Siege-train on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick
A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick
 The
The 

 With the advent of
With the advent of
Paolo Santini De Machinis or De machinis bellicis de Mariano Taccola, Paris, BnF, Département des manuscrits, Latin 7239
{{DEFAULTSORT:Siege Engine
 A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick
A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick city wall
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates ...
s and other fortification
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere' ...
s in siege warfare
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterize ...
. Some are immobile, constructed in place to attack enemy fortifications from a distance, while others have wheels to enable advancing up to the enemy fortification. There are many distinct types, such as siege tower
A Roman siege tower or breaching tower (or in the Middle Ages, a belfry''Castle: Stephen Biesty's Cross-Sections''. Dorling Kindersley Pub (T); 1st American edition (September 1994). Siege towers were invented in 300 BC. ) is a specialized siege ...
s that allow foot soldier
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marin ...
s to scale walls and attack the defenders, battering rams that damage walls or gates, and large ranged weapons (such as ballista
The ballista (Latin, from Greek βαλλίστρα ''ballistra'' and that from βάλλω ''ballō'', "throw"), plural ballistae, sometimes called bolt thrower, was an ancient missile weapon that launched either bolts or stones at a distant ...
e, catapults/trebuchet
A trebuchet (french: trébuchet) is a type of catapult that uses a long arm to throw a projectile. It was a common powerful siege engine until the advent of gunpowder. The design of a trebuchet allows it to launch projectiles of greater weight ...
s and other similar constructions) that attack from a distance by launching projectiles. Some complex siege engines were combinations of these types.
Siege engines are fairly large constructions – from the size of a small house to a large building. From antiquity up to the development of gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). Th ...
, they were made largely of wood, using rope or leather to help bind them, possibly with a few pieces of metal at key stress points. They could launch simple projectiles using natural materials to build up force by tension
Tension may refer to:
Science
* Psychological stress
* Tension (physics), a force related to the stretching of an object (the opposite of compression)
* Tension (geology), a stress which stretches rocks in two opposite directions
* Voltage or el ...
, torsion
Torsion may refer to:
Science
* Torsion (mechanics), the twisting of an object due to an applied torque
* Torsion of spacetime, the field used in Einstein–Cartan theory and
** Alternatives to general relativity
* Torsion angle, in chemistry
Bi ...
, or, in the case of trebuchets, human power or counterweights coupled with mechanical advantage
Mechanical advantage is a measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, mechanical device or machine system. The device trades off input forces against movement to obtain a desired amplification in the output force. The model for ...
. With the development of gunpowder and improved metallurgy, bombards and later heavy artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during siege ...
became the primary siege engines.
Collectively, siege engines or artillery together with the necessary soldier
A soldier is a person who is a member of an army. A soldier can be a conscripted or volunteer enlisted person, a non-commissioned officer, or an officer.
Etymology
The word ''soldier'' derives from the Middle English word , from Old French ...
s, sapper
A sapper, also called a pioneer or combat engineer, is a combatant or soldier who performs a variety of military engineering duties, such as breaching fortifications, demolitions, bridge-building, laying or clearing minefields, preparing ...
s, ammunition, and transport vehicles to conduct a siege are referred to as a siege train.
Antiquity
Ancient Assyria through the Roman Empire
The earliest siege engines appear to be simple movable roofed towers used for cover to advance to the defenders' walls in conjunction withscaling ladder
{{Unreferenced, date=May 2007
Escalade is the act of scaling defensive walls or ramparts with the aid of ladders. Escalade was a prominent feature of sieges in ancient and medieval warfare, and though it is no longer common in modern warfare ...
s, depicted during the Middle Kingdom of Egypt
The Middle Kingdom of Egypt (also known as The Period of Reunification) is the period in the history of ancient Egypt following a period of political division known as the First Intermediate Period. The Middle Kingdom lasted from approximately ...
. Advanced siege engines including battering rams were used by Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the ...
ns, followed by the catapult in ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of Classical Antiquity, classical antiquity ( AD 600), th ...
.
