Second Italian War of Independence on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Second Italian War of Independence, also called the Franco-Austrian War, the Austro-Sardinian War or Italian War of 1859 ( it, Seconda guerra d'indipendenza italiana; french: Campagne d'Italie), was fought by the
 The French Army, under Marshal François Certain Canrobert, moved into
The French Army, under Marshal François Certain Canrobert, moved into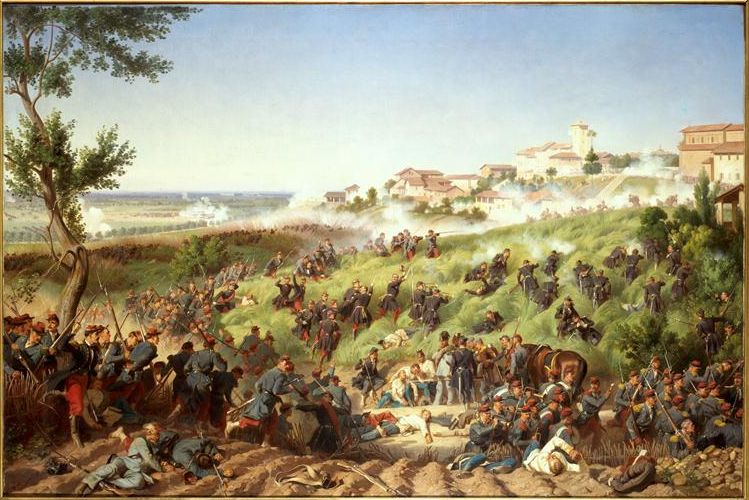  The Austrians, under Gyulai, captured
The Austrians, under Gyulai, captured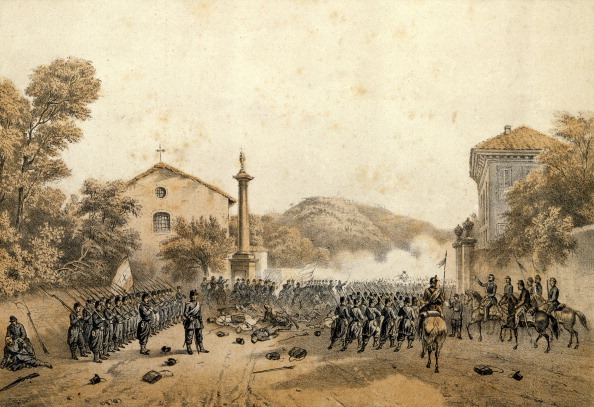 
 Replacing Gyulai was Emperor Franz Josef I, who planned to defend the well-fortified Austrian territory behind the Mincio River. The Piedmontese-French army had taken
Replacing Gyulai was Emperor Franz Josef I, who planned to defend the well-fortified Austrian territory behind the Mincio River. The Piedmontese-French army had taken
 Napoleon III signed the Villafranca Armistice with Austria in Villafranca for a combination of reasons. The Austrians had retreated to the Quadrilateral, which would be very costly to overrun. His absence in France had made the country vulnerable to attack. His actions in Italy were being criticised in France. He did not want Cavour and Piedmont to gain too much power, mostly at the expense of his men. He feared involvement of the German states. Most of
Napoleon III signed the Villafranca Armistice with Austria in Villafranca for a combination of reasons. The Austrians had retreated to the Quadrilateral, which would be very costly to overrun. His absence in France had made the country vulnerable to attack. His actions in Italy were being criticised in France. He did not want Cavour and Piedmont to gain too much power, mostly at the expense of his men. He feared involvement of the German states. Most of
online free
* Carter, Nick. "Hudson, Malmesbury and Cavour: British Diplomacy and the Italian Question, February 1858 to June 1859." ''Historical Journal ''40#2 (1997): 389–413
in JSTOR
* Coppa, Frank J. ''The origins of the Italian wars of independence'' (1992). * Schneid, Frederick C. ''The Second War of Italian Unification 1859–61'' (Bloomsbury Publishing, 2012). * old interpretations but useful on details; vol 1 goes to 1859
volume 2 online covers 1859–62
{{Authority control Conflicts in 1859 1859 in the Kingdom of Sardinia 1859 in the Austrian Empire 1859 in France France–Italy relations
Second French Empire
The Second French Empire (; officially the French Empire, ), was the 18-year Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 14 January 1852 to 27 October 1870, between the Second and the Third Republic of France.
