Shinkolobwe on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Shinkolobwe, or Kasolo, or Chinkolobew, or Shainkolobwe, was a
 The mineral deposits at Shinkolobwe were discovered in 1915 by English geologist Robert Rich Sharp (1881–1960).
The formations of the Shinkolobwe ore deposit form a spur of the Mine Series wedged into a fold- fault.
The mineral deposits at Shinkolobwe were discovered in 1915 by English geologist Robert Rich Sharp (1881–1960).
The formations of the Shinkolobwe ore deposit form a spur of the Mine Series wedged into a fold- fault.
 The first mine was opened in the
The first mine was opened in the
 The United States used Shinkolobwe's
The United States used Shinkolobwe's
The DRC and Uranium for Iran
Retrieved August 19, 2006.
Amherst.edu: photograph of Shinkolobwe
Google Maps: Shinkolobwe
{{Democratic Republic of the Congo topics Uranium mines Uranium mining in the Democratic Republic of the Congo Former mines in the Democratic Republic of the Congo Haut-Katanga Province Underground mines in the Democratic Republic of the Congo Belgian Congo in World War II World War II sites in the Democratic Republic of the Congo 1921 establishments in the Belgian Congo 2004 disestablishments in Africa 2000s disestablishments in the Democratic Republic of the Congo Geological type localities
radium
Radium is a chemical element with the symbol Ra and atomic number 88. It is the sixth element in group 2 of the periodic table, also known as the alkaline earth metals. Pure radium is silvery-white, but it readily reacts with nitrogen (rat ...
and uranium mine
Uranium mining is the process of extraction of uranium ore from the ground. Over 50 thousand tons of uranium were produced in 2019. Kazakhstan, Canada, and Australia were the top three uranium producers, respectively, and together account ...
in the Haut-Katanga Province
Haut-Katanga (French for "Upper Katanga") is one of the 21 new provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo created in the 2015 repartitioning. Haut-Katanga, Haut-Lomami, Lualaba, and Tanganyika provinces are the result of the dismember ...
of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
(DRC), located 20 km west of Likasi
Likasi (formerly official names: Jadotville (French) and Jadotstad ( Dutch)) is a city in Haut-Katanga Province, in the south-east of the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Demographics
Likasi has a population of around 635,000 (2015). During the 1990 ...
(formerly Jadotville), 20 km south of Kambove, and about 145 km northwest of Lubumbashi
Lubumbashi (former names: (French), ( Dutch)) is the second-largest city in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, located in the country's southeasternmost part, along the border with Zambia. The capital and principal city of the Haut-Katan ...
.
The mine produced the most economical uranium ore in the world and was used for the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
and subsequent nuclear weapons produced by the United States in the 1940s and 50s. Before World War II, uranium extracted here was originally taken to Belgium to be processed; this supply was captured by the Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
in 1940 and subsequently used for the unsuccessful German nuclear program.
The Shinkolobwe mine was officially closed in 2004.
Toponym
The mine's name was taken from the long-gone nearby village of Shinkolobwe, which is the indigenous thorny fruit in theLingala
Lingala (Ngala) (Lingala: ''Lingála'') is a Bantu language spoken in the northwest of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the northern half of the Republic of the Congo, in their capitals, Kinshasa and Brazzaville, and to a lesser degree i ...
language. It is also slang for "a man who is easygoing on the surface but who becomes angry when provoked".
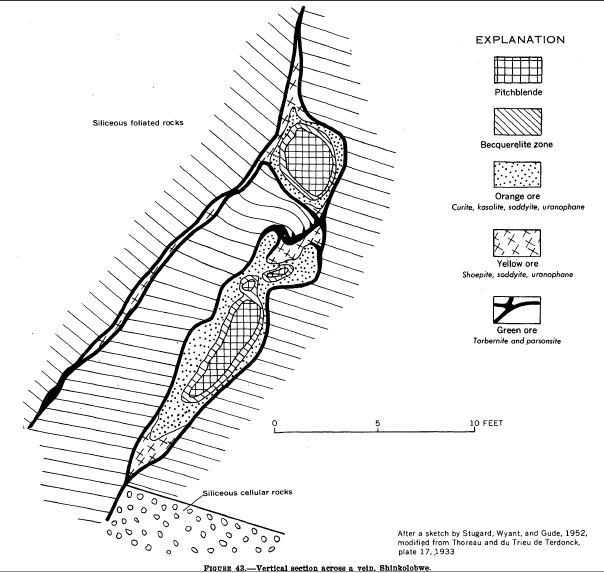
Geology
 The mineral deposits at Shinkolobwe were discovered in 1915 by English geologist Robert Rich Sharp (1881–1960).
