Russian battleship Sevastopol (1911) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Sevastopol'' (russian: Севастополь) was the first ship completed of the s of the
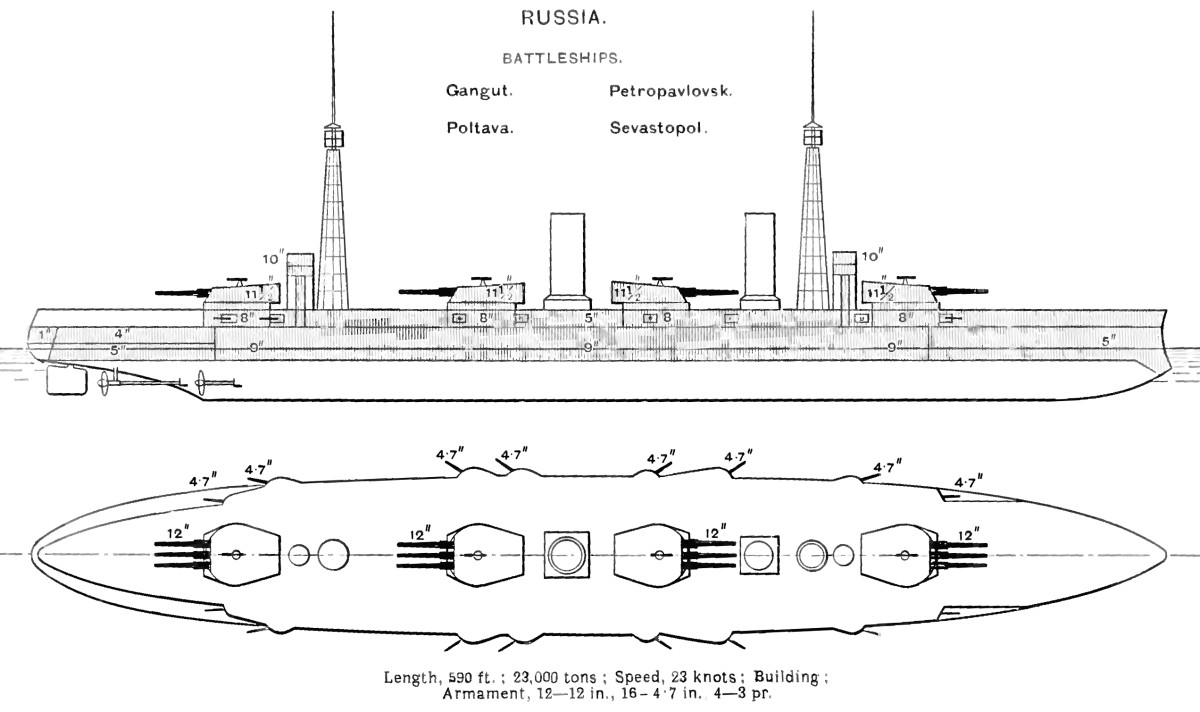 ''Sevastopol'' was long at the waterline and long
''Sevastopol'' was long at the waterline and long
Specifications
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sevastopol (1911) Gangut-class battleships World War I battleships of Russia 1911 ships Ships built at the Baltic Shipyard Maritime incidents in 1915 Maritime incidents in 1916 Maritime incidents in 1929 Maritime incidents in November 1941
Imperial Russian Navy
The Imperial Russian Navy () operated as the navy of the Russian Tsardom and later the Russian Empire from 1696 to 1917. Formally established in 1696, it lasted until dissolved in the wake of the February Revolution of 1917. It developed from a ...
, built before World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. The ''Gangut''s were the first class
Class or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used differentl ...
of Russian dreadnought
The dreadnought (alternatively spelled dreadnaught) was the predominant type of battleship in the early 20th century. The first of the kind, the Royal Navy's , had such an impact when launched in 1906 that similar battleships built after her ...
s. She was named after the Siege of Sevastopol during the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the de ...
