Sindh province on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of


 Sindh's first known village settlements date as far back as 7000 BC. Permanent settlements at
Sindh's first known village settlements date as far back as 7000 BC. Permanent settlements at
 The connection between the Sindh and
The connection between the Sindh and
Retrieved 11 December 2006. a view questioned by those who note the diffuse and blurred nature of Hindu and Buddhist practices in the region, especially that of the royalty to be patrons of both and those who believe that Chach may have been a Buddhist. The forces of Muhammad bin Qasim defeated
 In 1339
In 1339
abstract (formerly on AGU website)
(accessed via wayback machine 11 July 2015); se
press release on AGU website
(accessed 11 July 2015). to about 1850.Grove, J.M., ''Little Ice Ages: Ancient and Modern,'' Routledge, London (2 volumes) 2004.Matthews, J.A. and Briffa, K.R.
"The 'Little Ice Age': re-evaluation of an evolving concept"
''Geogr. Ann., 87,'' A (1), pp. 17–36 (2005). Retrieved 17 July 2015. According to Professor Baloch, the climate of Balochistan was very cold during this epoch and the region was uninhabitable during the winters so the Baloch people emigrated in waves to
 After the
After the
 In 1802, when Mir Ghulam Ali Khan Talpur succeeded as the Talpur
In 1802, when Mir Ghulam Ali Khan Talpur succeeded as the Talpur
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province by population after Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi Language, Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also Romanization, romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the I ...
. It shares land borders with the Pakistani provinces
The administrative units of Pakistan comprise four provinces, one federal territory, and two disputed territories: the provinces of Punjab, Sindh, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, and Balochistan; the Islamabad Capital Territory; and the administrative ...
of Balochistan
Balochistan ( ; bal, بلۏچستان; also romanised as Baluchistan and Baluchestan) is a historical region in Western and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian Sea coastline. ...
to the west and north-west and Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi Language, Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also Romanization, romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the I ...
to the north. It shares International border
Borders are usually defined as geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other subnational entities. Political border ...
with the Indian states of Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
and Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern ...
to the east; it is also bounded by the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channe ...
to the south. Sindh's landscape consists mostly of alluvial plain
An alluvial plain is a largely flat landform created by the deposition of sediment over a long period of time by one or more rivers coming from highland regions, from which alluvial soil forms. A floodplain is part of the process, being the smal ...
s flanking the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmi ...
, the Thar Desert
The Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Subcontinent that covers an area of and forms a natural boundary between India and Pakistan. It is the world's 20th-largest desert, ...
in the eastern portion of the province along the international border with India, and the Kirthar Mountains in the western portion of the province.
The economy of Sindh
The economy of Sindh is the 2nd largest of all the provinces in Pakistan. Much of Sindh's economy is influenced by the economy of Karachi, the largest city and economic capital of the country. Historically, Sindh's contribution to Pakistan's GDP ...
is the second-largest in Pakistan after the province of Punjab; its provincial capital of Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former c ...
is the most populous city in the country as well as its main financial hub. Sindh is home to a large portion of Pakistan's industrial sector and contains two of the country's busiest commercial seaports: Port Qasim
The Port Muhammad Bin Qasim ( ur, ''Bandar-gāh Muhammad bin Qāsim''), or Qasim Port Authority ( ur, ), also known as Port Qasim, is a deep-water seaport in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan, on the coastline of the Arabian Sea under the administra ...
and the Port of Karachi
The Port of Karachi ( ur, , ''Bandar gāh Karāchī'') is one of South Asia's largest and busiest deep-water seaports, handling about 60% of the nation's cargo (25 million tons per annum) located in Karachi, Pakistan. It is located on the Kar ...
. The remainder of Sindh consists of an agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
-based economy and produces fruits, consumer items and vegetables for other parts of the country.
Sindh is sometimes referred to as the ''Bab-ul Islam'' (), as it was one of the first regions of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
to fall under Islamic rule. Parts of the modern-day province were intermittently subject to raids by the Rashidun army
The Rashidun army () was the core of the Rashidun Caliphate's armed forces during the early Muslim conquests in the 7th century. The army is reported to have maintained a high level of discipline, strategic prowess and organization, granti ...
during the early Muslim conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests ( ar, الْفُتُوحَاتُ الإسْلَامِيَّة, ), also referred to as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. He estab ...
, but the region did not fall under Muslim rule until the Arab invasion of Sind occurred under the Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
, headed by Muhammad ibn Qasim in 712 CE. Ethnic Sindhi people
Sindhis ( sd, سنڌي Perso-Arabic: सिन्धी Devanagari; ) are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group who speak the Sindhi language and are native to the province of Sindh in Pakistan. After the partition of British Indian empire in 1947, m ...
constitute the largest group in the province; Sindh is also the place of residence for the overwhelming majority of Muhajirs (), a multiethnic group of Indian Muslims
Islam is India's second-largest religion, with 14.2% of the country's population, approximately 172.2 million people identifying as adherents of Islam in 2011 Census. India is also the country with the second or third largest number of Muslim ...
who migrated to the region after the Partition of British India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: India and Pakistan. T ...
in 1947. The province is well known for its distinct culture, which is strongly influenced by Sufism
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality ...
, an important marker of Sindhi identity for both Hindus
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
and Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
. Several important Sindhi Sufi shrines are located throughout the province and attract millions of devotees annually.
Sindh is prominent for its history during the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
under the Indus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900& ...
, and is home to two UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international coope ...
-designated World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
s: the Makli Necropolis and Mohenjo-daro
Mohenjo-daro (; sd, موئن جو دڙو'', ''meaning 'Mound of the Dead Men';Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, ot ...
who conquered Sindh in 325 BC under the command of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
referred to the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmi ...
as '' Indós'', hence the modern ''Indus''. The ancient Iranians referred to everything east of the river Indus as ''hind''. The word ''Sindh'' is a Persian derivative of the Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion ...
term ''Sindhu,'' meaning "river" - a reference to Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmi ...
.
Southworth suggests that the name ''Sindhu'' is in turn derived from ''Cintu'', a Dravidian word for date palm
''Phoenix dactylifera'', commonly known as date or date palm, is a flowering plant species in the palm family, Arecaceae, cultivated for its edible sweet fruit called dates. The species is widely cultivated across northern Africa, the Middle Eas ...
, a tree commonly found in Sindh.
The previous spelling "Sind" (from the Perso-Arabic ) was discontinued in 1988 by an amendment passed in Sindh Assembly, and is now spelt "Sindh."
History
Historical Period (7000 BC-1800)

Prehistoric period

 Sindh's first known village settlements date as far back as 7000 BC. Permanent settlements at
Sindh's first known village settlements date as far back as 7000 BC. Permanent settlements at Mehrgarh
Mehrgarh (; ur, ) is a Neolithic archaeological site (dated ) situated on the Kacchi Plain of Balochistan in Pakistan. It is located near the Bolan Pass, to the west of the Indus River and between the modern-day Pakistani cities of Quetta ...
, currently in Balochistan
Balochistan ( ; bal, بلۏچستان; also romanised as Baluchistan and Baluchestan) is a historical region in Western and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian Sea coastline. ...
, to the west expanded into Sindh. This culture blossomed over several millennia and gave rise to the Indus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900& ...
around 3000 BC.
Indus Valley civilisation
Sindh was the centre of theIndus Valley civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900& ...
, which rivaled the contemporary civilizations of Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
in size and scope, numbering nearly half a million inhabitants at its height with well-planned grid cities and sewer systems.
The primitive village communities in Balochistan
Balochistan ( ; bal, بلۏچستان; also romanised as Baluchistan and Baluchestan) is a historical region in Western and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian Sea coastline. ...
were still struggling against a difficult highland environment, a highly cultured people was trying to assert itself at Kot Diji
The ancient site at Kot Diji ( sd, ڪوٽ ڏیجي; ur, کوٹ ڈیجی) was the forerunner of the Indus Civilization. The occupation of this site is attested already at 3300 BCE. The remains consist of two parts; the citadel area on high ground ...
. This was one of the most developed urban civilizations of the ancient world. It flourished between the 25th and 15th centuries BC in the Indus valley sites of Mohenjo Daro
Mohenjo-daro (; sd, موئن جو دڙو'', ''meaning 'Mound of the Dead Men';Harappa
Harappa (; Urdu/ pnb, ) is an archaeological site in Punjab, Pakistan, about west of Sahiwal. The Bronze Age Harappan civilisation, now more often called the Indus Valley Civilisation, is named after the site, which takes its name from a ...
. The people had a high standard of art and craftsmanship and a well-developed system of quasi-pictographic writing which remains un-deciphered. The ruins of the well planned towns, the brick buildings of the common people, roads, public baths and the covered drainage system suggest a highly organized community.
There is no evidence of large palaces or large tombs for the elite. The grand and presumably holy site might have been the great bath, which is built upon an artificially created elevation. This civilization collapsed around 1700 BC for reasons that are uncertain; the cause is hotly debated and may have been a massive earthquake, which dried up the Ghaggar River. Skeletons discovered in the ruins of Moan Jo Daro ("mount of dead") were thought to indicate that the city was suddenly attacked and the population was wiped out, but further examinations showed that the marks on the skeletons were due to erosion and not of violence.
Early history
The ancient city of Roruka, identified with modernAror
Aror (Sindhi: اروهڙ) or Alor or Arorkot (Sindhi: اروهڙ ڪوٽ) is the medieval name of the city of Rohri (in Sindh, modern Pakistan). Aror once served as the capital of Sindh.
History
As Roruka, capital of the Sauvira Kingdom, it ...
/Rohri
Rohri (Sindhi: روهڙي; ur, ) is a city of Sukkur District, Sindh province, Pakistan. It is located on the east bank of the Indus River, located directly across from Sukkur, the third largest city in Sindh. Rohri town is the administrative ...
, was capital of the Sauvira Kingdom
Sauvīra was an ancient kingdom of the lower Indus Valley mentioned in the Late Vedic and early Buddhist literature and the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. It is often mentioned alongside the Sindhu Kingdom. Its capital city was Roruka, identified ...
, and finds mentioned early Buddhist literature as a major trading center. Sindh finds mention in the Indian epic ''Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the '' Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the K ...
'' as being part of Bharatvarsha. Sindh was conquered by the Persian Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was the largest empire the world had ...
in the sixth century BC. In the late fourth century BC, Sindh was conquered by a mixed army led by Macedonian Greeks under Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
. The region remained under control of Greek satraps for only a few decades. After Alexander's death, there was a brief period of Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
rule, before Sindh was traded to the Mauryan Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until ...
led by Chandragupta in 305 BC. During the rule of the Mauryan Emperor Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, s ...
, the Buddhist religion
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
spread to Sindh.
Mauryan rule ended in 185 BC with the overthrow of the last king by the Shunga
is a type of Japanese erotic art typically executed as a kind of ukiyo-e, often in woodblock print format. While rare, there are also extant erotic painted handscrolls which predate ukiyo-e. Translated literally, the Japanese word ''shunga' ...
Dynasty. In the disorder that followed, Greek rule returned when Demetrius I of Bactria led a Greco-Bactrian
The Bactrian Kingdom, known to historians as the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom or simply Greco-Bactria, was a Hellenistic-era Greek state, and along with the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the easternmost part of the Hellenistic world in Central Asia and the India ...
invasion of India and annexed most of the northwestern lands, including Sindh. Demetrius was later defeated and killed by a usurper, but his descendants continued to rule Sindh and other lands as the Indo-Greek Kingdom
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, also known historically as the Yavana Kingdom (Yavanarajya), was a Hellenistic-era Greek kingdom covering various parts of Afghanistan and the northwestern regions of the Indian subcontinent (p ...
. Under the reign of Menander I
Menander I Soter ( grc, Μένανδρος Σωτήρ, Ménandros Sōtḗr, Menander the Saviour; pi, मिलिन्दो, Milinda), was a Greco-Bactrian and later Indo-Greek King (reigned c.165/155Bopearachchi (1998) and (1991), respectivel ...
, many Indo-Greeks followed his example and converted to Buddhism.
In the late second century BC, Scythian
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
tribes shattered the Greco-Bactrian empire and invaded the Indo-Greek lands. Unable to take the Punjab region
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising a ...
, they invaded South Asia through Sindh, where they became known as Indo-Scythians
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centu ...
(later Western Satraps
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi:, ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central part of India (Saurashtra (region), Saurashtra and Malwa: modern Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajastha ...
). By the first century AD, the Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, ...
annexed Sindh. Kushan
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, ...
s under Kanishka
Kanishka I (Sanskrit: कनिष्क, '; Greco-Bactrian: Κανηϸκε ''Kanēške''; Kharosthi: 𐨐𐨞𐨁𐨮𐨿𐨐 '; Brahmi: '), or Kanishka, was an emperor of the Kushan dynasty, under whose reign (c. 127–150 CE) the empire ...
were great patrons of Buddhism and sponsored many building projects for local beliefs. Ahirs
Ahir or Aheer are a community of traditionally non-elite pastoralists in India, most members of which identify as being of the Indian Yadav community because they consider the two terms to be synonymous. The Ahirs are variously described as a ...
were also found in large numbers in Sindh. Abiria country of Abhira tribe
The Abhira tribe is mentioned in the ancient Indian epic Mahabharata. A historical people of the same name are mentioned in the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea''. They are thought to be people who moved in from eastern Iran in the aftermath of ...
was in southern Sindh.
The Kushan Empire was defeated in the mid-3rd century AD by the Sassanid Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
of Persia, who installed vassals known as the Kushanshahs in these far eastern territories. These rulers were defeated by the Kidarites
The Kidarites, or Kidara Huns, were a dynasty that ruled Bactria and adjoining parts of Central Asia and South Asia in the 4th and 5th centuries. The Kidarites belonged to a complex of peoples known collectively in India as the Huna, and in Eur ...
in the late fourth century.
