Sintashta culture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Sintashta culture (russian: Синташтинская культура, Sintashtinskaya kul'tura), around 2050–1900 BCE, is the first phase of the Sintashta–Petrovka culture. or Sintashta–Arkaim culture,. and is a late Middle
"Finnish vatsa – Sanskrit vatshá – and the formation of Indo–Iranian and Uralic languages"
in SUSA/JSFOu 96, 2017, p. 249. In 2020 Ventresca Miller et al. still claimed a period of 2400–1800 BCE,Ventresca Miller, Alicia R., et al., (2020 b)
"Ecosystems Engineering Among Ancient Pastoralists in Northern Central Asia"
in Frontiers in Earth Science, Volume 8, Article 168, 2 June 2020, p. 6: "...Middle Bronze Age (2400–1800 cal BCE) people, often referred to as Sintashta, constructed nucleated settlements, with population estimates ranging from 200 to 700 individuals..."Ventresca Miller, A. R., et al., (2020 a)
"Close management of sheep in ancient Central Asia: evidence for foddering, transhumance, and extended lambing seasons during the Bronze and Iron Ages"
in STAR, Science & Technology of Archaeological Research, p. 2: "...By 2300 cal BCE, Middle Bronze Age sites associated with Sintashta and Petrovka cultural groups in northern Kazakhstan heavily exploited domesticated cattle, sheep, and goats alongside horses with occasional hunting of wild fauna..." based on 44 earlier C14 calibrated datings by the
 According to Russian archaeologists, the Sintashta culture emerged from the interaction of two antecedent cultures, the Poltavka culture and the
According to Russian archaeologists, the Sintashta culture emerged from the interaction of two antecedent cultures, the Poltavka culture and the
File:Аркаим 2015.jpg, Aerial view of the Arkaim site
File:Панорама окрестностей Укрепленного поселения Аркаим.jpg, View of the Arkaim site and surrounding landscape
File:Укрепленное поселение Аркаим. Музеефицированный раскоп на двух жилищах.jpg, Excavation and partial building reconstruction
File:В музее - заповеднике Аркаим.jpg, chariot model, Arkaim museum
File:Аркаим Исторический парк - panoramio.jpg, Reconstructed burial mound
File:Sintashta1 copy.jpg, Sintashta ceramics and horse bridle cheekpieces
 analyzed the remains of four individuals ascribed to the Sintastha culture. One male carried haplogroup R1a and J1c1b1a, while the other carried R1a1a1b and J2b1a2a. The two females carried U2e1e and U2e1h respectively. The study found a close
analyzed the remains of four individuals ascribed to the Sintastha culture. One male carried haplogroup R1a and J1c1b1a, while the other carried R1a1a1b and J2b1a2a. The two females carried U2e1e and U2e1h respectively. The study found a close
Stanislav A. Grigoriev, "Ancient Indo-Europeans"
{{Central Asian history Archaeological cultures of Central Asia Indo-Iranian archaeological cultures Andronovo culture
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
archaeological culture
An archaeological culture is a recurring assemblage of types of artifacts, buildings and monuments from a specific period and region that may constitute the material culture remains of a particular past human society. The connection between thes ...
, located to the east of the Southern Urals, within the northern Eurasian steppe
The Eurasian Steppe, also simply called the Great Steppe or the steppes, is the vast steppe ecoregion of Eurasia in the temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublands biome. It stretches through Hungary, Bulgaria, Romania, Moldova and Transnistr ...
on the borders of Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whi ...
and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
. The whole Sintashta–Petrovka complex was dated in a recent publication by Stephan Lindner, based on a series of 19 calibrated radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was de ...
samples as belonging to c. 2050–1750 BCE. The phase of the Petrovka culture can be dated c. 1900–1750 BCE. The oldest reliable analysis of human remains from Sintashta is radiocarbon dated to a mean of cal BC (2335–2041 calBC), and genetically analyzed as Y-haplogroup R1a-Z93 < R-Z2124.