Historians in the 1930s ...
and the Savoyard Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia,The name of the state was originally Latin: , or when the kingdom was still considered to include Corsica. In Italian it is , in French , in Sardinian , and in Piedmontese . also referred to as the Kingdom of Savoy-S ...
against the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central- Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
in 1859 and played a crucial part in the process of Italian Unification
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single ...
.
A year prior to the war, in the Plombières Agreement, France agreed to support Sardinia's efforts to expel Austria from Italy in return for territorial compensation in the form of the Duchy of Savoy
The Duchy of Savoy ( it, Ducato di Savoia; french: Duché de Savoie) was a country in Western Europe that existed from 1416.
It was created when Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, raised the County of Savoy into a duchy for Amadeus VIII. The du ...
and the County of Nice
The County of Nice (french: Comté de Nice / Pays Niçois, it, Contea di Nizza/Paese Nizzardo, Niçard oc, Contèa de Niça/País Niçard) is a historical region of France located around the southeastern city of Nice and roughly equivalent t ...
. The two states signed a military alliance
A military alliance is a formal agreement between nations concerning national security. Nations in a military alliance agree to active participation and contribution to the defense of others in the alliance in the event of a crisis. (Online) ...
in January 1859. Sardinia mobilised its army on 9 March 1859, and Austria mobilized on 9 April.
On 23 April, Austria delivered an ultimatum to Sardinia demanding its demobilization. Upon Sardinia's refusal, the war began on 26 April. Austria invaded Sardinia three days later, and France declared war on Austria on 3 May.
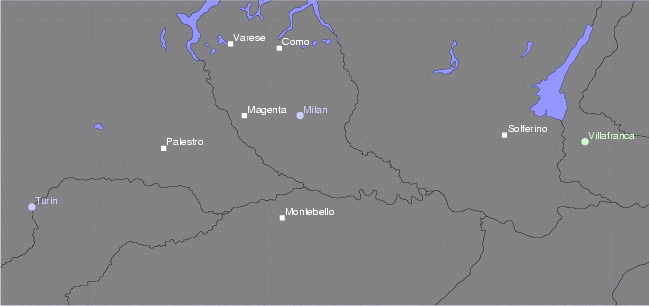
The Austrian invasion was stopped by the arrival of French troops in Piedmont that had begun in late April. The Austrians were defeated at the Battle of Magenta
The Battle of Magenta was fought on 4 June 1859 during the Second Italian War of Independence, resulting in a French-Sardinian victory under Napoleon III against the Austrians under Marshal Ferencz Gyulai.
It took place near the town of Mage ...
on 4 June and pushed back to Lombardy
(man), (woman) lmo, lumbard, links=no (man), (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, ...
, where the Franco-Sardinian victory at the Battle of Solferino
The Battle of Solferino (referred to in Italy as the Battle of Solferino and San Martino) on 24 June 1859 resulted in the victory of the allied Second French Empire, French Army under Napoleon III and Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia, Piedmont-Sard ...
on 24 June resulted in the end of the war and the signing of the Armistice of Villafranca on 12 July.
Austria ceded Lombardy to France, which, in turn, gave it to Sardinia. Exploiting the collapse of Austrian power in Italy, Sardinia annexed the United Provinces of Central Italy
The United Provinces of Central Italy, also known as Confederation of Central Italy or General Government of Central Italy, was a short-lived military government established by the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia. It was formed by a union of the for ...
, consisting of the Grand Duchy of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany ( it, Granducato di Toscana; la, Magnus Ducatus Etruriae) was an Italian monarchy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1859, replacing the Republic of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence. In th ...
, the Duchy of Parma
The Duchy of Parma and Piacenza ( it, Ducato di Parma e Piacenza, la, Ducatus Parmae et Placentiae), was an Italian state created in 1545 and located in northern Italy, in the current region of Emilia-Romagna.
