San Joaquin and Eastern Railroad on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The San Joaquin & Eastern Railroad (SJ&E) was a standard gauge common carrier railroad that operated in the
 The SJ&E was originally built to get men and supplies to the
The SJ&E was originally built to get men and supplies to the

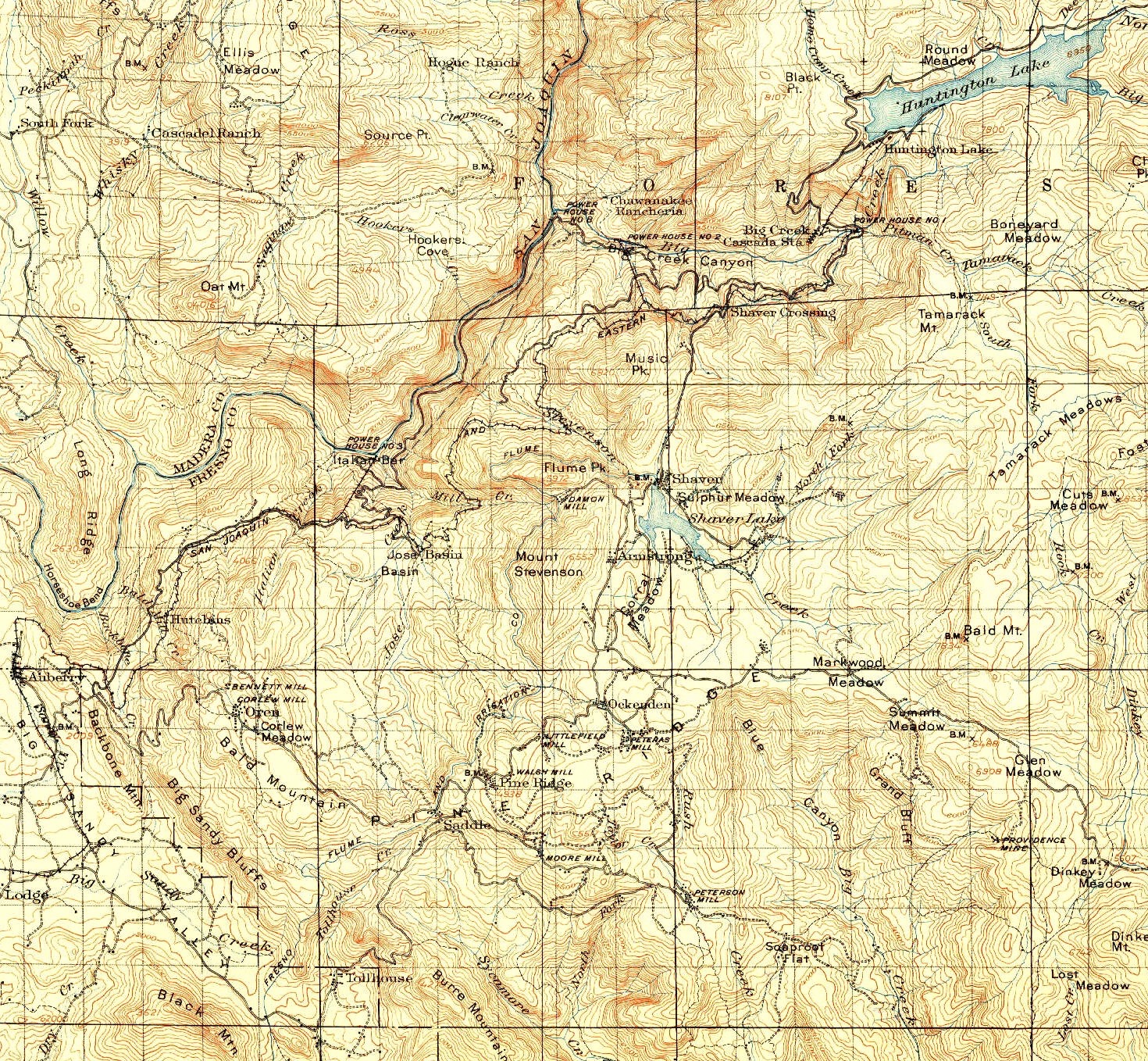 * El Prado MP 0.0 (near Friant) (Interchange with Southern Pacific Railroad)
* McKenzie
* Wellbarn MP 16.1
*
* El Prado MP 0.0 (near Friant) (Interchange with Southern Pacific Railroad)
* McKenzie
* Wellbarn MP 16.1
*
foothills
Foothills or piedmont are geographically defined as gradual increases in elevation at the base of a mountain range, higher hill range or an upland area. They are a transition zone between plains and low relief hills and the adjacent topogr ...
of the Sierra Nevada Mountains of Fresno County
Fresno County (), officially the County of Fresno, is a county located in the central portion of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 Census, the population was 1,008,654. The county seat is Fresno, the fifth-most populous city in Cali ...
in the U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...
of California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
. The line was abandoned in 1933. The railroad hauled primarily lumber and agricultural products.
