Siege of Boonesborough on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
}
The siege of Boonesborough was a military engagement which took place in September 1778 during the
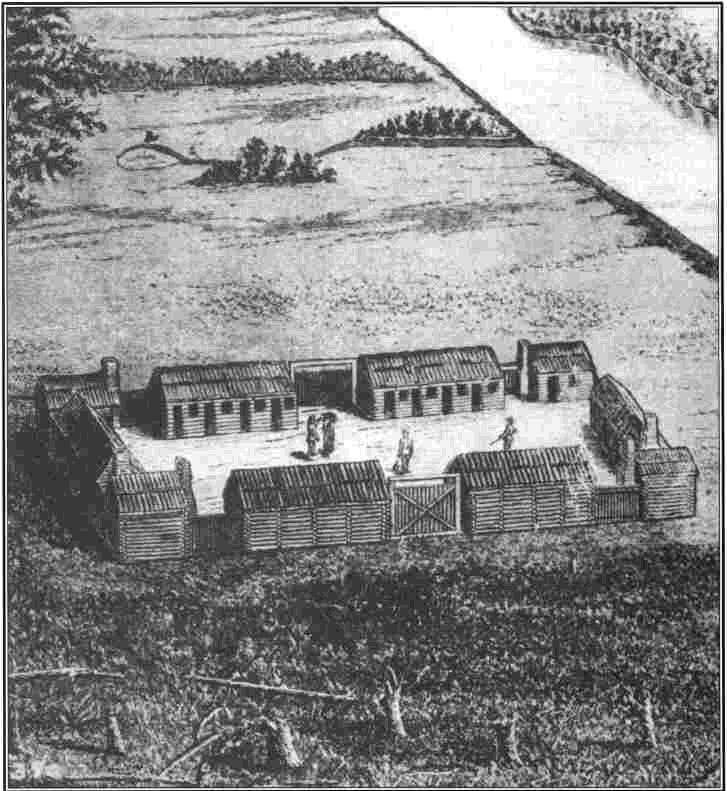 Unable to dislodge the Kentuckians from their fortified settlements, the Indians destroyed crops and killed cattle, hoping that food shortages would compel the Kentucky settlers to leave. With the food supply at Boonesborough running low, the settlers needed salt to preserve what meat they had. In January 1778, Daniel Boone led a party of thirty men to the salt springs on the Licking River. On February 7, 1778, when Boone was out hunting meat for the expedition, he was surprised and captured by warriors led by Blackfish. Because Boone's party was greatly outnumbered, he convinced his men to surrender rather than put up a fight.
Blackfish wanted to continue to Boonesborough and capture it since it was now poorly defended, but Boone convinced him that the women and children were not hardy enough to survive a winter trek as prisoners. Instead, Boone promised that Boonesborough would surrender willingly to the Shawnees the following spring. Boone was improvising, saying anything to keep the Shawnees from attacking Boonesborough. He did not have an opportunity to tell his men what he was doing, however, and many of them concluded that he had switched his loyalty to the British.
Boone and his men were taken as prisoners to Blackfish's town of Chillicothe. Per Shawnee custom, some of the prisoners were taken into the tribe to replace fallen warriors. The remainder were taken to Detroit, where Indians received a bounty from Governor Hamilton for each prisoner or scalp taken. Boone was adopted into a Shawnee family at Chillicothe, perhaps into Blackfish's family. He was given the name Sheltowee, meaning "Big Turtle". Like most of the other adoptees, Boone was watched closely, but he eventually escaped.
On June 16, 1778, when he learned that Blackfish was preparing to return to Boonesborough with a large force, Boone eluded his captors and raced home, covering the 160 miles (260 km) to Boonesborough in five days. Upon his return, some of the men were unsure about Boone's loyalty, since after surrendering the salt making party he had apparently lived quite happily among the Shawnees for months. Boone responded by leading a preemptive raid against the Shawnee village of Paint Lick Town on the other side of the Ohio River. This accomplished little and the raiding party hurried back to Boonesborough when they discovered that Blackfish had marched south.
