Russian language in Ukraine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The 19th century saw a dramatic increase in the urban Russian population in present-day Ukraine, as ethnic Russian settlers moved into and populated the newly industrialised and growing towns. At the beginning of the 20th century the Russians formed the largest ethnic group in almost all large cities within Ukraine's modern borders, including
The 19th century saw a dramatic increase in the urban Russian population in present-day Ukraine, as ethnic Russian settlers moved into and populated the newly industrialised and growing towns. At the beginning of the 20th century the Russians formed the largest ethnic group in almost all large cities within Ukraine's modern borders, including
, від 05.09.2017 № 2145-VIII (Сторінка 1 з 7) The law does state that persons belonging to the indigenous peoples of Ukraine are guaranteed the right to study at public pre-school institutes and primary schools in "the language of instruction of the respective indigenous people, along with the state language of instruction" in separate classes or groups. The

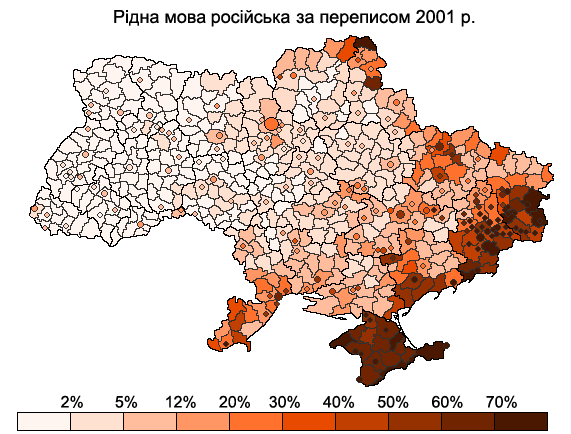 There is a large difference between the numbers of people whose native language is Russian and people who adopted Russian as their everyday communication language. Another thing to keep in mind is that the percentage of Russian-speaking citizens is significantly higher in cities than in rural areas across the whole country.
There is a large difference between the numbers of people whose native language is Russian and people who adopted Russian as their everyday communication language. Another thing to keep in mind is that the percentage of Russian-speaking citizens is significantly higher in cities than in rural areas across the whole country.
,
 The Russian language in Ukraine is recognized (along with all other languages) as the "language of a national minority". Ukrainian is the only state language; every other language is declared to be the "language of a national minority" in the
The Russian language in Ukraine is recognized (along with all other languages) as the "language of a national minority". Ukrainian is the only state language; every other language is declared to be the "language of a national minority" in the
of the Constitution says: "The state language of Ukraine is the Ukrainian language. The State ensures the comprehensive development and functioning of the Ukrainian language in all spheres of social life throughout the entire territory of Ukraine. In Ukraine, the free development, use and protection of Russian, and other languages of national minorities of Ukraine, is guaranteed." The Constitution declares Ukrainian language as the state language of the country, while other languages spoken in Ukraine are guaranteed constitutional protection, but are not in practice protected from book bans. The Ukrainian language was adopted as the state language by the Law on Languages adopted in
(in English) Ukraine signed the European Charter on Regional or Minority Languages in 1996, but it was only partially ratified, and only in 2002 by the
. Retrieved 2012-09-07. Russian was within weeks declared as a regional language in several southern and eastern oblasts and cities. On 23 February 2014, a bill repealing the law was approved by 232 deputies out of 450 but not signed into law by acting-president
,
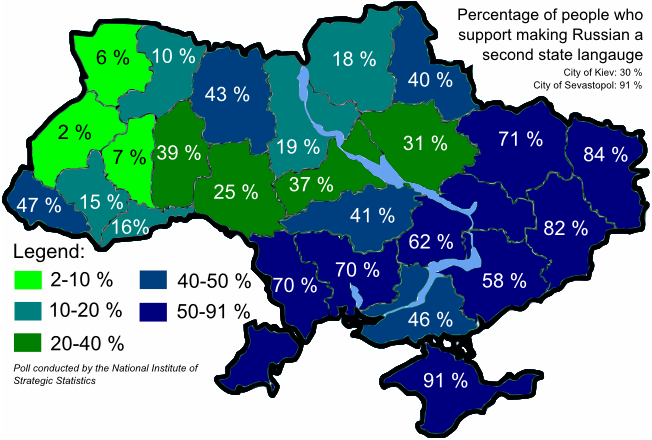
 According to a survey by the Research and Branding Group (June 2006), the majority of respondents supported the decisions of local authorities: 52% largely supported (including 69% of population of eastern oblasts and 56% of southern regions), 34% largely did not support the decisions, 9% – answered "partially support and partially not", 5% had no opinion. According to an all-Ukrainian poll carried out in February 2008 by "Ukrainian Democratic Circle" 15% of those polled said that the language issue should be immediately solved, in November 2009 this was 14.7%; in the November 2009 poll 35.8% wanted both the Russian and Ukrainian language to be state languages.
According to polling by
According to a survey by the Research and Branding Group (June 2006), the majority of respondents supported the decisions of local authorities: 52% largely supported (including 69% of population of eastern oblasts and 56% of southern regions), 34% largely did not support the decisions, 9% – answered "partially support and partially not", 5% had no opinion. According to an all-Ukrainian poll carried out in February 2008 by "Ukrainian Democratic Circle" 15% of those polled said that the language issue should be immediately solved, in November 2009 this was 14.7%; in the November 2009 poll 35.8% wanted both the Russian and Ukrainian language to be state languages.
According to polling by
 Historically, many famous writers of Russian literature were born and lived in Ukraine. Nikolai Gogol is probably the most famous example of shared Russo-Ukrainian heritage: Ukrainian by descent, he wrote in Russian, and significantly contributed to culture of both nations. Russian author Mikhail Bulgakov was born in
Historically, many famous writers of Russian literature were born and lived in Ukraine. Nikolai Gogol is probably the most famous example of shared Russo-Ukrainian heritage: Ukrainian by descent, he wrote in Russian, and significantly contributed to culture of both nations. Russian author Mikhail Bulgakov was born in
Mova i Natsiya
'', Drohobych, Vidrodzhennya, 1994, "the number of Ukrainian secondary schools has increased to 15,900, or 75% of their total number. In all, about 4.5 million students (67.4% of the total) are taught in Ukrainian, in Russian – 2.1 million (31.7%)..."
'
'' Volodymyr Malynkovych, ttp://www.igpi.ru/info/people/malink/1139380574.html Ukrainian perspective, Politicheskiy Klass, January 2006 but still higher than the proportion of ethnic Russians. The ''Law on Education'' formerly granted Ukrainian families (parents and their children) a right to choose their native language for schools and studies.Ukraine/ Compendium of Cultural Policies and Trends in Europe, 10th edition
, Council of Europe (2009) This was changed by a new law in 2017 that only allows the use of Ukrainian in secondary schools and higher.
Constitutional Court rules Russian, other languages can be used in Ukrainian courts
,
З подачі "Регіонів" Рада дозволила російську у судах
,
ЗМІ: Російська мова стала офіційною в українських судах
,
Російська мова стала офіційною в українських судах
, forUm (29 July 2010)

Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
is the most common first language
A first language, native tongue, native language, mother tongue or L1 is the first language or dialect that a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongu ...
in the Donbas and Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
regions of Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
and the city of Kharkiv
Kharkiv ( uk, wikt:Харків, Ха́рків, ), also known as Kharkov (russian: Харькoв, ), is the second-largest List of cities in Ukraine, city and List of hromadas of Ukraine, municipality in Ukraine.eastern
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
*Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
*Eastern Air Li ...
and southern portions of the country. The usage and status of the language is the subject of political disputes. Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
is the country's only state language since the adoption of the 1996 Constitution, which prohibits an official bilingual system at state level but also guarantees the free development, use and protection of Russian and other languages of national minorities. In 2017 a new ''Law on Education'' was passed which restricted the use of Russian as a language of instruction. Nevertheless, Russian remains a widely used language in Ukraine in pop culture and in informal and business communication.