History
Big Creek Hydroelectric Project
The Big Creek Hydroelectric Project is an extensive hydroelectric power scheme on the upper San Joaquin River system, in the Sierra Nevada of central California. The project is owned and operated by Southern California Edison (SCE). The use and reu ...
sites for the Pacific Light and Power Company (now Southern California Edison
Southern California Edison (or SCE Corp), the largest subsidiary of Edison International, is the primary electricity supply company for much of Southern California. It provides 15 million people with electricity across a service territory of ap ...
). The track was constructed for $1,055,728 by Stone & Webster Construction Company of Boston, the project's primary contractor. Grading commenced on February 16, 1912 and construction was completed on December 15, 1912. The 55 mile line started at El Prado (near Friant where it interchanged with the Southern Pacific Railroad. The SP branch continued on to Fresno where it intercepted the SP Mainline. From El Prado the line went east to Auberry and then terminated at Big Creek (Cascade/Cascada).
The railroad was known as the “crookedest railroad in the world”. The railroad featured 1073 curves up to 60 degrees. The railroad had 43 wooden trestles and 255 steep grades with the steepest at 5.3%.
The railroad was built for the sole reason of building the Big Creek hydroelectric project. When that was essentially complete, the need for the railroad ended. Over the years, it had only earned about 22% of what it cost to build and operate, leading to its nickname "Slow, Jerky, and Expensive. The line was abandoned and dismantled in 1933.
The caption on the picture is incorrect. The SJ&E ended at Big Creek. There was an incline that made it to the site of Huntington Lake for dam construction, but the RR proper never went that far.
Route & Station Stops

 * El Prado MP 0.0 (near Friant) (Interchange with Southern Pacific Railroad)
* McKenzie
* Wellbarn MP 16.1
*
* El Prado MP 0.0 (near Friant) (Interchange with Southern Pacific Railroad)
* McKenzie
* Wellbarn MP 16.1
*Lodge
Lodge is originally a term for a relatively small building, often associated with a larger one.
Lodge or The Lodge may refer to:
Buildings and structures Specific
* The Lodge (Australia), the official Canberra residence of the Prime Ministe ...
* Prather this stop was known as Lodge Station in 1914 it is near where Lodge road is today
* Auberry MP 26.1 the original road bed is 'SJ and E Rd' today
*Indian Mission
The Indian Mission, now the Luckhard Museum, is a historic Native American Christian mission located at 590 East Bay Street in Sebewaing, Michigan. It was built in 1849 and added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1972.
History
John ...
today it is known as Mono Wind
* Hutchens
* Lerona MP 34.9 the original road bed is known as 'Old Railroad Grade Bed Rd' today
*White Pine
''Pinus'', the pines, is a genus of approximately 111 extant tree and shrub species. The genus is currently split into two subgenera: subgenus ''Pinus'' (hard pines), and subgenus ''Strobus'' (soft pines). Each of the subgenera have been further ...
MP 43.0 near Shaver Crossing trestle
* West Portal MP 50.4 (with a 1-mile branch north to Powerhouse 2 on the San Joaquin River
The San Joaquin River (; es, Río San Joaquín) is the longest river of Central California. The long river starts in the high Sierra Nevada, and flows through the rich agricultural region of the northern San Joaquin Valley before reaching Suis ...
)
*Dawn
Dawn is the time that marks the beginning of twilight before sunrise. It is recognized by the appearance of indirect sunlight being scattered in Earth's atmosphere, when the centre of the Sun's disc has reached 18° below the observer's hori ...
Southern California Edison acquired Shaver Lake, and constructed a branch line from this point Shaver to build a new dam. Shaver Lake Railroad
The Shaver Lake Railroad was a standard gauge logging railroad that operated in the Sierra Nevada of Fresno County, California. The line was abandoned in 1927.
History
The Shaver Lake Railroad traces its beginnings to October 31, 1891, when t ...
* Big Creek (Cascada Station) MP 55.6
*Camp 2
*Dam 2 (of Huntington Lake
Huntington Lake is a reservoir in Fresno County, California on Big Creek, located in the Sierra Nevada at an elevation of 7000 ft. The lake receives water from Southern California Edison's Big Creek Hydroelectric Project, as well as the ...
)
Passenger Service
The railroad owned 5 passenger cars and the railroad's October 10, 1915 timetable showed an 8:00 a.m. departure from El Prado, arriving at Cascada at 2:25 p.m. The 55 mile trip operating on Mondays, Wednesdays and Fridays and returns on Tuesdays, Thursdays, and Saturdays. Passenger service continued as late as 1929. Some of the passenger traffic was attributed to tourists going to the resort at Huntington Lake during the summer.US Forest Service Fire Patrol
1913 U.S. Forest Service speeder fire patrol operated along the San Joaquin and Eastern Railroad, California. An auto mounted on car wheels and equipped with fire fighting tools.Locomotives
References
* * * * * * *Notes
{{DEFAULTSORT:San Joaquin Eastern Railroad Defunct California railroads History of the Sierra Nevada (United States) History of the San Joaquin Valley Railway lines opened in 1912 Railway lines closed in 1933 1912 establishments in California