Shoshenq II on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Heqakheperre Shoshenq II or Shoshenq IIa was a
 More significantly, Shoshenq II's intact burial did not contain a single object or heirloom naming Osorkon I—an unlikely situation if Osorkon did indeed bury his own son. Kitchen notes that this king's burial goods included a pectoral that was originally inscribed for the Great Chief of the Ma Shoshenq I—before the latter became king—and "a pair of bracellets of Shoshenq I as king but no later objects." This situation appears improbable if Shoshenq II was indeed Shoshenq C, Osorkon I's son who died and was buried by his own father. Other Dynasty 21 and 22 kings such as
More significantly, Shoshenq II's intact burial did not contain a single object or heirloom naming Osorkon I—an unlikely situation if Osorkon did indeed bury his own son. Kitchen notes that this king's burial goods included a pectoral that was originally inscribed for the Great Chief of the Ma Shoshenq I—before the latter became king—and "a pair of bracellets of Shoshenq I as king but no later objects." This situation appears improbable if Shoshenq II was indeed Shoshenq C, Osorkon I's son who died and was buried by his own father. Other Dynasty 21 and 22 kings such as
 Dr. Derry's medical examination of Shoshenq II's mummy reveals that the king died as a result of a massive septic infection from a head wound.
The final resting place of Shoshenq II was certainly a reburial because he was found interred in the tomb of another king,
Dr. Derry's medical examination of Shoshenq II's mummy reveals that the king died as a result of a massive septic infection from a head wound.
The final resting place of Shoshenq II was certainly a reburial because he was found interred in the tomb of another king,
* Guy Brunton, Some Notes on the Burial of Shashanq Heqa-Kheper-Re, Annales du Service des Antiquités de l'Égypte 39 (1939), 541-547 * N. Dautzenberg, 'Bemerkungen zu Schoschenq II., Takeloth II. und Pedubastis II', Göttinger Miszellen 144 (1995), 21-29 * D. E. Derry, Note on the Remains of Shashanq, Annales du Service des Antiquités de l'Égypte 39 (1939), 549-551 {{DEFAULTSORT:Shoshenq Ii 885 BC deaths 9th-century BC Pharaohs Pharaohs of the Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt Ancient Egyptian mummies Year of birth unknown
pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: '' pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until th ...
of the Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt
The Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt is also known as the Bubastite Dynasty, since the pharaohs originally ruled from the city of Bubastis. It was founded by Shoshenq I.
The Twenty-first, Twenty-second, Twenty-third, Twenty-fourth, and Twenty-f ...
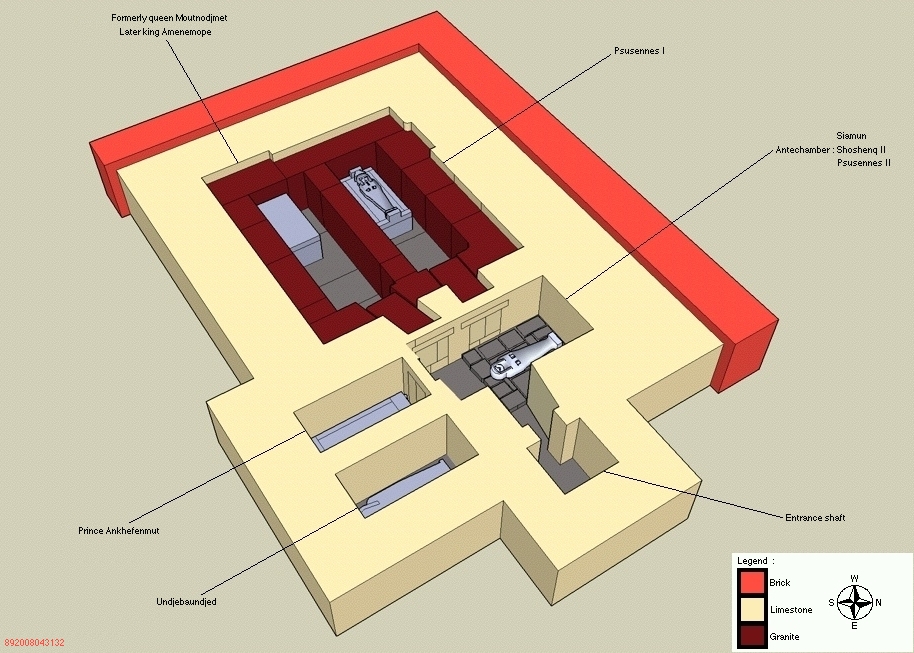
. He was the only ruler of this dynasty whose tomb was not plundered by tomb robbers. His final resting place was discovered within an antechamber of Psusennes I
Psusennes I ( egy, pꜣ-sbꜣ-ḫꜥ-n-njwt; Greek Ψουσέννης) was the third pharaoh of the 21st Dynasty who ruled from Tanis between 1047 and 1001 BC. ''Psusennes'' is the Greek version of his original name Pasibkhanu or Pasebakhaenniu ...