History of Russian language in Ukraine
The East Slavic languages originated in the language spoken in Rus in themedieval period
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
. Significant differences in spoken language in different regions began after the division of the Rus lands between the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragme ...
(from about 1240) and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lit ...
. The Lithuanian state eventually allied with the Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Królestwo Polskie; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a state in Central Europe. It may refer to:
Historical political entities
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom existing from 1025 to 1031
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom exi ...
in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
of 1569–1795. Muscovites under the Golden Horde developed what became the modern Russian language; people in the northern Lithuanian sector developed Belorussian, and in the southern (Polish) sector Ukrainian.
The ethnonym "Ukrainian" for the south-eastern Slavic people did not become well-established until the 19th century, although English-speakers (for example) called those peoples' land "Ukraine" in English from before the 18th century (the Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the first and foundational historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP). It traces the historical development of the English language, providing a co ...
traces the word "Ukrainian" in English back as far as 1804, and records its application to the Ukrainian language from 1886). The western part of the country, historically corresponding to former Austrian Galicia
The Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria,, ; pl, Królestwo Galicji i Lodomerii, ; uk, Королівство Галичини та Володимирії, Korolivstvo Halychyny ta Volodymyrii; la, Rēgnum Galiciae et Lodomeriae also known as ...
, Bukovina and Hungarian Transcarpathia, was generally known in German, French and English as " Ruthenia", and the people as "Ruthenians." The Russian imperial centre, however, preferred the names "Little" and "White" Russias for the Ukrainian and Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
ian lands respectively, as distinct from Great Russia
Great Russia, sometimes Great Rus' (russian: Великая Русь, , , , , ), is a name formerly applied to the territories of "Russia proper", the land that formed the core of Muscovy and later Russia. This was the land to which the et ...
.
No definitive geographical border separated people speaking Russian and those speaking Ukrainian – rather gradual shifts in vocabulary and pronunciation marked the areas between the historical cores of the languages. Since the 20th century, however, people have started to identify themselves with their spoken vernacular and to conform to the literary norms set by academics.
Although the ancestors of a small ethnic group of Russians – Goriuns
Goryuns, also Horiuns or Horyuny ( uk, горюни), a little-documented ethnic group of East Slavs, live around Putyvl, now in the Sumy Oblast of north-eastern Ukraine, in the past in Kursk Governorate of the Russian Empire. The dialect of the ...
resided in the Putyvl
Putyvl′Frank SysynBetween Poland and the Ukraine: The Dilemma of Adam Kysil, 1600-1653 - P. 25. (, ) or Putivl′ ( rus, Пути́вль, p=pʊˈtʲivlʲ) is a city in north-east Ukraine, in Sumy Oblast. The city served as the administrative c ...
region (in present-day northern Ukraine)
in the times of Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lit ...
or perhaps even earlier,F.D. Klimchuk, About ethnolinguistic history of Left Bank of Dnieper (in connection to the ethnogenesis of Goriuns). Published in "Goriuns: history, language, culture", Proceedings of International Scientific Conference, (Institute of Linguistics, Russian Academy of Sciences, February 13, 2004) the Russian language in Ukraine has primarily come to exist in that country through two channels: through the migration of ethnic Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
into Ukraine and through the adoption of the Russian language by Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Ort ...
.
Russian settlers
The first new waves of Russian settlers onto what is now Ukrainian territory came in the late-16th century to the empty lands ofSlobozhanshchyna
Sloboda Ukraine (literally: Borderland of free frontier guards; uk, Слобідська Україна, Slobidska Ukraina), or Slobozhanshchyna ( uk, Слобожанщина, Slobozhanshchyna, ), is a historical region, now located in Northeas ...
(in the region of Kharkiv
Kharkiv ( uk, wikt:Харків, Ха́рків, ), also known as Kharkov (russian: Харькoв, ), is the second-largest List of cities in Ukraine, city and List of hromadas of Ukraine, municipality in Ukraine.Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
had gained from the Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
, or from the Grand Duchy of Lithuania - although Ukrainian peasants from the Polish-Lithuanian west escaping harsh exploitative conditions outnumbered them.
More Russian speakers appeared in the northern, central and eastern territories of modern Ukraine during the late-17th century, following the Cossack Rebellion (1648–1657) which Bohdan Khmelnytsky led against Poland. The Khmelnytsky Uprising led to a massive movement of Ukrainian settlers to the Slobozhanshchyna region, which converted it from a sparsely inhabited frontier area to one of the major populated regions of the in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I ...
. Following the Pereyaslav Rada of 1654 the northern and eastern parts of present-day Ukraine came under the hegemony of the Russian Tsardom. This brought the first significant, but still small, wave of Russian settlers into central Ukraine (primarily several thousand soldiers stationed in garrisons, out of a population of approximately 1.2 million non-Russians). Although the number of Russian settlers in Ukraine prior to the 18th century remained small, the local upper-classes within the part of Ukraine acquired by Russia came to use the Russian language widely.
Beginning in the late 18th century, large numbers of Russians (as well as of Armenians, Bulgarians, Greeks and of other christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
and Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, who fled the Ottoman Emprire) settled in newly acquired lands in what is now southern Ukraine, a region then known as Novorossiya
Novorossiya, literally "New Russia", is a historical name, used during the era of the Russian Empire for an administrative area that would later become the southern mainland of Ukraine: the region immediately north of the Black Sea and Crimea. ...
("New Russia"). These lands – previously known as the Wild Fields
The Wild Fields ( uk, Дике Поле, translit=Dyke Pole, russian: Дикое Поле, translit=Dikoye Polye, pl, Dzikie pola, lt, Dykra, la, Loca deserta or , also translated as "the wilderness") is a historical term used in the Polish ...
– had been sparsely populated prior to the 18th century due to the threat of Crimean-Tatar raids, but once Saint Petersburg had eliminated the Tatar state as a threat, Russian nobles were granted large tracts of fertile land for working by newly arrived peasants, most of them ethnic Ukrainians but many of them Russians.
Dramatic increase of Russian settlers
 The 19th century saw a dramatic increase in the urban Russian population in present-day Ukraine, as ethnic Russian settlers moved into and populated the newly industrialised and growing towns. At the beginning of the 20th century the Russians formed the largest ethnic group in almost all large cities within Ukraine's modern borders, including
The 19th century saw a dramatic increase in the urban Russian population in present-day Ukraine, as ethnic Russian settlers moved into and populated the newly industrialised and growing towns. At the beginning of the 20th century the Russians formed the largest ethnic group in almost all large cities within Ukraine's modern borders, including Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Kyi ...
(54.2%), Kharkiv (63.1%), Odessa (49.09%), Mykolaiv
Mykolaiv ( uk, Миколаїв, ) is a city and municipality in Southern Ukraine, the administrative center of the Mykolaiv Oblast. Mykolaiv city, which provides Ukraine with access to the Black Sea, is the location of the most downriver brid ...
(66.33%), Mariupol
Mariupol (, ; uk, Маріу́поль ; russian: Мариу́поль) is a city in Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine. It is situated on the northern coast ( Pryazovia) of the Sea of Azov, at the mouth of the Kalmius River. Prior to the 2022 Russia ...
(63.22%), Luhansk
Luhansk (, ; uk, Луганськ, ), also known as Lugansk (, ; russian: Луганск, ), is a city in what is internationally recognised as Ukraine, although it is administered by Russia as capital of the Luhansk People's Republic (LPR). A ...
