SMS Wittelsbach on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
SMS was the
 On 1 March 1903, she became the flagship of ''KAdm'' Gustav Schmidt (Admiral), Gustav Schmidt, the deputy commander of I Squadron. That year, the squadron was occupied with the normal peacetime routine of individual and unit training, including a training cruise in the Baltic, followed by a voyage to Spain that lasted from 7 May to 10 June. In July, she embarked on the annual cruise to Norway with the rest of the squadron. The autumn maneuvers consisted of a blockade exercise in the
On 1 March 1903, she became the flagship of ''KAdm'' Gustav Schmidt (Admiral), Gustav Schmidt, the deputy commander of I Squadron. That year, the squadron was occupied with the normal peacetime routine of individual and unit training, including a training cruise in the Baltic, followed by a voyage to Spain that lasted from 7 May to 10 June. In July, she embarked on the annual cruise to Norway with the rest of the squadron. The autumn maneuvers consisted of a blockade exercise in the
 The ship participated in the uneventful winter cruise into the Kattegat and Skagerrak from 8 to 16 December. The first quarter of 1907 followed the previous pattern and, on 16 February, the Active Battle Fleet was re-designated the
The ship participated in the uneventful winter cruise into the Kattegat and Skagerrak from 8 to 16 December. The first quarter of 1907 followed the previous pattern and, on 16 February, the Active Battle Fleet was re-designated the
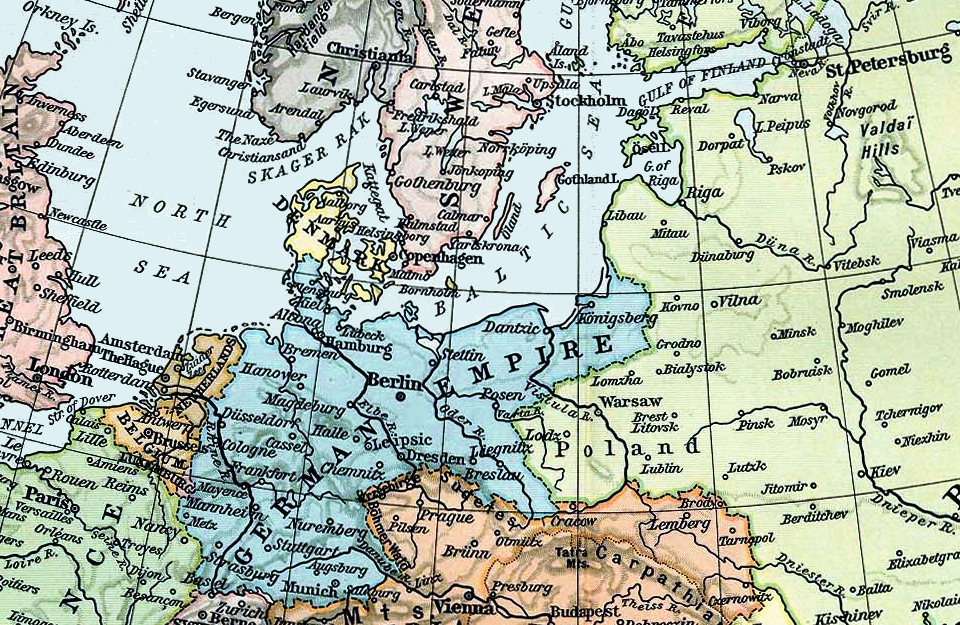 At the start of World War I, was mobilized as part of IV Battle Squadron, under the command of ''VAdm''
At the start of World War I, was mobilized as part of IV Battle Squadron, under the command of ''VAdm''
lead ship
The lead ship, name ship, or class leader is the first of a series or class of ships all constructed according to the same general design. The term is applicable to naval ships and large civilian vessels.
Large ships are very complex and may ...
of the of pre-dreadnought
Pre-dreadnought battleships were sea-going battleships built between the mid- to late- 1880s and 1905, before the launch of in 1906. The pre-dreadnought ships replaced the ironclad battleships of the 1870s and 1880s. Built from steel, protec ...
battleships, built for the Imperial German Navy
The Imperial German Navy or the Imperial Navy () was the navy of the German Empire, which existed between 1871 and 1919. It grew out of the small Prussian Navy (from 1867 the North German Federal Navy), which was mainly for coast defence. Kaise ...
. She was the first capital ship built under the Navy Law of 1898, brought about by Admiral Alfred von Tirpitz
Alfred Peter Friedrich von Tirpitz (19 March 1849 – 6 March 1930) was a German grand admiral, Secretary of State of the German Imperial Naval Office, the powerful administrative branch of the German Imperial Navy from 1897 until 1916. Prussi ...