It then came under the Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Gold ...
after dealing with the Kidarites. By the late fifth century, attacks by Hephthalite
The Hephthalites ( xbc, ηβοδαλο, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during th ...
tribes known as the Indo-Hephthalites or ''Hunas'' (Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
) broke through the Gupta Empire's northwestern borders and overran much of northwestern India.
Afterwards, Sindh came under the rule of Emperor Harshavardhan, then the Rai Dynasty
The Rai dynasty (c. 489–632 CE) was a polity of ancient Sindh.
Scholarship
Pre-Islamic Sindh has been the subject of voluminous scholarship concerning the eve of Arab conquests; otherwise, the paucity of source materials remains a severe hi ...
around 478. The Rais were overthrown by Chachar of Alor around 632. The Brahman dynasty ruled a vast territory that stretched from Multan
Multan (; ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan, on the bank of the Chenab River. Multan is Pakistan's seventh largest city as per the 2017 census, and the major cultural, religious and economic centre of southern Punjab.
Multan is one of the ol ...
in the north to the Rann of Kutch
The Rann of Kutch (alternately spelled as Kuchchh) is a large area of salt marshes that span the border between India and Pakistan. It is located in Gujarat (primarily the Kutch district), India, and in Sindh, Pakistan. It is divided into ...
, Alor was their capital.
Arrival of Islam

Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
was established by the initial Muslim invasions during the Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate ( ar, اَلْخِلَافَةُ ٱلرَّاشِدَةُ, al-Khilāfah ar-Rāšidah) was the first caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was ruled by the first four successive caliphs of Muhammad after his ...
. Al-Hakim ibn Jabalah al-Abdi, who attacked Makran
Makran ( fa, مكران), mentioned in some sources as Mecran and Mokrān, is the coastal region of Baluchistan. It is a semi-desert coastal strip in Balochistan, in Pakistan and Iran, along the coast of the Gulf of Oman. It extends westwards, f ...
in the year AD 649, was an early partisan of Ali ibn Abu Talib
ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, عَلِيّ بْن أَبِي طَالِب; 600 – 661 CE) was the last of four Rightly Guided Caliphs to rule Islam (r. 656 – 661) immediately after the death of Muhammad, and he was the first Shia Imam. ...
.MacLean, Derryl N. (1989), Religion and Society in Arab Sind, pp. 126, BRILL, During the caliphate of Ali, many Jats of Sindh had come under the influence of Shi'ism and some even participated in the Battle of Camel and died fighting for Ali. Under the Umayyads (661 – 750 AD), many Shias sought asylum in the region of Sindh, to live in relative peace in the remote area. Ziyad Hindi is one of those refugees.
Muhammad Ali Jinnah
Muhammad Ali Jinnah (, ; born Mahomedali Jinnahbhai; 25 December 1876 – 11 September 1948) was a barrister, politician, and the founder of Pakistan. Jinnah served as the leader of the All-India Muslim League from 1913 until the ...
claimed that the Pakistan movement
The Pakistan Movement ( ur, , translit=Teḥrīk-e-Pākistān) was a political movement in the first half of the 20th century that aimed for the creation of Pakistan from the Muslim-majority areas of British India. It was connected to the per ...
started when the first Muslim put his foot on the soil of Sindh, which he labelled the "Gateway of Islam" in India.
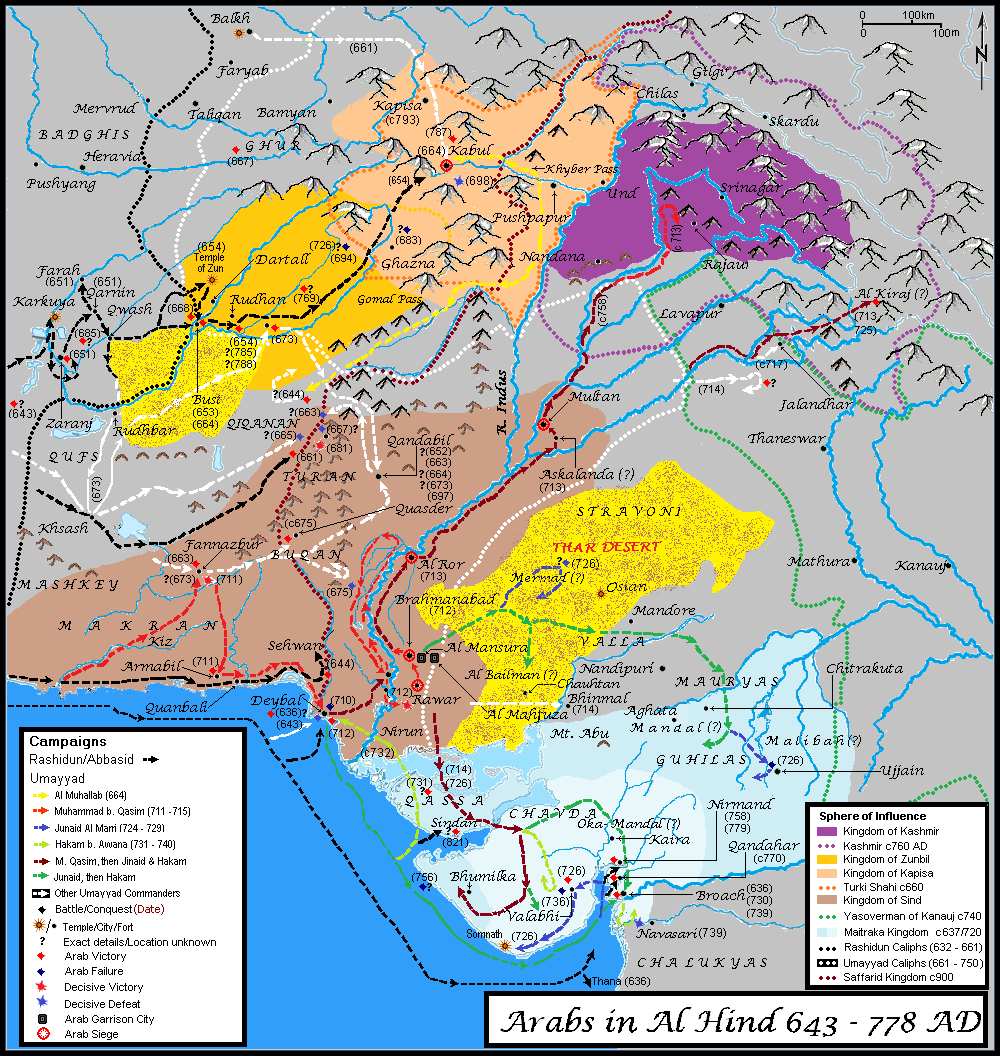
In 712, Muhammad bin Qasim
Muḥammad ibn al-Qāsim al-Thaqāfī ( ar, محمد بن القاسم الثقفي; –) was an Arab military commander in service of the Umayyad Caliphate who led the Muslim conquest of Sindh (part of modern Pakistan), inaugurating the Umayy ...
conquered the Sindh and Indus Valley
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
, bringing South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;; ...
n societies into contact with Islam. Raja Dahir Sen was a Hindu king that ruled over a Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
majority and that Chach of Alor
Chach (c. 631-671 AD) ( sd, چچ)Wink, André. (1991)''Al- Hind, the Making of the Indo-Islamic World: The slave kings and the Islamic conquest''. 2, p. 153 Leiden: Brill. was a Hindu Brahmin king of Sindh region of the Indian subcontinent in th ...
and his kin were regarded as usurpers of the earlier Buddhist Rai Dynasty
The Rai dynasty (c. 489–632 CE) was a polity of ancient Sindh.
Scholarship
Pre-Islamic Sindh has been the subject of voluminous scholarship concerning the eve of Arab conquests; otherwise, the paucity of source materials remains a severe hi ...
,Nicholas F. Gier, ''FROM MONGOLS TO MUGHALS: RELIGIOUS VIOLENCE IN INDIA 9TH-18TH CENTURIES'', presented at the Pacific Northwest Regional Meeting American Academy of Religion, Gonzaga University, May 200Retrieved 11 December 2006. a view questioned by those who note the diffuse and blurred nature of Hindu and Buddhist practices in the region, especially that of the royalty to be patrons of both and those who believe that Chach may have been a Buddhist. The forces of Muhammad bin Qasim defeated
Raja Dahir
Raja Dahiraud (; ''Raja Dahiraud ''; 663 – 712 CE) was the last Hindu ruler of Sindh in present-day Pakistan. In 711 CE his kingdom was invaded by the Umayyad Caliphate led by Muhammad bin Qasim where Dahiraud died while defending his ki ...
in alliance with the Hindu Jats
The Jat people ((), ()) are a traditionally agricultural community in Northern India and Pakistan. Originally pastoralists in the lower Indus river-valley of Sindh, Jats migrated north into the Punjab region in late medieval times, and su ...
and other regional governors.
In 711 AD, Muhammad bin Qasim
Muḥammad ibn al-Qāsim al-Thaqāfī ( ar, محمد بن القاسم الثقفي; –) was an Arab military commander in service of the Umayyad Caliphate who led the Muslim conquest of Sindh (part of modern Pakistan), inaugurating the Umayy ...
led an Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
force of 20,000 cavalry and 5 catapults. Muhammad bin Qasim defeated the Raja Dahir
Raja Dahiraud (; ''Raja Dahiraud ''; 663 – 712 CE) was the last Hindu ruler of Sindh in present-day Pakistan. In 711 CE his kingdom was invaded by the Umayyad Caliphate led by Muhammad bin Qasim where Dahiraud died while defending his ki ...
and captured the cities of Alor, Multan and Debal
Debal (Urdu, Arabic, sd, ) was an ancient port located near modern Karachi, Pakistan. It is adjacent to the nearby Manora Island and was administered by Mansura, and later Thatta.
Etymology
In Arabic history books, most notably in the early ...
. Sindh became the easternmost State of the Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
and was referred to as "Sind" on Arab maps, with lands further east known as "Hind". Muhammad bin Qasim built the city of Mansura as his capital; the city then produced famous historical figures such as Abu Mashar Sindhi
Abu Ma'shar Najih al-Sindi al-Madani (full name: , ar, أبو معشر نجيح بن عبد الرحمن السندي المدني), d. 787, was a Muslim historian and hadith scholar. A contemporary of Ibn Ishaq, he wrote the , fragments of whic ...
, Abu Ata al-Sindhi, Abu Raja Sindhi
Abu Raja Al-Sindi(Arabic)ابو راجه السندي (d. 321 AH/d. 10th century AD) was an Arabic scholar of Sindhi origin in what is now Pakistan. He specialised in the study of Quran, Hadith and Arab literature. He was also a teacher of Arab ...
. At the port city of Debal
Debal (Urdu, Arabic, sd, ) was an ancient port located near modern Karachi, Pakistan. It is adjacent to the nearby Manora Island and was administered by Mansura, and later Thatta.
Etymology
In Arabic history books, most notably in the early ...
, most of the Bawarij embraced Islam and became known as Sindhi Sailors, who were renowned for their navigation, geography and languages. After Bin Qasim left, the Arab Caliphate
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
ruled Sindh through the Governors.
By the year 750, Debal
Debal (Urdu, Arabic, sd, ) was an ancient port located near modern Karachi, Pakistan. It is adjacent to the nearby Manora Island and was administered by Mansura, and later Thatta.
Etymology
In Arabic history books, most notably in the early ...
(modern Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former c ...
) was second only to Basra
Basra ( ar, ٱلْبَصْرَة, al-Baṣrah) is an Iraqi city located on the Shatt al-Arab. It had an estimated population of 1.4 million in 2018. Basra is also Iraq's main port, although it does not have deep water access, which is han ...
; Sindhi sailors from the port city of Debal voyaged to Basra, Bushehr
Bushehr, Booshehr or Bushire ( fa, بوشهر ; also romanised as ''Būshehr'', ''Bouchehr'', ''Buschir'' and ''Busehr''), also known as Bandar Bushehr ( fa, ; also romanised as ''Bandar Būshehr'' and ''Bandar-e Būshehr''), previously Antio ...
, Musqat, Aden
Aden ( ar, عدن ' Yemeni: ) is a city, and since 2015, the temporary capital of Yemen, near the eastern approach to the Red Sea (the Gulf of Aden), some east of the strait Bab-el-Mandeb. Its population is approximately 800,000 peopl ...
, Kilwa
Kilwa Kisiwani (English: ''Kilwa Island'') is an island, national historic site, and hamlet community located in the township of Kilwa Masoko, the district seat of Kilwa District in the Tanzanian region of Lindi Region in southern Tanzania. Ki ...
, Zanzibar
Zanzibar (; ; ) is an insular semi-autonomous province which united with Tanganyika in 1964 to form the United Republic of Tanzania. It is an archipelago in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of the mainland, and consists of many small islan ...
, Sofala
Sofala, at present known as Nova Sofala, used to be the chief seaport of the Mwenemutapa Kingdom, whose capital was at Mount Fura. It is located on the Sofala Bank in Sofala Province of Mozambique. It was founded by Somali merchants. This name ...
, Malabar, Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
and Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
(where Sindhi merchants were known as the Santri
In Indonesia, ''santri'' is a term for someone who follows Islamic religious education in ''pesantren'' (Islamic boarding schools). Santri usually stay in the place until their education is complete. After completing their study period, some of ...