's tomb at Tanis
Tanis ( grc, Τάνις or Τανέως ) or San al-Hagar ( ar, صان الحجر, Ṣān al-Ḥaǧar; egy, ḏꜥn.t ; ; cop, ϫⲁⲛⲓ or or ) is the Greek name for ancient Egyptian ''ḏꜥn.t'', an important archaeological site in the ...
by Pierre Montet in 1939. Montet removed the coffin lid of Shoshenq II on March 20, 1939, in the presence of king Farouk of Egypt
Farouk I (; ar, فاروق الأول ''Fārūq al-Awwal''; 11 February 1920 – 18 March 1965) was the tenth ruler of Egypt from the Muhammad Ali dynasty and the penultimate King of Egypt and the Sudan, succeeding his father, Fuad I, in 1 ...
himself. It proved to contain many jewel-encrusted bracelets and pectorals, along with a beautiful hawkheaded silver coffin
A coffin is a funerary box used for viewing or keeping a corpse, either for burial or cremation.
Sometimes referred to as a casket, any box in which the dead are buried is a coffin, and while a casket was originally regarded as a box for j ...
and a gold funerary mask. The facemask had been placed upon the head of the king. Montet later discovered the intact tombs of two Twenty-first Dynasty kings (Psusennes I
Psusennes I ( egy, pꜣ-sbꜣ-ḫꜥ-n-njwt; Greek Ψουσέννης) was the third pharaoh of the 21st Dynasty who ruled from Tanis between 1047 and 1001 BC. ''Psusennes'' is the Greek version of his original name Pasibkhanu or Pasebakhaenniu ...
and Amenemope
Amenemope, also Amenemopet, Amenemipet or Amunemopet ''(ỉmn-m-ỉp3.t,'' Greek: ''αμενωφις;'' “Amun in Luxor”) is an Ancient Egyptian name. Its notable bearers were:
* Amenemope (pharaoh) (died 992 BC), pharaoh, 21st dynasty
* Amene ...
) a year later in February and April 1940 respectively. Shoshenq II's prenomen, Heqakheperre Setepenre, means "The manifestation of Ra rules, the chosen one of Ra."
Shoshenq II's enigmatic identity
There is a small possibility that Shoshenq II was the son ofShoshenq I
Hedjkheperre Setepenre Shoshenq I ( Egyptian ''ššnq''; reigned c. 943–922 BC)—also known as Shashank or Sheshonk or Sheshonq Ifor discussion of the spelling, see Shoshenq—was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the founder of the Twenty-sec ...
. Two bracelets from Shoshenq II's tomb mention king Shoshenq I while a pectoral was inscribed with the title 'Great Chief of the Ma Shoshenq,' a title which Shoshenq I employed under Psusennes II before he became king. These items may be interpreted as either evidence of a possible filial link between the two men or just mere heirlooms.
A high degree of academic uncertainty regarding the parentage of this king exists: some scholars today contend that Shoshenq II was actually a younger son of Shoshenq I
Hedjkheperre Setepenre Shoshenq I ( Egyptian ''ššnq''; reigned c. 943–922 BC)—also known as Shashank or Sheshonk or Sheshonq Ifor discussion of the spelling, see Shoshenq—was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the founder of the Twenty-sec ...
