Sciuromorphous on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The zygomasseteric system (or zygomasseteric structure) in
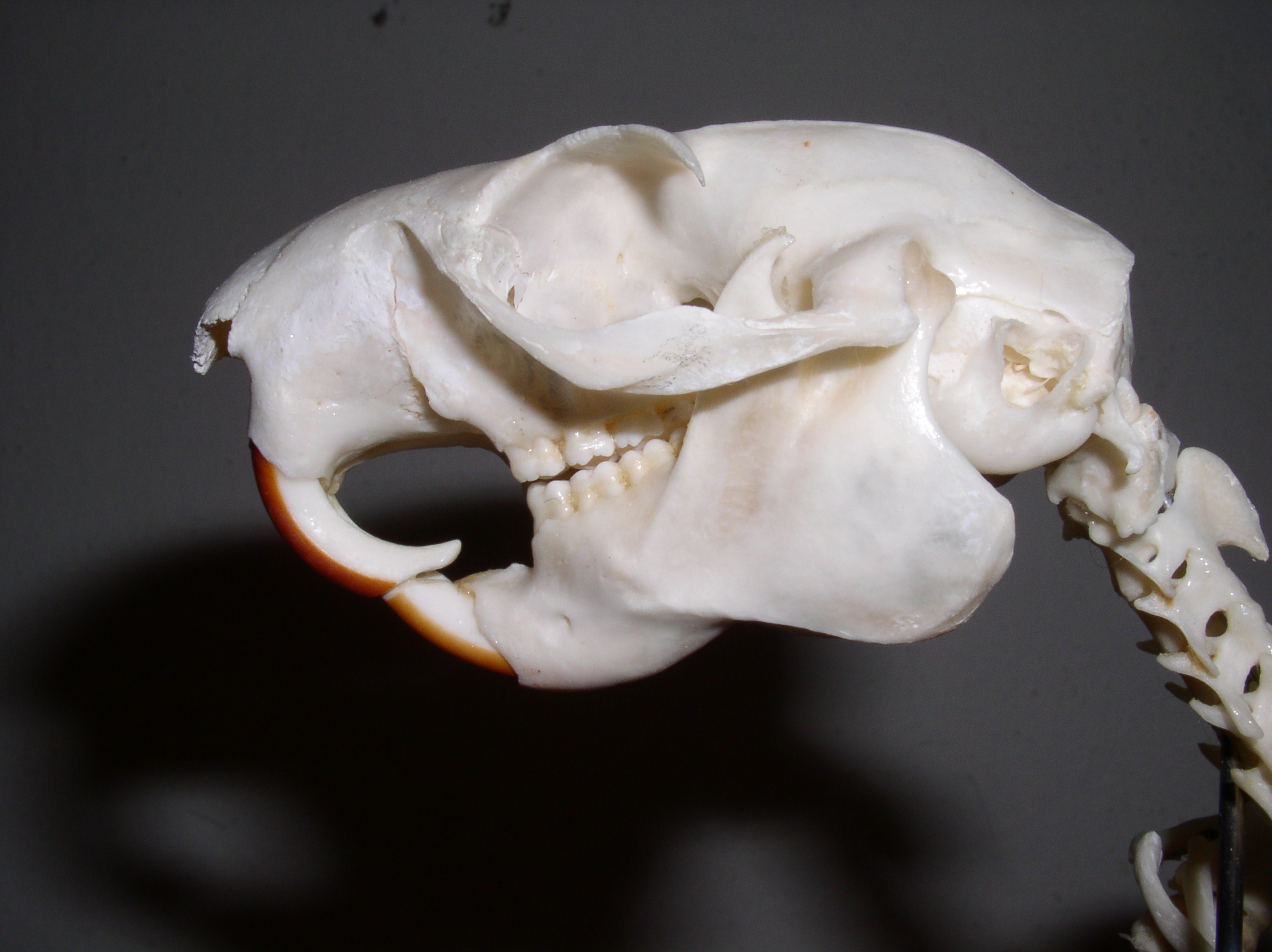 This condition is found in most members of the family
This condition is found in most members of the family
 This condition is found throughout the suborders
This condition is found throughout the suborders
 This condition is found in the
This condition is found in the
rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are n ...
s is the anatomical arrangement of the masseter muscle
In human anatomy, the masseter is one of the muscles of mastication. Found only in mammals, it is particularly powerful in herbivores to facilitate chewing of plant matter. The most obvious muscle of mastication is the masseter muscle, since it ...
of the jaw and the zygomatic arch
In anatomy, the zygomatic arch, or cheek bone, is a part of the skull formed by the zygomatic process of the temporal bone (a bone extending forward from the side of the skull, over the opening of the ear) and the temporal process of the zygo ...
of the skull. The anteroposterior or propalinal (front-to-back) motion of the rodent jaw is enabled by an extension of the zygomatic arch and the division of the masseter into a superficial, lateral and medial muscle. The four main types are described as protrogomorphous, sciuromorphous, hystricomorphous, and myomorphous.{*
Protrogomorphy
The members of this grade include nearly all of the pre-Oligocene rodents of North America and Asia and some of those of Europe. Several lineages survive into the Oligocene or early Miocene, with only one species still alive today, themountain beaver
The mountain beaver (''Aplodontia rufa'')Other names include mountain boomer, ground bear, giant mole, gehalis, lesser sasquatch, sewellel, suwellel, showhurll, showtl, and showte, as well as a number of Chinookan and other Native American terms ...