). During the Decline of the Abbasid Caliphate in 860s, the Habbari dynasty became semi-independent and was eliminated and Mansura was invaded by Sultan Mahmud Ghaznavi. Sindh then again became an easternmost client State of the Later Abbasid Caliphs ruled by the Soomro Dynasty
The Soomra (or Soomro) dynasty (, '' lit.'' the family/dynasty of the Soomras) was a late medieval dynasty of Sindh, and at times adjacent regions, located in what is now Pakistan.
Sources
The only contemporary literary source remains the ' ...
until the siege of Baghdad (1258)
The siege of Baghdad was a siege that took place in Baghdad in 1258, lasting for 13 days from January 29, 1258 until February 10, 1258. The siege, laid by Ilkhanate Mongol forces and allied troops, involved the investment, capture, and sac ...
. Mansura was the first capital of the Soomra Dynasty
The Soomra (or Soomro) dynasty (, '' lit.'' the family/dynasty of the Soomras) was a late medieval dynasty of Sindh, and at times adjacent regions, located in what is now Pakistan.
Sources
The only contemporary literary source remains the ' ...
and the last of the Habbari dynasty. Muslim geographers, historians and travelers such as al-Masudi
Al-Mas'udi ( ar, أَبُو ٱلْحَسَن عَلِيّ ٱبْن ٱلْحُسَيْن ٱبْن عَلِيّ ٱلْمَسْعُودِيّ, '; –956) was an Arab historian, geographer and traveler. He is sometimes referred to as the " Herodotu ...
, Ibn Hawqal
Muḥammad Abū’l-Qāsim Ibn Ḥawqal (), also known as Abū al-Qāsim b. ʻAlī Ibn Ḥawqal al-Naṣībī, born in Nisibis, Upper Mesopotamia; was a 10th-century Arab Muslim writer, geographer, and chronicler who travelled during the ye ...
, Istakhri
Abu Ishaq Ibrahim ibn Muhammad al-Farisi al-Istakhri () (also ''Estakhri'', fa, استخری, i.e. from the Iranian city of Istakhr, b. - d. 346 AH/AD 957) was a 10th-century travel-author and geographer who wrote valuable accounts in Arab ...
, Ahmed ibn Sahl al-Balkhi, al-Tabari
( ar, أبو جعفر محمد بن جرير بن يزيد الطبري), more commonly known as al-Ṭabarī (), was a Muslim historian and scholar from Amol, Tabaristan. Among the most prominent figures of the Islamic Golden Age, al-Tabari ...
, Baladhuri, Nizami, al-Biruni
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (973 – after 1050) commonly known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian in scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously the "founder of Indology", "Father of Co ...
, Saadi Shirazi
Saadi Shīrāzī ( fa, ابومحمّد مصلحالدین بن عبدالله شیرازی), better known by his pen name Saadi (; fa, سعدی, , ), also known as Sadi of Shiraz (, ''Saʿdī Shīrāzī''; born 1210; died 1291 or 1292), was ...
, Ibn Battutah and Katip Çelebi wrote about or visited the region, sometimes using the name "Sindh" for the entire area from the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channe ...
to the Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and western Afghanistan, Quote: "The Hindu Kush mountains run along the Afghan border with the North-West Frontier Province ...
.
Soomra dynasty period
When Sindh was under theArab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
Caliphate
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
, the Arab Habbari dynasty was in control. The Umayyads appointed Aziz al Habbari as the governor of Sindh. Habbaris ruled Sindh until Sultan Mahmud Ghaznavi defeated the Habbaris in 1024. Sultan Mahmud Ghaznavi viewed the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttal ...
to be the caliphs thus he removed the remaining influence of the Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
in the region and Sindh fell to Abbasid control following the defeat of the Habbaris. The Abbasid Caliphate then appointed Al Khafif from Samarra
Samarra ( ar, سَامَرَّاء, ') is a city in Iraq. It stands on the east bank of the Tigris in the Saladin Governorate, north of Baghdad. The city of Samarra was founded by Abbasid Caliph Al-Mutasim for his Turkish professional ar ...
; 'Soomro' means 'of Samarra' in Sindhi. The new governor of Sindh was to create a better, stronger and stable government. Once he became the governor, he allotted several key positions to his family and friends; thus Al-Khafif or Sardar Khafif Soomro formed the Soomro Dynasty
The Soomra (or Soomro) dynasty (, '' lit.'' the family/dynasty of the Soomras) was a late medieval dynasty of Sindh, and at times adjacent regions, located in what is now Pakistan.
Sources
The only contemporary literary source remains the ' ...
in Sindh; and became its first ruler. Until the siege of Baghdad (1258)
The siege of Baghdad was a siege that took place in Baghdad in 1258, lasting for 13 days from January 29, 1258 until February 10, 1258. The siege, laid by Ilkhanate Mongol forces and allied troops, involved the investment, capture, and sac ...
, the Soomro dynasty was the Abbasid Caliphate's functionary in Sindh, but after that it became independent.
When the Soomro dynasty
The Soomra (or Soomro) dynasty (, '' lit.'' the family/dynasty of the Soomras) was a late medieval dynasty of Sindh, and at times adjacent regions, located in what is now Pakistan.
Sources
The only contemporary literary source remains the ' ...
lost ties with the Abbasid Caliphate after the siege of Baghdad, the Soomra ruler Dodo-I established their rule from the shores of the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channe ...
to the Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi Language, Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also Romanization, romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the I ...
in the north and in the east to Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern ...
and in the west to Pakistani Balochistan
Balochistan ( ; bal, بلۏچستان; also romanised as Baluchistan and Baluchestan) is a historical region in Western and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian Sea coastline. ...
. The Soomro
Soomro ( sd, سومرو, सूमरो) or Soomra or Sumrah is a tribe having a local origin in Sindh who had later claimed to being either Rajputs or Arabs. They are found in Sindh, parts of Punjab especially bordering Sindh, Balochistan provi ...
s were one of the first indigenous Muslim dynasties in Sindh of Parmar
Parmar is a Rajput clan found in Northern and Central India, especially in Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana, Kutch, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh and North Maharashtra.
See also
* Paramara Dynasty
* Panwar Dynasty
* Pawa ...
Rajput
Rajput (from Sanskrit ''raja-putra'' 'son of a king') is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating from the Indian subcontinent. The term Ra ...
origin. They were the first Muslims to translate the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , ...
into the Sindhi language
Sindhi ( ; , ) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by about 30 million people in the Pakistani province of Sindh, where it has official status. It is also spoken by a further 1.7 million people in India, where it is a scheduled language, witho ...
. The Soomros created a chivalrous culture in Sindh, which eventually facilitated their rule centred at Mansura. It was later abandoned due to changes in the course of the Puran River; they ruled for the next 95 years until 1351. During this period, Kutch was ruled by the Samma Dynasty
The Samma dynasty ( sd, سمن جو راڄ, ) was a medieval Sindhi dynasty in the Indian subcontinent, that ruled Sindh, as well as parts of Kutch, Punjab and Balochistan from 1351 to 1524 CE, with their capital at Thatta known as Sa ...
, who enjoyed good relations with the Soomras in Sindh. Since the Soomro Dynasty
The Soomra (or Soomro) dynasty (, '' lit.'' the family/dynasty of the Soomras) was a late medieval dynasty of Sindh, and at times adjacent regions, located in what is now Pakistan.
Sources
The only contemporary literary source remains the ' ...
lost its support from the Abbasid Caliphate, the Sultans of Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
wanted a piece of Sindh. The Soomros successfully defended their kingdom for about 36 years, but their dynasties soon fell to the might of the Sultanate of Delhi
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526).
's massive armies such as the Tughluk
The Tughlaq dynasty ( fa, ), also referred to as Tughluq or Tughluk dynasty, was a Muslim dynasty of Indo- Turkic origin which ruled over the Delhi sultanate in medieval India. Its reign started in 1320 in Delhi when Ghazi Malik assumed the ...
s and the Khaljis.
Samma dynasty period
 In 1339
In 1339 Jam Unar
Jam Feruzuddin Al-Maroof Jam Unar bin Babinah ( sd, ڄام انڙ) was the first ruler of the Samma dynasty, which ruled Sindh and parts of Punjab from 1335–1520 C.E.
History
It was in 752 A.H. (1351 C.E.) that Jám Unar son of Babinah was ...
founded a Sindhi Muslim Rajput
Muslim Rajputs are the descendants of Rajputs of Northern regions of the Indian subcontinent who are followers of Islam. They converted from Hinduism to Islam from the medieval period in India onwards, retaining historically Hindu surnames suc ...
Samma Dynasty
The Samma dynasty ( sd, سمن جو راڄ, ) was a medieval Sindhi dynasty in the Indian subcontinent, that ruled Sindh, as well as parts of Kutch, Punjab and Balochistan from 1351 to 1524 CE, with their capital at Thatta known as Sa ...
and challenged the Sultans of Delhi
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it ...
. He used the title of the ''Sultan of Sindh''. The Samma tribe
Samma are a very large and important indigenous tribe of Sindh. The Samma are spread across Pakistan and North- West India being most concentrated in Sindh , their origin but are also found throughout the Punjab region as well as parts of Baloch ...
reached its peak during the reign of Jam Nizamuddin II
Jám Nizámuddín II ( sd, ڄام نظام الدين ثاني, ur, جام نظام الدين ثاني; 1439–1509), also known as Jam Nizam al-Din or Jám Nindó ( sd, ڄام نندو, links=no), was the Sultan of Sindh between 1461 and 1508 ...
(also known by the nickname Jám Nindó). During his reign from 1461 to 1509, Nindó greatly expanded the new capital of Thatta and its Makli hills, which replaced Debal
Debal (Urdu, Arabic, sd, ) was an ancient port located near modern Karachi, Pakistan. It is adjacent to the nearby Manora Island and was administered by Mansura, and later Thatta.
Etymology
In Arabic history books, most notably in the early ...
. He patronized Sindhi art, architecture and culture. The Samma had left behind a popular legacy especially in architecture, music and art. Important court figures included the poet Kazi Kadal, Sardar Darya Khan, Moltus Khan, Makhdoom Bilawal and the theologian
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the ...
Kazi Kaadan. However, Thatta was a port city; unlike garrison towns, it could not mobilize large armies against the Arghun
Arghun Khan (Mongolian Cyrillic: ''Аргун хан''; Traditional Mongolian: ; c. 1258 – 10 March 1291) was the fourth ruler of the Mongol empire's Ilkhanate, from 1284 to 1291. He was the son of Abaqa Khan, and like his father, was a dev ...
and Tarkhan Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
invaders, who killed many regional Sindhi Mirs
Hot Mobile ( he, הוט מובייל, formerly known as Mirs Communications Ltd. until May 2012), is a wireless telecommunications company based in Israel and a subsidiary of Hot Telecommunication Systems Ltd. (HOT).
Hot Mobile provides nationwid ...
and Amir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cer ...
s loyal to the Samma. Some parts of Sindh still remained under the Sultans of Delhi and the ruthless Arghuns and the Tarkhan
Tarkhan ( otk, 𐱃𐰺𐰴𐰣, Tarqan, mn, or ; fa, ترخان; ; ar , طرخان; alternative spellings ''Tarkan'', ''Tarkhaan'', ''Tarqan'', ''Tarchan'', ''Turxan'', ''Tarcan'', ''Turgan, Tárkány, Tarján'') is an ancient Central Asia ...
s sacked Thatta during the rule of Jam Feroz
Nasir al-Din Abu al-Fatah Firuz Shah II (Sindhi: نصيرالدين ابو الفتح فيروز شاھ ثاني), son of Jam Nizam al-Din commonly known as Jam Feroz (1508–1524/5), was the last ruler of the Samma Dynasty of Sindh. Jam Feroz pro ...
udin.
Migration of Baloch
According to Dr. Akhtar Baloch,Professor
Professor (commonly abbreviated as Prof.) is an academic rank at universities and other post-secondary education and research institutions in most countries. Literally, ''professor'' derives from Latin as a "person who professes". Professo ...
at University of Karachi
The University of Karachi ( sd, ; informally Karachi University, KU, or UoK) is a public research university located in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan. Established in June 1951 by an act of Parliament and as a successor to the University of Sindh ...
, and Nadeem Wagan, General Manager
A general manager (GM) is an executive who has overall responsibility for managing both the revenue and cost elements of a company's income statement, known as profit & loss (P&L) responsibility. A general manager usually oversees most or all of ...
at HANDS
A hand is a prehensile, multi- fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala (which has two opposable thumbs on eac ...
, the Balochi migrated from Balochistan
Balochistan ( ; bal, بلۏچستان; also romanised as Baluchistan and Baluchestan) is a historical region in Western and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian Sea coastline. ...
during the Little Ice Age
The Little Ice Age (LIA) was a period of regional cooling, particularly pronounced in the North Atlantic region. It was not a true ice age of global extent. The term was introduced into scientific literature by François E. Matthes in 1939. Ma ...
and settled in Sindh and Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi Language, Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also Romanization, romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the I ...
. The Little Ice Age is conventionally defined as a period extending from the sixteenth to the nineteenth centuries, (noted in Grove 2004:4). or alternatively, from about 1300Miller ''et al''. 2012. "Abrupt onset of the Little Ice Age triggered by volcanism and sustained by sea-ice/ocean feedbacks" ''Geophysical Research Letters'' 39, 31 Januaryabstract (formerly on AGU website)
(accessed via wayback machine 11 July 2015); se
press release on AGU website
(accessed 11 July 2015). to about 1850.Grove, J.M., ''Little Ice Ages: Ancient and Modern,'' Routledge, London (2 volumes) 2004.Matthews, J.A. and Briffa, K.R.