Unable to dislodge the Kentuckians from their fortified settlements, the Indians destroyed crops and killed cattle, hoping that food shortages would compel the Kentucky settlers to leave. With the food supply at Boonesborough running low, the settlers needed salt to preserve what meat they had. In January 1778, Daniel Boone led a party of thirty men to the salt springs on the Licking River. On February 7, 1778, when Boone was out hunting meat for the expedition, he was surprised and captured by warriors led by Blackfish. Because Boone's party was greatly outnumbered, he convinced his men to surrender rather than put up a fight.
Blackfish wanted to continue to Boonesborough and capture it since it was now poorly defended, but Boone convinced him that the women and children were not hardy enough to survive a winter trek as prisoners. Instead, Boone promised that Boonesborough would surrender willingly to the Shawnees the following spring. Boone was improvising, saying anything to keep the Shawnees from attacking Boonesborough. He did not have an opportunity to tell his men what he was doing, however, and many of them concluded that he had switched his loyalty to the British.
Boone and his men were taken as prisoners to Blackfish's town of Chillicothe. Per Shawnee custom, some of the prisoners were taken into the tribe to replace fallen warriors. The remainder were taken to Detroit, where Indians received a bounty from Governor Hamilton for each prisoner or scalp taken. Boone was adopted into a Shawnee family at Chillicothe, perhaps into Blackfish's family. He was given the name Sheltowee, meaning "Big Turtle". Like most of the other adoptees, Boone was watched closely, but he eventually escaped.
On June 16, 1778, when he learned that Blackfish was preparing to return to Boonesborough with a large force, Boone eluded his captors and raced home, covering the 160 miles (260 km) to Boonesborough in five days. Upon his return, some of the men were unsure about Boone's loyalty, since after surrendering the salt making party he had apparently lived quite happily among the Shawnees for months. Boone responded by leading a preemptive raid against the Shawnee village of Paint Lick Town on the other side of the Ohio River. This accomplished little and the raiding party hurried back to Boonesborough when they discovered that Blackfish had marched south.
 Gunfire was exchanged over the next several days. After the initial flurry of shooting, Boone—who reemerged as the natural leader even though as a captain he was outranked by Major Smith and Colonel
Gunfire was exchanged over the next several days. After the initial flurry of shooting, Boone—who reemerged as the natural leader even though as a captain he was outranked by Major Smith and Colonel
The Fort Boonesborough Foundation
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20060216205037/http://www.graphicenterprises.net/Re-Enacting/Still_Photography/Boonesborough/boonesborough.html Photographs from the 2005 reenactment of the siege {{coord, 37, 53, 59.2, N, 84, 15, 56.4, W, type:event_region:US-KY, display=title 1778 in Kentucky 1778 in the United States Battles involving Great Britain Boonesborough Battles involving the United States Boonesboro Boonesborough Boonesborough Madison County, Kentucky Boonesborough
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
. On September 7, Shawnee
The Shawnee are an Algonquian-speaking indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands. In the 17th century they lived in Pennsylvania, and in the 18th century they were in Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana and Illinois, with some bands in Kentucky a ...
chief Blackfish, who was allied to the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
, led an attack on the Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia ...
settlement of Boonesborough. Months before the battle, Blackfish had captured and adopted Daniel Boone
Daniel Boone (September 26, 1820) was an American pioneer and frontiersman whose exploits made him one of the first folk heroes of the United States. He became famous for his exploration and settlement of Kentucky, which was then beyond the we ...
, the founder of Boonesborough. Boone escaped the Shawnees in time to lead the defense of the settlement. Blackfish's siege was unsuccessful and was lifted after eleven days. Boone was then court-martialed by fellow officers who suspected him of harboring Loyalist sympathies. He was acquitted, but soon left the settlement.
Background
Settlement of Kentucky
In 1774, the Colony of Virginia defeated a coalition of Native Americans in the Ohio Country, primarilyShawnee
The Shawnee are an Algonquian-speaking indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands. In the 17th century they lived in Pennsylvania, and in the 18th century they were in Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana and Illinois, with some bands in Kentucky a ...
s, in Dunmore's War
Lord Dunmore's War—or Dunmore's War—was a 1774 conflict between the Colony of Virginia and the Shawnee and Mingo American Indian nations.
The Governor of Virginia during the conflict was John Murray, 4th Earl of Dunmore—Lord Dunmore. H ...