Originally a realm of the Farnese ...
, the Duchy of Modena and Reggio and the Papal Legations, on 22 March 1860. Two days later, Sardinia ceded Savoy
Savoy (; frp, Savouè ; french: Savoie ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps.
Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south.
Sa ...
and Nice
Nice ( , ; Niçard: , classical norm, or , nonstandard, ; it, Nizza ; lij, Nissa; grc, Νίκαια; la, Nicaea) is the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative ...
to France at the Treaty of Turin as compensation for its assistance.
Background
The Piedmontese, following their defeat by Austria in theFirst Italian War of Independence
The First Italian War of Independence ( it, Prima guerra d'indipendenza italiana), part of the Italian Unification (''Risorgimento''), was fought by the Kingdom of Sardinia (Piedmont) and Italian volunteers against the Austrian Empire and other ...
, recognized their need for allies. That led Prime Minister Camillo Benso, Count of Cavour to attempt to establish relations with other European powers, partially through Piedmont's participation in the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the ...
. In the peace conference at Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
after the Crimean War, Cavour attempted to bring attention to efforts for Italian unification. He found Britain and France to be sympathetic but refusing to go against Austrian wishes, as any movement towards Italian independence would threaten Austria's territory of Lombardy–Venetia. Private talks between Napoleon III and Cavour after the conference identified Napoleon as the most likely candidate to aid Italy although he was still uncommitted.
On 14 January 1858, Felice Orsini, an Italian, led an attempt on Napoleon III's life. The assassination attempt brought widespread sympathy for the Italian unity and had a profound effect on Napoleon III himself, who now was determined to help Piedmont against Austria to defuse the wider revolutionary activities, which governments in Italy might later allow to happen. After a covert meeting at Plombières on 21 July 1858, Napoleon III and Cavour on 28 January 1859 signed a secret treaty of alliance against Austria.
France would help Sardinia-Piedmont, if attacked, to fight against Austria if Sardinia-Piedmont gave Nice
Nice ( , ; Niçard: , classical norm, or , nonstandard, ; it, Nizza ; lij, Nissa; grc, Νίκαια; la, Nicaea) is the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative ...
and Savoy
Savoy (; frp, Savouè ; french: Savoie ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps.
Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south.
Sa ...
to France in return. The secret alliance served both countries by helping with the Sardinian-Piedmontese plan of unification of the Italian Peninsula under the House of Savoy
The House of Savoy ( it, Casa Savoia) was a royal dynasty that was established in 1003 in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, the family grew in power from ruling a small Alpine county north-west of Italy to absolute rule of ...
. It also weakened Austria, a fiery adversary of Napoleon III's French Second Empire.
Cavour, being unable to get French help unless the Austrians attacked first, provoked Vienna by a series of military maneuvers close to the border. Sardinia mobilised its army on 9 March 1859. Austria mobilised on 9 April 1859 and issued an ultimatum on 23 April demanding the complete demobilisation of the Sardinian Army. When it was not heeded, Austria started a war against Sardinia on 26 April.
The first French troops entered Piedmont on 25 April, and France declared war on Austria on 3 May.
Forces
The French Army for the Italian campaign had 170,000 soldiers, 2,000 horsemen and 312 guns, half of the whole French army. The army, under the command of Napoleon III, divided into five corps: the I Corps, led by Achille Baraguey d'Hilliers; the II Corps, led by Patrice de MacMahon; the III Corps, led by François Certain de Canrobert, the IV Corps; led byAdolphe Niel
Adolphe Niel (4 October 180213 August 1869) was a French Army general and statesman.
He was born at Muret, Haute-Garonne and entered the École Polytechnique in 1821. Niel entered the engineer school at Metz, became lieutenant in the Engineer ...
, and the V Corps, led by prince Napoléon Joseph Charles Paul Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
. The Imperial Guard
An imperial guard or palace guard is a special group of troops (or a member thereof) of an empire, typically closely associated directly with the Emperor or Empress. Usually these troops embody a more elite status than other imperial forces, i ...
was commanded by Auguste Regnaud de Saint-Jean d'Angély
Auguste Michel Étienne Regnaud de Saint-Jean d'Angély, later 2nd Count Regnaud de Saint-Jean d'Angély (30 July 1794, Paris – 1 February 1870 Cannes) was a Marshal of France, soldier and politician.
