Shuaib on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Shuaib, Shoaib, Shuayb or Shuʿayb ( ar, شعيب, ; meaning: "who shows the right path") is an ancient
Shuaib, Shoaib, Shuayb or Shuʿayb ( ar, شعيب, ; meaning: "who shows the right path") is an ancient
 The Qur'an states that Shuaib was appointed by God to be a prophet to the people of Midian. The people of this land were said to be especially notorious for cheating others through dishonesty and for idolatry. Shuʿayb's prophecy mainly involved calling the Midianites to the correct path of God, and forbidding them to worship false gods.
It is also said he told his people to stop being dishonest in their daily activities. Although he preached and prophesied for a sustained period of time, the majority of the people refused to listen to him. Shuayb, however, remained steadfast. He consistently preached powerfully against the wicked, telling them of the punishment that had befallen the sinful before them. Shuʿayb warned the people that their ignorance would lead to the destruction of Midian, giving historical examples of earlier prophets, including
The Qur'an states that Shuaib was appointed by God to be a prophet to the people of Midian. The people of this land were said to be especially notorious for cheating others through dishonesty and for idolatry. Shuʿayb's prophecy mainly involved calling the Midianites to the correct path of God, and forbidding them to worship false gods.
It is also said he told his people to stop being dishonest in their daily activities. Although he preached and prophesied for a sustained period of time, the majority of the people refused to listen to him. Shuayb, however, remained steadfast. He consistently preached powerfully against the wicked, telling them of the punishment that had befallen the sinful before them. Shuʿayb warned the people that their ignorance would lead to the destruction of Midian, giving historical examples of earlier prophets, including
Documents, Asare-Sabti
web.archive.org Retrieved 17 Nov 2018
 Shuaib, Shoaib, Shuayb or Shuʿayb ( ar, شعيب, ; meaning: "who shows the right path") is an ancient
Shuaib, Shoaib, Shuayb or Shuʿayb ( ar, شعيب, ; meaning: "who shows the right path") is an ancient Midian
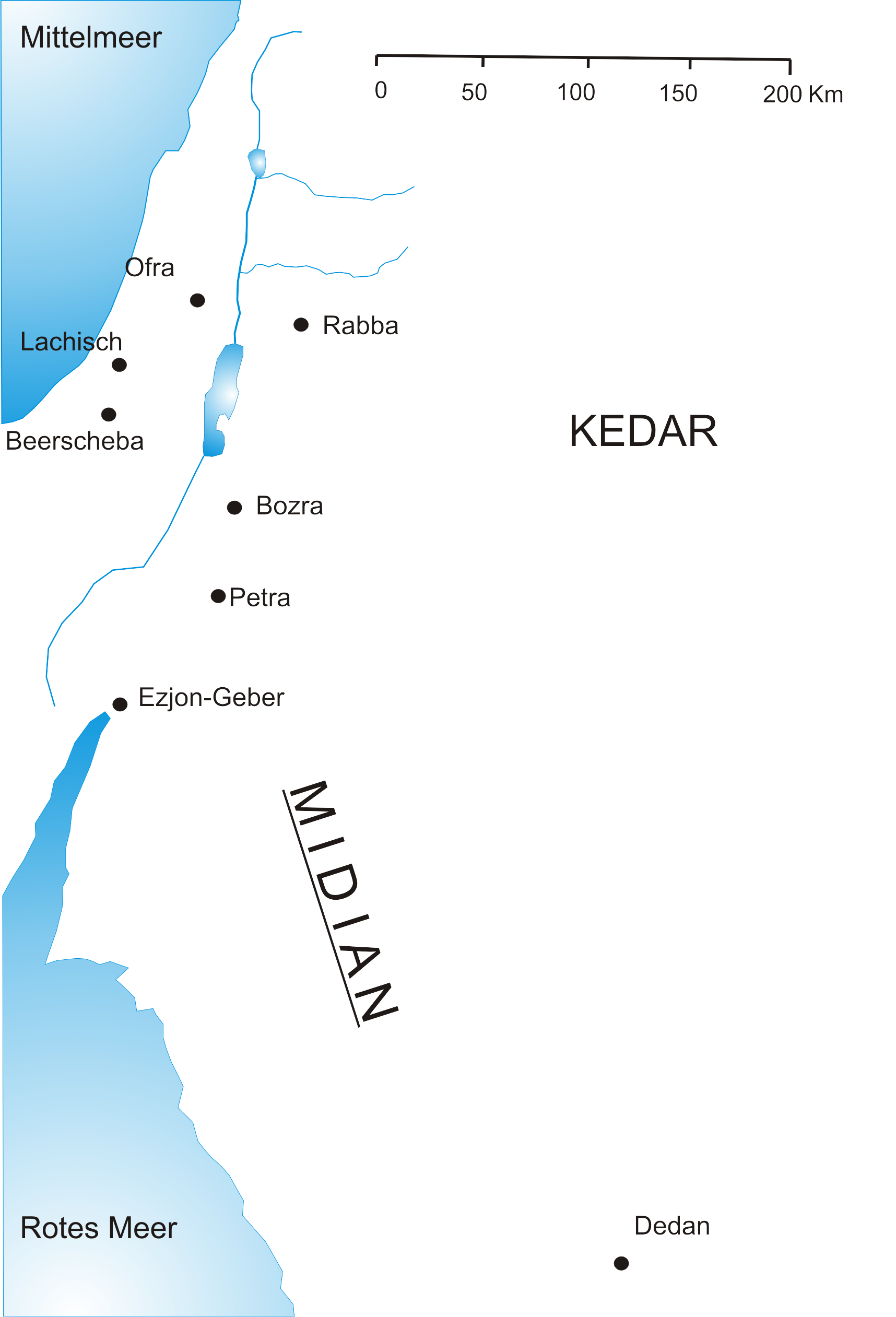
Midian (; he, מִדְיָן ''Mīḏyān'' ; ar, مَدْيَن, Madyan; grc-gre, Μαδιάμ, ''Madiam'') is a geographical place mentioned in the Hebrew Bible and Quran. William G. Dever states that biblical Midian was in the "northwest Ar ...