The Sintashta culture was previously dated to the period 2200–1800 BCE.Chernykh, E. N., (2009). Formation of the Eurasian Steppe Belt Cultures: Viewed Through the Lens of Archaeometallurgy and Radiocarbon Dating, in B. Hanks & K. Linduff (eds.), Social Complexity in Prehistoric Eurasia: Monuments, Metals and Mobility, Cambridge University Press, pp. 128–133.Parpola, Asko, (2017)"Finnish vatsa – Sanskrit vatshá – and the formation of Indo–Iranian and Uralic languages"
in SUSA/JSFOu 96, 2017, p. 249. In 2020 Ventresca Miller et al. still claimed a period of 2400–1800 BCE,Ventresca Miller, Alicia R., et al., (2020 b)
"Ecosystems Engineering Among Ancient Pastoralists in Northern Central Asia"
in Frontiers in Earth Science, Volume 8, Article 168, 2 June 2020, p. 6: "...Middle Bronze Age (2400–1800 cal BCE) people, often referred to as Sintashta, constructed nucleated settlements, with population estimates ranging from 200 to 700 individuals..."Ventresca Miller, A. R., et al., (2020 a)
"Close management of sheep in ancient Central Asia: evidence for foddering, transhumance, and extended lambing seasons during the Bronze and Iron Ages"
in STAR, Science & Technology of Archaeological Research, p. 2: "...By 2300 cal BCE, Middle Bronze Age sites associated with Sintashta and Petrovka cultural groups in northern Kazakhstan heavily exploited domesticated cattle, sheep, and goats alongside horses with occasional hunting of wild fauna..." based on 44 earlier C14 calibrated datings by the
Russian Academy of Sciences
The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; russian: Росси́йская акаде́мия нау́к (РАН) ''Rossíyskaya akadémiya naúk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific research institutes from across t ...
, which some other researchers consider outdated. The culture is named after
A namesake is a person, geographic location, or other entity bearing the name of another.
History
The word is first attested around 1635, and probably comes from the phrase "for one's name's sake",
which originates in English Bible translations ...
the Sintashta archaeological site, in Chelyabinsk Oblast
Chelyabinsk Oblast (russian: Челя́бинская о́бласть, ''Chelyabinskaya oblast'') is a federal subject (an oblast) of Russia in the Ural Mountains region, on the border of Europe and Asia. Its administrative center is the ...
, Russia, and spreads through Orenburg Oblast
Orenburg Oblast (russian: Оренбургская область, ''Orenburgskaya oblast'') is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the city of Orenburg. From 1938 to 1957, it bore the name ''Chkalov Oblast'' () ...
, Bashkortostan
The Republic of Bashkortostan or Bashkortostan ( ba, Башҡортостан Республикаһы, Bashqortostan Respublikahy; russian: Республика Башкортостан, Respublika Bashkortostan),; russian: Респу́блик� ...
, and Northern Kazakhstan.
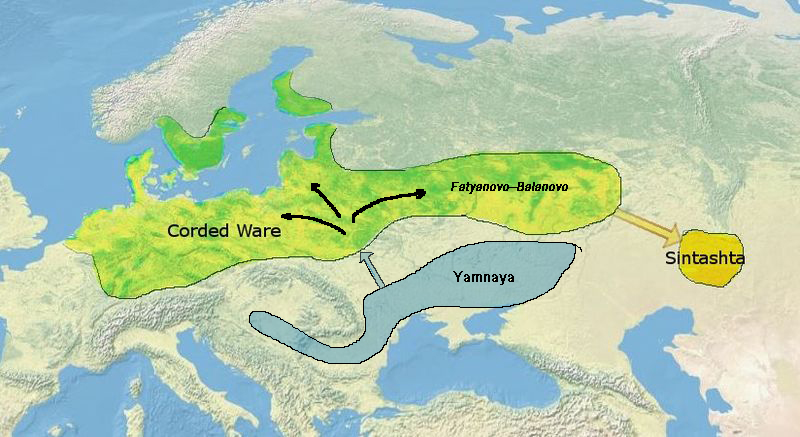
This culture is thought to represent an eastward migration of peoples from the Corded Ware culture. It is widely regarded as the origin of the Indo-Iranian languages
The Indo-Iranian languages (also Indo-Iranic languages or Aryan languages) constitute the largest and southeasternmost extant branch of the Indo-European language family (with over 400 languages), predominantly spoken in the geographical subr ...
.. The earliest known chariot
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000&n ...
s have been found in Sintashta burials, and the culture is considered a strong candidate for the origin of the technology, which spread throughout the Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by thei ...
and played an important role in ancient warfare
Ancient warfare is war that was conducted from the beginning of recorded history to the end of the ancient period. The difference between prehistoric and ancient warfare is more organization oriented than technology oriented. The development of ...