. She was completed during the winter of 1914–1915, but was not ready for combat until mid-1915. Her role was to defend the mouth of the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and E ...
against the Germans, who never tried to enter, so she spent her time training and providing cover for minelaying operations. Her crew joined the general mutiny
Mutiny is a revolt among a group of people (typically of a military, of a crew or of a crew of pirates) to oppose, change, or overthrow an organization to which they were previously loyal. The term is commonly used for a rebellion among member ...
of the Baltic Fleet
, image = Great emblem of the Baltic fleet.svg
, image_size = 150
, caption = Baltic Fleet Great ensign
, dates = 18 May 1703 – present
, country =
, allegiance = (1703–1721) (1721–1917) (1917–1922) (1922–1991)(1991–present)
...
after the February Revolution
The February Revolution ( rus, Февра́льская револю́ция, r=Fevral'skaya revolyutsiya, p=fʲɪvˈralʲskəjə rʲɪvɐˈlʲutsɨjə), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and somet ...
and joined the Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
s later that year. She was laid up in 1918 for lack of manpower, but her crew joined the Kronstadt Rebellion
The Kronstadt rebellion ( rus, Кронштадтское восстание, Kronshtadtskoye vosstaniye) was a 1921 insurrection of Soviet sailors and civilians against the Bolshevik government in the Russian SFSR port city of Kronstadt. Locat ...
of 1921. She was renamed ''Parizhskaya Kommuna'' after the rebellion was crushed to commemorate the Paris Commune
The Paris Commune (french: Commune de Paris, ) was a revolutionary government that seized power in Paris, the capital of France, from 18 March to 28 May 1871.
During the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71, the French National Guard had defended ...
and to erase the ship's 'betrayal' of the Communist Party
A communist party is a political party that seeks to realize the socio-economic goals of communism. The term ''communist party'' was popularized by the title of ''The Manifesto of the Communist Party'' (1848) by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. A ...
.
She was recommissioned in 1925, and refitted in 1928 in preparation for her transfer to the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
the following year. ''Parizhskaya Kommuna'' and the cruiser ''Profintern'' ran into a severe storm in the Bay of Biscay
The Bay of Biscay (), known in Spain as the Gulf of Biscay ( es, Golfo de Vizcaya, eu, Bizkaiko Golkoa), and in France and some border regions as the Gulf of Gascony (french: Golfe de Gascogne, oc, Golf de Gasconha, br, Pleg-mor Gwaskogn), ...
that severely damaged ''Parizhskaya Kommuna''s false bow. They had to put into Brest
Brest may refer to:
Places
*Brest, Belarus
**Brest Region
**Brest Airport
**Brest Fortress
*Brest, Kyustendil Province, Bulgaria
*Břest, Czech Republic
*Brest, France
**Arrondissement of Brest
**Brest Bretagne Airport
** Château de Brest
*Brest, ...
for repairs, but reached Sevastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
in January 1930. ''Parizhskaya Kommuna'' was comprehensively reconstructed in two stages during the 1930s that replaced her boilers, upgraded her guns, augmented her anti-aircraft armament, modernized her fire-control systems and gave her anti-torpedo bulge
The anti-torpedo bulge (also known as an anti-torpedo blister) is a form of defence against naval torpedoes occasionally employed in warship construction in the period between the First and Second World Wars. It involved fitting (or retrofitting ...
s. During World War II she provided gunfire support during the Siege of Sevastopol and related operations until she was withdrawn from combat in April 1942 when the risk from German aerial attack became too great. She was retained on active duty after the war until she became a training ship in 1954. She was broken up in 1956–1957.
Design and description
 ''Sevastopol'' was long at the waterline and long
''Sevastopol'' was long at the waterline and long overall
Overalls, also called bib-and-brace overalls or dungarees, are a type of garment usually used as protective clothing when working. The garments are commonly referred to as a "pair of overalls" by analogy with "pair of trousers".
Overalls were ...
. She had a beam
Beam may refer to:
Streams of particles or energy
*Light beam, or beam of light, a directional projection of light energy
**Laser beam
*Particle beam, a stream of charged or neutral particles
**Charged particle beam, a spatially localized grou ...
of and a draft
Draft, The Draft, or Draught may refer to:
Watercraft dimensions
* Draft (hull), the distance from waterline to keel of a vessel
* Draft (sail), degree of curvature in a sail
* Air draft, distance from waterline to the highest point on a vessel ...
of , more than designed. Her displacement was at load, over more than her designed displacement of .
''Sevastopol''s machinery was built by the Baltic Works. Ten Parsons
Parsons may refer to:
Places
In the United States:
* Parsons, Kansas, a city
* Parsons, Missouri, an unincorporated community
* Parsons, Tennessee, a city
* Parsons, West Virginia, a town
* Camp Parsons, a Boy Scout camp in the state of Washingt ...