"The 'Little Ice Age': re-evaluation of an evolving concept"
''Geogr. Ann., 87,'' A (1), pp. 17–36 (2005). Retrieved 17 July 2015. According to Professor Baloch, the climate of Balochistan was very cold during this epoch and the region was uninhabitable during the winters so the Baloch people emigrated in waves to
Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
and Punjab.
Mughal era
In the year 1524, the few remaining SindhiAmirs
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cerem ...
welcomed the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
and Babur
Babur ( fa, , lit= tiger, translit= Bābur; ; 14 February 148326 December 1530), born Mīrzā Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad, was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through hi ...
dispatched his forces to rally the Arghuns and the Tarkhans, branches of a Turkic dynasty. In the coming centuries, Sindh became a region loyal to the Mughals, a network of forts manned by cavalry and musketeers further extended Mughal power in Sindh. In 1540 a mutiny by Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri ( ps, شیرشاه سوری)
(1472, or 1486 – 22 May 1545), born Farīd Khān ( ps, فرید خان)
, was the founder of the Sur Empire in India, with its capital in Sasaram in modern-day Bihar. He standardized the silver coin ...
forced the Mughal Emperor Humayun
Nasir-ud-Din Muhammad ( fa, ) (; 6 March 1508 – 27 January 1556), better known by his regnal name, Humāyūn; (), was the second emperor of the Mughal Empire, who ruled over territory in what is now Eastern Afghanistan, Pakistan, Northe ...
to withdraw to Sindh, where he joined the Sindhi Emir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cer ...
Hussein Umrani. In 1541 Humayun
Nasir-ud-Din Muhammad ( fa, ) (; 6 March 1508 – 27 January 1556), better known by his regnal name, Humāyūn; (), was the second emperor of the Mughal Empire, who ruled over territory in what is now Eastern Afghanistan, Pakistan, Northe ...
married Hamida Banu Begum
Hamida Banu Begum ( 1527 – 29 August 1604), was the queen consort of the second Mughal emperor Humayun and the mother of his successor, the third Mughal emperor Akbar.Akbar
Abu'l-Fath Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar (25 October 1542 – 27 October 1605), popularly known as Akbar the Great ( fa, ), and also as Akbar I (), was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Hum ...
at Umarkot in the year 1542.
During the reign of Akbar the Great
Abu'l-Fath Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar (25 October 1542 – 27 October 1605), popularly known as Akbar the Great ( fa, ), and also as Akbar I (), was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Hum ...
, Sindh produced scholars and others such as Mir Ahmed Nasrallah Thattvi
Mir Ahmed Nasrallah Thattvi (d.1588) was born in Thatta, Sindh. He was among the well respected and well traveled Muslim scholars at the court of Mughal Emperor Akbar. He was the son of a Qazi (Kazi) in Thatta. During his early life he was in a ...
, Tahir Muhammad Thattvi Mir Tahir Muhammad Ibn Hassan Sabzavari Tattavi was a Sindhi Muslim poet and historian during the rule of the Mughal Empire, who composed poetry under the pen-name ''Nisyani''. His family emigrated to Thatta, Sindh from Iran. His original ancestra ...
and Mir Ali Sir Thattvi
Mir Ali Sher Thattavi, Qaune (b.1728 - d.1788) was a Sindhi Muslim historian born after the rule of Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb. It has been said that he composed his first verses of poetry while still a boy, he studied the Fatawa-e-Alamgiri and lat ...
and the Mughal chronicler Abu'l-Fazl ibn Mubarak
Abu'l-Fazl ibn Mubarak, also known as Abul sharma, Abu'l Fadl and Abu'l-Fadl 'Allami (14 January 1551 – 22 August 1602), was the grand vizier of the Mughal emperor Akbar, from his appointment in 1579 until his death in 1602. He was the aut ...
and his brother the poet Faizi was a descendant of a Sindhi Shaikh family from Rel, Siwistan in Sindh. Abu'l-Fazl ibn Mubarak was the author of ''Akbarnama
The ''Akbarnama'', which translates to ''Book of Akbar'', the official chronicle of the reign of Akbar, the third Mughal Emperor (), commissioned by Akbar himself and written by his court historian and biographer, Abu'l-Fazl ibn Mubarak. It was w ...
'' (an official biographical account of Akbar) and the ''Ain-i-Akbari
The ''Ain-i-Akbari'' ( fa, ) or the "Administration of Akbar", is a 16th-century detailed document recording the administration of the Mughal Empire under Emperor Akbar, written by his court historian, Abu'l Fazl in the Persian language. It for ...
'' (a detailed document recording the administration of the Mughal Empire).
Shah Jahan
Shihab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram (5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), better known by his regnal name Shah Jahan I (; ), was the fifth emperor of the Mughal Empire, reigning from January 1628 until July 1658. Under his emperorship, the Mugha ...
carved a subah
A Subah was the term for a province (State) in the Mughal Empire. The word is derived from Arabic and Persian. The governor/ruler of a ''Subah'' was known as a '' subahdar'' (sometimes also referred to as a "''Subeh''"), which later became ''sub ...
(imperial province), covering Sindh, called Thatta after its capital, out of Multan
Multan (; ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan, on the bank of the Chenab River. Multan is Pakistan's seventh largest city as per the 2017 census, and the major cultural, religious and economic centre of southern Punjab.
Multan is one of the ol ...
, further bordering on the Ajmer and Gujarat subahs as well as the rival Persian Safavid empire
Safavid Iran or Safavid Persia (), also referred to as the Safavid Empire, '. was one of the greatest Iranian empires after the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia, which was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often conside ...
.
During the Kalhora period, Sindhi literature began to flourish and historical figures such as Shah Abdul Latif Bhittai
Shah Abdul Latif Bhittai ( sd, شاھ عبداللطيف ڀٽائي, ur, ; 1689/1690 – 21 December 1752), commonly known by the honorifics ''Lakhino Latif'', ''Latif Ghot'', ''Bhittai'', and ''Bhit Jo Shah'', was a Sindhi Sufi mystic, and ...
, Sulatn-al-Aoliya Muhammad Zaman and Sachal Sarmast
Sachal Sarmast or Sacho Sarmast ( sd, سچو سرمست (1739–1827), born Abdul Wahab Farooqi ( ur, عبد الوہاب فاروقی) was a prominent and a legendary Sindhi Sufi poet from Sindh (Mehran) in modern-day Pakistan.
Biography
Sach ...
became prominent throughout the land. In 1603 Shah Jahan
Shihab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram (5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), better known by his regnal name Shah Jahan I (; ), was the fifth emperor of the Mughal Empire, reigning from January 1628 until July 1658. Under his emperorship, the Mugha ...
visited the State of Sindh; at Thatta, he was generously welcomed by the locals after the death of his father Jahangir
Nur-ud-Din Muhammad Salim (30 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was the fourth Mughal Emperor, who ruled from 1605 until he died in 1627. He was named after the Indian Sufi saint, Salim Chishti.
Ear ...
. Shah Jahan ordered the construction of the Shahjahan Mosque
The Shah Jahan Mosque ( ur, , sd, مسجد شاهجهاني،, fa, مسجد شاهجهان), also known as the Jamia Masjid of Thatta ( ur, , sd, شاھجھاني مسجد ٺٽو), is a 17th-century building that serves as the central mo ...
, which was completed during the early years of his rule under the supervision of Mirza Ghazi Beg
Mirza Ghazi Beg Tarkhan ( fa, میرزا غازى بیگ ترخان, r. 1599–1612 CE) of the Tarkhan dynasty in Sindh ruled from the capital city of Thatta. He was the most powerful Mughal governor who administered Sindh, during whose rule the ...
. During his reign, in 1659 in the Mughal Empire, Muhammad Salih Tahtawi of Thatta created a seamless celestial globe
Celestial globes show the apparent positions of the stars in the sky. They omit the Sun, Moon, and planets because the positions of these bodies vary relative to those of the stars, but the ecliptic, along which the Sun moves, is indicated.
...
with Arabic and Persian inscriptions using a wax casting method.
Sindh was home to several wealthy merchant-rulers such as Mir Bejar of Sindh, whose great wealth had attracted the close ties with the Sultan bin Ahmad of Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of ...
.
Kalhora Nawabs dynasty
In the year 1701, the Kalhora Nawabs were authorized in afirman
A firman ( fa, , translit=farmân; ), at the constitutional level, was a royal mandate or decree issued by a sovereign in an Islamic state. During various periods they were collected and applied as traditional bodies of law. The word firman co ...
by the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling ...
to administer subah
A Subah was the term for a province (State) in the Mughal Empire. The word is derived from Arabic and Persian. The governor/ruler of a ''Subah'' was known as a '' subahdar'' (sometimes also referred to as a "''Subeh''"), which later became ''sub ...
Sindh.
From 1752 to 1762, Marathas
The Marathi people ( Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a ...
collected Chauth
Chauth (from Sanskrit, meaning ''one fourth'') was a regular tax or tribute imposed from the early 18th century by the Maratha Empire in the Indian subcontinent. It was an annual tax nominally levied at 25% on revenue or produce, hence the name, ...
or tributes from Sindh, and was administered by 10,000 marathas Maratha power was decimated in the entire region after the Third Battle of Panipat in 1761. In 1762, Mian Ghulam Shah Kalhoro brought stability in Sindh, he reorganized and killed all the Maratha
The Marathi people ( Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed a ...
s and their prominent vassal the ''Rao of Kuch'' in the Thar Desert
The Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Subcontinent that covers an area of and forms a natural boundary between India and Pakistan. It is the world's 20th-largest desert, ...
with the help of Durrani empire. However the Marathas briefly again invaded Sindh in 1772.
Sikh empire
 After the
After the Sikhs
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism (Sikhi), a monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The ter ...
annexed Multan
Multan (; ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan, on the bank of the Chenab River. Multan is Pakistan's seventh largest city as per the 2017 census, and the major cultural, religious and economic centre of southern Punjab.
Multan is one of the ol ...
, the Kalhora Dynasty supported counterattacks against the Sikhs and defined their borders.
In 1783 a firman
A firman ( fa, , translit=farmân; ), at the constitutional level, was a royal mandate or decree issued by a sovereign in an Islamic state. During various periods they were collected and applied as traditional bodies of law. The word firman co ...
was issued which designated Mir Fateh Ali Khan Talpur as the new ''Nawab
Nawab ( Balochi: نواب; ar, نواب;
bn, নবাব/নওয়াব;
hi, नवाब;
Punjabi : ਨਵਾਬ;
Persian,
Punjabi ,
Sindhi,
Urdu: ), also spelled Nawaab, Navaab, Navab, Nowab, Nabob, Nawaabshah, Nawabshah or Nobab, ...
of Sindh'', and mediated peace particularly after the Battle of Halani The Battle of Halani was fought in 1783 between the Baloch tribe of Talpurs and the Sindhi tribe of Kalhora near Halani village for the control of the Sindh region, in modern-day Pakistan. The Talpurs, led by Mir Fateh Ali Khan Talpur, won the ba ...
and the defeat of the ruling Kalhora
The Kalhora () is a Sindhi tribe of Sindh, Pakistan, they claim Arab origin and direct descendants from Al-Hakim I and ultimately Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib, companion and paternal uncle of Islamic prophet Muhammad.
They founded the Kalhora D ...
by the Talpur Baloch tribes.
Talpurs
The Talpur dynasty was established by members of the Talpur tribe. The Talpur tribes migrated from Dera Ghazi Khan in Punjab to Sindh on the invitation of Kalhora to help them organize unruly Baloch tribes living in Sindh. Talpurs, who learned the Sindhi language, settled in northern Sindh. Very soon they united all the Baloch tribes of Sindh and formed a confederacy against the Kalhora Dynasty. Four branches of the dynasty were established following the defeat of the Kalhora dynasty at theBattle of Halani The Battle of Halani was fought in 1783 between the Baloch tribe of Talpurs and the Sindhi tribe of Kalhora near Halani village for the control of the Sindh region, in modern-day Pakistan. The Talpurs, led by Mir Fateh Ali Khan Talpur, won the ba ...
in 1743: one ruled lower Sindh from the city of Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River, in the northern part of Southern Indi ...
, another ruled over upper Sindh from the city of Khairpur, a third ruled around the eastern city of Mirpur Khas
Mirpur Khas (Sindhi and ; ''meaning "Town of the most-high Mirs"'') is the capital city of the Mirpur Khas District and Mirpur Khas Division in the Sindh province, Pakistan. Mirpur Khas is the 16th largest city in Sindh province and the 80th ...
, and a fourth was based in Tando Muhammad Khan
Tando Muhammad Khan ( sd, ٽنڊو محمد خان; ur, ) is a city and headquarter of the Tando Muhammad Khan District located in Sindh, Pakistan. Is is named after Mir Muhammad Khan Talpur Shahwani.
It is the 95th largest city of Pakistan, ...
. The Talpurs were ethnically Baloch, and Shia
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, mos ...
by faith. They ruled from 1783, until 1843, when they were in turn defeated by the forces of the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Sou ...
at the Battle of Miani and Dubbo
Dubbo () is a city in the Orana Region of New South Wales, Australia. It is the largest population centre in the Orana region, with a population of 43,516 at June 2021.
The city is located at the intersection of the Newell, Mitchell, and Go ...
. The northern Khairpur branch of the Talpur dynasty, however, continued to maintain a degree of sovereignty during the period colonial rule as the princely state of Khairpur, whose ruler elected to join the new Dominion of Pakistan
Between 14 August 1947 and 23 March 1956, Pakistan was an independent federal dominion in the Commonwealth of Nations, created by the passing of the Indian Independence Act 1947 by the British parliament, which also created the Dominion of ...
in October 1947 as an autonomous region, before being fully amalgamated in the West Pakistan
West Pakistan ( ur, , translit=Mag̱ẖribī Pākistān, ; bn, পশ্চিম পাকিস্তান, translit=Pôścim Pakistan) was one of the two Provincial exclaves created during the One Unit Scheme in 1955 in Pakistan. It was ...
in 1955.
