Signs and symptoms of HIV/AIDS on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
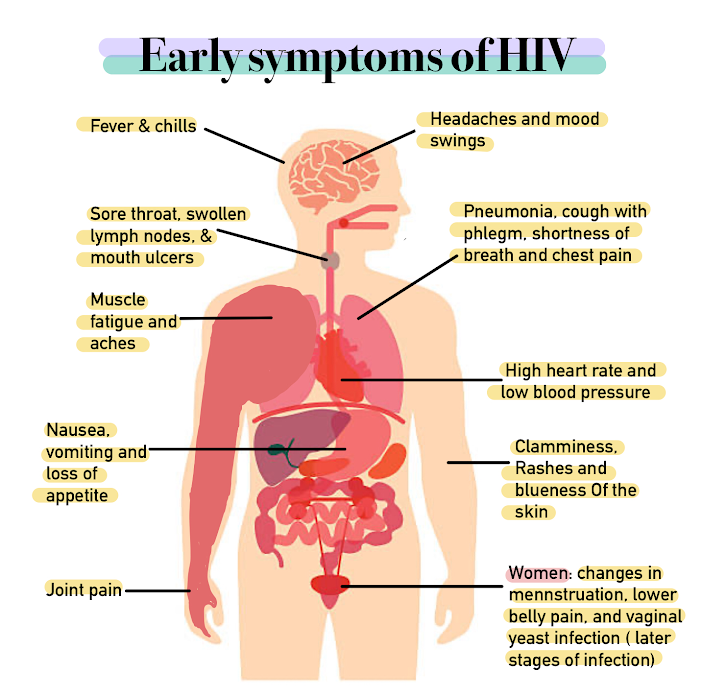 The stages of HIV infection are acute infection (also known as primary infection), latency and AIDS. Acute infection lasts for several weeks and may include symptoms such as
The stages of HIV infection are acute infection (also known as primary infection), latency and AIDS. Acute infection lasts for several weeks and may include symptoms such as
 Acute HIV infection, primary HIV infection or acute seroconversion syndrome is the second stage of
Acute HIV infection, primary HIV infection or acute seroconversion syndrome is the second stage of

 The symptoms of AIDS are primarily the result of conditions that do not normally develop in individuals with healthy
The symptoms of AIDS are primarily the result of conditions that do not normally develop in individuals with healthy
 People with HIV infections have substantially increased incidence of several cancers. This is primarily due to co-infection with an oncogenic
People with HIV infections have substantially increased incidence of several cancers. This is primarily due to co-infection with an oncogenic
 The stages of HIV infection are acute infection (also known as primary infection), latency and AIDS. Acute infection lasts for several weeks and may include symptoms such as
The stages of HIV infection are acute infection (also known as primary infection), latency and AIDS. Acute infection lasts for several weeks and may include symptoms such as fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
, swollen lymph nodes, inflammation of the throat, rash
A rash is a change of the human skin which affects its color, appearance, or texture.
A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, c ...
, muscle pain
Myalgia (also called muscle pain and muscle ache in layman's terms) is the medical term for muscle pain. Myalgia is a symptom of many diseases. The most common cause of acute myalgia is the overuse of a muscle or group of muscles; another like ...
, malaise, and mouth and esophageal sores. The latency stage involves few or no symptoms and can last anywhere from two weeks to twenty years or more, depending on the individual. AIDS, the final stage of HIV infection, is defined by low CD4+ T cell counts (fewer than 200 per μL), various opportunistic infections, cancers and other conditions.
Acute infection
 Acute HIV infection, primary HIV infection or acute seroconversion syndrome is the second stage of
Acute HIV infection, primary HIV infection or acute seroconversion syndrome is the second stage of HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune ...
infection. It occurs after the incubation stage, before the latency stage and the potential AIDS succeeding the latency stage.
During this period (usually days to weeks post-exposure) fifty to ninety percent of infected individuals develop an influenza or mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis (IM, mono), also known as glandular fever, is an infection usually caused by the Epstein–Barr virus (EBV). Most people are infected by the virus as children, when the disease produces few or no symptoms. In young adult ...
-like illness called acute HIV infection (or HIV prodrome), the most common symptoms of which may include fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
, lymphadenopathy, pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is inflammation of the back of the throat, known as the pharynx. It typically results in a sore throat and fever. Other symptoms may include a Rhinorrhea, runny nose, cough, headache, difficulty swallowing, swollen lymph nodes, and a ...
