SBIRS on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Space-Based Infrared System (SBIRS) is a
The Space-Based Infrared System (SBIRS) is a
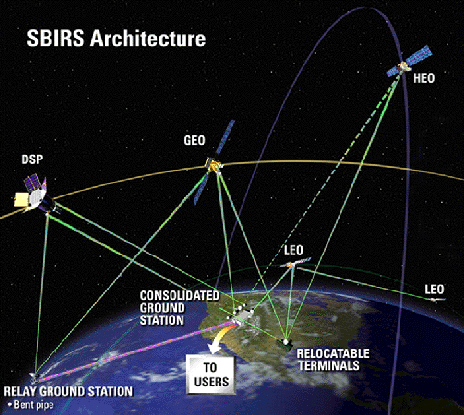
 SBIRS High (also now simply referred to as "SBIRS") is to consist of four dedicated satellites operating in geosynchronous Earth orbit, and sensors on two host satellites operating in a highly elliptical orbit. SBIRS High will replace the
SBIRS High (also now simply referred to as "SBIRS") is to consist of four dedicated satellites operating in geosynchronous Earth orbit, and sensors on two host satellites operating in a highly elliptical orbit. SBIRS High will replace the
 The SBIRS Low contract is now managed by the
The SBIRS Low contract is now managed by the
Space-Based Infrared System Low at Risk of Missing Initial Deployment Date, U.S. General Accounting Office, February 2001Fact Sheets: Space Based Infrared Systems: Space Based Infrared SystemsTactical Ballistic Missile Warning, U.S. Strategic Command
{{Jumpseat Reconnaissance satellites of the United States Missile defense Infrared technology Early warning systems Military space program of the United States Military satellites Equipment of the United States Space Force Early warning satellites Spacecraft launched by Atlas rockets Military equipment introduced in the 2000s
 The Space-Based Infrared System (SBIRS) is a
The Space-Based Infrared System (SBIRS) is a United States Space Force
The United States Space Force (USSF) is the space service branch of the U.S. Armed Forces, one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and the world's only independent space force. Along with its sister branch, the U.S. Air Force, the Space ...
system intended to meet the United States' Department of Defense Department of Defence or Department of Defense may refer to:
Current departments of defence
* Department of Defence (Australia)
* Department of National Defence (Canada)
* Department of Defence (Ireland)
* Department of National Defense (Philipp ...
infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
space surveillance needs through the first two to three decades of the 21st century. The SBIRS program is designed to provide key capabilities in the areas of missile warning, missile defense, battlespace
Battlespace or battle-space is a term used to signify a unified military strategy to integrate and combine armed forces for the military theatre of operations, including air, information, land, sea, cyber and outer space to achieve milit ...
characterization and technical intelligence via satellites in geosynchronous Earth orbit (GEO), sensors hosted on satellites in highly elliptical orbit
A highly elliptical orbit (HEO) is an elliptic orbit with high eccentricity, usually referring to one around Earth.
Examples of inclined HEO orbits include Molniya orbits, named after the Molniya Soviet communication satellites which used them ...
(HEO), and ground-based data processing and control.
A total of twelve satellites carrying SBIRS or STSS payloads had been launched: SBIRS GEO-1 ( USA-230, 2011), SBIRS GEO-2 ( USA-241, 2013), SBIRS GEO-3 ( USA-273, 2017), SBIRS GEO-4 ( USA-282, 2018), SBIRS GEO-5 ( USA-315, 2021), SBIRS GEO-6 ( USA-336, 2022), SBIRS HEO-1 ( USA-184, 2006), SBIRS HEO-2 ( USA-200, 2008), SBIRS HEO-3 ( USA-259, 2014), STSS-ATRR ( USA-205, 2009), STSS Demo 1 ( USA-208, 2009) and STSS Demo 2 ( USA-209, 2009). The manufacturing contract for SBIRS GEO-5 and SBIRS GEO-6 was awarded in 2014. Funding for SBIRS GEO-7 and SBIRS GEO-8 was canceled in 2019.
Background
Based on its experiences with the launching of short-range theater missiles byIraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
during the 1991 Persian Gulf War
The Gulf War was a 1990–1991 armed campaign waged by a Coalition of the Gulf War, 35-country military coalition in response to the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. Spearheaded by the United States, the coalition's efforts against Ba'athist Iraq, ...
, the U.S. Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD or DOD) is an executive branch department of the federal government charged with coordinating and supervising all agencies and functions of the government directly related to national secur ...