. was laid down in 1899 at the Wilhelmshaven
Wilhelmshaven (, ''Wilhelm's Harbour''; Northern Low Saxon: ''Willemshaven'') is a coastal town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the western side of the Jade Bight, a bay of the North Sea, and has a population of 76,089. Wilhelmsh ...
Navy Dockyard and completed in October 1902. She was armed with a main battery of four guns and had a top speed of .
The ship served in I Squadron of the German fleet for the majority of her peacetime career, which spanned from 1902 to 1910. During this period, she was occupied with extensive annual training and making good-will visits to foreign countries. The training exercises during this period provided the framework for the High Seas Fleet
The High Seas Fleet (''Hochseeflotte'') was the battle fleet of the German Imperial Navy and saw action during the First World War. The formation was created in February 1907, when the Home Fleet (''Heimatflotte'') was renamed as the High Seas ...
's operations during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. She was decommissioned in September 1910, but was reactivated in 1911 for training ship
A training ship is a ship used to train students as sailors. The term is mostly used to describe ships employed by navies to train future officers. Essentially there are two types: those used for training at sea and old hulks used to house class ...
duties, which lasted through 1914.
After the start of World War I in August 1914, was brought back to active duty in IV Battle Squadron. The ship served in the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
, including during the Battle of the Gulf of Riga
The Battle of the Gulf of Riga was a World War I naval operation of the German High Seas Fleet against the Russian Baltic Fleet in the Gulf of Riga in the Baltic Sea in August 1915. The operation's objective was to destroy the Russian naval for ...
in August 1915, but saw no combat with Russian forces. By late 1915, crew shortages and the threat from British submarines forced the to withdraw older battleships like . The ship then saw service in auxiliary roles, first as a training ship and then as a ship's tender
A ship's tender, usually referred to as a tender, is a boat, or a larger ship, used to service or support other boats or ships. This is generally done by transporting people or supplies to and from shore or another ship.
A second and distinctl ...
. After the war, she was converted into a tender for minesweeper
A minesweeper is a small warship designed to remove or detonate naval mines. Using various mechanisms intended to counter the threat posed by naval mines, minesweepers keep waterways clear for safe shipping.
History
The earliest known usage of ...
s in 1919. In July 1921, the ship was sold and broken up
Ship-breaking (also known as ship recycling, ship demolition, ship dismantling, or ship cracking) is a type of ship disposal involving the breaking up of ships for either a source of Interchangeable parts, parts, which can be sold for re-use, ...
for scrap metal
Scrap consists of recyclable materials, usually metals, left over from product manufacturing and consumption, such as parts of vehicles, building supplies, and surplus materials. Unlike waste, scrap has monetary value, especially recovered me ...
.
Description
After the German (Imperial Navy) ordered the four s in 1889, a combination of budgetary constraints, opposition in the (Imperial Diet), and a lack of a coherent fleet plan delayed the acquisition of further battleships. The Secretary of the (Imperial Navy Office), (''VAdm''—Vice Admiral) Friedrich von Hollmann struggled—ultimately successfully—throughout the early and mid-1890s to secure parliamentary approval for the first three s. In June 1897, Hollmann was replaced by (''KAdm''—Rear Admiral)Alfred von Tirpitz
Alfred Peter Friedrich von Tirpitz (19 March 1849 – 6 March 1930) was a German grand admiral, Secretary of State of the German Imperial Naval Office, the powerful administrative branch of the German Imperial Navy from 1897 until 1916. Prussi ...
, who quickly proposed and secured approval for the first Naval Law in early 1898. The law authorized the last two ships of the class, as well as the five ships of the , the first class of battleship built under Tirpitz's tenure. The s were broadly similar to the s, carrying the same armament but with a more comprehensive armor layout.
was long overall
__NOTOC__
Length overall (LOA, o/a, o.a. or oa) is the maximum length of a vessel's hull measured parallel to the waterline. This length is important while docking the ship. It is the most commonly used way of expressing the size of a ship, an ...
and had a beam
Beam may refer to:
Streams of particles or energy
*Light beam, or beam of light, a directional projection of light energy
**Laser beam
*Particle beam, a stream of charged or neutral particles
**Charged particle beam, a spatially localized grou ...
of and a draft
Draft, The Draft, or Draught may refer to:
Watercraft dimensions
* Draft (hull), the distance from waterline to keel of a vessel
* Draft (sail), degree of curvature in a sail
* Air draft, distance from waterline to the highest point on a vesse ...
of forward. She displaced as designed and up to at full load
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into wei ...