In Kush
Kush or Cush may refer to:
Bible
* Cush (Bible), two people and one or more places in the Hebrew Bible
Places
* Kush (mountain), a mountain near Kalat, Pakistan Balochistan
* Kush (satrapy), a satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire
* Hindu Kush, a ...
siege towers as well as battering rams were built from the 8th century BC and employed in Kushite siege warfare, such as the siege of Ashmunein
Hermopolis ( grc, Ἑρμούπολις ''Hermoúpolis'' "the City of Hermes", also ''Hermopolis Magna'', ''Hermoû pólis megálẽ'', egy, ḫmnw , Egyptological pronunciation: "Khemenu"; cop, Ϣⲙⲟⲩⲛ ''Shmun''; ar, الأشموني ...
in 715 BC.
The Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
ns used battering rams in the Siege of Plataea
The siege of Plataea took place in 429–427 BC, during the Peloponnesian War. At the beginning of the conflict, the Thebans attacked the city of Plataea, an Athenian ally on the border between Boeotia and Attica. The initial Theban attempt to capt ...
in 429 BC, but it seems that the Greeks limited their use of siege engines to assault ladders, though Peloponnesian forces used something resembling flamethrowers.
The first Mediterranean people to use advanced siege machinery were the Carthaginians
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' – the Latin equivalent of the ...
, who used siege tower
A Roman siege tower or breaching tower (or in the Middle Ages, a belfry''Castle: Stephen Biesty's Cross-Sections''. Dorling Kindersley Pub (T); 1st American edition (September 1994). Siege towers were invented in 300 BC. ) is a specialized siege ...
s and battering rams against the Greek colonies
Greek colonization was an organised colonial expansion by the Archaic Greeks into the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea in the period of the 8th–6th centuries BC.
This colonization differed from the migrations of the Greek Dark Ages in that i ...
of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
. These engines influenced the ruler of Syracuse, Dionysius I, who developed a catapult in 399 BC.
The first two rulers to make use of siege engines to a large extent were Philip II of Macedonia
Philip II of Macedon ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 382 – 21 October 336 BC) was the king (''basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the a ...
and Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
. Their large engines spurred an evolution that led to impressive machines, like the Demetrius Poliorcetes
Demetrius I (; grc, Δημήτριος; 337–283 BC), also called Poliorcetes (; el, Πολιορκητής, "The Besieger"), was a Macedonian nobleman, military leader, and king of Macedon (294–288 BC). He belonged to the Antigonid dynasty ...
' ''Helepolis
Helepolis ( el, ἑλέπολις, meaning: "Taker of Cities") is the Greek name for a movable siege tower.
The most famous was that invented by Polyidus of Thessaly, and improved by Demetrius I of Macedon and Epimachus of Athens, for the S ...
'' (or "Taker of Cities") of 304 BC: nine stories high and plated with iron, it stood tall and wide, weighing . The most used engines were simple battering rams, or ''tortoises'', propelled in several ingenious ways that allowed the attackers to reach the walls or ditches with a certain degree of safety. For sea sieges or battles, seesaw-like machines (''sambykē'' or ''sambuca'') were used. These were giant ladders, hinged and mounted on a base mechanism and used for transferring marines onto the sea walls of coastal towns. They were normally mounted on two or more ships tied together and some sambykē included shields at the top to protect the climbers from arrows. Other hinged engines were used to catch enemy equipment or even opposing soldiers with opposable appendices which are probably ancestors to the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
corvus
''Corvus'' is a widely distributed genus of medium-sized to large birds in the family Corvidae. It includes species commonly known as crows, ravens and rooks. The species commonly encountered in Europe are the carrion crow, the hooded crow ...
. Other weapons dropped heavy weights on opposing soldiers.
 The
The Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
preferred to assault enemy walls by building earthen ramps (''agger'') or simply scaling the walls, as in the early siege of the Samnite city of Silvium (306 BC). Soldiers working at the ramps were protected by shelters called ''vineae'', that were arranged to form a long corridor. Convex wicker shields were used to form a screen ('' plutei'' or plute in English) to protect the front of the corridor during construction of the ramp. Another Roman siege engine sometimes used resembled the Greek ditch-filling tortoise of Diades, this galley (unlike the ram-tortoise of Hegetor the Byzantium) called a ''musculus'' ("muscle") was simply used as cover for sappers to engineer an offensive ditch or earthworks. Battering rams were also widespread. The Roman Legion
The Roman legion ( la, legiō, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of 5,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) and of 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period o ...
s first used siege towers around 200 BC; in the first century BC, Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
accomplished a siege at Uxellodunum
Uxellodunum is an Iron Age hill fort, or ''oppidum'', located above the river Dordogne near the modern-day French village of Vayrac in the Lot department. This stronghold lay within the lands of the Cadurci tribe. According to Aulus Hirtiu ...
in Gaul using a ten-story siege tower. Romans were nearly always successful in besieging a city or fort, due to their persistence, the strength of their forces, their tactics, and their siege engines.