Biography
Auguste was the illegitimate son ...
.
Napoleon III participated in the war and showed up on the battlefield in the belief that it would motivate the French people during the war. That would prove successful.
The Sardinian Army had about 70,000 soldiers, 4,000 horsemen and 90 guns. It was divided into five divisions, led by Castelbrugo, Manfredo Fanti, Giovanni Durando
Giovanni Durando (23 June 1804 – 27 May 1869) was an Italian general and politician.
Biography
Born at Mondovì, in what is now the province of Cuneo, he entered the Royal Guard corps of the Kingdom of Sardinia in 1822. In the 1830s, after hav ...
, Enrico Cialdini and Domenico Cucchiari
Domenico is an Italian given name for males and may refer to:
People
* Domenico Alfani, Italian painter
* Domenico Allegri, Italian composer
* Domenico Alvaro, Italian mobster
* Domenico Ambrogi, Italian painter
* Domenico Auria, Italian archit ...
. Two volunteer formations, the Cacciatori delle Alpi
The Hunters of the Alps ( it, Cacciatori delle Alpi) were a military corps created by Giuseppe Garibaldi in Cuneo on 20 February 1859 to help the regular Sardinian army to free the northern part of Italy in the Second Italian War of Independ ...
and the Cacciatori degli Appennini, were also present. It was led by Victor Emmanuel II of Savoy, supported by Alfonso Ferrero la Marmora
Alfonso Ferrero La Marmora (; 18 November 18045 January 1878) was an Italian general and statesman. His older brothers include soldier and naturalist Alberto della Marmora and Alessandro Ferrero La Marmora, founder of the branch of the Italian ...
.
The Austrian Army fielded more men with 220,000 soldiers, 824 guns and 22,000 horsemen. It was led by Field Marshal
Field marshal (or field-marshal, abbreviated as FM) is the most senior military rank, ordinarily senior to the general officer ranks. Usually, it is the highest rank in an army and as such few persons are appointed to it. It is considered as ...
Ferenc ''Graf'' Gyulay.
The newly-formed United Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia also supported the Franco-Italian alliance. Their ruler, Alexandru Ioan Cuza, was given 10,000 rifles and ammunition by Napoleon III. Napoleon III, with his unwavering and very genuine sympathy, also sent a military mission to Bucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ro, București ) is the capital and largest city of Romania, as well as its cultural, industrial, and financial centre. It is located in the southeast of the country, on the banks of the Dâmbovița River, less than north o ...
. Encouraged, Cuza formed a new military camp at Ploiești
Ploiești ( , , ), formerly spelled Ploești, is a city and county seat in Prahova County, Romania. Part of the historical region of Muntenia, it is located north of Bucharest.
The area of Ploiești is around , and it borders the Blejoi commun ...
. As a result, Austria had to keep 30,000 troops in Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the A ...
, which could ill be spared from Italy.
War
 The French Army, under Marshal François Certain Canrobert, moved into
The French Army, under Marshal François Certain Canrobert, moved into Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
in the first massive military use of railways. The Austrian forces counted on a swift victory over the weaker Sardinian Army before French forces could arrive in Piedmont. However, Count Gyulai, the commander of the Austrian troops in Lombardy
(man), (woman) lmo, lumbard, links=no (man), (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, ...
, was very cautious and marched around the Ticino River in no specific direction until he crossed it to begin the offensive. Unfortunately for him, very heavy rains began to fall, which allowed the Piedmontese to flood the rice fields in front of his advance and slowed his army's march to a crawl.