('' Aplodontia rufa''). The molerats (family Bathyergidae) are considered secondarily protrogomorphous since their zygomatic condition is clearly derived from a hystricomorphous ancestor. The rostrum
Rostrum may refer to:
* Any kind of a platform for a speaker:
**dais
**pulpit
* Rostrum (anatomy), a beak, or anatomical structure resembling a beak, as in the mouthparts of many sucking insects
* Rostrum (ship), a form of bow on naval ships
* Ros ...
of protrogomorph rodents is unmodified and the infraorbital foramen
In human anatomy, the infraorbital foramen is one of two small holes in the skull's upper jawbone (maxillary bone), located below the eye socket and to the left and right of the nose. Both holes are used for blood vessels and nerves. In anatomica ...
is small. The superficial masseter originates on the lateral surface of the anterior maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. T ...
and inserts along the ventral margin of the angular process of the mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
. The lateral masseter inserts here as well and originates from the lateral portion of the zygomatic arch. The small medial masseter originates along the medial surface of the zygomatic arch and inserts along the dorsal portion of the mandible at the end of the tooth row.
Sciuromorphy
Sciuridae
Squirrels are members of the family Sciuridae, a family that includes small or medium-size rodents. The squirrel family includes tree squirrels, ground squirrels (including chipmunks and prairie dogs, among others), and flying squirrels. Squ ...
(suborder Sciuromorpha), and also in members of the Castoridae
The family Castoridae contains the two living species of beavers and their fossil relatives. A highly diverse group of rodents within this family once roamed the earth, but only a single genus is extant today, '' Castor''.
Characteristics
Ca ...
, the Eomyidae
Eomyidae is a family of extinct rodents from North America and Eurasia related to modern day pocket gophers and kangaroo rats. They are known from the Middle Eocene to the Late Miocene in North America and from the Late Eocene to the Pleis ...
, and the Geomyoidea
Geomyoidea is a superfamily of rodent that contains the pocket gophers ( Geomyidae), the kangaroo rats and mice ( Heteromyidae), and their fossil relatives.
Characteristics
Although dissimilar in overall appearance, gophers have been united wit ...
.
Relative to the primitive protrogomorphous condition, the superficial masseter remains unchanged. The lateral masseter has shifted forward and upward, behind and medial to the superficial masseter. Here it originates from a wide zygomatic plate developed on the anterior (maxillary) root of the zygomatic arch. This shift of origin changed the direction of pull of the anterior part of the lateral masseter from 30 to 60 degrees, greatly strengthening the forward component of the masseter contraction.
Hystricomorphy
 This condition is found throughout the suborders
This condition is found throughout the suborders Hystricomorpha
The term Hystricomorpha (from Greek ὕστριξ, ''hystrix'' 'porcupine' and Greek μορφή, ''morphē'' 'form') has had many definitions throughout its history. In the broadest sense, it refers to any rodent (except dipodoids) with a hystr ...
and Anomaluromorpha
Anomaluromorpha is a clade that unites the anomalures, springhares, and zenkerella. It has alternately been designated as either a suborder or infraorder. Most recently, recognized it as one of five suborders of rodents.
Characteristics
...
. In the suborder Myomorpha, it is found in the superfamily Dipodoidea and some fossil Muroidea
The Muroidea are a large superfamily of rodents, including mice, rats, voles, hamsters, lemmings, gerbils, and many other relatives. Although the Muroidea originated in Eurasia, they occupy a vast variety of habitats on every continent excep ...
(such as '' Pappocricetodon''). Hystricomorphy is also found in the African dormouse
A dormouse is a rodent of the family Gliridae (this family is also variously called Myoxidae or Muscardinidae by different taxonomists). Dormice are nocturnal animals found in Africa, Asia, and Europe. They are named for their long, dormant hibe ...
''Graphiurus
The African dormice (genus ''Graphiurus'') are dormice that live throughout sub-Saharan Africa in a variety of habitats. They are very agile climbers and have bushy tails. They eat invertebrates and small vertebrates.
Species
Genus ''Graphiurus' ...
'', which is a member of the suborder Sciuromorpha.
In hystricomorphs the medial masseter is enlarged and originates on the side of the rostrum (in extreme cases as far forward as the premaxilla), where it then passes through a greatly enlarged infraorbital foramen to insert on the mandible. This gives an almost horizontal resultant to the muscle contraction.
Myomorphy
 This condition is found in the
This condition is found in the Muroidea
The Muroidea are a large superfamily of rodents, including mice, rats, voles, hamsters, lemmings, gerbils, and many other relatives. Although the Muroidea originated in Eurasia, they occupy a vast variety of habitats on every continent excep ...
( Myomorpha) and most Gliridae ( Sciuromorpha: in the latter it is often referred to as pseudomyomorphy). suggest that the infraorbital foramen of the extinct sciurid subfamily Cedromurinae may have allowed for the passage of the masseter muscle. If true, this subfamily would represent an additional example of myomorphy in the rodent suborder Sciuromorpha.
Myomorphs combine characteristics found in both the sciuromorphous and hystricomorphous rodents. Both the lateral and medial masseter muscles have migrated, and both a large zygomatic plate as well as a large infraorbital foramen are present. This type gives the greatest anteroposterior component of any rodent zygomasseteric system, which might explain the success of the cosmopolitan Muroidea.
References
{{Reflist Rodent anatomy Skull