-type steam turbine
A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Charles Parsons in 1884. Fabrication of a modern steam turbin ...
s drove the four propellers. The engine rooms were located between turrets three and four in three transverse compartments. The outer compartments each had a high-pressure ahead and reverse turbine for each wing propeller shaft. The central engine room had two each low-pressure ahead and astern turbines as well as two cruising turbines driving the two center shafts. The engines had a total designed output of , but they produced during her sister
A sister is a woman or a girl who shares one or more parents with another individual; a female sibling. The male counterpart is a brother. Although the term typically refers to a familial relationship, it is sometimes used endearingly to refer to ...
s full-speed trials on 21 November 1915 and gave a top speed of . Twenty-five Yarrow boiler
Yarrow boilers are an important class of high-pressure water-tube boilers. They were developed by
Yarrow & Co. (London), Shipbuilders and Engineers and were widely used on ships, particularly warships.
The Yarrow boiler design is characteristic ...
s provided steam to the engines at a designed working pressure of . Each boiler was fitted with Thornycroft
Thornycroft was an English vehicle manufacturer which built coaches, buses, and trucks from 1896 until 1977.
History
In 1896, naval engineer John Isaac Thornycroft formed the Thornycroft Steam Carriage and Van Company which built its firs ...
oil sprayers for mixed oil/coal burning. They were arranged in two groups. The forward group consisted of two boiler rooms in front of the second turret, the foremost of which had three boilers while the second one had six. The rear group was between the second and third turrets and comprised two compartments, each with eight boilers. At full load she carried of coal and of fuel oil
Fuel oil is any of various fractions obtained from the distillation of petroleum (crude oil). Such oils include distillates (the lighter fractions) and residues (the heavier fractions). Fuel oils include heavy fuel oil, marine fuel oil (MFO), bun ...
and that provided her a range of at a speed of .
The main armament of the ''Gangut''s consisted of a dozen 52-caliber
In guns, particularly firearms, caliber (or calibre; sometimes abbreviated as "cal") is the specified nominal internal diameter of the gun barrel Gauge (firearms) , bore – regardless of how or where the bore is measured and whether the f ...
Obukhovskii Pattern 1907 guns mounted in four triple turrets distributed the length of the ship. The Russians did not believe that superfiring
Superfiring armament is a naval military building technique in which two (or more) turrets are located in a line, one behind the other, with the second turret located above ("super") the one in front so that the second turret can fire over the ...
turrets offered any advantage, discounting the value of axial fire and believing that superfiring turrets could not fire while over the lower turret because of muzzle blast
A muzzle blast is an explosive shockwave created at the muzzle of a firearm during shooting. Before a projectile leaves the gun barrel, it obturates the bore and "plugs up" the pressurized gaseous products of the propellant combustion behind i ...
problems. They also believed that distributing the turrets, and their associated magazine
A magazine is a periodical publication, generally published on a regular schedule (often weekly or monthly), containing a variety of content. They are generally financed by advertising, purchase price, prepaid subscriptions, or by a combinatio ...
s, over the length of the ship improved the survivability of the ship. Sixteen 50-caliber Pattern 1905 guns were mounted in casemate
A casemate is a fortified gun emplacement or armored structure from which artillery, guns are fired, in a fortification, warship, or armoured fighting vehicle.Webster's New Collegiate Dictionary
When referring to Ancient history, antiquity, th ...
s as the secondary battery intended to defend the ship against torpedo boat
A torpedo boat is a relatively small and fast naval ship designed to carry torpedoes into battle. The first designs were steam-powered craft dedicated to ramming enemy ships with explosive spar torpedoes. Later evolutions launched variants of se ...
s. The ships were completed with only a single 30-caliber ''Lender'' anti-aircraft (AA) gun mounted on the quarterdeck. Other AA guns were probably added during the course of World War I, but details are lacking.McLaughlin, pp. 220–21 Budzbon says that four were added to the roofs of the end turrets during the war. Four submerged torpedo tube
A torpedo tube is a cylindrical device for launching torpedoes.
There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to submarines and some surface ships, and deck-mounted units (also referred to as torpedo launchers) installed aboa ...
s were mounted with three torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, su ...
es for each tube.
Service
''Sevastopol'' was built by theBaltic Works
The OJSC Baltic Shipyard (''Baltiysky Zavod'', formerly Shipyard 189 named after Grigoriy Ordzhonikidze) (russian: Балтийский завод имени С. Орджоникидзе) is one of the oldest shipyards in Russia and is part of ...
in Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
. Her keel was laid down on 16 June 1909 and she was launched on 10 July 1911. She was commissioned on 30 November 1914 and reached Helsingfors
Helsinki ( or ; ; sv, Helsingfors, ) is the Capital city, capital, primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Finland, most populous city of Finland. Located on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, it is the seat of the region of U ...
late the next month where she was assigned to the First Battleship Brigade of the Baltic Fleet
, image = Great emblem of the Baltic fleet.svg
, image_size = 150
, caption = Baltic Fleet Great ensign
, dates = 18 May 1703 – present
, country =
, allegiance = (1703–1721) (1721–1917) (1917–1922) (1922–1991)(1991–present)
...