Modern period (1800–present)
Colonial period
 In 1802, when Mir Ghulam Ali Khan Talpur succeeded as the Talpur
In 1802, when Mir Ghulam Ali Khan Talpur succeeded as the Talpur Nawab
Nawab ( Balochi: نواب; ar, نواب;
bn, নবাব/নওয়াব;
hi, नवाब;
Punjabi : ਨਵਾਬ;
Persian,
Punjabi ,
Sindhi,
Urdu: ), also spelled Nawaab, Navaab, Navab, Nowab, Nabob, Nawaabshah, Nawabshah or Nobab, ...
, internal tensions broke out in the state. As a result, the following year the Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian confederation that came to dominate much of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of Sh ...
declared war on Sindh and Berar Subah, during which Arthur Wellesley took a leading role causing much early suspicion between the Emir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cer ...
s of Sindh and the East India Company administration. The East India Company made its first contacts in the Sindhi port city of Thatta, which according to a report was:
"a city as large as London containing 50,000 houses which were made of stone and mortar with largeverandah A veranda or verandah is a roofed, open-air gallery or porch, attached to the outside of a building. A veranda is often partly enclosed by a railing and frequently extends across the front and sides of the structure. Although the form ''vera ...s some three or four stories high ... the city has 3,000loom A loom is a device used to weave cloth and tapestry. The basic purpose of any loom is to hold the warp threads under tension to facilitate the interweaving of the weft threads. The precise shape of the loom and its mechanics may vary, but t ...s ... the textiles of Sindh were the flower of the whole produce of the East, the international commerce of Sindh gave it a place among that of Nations, Thatta has 400 schools and 4,000Dhow Dhow ( ar, داو, translit=dāwa; mr, script=Latn, dāw) is the generic name of a number of traditional sailing vessels with one or more masts with settee or sometimes lateen sails, used in the Red Sea and Indian Ocean region. Typically spo ...s at its docks, the city is guarded by well armedSepoy ''Sepoy'' () was the Persian-derived designation originally given to a professional Indian infantryman, traditionally armed with a musket, in the armies of the Mughal Empire. In the 18th century, the French East India Company and its ot ...s".
Bengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William and later Bengal Province, was a subdivision of the British Empire in India. At the height of its territorial jurisdiction, it covered large parts of what is now South Asia an ...
forces under General Charles James Napier
General Sir Charles James Napier, (; 10 August 178229 August 1853) was an officer and veteran of the British Army's Peninsular and 1812 campaigns, and later a Major General of the Bombay Army, during which period he led the military conquest o ...
arrived in Sindh in the mid-19th century and captured Sindh in February 1843. The Baloch coalition led by Talpur under Mir Nasir Khan Talpur Mir Nasir Khan Talpur was the last Amir of the land that included Sindh and parts of present-day Balochistan and was one of the most active administrators after the decline of the Mughal Empire. He made Hyderabad the capital of his empire and const ...
was defeated at the Battle of Miani during which 5,000 Talpur Baloch were killed in action. Shortly afterwards, Hoshu Sheedi commanded another army at the Battle of Dubbo, where 5,000 Baloch were also killed in action.
The first Agha Khan, who was escaping persecution in Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
and looking for an ally, helped the East India Company in their capture of Sindh. As a result, he was granted a lifetime pension.
A British journal by Thomas Postans mentions the Sindhi Amirs
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cerem ...
as prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of w ...
: "The Amirs as being the prisoners of 'Her Majesty'... they are maintained in strict seclusion; they are described as Broken-Hearted and Miserable men, maintaining much of the dignity of fallen greatness, and without any querulous or angry complaining at this unlivable source of sorrow, refusing to be comforted". Within weeks, Charles Napier and his forces occupied Sindh.
After 1853, the Company administration divided Sindh into districts and later made it part of the Bombay Presidency
The Bombay Presidency or Bombay Province, also called Bombay and Sind (1843–1936), was an administrative subdivision (province) of British India, with its capital in the city that came up over the seven islands of Bombay. The first mainl ...
.
In the year 1868, the Bombay Presidency assigned ''Narayan Jagannath Vaidya'' to replace the Abjad
An abjad (, ar, أبجد; also abgad) is a writing system in which only consonants are represented, leaving vowel sounds to be inferred by the reader. This contrasts with other alphabets, which provide graphemes for both consonants and vow ...
used in Sindhi, with the '' Khudabadi script''. The script was decreed a standard script by the Bombay Presidency
The Bombay Presidency or Bombay Province, also called Bombay and Sind (1843–1936), was an administrative subdivision (province) of British India, with its capital in the city that came up over the seven islands of Bombay. The first mainl ...
thus inciting anarchy in the Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
majority region. A powerful unrest followed, after which twelve separate periods of martial law
Martial law is the imposition of direct military control of normal civil functions or suspension of civil law by a government, especially in response to an emergency where civil forces are overwhelmed, or in an occupied territory.
Use
Martia ...
were imposed by the colonial government.
During the period of Company rule,the city saw the rise of nationalist leaders such as Sibghatullah Shah Rashidi
Sayyid Sibghatullah Shah Al-Rashidi II (Sindhi: صبغت الله شاهه راشدي ), Pir Pagaro the sixth, was a spiritual leader of the Hur Movement during Sindh's war for its freedom. ''Hur'' (Arabic: حر meaning "free", "not slave" ...
, who pioneered the Sindhi Muslim Hur Movement. He was hanged on 20March 1943 in Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River, in the northern part of Southern Indi ...
, Sindh. His burial place is unknown.
During the colonial period, railways, printing presses and bridges were introduced in the province. Writers like Mirza Kalich Beg
Mirza Kalich Baig ( sd, مرزا قليچ بيگ) was a scholar within Sindhi literature. He was born on 4 October 1853 in Tando Thoro on the bank of Phuleli Canal in Hyderabad, British India (presently in Pakistan).
Family chronicle
The live ...
compiled and traced the literary history of Sindh. Although Sindh had a culture of religious syncretism, communal harmony and tolerance due to Sindh's strong Sufi culture in which both Sindhi Muslims and Sindhi Hindus partook,Priya Kumar & Rita Kothari (2016) Sindh, 1947 and Beyond, ''South Asia: Journal of South Asian Studies'', 39:4, 775, the mostly Muslim peasantry was oppressed by the Hindu moneylending class and also by the landed Muslim elite. Sindhi Muslims eventually demanded the separation of Sindh from the Bombay Presidency, a move opposed by Sindhi Hindus.Ansari, p. 77.
By 1936 Sindh was separated from the Bombay Presidency. Elections in 1937 resulted in local Sindhi Muslim parties winning the bulk of seats. By the mid-1940s the Muslim League Muslim League may refer to:
Political parties Subcontinent
; British India
*All-India Muslim League, Mohammed Ali Jinah, led the demand for the partition of India resulting in the creation of Pakistan.
**Punjab Muslim League, a branch of the organ ...
gained a foothold in the province and after winning over the support of local Sufi ''pirs'', it didn't take long for the overwhelming majority of Sindhi Muslims to campaign for the creation of Pakistan.
Modern period
Prior to its struggle for Pakistan during colonial period, in 1947 Sindh joined Pakistan after Muslim League's majorvictory
The term victory (from Latin ''victoria'') originally applied to warfare, and denotes success achieved in personal combat, after military operations in general or, by extension, in any competition. Success in a military campaign constitutes ...
against Indian National Congress at first it was proposed that the eastern half of Sindh (Tharparkar Region or simply Thar) was to be carved out from Sindh and be given to India due to its majority Hindu population, but that plan was never made official and Sindh as a whole was acceded to Pakistan.
When Sindh joined Pakistan in 1947 it comprised three polities: Karachi (Then Federal Capital of Pakistan), Sind Province
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
(Inherited from British India) and Khairpur (Princely State), in 1955 when One Unit Policy was implemented all of these 3 polities merged to form West Pakistan however in 1970 when One Unit Policy was abolished a single, united province of Sindh came into being with Karachi as its capital
Population
Demographics
Sindh has the second highestHuman Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, w ...
out of all of Pakistan's provinces at 0.628. The 2017 Census of Pakistan indicated a population of 47.9 million.
The major ethnic group of the province is the Sindhis
Sindhis ( sd, سنڌي Perso-Arabic: सिन्धी Devanagari; ) are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group who speak the Sindhi language and are native to the province of Sindh in Pakistan. After the partition of British Indian empire in 1947, man ...
, but there is also a significant presence of other groups. Sindhis of Baloch origin make up about 30% of the total Sindhi population (although they speak Sindhi or Saraiki as their native tongue), while Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
'' Muhajirs make up over 19% of the total population of the province, while

 Islam in Sindh has a long history, starting with the capture of Sindh by Muhammad Bin Qasim in 712 CE. Over time, the majority of the population in Sindh converted to Islam, especially in rural areas. Today, Muslims make up over 90% of the population, and are more dominant in urban than rural areas. Islam in Sindh has a strong Sufi ethos with numerous Muslim saints and mystics, such as the Sufi poet
Islam in Sindh has a long history, starting with the capture of Sindh by Muhammad Bin Qasim in 712 CE. Over time, the majority of the population in Sindh converted to Islam, especially in rural areas. Today, Muslims make up over 90% of the population, and are more dominant in urban than rural areas. Islam in Sindh has a strong Sufi ethos with numerous Muslim saints and mystics, such as the Sufi poet
 Sindh is in the western corner of South Asia, bordering the
Sindh is in the western corner of South Asia, bordering the  Sindh is divided into three main geographical regions: ''Siro'' ("upper country"), aka Upper Sindh, which is above Sehwan; ''Vicholo'' ("middle country"), or Middle Sindh, from Sehwan to
Sindh is divided into three main geographical regions: ''Siro'' ("upper country"), aka Upper Sindh, which is above Sehwan; ''Vicholo'' ("middle country"), or Middle Sindh, from Sehwan to
 The province is mostly arid with scant vegetation except for the irrigated Indus Valley. The dwarf palm, ''Acacia Rupestris'' (kher), and ''
The province is mostly arid with scant vegetation except for the irrigated Indus Valley. The dwarf palm, ''Acacia Rupestris'' (kher), and ''
 Among the wild animals, the
Among the wild animals, the
 Sindh lies in a
Sindh lies in a
 In 2008, after the public elections, the new government decided to restore the structure of Divisions of all provinces. In Sindh after the lapse of the Local Governments Bodies term in 2010 the Divisional Commissioners system was to be restored.
In July 2011, following excessive violence in the city of Karachi and after the political split between the ruling PPP and the majority party in Sindh, the MQM and after the resignation of the MQM Governor of Sindh, PPP and the Government of Sindh decided to restore the commissionerate system in the province. As a consequence, the five divisions of Sindh were restored – namely Karachi, Hyderabad, Sukkur, Mirpurkhas and Larkana with their respective districts. Subsequently, two new divisions have been added in Sindh, Banbore and Nawab Shah/Shaheed Benazirabad division.
Karachi district has been de-merged into its five original constituent districts:
In 2008, after the public elections, the new government decided to restore the structure of Divisions of all provinces. In Sindh after the lapse of the Local Governments Bodies term in 2010 the Divisional Commissioners system was to be restored.
In July 2011, following excessive violence in the city of Karachi and after the political split between the ruling PPP and the majority party in Sindh, the MQM and after the resignation of the MQM Governor of Sindh, PPP and the Government of Sindh decided to restore the commissionerate system in the province. As a consequence, the five divisions of Sindh were restored – namely Karachi, Hyderabad, Sukkur, Mirpurkhas and Larkana with their respective districts. Subsequently, two new divisions have been added in Sindh, Banbore and Nawab Shah/Shaheed Benazirabad division.
