Selenium rectifier on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A selenium rectifier is a type of
A selenium rectifier is a type of


 Selenium rectifiers are able to withstand repetitive significant overload without the need of special protective measures. It is commonly used in electroplating rectifier under 200,000A and electrostatic precipitators operating between 30 to 100kV
Selenium rectifiers are able to withstand repetitive significant overload without the need of special protective measures. It is commonly used in electroplating rectifier under 200,000A and electrostatic precipitators operating between 30 to 100kV
US Patent 3218472
Transistor switch with noise rejection provided by variable capacitance feedback diode. that used selenium diodes with similar characteristics to silicon but cost less than one cent. The
(archive)
/small> * ''S.T. Selenium Rectifier Handbook''; 1st Ed; Sarkes Tarzian; 80 pages; 1950.(archive)
/small>
 A selenium rectifier is a type of
A selenium rectifier is a type of metal rectifier
A metal rectifier is an early type of semiconductor rectifier in which the semiconductor is copper oxide, germanium or selenium. They were used in power applications to convert alternating current to direct current in devices such as radios and ...
, invented in 1933. They were used in power supplies
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a res ...
for electronic equipment and in high-current battery-charger applications until they were superseded by silicon diode
A diode is a two- terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other.
A diod ...
rectifiers in the late 1960s. The arrival of the alternator
An alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. For reasons of cost and simplicity, most alternators use a rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature.Gor ...
in some automobiles was the result of compact, low-cost, high-current silicon rectifiers. These units were small enough to be inside the alternator case, unlike the selenium
Selenium is a chemical element with the symbol Se and atomic number 34. It is a nonmetal (more rarely considered a metalloid) with properties that are intermediate between the elements above and below in the periodic table, sulfur and tellurium, ...