—who outlived Osorkon I and Takelot I—due to the discovery of the aforementioned items naming the founder of the 22nd Dynasty within his intact royal Tanite tomb. As the German Egyptologist Karl Jansen-Winkeln observes in the recent (2005) book on Egyptian chronology: "The commonly assumed identification of this king with the (earlier) HP and son of Osorkon I y KA Kitchen
Y, or y, is the twenty-fifth and penultimate letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. According to some authorities, it is the sixth (or seventh ...
does not appear to be very probable."Karl Jansen-Winkeln, The Chronology of the Third Intermediate Period: Dyns 22-24 in 'Handbook of Egyptian Chronology,' ed. Rolf Krauss, Erik Hornung, David Warburton, Brill: 2005, p.237 A forensic examination of Shoshenq II's body by Dr. Douglas Derry, the head of Cairo Museum's anatomy department, reveals that he was a man in his fifties when he died. Hence, Shoshenq II could have easily survived Osorkon I
Sekhemkheperre Osorkon I was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the 22nd Dynasty. Osorkon's territory included much of the Levant.
The Osorkon Bust found at Byblos is one of the five Byblian royal inscriptions.
Biography
The son of Shoshenq I and ...
's 35-year reign and ruled Egypt for a few years before Takelot I
Hedjkheperre Setepenre Takelot I was an ancient Libyan ruler who was pharaoh during the Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt.
Reign
Takelot I was the son of Osorkon I and Queen Tashedkhons, who ruled Egypt for thirteen years according to Manetho. Tak ...
came to power. Moreover, Sextus Julius Africanus
Sextus Julius Africanus (c. 160 – c. 240; Greek: Σέξτος Ἰούλιος ὁ Ἀφρικανός or ὁ Λίβυς) was a Christian traveler and historian of the late second and early third centuries. He is important chiefly because o ...
's generally more accurate copy of Manetho
Manetho (; grc-koi, Μανέθων ''Manéthōn'', ''gen''.: Μανέθωνος) is believed to have been an Egyptian priest from Sebennytos ( cop, Ϫⲉⲙⲛⲟⲩϯ, translit=Čemnouti) who lived in the Ptolemaic Kingdom in the early third ...
's Epitome explicitly states that “3 Kings” intervened between Osorkon I and Takelot I. While Manetho's suggested position for these three kings cannot be presently verified due to the paucity of evidence for this period and the brevity of their reigns, another of these poorly known monarchs would be Tutkheperre Shoshenq who was an early Dynasty 22 ruler since he is now monumentally attested in both Lower and Upper Egypt at Bubastis and Abydos respectively. Evidence that Shoshenq II was a predecessor of Osorkon II is indicated by the fact that his hawk-headed coffin is stylistically similar to "a hawk-headed lid" which enclosed the granite coffin of king Harsiese A, from Medinet Habu
Medinet Habu ( ar, مدينة هابو; Egyptian: ''Tjamet'' or ''Djamet''; cop, ''Djeme'' or ''Djemi'') is an archaeological locality situated near the foot of the Theban Hills on the West Bank of the River Nile opposite the modern city of Lu ...
. Harsiese A was an early contemporary of Osorkon II and likely Takelot I too since the latter did not firmly control Upper Egypt in his reign. This implies that Shoshenq II and Harsiese A were near contemporaries since Harsiese A was the son of the High Priest of Amun
Amun (; also ''Amon'', ''Ammon'', ''Amen''; egy, jmn, reconstructed as ( Old Egyptian and early Middle Egyptian) → (later Middle Egyptian) → ( Late Egyptian), cop, Ⲁⲙⲟⲩⲛ, Amoun) romanized: ʾmn) was a major ancient Egypt ...
Shoshenq C at Thebes and, thus, the grandson of Osorkon I.
Harsiese's funerary evidence places Shoshenq II roughly one or two generations after Osorkon I and may date him to the brief interval between Takelot I and Osorkon I at Tanis. In this case, the objects naming Shoshenq I in this king's tomb would simply be heirlooms, rather than proof of an actual filial relation between Shoshenq I and II. This latter interpretation is endorsed by Jürgen von Beckerath
Jürgen von Beckerath (19 February 1920, Hanover – 26 June 2016, Schlehdorf) was a German Egyptologist. He was a prolific writer who published countless articles in journals such as '' Orientalia'', ''Göttinger Miszellen'' (GM), '' Journal o ...