 The Austrians, under Gyulai, captured
The Austrians, under Gyulai, captured Novara
Novara (, Novarese: ) is the capital city of the province of Novara in the Piedmont region in northwest Italy, to the west of Milan. With 101,916 inhabitants (on 1 January 2021), it is the second most populous city in Piedmont after Turin. It i ...
on 30 April and Vercelli
Vercelli (; pms, Vërsèj ), is a city and ''comune'' of 46,552 inhabitants (January 1, 2017) in the Province of Vercelli, Piedmont, northern Italy. One of the oldest urban sites in northern Italy, it was founded, according to most historians, ...
on 2 May and advanced on Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese language, Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital ...
from 7 May onward. The Franco-Sardinian move to strengthen the Alessandria
Alessandria (; pms, Lissandria ) is a city and ''comune'' in Piedmont, Italy, and the capital of the Province of Alessandria. The city is sited on the alluvial plain between the Tanaro and the Bormida rivers, about east of Turin.
Alessandri ...
and Po River
The Po ( , ; la, Padus or ; Ancient Ligurian: or ) is the longest river in Italy. It flows eastward across northern Italy starting from the Cottian Alps. The river's length is either or , if the Maira, a right bank tributary, is included. T ...
bridges around Casale Monferrato
Casale Monferrato () is a town in the Piedmont region of Italy, in the province of Alessandria. It is situated about east of Turin on the right bank of the Po, where the river runs at the foot of the Montferrat hills. Beyond the river lies the ...
forced the Austrians to halt their advance on 9 May and to fall back on 10 May. Napoleon III left Paris on 10 May, landed at Genoa on 12 May and arrived in Alessandria on 14 May. He took the command of the operations of the war, whose first major clash was at Montebello on 20 May, a battle between an Austrian Corps under Stadion and a single division of the French I Corps, under Forey. Although the Austrian contingent was three times as large, the French were victorious, which made Gyulai still more cautious. In early June, Gyulai had advanced to the rail centre of Magenta
Magenta () is a color that is variously defined as pinkish- purplish- red, reddish-purplish-pink or mauvish-crimson. On color wheels of the RGB (additive) and CMY (subtractive) color models, it is located exactly midway between red and blu ...
and left his army spread out. Napoleon III attacked Ticino head on with part of his force and sent many other troops to the north to flank the Austrians. The plan worked and caused Gyulai to retreat east to the quadrilateral fortresses in Lombardy, where he was relieved of his post as commander.

 Replacing Gyulai was Emperor Franz Josef I, who planned to defend the well-fortified Austrian territory behind the Mincio River. The Piedmontese-French army had taken
Replacing Gyulai was Emperor Franz Josef I, who planned to defend the well-fortified Austrian territory behind the Mincio River. The Piedmontese-French army had taken Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
and slowly marched further east to finish off Austria in the war before Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
could get involved. The Austrians found out that the French had halted at Brescia
Brescia (, locally ; lmo, link=no, label= Lombard, Brèsa ; lat, Brixia; vec, Bressa) is a city and '' comune'' in the region of Lombardy, Northern Italy. It is situated at the foot of the Alps, a few kilometers from the lakes Garda and Iseo ...
and decided that they should counterattack along the river Chiese. The two armies met accidentally around Solferino
Solferino ( Upper Mantovano: ) is a small town and municipality in the province of Mantua, Lombardy, northern Italy, approximately south of Lake Garda.
It is best known as being close to the site of the Battle of Solferino on 24 June 1859, par ...
, which precipitated a confused series of battles.
A French corps held off three Austrian corps all day at Medole and kept them from joining the larger battle around Solferino, where, after a day-long battle, the French broke through. Ludwig von Benedek with the Austrian VIII Corps was separated from the main force and defended Pozzolengo against the Piedmontese part of the opposing army. It was successful, but the entire Austrian army retreated after the breakthrough at Solferino and withdrew back into the Quadrilateral.
Meanwhile, in the north of Lombardy, the Italian volunteers of Giuseppe Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he is known as ''Gioxeppe Gaibado''. In his particular Niçard dialect of Ligurian, he was known as ''Jousé'' or ''Josep''. 4 July 1807 – 2 June 1882) was an Italian general, pa ...
's ''Hunters of the Alps
The Hunters of the Alps ( it, Cacciatori delle Alpi) were a military corps created by Giuseppe Garibaldi in Cuneo on 20 February 1859 to help the regular Sardinian army to free the northern part of Italy in the Second Italian War of Independe ...