units that preceded silicon devices.
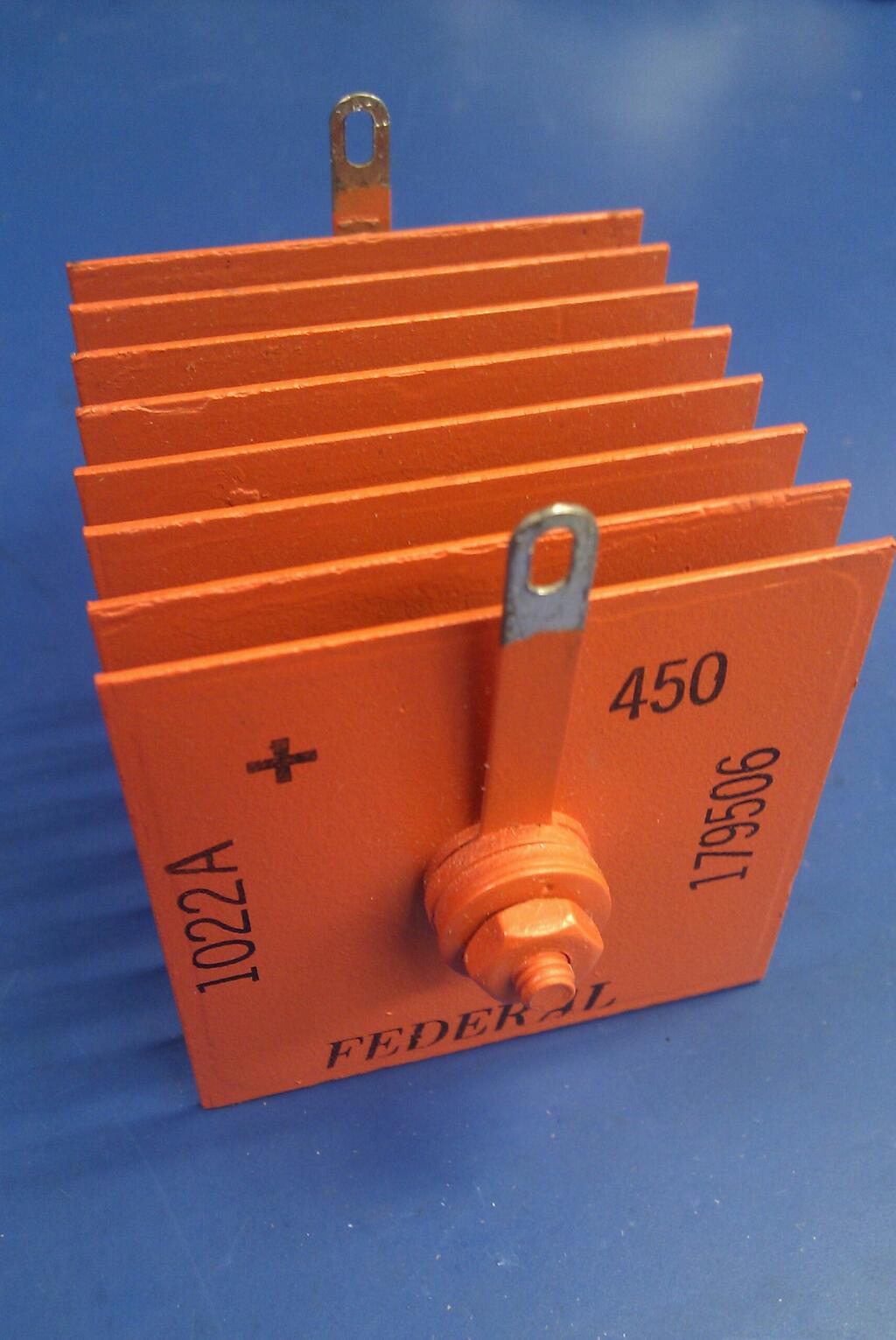
The rectifying properties of selenium, amongst other semiconductors, were observed by Braun, Schuster and Siemens between 1874 and 1883. The photoelectric and rectifying properties of selenium were also observed by Adams and Day in 1876 and C. E. Fitts around 1886, but practical rectifier devices were not manufactured routinely until the 1930s. Compared with the earlier copper-oxide rectifier, the selenium cell could withstand higher voltage, but at a lower current capacity per unit area.
Construction
Selenium
Selenium is a chemical element with the symbol Se and atomic number 34. It is a nonmetal (more rarely considered a metalloid) with properties that are intermediate between the elements above and below in the periodic table, sulfur and tellurium, ...
rectifiers are made from stacks of aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ha ...
or steel plates coated with about 1 μm of bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element with the symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs ...
or nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow ...
. A much thicker layer of selenium (50 to 60 μm) doped with a halogen is deposited on top of the thin metal plating
Plating is a surface covering in which a metal is deposited on a conductive surface. Plating has been done for hundreds of years; it is also critical for modern technology. Plating is used to decorate objects, for corrosion inhibition, to impro ...
. The selenium is then converted into polycrystalline gray (hexagonal) form by annealing. Cadmium selenide forms by reaction of the selenium with the tin-cadmium alloy and the CdSe-Se heterojunction A heterojunction is an interface between two layers or regions of dissimilar semiconductors. These semiconducting materials have unequal band gaps as opposed to a homojunction. It is often advantageous to engineer the electronic energy bands in ma ...
is the active rectifying junction. Each plate is able to withstand about 20 volts in the reverse direction. The metal squares, or disks, also serve as heat sink
A heat sink (also commonly spelled heatsink) is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant, where it is dissipated away from the device, th ...