, in his 1997 book, ''Chronologie des Pharaonischen Ägypten'' who believes Shoshenq II was actually an elder brother of Takelot I. The view that Shoshenq II was an elder brother of Takelot I is also endorsed by Norbert Dautzenberg in a GM 144 paper. Von Beckerath, however, places Shoshenq II between the reigns of Takelot I and Osorkon II at Tanis.J. von Beckerath, pp.98 & 191
Kenneth Kitchen
Kenneth Anderson Kitchen (born 1932) is a British biblical scholar, Ancient Near Eastern historian, and Personal and Brunner Professor Emeritus of Egyptology and honorary research fellow at the School of Archaeology, Classics and Egyptology, Univ ...
, in his latest 1996 edition of '’The Third Intermediate Period in Egypt (c.1100–650 BC)’', maintains that Shoshenq II was the High Priest of Amun Shoshenq C, son of Osorkon I
Sekhemkheperre Osorkon I was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the 22nd Dynasty. Osorkon's territory included much of the Levant.
The Osorkon Bust found at Byblos is one of the five Byblian royal inscriptions.
Biography
The son of Shoshenq I and ...
and Queen Maatkare, who was appointed as the junior coregent to the throne but predeceased his father. Kitchen suggests such a coregency is reflected on the bandages of the Ramesseum
The Ramesseum is the memorial temple (or mortuary temple) of Pharaoh Ramesses II ("Ramesses the Great", also spelled "Ramses" and "Rameses"). It is located in the Theban Necropolis in Upper Egypt, on the west of the River Nile, across from the ...
mummy
A mummy is a dead human or an animal whose soft tissues and organs have been preserved by either intentional or accidental exposure to chemicals, extreme cold, very low humidity, or lack of air, so that the recovered body does not decay fu ...
of Nakhtefmut, which contain the dates "Year 3 lank and "Year 33 Second Heb Sed" respectively. The “Year 33” date mentioned here almost certainly refers to Osorkon I since Nakhtefmut wore a ring which bore this king's prenomen. Kitchen infers from this evidence that Year 33 of Osorkon I is equivalent to Year 3 of Shoshenq II, and that the latter was Shoshenq C himself.
Unfortunately, however, the case for a coregency between Osorkon I and Shoshenq II is uncertain because there is no clear evidence that the Year 3 and Year 33 bandages on Naktefmut's body were made at the same time. These two dates were not written on a single piece of mummy linen—which would denote a true coregency. Rather, the dates were written on two separate and unconnected mummy bandages which were likely woven and used over a period of several years, as the burial practices of the Amun priests show. A prime example is the Mummy of Khonsmaakheru in Hamburg which contains separate bandages dating to Years 11, 12, and 23 of Osorkon I
Sekhemkheperre Osorkon I was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the 22nd Dynasty. Osorkon's territory included much of the Levant.
The Osorkon Bust found at Byblos is one of the five Byblian royal inscriptions.
Biography
The son of Shoshenq I and ...
—or a minimum period of 12 Years between their creation and final use. (Altenmüller: 2000) A second example is the mummy of Djedptahiufankh, the Third or Fourth Prophet of Amun, which bears various bandages from Years 5, 10, and 11 of Shoshenq I
Hedjkheperre Setepenre Shoshenq I ( Egyptian ''ššnq''; reigned c. 943–922 BC)—also known as Shashank or Sheshonk or Sheshonq Ifor discussion of the spelling, see Shoshenq—was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the founder of the Twenty-sec ...
, or a spread of six years in their final use for embalming purposes. As these two near contemporary examples show, the temple priests simply reused whatever old or recycled linens which they could gain access to for their mummification rituals. The Year 3 mummy linen would, hence, belong to the reign of Osorkon's successor. Secondly, none of the High Priest Shoshenq C's own children—the priest Osorkon whose funerary papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, '' Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'') can also refer to ...