. In the treaty that ended the war, the Ohio River was established as the boundary between Shawnee lands north of the river and western Virginia (present West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the B ...
and much of Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia ...
) to the south. The Native Americans were not unified, however, and many leaders did not recognize the treaty—which ceded their prime hunting grounds—to be binding.
In 1775, Richard Henderson of North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and ...
purchased a large amount of Kentucky land from the Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
s, who also hunted in Kentucky, on which he intended to establish a colony called Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
. Henderson's employee Daniel Boone
Daniel Boone (September 26, 1820) was an American pioneer and frontiersman whose exploits made him one of the first folk heroes of the United States. He became famous for his exploration and settlement of Kentucky, which was then beyond the we ...
blazed the Wilderness Trail into central Kentucky and built Fort Boone, soon renamed Boonesborough. Boonesborough and the rest of Transylvania became part of Virginia in 1776. Several families from the east soon settled there. Shawnees to the north were unhappy about American expansion into Kentucky, and they sporadically attacked Boonesborough.
Meanwhile, the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
had begun in the east. In 1777, British officials opened a new front in the war with the American colonists by recruiting and arming Native American war parties to raid the Kentucky settlements. Henry Hamilton, the British Lieutenant Governor of Canada at Fort Detroit
Fort Pontchartrain du Détroit or Fort Detroit (1701–1796) was a fort established on the north bank of the Detroit River by the French officer Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac and the Italian Alphonse de Tonty in 1701. In the 18th century, Fre ...
, found willing allies in leaders such as Shawnee chief Blackfish, who hoped to drive the American colonists out of Kentucky and reclaim their hunting grounds. As the raids intensified, Americans who strayed from fortified settlements like Boonesborough were likely to be killed or captured. American Indians brought 129 scalps and 77 prisoners to Hamilton in 1777.
Capture of Daniel Boone
 Unable to dislodge the Kentuckians from their fortified settlements, the Indians destroyed crops and killed cattle, hoping that food shortages would compel the Kentucky settlers to leave. With the food supply at Boonesborough running low, the settlers needed salt to preserve what meat they had. In January 1778, Daniel Boone led a party of thirty men to the salt springs on the Licking River. On February 7, 1778, when Boone was out hunting meat for the expedition, he was surprised and captured by warriors led by Blackfish. Because Boone's party was greatly outnumbered, he convinced his men to surrender rather than put up a fight.
Blackfish wanted to continue to Boonesborough and capture it since it was now poorly defended, but Boone convinced him that the women and children were not hardy enough to survive a winter trek as prisoners. Instead, Boone promised that Boonesborough would surrender willingly to the Shawnees the following spring. Boone was improvising, saying anything to keep the Shawnees from attacking Boonesborough. He did not have an opportunity to tell his men what he was doing, however, and many of them concluded that he had switched his loyalty to the British.
Boone and his men were taken as prisoners to Blackfish's town of Chillicothe. Per Shawnee custom, some of the prisoners were taken into the tribe to replace fallen warriors. The remainder were taken to Detroit, where Indians received a bounty from Governor Hamilton for each prisoner or scalp taken. Boone was adopted into a Shawnee family at Chillicothe, perhaps into Blackfish's family. He was given the name Sheltowee, meaning "Big Turtle". Like most of the other adoptees, Boone was watched closely, but he eventually escaped.
On June 16, 1778, when he learned that Blackfish was preparing to return to Boonesborough with a large force, Boone eluded his captors and raced home, covering the 160 miles (260 km) to Boonesborough in five days. Upon his return, some of the men were unsure about Boone's loyalty, since after surrendering the salt making party he had apparently lived quite happily among the Shawnees for months. Boone responded by leading a preemptive raid against the Shawnee village of Paint Lick Town on the other side of the Ohio River. This accomplished little and the raiding party hurried back to Boonesborough when they discovered that Blackfish had marched south.
Unable to dislodge the Kentuckians from their fortified settlements, the Indians destroyed crops and killed cattle, hoping that food shortages would compel the Kentucky settlers to leave. With the food supply at Boonesborough running low, the settlers needed salt to preserve what meat they had. In January 1778, Daniel Boone led a party of thirty men to the salt springs on the Licking River. On February 7, 1778, when Boone was out hunting meat for the expedition, he was surprised and captured by warriors led by Blackfish. Because Boone's party was greatly outnumbered, he convinced his men to surrender rather than put up a fight.