(DoD) concluded that expanded theater missile warning capabilities were needed, and it began planning for an improved infrared satellite sensor capability that would support both long-range strategic and short-range theater ballistic missile warning and defense operations. In 1994, DoD studied consolidating various infrared space requirements, such as for ballistic missile warning and defense, technical intelligence, and battlespace characterization, and it selected SBIRS to replace and enhance the capabilities provided by the Defense Support Program
The Defense Support Program (DSP) is a program of the United States Space Force that operated the reconnaissance satellites which form the principal component of the ''Satellite Early Warning System'' used by the United States.
DSP satellite ...
(DSP). DSP satellites are built with infrared detectors that can sense missile plumes, and have been providing early warning for long-range ballistic missile launches for over 30 years. DoD had previously attempted to replace DSP with:
*the Advanced Warning System in the early 1980s
*the Boost Surveillance and Tracking System in the late 1980s
*the Follow-on Early Warning System in the early 1990s
According to the Government Accountability Office (GAO), these attempts failed due to immature technology, high cost, and affordability issues. SBIRS is to use more sophisticated infrared technologies than the DSP to enhance the detection of strategic and theater ballistic missile launches and the performance of the missile-tracking function.
The original contract consisted of 2 SBIRS HEO satellite sensors and 2-3 SBIRS GEO sensors (and satellites) with an option to buy a total of 5 GEOs. A complement of satellites in low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never mor ...
(LEO) was planned as part of the program (SBIRS-Low), but this has been moved into the Space Tracking and Surveillance System
The Space Tracking and Surveillance System (STSS) (formerly SBIRS-Low) was a pair of satellites developed by the United States Missile Defense Agency (MDA) to research the space-based detection and tracking of ballistic missiles. Data from STSS ...
(STSS) program.
SBIRS continues to struggle with cost overruns, with Nunn-McCurdy breaches occurring in 2001 and 2005. By September 2007, the expected project cost had increased to US$10.4 billion. In December 2005, following the third SBIRS Nunn-McCurdy violation, the government decided to compete SBIRS GEO-4 and SBIRS GEO-5, with an option to buy the SBIRS GEO-3 contingent based on the performance of the first two.
On 2 June 2009, Lockheed Martin announced it had been awarded a contract for the third SBIRS HEO payload and the third SBIRS GEO satellite, and for associated ground equipment modifications. On 10 July 2009, Lockheed Martin was awarded US$262.5 million as down payment by the USAF towards the purchase of a fourth satellite. The first SBIRS GEO satellite of the SBIRS program, SBIRS GEO-1, was successfully launched from Cape Canaveral on an Atlas V
Atlas V is an expendable launch system and the fifth major version in the Atlas launch vehicle family. It was originally designed by Lockheed Martin, now being operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA), a joint venture between Lockheed Mart ...
launch vehicle on 7 May 2011. In June 2014, Lockheed Martin was contracted by the USAF
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Aerial warfare, air military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part ...
to build SBIRS GEO-5 and SBIRS GEO-6, at a cost of US$1.86 billion.
The FY 2021 budget allocates US$2.5 billion to SBIRS for the United States Space Force
The United States Space Force (USSF) is the space service branch of the U.S. Armed Forces, one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and the world's only independent space force. Along with its sister branch, the U.S. Air Force, the Space ...
.
SBIRS High
 SBIRS High (also now simply referred to as "SBIRS") is to consist of four dedicated satellites operating in geosynchronous Earth orbit, and sensors on two host satellites operating in a highly elliptical orbit. SBIRS High will replace the
SBIRS High (also now simply referred to as "SBIRS") is to consist of four dedicated satellites operating in geosynchronous Earth orbit, and sensors on two host satellites operating in a highly elliptical orbit. SBIRS High will replace the Defense Support Program
The Defense Support Program (DSP) is a program of the United States Space Force that operated the reconnaissance satellites which form the principal component of the ''Satellite Early Warning System'' used by the United States.
DSP satellite ...
(DSP) satellites and is intended primarily to provide enhanced strategic and theater ballistic missile warning capabilities. SBIRS High GEO 1 was launched on 7 May 2011. Two SBIRS sensors hosted on two classified satellites in highly elliptical orbit have already been launched, probably as part of the NROL-22 (USA 184) and NROL-28 (USA 200) launches in 2006 and 2008. USA 184 and USA 200 are believed by analysts to be ELINT
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is intelligence-gathering by interception of '' signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly used in communication ...
satellites in the family of JUMPSEAT
In aviation, a jump seat or jumpseat is an auxiliary seat for individuals—other than normal passengers—who are not operating the aircraft. In general, the term 'jump seat' can also refer to a seat in any type of vehicle which can fold up out ...
and TRUMPET
The trumpet is a brass instrument commonly used in classical and jazz ensembles. The trumpet group ranges from the piccolo trumpet—with the highest register in the brass family—to the bass trumpet, pitched one octave below the standard ...