. ''Sevastopol'' and her sister
A sister is a woman or a girl who shares one or more parents with another individual; a female sibling. The male counterpart is a brother. Although the term typically refers to a familial relationship, it is sometimes used endearingly to refer to ...
provided distant cover for minelaying
A minelayer is any warship, submarine or military aircraft deploying explosive mines. Since World War I the term "minelayer" refers specifically to a naval ship used for deploying naval mines. "Mine planting" was the term for installing controll ...
operations south of Liepāja
Liepāja (; liv, Līepõ; see #Names and toponymy, other names) is a state city in western Latvia, located on the Baltic Sea. It is the largest-city in the Kurzeme Planning Region, Kurzeme Region and the third-largest city in the country after R ...
on 27 August, the furthest that any Russian dreadnought ventured out of the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and E ...
during World War I. She ran aground on 10 September and was under repair for two months. On 17 October a half-charge of powder was dropped and ignited when it impacted the floor of the forward magazine. Flooding the magazine prevented an explosion, but the fire killed two men and burned a number of others. She saw no action of any kind during 1916, but hit underwater rocks twice that year, suffering minor damage each time. Her crew joined the general mutiny of the Baltic Fleet on 16 March 1917, after the idle sailors received word of the February Revolution
The February Revolution ( rus, Февра́льская револю́ция, r=Fevral'skaya revolyutsiya, p=fʲɪvˈralʲskəjə rʲɪvɐˈlʲutsɨjə), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and somet ...
in Saint Petersburg. The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace, separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russian SFSR, Russia and the Central Powers (German Empire, Germany, Austria-Hungary, Kingdom of ...
required the Soviets to evacuate their base at Helsinki in March 1918 or have them interned by newly independent Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
, even though the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and E ...
was still frozen over. ''Sevastopol'' and her sisters led the first group of ships out on 12 March and reached Kronstadt
Kronstadt (russian: Кроншта́дт, Kronshtadt ), also spelled Kronshtadt, Cronstadt or Kronštádt (from german: link=no, Krone for "crown" and ''Stadt'' for "city") is a Russian port city in Kronshtadtsky District of the federal city of ...
five days later in what became known as the 'Ice Voyage'.
The crew of the ''Sevastopol'' joined the Kronstadt Rebellion
The Kronstadt rebellion ( rus, Кронштадтское восстание, Kronshtadtskoye vosstaniye) was a 1921 insurrection of Soviet sailors and civilians against the Bolshevik government in the Russian SFSR port city of Kronstadt. Locat ...
of March 1921. She returned fire when the Bolsheviks began to bombard Kronstadt Island and was hit by three 12-inch shells that killed or wounded 102 sailors. After the rebellion was bloodily crushed, she was renamed ''Parizhskaya Kommuna'' after the Paris Commune
The Paris Commune (french: Commune de Paris, ) was a revolutionary government that seized power in Paris, the capital of France, from 18 March to 28 May 1871.
During the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71, the French National Guard had defended ...
on 31 March 1921. She was refitted several times before she was recommissioned on 17 September 1925. She was refitted again in 1928 at the Baltic Shipyard, in preparation for her transfer to the Black Sea Fleet
Chernomorskiy flot
, image = Great emblem of the Black Sea fleet.svg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Great emblem of the Black Sea fleet
, dates = May 13, ...
. Her forward funnel was raised and the upper part was angled aft in an attempt to keep the exhaust gases out of the control and gunnery spaces, while three 3-inch 'Lender' AA guns were added to the roofs of the fore and aft turrets. She received some additional rangefinder
A rangefinder (also rangefinding telemeter, depending on the context) is a device used to measure distances to remote objects. Originally optical devices used in surveying, they soon found applications in other fields, such as photography an ...
s and she was given a false bow to improve her sea-keeping ability. She sailed for the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
on 22 November 1929, in company of the cruiser ''Profintern'', encountering a bad storm in the Bay of Biscay. The open-topped bow lacked enough drainage and tended to trap a lot of water which badly damaged both the false bow and the supporting structure. ''Parizhskaya Kommuna'' was forced to put into Brest
Brest may refer to:
Places
*Brest, Belarus
**Brest Region
**Brest Airport
**Brest Fortress
*Brest, Kyustendil Province, Bulgaria
*Břest, Czech Republic
*Brest, France
**Arrondissement of Brest
**Brest Bretagne Airport
** Château de Brest
*Brest, ...
for repairs, which included the removal of the bulwark that retained so much water. Both ships arrived at Sevastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
on 18 January 1930 and ''Parizhskaya Kommuna'' became the flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the fi ...
of the Black Sea Fleet.