, (68.16%), Kherson (47.21%), Melitopol (42.8%), Ekaterinoslav
Dnipro, previously called Dnipropetrovsk from 1926 until May 2016, is Ukraine's fourth-largest city, with about one million inhabitants. It is located in the eastern part of Ukraine, southeast of the Ukrainian capital Kyiv on the Dnieper Rive ...
, (41.78%), Kropyvnytskyi
Kropyvnytskyi ( uk, Кропивницький, Kropyvnytskyi ) is a city in central Ukraine on the Inhul river with a population of . It is an administrative center of the Kirovohrad Oblast.
Over its history, Kropyvnytskyi has changed its nam ...
(34.64%), Simferopol
Simferopol () is the second-largest city in the Crimean Peninsula. The city, along with the rest of Crimea, is internationally recognised as part of Ukraine, and is considered the capital of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea. However, it is ...
(45.64%), Yalta
Yalta (: Я́лта) is a resort city on the south coast of the Crimean Peninsula surrounded by the Black Sea. It serves as the administrative center of Yalta Municipality, one of the regions within Crimea. Yalta, along with the rest of Cri ...
(66.17%), Kerch
Kerch ( uk, Керч; russian: Керчь, ; Old East Slavic: Кърчевъ; Ancient Greek: , ''Pantikápaion''; Medieval Greek: ''Bosporos''; crh, , ; tr, Kerç) is a city of regional significance on the Kerch Peninsula in the east of t ...
(57.8%), Sevastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
(63.46%).Дністрянський М.С. Етнополітична географія України. Лівів Літопис, видавництво ЛНУ імені Івана Франка, 2006, page 342 The Ukrainian migrants who settled in these cities entered a Russian-speaking milieu (particularly with Russian-speaking administration) and needed to adopt the Russian language.
Suppression and fostering of the Ukrainian language
TheRussian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
promoted the spread of the Russian language among the native Ukrainian population, actively refusing to acknowledge the existence of a Ukrainian language.
Alarmed by the threat of Ukrainian separatism (in its turn influenced by the 1863 demands of Polish nationalists), the Russian Minister of Internal Affairs Pyotr Valuev
Count Pyotr Aleksandrovich ValuevAlso transliterated Peter Alexandrovich Valuyev. ( rus, Граф Пётр Алекса́ндрович Валу́ев; September 22, 1815 – January 27, 1890) was a Russian statesman and writer.
Life
Valuev ...
in 1863 issued a secret decree that banned the publication of religious texts and educational texts written in the Ukrainian language as non-grammatical, but allowed all other texts, including fiction. The Emperor Alexander II in 1876 expanded this ban by issuing the Ems Ukaz
The Ems Ukaz or Ems Ukase (russian: Эмский указ, Emskiy ukaz; uk, Емський указ, Ems’kyy ukaz), was a secret decree (''ukaz'') of Emperor Alexander II of Russia issued on May 18, 1876, banning the use of the Ukrainian lang ...
(which lapsed in 1905). The Ukaz banned all Ukrainian-language books and song-lyrics, as well as the importation of such works. Furthermore, Ukrainian-language public performances, plays, and lectures were forbidden. In 1881 the decree was amended to allow the publishing of lyrics and dictionaries, and the performances of some plays in the Ukrainian language with local officials' approval. Ukrainian-only troupes were, however, forbidden. Approximately 9% of the population spoke Russian at the time of the Russian Empire Census of 1897. as opposed to 44.31% of the total population of the Empire.
In 1918 the Soviet Council of People's Commissars
The Councils of People's Commissars (SNK; russian: Совет народных комиссаров (СНК), ''Sovet narodnykh kommissarov''), commonly known as the ''Sovnarkom'' (Совнарком), were the highest executive authorities of ...
decreed that nationalities under their control had the right to education in their own language.
Thus Ukrainians in the Soviet era
The history of Soviet Russia and the Soviet Union (USSR) reflects a period of change for both Russia and the world. Though the terms "Soviet Russia" and "Soviet Union" often are synonymous in everyday speech (either acknowledging the dominance ...
were entitled to study and learn in the Ukrainian language. During the Soviet times, the attitude to Ukrainian language and culture went through periods of promotion (policy of " korenization", to ), suppression (during the subsequent period of Stalinism), and renewed Ukrainization
Ukrainization (also spelled Ukrainisation), sometimes referred to as Ukrainianization (or Ukrainianisation) is a policy or practice of increasing the usage and facilitating the development of the Ukrainian language and promoting other elements of ...
(notably in the epoch of Khrushchev, to 1964). Ukrainian cultural organizations, such as theatres or the Writers' Union, were funded by the central administration. While officially there was no state language
An official language is a language given supreme status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically the term "official language" does not refer to the language used by a people or country, but by its government (e.g. judiciary, ...
in the Soviet Union until 1990, Russian in practice had an implicitly privileged position as the only language widely spoken across the country. In 1990 Russian became legally the official all-Union language of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, with constituent republics having rights to declare their own official languages. The Ukrainian language, despite official encouragement and government funding, like other regional languages, was often frowned upon or quietly discouraged, which led to a gradual decline in its usage.
Ukrainization in modern Ukraine
Since the Euromaidan of 2013–2014, the Ukrainian government has issued several laws aimed at encouraging Ukrainization in the media, in education and in other spheres. In February 2017, the Ukrainian government banned the commercial importation of books from Russia, which had accounted for up to 60% of all titles sold in Ukraine. On May 23, 2017, the Ukrainian parliament approved the law that most broadcast content should be in Ukrainian (75% of national carriers and 50% of local carriers). The 2017 law on education provides that Ukrainian language is the language of education at all levels except for one or more subjects that are allowed to be taught in two or more languages, namelyEnglish
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
or one of the other official languages of the European Union
The European Union (EU) has 24 official languages, of which threeEnglish, French and Germanhave the higher status of "procedural" languages of the European Commission (whereas the European Parliament accepts all official languages as working la ...
(i.e. excluding Russian).Про освіту, від 05.09.2017 № 2145-VIII (Сторінка 1 з 7) The law does state that persons belonging to the indigenous peoples of Ukraine are guaranteed the right to study at public pre-school institutes and primary schools in "the language of instruction of the respective indigenous people, along with the state language of instruction" in separate classes or groups. The
Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe
The Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe (PACE) is the parliamentary arm of the Council of Europe, a 46-nation international organisation dedicated to upholding human rights, democracy and the rule of law.
The Assembly is made up ...
(PACE) has expressed concern with this measure and with the lack of "real consultation" with the representatives of national minorities. In July 2018, The Mykolaiv
Mykolaiv ( uk, Миколаїв, ) is a city and municipality in Southern Ukraine, the administrative center of the Mykolaiv Oblast. Mykolaiv city, which provides Ukraine with access to the Black Sea, is the location of the most downriver brid ...
Okrug
An ''okrug, ; russian: о́круг, ókrug; sr, округ, okrug, ; uk, о́круг, о́kruh; be, акруга, akruha; pl, okręg; ab, оқрҿс; mhr, йырвел, '' is a type of administrative division in some Slavic states. Th ...
Administrative Court liquidated the status of Russian as a regional language, on the suit (bringing to the norms of the national legislation due to the recognition of the law "On the principles of the state language policy" by the Constitutional Court of Ukraine
The Constitutional Court of Ukraine ( ua, Конституційний Суд України) is the sole body of constitutional jurisdiction in Ukraine. The Constitutional Court of Ukraine interprets the Constitution of Ukraine in terms of l ...
as unconstitutional) of the First Deputy Prosecutor of the Mykolaiv Oblast
Mykolaiv Oblast ( uk, Микола́ївська о́бласть, translit=Mykoláyivsʹka óblastʹ, ), also referred to as Mykolaivshchyna ( uk, Микола́ївщина, Mykoláivshchyna, ) is an oblast (province) of Ukraine. The administra ...