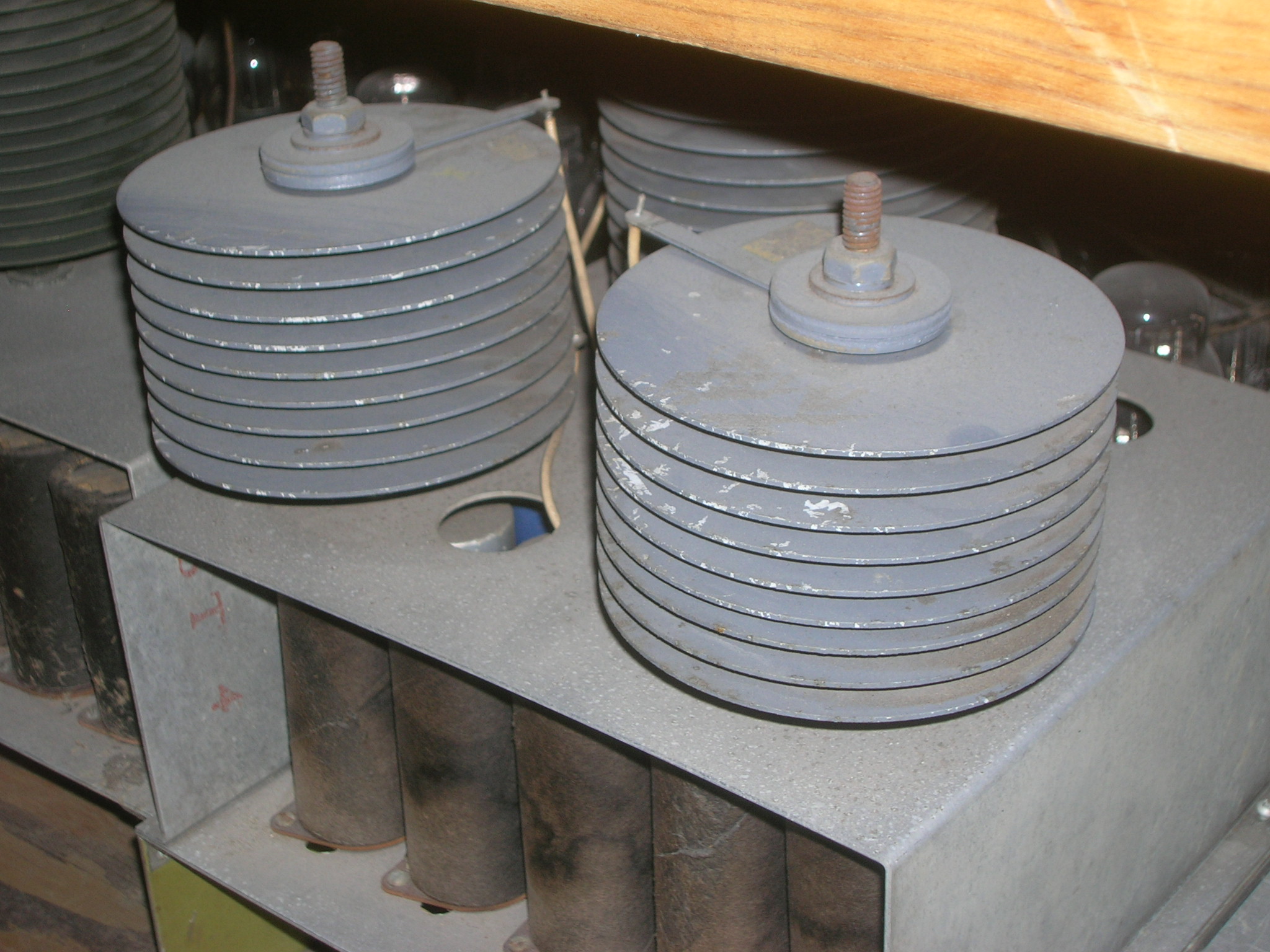
s in addition to providing a mounting place for the selenium disks. Plates can be stacked indefinitely to withstand higher voltages. Stacks of thousands of miniature selenium disks have been used as high-voltage rectifiers in television set
A television set or television receiver, more commonly called the television, TV, TV set, telly, tele, or tube, is a device that combines a tuner, display, and loudspeakers, for the purpose of viewing and hearing television broadcasts, or using ...
s and photocopy machines.