. Sintashta settlements are also remarkable for the intensity of copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
mining and bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids suc ...
metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sc ...
carried out there, which is unusual for a steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate gras ...
culture.. Among the main features of the Sintashta culture are high levels of militarism and extensive fortified settlements, of which 23 are known.
Origin
 According to Russian archaeologists, the Sintashta culture emerged from the interaction of two antecedent cultures, the Poltavka culture and the
According to Russian archaeologists, the Sintashta culture emerged from the interaction of two antecedent cultures, the Poltavka culture and the Abashevo culture
The Abashevo culture (russian: Абашевская культура, Abashevskaya kul'tura) is an early Bronze Age, ca. 2300–1850 BC, archaeological culture found in the valleys of the Volga and Kama River north of the Samara bend and into ...
. Because of the difficulty of identifying the remains of Sintashta sites beneath those of later settlements, the culture was only distinguished in the 1990s from the Andronovo culture
The Andronovo culture (russian: Андроновская культура, translit=Andronovskaya kul'tura) is a collection of similar local Late Bronze Age cultures that flourished 2000–1450 BC,Grigoriev, Stanislav, (2021)"Andronovo ...
. It was then recognised as a distinct entity, forming part of the "Andronovo horizon". Results from a genetic study published in ''Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are ...
'' in 2015 suggested that the Sintashta culture emerged as a result of an eastward migration of peoples from the Corded Ware culture.
Morphological data suggests that the Sintashta culture might have emerged as a result of a mixture of steppe ancestry from the Poltavka culture and Catacomb culture
The Catacomb culture (russian: Катакомбная культура, Katakombnaya kul'tura, uk, Катакомбна культура, Katakombna kul'tura) was a Bronze Age culture which flourished on the Pontic steppe in 2500–1950 BC.Par ...
, with ancestry from Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
forest hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fung ...
s.
Even though other researchers think it's an outdated chronology, Ventresca Miller et al. still claim that the first Sintashta settlements appeared around 2400 BCE and lasted until 1800 BCE with population estimates in each site ranging from 200 to 700 individuals, during a period of climatic change that saw the already arid Kazakh steppe region become even colder and drier. The marshy lowlands around the Ural and upper Tobol river
The Tobol (russian: Тобол, kk, Тобыл ''Tobyl'') is a river in Western Siberia (in Kazakhstan and Russia) and the main (left) tributary of the Irtysh. Its length is , and the area of its drainage basin is .
History
The Tobol River wa ...
s, previously favoured as winter refuges, became increasingly important for survival. Under these pressures both Poltavka and Abashevo herders settled permanently in river valley strongholds, eschewing more defensible hill-top locations. Ventresca Miller et al. also claims that "by 2300 cal BCE, Middle Bronze Age sites associated with Sintashta and Petrovka cultural groups in northern Kazakhstan heavily exploited domesticated cattle, sheep, and goats alongside horses with occasional hunting of wild fauna".
Its immediate predecessor in the Ural-Tobol steppe was the Poltavka culture, an offshoot of the cattle-herding Yamnaya horizon that moved east into the region between 2800 and 2600 BCE. Several Sintashta towns were built over older Poltavka settlements or close to Poltavka cemeteries, and Poltavka motifs are common on Sintashta pottery.
Sintashta material culture
Material culture is the aspect of social reality grounded in the objects and architecture that surround people. It includes the usage, consumption, creation, and trade of objects as well as the behaviors, norms, and rituals that the objects crea ...
also shows the influence of the late Abashevo culture
The Abashevo culture (russian: Абашевская культура, Abashevskaya kul'tura) is an early Bronze Age, ca. 2300–1850 BC, archaeological culture found in the valleys of the Volga and Kama River north of the Samara bend and into ...
, derived from the Fatyanovo-Balanovo culture, a collection of Corded Ware
The Corded Ware culture comprises a broad archaeological horizon of Europe between ca. 3000 BC – 2350 BC, thus from the late Neolithic, through the Copper Age, and ending in the early Bronze Age. Corded Ware culture encompassed a ...
settlements in the forest steppe zone north of the Sintashta region that were also predominantly pastoralist..
Society
Linguistic identity
The people of the Sintashta culture are thought to have spokenProto-Indo-Iranian
Proto-Indo-Iranian, also Proto-Indo-Iranic is the reconstructed proto-language of the Indo-Iranian/Indo-Iranic branch of Indo-European. Its speakers, the hypothetical Proto-Indo-Iranians, are assumed to have lived in the late 3rd millennium ...