, P. Denon C, is located in the Russian National Library in St. Petersburg or a second priest named Harsiese (likely king Harsiese A) who dedicated a Bes BES or Bes may refer to:
* Bes, Egyptian deity
* Bes (coin), Roman coin denomination
* Bes (Marvel Comics), fictional character loosely based on the Egyptian deity
Abbreviations
* Bachelor of Environmental Studies, a degree
* Banco Espírito ...
statue in memory of his father, now in Durham Museum
The Durham Museum (formerly known as the Durham Western Heritage Museum) is located at 801 South 10th Street in downtown Omaha, Nebraska. The museum is dedicated to preserving and displaying the history of the United States' western region. The ...
—give royal titles to their father on their own funerary objects. The priest Osorkon only calls himself the "son of the High Priest Shoshenq", rather than the title "King's Son" in his funerary papyri, which would presumably have been created long after his father's death.
On Harsiese, Jacquet-Gordon notes that "there is no good evidence to suggest that the 1st prophet Shoshenq C ever claimed or was accorded royal rank." She observes that Harsiese designated his father as a High Priest of Amun on a Bes BES or Bes may refer to:
* Bes, Egyptian deity
* Bes (coin), Roman coin denomination
* Bes (Marvel Comics), fictional character loosely based on the Egyptian deity
Abbreviations
* Bachelor of Environmental Studies, a degree
* Banco Espírito ...
statue without any accompanying royal name or prenomen and stresses that if Shoshenq C "had venthe slightest pretensions to royal rank, his son would not have omitted to mention this fact. We must therefore conclude that he had no such pretensions." This implies that the High Priest Shoshenq C was not king Shoshenq II. While Shoshenq C's name is indeed written in a cartouche on the Bes statue, no actual royal name or prenomen is ever given. An example of a king's son who enclosed his name in a cartouche on a monument but never inherited the throne was Wadjmose, a son of the New Kingdom king Thutmose I
Thutmose I (sometimes read as Thutmosis or Tuthmosis I, Thothmes in older history works in Latinized Greek; Ancient Egyptian: '' ḏḥwtj- ms'', ''Tʼaḥawtī-mīsaw'', , meaning "Thoth is born") was the third pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty of E ...
.
Independent reign
 More significantly, Shoshenq II's intact burial did not contain a single object or heirloom naming Osorkon I—an unlikely situation if Osorkon did indeed bury his own son. Kitchen notes that this king's burial goods included a pectoral that was originally inscribed for the Great Chief of the Ma Shoshenq I—before the latter became king—and "a pair of bracellets of Shoshenq I as king but no later objects." This situation appears improbable if Shoshenq II was indeed Shoshenq C, Osorkon I's son who died and was buried by his own father. Other Dynasty 21 and 22 kings such as
More significantly, Shoshenq II's intact burial did not contain a single object or heirloom naming Osorkon I—an unlikely situation if Osorkon did indeed bury his own son. Kitchen notes that this king's burial goods included a pectoral that was originally inscribed for the Great Chief of the Ma Shoshenq I—before the latter became king—and "a pair of bracellets of Shoshenq I as king but no later objects." This situation appears improbable if Shoshenq II was indeed Shoshenq C, Osorkon I's son who died and was buried by his own father. Other Dynasty 21 and 22 kings such as Amenemope
Amenemope, also Amenemopet, Amenemipet or Amunemopet ''(ỉmn-m-ỉp3.t,'' Greek: ''αμενωφις;'' “Amun in Luxor”) is an Ancient Egyptian name. Its notable bearers were:
* Amenemope (pharaoh) (died 992 BC), pharaoh, 21st dynasty
* Amene ...
and Takelot I
Hedjkheperre Setepenre Takelot I was an ancient Libyan ruler who was pharaoh during the Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt.
Reign
Takelot I was the son of Osorkon I and Queen Tashedkhons, who ruled Egypt for thirteen years according to Manetho. Tak ...
, for instance, employed grave goods
Grave goods, in archaeology and anthropology, are the items buried along with the body.