, rash
A rash is a change of the human skin which affects its color, appearance, or texture.
A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, c ...
, myalgia, malaise, mouth and esophageal sores, and may also include, but less commonly, headache, nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the ...
and vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteri ...
, fatigue, ulcers in the mouth or on the genitals, enlarged liver/spleen, weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat ( adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other co ...
, thrush, night sweats and diarrhea and neurological symptoms. Infected individuals may experience all, some, or none of these symptoms. The duration of symptoms varies, averaging 28 days and usually lasts at least a week.
Because of the nonspecific nature of these symptoms, they are often not recognized as signs of HIV infection. Even if patients go to their doctors or a hospital, they will often be misdiagnosed as having one of the more common infectious disease
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
s with the same symptoms. As a consequence, these primary symptoms are not used to diagnose HIV infection, as they do not develop in all cases and because many are caused by other more common diseases. However, recognizing the syndrome can be important because the patient is much more infectious during this period.
Latency
A strong immune defense reduces the number of viral particles in the blood stream, marking the start of secondary or chronic HIV infection. The secondary stage of HIV infection can vary between two weeks and 10 years. During the secondary phase of infection, HIV is active withinlymph nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that inclu ...
, which typically become persistently swollen, in response to large amounts of virus that become trapped in the follicular dendritic cells
Follicular dendritic cells (FDC) are cells of the immune system found in primary and secondary lymph follicles (lymph nodes) of the B cell areas of the lymphoid tissue. Unlike dendritic cells (DC), FDCs are not derived from the bone-marrow hema ...
(FDC) network. The surrounding tissues that are rich in CD4+ T cells may also become infected, and viral particles accumulate both in infected cells and as free virus. Individuals who are in this phase are still infectious. During this time, CD4+ CD45RO+ T cells carry most of the proviral load.
A small percentage of HIV-1 infected individuals retain high levels of CD4+ T-cells without antiretroviral therapy. However, most have detectable viral load and will eventually progress to AIDS without treatment. These individuals are classified as HIV controllers or long-term nonprogressors (LTNP). People who maintain CD4+ T cell counts and also have low or clinically undetectable viral load without anti-retroviral treatment are known as elite controllers or elite suppressors (ES).
AIDS
 The symptoms of AIDS are primarily the result of conditions that do not normally develop in individuals with healthy
The symptoms of AIDS are primarily the result of conditions that do not normally develop in individuals with healthy immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splint ...
s. Most of these conditions are opportunistic infections
An opportunistic infection is an infection caused by pathogens (bacteria, fungi, parasites or viruses) that take advantage of an opportunity not normally available. These opportunities can stem from a variety of sources, such as a weakened immune ...
caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
and parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
s that are normally controlled by the elements of the immune system that HIV damages. These infections affect nearly every organ system
An organ system is a biological system consisting of a group of organs that work together to perform one or more functions. Each organ has a specialized role in a plant or animal body, and is made up of distinct tissues.
Plants
Plants have ...
.
A declining CD4+/CD8+ ratio is predictive of the progression of HIV to AIDS.
People with AIDS also have an increased risk of developing various cancers such as Kaposi's sarcoma
Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) is a type of cancer that can form masses in the skin, in lymph nodes, in the mouth, or in other organs. The skin lesions are usually painless, purple and may be flat or raised. Lesions can occur singly, multiply in a limit ...
, cervical cancer and cancers of the immune system known as lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enla ...
s. Additionally, people with AIDS often have systemic symptoms of infection like fevers, sweats (particularly at night), swollen glands, chills, weakness, and weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat ( adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other co ...
. The specific opportunistic infections that AIDS patients develop depend in part on the prevalence of these infections in the geographic area in which the patient lives.
Pulmonary
Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) (originally known as ''Pneumocystis carinii'' pneumonia) is relatively rare in healthy,immunocompetent
In immunology, immunocompetence is the ability of the body to produce a normal immune response following exposure to an antigen. Immunocompetence is the opposite of immunodeficiency (also known as ''immuno-incompetence'' or being ''immuno-compro ...
people, but common among HIV-infected individuals. It is caused by ''Pneumocystis jirovecii
''Pneumocystis jirovecii'' (previously ''P. carinii'') is a yeast-like fungus of the genus ''Pneumocystis''. The causative organism of ''Pneumocystis'' pneumonia, it is an important human pathogen, particularly among immunocompromised hosts. Pr ...