, the ancestor of the Indo-Iranian language family. This identification is based primarily on similarities between sections of the ''Rig Veda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one ...
'', a religious text which includes ancient Indo-Iranian hymns recorded in Vedic Sanskrit
Vedic Sanskrit was an ancient language of the Indo-Aryan subgroup of the Indo-European language family. It is attested in the Vedas and related literature compiled over the period of the mid- 2nd to mid-1st millennium BCE. It was orally preser ...
, and the funerary rituals of the Sintashta culture as revealed by archaeology. Many cultural similarities with Sintashta have also been detected in the Nordic Bronze Age of Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and S ...
.
There is linguistic evidence of interaction between Finno-Ugric and Indo-Iranian languages, showing influences from the Indo-Iranians into the Finno-Ugric culture.
From the Sintashta culture the Indo-Iranian followed the migrations of the Indo-Iranians
Indo-Iranian peoples, also known as Indo-Iranic peoples by scholars, and sometimes as Arya or Aryans from their self-designation, were a group of Indo-European peoples who brought the Indo-Iranian languages, a major branch of the Indo-European l ...
to Anatolia, India and Iran. From the 9th century BCE onward, Iranian languages also migrated westward with the Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Cent ...
back to the Pontic steppe where the proto-Indo-Europeans came from.
Warfare
The preceding Abashevo culture was already marked by endemic intertribal warfare; intensified by ecological stress and competition for resources in the Sintashta period. This drove the construction of fortifications on an unprecedented scale and innovations in military technique such as the invention of the war chariot. Increased competition between tribal groups may also explain the extravagant sacrifices seen in Sintashta burials, as rivals sought to outdo one another in acts ofconspicuous consumption
In sociology and in economics, the term conspicuous consumption describes and explains the consumer practice of buying and using goods of a higher quality, price, or in greater quantity than practical. In 1899, the sociologist Thorstein Veblen c ...
analogous to the North American potlatch
A potlatch is a gift-giving feast practiced by Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast of Canada and the United States,Harkin, Michael E., 2001, Potlatch in Anthropology, International Encyclopedia of the Social and Behavioral Scie ...
tradition.
Sintashta artefact types such as spearheads, trilobed arrowheads, chisels, and large shaft-hole axes were taken east. Many Sintashta graves are furnished with weapons, although the composite bow associated later with chariotry does not appear. Higher-status grave goods include their infamous chariots, as well as axes, mace-heads, spearheads, and cheek-pieces. Sintashta sites have produced finds of horn and bone, interpreted as furniture (grips, arrow rests, bow ends, string loops) of bows; there is no indication that the bending parts of these bows included anything other than wood. Arrowheads are also found, made of stone or bone rather than metal. These arrows are short, 50–70 cm long, and the bows themselves may have been correspondingly short.
Metal production
The Sintashta economy came to revolve around copper metallurgy. Copper ores from nearby mines (such as Vorovskaya Yama) were taken to Sintashta settlements to be processed into copper and arsenical bronze. This occurred on an industrial scale: all the excavated buildings at the Sintashta sites ofSintashta
Sintashta (russian: Синташта́) is an archaeological site in Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia. It is the remains of a fortified settlement dating to the Bronze Age, ''c''. 2800–1600 BC, and is the type site of the Sintashta culture. The site h ...
, Arkaim and Ust'e contained the remains of smelting
Smelting is a process of applying heat to ore, to extract a base metal. It is a form of extractive metallurgy. It is used to extract many metals from their ores, including silver, iron, copper, and other base metals. Smelting uses heat and a c ...
ovens and slag
Slag is a by-product of smelting ( pyrometallurgical) ores and used metals. Broadly, it can be classified as ferrous (by-products of processing iron and steel), ferroalloy (by-product of ferroalloy production) or non-ferrous/base metals (by-p ...
. Around 10% of graves, mostly adult male, contained artifacts related to bronze metallurgy (molds, ceramic nozzles, ore and slag remains, metal bars and drops). However, these metal-production related grave goods rarely co-occur with higher-status grave goods. This likely means that those who engaged in metal production were not at the top of the social-hierarchy, even though being buried at a cemetery evidences some sort of higher status.
Much of Sintashta metal was destined for export to the cities of the Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex
The Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex (short BMAC) or Oxus Civilization, recently dated to c. 2250–1700 BC,Lyonnet, Bertille, and Nadezhda A. Dubova, (2020b)"Questioning the Oxus Civilization or Bactria- Margiana Archaeological Cultu ...
