Sick sinus syndrome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sinus node dysfunction (SND), also known as sick sinus syndrome (SSS), is a group of abnormal heart rhythms ( arrhythmias) usually caused by a malfunction of the
 The most common complication of sinus node dysfunction is the development of tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome with abnormal atrial rhythms such as atrial tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, and flutter. These rhythms increases the risk of clot formation in the atrium, embolization, and stroke.
Developing sinus arrest, sinus node exit block,
The most common complication of sinus node dysfunction is the development of tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome with abnormal atrial rhythms such as atrial tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, and flutter. These rhythms increases the risk of clot formation in the atrium, embolization, and stroke.
Developing sinus arrest, sinus node exit block,
sinus node
The sinoatrial node (also known as the sinuatrial node, SA node or sinus node) is an oval shaped region of special cardiac muscle in the upper back wall of the right atrium made up of cells known as pacemaker cells. The sinus node is approxima ...
, the heart's primary pacemaker. Tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome is a variant of sick sinus syndrome in which the arrhythmia alternates between fast and slow heart rates.
Signs and symptoms
Often sinus node dysfunction produces no symptoms, especially early in the disease course. Signs and symptoms usually appear in more advanced disease and more than 50% of patients will present with syncope or transient near-fainting spells as well as bradycardias that are accompanied by rapid heart rhythms, referred to as tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome Other presenting signs or symptoms can include confusion, fatigue, palpitations, chest pain,shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing di ...
, headache, and nausea. Patients can also present with symptoms of congestive heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, ...
, stroke or transient ischemic attack
A transient ischemic attack (TIA), commonly known as a mini-stroke, is a minor stroke whose noticeable symptoms usually end in less than an hour. TIA causes the same symptoms associated with strokes, such as weakness or numbness on one side of ...
s due to the abnormal rhythm.
Complications
 The most common complication of sinus node dysfunction is the development of tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome with abnormal atrial rhythms such as atrial tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, and flutter. These rhythms increases the risk of clot formation in the atrium, embolization, and stroke.
Developing sinus arrest, sinus node exit block,
The most common complication of sinus node dysfunction is the development of tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome with abnormal atrial rhythms such as atrial tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, and flutter. These rhythms increases the risk of clot formation in the atrium, embolization, and stroke.
Developing sinus arrest, sinus node exit block, sinus bradycardia
Sinus bradycardia is a sinus node dysfunction giving a heart rate that is lower than the normal 60–100 beats per minute (bpm) in humans. Bradycardia is generally defined to be a heart rate of under 60 bpm.
Signs and symptoms
The decreased hea ...
, atrioventricular block
Atrioventricular block (AV block) is a type of heart block that occurs when the electrical signal traveling from the atria, or the upper chambers of the heart, to ventricles, or the lower chambers of the heart, is impaired. Normally, the sinoatr ...
, and other types of abnormal rhythms are also common complications. Sinus node dysfunction has a close association with the presence of atrial fibrillation due to their shared etiology of remodeling.
Causes
Sinus node dysfunction can be caused by intrinsic and extrinsic factors that affect the normal functioning of the sinus node. Intrinsic causes can include degeneration, dysfunction, or remodeling of the sinus node while extrinsic causes can create or worsen underlying atrial arrhythmias. Intrinsic causes tend to be responsible for permanent sinus node dysfunction while extrinsic causes are more commonly temporary.Intrinsic causes
Age-related degenerative fibrosis of the sinus node is often identified as the most common intrinsic cause. Other intrinsic causes include inherited ion channel dysfunctions, remodeling diseases such as heart failure and atrial fibrillation, infiltrative diseases such assarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (also known as ''Besnier-Boeck-Schaumann disease'') is a disease involving abnormal collections of inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly a ...
, amyloidosis, hemochromatosis
Iron overload or hemochromatosis (also spelled ''haemochromatosis'' in British English) indicates increased total accumulation of iron in the body from any cause and resulting organ damage. The most important causes are hereditary haemochromatos ...