ite '' Nabi'' (Prophet
In religion, a prophet or prophetess is an individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divine being and is said to speak on behalf of that being, serving as an intermediary with humanity by delivering messages or teachings from the ...
) in Islam, and the most revered prophet in the Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
faith. Shuayb is traditionally identified with the Biblical Jethro, Moses' father-in-law. Shuaib is mentioned in the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , ...
a total of 11 times. He is believed to have lived after Ibrahim
Ibrahim ( ar, إبراهيم, links=no ') is the Arabic name for Abraham, a Biblical patriarch and prophet in Islam.
For the Islamic view of Ibrahim, see Abraham in Islam.
Ibrahim may also refer to:
* Ibrahim (name), a name (and list of people w ...
(Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Je ...
), and Muslims believe that he was sent as a prophet to a community: the Midianites, who are also known as the ''Aṣḥāb al-Aykah'' ("Companions of the Wood"), since they used to worship a large tree. To the people, Shuaib proclaimed the straight path and warned the people to end their fraudulent ways. When the community did not repent, Allāh
Allah (; ar, الله, translit=Allāh, ) is the common Arabic word for God. In the English language, the word generally refers to God in Islam. The word is thought to be derived by contraction from '' al- ilāh'', which means "the god", an ...
( God) destroyed the community.
Shuaib is understood by Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
s to have been one of the few Arabian prophets mentioned by name in the Qur'an, the others being Saleh, Hud, and Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mon ...
. It is said that he was known by Muslims as "the eloquent preacher amongst the prophets", because he was, according to tradition, granted talent and eloquence in his language.
The Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
revere Shuaib as an important figure in their faith, and hold an annual pilgrimage to Nabi Shu'ayb, the purported location of his tomb, in the Lower Galilee The Lower Galilee (; ar, الجليل الأسفل, translit=Al Jalil Al Asfal) is a region within the Northern District (Israel), Northern District of Israel. The Lower Galilee is bordered by the Jezreel Valley to the south; the Upper Galilee to t ...
.
Historical context
The area to which Shuʿayb was sent to is named Madyan'' in the Qur'an, known in English asMidian
Midian (; he, מִדְיָן ''Mīḏyān'' ; ar, مَدْيَن, Madyan; grc-gre, Μαδιάμ, ''Madiam'') is a geographical place mentioned in the Hebrew Bible and Quran. William G. Dever states that biblical Midian was in the "northwest Ar ...
, which is frequently referred to in the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus ...
. The Midianites were said to be of Arab descent, though being neighbors of the Biblical Canaanites
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus Te ...
, they intermixed with them. It is said they were a wandering tribe, and that their principal territory at the time of Musa
Musa may refer to:
Places
*Mūša, a river in Lithuania and Latvia
* Musa, Azerbaijan, a village in Yardymli Rayon
* Musa, Iran, a village in Ilam Province
* Musa, Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari, Iran
* Musa, Kerman, Iran
* Musa, Bukan, West Azerbaija ...
(Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu ( Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pr ...
) was the Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai (now usually ) (, , cop, Ⲥⲓⲛⲁ), is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a ...
.
Disputed identification with Jethro
Jethro is mentioned in theBible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus ...
(Exodus 3:1) as the father in law of Moses. Although Shuaib is frequently identified with the Midianite priest Jethro, most modern scholars reject this identification. Classical commentators, such as Ibn Kathir
Abū al-Fiḍā’ ‘Imād ad-Dīn Ismā‘īl ibn ‘Umar ibn Kathīr al-Qurashī al-Damishqī (Arabic: إسماعيل بن عمر بن كثير القرشي الدمشقي أبو الفداء عماد; – 1373), known as Ibn Kathīr (, was ...