. Unlike her sister ships, was completed with provisions for a squadron commander's staff, including a larger bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually somethi ...
. The ship was propelled by three 3-cylinder vertical triple expansion engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be tr ...
s that drove three screws. Steam was provided by six cylindrical and six water-tube boiler
A high pressure watertube boiler (also spelled water-tube and water tube) is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by the fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-gen ...
s, all coal-fired. s powerplant was rated at , which generated a top speed of . The ship had a cruising radius of at a speed of . She had a crew of 30 officers and 650 enlisted men.
s armament consisted of a main battery
A main battery is the primary weapon or group of weapons around which a warship is designed. As such, a main battery was historically a gun or group of guns, as in the broadsides of cannon on a ship of the line. Later, this came to be turreted ...
of four 24 cm (9.4 in) SK L/40 guns in twin gun turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechani ...
s, one fore and one aft of the central superstructure. Her secondary armament
Secondary armament is a term used to refer to smaller, faster-firing weapons that were typically effective at a shorter range than the main (heavy) weapons on military systems, including battleship- and cruiser-type warships, tanks/armored ...
consisted of eighteen 15 cm (5.9 inch) SK L/40 guns and twelve 8.8 cm (3.45 in) SK L/30 quick-firing guns. The armament suite was rounded out with six torpedo tube
A torpedo tube is a cylindrical device for launching torpedoes.
There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to submarines and some surface ships, and deck-mounted units (also referred to as torpedo launchers) installed aboa ...
s, all in above-water swivel mounts. The ship was protected with Krupp armor
Krupp armour was a type of steel naval armour used in the construction of capital ships starting shortly before the end of the nineteenth century. It was developed by Germany's Krupp Arms Works in 1893 and quickly replaced Harvey armour as the p ...
plate. Her armored belt
Belt armor is a layer of heavy metal vehicle armor, armor plated onto or within the outer hulls of warships, typically on battleships, battlecruisers and cruisers, and aircraft carriers.
The belt armor is designed to prevent projectiles from p ...
was thick in the central citadel
A citadel is the core fortified area of a town or city. It may be a castle, fortress, or fortified center. The term is a diminutive of "city", meaning "little city", because it is a smaller part of the city of which it is the defensive core.
I ...
that protected her magazines
A magazine is a periodical publication, generally published on a regular schedule (often weekly or monthly), containing a variety of content. They are generally financed by advertising, purchase price, prepaid subscriptions, or by a combination ...
and machinery spaces, and the deck was thick. The main battery turrets had of armor plating.
Service history
Construction to 1905
skeel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element on a vessel. On some sailboats, it may have a hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose, as well. As the laying down of the keel is the initial step in the construction of a ship, in Br ...
was laid down
Laying the keel or laying down is the formal recognition of the start of a ship's construction. It is often marked with a ceremony attended by dignitaries from the shipbuilding company and the ultimate owners of the ship.
Keel laying is one o ...
on 30 September 1899 at the ''Kaiserliche Werft'' (Imperial Shipyard) in Wilhelmshaven
Wilhelmshaven (, ''Wilhelm's Harbour''; Northern Low Saxon: ''Willemshaven'') is a coastal town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the western side of the Jade Bight, a bay of the North Sea, and has a population of 76,089. Wilhelmsh ...
, listed under construction number 25. She was ordered under the contract name "C", as a new unit for the fleet. was launched on 3 July 1900, with Kaiser Wilhelm II
, house = Hohenzollern
, father = Frederick III, German Emperor
, mother = Victoria, Princess Royal
, religion = Lutheranism (Prussian United)
, signature = Wilhelm II, German Emperor Signature-.svg
Wilhelm II (Friedrich Wilhelm Viktor ...
in attendance; Rupprecht, Crown Prince of Bavaria
Rupprecht, Crown Prince of Bavaria, Duke of Bavaria, Franconia and in Swabia, Count Palatine by (the) Rhine (''Rupprecht Maria Luitpold Ferdinand''; English: ''Robert Maria Leopold Ferdinand''; 18 May 1869 – 2 August 1955), was the last hei ...
, of the House of Wittelsbach, gave a speech at her launching ceremony. Completion of the ship was delayed due to a collision with the ironclad , which accidentally rammed ''Wittelsbach'' in July 1902 while she was fitting out
Fitting out, or outfitting, is the process in shipbuilding that follows the float-out/launching of a vessel and precedes sea trials. It is the period when all the remaining construction of the ship is completed and readied for delivery to her o ...