The formations of the Shinkolobwe ore deposit form a spur of the Mine Series wedged into a fold- fault.
The mineral deposits at Shinkolobwe were discovered in 1915 by English geologist Robert Rich Sharp (1881–1960).
The formations of the Shinkolobwe ore deposit form a spur of the Mine Series wedged into a fold- fault. Uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
minerals, and associated cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, p ...
, silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical ...
, nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow t ...
, bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element with the symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs ...
and arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, b ...
, occur as massive sulfide ore in veinlets along fractures
Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displ ...
, joints, and minor faults within the Katanga synclinorium
In structural geology, a syncline is a fold with younger layers closer to the center of the structure, whereas an anticline is the inverse of a syncline. A synclinorium (plural synclinoriums or synclinoria) is a large syncline with superimpose ...
. Uraninite
Uraninite, formerly pitchblende, is a radioactive, uranium-rich mineral and ore with a chemical composition that is largely UO2 but because of oxidation typically contains variable proportions of U3O8. Radioactive decay of the uranium causes ...
mineralization occurred 630 Ma, when uraniferous solutions percolated into the dolomitic
Dolomite () is an anhydrous carbonate mineral composed of calcium magnesium carbonate, ideally The term is also used for a sedimentary carbonate rock composed mostly of the mineral dolomite. An alternative name sometimes used for the dolomitic ...
shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especiall ...
s of the Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of th ...
Mine Series (Serie des Mines), under the Roche Argilotalqueuse (R.A.T.) nappe. The Mine Series is a Schist
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock showing pronounced schistosity. This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a low-power hand lens, oriented in such a way that the rock is easily split into thin flakes ...
-Dolomite Dolomite may refer to:
*Dolomite (mineral), a carbonate mineral
*Dolomite (rock), also known as dolostone, a sedimentary carbonate rock
*Dolomite, Alabama, United States, an unincorporated community
*Dolomite, California, United States, an unincor ...
System postulated to be in the Roan System. This schistose-dolomite appears structurally between two contacts of the Kundelungu System, the Middle Kundelungu and the Lower Kundelungu, of the Katanga Group. The Lower and Upper Kundelungu form a double syncline, the northern limb of which overlies the Shinkolobwe Fault. These structural complexities aside, the Katanga stratigraphic column consists, top to bottom, of the Precambrian Kundelungu System (Upper, Middle and Lower), the Grand Conglomerate and Mwashya Systems, the Schist-Dolomite System (Roan System-Mine Series of R.G.S., C.M.N., S.D., R.S.C., R.S.F., D. Strat., R.A.T. Gr., and R.A.T.) and the Kibara Group.
Uraninite crystals from 1 to 4 centimeter cubes were common. New minerals identified here include ianthinite, becquerelite, schoepite, curite, fourmarierite, masuyite, vandendriesscheite, richetite, billietite, vandenbrandeite
Vandenbrandeite is a mineral named after a belgian geologist, Pierre Van den Brande, who discovered an ore deposit. It was named in 1932, and has been a valid mineral ever since then.
Properties
Vandenbrandeite grows in microcrystals, up to ha ...
, kasolite, soddyite, sklodowskite, cuprosklodowskite, dewindtite, dumontite, renardite, parsonsite, saleite, sharpite, studtite, and diderichite. Similar uraninite deposits occur 36 km west at Swampo, and 120 km west at Kalongwe.
Surface ores consist of oxidized minerals from supergene
A supergene is a chromosomal region encompassing multiple neighboring genes that are inherited together because of close genetic linkage, i.e. much less recombination than would normally be expected. This mode of inheritance can be due to genom ...
alteration above the water table and the formation of uranyl
The uranyl ion is an oxycation of uranium in the oxidation state +6, with the chemical formula . It has a linear structure with short U–O bonds, indicative of the presence of multiple bonds between uranium and oxygen. Four or more ligands may ...
minerals. Below the water table, hypogene ores include uraninite (pitchblende), cobalt-nickel sulfides and selenides.
History
 The first mine was opened in the
The first mine was opened in the Belgian Congo
The Belgian Congo (french: Congo belge, ; nl, Belgisch-Congo) was a Belgian colony in Central Africa from 1908 until independence in 1960. The former colony adopted its present name, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), in 1964.
