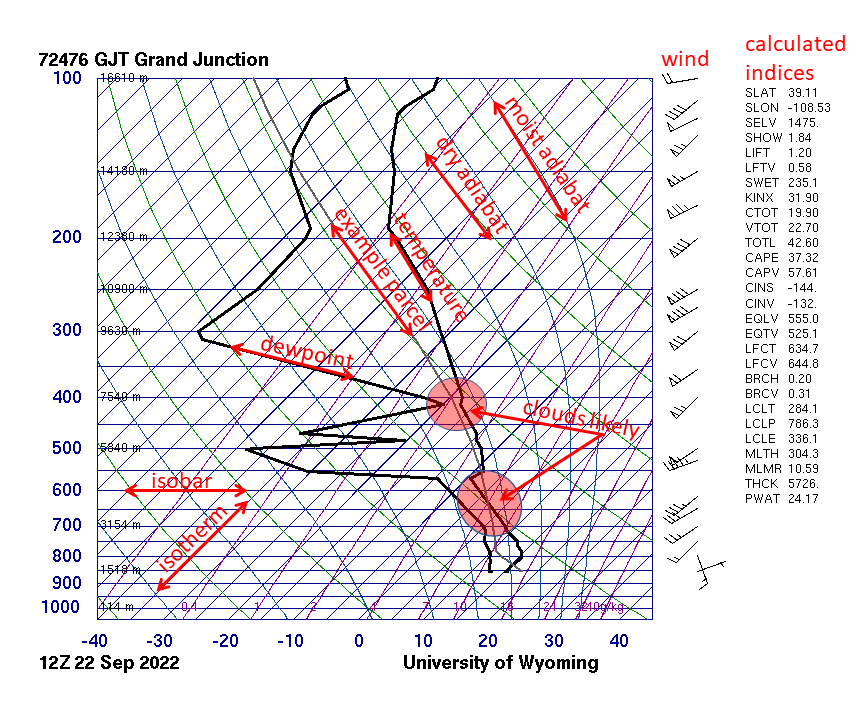 A skew-T log-P diagram is one of four
A skew-T log-P diagram is one of four
Downloadable/printable skew-T log-P diagrams in PDF format
NOAA observed sounding archive
Printable blank skew-T log-P diagrams in multiple densities
NOAA Skew-T log-P page
Diagrams Atmospheric thermodynamics {{climate-stub
 A skew-T log-P diagram is one of four
A skew-T log-P diagram is one of four thermodynamic diagrams
Thermodynamic diagrams are diagrams used to represent the thermodynamic states of a material (typically fluid) and the consequences of manipulating this material. For instance, a temperature–entropy diagram ( T–s diagram) may be used to demon ...
commonly used in weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmosphere, the ...
analysis and forecasting. In 1947, N. Herlofson proposed a modification to the emagram
An emagram is one of four thermodynamic diagrams used to display temperature lapse rate and moisture content profiles in the atmosphere. The emagram has axes of temperature (T) and pressure (p). In the emagram, the dry adiabats make an angle of a ...
that allows straight, horizontal isobars and provides for a large angle between isotherms
A contour line (also isoline, isopleth, or isarithm) of a function of two variables is a curve along which the function has a constant value, so that the curve joins points of equal value. It is a plane section of the three-dimensional graph ...
and dry adiabat
In thermodynamics, an adiabatic process (Greek: ''adiábatos'', "impassable") is a type of thermodynamic process that occurs without transferring heat or mass between the thermodynamic system and its environment. Unlike an isothermal process, a ...
s, similar to that in the tephigram
A tephigram is one of four thermodynamic diagrams commonly used in weather analysis and forecasting. The name evolved from the original name "T-\phi-gram" to describe the axes of temperature (T) and entropy (\phi) used to create the plot. Usuall ...
. It was thus more suitable for some of the newer analysis techniques being invented by the United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Si ...
.
Such a diagram has pressure plotted on the vertical axis, with a logarithmic scale
A logarithmic scale (or log scale) is a way of displaying numerical data over a very wide range of values in a compact way—typically the largest numbers in the data are hundreds or even thousands of times larger than the smallest numbers. Such a ...
(thus the "log-P" part of the name), and the temperature plotted skewed
In probability theory and statistics, skewness is a measure of the asymmetry of the probability distribution of a real-valued random variable about its mean. The skewness value can be positive, zero, negative, or undefined.
For a unimodal d ...
, with isothermal lines at 45° to the plot (thus the "skew-T" part of the name). Plotting a hypothetical set of measurements with constant temperature for all altitudes would result in a line angled 45° to the right. In practice, since temperature usually drops with altitude, the graphs are usually mostly vertical (see examples linked to below).
The major use for skew-T log-P diagrams is the plotting of radiosonde soundings, which give a vertical profile of the temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied o ...
and dew point
The dew point is the temperature to which air must be cooled to become saturated with water vapor, assuming constant air pressure and water content. When cooled below the dew point, moisture capacity is reduced and airborne water vapor will ...
temperature throughout the troposphere
The troposphere is the first and lowest layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, and contains 75% of the total mass of the planetary atmosphere, 99% of the total mass of water vapour and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. Fro ...
and lower stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is an atmospheric layer composed of stratified temperature layers, with the warm layers of air h ...
. The isopleths on the diagram can then be used to simplify many tedious calculations involved, which were previously performed by hand or not at all. Many skew-T log-P diagrams also include a vertical representation of the wind speed and direction using wind barbs. Important atmospheric characteristics such as saturation
Saturation, saturated, unsaturation or unsaturated may refer to:
Chemistry
* Saturation, a property of organic compounds referring to carbon-carbon bonds
**Saturated and unsaturated compounds
** Degree of unsaturation
**Saturated fat or fatty aci ...
, atmospheric instability, and wind shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizont ...
are critical in severe weather forecasting
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the conditions of the atmosphere for a given location and time. People have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia and formally since the 19th cen ...
, by which skew-T log-P diagrams allow quick visual analysis. The diagrams are widely used by glider pilots to forecast the strength of thermal
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example ...
s and the height of the base of the associated cumulus clouds.
See also
*Thermodynamic diagrams
Thermodynamic diagrams are diagrams used to represent the thermodynamic states of a material (typically fluid) and the consequences of manipulating this material. For instance, a temperature–entropy diagram ( T–s diagram) may be used to demon ...
* Tephigram
A tephigram is one of four thermodynamic diagrams commonly used in weather analysis and forecasting. The name evolved from the original name "T-\phi-gram" to describe the axes of temperature (T) and entropy (\phi) used to create the plot. Usuall ...
* Emagram
An emagram is one of four thermodynamic diagrams used to display temperature lapse rate and moisture content profiles in the atmosphere. The emagram has axes of temperature (T) and pressure (p). In the emagram, the dry adiabats make an angle of a ...
* Stüve diagram
A Stüve diagram is one of four thermodynamic diagrams commonly used in weather analysis and forecasting.
It was developed circa 1927 by the German meteorologist Georg Stüve (1888–1935) and quickly gained widespread acceptance in the United St ...
* Meteogram
Bibliography
* * *External links
Downloadable/printable skew-T log-P diagrams in PDF format
NOAA observed sounding archive
Printable blank skew-T log-P diagrams in multiple densities
NOAA Skew-T log-P page
Diagrams Atmospheric thermodynamics {{climate-stub