. She was commissioned on 15 October 1902, and thereafter began sea trials
A sea trial is the testing phase of a watercraft (including boats, ships, and submarines). It is also referred to as a "shakedown cruise" by many naval personnel. It is usually the last phase of construction and takes place on open water, and i ...
, which were completed in December. After trials ended, was transferred from Wilhelmshaven to Kiel
Kiel () is the capital and most populous city in the northern German state of Schleswig-Holstein, with a population of 246,243 (2021).
Kiel lies approximately north of Hamburg. Due to its geographic location in the southeast of the Jutland ...
in the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
, but she ran aground in the Great Belt
The Great Belt ( da, Storebælt, ) is a strait between the major islands of Zealand (''Sjælland'') and Funen (''Fyn'') in Denmark. It is one of the three Danish Straits.
Effectively dividing Denmark in two, the Belt was served by the Great B ...
in heavy fog on 13 December. The crew attempted to free the ship by removing stores to lighten her, and the battleship and the armored cruiser
The armored cruiser was a type of warship of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was designed like other types of cruisers to operate as a long-range, independent warship, capable of defeating any ship apart from a battleship and fast eno ...
attempted to pull her free without success, before additional tugs and other vessels arrived to pull free on 20 December. After arriving in Kiel, she entered [ for repairs.
 On 1 March 1903, she became the flagship of ''KAdm'' Gustav Schmidt (Admiral), Gustav Schmidt, the deputy commander of I Squadron. That year, the squadron was occupied with the normal peacetime routine of individual and unit training, including a training cruise in the Baltic, followed by a voyage to Spain that lasted from 7 May to 10 June. In July, she embarked on the annual cruise to Norway with the rest of the squadron. The autumn maneuvers consisted of a blockade exercise in the
On 1 March 1903, she became the flagship of ''KAdm'' Gustav Schmidt (Admiral), Gustav Schmidt, the deputy commander of I Squadron. That year, the squadron was occupied with the normal peacetime routine of individual and unit training, including a training cruise in the Baltic, followed by a voyage to Spain that lasted from 7 May to 10 June. In July, she embarked on the annual cruise to Norway with the rest of the squadron. The autumn maneuvers consisted of a blockade exercise in the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
, a cruise of the entire fleet first to Norwegian waters and then to Kiel in early September, and finally a mock attack on Kiel. The exercises concluded on 12 September. The year's training schedule concluded with a cruise into the eastern Baltic that started on 23 November and a cruise into the Skagerrak
The Skagerrak (, , ) is a strait running between the Jutland peninsula of Denmark, the southeast coast of Norway and the west coast of Sweden, connecting the North Sea and the Kattegat sea area through the Danish Straits to the Baltic Sea.
T ...
that began on 1 December. and I Squadron participated in an exercise in the Skagerrak from 11 to 21 January 1904. Further squadron exercises followed from 8 to 17 March, and a major fleet exercise took place in the North Sea in May. In July, I Squadron and I Scouting Group
The I Scouting Group (german: I. Aufklärungsgruppe) was a special reconnaissance unit within the German Kaiserliche Marine. The unit was famously commanded by Admiral Franz von Hipper during World War I. The I Scouting Group was one of the most ...
visited Britain, including a stop at Plymouth on 10 July. The German fleet departed on 13 July, bound for the Netherlands; I Squadron anchored in Vlissingen
Vlissingen (; zea, label= Zeelandic, Vlissienge), historically known in English as Flushing, is a municipality and a city in the southwestern Netherlands on the former island of Walcheren. With its strategic location between the Scheldt river ...
the following day. There, the ships were visited by Queen Wilhelmina. I Squadron remained in Vlissingen until 20 July, when they departed for a cruise in the northern North Sea with the rest of the fleet. The squadron stopped in Molde, Norway, on 29 July, while the other units went to other ports.
The fleet reassembled on 6 August and steamed back to Kiel, where it conducted a mock attack on the harbor on 12 August. During its cruise in the North Sea, the fleet experimented with wireless telegraphy
Wireless telegraphy or radiotelegraphy is transmission of text messages by radio waves, analogous to electrical telegraphy using cables. Before about 1910, the term ''wireless telegraphy'' was also used for other experimental technologies for ...
on a large scale and searchlights at night for communication and recognition signals. Immediately after returning to Kiel, the fleet began preparations for the autumn maneuvers, which began on 29 August in the Baltic. The fleet moved to the North Sea on 3 September, where it took part in a major landing operation
A landing operation is a military
action during which a landing force, usually utilizing landing craft, is transferred to land with the purpose of power projection ashore. With the proliferation of aircraft, a landing may refer to amphibious force ...