''.
Before the advent of effective diagnosis, treatment and routine prophylaxis
Preventive healthcare, or prophylaxis, consists of measures taken for the purposes of disease prevention.Hugh R. Leavell and E. Gurney Clark as "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting physical and mental hea ...
in Western countries, it was a common immediate cause of death. In developing countries, it is still one of the first indications of AIDS in untested individuals, although it does not generally occur unless the CD4 count is less than 200 cells per µL of blood.
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, i ...
(TB) is unique among infections associated with HIV because it is transmissible to immunocompetent people via the respiratory route, and is not easily treatable once identified. Multidrug resistance is a serious problem. Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, i ...
with HIV co-infection (TB/HIV) is a major world health problem according to the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
: in 2007, 456,000 deaths among incident TB cases were HIV-positive, a third of all TB deaths and nearly a quarter of the estimated 2 million HIV deaths in that year. Even though its incidence has declined because of the use of directly observed therapy and other improved practices in Western countries, this is not the case in developing countries where HIV is most prevalent. In early-stage HIV infection (CD4 count >300 cells per µL), TB typically presents as a pulmonary disease. In advanced HIV infection, TB often presents atypically with extrapulmonary (systemic) disease a common feature. Symptoms are usually constitutional and are not localized to one particular site, often affecting bone marrow, bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
, urinary and gastrointestinal tracts, liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
, regional lymph nodes, and the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
.
Gastrointestinal
Esophagitis
Esophagitis, also spelled oesophagitis, is a disease characterized by inflammation of the esophagus. The esophagus is a tube composed of a mucosal lining, and longitudinal and circular smooth muscle fibers. It connects the pharynx to the stomach; s ...
is an inflammation of the lining of the lower end of the esophagus
The esophagus ( American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to ...
(gullet or swallowing tube leading to the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
). In HIV-infected individuals, this is normally due to fungal (candidiasis
Candidiasis is a fungal infection due to any type of '' Candida'' (a type of yeast). When it affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the mouth ...
) or viral ( herpes simplex-1 or cytomegalovirus) infections. In rare cases, it could be due to mycobacteria.
Unexplained chronic diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin w ...
in HIV infection is due to many possible causes, including common bacterial ('' Salmonella'', ''Shigella
''Shigella'' is a genus of bacteria that is Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, non-spore-forming, nonmotile, rod-shaped, and genetically closely related to '' E. coli''. The genus is named after Kiyoshi Shiga, who first discovered it in 1 ...
'', ''Listeria
''Listeria'' is a genus of bacteria that acts as an intracellular parasite in mammals. Until 1992, 17 species were known, each containing two subspecies. By 2020, 21 species had been identified. The genus is named in honour of the British pio ...
'' or '' Campylobacter'') and parasitic infections; and uncommon opportunistic infections such as cryptosporidiosis
Cryptosporidiosis, sometimes informally called crypto, is a parasitic disease caused by '' Cryptosporidium'', a genus of protozoan parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa. It affects the distal small intestine and can affect the respiratory tra ...
, microsporidiosis
Microsporidiosis is an opportunistic intestinal infection that causes diarrhea and wasting in immunocompromised individuals ( HIV, for example). It results from different species of microsporidia, a group of microbial (unicellular) fungi.
In HI ...
, ''Mycobacterium avium
''Mycobacterium avium ''complex is a group of mycobacteria comprising ''Mycobacterium intracellulare'' and ''Mycobacterium avium'' that are commonly grouped because they infect humans together; this group, in turn, is part of the group of nontu ...
'' complex (MAC) and viruses, astrovirus
Astroviruses are a type of virus that was first discovered in 1975 using electron microscopes following an outbreak of diarrhea in humans. In addition to humans, astroviruses have now been isolated from numerous mammalian animal species (and a ...
, adenovirus, rotavirus
''Rotavirus'' is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses in the family ''Reoviridae''. Rotaviruses are the most common cause of diarrhoeal disease among infants and young children. Nearly every child in the world is infected with a rotavirus ...
and cytomegalovirus, (the latter as a course of colitis
Colitis is swelling or inflammation of the large intestine ( colon). Colitis may be acute and self-limited or long-term. It broadly fits into the category of digestive diseases.
In a medical context, the label ''colitis'' (without qualification ...
).