Karachi district has been de-merged into its five original constituent districts:





 The following is a chart of the education market of Sindh estimated by the government in 1998:
Major public and private educational institutes in Sindh include:
*
The following is a chart of the education market of Sindh estimated by the government in 1998:
Major public and private educational institutes in Sindh include:
*
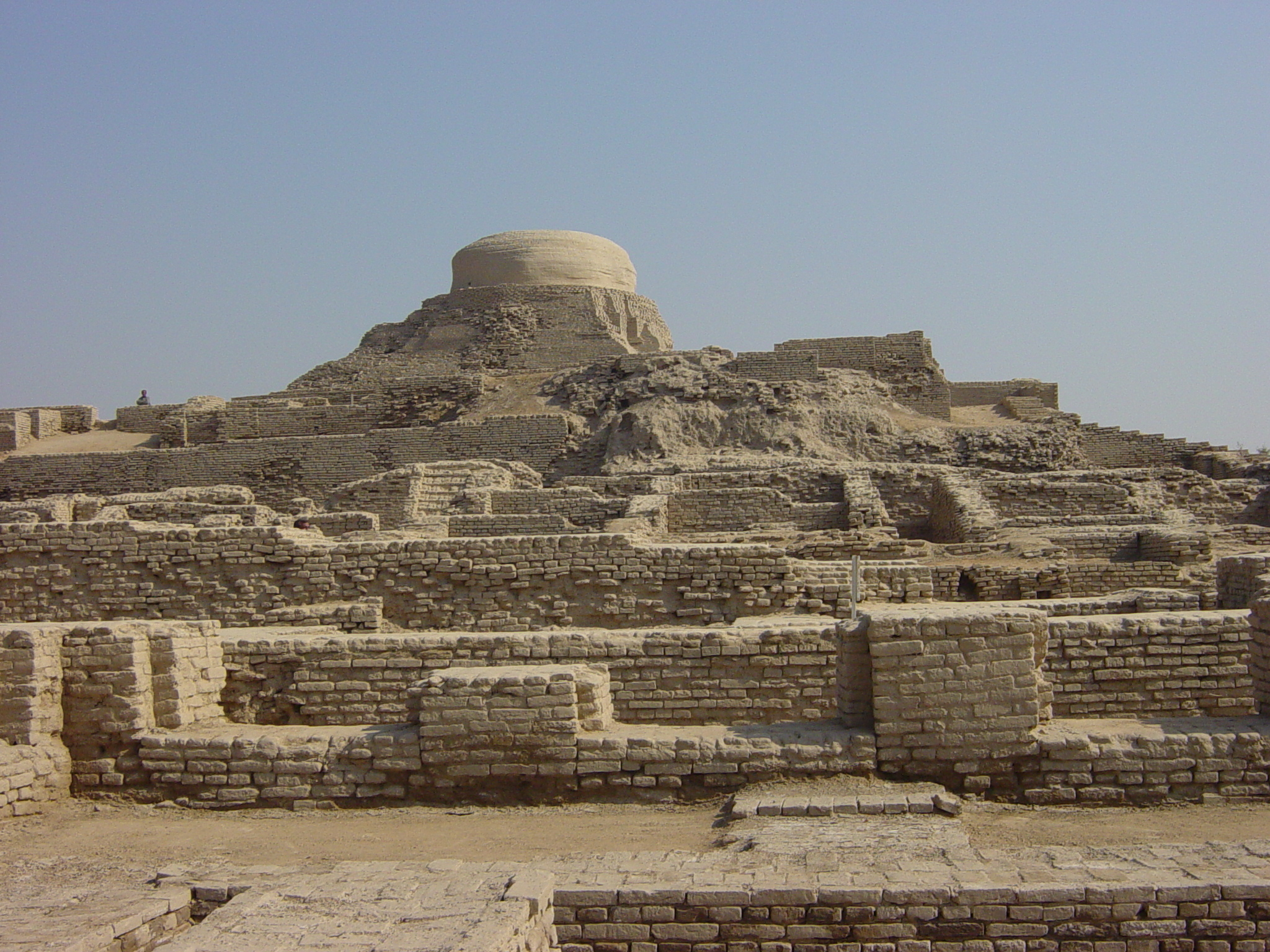


 Sindh has a rich heritage of traditional handicraft that has evolved over the centuries. Perhaps the most professed exposition of Sindhi culture is in the handicrafts of Haala, Hala, a town some 30 kilometres from
Sindh has a rich heritage of traditional handicraft that has evolved over the centuries. Perhaps the most professed exposition of Sindhi culture is in the handicrafts of Haala, Hala, a town some 30 kilometres from 
File:Sukkur bridge hdr.jpg, Sukkur Bridge
File:Gorakh Hill Morning.jpg, Gorakh Hill, Gorakh Hill Station
File:FaizMahal.jpg, Faiz Mahal, Khairpur, Pakistan, Khairpur
File:Rani Kort Wall & Forte View.jpg, Ranikot Fort, one of the largest forts in the world
File:PK Chaukhandi Necropolis near Karachi asv2020-02 img09.jpg, Chaukhandi tombs
File:Bhodesar temple, Nagarparkar.JPG, Remains of 9th century Jainism, Jain Nagarparkar Jain Temples, temple in Bhodesar near Nagarparkar.
File:Mohenjodaro Sindh.jpeg, Excavated ruins of
Sindh Transport Department official website
Government of Sindh
* Guide o
Sindh
* {{Authority control Sindh, Provinces of Pakistan States and territories established in 1970 1970 establishments in Pakistan Sindhi-speaking countries and territories Populated places established in the 7th millennium BC 7th-millennium BC establishments
'' Muhajirs make up over 19% of the total population of the province, while
Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a British Th ...
are 10% and Pashtun
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically r ...
s represent 7%.
In August 1947, before the partition of India, the total population of Sindh was 3,887,070 out of which 2,832,000 (around 73%) were Muslims, 1,015,000 (around 26%) were Hindus and the remaining were Sikhs and Jains.
Religion

 Islam in Sindh has a long history, starting with the capture of Sindh by Muhammad Bin Qasim in 712 CE. Over time, the majority of the population in Sindh converted to Islam, especially in rural areas. Today, Muslims make up over 90% of the population, and are more dominant in urban than rural areas. Islam in Sindh has a strong Sufi ethos with numerous Muslim saints and mystics, such as the Sufi poet
Islam in Sindh has a long history, starting with the capture of Sindh by Muhammad Bin Qasim in 712 CE. Over time, the majority of the population in Sindh converted to Islam, especially in rural areas. Today, Muslims make up over 90% of the population, and are more dominant in urban than rural areas. Islam in Sindh has a strong Sufi ethos with numerous Muslim saints and mystics, such as the Sufi poet Shah Abdul Latif Bhittai
Shah Abdul Latif Bhittai ( sd, شاھ عبداللطيف ڀٽائي, ur, ; 1689/1690 – 21 December 1752), commonly known by the honorifics ''Lakhino Latif'', ''Latif Ghot'', ''Bhittai'', and ''Bhit Jo Shah'', was a Sindhi Sufi mystic, and ...
, having lived in Sindh historically. One popular legend which highlights the strong Sufi presence in Sindh is that 125,000 Sufi saints and mystics are buried on Makli Hill near Thatta. The development of Sufism in Sindh was similar to the development of Sufism in other parts of the Muslim world. In the 16th century two Sufi tareeqat (orders) – Qadria and Naqshbandia – were introduced in Sindh. Sufism continues to play an important role in the daily lives of Sindhis.
Sindh also has Pakistan's highest percentage of Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
overall, which accounts 8.7% of the population, roughly around 4.2 million people, and 13.3% of the province's rural population as per 2017 Pakistani census report. These numbers also include the scheduled caste
The Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) are officially designated groups of people and among the most disadvantaged socio-economic groups in India. The terms are recognized in the Constitution of India and the groups are designa ...
population, which stands at 1.7% of the total in Sindh (or 3.1% in rural areas), and is believed to have been under-reported, with some community members instead counted under the main Hindu category. Although, Pakistan Hindu Council
Pakistan Hindu council () is the representative body of all Hindus of Pakistan which was formed in the year 2005 by Ramesh Kumar Vankwani.
History
The Pakistan Hindu Council was founded by the Ramesh Kumar Vankwani, Hindu activist and member of ...
claimed that there are 6,842,526 Hindus living in Sindh Province covering around 14.29% of the region's population. Umerkot district in the Thar Desert is Pakistan's only Hindu-majority district. The Shri Ramapir Temple in Tandoallahyar whose annual festival is the second largest Hindu pilgrimage in Pakistan is in Sindh. Sindh is also the only province in Pakistan to have a separate law for governing Hindu marriages.
There are approximately 10,000 Sikhs in Sindh.
Languages
According to the 2017 census, the most widely spoken language in the province isSindhi
Sindhi may refer to:
*something from, or related to Sindh, a province of Pakistan
* Sindhi people, an ethnic group from the Sindh region
* Sindhi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by them
People with the name
* Sarkash Sindhi (1940–2012 ...
, the first language of % of the population. It is followed by Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
'' Pashto Pashto (,; , ) is an Eastern Iranian language in the Indo-European language family. It is known in historical Persian literature as Afghani (). Spoken as a native language mostly by ethnic Pashtuns, it is one of the two official langua ...
(%), '' Pashto Pashto (,; , ) is an Eastern Iranian language in the Indo-European language family. It is known in historical Persian literature as Afghani (). Spoken as a native language mostly by ethnic Pashtuns, it is one of the two official langua ...
Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a British Th ...
(%), Saraiki (%), Balochi (2%) and Hindko
Hindko (, romanized: , ) is a cover term for a diverse group of Lahnda dialects spoken by several million people of various ethnic backgrounds in several areas in northwestern Pakistan, primarily in the provinces of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Punj ...
().
Other minority languages include Kutchi, Gujarati
Gujarati may refer to:
* something of, from, or related to Gujarat, a state of India
* Gujarati people, the major ethnic group of Gujarat
* Gujarati language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by them
* Gujarati languages, the Western Indo-Aryan sub- ...
, Aer, Bagri, Bhaya, Brahui, Dhatki
Dhatki (धाटकी; ڍاٽڪي), also known as Dhatti (धाटी; ڍاٽي) or Thari (थारी; ٿَري), is one of the Rajasthani languages of the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family. Dhatki is closely related ...
, Ghera, Goaria, Gurgula, Jadgali
Jaḍgālī is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Jadgal, an ethno-linguistic group of Pakistan and Iran. It is one of only two Indo-Aryan languages found on the Iranian plateau. It is a dialect of Sindhi most closely related to Lasi.
The ...
, Jandavra, Jogi, Kabutra, Kachi Koli
Kachi Koli is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in Pakistan and India. Part of the Gujarati
Gujarati may refer to:
* something of, from, or related to Gujarat, a state of India
* Gujarati people, the major ethnic group of Gujarat
* Gujarati lan ...
, Parkari Koli, Wadiyari Koli, Loarki, Marwari, Sansi, and Vaghri.
Karachi city is Pakistan's most multiethnic city. Urdu-speakers form a plurality, while Pashtos are the second-largest group. Sindhis themselves are 8.1% of the population in Karachi, a number that has increased due to migration of rural Sindhis to the city for work.
Geography and nature
Iranian plateau
The Iranian plateau or Persian plateau is a geological feature in Western Asia, Central Asia, and South Asia. It comprises part of the Eurasian Plate and is wedged between the Arabian Plate and the Indian Plate; situated between the Zagros ...
in the west. Geographically it is the third largest province of Pakistan, stretching about from north to south and (extreme) or (average) from east to west, with an area of of Pakistani territory. Sindh is bounded by the Thar Desert
The Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Subcontinent that covers an area of and forms a natural boundary between India and Pakistan. It is the world's 20th-largest desert, ...
to the east, the Kirthar Mountains to the west and the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channe ...
and Rann of Kutch
The Rann of Kutch (alternately spelled as Kuchchh) is a large area of salt marshes that span the border between India and Pakistan. It is located in Gujarat (primarily the Kutch district), India, and in Sindh, Pakistan. It is divided into ...
to the south. In the centre is a fertile plain along the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmi ...
.
Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River, in the northern part of Southern Indi ...
; and ''Lāṟu'' ("sloping, descending country"), or Lower Sindh, mostly consisting of the Indus Delta
The Indus River Delta ( ur, سندھ ڈیلٹا, sd, سنڌو ٽِڪور), forms where the Indus River flows into the Arabian Sea, mostly in the southern Sindh province of Pakistan with a small portion in the Kutch Region of India. The delta ...
below Hyderabad.
Flora
 The province is mostly arid with scant vegetation except for the irrigated Indus Valley. The dwarf palm, ''Acacia Rupestris'' (kher), and ''
The province is mostly arid with scant vegetation except for the irrigated Indus Valley. The dwarf palm, ''Acacia Rupestris'' (kher), and ''Tecomella undulata
''Tecomella undulata'' is a tree species, locally known as rohida, found in Oman, and from southwest Iran to northwest India. It is the only species in the monotypic genus ''Tecomella''. It is a medium-sized tree that produces quality timber and ...
'' ( lohirro) trees are typical of the western hill region. In the Indus valley, the '' Acacia nilotica'' (babul) (babbur) is the most dominant and occurs in thick forests along the Indus banks. The ''Azadirachta indica
''Azadirachta indica'', commonly known as neem, nimtree or Indian lilac, is a tree in the mahogany family Meliaceae. It is one of two species in the genus ''Azadirachta'', and is native to the Indian subcontinent and most of the countries in Af ...
'' (neem) (nim), ''Zizyphys vulgaris'' (bir) (ber), ''Tamarix orientalis'' (jujuba lai) and ''Capparis aphylla
''Capparis decidua'', commonly known as karira, is a useful plant in its marginal habitat.
Description
It is a small much-branched tree or shrub. It bears a mass of slender, gray-green leafless branches, the small caducous leaves being found ...
'' (kirir) are among the more common trees.
Mango, date palms and the more recently introduced banana, guava, orange and chiku
''Manilkara zapota'', commonly known as sapodilla (), sapote, naseberry, nispero or chicle, is a long-lived, evergreen tree native to southern Mexico, Central America and the Caribbean. An example natural occurrence is in coastal Yucatán in th ...
are the typical fruit-bearing trees. The coastal strip and the creeks abound in semi-aquatic and aquatic plants and the inshore Indus delta islands have forests of ''Avicennia tomentosa'' (timmer) and '' Ceriops candolleana'' (chaunir) trees. Water lilies grow in abundance in the numerous lake and ponds, particularly in the lower Sindh region.
Fauna
 Among the wild animals, the
Among the wild animals, the Sindh ibex
The Sindh ibex or Sindhi wild goat (''Capra aegagrus blythi'') is a vulnerable subspecies of wild goat endemic to southern Pakistan.
Description
Sindh ibex are rather stocky animals with thick-set bodies and strong limbs terminating in broad ...
(sareh), blackbuck
The blackbuck (''Antilope cervicapra''), also known as the Indian antelope, is an antelope native to India and Nepal. It inhabits grassy plains and lightly forested areas with perennial water sources.
It stands up to high at the shoulder. Ma ...