, after which the ships took the ground troops from IX Corps 9 Corps, 9th Corps, Ninth Corps, or IX Corps may refer to:
France
* 9th Army Corps (France)
* IX Corps (Grande Armée), a unit of the Imperial French Army during the Napoleonic Wars
Germany
* IX Corps (German Empire), a unit of the Imperial Germ ...
who had participated in the exercises to Altona for a parade for Wilhelm II. The ships then conducted their own parade for the Kaiser off Helgoland
Heligoland (; german: Helgoland, ; Heligolandic Frisian: , , Mooring Frisian: , da, Helgoland) is a small archipelago in the North Sea. A part of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein since 1890, the islands were historically possessions ...
on 6 September. Three days later, the fleet returned to the Baltic via the Kaiser Wilhelm Canal
The Kiel Canal (german: Nord-Ostsee-Kanal, literally "North- oEast alticSea canal", formerly known as the ) is a long freshwater canal in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. The canal was finished in 1895, but later widened, and links the ...
, where it participated in further landing operations with IX Corps and the Guards Corps. On 15 September, the maneuvers came to an end. became the squadron flagship on 1 October, flying the flag of ''KAdm'' Friedrich von Baudissin. I Squadron went on its winter training cruise, this time to the eastern Baltic, from 22 November to 2 December.
1905–1914
took part in a pair of training cruises with I Squadron during 9–19 January and 27 February – 16 March 1905. Individual and squadron training followed, with an emphasis on gunnery drills. On 12 July, the fleet began a major training exercise in the North Sea. The fleet then cruised through theKattegat
The Kattegat (; sv, Kattegatt ) is a sea area bounded by the Jutlandic peninsula in the west, the Danish Straits islands of Denmark and the Baltic Sea to the south and the provinces of Bohuslän, Västergötland, Halland and Skåne in Sweden ...
and stopped in Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan ar ...
and Stockholm. The summer cruise ended on 9 August, though the autumn maneuvers that would normally have begun shortly thereafter were delayed by a visit from the British Channel Fleet that month. The British fleet stopped in Danzig, Swinemünde, and Flensburg, where it was greeted by units of the German Navy; and the main German fleet was anchored at Swinemünde for the occasion. Politically, the visit was strained by the developing Anglo-German naval arms race
The arms race between Great Britain and Germany that occurred from the last decade of the nineteenth century until the advent of World War I in 1914 was one of the intertwined causes of that conflict. While based in a bilateral relationship tha ...
. As a result of the British visit, the 1905 autumn maneuvers were shortened considerably, from 6 to 13 September, and consisted only of exercises in the North Sea. The first exercise presumed a naval blockade in the German Bight, and the second envisioned a hostile fleet attempting to force the defenses of the Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Re ...
. In September, Maximilian von Spee
Maximilian Johannes Maria Hubert Reichsgraf von Spee (22 June 1861 – 8 December 1914) was a naval officer of the German ''Kaiserliche Marine'' (Imperial Navy), who commanded the East Asia Squadron during World War I. Spee entered the navy in ...
, who would go on to command the East Asia Squadron
The German East Asia Squadron (german: Kreuzergeschwader / Ostasiengeschwader) was an Imperial German Navy cruiser squadron which operated mainly in the Pacific Ocean between the mid-1890s until 1914, when it was destroyed at the Battle of the ...
at the outbreak of World War I, took command of the ship.
In October, I Squadron went on a cruise in the Baltic. In early December, I and II Squadrons went on their regular winter cruise—this time to Danzig, where they arrived on 12 December. While on the return trip to Kiel, the fleet conducted tactical exercises. The fleet undertook a heavier training schedule in 1906 than in previous years. The ships were occupied with individual, division and squadron exercises throughout April. Starting on 13 May, major fleet exercises took place in the North Sea and lasted until 8 June with a cruise around the Skagen
Skagen () is Denmark's northernmost town, on the east coast of the Skagen Odde peninsula in the far north of Jutland, part of Frederikshavn Municipality in Nordjylland, north of Frederikshavn and northeast of Aalborg. The Port of Skage ...
into the Baltic. The fleet began its usual summer cruise to Norway in mid-July. The fleet was present for the birthday of Norwegian King Haakon VII
Haakon VII (; born Prince Carl of Denmark; 3 August 187221 September 1957) was the King of Norway from November 1905 until his death in September 1957.