; TRUMPET has been reported to have carried an infrared sensor called HERITAGE
Heritage may refer to:
History and society
* A heritage asset is a preexisting thing of value today
** Cultural heritage is created by humans
** Natural heritage is not
* Heritage language
Biology
* Heredity, biological inheritance of physica ...
.
The prime contractor for SBIRS is Lockheed Martin, with Northrop Grumman
Northrop Grumman Corporation is an American multinational aerospace and defense technology company. With 90,000 employees and an annual revenue in excess of $30 billion, it is one of the world's largest weapons manufacturers and military techn ...
as the major subcontractor. Lockheed Martin also provides the satellite for SBIRS GEO. The system's expected deployment was delayed from December 2009 to 2011 because of problems with Lockheed's workmanship on system components, including unresolved software malfunctions and several broken solder joints in a subcontract procured gyroscope assembly on the first spacecraft being built.
It was feared that a further launch postponement into late 2011 would lead to conflict with the planned launches of NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
's Juno
Juno commonly refers to:
*Juno (mythology), the Roman goddess of marriage and queen of the gods
*Juno (film), ''Juno'' (film), 2007
Juno may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Fictional characters
*Juno, in the film ''Jenny, Juno''
*Ju ...
spacecraft and Mars Science Laboratory
Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) is a robotic space probe mission to Mars launched by NASA on November 26, 2011, which successfully landed ''Curiosity'', a Mars rover, in Gale Crater on August 6, 2012. The overall objectives include investigati ...
, which would all use the same launch facility. However, the first GEO launch, SBIRS GEO-1, was successfully conducted on 7 May 2011.
According to a Reuters report, the first two SBIRS GEO satellites started operations in 2013. SBIRS GEO-3 launched on 20 January 2017, and SBIRS GEO-4 was successfully deployed on 20 January 2018. In 2017, the United States Air Force requested US$1.4 billion in Fiscal Year 2018 for SBIRS, and funds for advance procurement of SBIRS 7 and 8. While US$643 million in funding was provided for SBIRS in Fiscal Year 2019, funding for SBIRS 7 and 8 was eliminated in favor of a new program, NG-OPIR (Next Generation Overhead Persistent Infrared). Plans remained to launch SBIRS GEO-5 in 2021 and SBIRS GEO-6 in 2022. SBIRS GEO-5 was successfully launched on 18 May 2021, while SBIRS GEO-6 was successfully launched on 4 August 2022.
SBIRS Low (Space Tracking and Surveillance System)
 The SBIRS Low contract is now managed by the
The SBIRS Low contract is now managed by the Missile Defense Agency
The Missile Defense Agency (MDA) is the section of the United States government's Department of Defense responsible for developing a layered defense against ballistic missiles. It had its origins in the Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI) which w ...
(MDA) and has been renamed the Space Tracking and Surveillance System
The Space Tracking and Surveillance System (STSS) (formerly SBIRS-Low) was a pair of satellites developed by the United States Missile Defense Agency (MDA) to research the space-based detection and tracking of ballistic missiles. Data from STSS ...
(STSS).
Original SBIRS Low
The SBIRS Low program was originally expected to consist of about 24 satellites in low Earth orbit. The primary purpose of SBIRS Low was the tracking of ballistic missiles; with discrimination between warheads and other objects, such as decoys, that separate from the missile bodies throughout the middle portion of their flights. The system was to have two major sensors, coordinated by an on-board computer: *a scanning infrared sensor, designed to acquire ballistic missiles in the early stages of flight, and *a tracking infrared sensor, designed to follow missiles, warheads, and other objects such as debris and decoys during the middle and later stages of flight. The tracking sensor would be cooled to very low temperatures. SBIRS Low's original deployment schedule was 2010, the date when its capabilities were said to be needed by the National Missile Defense System.Space Tracking and Surveillance System
In 2001, the Missile Defense Agency assessed the programs needed for a national ballistic missile defense system (BMDS) and found that they were lacking in the relatively new arena of space. The MDA decided to absorb the SBIRS Low constellation in its very early stages of development and renamed the program theSpace Tracking and Surveillance System
The Space Tracking and Surveillance System (STSS) (formerly SBIRS-Low) was a pair of satellites developed by the United States Missile Defense Agency (MDA) to research the space-based detection and tracking of ballistic missiles. Data from STSS ...
(STSS). This transition changed the direction of the program somewhat, but the overall mission remained the same — detection and tracking of ballistic missiles through all phases of flight.
References
External links
Space-Based Infrared System Low at Risk of Missing Initial Deployment Date, U.S. General Accounting Office, February 2001
{{Jumpseat Reconnaissance satellites of the United States Missile defense Infrared technology Early warning systems Military space program of the United States Military satellites Equipment of the United States Space Force Early warning satellites Spacecraft launched by Atlas rockets Military equipment introduced in the 2000s