The first documented occurrence of ancient siege artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during siege ...
pieces in Europe was the ''gastraphetes
The gastraphetes ( grc, γαστραφέτης, , belly-releaser), also called belly bow or belly shooter, was a hand-held crossbow used by the Ancient Greeks. It was described in the 1st century AD by the Greek author Heron of Alexandria in his ...
'' ("belly-bow"), a kind of large crossbow. These were mounted on wooden frames. Greater machines forced the introduction of pulley system for loading the projectiles, which had extended to include stones also. Later torsion siege engine
A torsion siege engine is a type of siege engine that utilizes torsion to launch projectiles. They were initially developed by the ancient Macedonians, specifically Philip II of Macedon and Alexander the Great, and used through the Middle Ages u ...
s appeared, based on sinew springs. The onager
The onager (; ''Equus hemionus'' ), A new species called the kiang (''E. kiang''), a Tibetan relative, was previously considered to be a subspecies of the onager as ''E. hemionus kiang'', but recent molecular studies indicate it to be a distinct ...
was the main Roman invention in the field.

Ancient China
: The earliest documented occurrence of ancient siege-artillery pieces in China was the levered principled traction catapult and an high siege crossbow from the Mozi (Mo Jing), a Mohist text written at about the 4th – 3rd century BC by followers of Mozi who founded the Mohist school of thought during the late Spring and Autumn period and the earlyWarring States period
The Warring States period () was an era in ancient Chinese history characterized by warfare, as well as bureaucratic and military reforms and consolidation. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded with the Qin wars of conquest ...
. Much of what we now know of the siege technology of the time comes from Books 14 and 15 (Chapters 52 to 71) on Siege Warfare from the Mo Jing. Recorded and preserved on bamboo strips, much of the text is now extremely corrupted. However, despite the heavy fragmentation, Mohist diligence and attention to details which set Mo Jing apart from other works ensured that the highly descriptive details of the workings of mechanical devices like Cloud Ladders, Rotating Arcuballistas and Levered Catapults, records of siege techniques and usage of siege weaponry can still be found today.Liang, Jieming (2006). ''Chinese Siege Warfare: Mechanical Artillery & Siege Weapons of Antiquity'', pp. Appendix D
Elephant
Indian, Sri Lankan, Chinese and Southeast Asian kingdoms usedwar elephant
A war elephant was an elephant that was trained and guided by humans for combat. The war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, break their ranks and instill terror and fear. Elephantry is a term for specific military units using elepha ...
s as battering rams.
Middle Ages
Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
designs include a large number of catapults such as the mangonel
The mangonel, also called the traction trebuchet, was a type of trebuchet used in Ancient China starting from the Warring States period, and later across Eurasia by the 6th century AD. Unlike the later counterweight trebuchet, the mangonel o ...
, onager
The onager (; ''Equus hemionus'' ), A new species called the kiang (''E. kiang''), a Tibetan relative, was previously considered to be a subspecies of the onager as ''E. hemionus kiang'', but recent molecular studies indicate it to be a distinct ...
, the ballista
The ballista (Latin, from Greek βαλλίστρα ''ballistra'' and that from βάλλω ''ballō'', "throw"), plural ballistae, sometimes called bolt thrower, was an ancient missile weapon that launched either bolts or stones at a distant ...
, the traction trebuchet
A trebuchet (french: trébuchet) is a type of catapult that uses a long arm to throw a projectile. It was a common powerful siege engine until the advent of gunpowder. The design of a trebuchet allows it to launch projectiles of greater weight ...