Blackfish wanted to continue to Boonesborough and capture it since it was now poorly defended, but Boone convinced him that the women and children were not hardy enough to survive a winter trek as prisoners. Instead, Boone promised that Boonesborough would surrender willingly to the Shawnees the following spring. Boone was improvising, saying anything to keep the Shawnees from attacking Boonesborough. He did not have an opportunity to tell his men what he was doing, however, and many of them concluded that he had switched his loyalty to the British.
Boone and his men were taken as prisoners to Blackfish's town of Chillicothe. Per Shawnee custom, some of the prisoners were taken into the tribe to replace fallen warriors. The remainder were taken to Detroit, where Indians received a bounty from Governor Hamilton for each prisoner or scalp taken. Boone was adopted into a Shawnee family at Chillicothe, perhaps into Blackfish's family. He was given the name Sheltowee, meaning "Big Turtle". Like most of the other adoptees, Boone was watched closely, but he eventually escaped.
On June 16, 1778, when he learned that Blackfish was preparing to return to Boonesborough with a large force, Boone eluded his captors and raced home, covering the 160 miles (260 km) to Boonesborough in five days. Upon his return, some of the men were unsure about Boone's loyalty, since after surrendering the salt making party he had apparently lived quite happily among the Shawnees for months. Boone responded by leading a preemptive raid against the Shawnee village of Paint Lick Town on the other side of the Ohio River. This accomplished little and the raiding party hurried back to Boonesborough when they discovered that Blackfish had marched south.
Negotiations
On September 7, 1778, Blackfish's force arrived outside Boonesborough. Boone counted 444 Native Americans and 12 white men. The former were mostly Shawnees, with a number ofCherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
s, Wyandot
Wyandot may refer to:
Native American ethnography
* Wyandot people, also known as the Huron
* Wyandot language
Wyandot (sometimes spelled Wandat) is the Iroquoian language traditionally spoken by the people known variously as Wyandot or Wya ...
s, Miamis
The Miami ( Miami-Illinois: ''Myaamiaki'') are a Native American nation originally speaking one of the Algonquian languages. Among the peoples known as the Great Lakes tribes, they occupied territory that is now identified as North-central Indi ...
, Delawares, and Mingos. The latter were French-Canadian militiamen from Detroit, former French subjects now fighting on behalf of the British Crown. Although this was the largest force yet sent against the Kentucky settlements, taking a fortified position like Boonesborough would still be difficult without artillery to reduce the stronghold. Blackfish called Boone out of the fort for a parley and reminded Boone of his promise to surrender the settlement. Blackfish presented letters from Governor Hamilton which proclaimed that the settlers would be well treated and taken to Detroit if they surrendered. If they did not surrender, there were no guarantees. Boone told Blackfish that he would present the offer to the others. He could not make this decision himself, Boone said, since during his captivity other officers had assumed command.
Back in the fort, Boone outlined the situation. The consensus was to fight rather than surrender. The decision was made to prolong the negotiations with Blackfish as long as possible, since reinforcements from Virginia were expected. Boone and Major William Bailey Smith went outside again and told Blackfish that they feared that the trip to Detroit would be too hard on the women and children. Blackfish pointed out that he had brought 40 horses to transport those unable to walk. Boone asked for another day to consult with the others. Leaders from the two sides smoked a ceremonial pipe
A ceremonial pipe is a particular type of smoking pipe, used by a number of cultures of the indigenous peoples of the Americas in their sacred ceremonies. Traditionally they are used to offer prayers in a religious ceremony, to make a ceremonial ...
together to mark the peace agreement, and then broke off negotiations for the day. Over the next two days, settlers in the fort prepared for the siege. Based on faulty intelligence received from Hamilton in Detroit, Blackfish believed that there were at least 200 militiamen in the fort, when in fact there were only about 40 effective gunmen inside. The Kentuckians reinforced the illusion of a greater number of men by having some of the women in the fort carry weapons while dressed in men's clothing.