Use
 Selenium rectifiers are able to withstand repetitive significant overload without the need of special protective measures. It is commonly used in electroplating rectifier under 200,000A and electrostatic precipitators operating between 30 to 100kV
Selenium rectifiers are able to withstand repetitive significant overload without the need of special protective measures. It is commonly used in electroplating rectifier under 200,000A and electrostatic precipitators operating between 30 to 100kV
Radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmi ...
and television receivers used them from about 1947 to 1975 to provide up to a few hundred volts of plate voltage. Vacuum-tube rectifiers had efficiencies of only 60% compared to the 85% of selenium rectifiers, partially because vacuum-tube rectifiers required heating. Selenium rectifiers have no warm-up time, unlike high-vacuum rectifiers. Selenium rectifiers were also cheaper and simpler to specify and install than vacuum tubes. However, they were later replaced by silicon diodes with high efficiencies (close to 100% at high voltages). Selenium rectifiers had the capability to act as current limiters, which can temporarily protect the rectifier during a short circuit and provide stable current for charging batteries.
Properties
A selenium rectifier is about the same size as a copper-oxide rectifier, but is much larger than a silicon or germanium diode. Selenium rectifiers have a long but not indefinite service life of 60,000 to 100,000 hours, depending on rating and cooling. The rectifier can show some unforming of the rectifier characteristic after long storage. Each cell can withstand a reverse voltage around 25 volts and has a forward voltage drop around 1 volt, which limits the efficiency at low voltages. Selenium rectifiers have an operating temperature limit of 130 °C and are not suitable for high-frequency circuits.Replacement
Selenium rectifiers had a shorter lifespan than desired. During catastrophic failure they produced significant quantities of malodorous and highly toxic hydrogen selenide that let the repair technician know what the problem was. By far the most common failure mode was a progressive increase in forward resistance, increasing forwardvoltage drop
Voltage drop is the decrease of electrical potential along the path of a current flowing in an electrical circuit. Voltage drops in the internal resistance of the source, across conductors, across contacts, and across connectors are undesirab ...
and reducing the rectifier's efficiency. During the 1960s they began to be superseded by silicon rectifiers
A diode is a two- terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other.
A diod ...
, which exhibited lower forward voltage drop, lower cost, and higher reliability.
Selenium diode computer logic
In 1961 IBM started developing a low-speed computer logic familyTransistor switch with noise rejection provided by variable capacitance feedback diode. that used selenium diodes with similar characteristics to silicon but cost less than one cent. The
terminal
Terminal may refer to:
Computing Hardware
* Terminal (electronics), a device for joining electrical circuits together
* Terminal (telecommunication), a device communicating over a line
* Computer terminal, a set of primary input and output dev ...
development departments were begging for low cost and did not need speed. It was possible to punch 1/8-inch discs from a sheet of selenium diode. GE claimed that they could make reliable selenium diodes. A design was achieved for a DDTL circuit with two levels of diode logic
Diode logic (DL), or diode-resistor logic (DRL), is the construction of Boolean logic gates from diodes. Diode logic was used extensively in the construction of early computers, where semiconductor diodes could replace bulky and costly active v ...
feeding one alloy transistor and no series input resistor or speed-up capacitor. The family was called SMAL or SMALL, for "selenium matrix alloy logic". The alloy transistor proved to be too fast for the selenium diode recovery. To solve this problem, a selenium diode was connected around the base–emitter to slow it down. The two-level logic was similar to the PLAs programmable logic array that would come on the market many years later. Nearly any static logic function that yielded one output could be achieved with one transistor and a handful of cheap diodes. Several years later the selenium diodes were found to be not reliable and were replaced by silicon diodes. The logic family was packaged on SMS cards.
Further reading
* ''F.T. Selenium Rectifier Handbook''; 2nd Ed; Federal Telephone and Radio; 80 pages; 1953./small> * ''S.T. Selenium Rectifier Handbook''; 1st Ed; Sarkes Tarzian; 80 pages; 1950.
/small>
References
{{Reflist Diodes Selenium Rectifiers