'' defeated the Austrians at Varese
Varese ( , , or ; lmo, label=Varesino, Varés ; la, Baretium; archaic german: Väris) is a city and ''comune'' in north-western Lombardy, northern Italy, north-west of Milan. The population of Varese in 2018 has reached 80,559.
It is the ca ...
and Como
Como (, ; lmo, Còmm, label= Comasco , or ; lat, Novum Comum; rm, Com; french: Côme) is a city and '' comune'' in Lombardy, Italy. It is the administrative capital of the Province of Como.
Its proximity to Lake Como and to the Alps ...
, and the Piedmontese-French Navy landed 3,000 soldiers and conquered the islands of Losinj (Lussino) and Cres
Cres (; dlm, Crepsa, vec, Cherso, it, Cherso, la, Crepsa, Greek: Χέρσος, ''Chersos'') is an Adriatic island in Croatia. It is one of the northern islands in the Kvarner Gulf and can be reached via ferry from Rijeka, the island K ...
(Cherso), in Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see names in other languages) is one of the four historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of the Adriatic Sea, str ...
.
Peace
 Napoleon III signed the Villafranca Armistice with Austria in Villafranca for a combination of reasons. The Austrians had retreated to the Quadrilateral, which would be very costly to overrun. His absence in France had made the country vulnerable to attack. His actions in Italy were being criticised in France. He did not want Cavour and Piedmont to gain too much power, mostly at the expense of his men. He feared involvement of the German states. Most of
Napoleon III signed the Villafranca Armistice with Austria in Villafranca for a combination of reasons. The Austrians had retreated to the Quadrilateral, which would be very costly to overrun. His absence in France had made the country vulnerable to attack. His actions in Italy were being criticised in France. He did not want Cavour and Piedmont to gain too much power, mostly at the expense of his men. He feared involvement of the German states. Most of Lombardy
(man), (woman) lmo, lumbard, links=no (man), (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, ...
, with its capital, Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
, except only the Austrian fortresses of Mantua
Mantua ( ; it, Mantova ; Lombard and la, Mantua) is a city and '' comune'' in Lombardy, Italy, and capital of the province of the same name.
In 2016, Mantua was designated as the Italian Capital of Culture. In 2017, it was named as the Eur ...
and Legnago
Legnago () is a town and '' comune'' in the Province of Verona, Veneto, northern Italy, with population (2012) of 25,439. It is located on the Adige river, about from Verona. Its fertile land produces crops of rice, other cereals, sugar, and ...
and the surrounding territory, was transferred from Austria to France, which would immediately cede the territories to Sardinia. The rulers of Central Italy, who had been expelled by revolution shortly after the beginning of the war, were to be restored.
The agreement, made by Napoleon behind the backs of his Sardinian allies, led to great outrage in Sardinia-Piedmont, and Cavour resigned in protest. However, the terms of Villafranca were never to come into effect. Although they were reaffirmed by the final Treaty of Zürich in November, the agreement had become a dead letter. The Central Italian states were occupied by the Piedmontese, who showed no willingness to restore the previous rulers, and the French showed no willingness to force them to abide by the terms of the treaty.
The Austrians were left to look on in frustration at the French failure to carry out the terms of the treaty. Austria had emerged triumphantly after the suppression of liberal movements in 1849, but its status as a great power on the European scene was now seriously challenged and its influence in Italy severely weakened.
The next year, with French and British approval, the Central Italian states (Duchy of Parma
The Duchy of Parma and Piacenza ( it, Ducato di Parma e Piacenza, la, Ducatus Parmae et Placentiae), was an Italian state created in 1545 and located in northern Italy, in the current region of Emilia-Romagna.
Originally a realm of the Farnese ...
, Duchy of Modena, Grand Duchy of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany ( it, Granducato di Toscana; la, Magnus Ducatus Etruriae) was an Italian monarchy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1859, replacing the Republic of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence. In th ...
and the Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope fro ...
) were annexed by the Kingdom of Sardinia, and France would take its deferred rewards of Savoy
Savoy (; frp, Savouè ; french: Savoie ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps.
Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south.
Sa ...
and Nice
Nice ( , ; Niçard: , classical norm, or , nonstandard, ; it, Nizza ; lij, Nissa; grc, Νίκαια; la, Nicaea) is the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative ...