. In October and December 2018, parliaments of the city of Kherson and of Kharkiv Oblast
Kharkiv Oblast ( uk, Харківська́ о́бласть, translit=Kharkivska oblast), also referred to as Kharkivshchyna ( uk, Ха́рківщина), is an oblast (province) of eastern Ukraine. The oblast borders Russia to the north, Luhan ...
also abolished the status of the Russian language as a regional one.
In January 2022, a law requiring all print media to be published in Ukrainian came into force. It did not ban publication in Russian, however it stipulated that a Ukrainian version of equivalent circulation and scope must be published – which is not a profitable option for publishers. Critics argue that the law could disenfranchise the country's Russian-speakers.
Current usage statistics
2001 Census
According to official data from the2001 Ukrainian census
The Ukrainian Census of 2001 is to date the only census of the population of independent Ukraine. It was conducted by the State Statistics Committee of Ukraine on 5 December 2001, twelve years after the last Soviet Union census in 1989.
, the Russian language is native for 29.6% of Ukraine's population (about 14.3 million people). Ethnic Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
form 56% of the total Russian-native-language population, while the remainder are people of other ethnic background: 5,545,000 Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Ort ...
, 172,000 Belarusians, 86,000 Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, 81,000 Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
, 62,000 Bulgarians
Bulgarians ( bg, българи, Bǎlgari, ) are a nation and South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and the rest of Southeast Europe.
Etymology
Bulgarians derive their ethnonym from the Bulgars. Their name is not completely unders ...
, 46,000 Moldovans
Moldovans, sometimes referred to as Moldavians ( ro, moldoveni , Moldovan Cyrillic: молдовень), are a Romance-speaking ethnic group and the largest ethnic group of the Republic of Moldova (75.1% of the population as of 2014) and a sign ...
, 43,000 Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
, 43,000 in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
, 22,000 Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in C ...
, 21,000 Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
, 15,000 Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg
, flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars
, image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg
, caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace ...
.
Therefore, the Russian-speaking population in Ukraine forms the largest linguistic group in modern Europe with its language being non-official in the state. The Russian-speaking population of Ukraine constitutes the largest Russophone
This article details the geographical distribution of Russian-speakers. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, the status of the Russian language often became a matter of controversy. Some Post-Soviet states adopted policies of derussi ...
community outside the Russian Federation
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
.
Polls
According to July 2012 polling byRATING
A rating is an evaluation or assessment of something, in terms of quality, quantity, or some combination of both.
Rating or ratings may also refer to:
Business and economics
* Credit rating, estimating the credit worthiness of an individual, c ...
, 50% of the surveyed adult residents over 18 years of age considered their native language to be Ukrainian, 29% said Russian, 20% identified both Russian and Ukrainian as their native language, 1% gave another language. 5% could not decide which language is their native one.The language question, the results of recent research in 2012,
RATING
A rating is an evaluation or assessment of something, in terms of quality, quantity, or some combination of both.
Rating or ratings may also refer to:
Business and economics
* Credit rating, estimating the credit worthiness of an individual, c ...
(25 May 2012) Almost 80% of respondents stated they did not have any problems using their native language in 2011. 8% stated they had experienced difficulty in the execution (understanding) of official documents; mostly middle-aged and elderly people in South Ukraine and the Donbass
The Donbas or Donbass (, ; uk, Донба́с ; russian: Донба́сс ) is a historical, cultural, and economic region in eastern Ukraine. Parts of the Donbas are controlled by Russian separatist groups as a result of the Russo-Ukrai ...
.
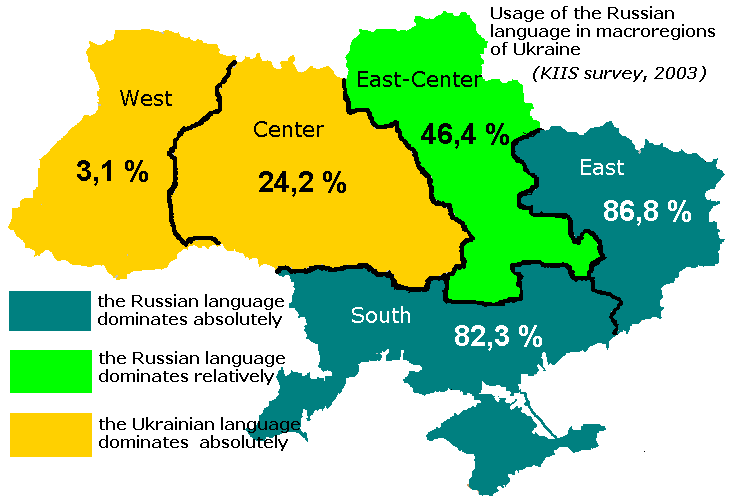
According to a 2004 public opinion poll by the Kyiv International Institute of Sociology, the number of people using Russian language in their homes considerably exceeds the number of those who declared Russian as their native language in the census. According to the survey, Russian is used at home by 43–46% of the population of the country (in other words a similar proportion to Ukrainian) and Russophones make a majority of the population in Eastern and Southern regions of Ukraine:
* Autonomous Republic of Crimea — 97% of the population
* Dnipropetrovsk Oblast
Dnipropetrovsk Oblast ( uk, Дніпропетро́вська о́бласть, translit=Dnipropetrovska oblast), also referred to as Dnipropetrovshchyna ( uk, Дніпропетро́вщина), is an oblast (province) of central-eastern Ukra ...
— 72%
* Donetsk Oblast — 93%
* Luhansk Oblast
Luhansk Oblast ( uk, Луга́нська о́бласть, translit=Luhanska oblast; russian: Луганская область, translit=Luganskaya oblast; also referred to as Luhanshchyna, uk, Луга́нщина) is the easternmost oblast ...
— 89%
* Zaporizhzhia Oblast
Zaporizhzhia Oblast ( uk, Запорі́зька о́бласть, translit=Zaporizka oblast), also referred to as Zaporizhzhia ( uk, Запорі́жжя, links=no), is an oblast (province) of southeast Ukraine. Its capital is Zaporizhzhia. The ...
— 81%
* Odessa Oblast
Odesa Oblast ( uk, Оде́ська о́бласть, translit=Odeska oblast), also referred to as Odeshchyna ( uk, Оде́щина) is an oblast (province) of southwestern Ukraine, located along the northern coast of the Black Sea. Its administ ...
— 85%
* Kharkiv Oblast
Kharkiv Oblast ( uk, Харківська́ о́бласть, translit=Kharkivska oblast), also referred to as Kharkivshchyna ( uk, Ха́рківщина), is an oblast (province) of eastern Ukraine. The oblast borders Russia to the north, Luhan ...
— 74%
* Mykolaiv Oblast
Mykolaiv Oblast ( uk, Микола́ївська о́бласть, translit=Mykoláyivsʹka óblastʹ, ), also referred to as Mykolaivshchyna ( uk, Микола́ївщина, Mykoláivshchyna, ) is an oblast (province) of Ukraine. The administra ...
— 66%
Russian language dominates in informal communication in the capital of Ukraine, Kyiv. It is also used by a sizeable linguistic minority (4-5% of the total population) in Central and Western Ukraine. 83% of Ukrainians responding to a 2008 Gallup poll preferred to use Russian instead of Ukrainian to take the survey.