(first designed in China in the 3rd century BC and brought over to Europe in the 4th century AD), and the counterweight trebuchet (first described by Mardi bin Ali al-Tarsusi in the 12th century, though of unknown origin). These machines used mechanical energy to fling large projectiles to batter down stone walls. Also used were the battering ram and the siege tower
A Roman siege tower or breaching tower (or in the Middle Ages, a belfry''Castle: Stephen Biesty's Cross-Sections''. Dorling Kindersley Pub (T); 1st American edition (September 1994). Siege towers were invented in 300 BC. ) is a specialized siege ...
, a wooden tower on wheels that allowed attackers to climb up and over castle walls, while protected somewhat from enemy arrows.
A typical military confrontation in medieval times was for one side to lay siege to an opponent's castle. When properly defended, they had the choice whether to assault the castle directly or to starve the people out by blocking food deliveries, or to employ war machines specifically designed to destroy or circumvent castle defenses. Defending soldiers also used trebuchets and catapults as a defensive advantage.
Other tactics included setting fires against castle walls in an effort to decompose the cement that held together the individual stones so they could be readily knocked over. Another indirect means was the practice of mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic ...
, whereby tunnels were dug under the walls to weaken the foundations and destroy them. A third tactic was the catapulting of diseased animals or human corpses over the walls in order to promote disease which would force the defenders to surrender, an early form of biological warfare
Biological warfare, also known as germ warfare, is the use of biological toxins or infectious agents such as bacteria, viruses, insects, and fungi with the intent to kill, harm or incapacitate humans, animals or plants as an act of war. ...
.
Modern era

 With the advent of
With the advent of gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). Th ...
, firearms such as the arquebus
An arquebus ( ) is a form of long gun that appeared in Europe and the Ottoman Empire during the 15th century. An infantryman armed with an arquebus is called an arquebusier.
Although the term ''arquebus'', derived from the Dutch word ''Haakbus ...
and cannon
A cannon is a large- caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder ...
—eventually the petard
A petard is a small bomb used for blowing up gates and walls when breaching fortifications. It is of French origin and dates back to the 16th century. A typical petard was a conical or rectangular metal device containing of gunpowder, with a s ...
, mortar and artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during siege ...
—were developed. These weapons proved so effective that fortification
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere' ...
s, such as city wall
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates ...
s, had to be low and thick, as exemplified by the designs of Vauban.
The development of specialized siege artillery, as distinct from field artillery, culminated during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
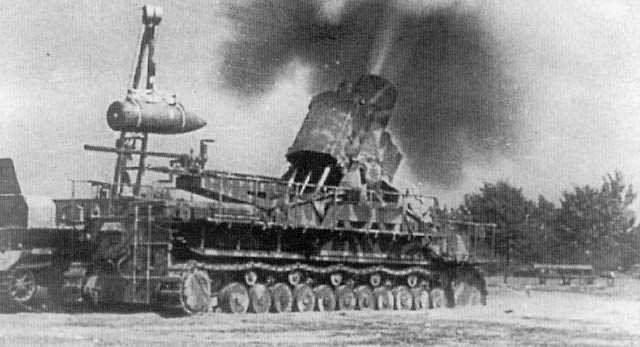
. During the First World War, huge siege guns such as Big Bertha were designed to see use against the modern fortresses of the day. The apex of siege artillery was reached with the German Schwerer Gustav
Schwerer Gustav (English: ''Heavy Gustav'') was a German railway gun. It was developed in the late 1930s by Krupp in Rügenwalde as siege artillery for the explicit purpose of destroying the main forts of the French Maginot Line, the strongest ...
gun, a huge caliber railway gun
A railway gun, also called a railroad gun, is a large artillery piece, often surplus naval artillery, mounted on, transported by, and fired from a specially designed railway wagon. Many countries have built railway guns, but the best-known are ...
, built during early World War II. Schwerer Gustav was initially intended to be used for breaching the French Maginot Line of fortifications, but was not finished in time and (as a sign of the times) the Maginot Line was circumvented by rapid mechanized forces instead of breached in a head-on assault. The long time it took to deploy and move the modern siege guns made them vulnerable to air attack and it also made them unsuited to the rapid troop movements of modern warfare.
See also
References
Sources
* *External links
Paolo Santini De Machinis or De machinis bellicis de Mariano Taccola, Paris, BnF, Département des manuscrits, Latin 7239
{{DEFAULTSORT:Siege Engine