, say Shuʿayb was a great-grandson of Abraham: Shuʿayb is believed to have been the son of Mikil, son of Midian, son of Abraham. That would render impossible the identification with Jethro, who lived at the time of Moses, purportedly hundreds of years after Abraham.
Prophecy in Midian
 The Qur'an states that Shuaib was appointed by God to be a prophet to the people of Midian. The people of this land were said to be especially notorious for cheating others through dishonesty and for idolatry. Shuʿayb's prophecy mainly involved calling the Midianites to the correct path of God, and forbidding them to worship false gods.
It is also said he told his people to stop being dishonest in their daily activities. Although he preached and prophesied for a sustained period of time, the majority of the people refused to listen to him. Shuayb, however, remained steadfast. He consistently preached powerfully against the wicked, telling them of the punishment that had befallen the sinful before them. Shuʿayb warned the people that their ignorance would lead to the destruction of Midian, giving historical examples of earlier prophets, including
The Qur'an states that Shuaib was appointed by God to be a prophet to the people of Midian. The people of this land were said to be especially notorious for cheating others through dishonesty and for idolatry. Shuʿayb's prophecy mainly involved calling the Midianites to the correct path of God, and forbidding them to worship false gods.
It is also said he told his people to stop being dishonest in their daily activities. Although he preached and prophesied for a sustained period of time, the majority of the people refused to listen to him. Shuayb, however, remained steadfast. He consistently preached powerfully against the wicked, telling them of the punishment that had befallen the sinful before them. Shuʿayb warned the people that their ignorance would lead to the destruction of Midian, giving historical examples of earlier prophets, including Noah
Noah ''Nukh''; am, ኖህ, ''Noḥ''; ar, نُوح '; grc, Νῶε ''Nôe'' () is the tenth and last of the pre-Flood patriarchs in the traditions of Abrahamic religions. His story appears in the Hebrew Bible (Book of Genesis, chapters 5� ...
, Hud, Saleh and Lot, all of whose people had been destroyed by God.
The people taunted Shuʿayb and told him that, were it not for the prestigious family he came from, he would surely have been stoned to death. Shuayb replied, "Is my family of more consideration with you than God?" When the Midianites refused to believe, they were destroyed by a mighty earthquake. The Qur'an, however, mentions that Shuʿayb, and his believing companions, were rescued from the thunderous punishment.
Parallels with other prophets
Shuayb's mission is often mentioned in the Qur'an with the mission of Noah, Hud, Saleh and Lot. Scholars have pointed out that these fiveprophet
In religion, a prophet or prophetess is an individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divine being and is said to speak on behalf of that being, serving as an intermediary with humanity by delivering messages or teachings from the ...
s exemplify the early prophetic missions:Wheeler, ''A-Z of Prophets in Islam and Judaism'', ''Shuayb'' The prophet would be sent to his community; the community would pay no attention to his warning and would instead threaten him with punishment; after years of preaching, God would ask him to leave his community, while his people were subsequently destroyed in a punishment. Scholars chronologically interpret the listing of the five prophets, so Shuʿayb was a descendant of Noah (preached about the Great Flood
A flood myth or a deluge myth is a myth in which a great flood, usually sent by a deity or deities, destroys civilization, often in an act of divine retribution. Parallels are often drawn between the flood waters of these myths and the primaeval ...
) and the Prophet Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the ...
.
Claimed burial places of Shuayb
One claimed tomb of Shuayb is found inJordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
, () west of the town of Mahis
Mahis ( ar, ماحص, Māḥis, alternatively spelled Mahas) is a town in the Balqa Governorate northwest from the governorate's capital Salt, and west of Amman. Its population was 17,754 in 2015. Most of the population of Mahis descends from the ...
, in an area called ''Wādī Shuʿayb'' ( ar, وَادِي شُـعَـيْـب).
The Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
believe the tomb of Nabi Shu'ayb is located near Hittin, in the Lower Galilee The Lower Galilee (; ar, الجليل الأسفل, translit=Al Jalil Al Asfal) is a region within the Northern District (Israel), Northern District of Israel. The Lower Galilee is bordered by the Jezreel Valley to the south; the Upper Galilee to t ...
. Each year, on the 25th of April, the Druze gather at the site to discuss community affairs.
There is also a tomb in the southwest of Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
(in the village Guriyeh, Shushtar) which has been recorded as the tomb of Shuayb.web.archive.org Retrieved 17 Nov 2018
See also
*Biblical narratives and the Qur'an
The Quran, the central religious text of Islam, contains references to more than fifty people and events also found in the Bible. While the stories told in each book are generally comparable, there are also some notable differences. Knowi ...
* Jabal An-Nabi Shu'ayb
* Legends and the Qur'an
The Quran, the central religious text of Islam, contains references to more than fifty people and events also found in the Bible. While the stories told in each book are generally comparable, there are also some notable differences. Knowing t ...
* '' Qiṣaṣ al-Anbiyāʾ'' ("Stories of the Prophets")
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Shuayb (Prophet) Prophets of the Quran Prophets in the Druze faith Midian Jethro (biblical figure)