(BMAC) in Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
. The metal trade between Sintashta and the BMAC for the first time connected the steppe region to the ancient urban civilisations of the Near East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
: the empires and city-states of Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
and Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
provided an almost bottomless market for metals. These trade routes later became the vehicle through which horses, chariots and ultimately Indo-Iranian-speaking people entered the Near East from the steppe...
Gallery
Physical type
Physical remains of the Sintashta people have revealed that they were Caucasoid with dolichocephalic skulls. Sintashta skulls are very similar to those of the preceding Fatyanovo–Balanovo culture andAbashevo culture
The Abashevo culture (russian: Абашевская культура, Abashevskaya kul'tura) is an early Bronze Age, ca. 2300–1850 BC, archaeological culture found in the valleys of the Volga and Kama River north of the Samara bend and into ...
, which ultimately trace their origin to Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
, and those of the succeeding Srubnaya culture
The Srubnaya culture (russian: Срубная культура, Srubnaya kul'tura, ua, Зрубна культура, Zrubna kul'tura), also known as Timber-grave culture, was a Late Bronze Age 1850–1450 BC cultureParpola, Asko, (2012)"Format ...
and Andronovo culture
The Andronovo culture (russian: Андроновская культура, translit=Andronovskaya kul'tura) is a collection of similar local Late Bronze Age cultures that flourished 2000–1450 BC,Grigoriev, Stanislav, (2021)"Andronovo ...
. Skulls of the related Potapovka culture
Potapovka culture (russian: Потаповская культура, Potapovskaya kul'tura) was a Bronze Age culture which flourished on the middle Volga in 2100—1800 BC.
The Potapovka culture emerged out of the Poltavka culture with infl ...
are less dolichocephalic, possibly as a result of admixture between Sintashta people and descendants of the Yamnaya culture
The Yamnaya culture or the Yamna culture (russian: Ямная культура, ua, Ямна культура lit. 'culture of pits'), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, was a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archa ...
and Poltavka culture, who although of a similar Europoid type, were less dolichocephalic than Sintashta. The physical type of Abashevo, Sintashta, Andronovo and Srubnaya is later observed among the Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Cent ...
.
Genetics
 analyzed the remains of four individuals ascribed to the Sintastha culture. One male carried haplogroup R1a and J1c1b1a, while the other carried R1a1a1b and J2b1a2a. The two females carried U2e1e and U2e1h respectively. The study found a close
analyzed the remains of four individuals ascribed to the Sintastha culture. One male carried haplogroup R1a and J1c1b1a, while the other carried R1a1a1b and J2b1a2a. The two females carried U2e1e and U2e1h respectively. The study found a close autosomal
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosom ...
genetic relationship between peoples of Corded Ware culture and Sintashta culture, which "suggests similar genetic sources of the two," and may imply that "the Sintashta derives directly from an eastward migration of Corded Ware peoples." Sintashta individuals and Corded Ware individuals both had a relatively higher ancestry proportion derived from the Central Europe, and both differed markedly in such ancestry from the population of the Yamnaya Culture and most individuals of the Poltavka Culture that preceded Sintashta in the same geographic region. The Bell Beaker culture
The Bell Beaker culture, also known as the Bell Beaker complex or Bell Beaker phenomenon, is an archaeological culture named after the inverted-bell beaker drinking vessel used at the very beginning of the European Bronze Age. Arising from ar ...
, the Unetice culture and contemporary Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and S ...
n cultures were also found to be closely genetically related to Corded Ware. A particularly high lactose tolerance
Lactase persistence is the continued activity of the lactase enzyme in adulthood, allowing the digestion of lactose in milk. In most mammals, the activity of the enzyme is dramatically reduced after weaning. In some human populations, though, lact ...
was found among Corded Ware and the closely related Nordic Bronze Age. In addition, the study found the Sintashta culture to be closely genetically related to the succeeding Andronovo culture
The Andronovo culture (russian: Андроновская культура, translit=Andronovskaya kul'tura) is a collection of similar local Late Bronze Age cultures that flourished 2000–1450 BC,Grigoriev, Stanislav, (2021)"Andronovo ...
.
analyzed the remains of several members of the Sintashta culture. mtDNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA ...
was extracted from two females buried at the Petrovka settlement
The Petrovka fortified settlement, namesake of the 2nd millennium BC Sintashta-Petrovka culture lies at the Ishim River, near the modern village of Petrovka in Zhambyl District, North Kazakhstan Region, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially t ...