On the evening of September 8, Blackfish and Boone met again. Boone told a surprised Blackfish that the fort would not surrender. Blackfish proposed that a formal treaty conference with all of the leaders be held on the next day. The treaty session began on September 9, with leaders from the two sides sharing a meal outside the fort. Afterwards, the council began. In case of trouble, both sides had gunmen covering the meeting from a distance. Blackfish demanded to know "by what right had the white people taken possession of this country." Boone replied that they had bought the land from the Cherokees at Sycamore Shoals
The Sycamore Shoals of the Watauga River, usually shortened to Sycamore Shoals, is a rocky stretch of river rapids along the Watauga River in Elizabethton, Tennessee. Archeological excavations have found Native Americans lived near the shoals s ...
. A Cherokee chief confirmed that this was true. Blackfish accepted this answer and then proposed that if the settlers would pledge their allegiance to King George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
, the Shawnees would accept the Ohio River boundary and both sides would live in peace. A treaty to this effect (which does not survive) was then signed.
The Shawnees then approached the Americans to shake hands and seal the agreement. What happened next is unclear. According to one popular interpretation, the Shawnees, having failed to secure the surrender of Boonesborough, attempted to seize the American leaders. However, as historian John Mack Faragher and others have argued, there is little evidence that this was the Shawnees' intention. A scuffle broke out, and marksmen from both sides opened fire. Despite a few injuries, all but one of the Americans managed to scramble back into the fort-the last one had to take cover next to a tree stump by the main gate. The Indians rushed the gate but were driven back by heavy gunfire. Negotiations were over; the formal siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characteriz ...
had begun. The last delegate spent a harrowing day with the battle raging around him. He finally managed to crawl inside when someone opened the gate slightly after nightfall.
Siege
 Gunfire was exchanged over the next several days. After the initial flurry of shooting, Boone—who reemerged as the natural leader even though as a captain he was outranked by Major Smith and Colonel
Gunfire was exchanged over the next several days. After the initial flurry of shooting, Boone—who reemerged as the natural leader even though as a captain he was outranked by Major Smith and Colonel Richard Callaway
Richard Callaway (June 14, 1717 – November 8, 1780) was an American frontiersman, military officer, politician, and hunter who was one of the first white settlers in modern-day Kentucky. Born in Essex County, Virginia, Callaway joined Daniel B ...
—urged the Kentuckians to conserve their gunpowder. At night, Native Americans ran up to the walls and attempted to throw burning torches onto the roofs of the houses within. This was ineffective, however, because the warriors made easy targets for the Kentucky marksmen.
On September 11, Lieutenant
A lieutenant ( , ; abbreviated Lt., Lt, LT, Lieut and similar) is a commissioned officer rank in the armed forces of many nations.
The meaning of lieutenant differs in different militaries (see comparative military ranks), but it is often ...
Antoine Dagneaux de Quindre, leading 11 men from Detroit Militia
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the List of municipalities in Michigan, largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the Canada–United States border, United States–Canada border, and the County seat, seat of gov ...
, convinced his Indian allies to begin digging a tunnel from the bank of the river towards the fort. Known as mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic ...
, the goal was to place barrels of gunpowder in the tunnel under a section of the fort's walls. When these barrels were exploded, the wall would collapse, leaving a place for the attackers to rush in. When the defenders inside the fort heard the digging, they began to dig a countermine, hoping to collapse the attackers' tunnel prematurely. The diggers on both sides began to yell taunts at each other. Heavy rains caused the Indians' tunnel to collapse before it reached the fort.
Boone's brother Squire Boone
In the Middle Ages, a squire was the shield- or armour-bearer of a knight.
Use of the term evolved over time. Initially, a squire served as a knight's apprentice. Later, a village leader or a lord of the manor might come to be known as a " ...
was known as an inventor. He fashioned a makeshift wooden cannon, reinforced with iron bands, which was fired once or twice at groups of Indians before it cracked. Squire Boone also made squirt guns out of old musket barrels, which were used to put out fires on the roofs. The Shawnees launched their final assault on September 17, again trying to set fire to the fort. They were beaten back, and a heavy rain helped to put out the fires. The Shawnees lost more men killed in this attack than on all previous days. The next day, they gradually broke off the siege. They separated into scattered war parties and raided other settlements, inflicting far more damage in their traditional mode of warfare than they had done during the siege. The two Boonesborough fatalities during the siege were a slave named London and David Bondurant.