, wild sheep ( Urial or gadh) and wild bear are found in the western rocky range. The leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus '' Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, ...
is now rare and the Asiatic cheetah
The Asiatic cheetah (''Acinonyx jubatus venaticus'') is a critically endangered cheetah subspecies currently only surviving in Iran. It once occurred from the Arabian Peninsula and the Near East to the Caspian region, Transcaucasus, Kyzylkum ...
extinct. The Pirrang (large tiger cat or fishing cat) of the eastern desert region is also disappearing. Deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the re ...
occur in the lower rocky plains and in the eastern region, as do the Striped hyena (charakh), jackal
Jackals are medium-sized canids native to Africa and Eurasia. While the word "jackal" has historically been used for many canines of the subtribe canina, in modern use it most commonly refers to three species: the closely related black-backed ...
, fox, porcupine
Porcupines are large rodents with coats of sharp spines, or quills, that protect them against predation. The term covers two families of animals: the Old World porcupines of family Hystricidae, and the New World porcupines of family, Erethiz ...
, common gray mongoose and hedgehog
A hedgehog is a spiny mammal of the subfamily Erinaceinae, in the eulipotyphlan family Erinaceidae. There are seventeen species of hedgehog in five genera found throughout parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa, and in New Zealand by introductio ...
. The Sindhi phekari, red lynx or Caracal cat, is found in some areas. Phartho (hog deer) and wild bear occur, particularly in the central inundation belt. There are bats, lizards and reptiles, including the cobra, lundi (viper) and the mysterious Sindh krait
''Bungarus'' is a genus of venomous elapid snakes, the kraits ("krait" is pronounced , rhyming with "kite"), found in South and Southeast Asia. The genus ''Bungarus'' has 16 species.
Distribution
Kraits are found in tropical Asia, from near Ira ...
of the Thar region, which is supposed to suck the victim's breath in his sleep.
Some unusual sightings of Asian cheetah occurred in 2003 near the Balochistan
Balochistan ( ; bal, بلۏچستان; also romanised as Baluchistan and Baluchestan) is a historical region in Western and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian Sea coastline. ...
border in Kirthar Mountains. The rare houbara bustard
The houbara bustard (''Chlamydotis undulata''), also known as African houbara, is a relatively small bustard native to North Africa, where it lives in arid habitats. The global population is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List since 2014. ...
find Sindh's warm climate suitable to rest and mate. Unfortunately, it is hunted by locals and foreigners.
Crocodiles are rare and inhabit only the backwaters of the Indus, eastern Nara channel and Karachi backwater. Besides a large variety of marine fish, the plumbeous dolphin, the beaked dolphin, rorqual or blue whale and skates frequent the seas along the Sindh coast. The Pallo (Sable fish), a marine fish, ascends the Indus annually from February to April to spawn. The Indus river dolphin
The Indus river dolphin (''Platanista minor''), also known as the ''bhulan'' in Urdu and Sindhi, is a species of toothed whale in the family Platanistidae. It is endemic to the Indus River Basin of Pakistan and northwestern India. This dolphi ...
is among the most endangered species in Pakistan and is found in the part of the Indus river in northern Sindh. Hog deer and wild bear occur, particularly in the central inundation belt.
Although Sindh has a semi arid climate, through its coastal and riverine forests, its huge fresh water lakes and mountains and deserts, Sindh supports a large amount of varied wildlife. Due to the semi-arid climate of Sindh the left out forests support an average population of jackals and snakes. The national parks
A national park is a natural park in use for conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or owns. Although individua ...
established by the Government of Pakistan in collaboration with many organizations such as World Wide Fund for Nature
The World Wide Fund for Nature Inc. (WWF) is an international non-governmental organization founded in 1961 that works in the field of wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment. It was formerly named the W ...
and Sindh Wildlife Department
The fauna of Sindh live in an area with a semi arid climate. With its coastal and riverine forests, its huge fresh water lakes, mountains and deserts, Sindh supports a large and varied wildlife population.
Habitat and wildlife
Due to the climat ...
support a huge variety of animals and birds. The Kirthar National Park
The Kirthar National Park ( ur, ), Sindhi (کيرٿرنيشنل پارڪ) is situated in the Kirthar Mountains in Jamshoro District in Sindh, Pakistan. The park was established in 1974, and encompasses over - making it the third largest natio ...
in the Kirthar range spreads over more than 3000 km2 of desert, stunted tree forests and a lake. The KNP supports Sindh ibex
The Sindh ibex or Sindhi wild goat (''Capra aegagrus blythi'') is a vulnerable subspecies of wild goat endemic to southern Pakistan.
Description
Sindh ibex are rather stocky animals with thick-set bodies and strong limbs terminating in broad ...
, wild sheep (urial) and black bear along with the rare leopard. There are also occasional sightings of The Sindhi phekari, ped lynx or Caracal cat. There is a project to introduce tiger
The tiger (''Panthera tigris'') is the largest living Felidae, cat species and a member of the genus ''Panthera''. It is most recognisable for its dark vertical stripes on orange fur with a white underside. An apex predator, it primarily pr ...
s and Asian elephant
The Asian elephant (''Elephas maximus''), also known as the Asiatic elephant, is the only living species of the genus '' Elephas'' and is distributed throughout the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, from India in the west, Nepal in t ...
s too in KNP near the huge Hub Dam Lake. Between July and November when the monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
winds blow onshore from the ocean, giant olive ridley
The olive ridley sea turtle (''Lepidochelys olivacea''), also known commonly as the Pacific ridley sea turtle, is a species of turtle in the family Cheloniidae. The species is the second-smallest and most abundant of all sea turtles found in ...
turtles lay their eggs along the seaward side. The turtles are protected species. After the mothers lay and leave them buried under the sands the SWD and WWF officials take the eggs and protect them until they are hatched to keep them from predators.
Climate
 Sindh lies in a
Sindh lies in a tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
to subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° north a ...
region; it is hot in the summer and mild to warm in winter. Temperatures frequently rise above between May and August, and the minimum average temperature of occurs during December and January in the northern and higher elevated regions. The annual rainfall averages about seven inches, falling mainly during July and August. The southwest monsoon wind begins in mid-February and continues until the end of September, whereas the cool northerly wind blows during the winter months from October to January.
Sindh lies between the two monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
s—the southwest monsoon from the Indian Ocean and the northeast or retreating monsoon, deflected towards it by the Himalayan mountains—and escapes the influence of both. The region's scarcity of rainfall is compensated by the inundation of the Indus twice a year, caused by the spring and summer melting of Himalayan snow and by rainfall in the monsoon season.
Sindh is divided into three climatic regions: Siro (the upper region, centred on Jacobabad
Jacobabad ( ur, and sd, جيڪب آباد; formerly Khanger or Khangarh) is a city in Sindh, Pakistan, serving as both the capital city of Jacobabad District and the administrative center of Jacobabad Taluka, an administrative subdivisi ...
), Wicholo (the middle region, centred on Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River, in the northern part of Southern Indi ...
), and Lar (the lower region, centred on Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former c ...
). The thermal equator passes through upper Sindh, where the air is generally very dry. Central Sindh's temperatures are generally lower than those of upper Sindh but higher than those of lower Sindh. Dry hot days and cool nights are typical during the summer. Central Sindh's maximum temperature typically reaches . Lower Sindh has a damper and humid maritime climate affected by the southwestern winds in summer and northeastern winds in winter, with lower rainfall
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water f ...
than Central Sindh. Lower Sindh's maximum temperature reaches about . In the Kirthar range at and higher at Gorakh Hill and other peaks in Dadu District, temperatures near freezing have been recorded and brief snowfall is received in the winters.
Major cities
Government
Sindh province
TheProvincial Assembly of Sindh
The Provincial Assembly of Sindh ( ur, ) is a unicameral legislature of elected representatives of the Pakistani province of Sindh, and is located in Karachi, the provincial capital. It was established under Article 106 of the Constitution of ...
is a unicameral
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature, which consists of one house or assembly, that legislates and votes as one.
Unicameral legislatures exist when there is no widely perceived need for multi ...
and consists of 168 seats, of which 5% are reserved for non-Muslims and 17% for women. The provincial capital of Sindh is Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former c ...
. The provincial government
A state government is the government that controls a subdivision of a country in a federal form of government, which shares political power with the federal or national government. A state government may have some level of political autonomy, ...
is led by Chief Minister who is directly elected by the popular and landslide votes; the Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
serves as a ceremonial representative nominated and appointed by the President of Pakistan
The president of Pakistan ( ur, , translit=s̤adr-i Pākiṣṭān), officially the President of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is the ceremonial head of state of Pakistan and the commander-in-chief of the Pakistan Armed Forces.Chief Secretary Sindh
The Chief Secretary Sindh (Urdu: ), also referred to as CS Sindh, is the chief and highest-ranking official of the Government of Sindh. The appointment of the Chief Secretary is made by the Prime Minister of Pakistan. The position of Chief Secret ...
, who is appointed by the Prime Minister of Pakistan
The prime minister of Pakistan ( ur, , romanized: Wazīr ē Aʿẓam , ) is the head of government of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. Executive authority is vested in the prime minister and his chosen cabinet, despite the president of Pak ...
. Most of the influential Sindhi tribes in the province are involved in Pakistan's politics.
In addition, Sindh's politics leans towards the left-wing
Left-wing politics describes the range of political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy. Left-wing politics typically involve a concern for those in soci ...
and its political culture serves as a dominant place for the left-wing spectrum in the country. The province's trend towards the Pakistan Peoples Party
The Pakistan People's Party ( ur, , ; PPP) is a centre-left, social-democratic political party in Pakistan. It is currently the third largest party in the National Assembly and second largest in the Senate of Pakistan. The party was founded i ...
(PPP) and away from the Pakistan Muslim League (N)
The Pakistan Muslim League (Nawaz) ( ur, , translit=Pākistān Muslim Līg (Nūn) PML(N) or PML-N) is a Centre-right politics, centre-right and Liberal conservatism, liberal conservative political party in Pakistan. Alongside the Pakistan Teh ...
can be seen in nationwide general elections, in which Sindh is a stronghold of the PPP. The PML(N) has a limited support due to its centre-right agenda.
In metropolitan cities such as Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former c ...
and Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River, in the northern part of Southern Indi ...
, the MQM MQM may refer to:
* Muttahida Qaumi Movement – London (MQM)
* Muttahida Qaumi Movement – Pakistan
Muttahida Qaumi Movement (Pakistan) ( ur, MQM-P) is a Social liberal Muhajir nationalist Secular political party. The leader of the part ...
(another party of the left with the support of ''Muhajirs'') has a considerable vote bank and support. Minor leftist parties such as the People's Movement also found support in rural areas of the province.
Divisions
 In 2008, after the public elections, the new government decided to restore the structure of Divisions of all provinces. In Sindh after the lapse of the Local Governments Bodies term in 2010 the Divisional Commissioners system was to be restored.
In July 2011, following excessive violence in the city of Karachi and after the political split between the ruling PPP and the majority party in Sindh, the MQM and after the resignation of the MQM Governor of Sindh, PPP and the Government of Sindh decided to restore the commissionerate system in the province. As a consequence, the five divisions of Sindh were restored – namely Karachi, Hyderabad, Sukkur, Mirpurkhas and Larkana with their respective districts. Subsequently, two new divisions have been added in Sindh, Banbore and Nawab Shah/Shaheed Benazirabad division.
Karachi district has been de-merged into its five original constituent districts:
In 2008, after the public elections, the new government decided to restore the structure of Divisions of all provinces. In Sindh after the lapse of the Local Governments Bodies term in 2010 the Divisional Commissioners system was to be restored.
In July 2011, following excessive violence in the city of Karachi and after the political split between the ruling PPP and the majority party in Sindh, the MQM and after the resignation of the MQM Governor of Sindh, PPP and the Government of Sindh decided to restore the commissionerate system in the province. As a consequence, the five divisions of Sindh were restored – namely Karachi, Hyderabad, Sukkur, Mirpurkhas and Larkana with their respective districts. Subsequently, two new divisions have been added in Sindh, Banbore and Nawab Shah/Shaheed Benazirabad division.
Karachi district has been de-merged into its five original constituent districts: Karachi East
Karachi East District ( ur, ) is an administrative district of Karachi Division in Sindh, Pakistan.
Map of Karachi Division
History
The district was established in 1972.
The district was abolished in 2000, and was divided into four ...
, Karachi West
Karachi West District ( ur, ) is an administrative district of Karachi Division in Sindh, Pakistan.
History
The District was abolished in 2000 and divided into five towns namely:
* Lyari Town
*Kemari Town,
* SITE Town,
* Baldia Town
...
, Karachi Central
Karachi Central District ( ur, ) is an administrative district of Karachi Division in Sindh, Pakistan.
History
The District was abolished in 2000 and divided into four towns namely Liaquatabad Town, North Nazimabad Town, Gulberg Town and ...
, Karachi South
Karachi South District ( ur, ) is an administrative district of Karachi Division in Sindh, Pakistan.
History
Karachi South District is the economic backbone of the country. It has Head Offices of many Corporations, Companies and Banks. Chie ...
and Malir
Malir Town ( sd, ملير ٽائون, ur, ) lies in the northern part of the city that was named after the Malir River.
History
Administrative status
2000
The federal government under introduced local government reforms in the year 2 ...
. Recently Korangi has been upgraded to the status of the sixth district of Karachi. These six districts form the Karachi Division now. In 2020, the Kemari District
Keamari District ( sd, ڪياماڙي ضلعو, ur, is an administrative district of Karachi Division in Sindh, Pakistan.
History
Keamari District was created after splitting Karachi West District in 2020.
Demographics
At the time of the 2 ...
was created after splitting Karachi West District
Karachi West District ( ur, ) is an administrative district of Karachi Division in Sindh, Pakistan.