In some cases, diarrhea may be a side effect of several drugs used to treat HIV, or it may simply accompany HIV infection, particularly during primary HIV infection. It may also be a side effect of antibiotics used to treat bacterial causes of diarrhea (common for '' Clostridium difficile''). In the later stages of HIV infection, diarrhea is thought to be a reflection of changes in the way the intestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans ...
absorbs nutrients, and may be an important component of HIV-related wasting
In medicine, wasting, also known as wasting syndrome, refers to the process by which a debilitating disease causes muscle and fat tissue to "waste" away. Wasting is sometimes referred to as "acute malnutrition" because it is believed that epis ...
.
Neurological and psychiatric
HIV infection may lead to a variety of neuropsychiatric sequelae, either by infection of the now susceptible nervous system by organisms, or as a direct consequence of the illness itself.Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by '' Toxoplasma gondii'', an apicomplexan. Infections with toxoplasmosis are associated with a variety of neuropsychiatric and behavioral conditions. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or mont ...
is a disease caused by the single-celled parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
''Toxoplasma gondii
''Toxoplasma gondii'' () is an obligate intracellular parasitic protozoan (specifically an apicomplexan) that causes toxoplasmosis. Found worldwide, ''T. gondii'' is capable of infecting virtually all warm-blooded animals, but felids, such as d ...
''; it usually infects the brain, causing toxoplasma encephalitis, but it can also infect and cause disease in the eyes and lungs. Cryptococcal meningitis is an infection of the meninx (the membrane covering the brain and spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
) by the fungus ''Cryptococcus neoformans
''Cryptococcus neoformans'' is an encapsulated yeast belonging to the class Tremellomycetes and an obligate aerobe that can live in both plants and animals. Its teleomorph is a filamentous fungus, formerly referred to ''Filobasidiella neoforman ...
''. It can cause fevers, headache, fatigue, nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the ...
, and vomiting. Patients may also develop seizure
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with l ...
s and confusion; left untreated, it can be lethal.
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) is a demyelinating disease
A demyelinating disease is any disease of the nervous system in which the myelin sheath of neurons is damaged. This damage impairs the conduction of signals in the affected nerves. In turn, the reduction in conduction ability causes deficiency i ...
, in which the gradual destruction of the myelin
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be ...
sheath covering the axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action p ...
s of nerve cells impairs the transmission of nerve impulses. It is caused by a virus called JC virus which occurs in 70% of the population in latent
Latency or latent may refer to:
Science and technology
* Latent heat, energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic system, during a constant-temperature process
* Latent variable, a variable that is not directly observed but inferred ...
form, causing disease only when the immune system has been severely weakened, as is the case for AIDS patients. It progresses rapidly, usually causing death within months of diagnosis.
HIV-associated dementia
HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND) are neurological disorders associated with HIV infection and AIDS. It is a syndrome of progressive deterioration of memory, cognition, behavior, and motor function in HIV-infected individuals during ...
(HAD) is a metabolic encephalopathy
Encephalopathy (; from grc, ἐνκέφαλος "brain" + πάθος "suffering") means any disorder or disease of the brain, especially chronic degenerative conditions. In modern usage, encephalopathy does not refer to a single disease, but r ...
induced by HIV infection and fueled by immune activation of HIV infected brain macrophages and microglia. These cells are productively infected by HIV and secrete neurotoxins of both host and viral origin. Specific neurological impairments are manifested by cognitive, behavioral, and motor abnormalities that occur after years of HIV infection and are associated with low CD4+ T cell levels and high plasma viral loads.
Prevalence is 10–20% in Western countries but only 1–2% of HIV infections in India. This difference is possibly due to the HIV subtype in India. AIDS related mania is sometimes seen in patients with advanced HIV illness; it presents with more irritability and cognitive impairment and less euphoria than a manic episode
Mania, also known as manic syndrome, is a mental and behavioral disorder defined as a state of abnormally elevated arousal, affect, and energy level, or "a state of heightened overall activation with enhanced affective expression together wit ...
associated with true bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with ...
. Unlike the latter condition, it may have a more chronic course. This syndrome is less frequently seen with the advent of multi-drug therapy.
Tumors
 People with HIV infections have substantially increased incidence of several cancers. This is primarily due to co-infection with an oncogenic
People with HIV infections have substantially increased incidence of several cancers. This is primarily due to co-infection with an oncogenic DNA virus
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and ...