. The last move was vehemently opposed by Italian national hero Garibaldi, a native of Nice, and directly led to Garibaldi's expedition to Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, which would complete the preliminary Unification of Italy
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single ...
.
During the war, Prussia had also mobilised 132,000 men in 1859 but never joined the fighting. The weaknesses laid bare during the mobilisation caused the Prussian Army to initiate military reforms, which were the base for its superiority and rapid victories against Austria in 1866 and France in 1870-71, which led to a united Germany under Prussian dominance.Lohner, Henry; ''Wie wird man schnell reich?;'' Norderstedt 2011; S. 78;
Timeline
* 27 April: A peaceful revolution in Tuscany ousts Archduke Leopold II and installs a provisional government * 20 May: French infantry and Sardinian cavalry defeat the Austrian army, which retreated, near Montebello. * 26 May: Garibaldi's ''Hunters of the Alps
The Hunters of the Alps ( it, Cacciatori delle Alpi) were a military corps created by Giuseppe Garibaldi in Cuneo on 20 February 1859 to help the regular Sardinian army to free the northern part of Italy in the Second Italian War of Independe ...
'' confront Austrian forces led by Field Marshal-Lieutenant Carl Baron Urban at Varese.
* 27 May: ''Hunters of the Alps'' defeat Urban at San Fermo, entering Como
Como (, ; lmo, Còmm, label= Comasco , or ; lat, Novum Comum; rm, Com; french: Côme) is a city and '' comune'' in Lombardy, Italy. It is the administrative capital of the Province of Como.
Its proximity to Lake Como and to the Alps ...
.
* 30 May: French and Sardinian forces defeat the Austrian army at the Battle of Palestro
The Battle of Palestro was fought on 30–31 May 1859 between the Austrian Empire and the combined forces of the Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont and France. The Franco-Piedmontese forces were victorious. It was fought just south to Palestro, a tow ...
.
* 4 June: In the Battle of Magenta
The Battle of Magenta was fought on 4 June 1859 during the Second Italian War of Independence, resulting in a French-Sardinian victory under Napoleon III against the Austrians under Marshal Ferencz Gyulai.
It took place near the town of Mage ...
, the French defeat Austrians.
* 21 June/24 June: In the Battle of Solferino
The Battle of Solferino (referred to in Italy as the Battle of Solferino and San Martino) on 24 June 1859 resulted in the victory of the allied Second French Empire, French Army under Napoleon III and Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia, Piedmont-Sard ...
, Sardinians and Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A neph ...
of France defeat an army commanded by Emperor Franz Joseph of Austria
Franz Joseph I or Francis Joseph I (german: Franz Joseph Karl, hu, Ferenc József Károly, 18 August 1830 – 21 November 1916) was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, and the Grand title of the Emperor of Austria, other states of the Habsburg m ...
himself in northern Italy. The battle inspires Henri Dunant to found the Red Cross
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a Humanitarianism, humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million Volunteering, volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure re ...
.
* 11 July: Franz Joseph, faced with the revolution in Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Cr ...
, meets Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A neph ...
at Villafranca, where they signed an armistice.
References
Further reading
* Blumberg, Arnold. ''A Carefully Planned Accident: The Italian War of 1859'' (Susquehanna University Press. 1990). Pp. 238. * Bossoli, Carlo . ''The War in Italy: the Second Italian War of Independence, 1859'' (1860), illustratedonline free
* Carter, Nick. "Hudson, Malmesbury and Cavour: British Diplomacy and the Italian Question, February 1858 to June 1859." ''Historical Journal ''40#2 (1997): 389–413
in JSTOR
* Coppa, Frank J. ''The origins of the Italian wars of independence'' (1992). * Schneid, Frederick C. ''The Second War of Italian Unification 1859–61'' (Bloomsbury Publishing, 2012). * old interpretations but useful on details; vol 1 goes to 1859
volume 2 online covers 1859–62
{{Authority control Conflicts in 1859 1859 in the Kingdom of Sardinia 1859 in the Austrian Empire 1859 in France France–Italy relations