, and connective tissue disease
A connective tissue disease (collagenosis) is any disease that has the connective tissues of the body as a target of pathology. Connective tissue is any type of biological tissue with an extensive extracellular matrix that supports, binds togeth ...
s, inflammatory etiology such as rheumatic fever, Chagas disease, and Lyme disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a vector-borne disease caused by the ''Borrelia'' bacterium, which is spread by ticks in the genus ''Ixodes''. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migran ...
, as well as atherosclerotic and ischemic changes to the sinus node artery.
Inherited sinus node dysfunction has been associated with mutations of the gene responsible for the formation of the alpha subunit of the sodium channel ( SCN5A).
Extrinsic causes
Common cardiac pharmacology such as beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin, sympatholytic medication, and other antiarrhythmics can alter sinus node function to create an arrhythmia such as sick sinus syndrome. Electrolyte abnormalities such ashyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium (K+) in the blood. Normal potassium levels are between 3.5 and 5.0mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0mEq/L) with levels above 5.5mmol/L defined as hyperkalemia. Typically hyperkalemia does not cause symptoms. Occasi ...
, hypokalemia
Hypokalemia is a low level of potassium (K+) in the blood serum. Mild low potassium does not typically cause symptoms. Symptoms may include feeling tired, leg cramps, weakness, and constipation. Low potassium also increases the risk of an abno ...
, and hypocalcemia
Hypocalcemia is a medical condition characterized by low calcium levels in the blood serum. The normal range of blood calcium is typically between 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L) while levels less than 2.1 mm ...
can also alter normal sinus node functioning. Hypothyroidism, hypoxia, hypothermia
Hypothermia is defined as a body core temperature below in humans. Symptoms depend on the temperature. In mild hypothermia, there is shivering and mental confusion. In moderate hypothermia, shivering stops and confusion increases. In severe ...
, and various toxins have also been associated with sinus node dysfunctions.
Diagnosis

Electrocardiogram
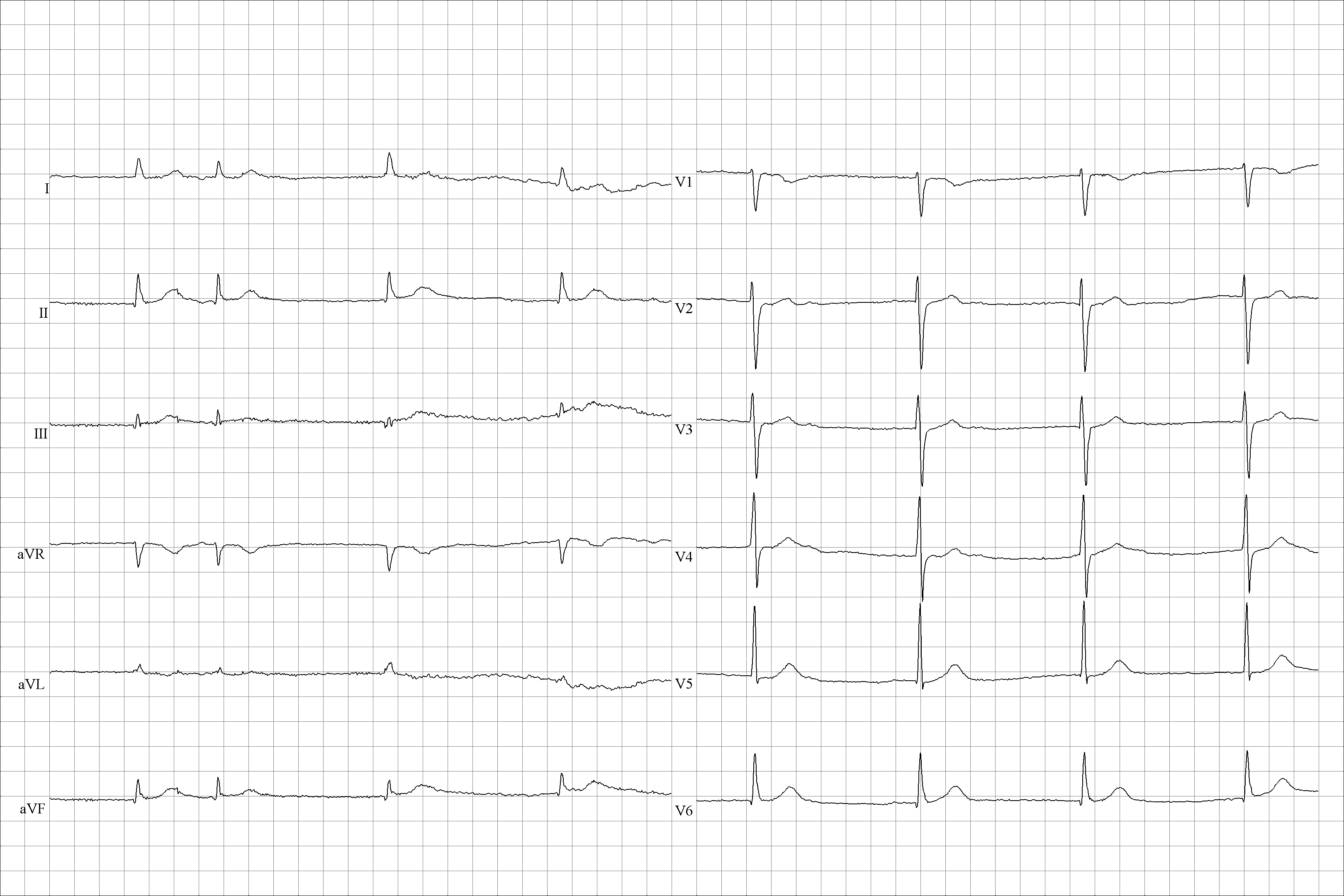
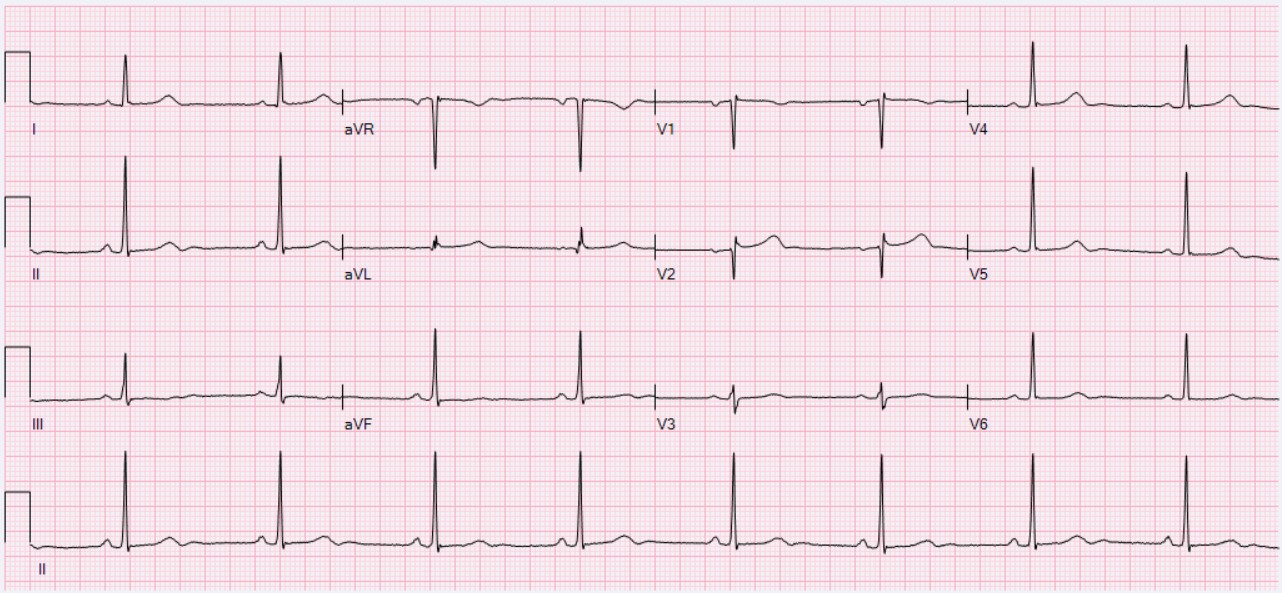
The primary 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) finding in sinus node dysfunction is inappropriatesinus bradycardia
Sinus bradycardia is a sinus node dysfunction giving a heart rate that is lower than the normal 60–100 beats per minute (bpm) in humans. Bradycardia is generally defined to be a heart rate of under 60 bpm.