Colo ...
in 1921. Uranium-bearing ore was initially exported to Olen, Belgium
Olen () is a municipality located in the Belgian province of Antwerp. The municipality comprises three towns, situated on a south–north axis:
*South of the motorway E313 and the Albert Canal is Olen proper, also called Olen-Centrum (Saint-Marti ...
for the extraction of radium
Radium is a chemical element with the symbol Ra and atomic number 88. It is the sixth element in group 2 of the periodic table, also known as the alkaline earth metals. Pure radium is silvery-white, but it readily reacts with nitrogen (rat ...
, and uranium. Only the richest ore was sent to Olen, with the remainder held in reserve. Open-cut mining was suspended at level 57 m and at the level 79 m underground in 1936, though exploration had commenced at level 114 m, and water pumps installed at level 150 m.
Both Britain and France expressed interest in the Belgium inventory of uranium ore in 1939. Nothing further happened though after the Nazis occupied Belgium in 1940, gaining control of the ore still "on the docks".
Open-cut operations restarted in 1944, and underground in 1945. This required pumping the mine dry since the water table was at about 45 m. The 255 m level was reached in 1955.
Manhattan Project
 The United States used Shinkolobwe's
The United States used Shinkolobwe's uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
resources to supply the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
to construct the atomic bomb
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
in World War II. Edgar Sengier, then director of Union Minière du Haut Katanga, had stockpiled 1,200 tonnes of uranium ore in a warehouse on Staten Island
Staten Island ( ) is a Boroughs of New York City, borough of New York City, coextensive with Richmond County, in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. Located in the city's southwest portion, the borough is separated from New Jersey b ...
, New York. This ore and an additional 3,000 tonnes of ore stored above-ground at the mine was purchased by Colonel Ken Nichols
Major General Kenneth David Nichols CBE (13 November 1907 – 21 February 2000), also known by Nick, was an officer in the United States Army, and a civil engineer who worked on the secret Manhattan Project, which developed the atomic bomb dur ...
for use in the project. Nichols wrote:
In 1940, 1,200 tons of stockpiled uranium ore were shipped to the US by Sengier's African Metals Corp., a commercial arm of Union Minière. Then, after the September 1942 agreement with Nichols, an average of 400 tons of uranium oxide were shipped to the US each month. Initially, the port of Lobito
Lobito is a municipality in Angola. It is located in Benguela Province, on the Atlantic Coast north of the Catumbela Estuary. The Lobito municipality had a population of 393,079 in 2014.
History
The city was founded in 1843 and owes its existe ...
was used to ship the ore, but later Matadi was used to improve security. Only two shipments were lost at sea. The aerodromes in Elizabethville and Leopoldville were also expanded. Additionally, the mine was reopened with the help of the United States Army Corps of Engineers
, colors =
, anniversaries = 16 June (Organization Day)
, battles =
, battles_label = Wars
, website =
, commander1 = ...
, which involved draining the water and retooling the facility. Finally, the Office of Strategic Services
The Office of Strategic Services (OSS) was the intelligence agency of the United States during World War II. The OSS was formed as an agency of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) to coordinate espionage activities behind enemy lines for all branc ...
were enlisted to deal with the threat of smuggling to Germany.
American interest in the Shinkolobwe mine for the purpose of developing of nuclear weapons led to the implementation of extensive security measures. Shinkolobwe's location was removed from maps and journalists were denied access to the mine and official information.
Cold War era
Just as a lack of uranium ore impeded the German and Japanese attempts to make an atomic bomb, the Americans wanted to maintain their monopoly against the Soviets. Security measures were slightly more relaxed in the wake of World War II, but in the 1950s, most journalists were able to gather only scraps of information on the mine's operation, from unofficial sources. In 1950, a uranium processing plant was said to be under construction near the mine. At the time, Shinkolobwe was believed to contain roughly half of the world's known reserves of uranium. In 1947, the U.S. received 1,440 tons of uranium concentrates from the Belgian Congo, 2,792 in 1951, and 1,600 in 1953. A processing plant was added nearby, and for increased security, a garrison was also established, with a supporting NATO military base in Kamina.Jadotville
Likasi (formerly official names: Jadotville ( French) and Jadotstad (Dutch)) is a city in Haut-Katanga Province, in the south-east of the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Demographics
Likasi has a population of around 635,000 (2015). During the 1990 ...
became a security checkpoint for foreigners. However, by the time of Congo independence, Union Minière had sealed the mine with concrete.