According to data obtained by the "Public opinion" foundation (2002), the population of the oblast
An oblast (; ; Cyrillic (in most languages, including Russian and Ukrainian): , Bulgarian: ) is a type of administrative division of Belarus, Bulgaria, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Ukraine, as well as the Soviet Union and the Kingdo ...
centres prefers to use Russian (75%). Continuous Russian linguistic areas occupy certain regions of Crimea, Donbas, Slobozhanshchyna
Sloboda Ukraine (literally: Borderland of free frontier guards; uk, Слобідська Україна, Slobidska Ukraina), or Slobozhanshchyna ( uk, Слобожанщина, Slobozhanshchyna, ), is a historical region, now located in Northeas ...
, southern parts of Odessa and Zaporizhia oblasts, while Russian linguistic enclaves exist in central and northern Ukraine.
Russian language in Ukrainian politics
 The Russian language in Ukraine is recognized (along with all other languages) as the "language of a national minority". Ukrainian is the only state language; every other language is declared to be the "language of a national minority" in the
The Russian language in Ukraine is recognized (along with all other languages) as the "language of a national minority". Ukrainian is the only state language; every other language is declared to be the "language of a national minority" in the Constitution of Ukraine
The Constitution of Ukraine ( uk, Конституція України, translit=Konstytutsiia Ukrainy) is the fundamental law of Ukraine. The constitution was adopted and ratified at the 5th session of the ''Verkhovna Rada'', the parliament ...
adopted by the parliament in 1996, but only Russian is explicitly named. Article 10 of the Constitution reads: ''"In Ukraine, the free development, use and protection of Russian, and other languages of national minorities of Ukraine, is guaranteed''".Article 10of the Constitution says: "The state language of Ukraine is the Ukrainian language. The State ensures the comprehensive development and functioning of the Ukrainian language in all spheres of social life throughout the entire territory of Ukraine. In Ukraine, the free development, use and protection of Russian, and other languages of national minorities of Ukraine, is guaranteed." The Constitution declares Ukrainian language as the state language of the country, while other languages spoken in Ukraine are guaranteed constitutional protection, but are not in practice protected from book bans. The Ukrainian language was adopted as the state language by the Law on Languages adopted in
Ukrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic ( uk, Украї́нська Радя́нська Соціалісти́чна Респу́бліка, ; russian: Украи́нская Сове́тская Социалисти́ческая Респ ...
in 1989; Russian was specified as the language of communication with the other republics of Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
.On Languages in the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic. Law. 1989(in English) Ukraine signed the European Charter on Regional or Minority Languages in 1996, but it was only partially ratified, and only in 2002 by the
Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
The issue of Russian receiving the status of second official language has been the subject of extended controversial discussion ever since Ukraine became independent in 1991. In every Ukrainian election, many politicians, such as former president Leonid Kuchma
Leonid Danylovych Kuchma ( uk, Леоні́д Дани́лович Ку́чма; born 9 August 1938) is a Ukrainian politician who was the second president of Ukraine from 19 July 1994 to 23 January 2005. Kuchma's presidency saw numerous corru ...
, were elected by Ukrainians after making Russian language rights a key part of their platform. The recent President of Ukraine
The president of Ukraine ( uk, Президент України, Prezydent Ukrainy) is the head of state of Ukraine. The president represents the nation in international relations, administers the foreign political activity of the state, condu ...
, Viktor Yanukovych
Viktor Fedorovych Yanukovych ( uk, Віктор Федорович Янукович, ; ; born 9 July 1950) is a former politician who served as the fourth president of Ukraine from 2010 until he was removed from office in the Revolution of D ...
continued this practice when he was opposition leader. In an interview with Kommersant
''Kommersant'' (russian: Коммерсантъ, , ''The Businessman'' or Commerce Man, often shortened to Ъ) is a nationally distributed daily newspaper published in Russia mostly devoted to politics and business. The TNS Media and NRS Russia ...
, during the 2010 Ukrainian presidential election-campaign, he stated that the status of Russian in Ukraine "is too politicized" and said that if elected president in 2010, he would "have a real opportunity to adopt a law on languages, which implements the requirements of the European Charter of regional languages". He implied this law would need 226 votes in the Ukrainian parliament
The Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine ( uk, Верхо́вна Ра́да Украї́ни, translit=, Verkhovna Rada Ukrainy, translation=Supreme Council of Ukraine, Ukrainian abbreviation ''ВРУ''), often simply Verkhovna Rada or just Rada, is the ...
(50% of the votes instead of the 75% of the votes needed to change the constitution of Ukraine
The Constitution of Ukraine ( uk, Конституція України, translit=Konstytutsiia Ukrainy) is the fundamental law of Ukraine. The constitution was adopted and ratified at the 5th session of the ''Verkhovna Rada'', the parliament ...
). After his early 2010 election as president, Yanukovych stated (on March 9, 2010) "Ukraine will continue to promote the Ukrainian language as its only state language". At the same time, he stressed that it also necessary to develop other regional languages.
In 1994, a referendum took place in the Donetsk Oblast and the Luhansk Oblast
Luhansk Oblast ( uk, Луга́нська о́бласть, translit=Luhanska oblast; russian: Луганская область, translit=Luganskaya oblast; also referred to as Luhanshchyna, uk, Луга́нщина) is the easternmost oblast ...
, with around 90% supporting the Russian language gaining status of an official language alongside Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
, and for the Russian language to be an official language on a regional level, but it was ignored by Parliament.
Former president Viktor Yushchenko
Viktor Andriyovych Yushchenko ( uk, Віктор Андрійович Ющенко, ; born 23 February 1954) is a Ukrainian politician who was the third president of Ukraine from 23 January 2005 to 25 February 2010.
As an informal leader of th ...
, during his 2004 Presidential campaign, also claimed a willingness to introduce more equality for Russian speakers. His clipping service
A media monitoring service, a press clipping service or a clipping service as known in earlier times, provides clients with copies of media content, which is of specific interest to them and subject to changing demand; what they provide may include ...
spread an announcement of his promise to make Russian language proficiency obligatory for officials who interact with Russian-speaking citizens. In 2005 Yushchenko stated that he had never signed this decree project. The controversy was seen by some as a deliberate policy of Ukrainization
Ukrainization (also spelled Ukrainisation), sometimes referred to as Ukrainianization (or Ukrainianisation) is a policy or practice of increasing the usage and facilitating the development of the Ukrainian language and promoting other elements of ...
.
In 2006, the Kharkiv City Rada was the first to declare Russian to be a regional language. Following that, almost all southern and eastern oblasts (Luhansk
Luhansk (, ; uk, Луганськ, ), also known as Lugansk (, ; russian: Луганск, ), is a city in what is internationally recognised as Ukraine, although it is administered by Russia as capital of the Luhansk People's Republic (LPR). A ...
, Donetsk, Mykolaiv
Mykolaiv ( uk, Миколаїв, ) is a city and municipality in Southern Ukraine, the administrative center of the Mykolaiv Oblast. Mykolaiv city, which provides Ukraine with access to the Black Sea, is the location of the most downriver brid ...
, Kharkiv
Kharkiv ( uk, wikt:Харків, Ха́рків, ), also known as Kharkov (russian: Харькoв, ), is the second-largest List of cities in Ukraine, city and List of hromadas of Ukraine, municipality in Ukraine.Zaporizhia
Zaporizhzhia ( uk, Запоріжжя) or Zaporozhye (russian: Запорожье) is a city in southeast Ukraine, situated on the banks of the Dnieper River. It is the administrative centre of Zaporizhzhia Oblast. Zaporizhzhia has a populatio ...
, and Kherson oblasts), and many major southern and eastern cities (Sevastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
, Dnipropetrovsk, Donetsk
Donetsk ( , ; uk, Донецьк, translit=Donets'k ; russian: Донецк ), formerly known as Aleksandrovka, Yuzivka (or Hughesovka), Stalin and Stalino (see also: cities' alternative names), is an industrial city in eastern Ukraine loca ...