. They were found to be carrying subclades of U2 and U5. The remains of fifty individuals from the fortified Sintastha settlement of Kamennyi Ambar was analyzed. This was the largest sample of ancient DNA ever sampled from a single site. The Y-DNA from thirty males was extracted. Eighteen carried R1a and various subclades of it (particularly subclades of R1a1a1), five carried subclades of R1b
Haplogroup R1b (R-M343), previously known as Hg1 and Eu18, is a human Y-chromosome haplogroup.
It is the most frequently occurring paternal lineage in Western Europe, as well as some parts of Russia (e.g. the Bashkirs) and pockets of Central ...
(particularly subclades of R1b1a1a), two carried Q1a and a subclade of it, one carried I2a1a1a, and four carried unspecified R1 clades. The majority of mtDNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA ...
samples belonged to various subclades of U, while W, J, T, H and K also occurred. A Sintashta male buried at Samara
Samara ( rus, Сама́ра, p=sɐˈmarə), known from 1935 to 1991 as Kuybyshev (; ), is the largest city and administrative centre of Samara Oblast. The city is located at the confluence of the Volga and the Samara rivers, with a population ...
was found to be carrying R1b1a1a2 and J1c1b1a. The authors of the study found the Sintashta people to be closely genetically related to the people of the Corded Ware culture, the Srubnaya culture
The Srubnaya culture (russian: Срубная культура, Srubnaya kul'tura, ua, Зрубна культура, Zrubna kul'tura), also known as Timber-grave culture, was a Late Bronze Age 1850–1450 BC cultureParpola, Asko, (2012)"Format ...
, the Potapovka culture
Potapovka culture (russian: Потаповская культура, Potapovskaya kul'tura) was a Bronze Age culture which flourished on the middle Volga in 2100—1800 BC.
The Potapovka culture emerged out of the Poltavka culture with infl ...
, and the Andronovo culture
The Andronovo culture (russian: Андроновская культура, translit=Andronovskaya kul'tura) is a collection of similar local Late Bronze Age cultures that flourished 2000–1450 BC,Grigoriev, Stanislav, (2021)"Andronovo ...
. These were found to harbor mixed ancestry from the Yamnaya culture
The Yamnaya culture or the Yamna culture (russian: Ямная культура, ua, Ямна культура lit. 'culture of pits'), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, was a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archa ...
and peoples of the Central European Middle Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
. Sintashta people were deemed "genetically almost indistinguishable" from samples taken from the northwestern areas constituting the core of the Andronovo culture, which were "genetically largely homogeneous". The genetic data suggested that the Sintashta culture was ultimately derived of a remigration of Central European peoples with steppe ancestry back into the steppe. Some Sintastha individuals displayed similarities with earlier samples collected at Khvalynsk.
Horse genetics
The dispersal of the DOM2 genetic lineage, believed to be the ancestor of all modern domesticated horses, is linked with the populations which preceded the Sintashta culture and their expansions. A genetic study published in 2021 suggests that these horses were selectively bred for desired traits including docility, stress tolerance, endurance running, and higher weight-carrying thresholds.See also
*Sintashta
Sintashta (russian: Синташта́) is an archaeological site in Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia. It is the remains of a fortified settlement dating to the Bronze Age, ''c''. 2800–1600 BC, and is the type site of the Sintashta culture. The site h ...
* Arkaim
* Petrovka settlement
The Petrovka fortified settlement, namesake of the 2nd millennium BC Sintashta-Petrovka culture lies at the Ishim River, near the modern village of Petrovka in Zhambyl District, North Kazakhstan Region, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially t ...
* Country of Towns
* Cimmerians
The Cimmerians (Akkadian: , romanized: ; Hebrew: , romanized: ; Ancient Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people originating in the Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into Wes ...
* Karasuk culture
* Scytho-Siberian world
* Indo-Iranians
Indo-Iranian peoples, also known as Indo-Iranic peoples by scholars, and sometimes as Arya or Aryans from their self-designation, were a group of Indo-European peoples who brought the Indo-Iranian languages, a major branch of the Indo-European l ...
* Vedic period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (ca. 1300–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, betwe ...
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Stanislav A. Grigoriev, "Ancient Indo-Europeans"
{{Central Asian history Archaeological cultures of Central Asia Indo-Iranian archaeological cultures Andronovo culture