Despite the US presence in the 1940s and 1950s, in 1960, due to increase opening of Uranium mines from the American Homeland and the independence of the Congo, the United States left the mine. Hence, the sealing of the mine by Union Minière.
Israeli yellowcake
Israeli in 1968 obtained yellowcake (processed uranium ore) to support the Israeli nuclear weapons effort in a clandestine operation afterFrance
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
stopped supplying it with uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
fuel for the Dimona nuclear reactor in reaction to the 1967 Arab-Israeli War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab states (primarily Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 Jun ...
. Numerous sources believe that in 1968 Israel managed to obtain 200 tonnes of yellowcake from the Belgian mining company Union Minière. The company collaborated with Mossad
Mossad ( , ), ; ar, الموساد, al-Mōsād, ; , short for ( he, המוסד למודיעין ולתפקידים מיוחדים, links=no), meaning 'Institute for Intelligence and Special Operations'. is the national intelligence agency ...
in shipping out the ore from Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
to Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the List of cities in Italy, sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian ce ...
for a European front company which then surreptitiously transferred the ore to another vessel at night on the Mediterranean Sea.
Closure
The mine was officially closed on January 28, 2004, by presidential decree. However eight people died and a further thirteen people were injured in July 2004 when part of the old mine collapsed. Although industrial production has ceased with cement lids sealing off the mine shafts, there is evidence that someartisanal mining
An artisanal miner or small-scale miner (ASM) is a subsistence miner who is not officially employed by a mining company, but works independently, mining minerals using their own resources, usually by hand.
Small-scale mining includes enterprises ...
still goes on here. A United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
inter-agency mission, led by the UN Office for Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) and the United Nations Environment Programme
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the United Nations Conference on th ...
(UNEP), and organised through their Joint Environment Unit, visited the mine. The UNEP/OCHA concluded:
Artisanal mining and smuggling
On July 18, 2006, the DRC Sanctions Committee (United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the Organs of the United Nations, six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international security, international peace and security, recommending the admi ...
Committee Established Pursuant to Resolution 1533 (2004), to give it its full name) released a report dated June 15, 2006, which stated that artisanal mining for various minerals continues at the Shinkolobwe mine:
On August 9, 2006, the British ''Sunday Times
''The Sunday Times'' is a British newspaper whose circulation makes it the largest in Britain's quality press market category. It was founded in 1821 as ''The New Observer''. It is published by Times Newspapers Ltd, a subsidiary of News UK, whi ...
'' published a report claiming that Iran was seeking to import "bomb-making uranium" from the Shinkolobwe mine, providing no evidence but quoting the UN report of July 18, 2006. It gives "Tanzanian customs officials" as its sole source for the claim that the uranium was destined for processing in the former Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
republic of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
via the Iranian port of Bandar Abbas
Bandar Abbas or Bandar-e ‘Abbās ( fa, , , ), is a port city and capital of Hormozgān Province on the southern coast of Iran, on the Persian Gulf. The city occupies a strategic position on the narrow Strait of Hormuz (just across from Musan ...
. American journalist Douglas Farah
Douglas Farah is an American journalist, author and national security consultant. Farah served as United Press International bureau chief in El Salvador from 1985 to 1987, and a freelance journalist for ''The Washington Post'', ''Newsweek'', and ...
has compared this to North Korean attempts to get uranium from the same mine.Retrieved August 19, 2006.
See also
*K-65 residues K-65 residues are the very radioactive mill residues resulting from the uniquely concentrated uranium ore discovered before WW II in Katanga province (Shinkolobwe mine) of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (formerly Belgian Congo).
According t ...
* Operation Plumbat
Operation Plumbat is believed to have been an Israeli covert operation in 1968 to obtain yellowcake (processed uranium ore) to support the Israeli nuclear weapons effort.
France stopped supplying Israel with uranium fuel for the Dimona nuclear ...
References
External links
Amherst.edu: photograph of Shinkolobwe
Google Maps: Shinkolobwe
{{Democratic Republic of the Congo topics Uranium mines Uranium mining in the Democratic Republic of the Congo Former mines in the Democratic Republic of the Congo Haut-Katanga Province Underground mines in the Democratic Republic of the Congo Belgian Congo in World War II World War II sites in the Democratic Republic of the Congo 1921 establishments in the Belgian Congo 2004 disestablishments in Africa 2000s disestablishments in the Democratic Republic of the Congo Geological type localities