Originally a Danish prince, he was born in Copenhagen as the son of the future Frederick ...
on 3 August. The German ships departed the following day for Helgoland, to join exercises being conducted there. The fleet was back in Kiel by 15 August, where preparations for the autumn maneuvers began. On 22–24 August, the fleet took part in landing exercises in Eckernförde Bay
Eckernförde Bay (german: Eckernförder Bucht; da, Egernførde Fjord or Egernfjord) is a firth and a branch of the Bay of Kiel between the Danish Wahld peninsula in the south and the Schwansen peninsula in the north in the Baltic Sea off the land ...
outside Kiel. The maneuvers were paused from 31 August to 3 September when the fleet hosted vessels from Denmark and Sweden, along with a Russian squadron from 3 to 9 September in Kiel. The maneuvers resumed on 8 September and lasted five more days.
 The ship participated in the uneventful winter cruise into the Kattegat and Skagerrak from 8 to 16 December. The first quarter of 1907 followed the previous pattern and, on 16 February, the Active Battle Fleet was re-designated the
The ship participated in the uneventful winter cruise into the Kattegat and Skagerrak from 8 to 16 December. The first quarter of 1907 followed the previous pattern and, on 16 February, the Active Battle Fleet was re-designated the High Seas Fleet
The High Seas Fleet (''Hochseeflotte'') was the battle fleet of the German Imperial Navy and saw action during the First World War. The formation was created in February 1907, when the Home Fleet (''Heimatflotte'') was renamed as the High Seas ...
. From the end of May to early June the fleet went on its summer cruise in the North Sea, returning to the Baltic via the Kattegat. This was followed by the regular cruise to Norway from 12 July to 10 August. During the autumn maneuvers, which lasted from 26 August to 6 September, the fleet conducted landing exercises in northern Schleswig
The Duchy of Schleswig ( da, Hertugdømmet Slesvig; german: Herzogtum Schleswig; nds, Hartogdom Sleswig; frr, Härtochduum Slaswik) was a duchy in Southern Jutland () covering the area between about 60 km (35 miles) north and 70 km ...
with IX Corps. The winter training cruise went into the Kattegat from 22 to 30 November. In May 1908, the fleet went on a major cruise into the Atlantic instead of its normal voyage in the North Sea, which included a stop in Horta in the Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, map_alt=Location of the Azores within the European Union
, map_caption=Location of the Azores wi ...
. The fleet returned to Kiel on 13 August to prepare for the autumn maneuvers, which lasted from 27 August to 7 September. Division exercises in the Baltic immediately followed from 7 to 13 September. After the end of the maneuvers, was relieved as the squadron flagship by the new battleship and became the flagship of the deputy commander.
was replaced as the deputy command flagship on 20 September 1910, again by , for decommissioning. Her crew was sent to man the newly commissioned dreadnought battleship
The dreadnought (alternatively spelled dreadnaught) was the predominant type of battleship in the early 20th century. The first of the kind, the Royal Navy's , had such an impact when launched in 1906 that similar battleships built after her ...
. After a year in reserve, was reactivated on 16 October 1911 to replace the battleship in the Reserve Division of the North Sea. From 31 March to 28 April 1912, she operated with the Training Squadron, and on 9 May returned to the Reserve Division, this time relieving the battleship . She took part in the annual fleet maneuvers that year as the flagship of III Squadron, then commanded by ''VAdm'' Max Rollmann. returned for another stint in the Training Squadron from 30 March to 21 April 1913. Wilhelm II commissioned a statue of Frithjof that he gave to Norway; was used to transport the statue, departing Kiel on 5 July and arriving in Balholmen two days later. The ship was back in Germany in time for the fleet maneuvers in August, where she was assigned to V Division of III Squadron. After the completion of the maneuvers, she returned to the Reserve Division.
World War I
 At the start of World War I, was mobilized as part of IV Battle Squadron, under the command of ''VAdm''
At the start of World War I, was mobilized as part of IV Battle Squadron, under the command of ''VAdm'' Ehrhard Schmidt
Ehrhard Schmidt (18 May 1863 – 18 July 1946) was an admiral of the ''Kaiserliche Marine'' (Imperial German Navy) during World War I.
Career
At age 15 he entered the navy and saw service at several branches at sea and on land. Among them were ...
; she served as the flagship of the squadron, which also included her four sister ships and the battleships and . On 26 August 1914, the ships were sent to rescue the stranded light cruiser
A light cruiser is a type of small or medium-sized warship. The term is a shortening of the phrase "light armored cruiser", describing a small ship that carried armor in the same way as an armored cruiser: a protective belt and deck. Prior to th ...