, especially Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is the ninth known human herpesvirus; its formal name according to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) is ''Human gammaherpesvirus 8'', or HHV-8 in short. Like other herpesvir ...
(KSHV) (also known as human herpesvirus-8 HV-8, and human papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and res ...
(HPV).
Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) is the most common tumor in HIV-infected patients. The appearance of this tumor in young homosexual men in 1981 was one of the first signals of the AIDS epidemic. Caused by a gammaherpes virus called Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpes virus (KSHV), it often appears as purplish nodules on the skin, but can affect other organs, especially the mouth, gastrointestinal tract, and lungs. High-grade B cell lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enla ...
s such as Burkitt's lymphoma, Burkitt's-like lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and primary central nervous system lymphoma
Primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL), also termed primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system (DLBCL-CNS), is a primary intracranial tumor appearing mostly in patients with severe immunodeficiency (typically pa ...
present more often in HIV-infected patients. These particular cancers often foreshadow a poor prognosis. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) or KSHV cause many of these lymphomas. In HIV-infected patients, lymphoma often arises in extranodal sites such as the gastrointestinal tract. When they occur in an HIV-infected patient, KS and aggressive B cell lymphomas confer a diagnosis of AIDS.
Invasive cervical cancer in HIV-infected women is also considered AIDS-defining, it is caused by human papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and res ...
(HPV).
In addition to the AIDS-defining tumors listed above, HIV-infected patients are at increased risk of certain other tumors, notably Hodgkin's disease, anal
Anal may refer to:
Related to the anus
*Related to the anus of animals:
** Anal fin, in fish anatomy
** Anal vein, in insect anatomy
** Anal scale, in reptile anatomy
*Related to the human anus:
** Anal sex, a type of sexual activity involving s ...
and rectal carcinomas, hepatocellular carcinomas, head and neck cancer
Head and neck cancer develops from tissues in the lip and oral cavity (mouth), larynx (throat), salivary glands, nose, sinuses or the skin of the face. The most common types of head and neck cancers occur in the lip, mouth, and larynx. Symptoms ...
s, and lung cancer. Some of these are causes by viruses, such as Hodgkin's disease (EBV), anal/rectal cancers (HPV), head and neck cancers (HPV), and hepatocellular carcinoma (hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection.
Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. ...
or C). Other contributing factors include exposure to carcinogens (cigarette smoke for lung cancer), or living for years with subtle immune defects.
The incidence of many common tumors, such as breast cancer or colon cancer, does not increase in HIV-infected patients. In areas where HAART
The management of HIV/AIDS normally includes the use of multiple antiretroviral drugs as a strategy to control HIV infection. There are several classes of antiretroviral agents that act on different stages of the HIV life-cycle. The use of multip ...
is extensively used to treat AIDS, the incidence of many AIDS-related malignancies has decreased, but at the same time malignant cancers overall have become the most common cause of death of HIV-infected patients. In recent years, an increasing proportion of these deaths have been from non-AIDS-defining cancers.
In line with the treatment of cancer, chemotherapy has shown promise in increasing the number of uninfected T-cells and diminishing the viral load.
Other infections
People with AIDS often develop opportunistic infections that present withnon-specific symptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showin ...
s, especially low-grade fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
s and weight loss. These include opportunistic infection with '' Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare'' and cytomegalovirus (CMV). CMV can cause colitis, as described above, and CMV retinitis can cause blindness.
Talaromycosis
Talaromycosis is a fungal infection that presents with painless skin lesions of face and neck, fever, anaemia, large lymph glands and liver.
It is caused by the fungus'' Talaromyces marneffei'', which is found in soil and decomposing organic ma ...
due to '' Talaromyces marneffei'' is now the third most common opportunistic infection (after extrapulmonary tuberculosis and cryptococcosis
Cryptococcosis is a potentially fatal fungal infection of mainly the lungs, presenting as a pneumonia, and brain, where it appears as a meningitis. Cough, difficulty breathing, chest pain and fever are seen when the lungs are infected. When the ...
) in HIV-positive individuals within the endemic area of Southeast Asia.
An infection that often goes unrecognized in people with AIDS is Parvovirus B19. Its main consequence is anemia, which is difficult to distinguish from the effects of antiretroviral drugs used to treat AIDS itself.
References
Notes
{{DEFAULTSORT:Signs and symptoms of HIV AIDS HIV/AIDS