Signs and symptoms
The decreased hea ...
. Sinus node dysfunction can also present with sudden sinus arrest with or without junctional escape, sinoatrial block, prolonged asystolic period followed by tachycardias, or tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome presenting as various atrial arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation, flutter, tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal ( ...
, or paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) is a type of supraventricular tachycardia, named for its intermittent episodes of abrupt onset and termination. Often people have no symptoms. Otherwise symptoms may include palpitations, increased h ...
.
Clinical diagnosis
Diagnosing sinus node dysfunction requires clinical symptoms as well as ECG abnormalities. If ECG findings cannot be identified, prolonged cardiac monitoring should be pursued either with aHolter monitor
In medicine, a Holter monitor (often simply Holter) is a type of ambulatory electrocardiography device, a portable device for cardiac monitoring (the monitoring of the electrical activity of the cardiovascular system) for at least 24 hours.
...
in an outpatient setting or telemetry while inpatient, due to the transient nature of abnormal ECG findings. If Holter or telemetry monitoring fails to identify ECG changes and suspicion of sinus node dysfunction remains high due to severe symptoms or episodes of syncope, implantable loop recorder
An implantable loop recorder (ILR), also known as an insertable cardiac monitor (ICM), is a small device that is implanted under the skin of the chest for cardiac monitoring, to record the heart's electrical activity for an extended period).
s should be considered for extended monitoring up to 24 months.
Exercise stress tests can be utilized to identify intrinsic causes of sinus node dysfunction. Tilt table test
A tilt table test (TTT), occasionally called upright tilt testing (UTT), is a medical procedure often used to diagnose dysautonomia or syncope. Patients with symptoms of dizziness or lightheadedness, with or without a loss of consciousness ...
s can be used to discriminate bradycardia caused by dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system.
Treatment
The primary reason for considering treatment is the presence of symptoms. Pacemaker implantation is the primary treatment modality of symptomatic sinus node dysfunction. The goal of this treatment modality is to relieve symptoms associated with sinus node dysfunction and improve quality of life. Dual chamber pacemakers are preferred due to the possibility of developingatrioventricular block
Atrioventricular block (AV block) is a type of heart block that occurs when the electrical signal traveling from the atria, or the upper chambers of the heart, to ventricles, or the lower chambers of the heart, is impaired. Normally, the sinoatr ...
as well as long term cost-effectiveness relative to single-chamber atrial pacemakers.
In tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome, medication-based management can treat atrial tachyarrhythmias. However, these medications may exacerbate underlying bradyarrhythmia. Therefore, a dual-chamber pacemaker capable of managing atrial tachyarrhythmias as well as bradyarrhythmias is implanted before drug therapy is begun.
Epidemiology
Overall incidence of sinus node dysfunction increases with age with 1 in 1000 in adults over 45 years old and 1 in 600 cardiac patients over 65 years old. Sinus node dysfunction is the primary indication for approximately 30%-50% of all pacemaker implantation in the United States. Sinus node dysfunction is a relatively uncommon syndrome in the young and middle-aged population.References
External links
{{Heart diseases Cardiac arrhythmia Syndromes affecting the heart