Aftermath
After the siege, Colonel Richard Callaway brought charges against Boone, alleging that Boone "was in favour of the British government". Joining Callaway was CaptainBenjamin Logan
Benjamin Logan (May 1, 1743 – December 11, 1802) was an American pioneer, soldier, and politician from Virginia, then Shelby County, Kentucky. As colonel of the Kentucky County, Virginia militia during the American Revolutionary War, he was s ...
from nearby Logan's Station. Logan and Callaway both had nephews who had been surrendered by Boone at the salt licks and were still prisoners. In the court-martial proceedings, held at Logan's Fort, there were four charges against Boone:
:#Boone had surrendered the salt making party without a fight;
:#While in captivity, Boone had promised to surrender Boonesborough to the British;
:#After his return, he had led the Paint Lick expedition, which weakened Boonesborough at a time when Blackfish's army was expected;
:#Boone had exposed the officers to ambush by agreeing to meet the Indians at the peace treaty outside the fort.
After listening to all the testimony, the court found Boone "not guilty", and even promoted him to major because of his actions. Despite this vindication, Boone was humiliated by the episode and rarely spoke of it again. Boone then went to North Carolina to retrieve his family, who had returned there during his captivity, believing him to be dead. When Boone came back to Kentucky, he established a new settlement called Boone's Station rather than resettle in the place where he had been court-martialed. While Boone was in North Carolina, a retaliatory raid was launched against Blackfish's town of Chillicothe in the spring of 1779. Blackfish successfully defended his village but was shot in the leg and later died when the wound became infected. On March 8, 1780, Richard Callaway was caught outside Boonesborough by Shawnees and was mutilated, scalped and killed.
In popular culture
The siege of Boonesborough was dramatized in an episode of the 1964 CBS television series "The Great Adventure", withPeter Graves
Peter Graves (born Peter Duesler Aurness; March 18, 1926 – March 14, 2010) was an American actor. He was best known for his role as Jim Phelps in the CBS television series ''Mission: Impossible (1966 TV series), Mission: Impossible'' from 1967 ...
starring as Daniel Boone. The events are now reenacted yearly at Fort Boonesborough State Park
Fort Boonesborough was a frontier fort in Kentucky, founded by Daniel Boone and his men following their crossing of the Kentucky River on April 1, 1775. The settlement they founded, known as Boonesborough, Kentucky, is Kentucky's second oldest Eu ...
. The events surrounding the Siege of Boonesborough were the subject of Allan W. Eckert's historical novel ''The Court-Martial of Daniel Boone''. ''The Court-Martial of Daniel Boone'', (1973), Little Brown & Company, ; 2000 paperback reprint edition, Backinprint.com,
See also
*List of battles fought in Kentucky
This is an incomplete list of military confrontations that have occurred within the boundaries of the modern US State of Kentucky since European contact. The region was part of New France from 1679 to 1763, ruled by Great Britain from 1763 to 1783, ...
References
Bibliography
*Bakeless, John. ''Daniel Boone: Master of the Wilderness''. Originally published 1939, reprinted University of Nebraska Press, 1989. *Draper, Lyman Copeland. ''The Life of Daniel Boone''. Written in the 19th century but unpublished; edited by Ted Franklin Belue and published in Mechanicsburg, Pennsylvania: Stackpole Books, 1998. *Elliott, Lawrence. ''The Long Hunter: A New Life of Daniel Boone''. New York: Reader's Digest Press, 1976. *Faragher, John Mack. ''Daniel Boone: The Life and Legend of an American Pioneer''. New York: Holt, 1992. *Lofaro, Michael A. ''Daniel Boone: An American Life''. Lexington, Kentucky: University Press of Kentucky, 2003.External links
The Fort Boonesborough Foundation
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20060216205037/http://www.graphicenterprises.net/Re-Enacting/Still_Photography/Boonesborough/boonesborough.html Photographs from the 2005 reenactment of the siege {{coord, 37, 53, 59.2, N, 84, 15, 56.4, W, type:event_region:US-KY, display=title 1778 in Kentucky 1778 in the United States Battles involving Great Britain Boonesborough Battles involving the United States Boonesboro Boonesborough Boonesborough Madison County, Kentucky Boonesborough