, Yalta
Yalta (: Я́лта) is a resort city on the south coast of the Crimean Peninsula surrounded by the Black Sea. It serves as the administrative center of Yalta Municipality, one of the regions within Crimea. Yalta, along with the rest of Cri ...
, Luhansk
Luhansk (, ; uk, Луганськ, ), also known as Lugansk (, ; russian: Луганск, ), is a city in what is internationally recognised as Ukraine, although it is administered by Russia as capital of the Luhansk People's Republic (LPR). A ...
, Zaporizhia
Zaporizhzhia ( uk, Запоріжжя) or Zaporozhye (russian: Запорожье) is a city in southeast Ukraine, situated on the banks of the Dnieper River. It is the administrative centre of Zaporizhzhia Oblast. Zaporizhzhia has a populatio ...
, Kryvyi Rih
Kryvyi Rih ( uk, Криви́й Ріг , lit. "Curved Bend" or "Crooked Horn"), also known as Krivoy Rog (Russian: Кривой Рог) is the largest city in central Ukraine, the 7th most populous city in Ukraine and the 2nd largest by area. K ...
, Odessa) followed suit. Several courts overturned the decision to change the status of the Russian language in the cities of Kryvyi Rih, Kherson, Dnipropetrovsk, Zaporizhia and Mykolaiv while in Donetsk, Mykolaiv and Kharkiv oblasts it was retained.
In August 2012, a law on regional languages entitled any local language spoken by at least a 10% minority to be declared official within that area.Yanukovych signs language bill into law. Retrieved 2012-09-07. Russian was within weeks declared as a regional language in several southern and eastern oblasts and cities. On 23 February 2014, a bill repealing the law was approved by 232 deputies out of 450 but not signed into law by acting-president
Oleksandr Turchynov
Oleksandr Valentynovych Turchynov ( uk, Олександр Валентинович Турчинов; born 31 March 1964) is a Ukrainian politician, screenwriter, Baptist minister and economist. He is the former Secretary of the National S ...
. On 28 February 2018, the Constitutional Court of Ukraine
The Constitutional Court of Ukraine ( ua, Конституційний Суд України) is the sole body of constitutional jurisdiction in Ukraine. The Constitutional Court of Ukraine interprets the Constitution of Ukraine in terms of l ...
ruled on the matter.Constitutional Court declares unconstitutional language law of Kivalov-Kolesnichenko,
Ukrinform
The National News Agency of Ukraine ( uk, Українське національне інформаційне агентство), or Ukrinform ( uk, Укрінформ), is a state information and news agency, and international broadcaster of ...
(28 February 2018)
In December 2016, the importation of "anti-Ukrainian" books from Russia was restricted. In February 2017 the Ukrainian government completely banned the commercial importation of books from Russia, which had accounted for up to 60% of all titles sold.
Surveys on the status of the Russian language
RATING
A rating is an evaluation or assessment of something, in terms of quality, quantity, or some combination of both.
Rating or ratings may also refer to:
Business and economics
* Credit rating, estimating the credit worthiness of an individual, c ...
, the level of support for granting Russian the status of a state language decreased (from 54% to 46%) and the number of opponents increased (from 40% to 45%) between 2009 and May 2012; in July 2012 41% of respondents supported granting Russian the status of a state language and 51% opposed it. (In July 2012) among the biggest supporters of bilingualism were residents of the Donets Basin (85%), South Ukraine (72%) and East Ukraine
Eastern Ukraine or east Ukraine ( uk, Східна Україна, Skhidna Ukrayina; russian: Восточная Украина, Vostochnaya Ukraina) is primarily the territory of Ukraine east of the Dnipro (or Dnieper) river, particularly Khark ...
(50%). A further poll conducted by RATING in September–October 2012 found 51% opposed granting official status to the Russian language, whereas 41% supported it. The largest regions of support were Donbas (75%), southern (72%) and eastern (53%), whereas nearly 70% of northern and central Ukraine, and 90% of western Ukraine were in opposition. A survey conducted in February 2015 by the Kyiv International Institute of Sociology found that support for Russian as a state language had dropped to 19% (37% in the south, 31% in Donbas and other eastern oblasts). 52% (West: 44%, Central: 57%; South: 43%; East: 61%) said that Russian should be official only in regions where the majority wanted it and 21% said it should be removed from official use.
Other surveys
The Russo-Ukrainian director of the Kyiv branch of the , , presented the results of a poll carried out by the Research & Branding Group in late 2006. As reported by the Russian-languageREGNUM News Agency
REGNUM News Agency is a Russian nationwide online news service disseminating news from Russia and abroad from its own correspondents, affiliate agencies and partners. REGNUM covers events in all regions of Russia as well as neighboring countries ...
, it found that "68% of Ukrainians are fluent in Russian and 57% are fluent in Ukrainian."
Although a census conducted in Ukrainian showed that Russian speakers comprise about 30% (2001 census), 39% of Ukrainians interviewed in a 2006 survey believed that the rights of Russophones were violated because the Russian language is not official in the country, whereas 38% had the opposite position.
According to a poll carried out by the Social Research Center at the National University of Kyiv-Mohyla Academy
National University of Kyiv-Mohyla Academy ( NaUKMA) ( uk, Національний університет «Києво-Могилянська академія» (НаУКМА)) is a national, research university located in Kyiv, Ukraine. The ...
in late 2009 ideological issues were ranked third (15%) as reasons to organize mass protest actions (in particular, the issues of joining NATO, the status of the Russian language, the activities of left- and right-wing political groups, etc.); behind economic issues (25%) and problems of ownership (17%). According to a March 2010 survey, forced Ukrainization and Russian language suppression are of concern to 4.8% of the population.
According to 2016-2017 polls by the Kyiv International Institute of Sociology, Rating
A rating is an evaluation or assessment of something, in terms of quality, quantity, or some combination of both.
Rating or ratings may also refer to:
Business and economics
* Credit rating, estimating the credit worthiness of an individual, c ...
, and GfK Ukraine, about 1% of respondents across the country, and fewer than 3% of respondents in eastern parts of Ukraine, found the status of the Russian language to be an important political issue. The same 2017 polls indicated 64% support for state policies favoring the usage of the Ukrainian language.
Use of Russian in specific spheres
Russian literature of Ukraine
 Historically, many famous writers of Russian literature were born and lived in Ukraine. Nikolai Gogol is probably the most famous example of shared Russo-Ukrainian heritage: Ukrainian by descent, he wrote in Russian, and significantly contributed to culture of both nations. Russian author Mikhail Bulgakov was born in
Historically, many famous writers of Russian literature were born and lived in Ukraine. Nikolai Gogol is probably the most famous example of shared Russo-Ukrainian heritage: Ukrainian by descent, he wrote in Russian, and significantly contributed to culture of both nations. Russian author Mikhail Bulgakov was born in Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Kyi ...
, as well as poet Ilya Erenburg. A number of notable Russian writers and poets hailed from Odessa, including Ilya Ilf and Yevgeny Petrov, Anna Akhmatova
Anna Andreyevna Gorenko rus, А́нна Андре́евна Горе́нко, p=ˈanːə ɐnˈdrʲe(j)ɪvnə ɡɐˈrʲɛnkə, a=Anna Andreyevna Gorenko.ru.oga, links=yes; uk, А́нна Андрі́ївна Горе́нко, Ánna Andríyivn ...
, Isaak Babel
Isaac Emmanuilovich Babel (russian: Исаак Эммануилович Бабель, p=ˈbabʲɪlʲ; – 27 January 1940) was a Russian writer, journalist, playwright, and literary translator. He is best known as the author of '' Red Cavalry' ...
. Russian child poet Nika Turbina
Nika Georgievna Turbina (russian: Ника Гeopгиeвна Туpбина; 17 December 1974, Yalta – 11 May 2002, Moscow) was a Russian poet. She became famous for her profound and emotional poems which she wrote at an early age.