They are usually personal possessions, supplies to smooth the deceased's journey into the afterlife or offerings to the gods. Grave goods may be classed as a ...
which mentioned their parent's names in their own tombs. This suggests that Heqakheperre Shoshenq II was not a son of Osorkon I but someone else's son, perhaps Shoshenq I. Karl Jansen-Winkeln writes in the most recent book on Egyptian chronology that:
: As the individuals interred in the aniteroyal tombs often bore objects belonging to their parents, this king (Shoshenq II) is probably a son of Shoshenq I.
Since this pharaoh's funerary objects such as his silver coffin, jewel pectorals, and cartonnage all give him the unique royal name Heqakheperre, he was most likely a genuine king of the 22nd Dynasty in his own right, and not just a minor coregent. Jürgen von Beckerath
Jürgen von Beckerath (19 February 1920, Hanover – 26 June 2016, Schlehdorf) was a German Egyptologist. He was a prolific writer who published countless articles in journals such as '' Orientalia'', ''Göttinger Miszellen'' (GM), '' Journal o ...
adopts this interpretation of the evidence and assigns Shoshenq II an independent reign of 2 years at Tanis. In their 2005 academic publication on Egyptian chronology, the Egyptologists Rolf Krauss and David Alan Warburton also ascribed Shoshenq II an independent reign of between 1 to 2 years in the 22nd dynasty although they place Shoshenq II's brief reign between that of Takelot I and Osorkon II. The German Egyptologist Thomas Schneider, in a 2010 paper, has accepted the validity of the reference in Manetho's epitome to the "3 anitekings" from Africanus' version and placed the reigns of both Shoshenq II and Tutkheperre Shoshenq in the interval between Osorkon I
Sekhemkheperre Osorkon I was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the 22nd Dynasty. Osorkon's territory included much of the Levant.
The Osorkon Bust found at Byblos is one of the five Byblian royal inscriptions.
Biography
The son of Shoshenq I and ...
and Takelot I
Hedjkheperre Setepenre Takelot I was an ancient Libyan ruler who was pharaoh during the Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt.
Reign
Takelot I was the son of Osorkon I and Queen Tashedkhons, who ruled Egypt for thirteen years according to Manetho. Tak ...
. The exclusive use of silver for the creation of Shoshenq II's coffin is a potent symbol of his power because silver "was considerably rarer in Egypt than gold."
Death and burial

 Dr. Derry's medical examination of Shoshenq II's mummy reveals that the king died as a result of a massive septic infection from a head wound.
The final resting place of Shoshenq II was certainly a reburial because he was found interred in the tomb of another king,
Dr. Derry's medical examination of Shoshenq II's mummy reveals that the king died as a result of a massive septic infection from a head wound.
The final resting place of Shoshenq II was certainly a reburial because he was found interred in the tomb of another king, Psusennes I
Psusennes I ( egy, pꜣ-sbꜣ-ḫꜥ-n-njwt; Greek Ψουσέννης) was the third pharaoh of the 21st Dynasty who ruled from Tanis between 1047 and 1001 BC. ''Psusennes'' is the Greek version of his original name Pasibkhanu or Pasebakhaenniu ...
of the Twenty-first Dynasty. Scientists have found evidence of plant growth on the base of Shoshenq II's coffin, which suggests that Shoshenq II's original tomb had become waterlogged,Derry, pp.549-551 hence a need to rebury him and his funerary equipment in another tomb. As Aidan Dodson writes:
References
Further reading
* Altenmüller, Hartwig. (2000). "Lederbänder und Lederanhänger von der Mumie des Chonsu-maacheru" and "Die Mumienbinden des Chonsu-maacheru" in ''Alt-Ägypten'' 30, pp. 73–76, 88–89, 102–11* Guy Brunton, Some Notes on the Burial of Shashanq Heqa-Kheper-Re, Annales du Service des Antiquités de l'Égypte 39 (1939), 541-547 * N. Dautzenberg, 'Bemerkungen zu Schoschenq II., Takeloth II. und Pedubastis II', Göttinger Miszellen 144 (1995), 21-29 * D. E. Derry, Note on the Remains of Shashanq, Annales du Service des Antiquités de l'Égypte 39 (1939), 549-551 {{DEFAULTSORT:Shoshenq Ii 885 BC deaths 9th-century BC Pharaohs Pharaohs of the Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt Ancient Egyptian mummies Year of birth unknown