History
The District was abolished in 2000 and divided into five towns namely:
* Lyari Town
* Kemari Town,
* SITE Town,
* Baldia Town ...
. Currently the Sindh government is planning to divide the Tharparkar district
Tharparkar (Dhatki/ sd, ٿرپارڪر, ur, ), also known as Thar, is a district in Sindh province in Pakistan headquartered at Mithi. Before Indian independence it was known as the Thar and Parkar district.
The district is the largest in Si ...
into Tharparkar and Chhachro district.
Districts
Lower-level subdivisions
In Sindh,taluka
A tehsil (, also known as tahsil, taluka, or taluk) is a local unit of administrative division in some countries of South Asia. It is a subdistrict of the area within a district including the designated populated place that serves as its administr ...
s are equivalent to the tehsil
A tehsil (, also known as tahsil, taluka, or taluk) is a local unit of administrative division in some countries of South Asia. It is a subdistrict of the area within a district including the designated populated place that serves as its adminis ...
s used elsewhere in the country, supervisory tapa
Supervision is an act or instance of directing, managing, or oversight.
Etymology
The English noun "supervision" derives from the two Latin words "super" (above) and "videre" (see, observe).
Spelling
The spelling is "Supervision" in Standard E ...
s correspond with the kanungo circles used elsewhere, tapas correspond with the patwar circles used in other provinces, and dehs are equivalent to the mouza
In Bangladesh, Pakistan and parts of India a mouza or mauza (also mouja) is a type of administrative district, corresponding to a specific land area within which there may be one or more settlements. Before the 20th century, the term referred to a ...
s used elsewhere.
Economy



Education
 The following is a chart of the education market of Sindh estimated by the government in 1998:
Major public and private educational institutes in Sindh include:
*
The following is a chart of the education market of Sindh estimated by the government in 1998:
Major public and private educational institutes in Sindh include:
* Adamjee Government Science College
Adamjee Government Science College (AGSC) ( ur, ) is an educational institution in Karachi, Pakistan.
It was established in 1961, by All Pakistan Memon Educational and Welfare Society through the financial help and efforts of late Sir Adamje ...
* Aga Khan University
Aga Khan University is a non-profit institution and an agency of the Aga Khan Development Network. It was Founded in 1983 as Pakistan's first private university. Starting in 2000, the university expanded to Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, the United Ki ...
* APIIT
The Asia Pacific Institute of Information Technology (abbreviated as APIIT) ( ur, ) is an educational organisation specializing in providing education and training programs in computing and information technology. Founded by Datuk Dr Parmjit ...
* Applied Economics Research Centre
The Applied Economics Research Centre (AERC) () is a research institute of University of Karachi. It was established in 1973 by the Government of Sindh and financially assisted by Ford Foundation. Prof. Dr. Ehsan Rasheed, the distinguished alu ...
* Bahria University
Bahria University (BU; ur, ) is a public-sector university established in 2000 by the Pakistan Navy at Shangrilla Road, Sector E-8/1 in Islamabad, Pakistan. The university maintains campuses in Karachi and Lahore.
Established by the Pakistan Na ...
* Baqai Medical University
* Chandka Medical College Larkana
* Cadet College Petaro
Cadet College Petaro is a military boarding school in Jamshoro District of the southern province of Sindh in Pakistan; about 20 miles (32 km) from Hyderabad which is under administration of Pakistan Navy.
Its campus occupies over 700 acres ...
* College of Digital Sciences
* College of Physicians & Surgeons Pakistan
The College of Physicians and Surgeons Pakistan ( ur, , abbreviated as CPSP) is a regulatory college established in 1962 by a special act of the Parliament of Pakistan to oversee the postgraduate medical education and professional development. I ...
* COMMECS Institute of Business and Emerging Sciences
Commecs College ( ur, ) is a higher secondary intermediate school in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan.
Commecs College is a not-for-profit, co-educational institution founded in 1993 by COMMECS, the alumni of the Govt. College of Commerce & Econom ...
* D. J. Science College
* Dawood University of Engineering & Technology
The Dawood University of Engineering and Technology (initials:DUET) ( ur, ) is a public university located in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan.
* Defence Authority Degree College for Men
* Dow International Medical College
Dow International Medical College ( ur, ) is a government-owned public sector medical college in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan, which is recognized by the Pakistan Medical and Dental Council (PMDC) . Admittance is limited to 150 students per year. ...
* Dow University of Health Sciences
The Dow University of Health Sciences (DUHS) is a public medical university located in the Urban metropolitan area of Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan. It was founded by Sir Hugh Dow, the then Governor of Sindh, in 1945.
The university comprises two ...
* Fatima Jinnah Dental College
Fatima Jinnah Dental College ( ur, ), commonly referred to by the acronym FJDC, is the oldest dental school in Karachi and one of the oldest in Pakistan. Established in 1992, it is run and managed by a duly registered Fatima Jinnah Dental Colleg ...
* Federal Urdu University
The Federal Urdu University of Arts, Science and Technology ( ur, ); alternatively known as FUUAST) is a public university primarily located at Islamabad, Pakistan. The university has two satellite campuses; the central campus is located in Is ...
* GBELS Dourai Mahar Taluka Daur Distt: Shaheed Benazirabad
* Ghulam Muhammad Mahar Medical College Sukkur
* Government College for Men Nazimabad
Government College for Men, Nazimabad is an all-male degree college located in Karachi, Pakistan, adjacent to the flyover located in Nazimabad town.
Departments
The college has the following departments:
* Botany
* Chemistry
* Computer Scien ...
* Government College Hyderabad
* Government College of Commerce & Economics
Government College of Commerce & Economics, ( ur, ) founded as the Basant Singh Asumal College of Commerce & Economics, is an institution of commerce education in the city of Karachi. It is located on Dr. Ziauddin Ahmed Road, opposite Bagh-e-Ji ...
* Government College of Technology, Karachi
* Government Degree College Matiari
* Government High School Ranipur
* Government Islamia Science College Sukkur
* Government Muslim Science College Hyderabad
* Government National College (Karachi)
* Greenwich University (Karachi)
* Hamdard University
* Hussain Ebrahim Jamal Research Institute of Chemistry
* Imperial Science College Nawabshah
* Indus Valley Institute of Art and Architecture
* Institute of Business Administration, Karachi
* Institute of Business Administration, Sukkar
* Institute of Business Management
* Institute of Industrial Electronics Engineering
* Institute of Sindhology
* Iqra University
* Islamia Science College (Karachi)
* Isra University Hyderabad
* Jinnah Medical & Dental College
* Jinnah Polytechnic Institute
* Jinnah Post Graduate Medical Centre
* Jinnah University for Women
* KANUPP Institute of Nuclear Power Engineering
* Karachi Institute of Economics and Technology
* Karachi School of Business and Leadership
* Liaquat University of Medical & Health Sciences
* Mehran University of Engineering and Technology
* Mohammad Ali Jinnah University
* National Academy of Performing Arts
* National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences
* National University of Modern Languages
* National University of Sciences and Technology, Pakistan, National University of Sciences and Technology
* NED University of Engineering and Technology
* Ojha Institute of Chest Diseases
* PAF Institute of Aviation Technology
* TES Public School, Daur
* Pakistan Navy Engineering College
* Pakistan Shipowners' College
* Pakistan Steel Cadet College
* Peoples Medical College for Girls Nawabshah
* PIA Training Centre Karachi
* Provincial Institute of Teachers Education Nawabshah
* Public School Hyderabad
* Quaid-e-Awam University of Engineering, Science and Technology, Nawabshah
* Rana Liaquat Ali Khan Government College of Home Economics
* Saint Patrick's College, Karachi
* Shah Abdul Latif Bhitai University
* Shaheed Benazir Bhutto Medical College
* Shaheed Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto Institute of Science and Technology
* Sindh Agriculture University
* Sindh Medical College
* Superior College of Science Hyderabad
* Sindh Muslim Law College
* Sir Syed Government Girls College
* Sir Syed University of Engineering and Technology
* St. Joseph's College (Karachi), St. Joseph's College
* Sukkur Institute of Science & Technology
* Textile Institute of Pakistan
* University of Karachi
The University of Karachi ( sd, ; informally Karachi University, KU, or UoK) is a public research university located in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan. Established in June 1951 by an act of Parliament and as a successor to the University of Sindh ...
* University of Sindh
* Usman Institute of Technology
* Ziauddin Medical University
Culture
The rich culture, art and architectural landscape of Sindh have fascinated historians. The culture, folktales, art and music of Sindh form a mosaic of human history.Cultural heritage


 Sindh has a rich heritage of traditional handicraft that has evolved over the centuries. Perhaps the most professed exposition of Sindhi culture is in the handicrafts of Haala, Hala, a town some 30 kilometres from
Sindh has a rich heritage of traditional handicraft that has evolved over the centuries. Perhaps the most professed exposition of Sindhi culture is in the handicrafts of Haala, Hala, a town some 30 kilometres from Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River, in the northern part of Southern Indi ...
. Hala's artisans manufacture high-quality and impressively priced wooden handicrafts, textiles, paintings, handmade paper products, and blue pottery. Lacquered wood works known as Jandi, painting on wood, tiles, and pottery known as Kashi, hand weaved textiles including ''khadi'', ''susi'', and ''ajraks'' are synonymous with Sindhi culture preserved in Hala's handicraft.
The work of Sindhi artisans was sold in ancient markets of Damascus, Baghdad, Basra, Istanbul, Cairo and Samarkand. Referring to the lacquer work on wood locally known as Jandi, T. Posten (an English traveller who visited Sindh in the early 19th century) asserted that the articles of Hala could be compared with exquisite specimens of China. Technological improvements such as the spinning wheel (Charkha (spinning wheel), charkha) and treadle (pai-chah) in the weaver's loom were gradually introduced and the processes of designing, dyeing and printing by block were refined. The refined, lightweight, colourful, washable fabrics from Hala became a luxury for people used to the woollens and linens of the age.
Non-governmental organisations (NGOs) such as the World Wildlife Fund, Pakistan, play an important role to promote the culture of Sindh. They provide training to women artisans in Sindh so they get a source of income. They promote their products under the name of "Crafts Forever". Many women in rural Sindh are skilled in the production of caps. Sindhi caps are manufactured commercially on a small scale at New Saeedabad and Hala New. Sindhi people began celebrating Sindhi Topi Day on 6 December 2009, to preserve the historical culture of Sindh by wearing Ajrak and Sindhi topi.
Tourism
Mohenjo-daro
Mohenjo-daro (; sd, موئن جو دڙو'', ''meaning 'Mound of the Dead Men';Kot Diji
The ancient site at Kot Diji ( sd, ڪوٽ ڏیجي; ur, کوٹ ڈیجی) was the forerunner of the Indus Civilization. The occupation of this site is attested already at 3300 BCE. The remains consist of two parts; the citadel area on high ground ...
File:Bakirwarolake.jpg, Bakri Waro Lake, Khairpur
File:PK Karachi asv2020-02 img32 National Museum.jpg, National Museum of Pakistan
File:PK Kirthar NP asv2020-02 img18.jpg, Kirthar National Park
The Kirthar National Park ( ur, ), Sindhi (کيرٿرنيشنل پارڪ) is situated in the Kirthar Mountains in Jamshoro District in Sindh, Pakistan. The park was established in 1974, and encompasses over - making it the third largest natio ...
File:Karoonjhar Mountains.jpg, alt=Karoonjhar Mountains, Tharparkar, Karoonjhar Mountains, Tharparkar
File:Shahjahan mosque.jpg, Shah Jahan Mosque, Thatta
File:Mausoleum of Shah Abdul Latif Bhittai 05.jpg, Tomb of Shah Abdul Latif Bhittai
Shah Abdul Latif Bhittai ( sd, شاھ عبداللطيف ڀٽائي, ur, ; 1689/1690 – 21 December 1752), commonly known by the honorifics ''Lakhino Latif'', ''Latif Ghot'', ''Bhittai'', and ''Bhit Jo Shah'', was a Sindhi Sufi mystic, and ...
File:Keenjhar Lake view 1.jpg, Keenjhar Lake
File:Shrine Lal Shahbaz Qalandar, Sehwan Shareed, Pakistan.jpg, Lal Shahbaz Qalandar
See also
* Arab Sind * Bagh Prints * Brahma from Mirpur-Khas *Debal
Debal (Urdu, Arabic, sd, ) was an ancient port located near modern Karachi, Pakistan. It is adjacent to the nearby Manora Island and was administered by Mansura, and later Thatta.
Etymology
In Arabic history books, most notably in the early ...
* Institute of Sindhology
* List of cities in Sindh
* List of cities in Sindh by population
* List of cultural heritage sites in Sindh
* List of medical schools in Sindh
* List of districts of Pakistan
* List of Sindhi people
* Sindhi clothing
* Provincial Highways of Sindh
* Sindh cricket team
* Mansura, Sindh
* Mohenjodaro
* Muhajir Sooba
* Sind Division
* Sindhu Kingdom
* Sufism in Sindh
* Tomb paintings of Sindh
References
111 Asad Umar takes charge as Chief Secretary on 5 August 2018.Bibliography
* Ansari, Sarah F.D. (1992) ''Sufi saints and state power: the pirs of Sind, 1843–1947'', No. 50. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge. . * *External links
Sindh Transport Department official website
Government of Sindh
* Guide o
Sindh
* {{Authority control Sindh, Provinces of Pakistan States and territories established in 1970 1970 establishments in Pakistan Sindhi-speaking countries and territories Populated places established in the 7th millennium BC 7th-millennium BC establishments