, which had run aground off Odensholm
Osmussaar ( sv, Odensholm, german: Odinsholm) is an Estonian island situated in the mouth of the Gulf of Finland in the Baltic Sea, 7.5 km off the Estonian mainland. Administratively the island is part of Lääne-Nigula Parish in Lääne ...
in the eastern Baltic, but by 28 August, the ship's crew had been forced to detonate explosives to destroy before the relief force had arrived. As a result, and the rest of the squadron returned to Bornholm that day. Starting on 3 September, IV Squadron, assisted by the armored cruiser , conducted a sweep into the Baltic. The operation lasted until 9 September and failed to bring Russian naval units to battle.
Two days later the ships were transferred to the North Sea, but stayed there only briefly, returning to the Baltic on 20 September. From 22 to 26 September, the squadron took part in a sweep into the eastern Baltic in an unsuccessful attempt to find and destroy Russian warships. From 4 December 1914 to 2 April 1915, the ships of the IV Squadron were tasked with coastal defense duties along Germany's North Sea coast against incursions from the British Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
. On 3 April, went into drydock in Kiel for periodic maintenance, before conducting training exercises in the western Baltic with the other ships of VII Division of IV Squadron, which included , , and .
The German Army requested naval assistance for its campaign against Russia; Prince Heinrich, the commander of all naval forces in the Baltic, made VII Division, IV Scouting Group, and the torpedo boats of the Baltic fleet available for the operation. On 6 May, the IV Squadron ships were tasked with providing support to the assault on Libau. and the other ships were stationed off Gotland to intercept any Russian cruisers that might attempt to intervene in the landings; the Russians did not do so. After cruisers from IV Scouting Group encountered Russian cruisers off Gotland, the ships of VII Division deployed—with a third dummy funnel
A funnel is a tube or pipe that is wide at the top and narrow at the bottom, used for guiding liquid or powder into a small opening.
Funnels are usually made of stainless steel, aluminium, glass, or plastic. The material used in its construct ...
erected to disguise them as the more powerful s—along with the cruiser . The ships advanced as far as the island of Utö on 9 May and to Kopparstenarna the following day, but by then the Russian cruisers had withdrawn. Later that day, the British submarines and spotted IV Squadron, but were too far away to attack them.
From 27 May to 4 July, was back in the North Sea, patrolling the mouths of the Jade, Ems, and Elbe rivers. During this period, the naval high command realized that the old -class ships would be useless in action against the Royal Navy, but could be effectively used against the much weaker Russian forces in the Baltic. As a result, the battleships were transferred back to the Baltic in July, and they departed Kiel on the 7th, bound for Danzig. On 10 July, the ships proceeded further east to Neufahrwassar, along with the vessels of VIII Torpedo-boat Flotilla; after arriving, ran aground and Schmidt transferred his flag to . She was able to free herself and was not damaged in the incident, and the following day Schmidt returned to the ship. The IV Squadron ships sortied on 12 July to make a demonstration, returning to Danzig on 21 July without encountering Russian forces.
Battle of the Gulf of Riga
The following month, the naval high command began an operation against theGulf of Riga
The Gulf of Riga, Bay of Riga, or Gulf of Livonia ( lv, Rīgas līcis, et, Liivi laht) is a bay of the Baltic Sea between Latvia and Estonia.
The island of Saaremaa (Estonia) partially separates it from the rest of the Baltic Sea. The main c ...
in support of the Gorlice–Tarnów Offensive
The Gorlice–Tarnów offensive during World War I was initially conceived as a minor German offensive to relieve Russian pressure on the Austro-Hungarians to their south on the Eastern Front, but resulted in the Central Powers' chief offensi ...
that the Army was waging. The Baltic naval forces were reinforced with significant elements of the High Seas Fleet, including I Battle Squadron
The I Battle Squadron was a unit of the German Imperial Navy before and during World War I. Being part of the High Seas Fleet, the squadron saw action throughout the war, including the Battle of Jutland on 31 May – 1 June 1916, where it for ...
, I Scouting Group, II Scouting Group
II is the Roman numeral for 2.
II may also refer to:
Biology and medicine
* Image intensifier, medical imaging equipment
* Invariant chain, a polypeptide involved in the formation and transport of MHC class II protein
*Optic nerve, the second ...