She wrote her ...
was born in Yalta
Yalta (: Я́лта) is a resort city on the south coast of the Crimean Peninsula surrounded by the Black Sea. It serves as the administrative center of Yalta Municipality, one of the regions within Crimea. Yalta, along with the rest of Cri ...
, Crimea.
A significant number of contemporary authors from Ukraine write in Russian. This is especially notable within science fiction
Science fiction (sometimes shortened to Sci-Fi or SF) is a genre of speculative fiction which typically deals with imaginative and futuristic concepts such as advanced science and technology, space exploration, time travel, parallel uni ...
and fantasy
Fantasy is a genre of speculative fiction involving magical elements, typically set in a fictional universe and sometimes inspired by mythology and folklore. Its roots are in oral traditions, which then became fantasy literature and d ...
genres. Kharkiv is considered the "capital city" of Ukrainian sci-fi and fantasy, it is home to several popular Russophone Ukrainian writers, such as H. L. Oldie
Henry Lion Oldie or H. L. Oldie (russian: Генри Лайон Олди, Г. Л. Олди) is the pen name of Ukrainian science fiction and fantasy writers Dmitry Gromov and Oleg Ladyzhensky. Both authors reside in Kharkiv, Ukraine, and write i ...
(pen name for Oleg Ladyzhensky and Dmitry Gromov), Alexander Zorich, Andrei Valentinov, and Yuri Nikitin. Science fiction convention
Science fiction conventions are gatherings of fans of the speculative fiction genre, science fiction. Historically, science fiction conventions had focused primarily on literature, but the purview of many extends to such other avenues of expre ...
''Zvezdny Most'' (Rus. for "Star Bridge") is held in Kharkiv annually. Russophone Ukrainian writers also hail from Kyiv, those include Marina and Sergey Dyachenko and Vladimir Arenev. Max Frei
Max Frei (russian: Макс Фрай) is the pen name of Svetlana Yuryevna Martynchik (russian: Светла́на Ю́рьевна Марты́нчик; uk, Світлана Юріївна Мартинчик) (born 1965 in Odesa, Ukrainian SSR, ...
hails from Odessa, and Vera Kamsha
Vera Viktorovna Kamsha (russian: Вера Викторовна Камша; born November 5, 1962 in Lviv, Ukrainian SSR) is a Russian author of high fantasy and a journalist.
Biography
Kamsha graduated from Lviv Polytechnic, after which she mo ...
was born in Lviv
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in western Ukraine, and the seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is one of the main cultural centres of Ukrain ...
. Other Russophone Ukrainian writers of sci-fi and fantasy include Vladimir Vasilyev Vladimir Vasiliev may refer to:
* Vladimir Vasiliev (dancer) (born 1940), dancer with the Bolshoi Ballet
* Vladimir Vasilyev (rower) (born 1948), Soviet Olympic rower
* Vladimir Vasilyev (politician) (born 1949), Russian politician
* Vladimir Vas ...
, Vladislav Rusanov Vladislav Rusanov may refer to:
* Vladislav Rusanov (writer)
* Vladislav Rusanov (footballer)
Vladislav Rusanov (russian: Владислав Русанов, known until 2020 as Vladislav Bakonin, (russian: Владислав Баконин); born ...
, Alexander Mazin
Alexander Vladimirovich Mazin (russian: Александр Владимирович Мазин) is a Ukrainian-born Russian writer, poet, and songwriter, specializing in the genres of science fiction, fantasy, and alternate history.
Born in 1959 ...
and Fyodor Berezin
Fyodor Dmitrievich Berezin (russian: Фёдор Дмитриевич Березин; born February 7, 1960) is a Russian science fiction writer. He has published 3 novel series, and 2 separate works, scoring him awards at the International Scienc ...
. ''RBG-Azimuth
''RBG-Azimuth'' (''GDC-Azimuth) was a quarterly Ukrainian bilingual (Russophone and Ukrainophone) science fiction magazine, published since 2006. Its stories were written in the Russian language by authors living around the world. This included ...
'', Ukraine's largest sci-fi and fantasy magazine, is published in Russian, as well as now defunct ''Realnost Fantastiki''.
Outside science fiction and fantasy, there is also a number of Russophone realist writers and poets. Ukrainian literary magazine ''Sho'' listed Alexander Kabanov, Boris Khersonsky, Andrey Polyakov, Andrey Kurkov
Andrey Yuryevich Kurkov ( uk, Андрій Юрійович Курков; russian: Андре́й Ю́рьевич Курко́в; born 23 April 1961 in Leningrad, USSR) is a Ukrainian author and public intellectual who writes in Russian. He is ...
and Vladimir Rafeyenko as best Russophone Ukrainian writers of 2013.
According to H. L. Oldie, writing in Russian is an easier way for Ukrainian authors to be published and reach a broader audience. The authors say that it is because of Ukraine's ineffective book publishing policy: while Russian publishers are interested in popular literature, Ukrainian publishers rely mostly on grant
Grant or Grants may refer to:
Places
*Grant County (disambiguation)
Australia
* Grant, Queensland, a locality in the Barcaldine Region, Queensland, Australia
United Kingdom
* Castle Grant
United States
* Grant, Alabama
* Grant, Inyo County, ...
givers. Many Ukrainian publishers agree and complain about low demand and low profitability for books in Ukrainian, compared to books in Russian.
In the media
A 2012 study showed that: * on the radio, 3.4% of songs were in Ukrainian while 60% were in Russian * over 60% of newspapers, 83% of journals and 87% of books were in Russian * 28% of TV programs were in Ukrainian, even on state-owned channels Russian-language programming is sometimes subtitled in Ukrainian, and commercials during Russian-language programs are in Ukrainian on Ukraine-based media. On March 11, 2014, amidst pro-Russian unrest in Ukraine, the Ukrainian National Council on Television and Radio Broadcasting shut down the broadcast ofRussia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
n television channels Rossiya 24, Channel One Russia
Channel One ( rus, Первый канал, r=Pervyy kanal, p=ˈpʲervɨj kɐˈnal, t=First Channel) is a Russian state-controlled television channel. It is the first television channel to broadcast in the Russian Federation. Its headquarters ...
, RTR Planeta, and NTV Mir in Ukraine. Since 19 August 2014 Ukraine has blocked 14 Russian television channels "to protect its media space from aggression from Russia, which has been deliberately inciting hatred and discord among Ukrainian citizens".
In early June 2015, 162 Russian movies and TV series were banned in Ukraine because they were seen to contain popularization, agitation and/or propaganda for the 2014–15 Russian military intervention in Ukraine
The Russo-Ukrainian War; uk, російсько-українська війна, rosiisko-ukrainska viina. has been ongoing between Russia (alongside Russian separatists in Ukraine) and Ukraine since February 2014. Following Ukraine's Revo ...
(this military intervention is denied by Russia). All movies that feature "unwanted" Russian or Russia-supporting actors were also banned.
On the Internet
Russian is by far the preferred language on websites in Ukraine (80.1%), followed by English (10.1%), then Ukrainian (9.5%). The Russian language version ofWikipedia
Wikipedia is a multilingual free online encyclopedia written and maintained by a community of volunteers, known as Wikipedians, through open collaboration and using a wiki-based editing system. Wikipedia is the largest and most-read refer ...
is five times more popular within Ukraine than the Ukrainian one, with these numbers matching those for the 2008 Gallup poll cited above (in which 83% of Ukrainians preferred to take the survey in Russian and 17% in Ukrainian.)