, and II Torpedo-boat Flotilla. Prince Heinrich planned that Schmidt's ships would force their way into the Gulf and destroy the Russian warships in Riga, while the heavy units of the High Seas Fleet would patrol to the north to prevent any of the main Russian Baltic Fleet that might try to interfere with the operation. The Germans launched their attack on 8 August, initiating the Battle of the Gulf of Riga
The Battle of the Gulf of Riga was a World War I naval operation of the German High Seas Fleet against the Russian Baltic Fleet in the Gulf of Riga in the Baltic Sea in August 1915. The operation's objective was to destroy the Russian naval for ...
. Minesweeper
A minesweeper is a small warship designed to remove or detonate naval mines. Using various mechanisms intended to counter the threat posed by naval mines, minesweepers keep waterways clear for safe shipping.
History
The earliest known usage of ...
s attempted to clear a path through the Irbe Strait
Irbe Strait, also known as Irben Strait ( et, Kura kurk, lv, Irbes jūras šaurums, liv, Sūr mer), forms the main exit out of the Gulf of Riga to the Baltic Sea, between the Sõrve Peninsula forming the southern end of the island Saaremaa in ...
, covered by and , while and the rest of the squadron remained outside the strait. The Russian battleship attacked the Germans in the strait, forcing them to withdraw.
During the action, the cruiser and the torpedo boat were damaged by mines and the torpedo boats and were mined and sunk. Schmidt withdrew his ships to re-coal and Prince Heinrich debated making another attempt, as by that time it had become clear that the German Army's advance toward Riga had stalled. Prince Heinrich attempted to force the channel a second time using two dreadnought battleships from I Squadron to cover the minesweepers and leaving behind in Libau. Following the unsuccessful second attempt, Schmidt became the I Squadron commander on 26 August, being replaced as the IV Squadron commander by ''VAdm'' Friedrich Schultz, who also made his flagship.
Subsequent activity
On 9 September, and her four sisters sortied in an attempt to locate Russian warships off Gotland, but returned to port two days later without having engaged any opponents. On 7 and 8 October, she, , and four torpedo boats covered a minelaying operation. By this point in the war, the Navy was encountering difficulties in manning more important vessels. The threat from submarines in the Baltic convinced the German navy to withdraw the elderly -class ships from active service. and most of the other IV Squadron ships left Libau on 10 November, bound for Kiel; upon arrival the following day, they were designated the Reserve Division of the Baltic, commanded by (Commodore) Walter Engelhardt. The ships were anchored in Schilksee in Kiel, with as the divisional flagship. On 31 January 1916, the division was dissolved, and the ships were dispersed for subsidiary duties. was decommissioned on 24 August, and was initially used as atraining ship
A training ship is a ship used to train students as sailors. The term is mostly used to describe ships employed by navies to train future officers. Essentially there are two types: those used for training at sea and old hulks used to house class ...
based in Kiel. The ship was then transferred to Wilhelmshaven for use as a fleet tender in October 1917, where she supported the battleship , which was by then being used as a training ship for engine room
On a ship, the engine room (ER) is the compartment where the machinery for marine propulsion is located. To increase a vessel's safety and chances of surviving damage, the machinery necessary for the ship's operation may be segregated into var ...
personnel. On 6 August 1918, the decided to convert into a target ship
A target ship is a vessel — typically an obsolete or captured warship — used as a seaborne target for naval gunnery practice or for weapons testing. Targets may be used with the intention of testing effectiveness of specific types of ammunit ...
, but the war ended with Germany's defeat before the work could begin. was reactivated for service with the newly constituted Reichsmarine
The ''Reichsmarine'' ( en, Realm Navy) was the name of the German Navy during the Weimar Republic and first two years of Nazi Germany. It was the naval branch of the ''Reichswehr'', existing from 1919 to 1935. In 1935, it became known as the '' ...
on 1 June 1919, and was converted into a depot ship
A depot ship is an auxiliary ship used as a mobile or fixed base for submarines, destroyers, minesweepers, fast attack craft, landing craft, or other small ships with similarly limited space for maintenance equipment and crew dining, berthing and ...
for minesweepers. She carried 12 of these shallow-draft vessels. The ship served in this capacity from 20 July 1920 to 8 March 1921. was stricken from the Navy List and sold four months later, on 7 July, for 3,561,000 Marks
Marks may refer to:
Business
* Mark's, a Canadian retail chain
* Marks & Spencer, a British retail chain
* Collective trade marks, trademarks owned by an organisation for the benefit of its members
* Marks & Co, the inspiration for the novel ...
. The ship was then broken up for scrap in Wilhelmshaven.
Notes
Footnotes
Citations
References
* * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Wittelsbach Wittelsbach-class battleships World War I battleships of Germany 1900 ships Ships built in Wilhelmshaven