While government organizations are required to have their websites in Ukrainian, Ukrainian usage of the Internet is mostly in the Russian language. According to DomainTyper, the top ranking .ua
.ua is the Internet country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for Ukraine. To register at the second-level (example) domainname.ua, possession of the exact trademark (matching the domain name) is required. It is not required for third-level domain ...
domains are google.com.ua, yandex.ua, ex.ua and i.ua, all of which use the Russian language as default. According to 2013 UIA research, four of the five most popular websites (aside from Google
Google LLC () is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company focusing on Search Engine, search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, software, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, ar ...
) in Ukraine were Russian or Russophone: those are Vkontakte
VK (short for its original name ''VKontakte''; russian: ВКонтакте, meaning ''InContact'') is a Russian online social media and social networking service based in Saint Petersburg. VK is available in multiple languages but it is predomin ...
, Mail.ru
VK, known as Mail.ru Group until 12 October 2021, is a Russian technology company. It started in 1998 as an e-mail service and went on to become a major corporate figure in the Russian-speaking segment of the Internet.
VK operates an e-mail s ...
, Yandex
Yandex LLC (russian: link=no, Яндекс, p=ˈjandəks) is a Russian multinational technology company providing Internet-related products and services, including an Internet search engine, information services, e-commerce, transportation, map ...
, and Odnoklassniki
Odnoklassniki ( rus, Одноклассники, t=Classmates) is a social network service used mainly in Russia and former Soviet Republics. The site was developed by Albert Popkov and launched on March 4, 2006.
The website currently has more ...
. The top Ukrainian language website in this rank is Ukr.net, which was only the 8th most popular, and even Ukr.net uses both languages interchangeably.
On May 15, 2017, Ukrainian president Poroshenko issued a decree that demanded all Ukrainian internet providers to block access to all most popular Russian social media and websites, including VK, Odnoklassniki
Odnoklassniki ( rus, Одноклассники, t=Classmates) is a social network service used mainly in Russia and former Soviet Republics. The site was developed by Albert Popkov and launched on March 4, 2006.
The website currently has more ...
, Mail.ru
VK, known as Mail.ru Group until 12 October 2021, is a Russian technology company. It started in 1998 as an e-mail service and went on to become a major corporate figure in the Russian-speaking segment of the Internet.
VK operates an e-mail s ...
, Yandex
Yandex LLC (russian: link=no, Яндекс, p=ˈjandəks) is a Russian multinational technology company providing Internet-related products and services, including an Internet search engine, information services, e-commerce, transportation, map ...
citing matters of national security in the context of the war in Donbas
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
and explaining it as a response to " massive Russian cyberattacks across the world". On the following day the demand for applications that allowed to access blocked websites skyrocketed in Ukrainian segments of App Store
An App Store (or app marketplace) is a type of digital distribution platform for computer software called applications, often in a mobile context. Apps provide a specific set of functions which, by definition, do not include the running of the c ...
and Google Play
Google Play, also known as the Google Play Store and formerly the Android Market, is a digital distribution service operated and developed by Google. It serves as the official app store for certified devices running on the Android operating sy ...
. The ban was condemned by Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human r ...
that called it "a cynical, politically expedient attack on the right to information affecting millions of Ukrainians, and their personal and professional lives", while head of Council of Europe expressed a "strong concern" about the ban.
In education
Among private secondary schools, each individual institution decides whether to study Russian or not. The number of Russian-teaching schools has reduced sinceUkrainian independence
Ukraine emerged as the concept of a nation, and the Ukrainians as a nationality, with the Ukrainian National Revival which began in the late 18th and early 19th century. The first wave of national revival is traditionally connected with the publ ...
in 1991 and in 2021 it is much lower than the proportion of Russophones,Vasyl Ivanyshyn, Yaroslav Radevych-Vynnyts'kyi, Mova i Natsiya
'', Drohobych, Vidrodzhennya, 1994, "the number of Ukrainian secondary schools has increased to 15,900, or 75% of their total number. In all, about 4.5 million students (67.4% of the total) are taught in Ukrainian, in Russian – 2.1 million (31.7%)..."
'
'' Volodymyr Malynkovych, ttp://www.igpi.ru/info/people/malink/1139380574.html Ukrainian perspective, Politicheskiy Klass, January 2006 but still higher than the proportion of ethnic Russians. The ''Law on Education'' formerly granted Ukrainian families (parents and their children) a right to choose their native language for schools and studies.Ukraine/ Compendium of Cultural Policies and Trends in Europe, 10th edition
, Council of Europe (2009) This was changed by a new law in 2017 that only allows the use of Ukrainian in secondary schools and higher.
Higher education
Higher education is tertiary education leading to award of an academic degree. Higher education, also called post-secondary education, third-level or tertiary education, is an optional final stage of formal learning that occurs after comple ...
institutions in Ukraine generally use Ukrainian as the language of instruction.
According to parliamentarians of the Supreme Council of Crimea
Verkhovna Rada of Crimea or the Supreme Council of Crimea, officially the Supreme Council of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea ( uk, Верховна Рада Автономної Республіки Крим, Verkhovna Rada Avtonomnoï Respubl ...
, in 2010 90% students of Crimea were studying in Russian language schools. At the same time, only 7% of students in Crimea were studying in Ukrainian language
Ukrainian ( uk, украї́нська мо́ва, translit=ukrainska mova, label=native name, ) is an East Slavic language of the Indo-European language family. It is the native language of about 40 million people and the official state lan ...
schools. In 2012, the only Ukrainian boarding school (50 pupils) in Sevastopol was closed, and children who would not study in Russian language were to be transferred to a boarding school for children with intellectual disabilities
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability in the United Kingdom and formerly mental retardation, Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010). is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by signif ...
.
In courts
Since 1 January 2010, court proceedings have been allowed to take place in Russian on mutual consent of parties. Citizens who are unable to speakUkrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
or Russian are allowed to use their native language or the services of an interpreter.,
Kyiv Post
The ''Kyiv Post'' is the oldest English-language newspaper in Ukraine, founded in October 1995 by Jed Sunden.
History
American Jed Sunden founded the ''Kyiv Post'' weekly newspaper on Oct. 18, 1995 and later created KP Media for his holdings. ...
(15 December 2011)З подачі "Регіонів" Рада дозволила російську у судах
,
Ukrayinska Pravda
''Ukrainska Pravda'' ( uk, Українська правда, lit=Ukrainian Truth) is a Ukrainian online newspaper founded by Georgiy Gongadze on 16 April 2000 (the day of the Ukrainian constitutional referendum). Published mainly in Ukrai ...
(23 June 2009)ЗМІ: Російська мова стала офіційною в українських судах
,
Novynar
''Novynar'' (Ukrainian: ''Newsmaker'') was a weekly news magazine briefly published in Kyiv, Ukraine, from 2007 to 2008.
History and profile
''Novynar'' was first published in August 2007. Its website was also launched on the same date. It was e ...
(29 July 2010)Російська мова стала офіційною в українських судах
, forUm (29 July 2010)
In business
, business affairs in Ukraine were mainly dealt with in Russian. Advanced technical and engineering courses at the university level in Ukraine were taught in Russian, which was changed according to the 2017 law "On Education".See also
*Russians in Ukraine
Russians are the largest ethnic minority in Ukraine. This community forms the largest single Russian community outside of Russia in the world. In the 2001 Ukrainian census, 8,334,100 identified as ethnic Russians (17.3% of the population of ...
* Surzhyk
* Russian book ban in Ukraine
* Language ombudsman (Ukraine)
References
Further reading
* 160 pages. * 231 pages. * * 264 pages. * 384 pages. and * 256 pages. * 417 pages. * * 213 pages. {{DEFAULTSORT:Russian Language In UkraineUkraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
Languages of Ukraine
Russian-Ukrainian culture
Russia–Ukraine relations
Russification
Social history of Ukraine