Reconstruction
She temporarily mounted an importedHeinkel
Heinkel Flugzeugwerke () was a German aircraft manufacturing company founded by and named after Ernst Heinkel. It is noted for producing bomber aircraft for the Luftwaffe in World War II and for important contributions to high-speed flight, with ...
aircraft catapult
An aircraft catapult is a device used to allow aircraft to take off from a very limited amount of space, such as the deck of a vessel, but can also be installed on land-based runways in rare cases. It is now most commonly used on aircraft carrier ...
atop the third turret between 1930 and 1933. It was transferred to the cruiser when the battleship began the first stage of her reconstruction in November 1933. This was based on that done for her sister ''Oktyabrskaya Revolyutsiya'', but was even more extensive. Her rear superstructure was enlarged and a new structure was built just forward of it which required the repositioning of the mainmast forward. This did not leave enough room for a derrick
A derrick is a lifting device composed at minimum of one guyed mast, as in a gin pole, which may be articulated over a load by adjusting its guys. Most derricks have at least two components, either a guyed mast or self-supporting tower, and a ...
, as was fitted in ''Marat'', and two large booms were fitted to handle aircraft while the existing boat cranes remained in place. The mast had to be reinforced by two short legs to handle the weight of the booms and their loads. Her false bow was reworked into a real forecastle
The forecastle ( ; contracted as fo'c'sle or fo'c's'le) is the upper deck of a sailing ship forward of the foremast, or, historically, the forward part of a ship with the sailors' living quarters. Related to the latter meaning is the phrase " be ...
like those fitted to her sisters. All twenty-five of her old boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central h ...
s were replaced by a dozen oil-fired boilers originally intended for the s. The space saved was used to add another inboard longitudinal watertight bulkhead that greatly improved her underwater protection.
Her turrets were modified to use a fixed loading angle of 6° and fitted with more powerful elevating motors which increased their rate of fire to two rounds per minute. Their maximum elevation was increased to 40° which extended their range to and they were redesignated as MK-3-12 Mod. She landed her old 'Lender' AA guns and replaced them with six semi-automatic ''21-K'' AA guns, three atop the fore and aft turrets. Three 34-K each were mounted on platforms on the fore and aft superstructures as well as a total of twelve DShK
The DShK 1938 (Cyrillic: ДШК, for russian: Дегтярёва-Шпагина Крупнокалиберный, Degtyaryova-Shpagina Krupnokaliberny, links=no, "Degtyaryov-Shpagin large-calibre") is a Soviet heavy machine gun with a V-shaped but ...
M machine gun
A machine gun is a fully automatic, rifled autoloading firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles (including assault rifles and battle rifles) a ...
s. Her fire-control system was completely revised with a pair of KDP-6 fire control director, equipped with two Zeiss Zeiss or Zeiß may refer to:
People
*Carl Zeiss (1816–1888), German optician and entrepreneur
*Emil Zeiß (1833–1910), German Protestant minister and painter
Companies
*Carl Zeiss AG, German manufacturer of optics, industrial measurem ...
rangefinder
A rangefinder (also rangefinding telemeter, depending on the context) is a device used to measure distances to remote objects. Originally optical devices used in surveying, they soon found applications in other fields, such as photography an ...
s positioned atop both superstructures.McLaughlin, p. 345 Her original Pollen Argo Clock mechanical fire-control computer was replaced with a copy of a Vickers Ltd
Vickers Limited was a British engineering conglomerate. The business began in Sheffield in 1828 as a steel foundry and became known for its church bells, going on to make shafts and propellers for ships, armour plate and then artillery. Entir ...
fire-control computer, designated AKUR by the Soviets, as well as a copy of a Sperry Sperry may refer to:
Places
In the United States:
*Sperry, Iowa, community in Des Moines County
*Sperry, Missouri
*Sperry, Oklahoma, town in Tulsa County
*Sperry Chalet, historic backcountry chalet, Glacier National Park, Montana
*Sperry Glacier, ...
stable vertical gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rota ...
. She also received the first stabilized anti-aircraft directors in the Soviet fleet, SVP-1s that were fitted on each side of the forward superstructure. They were manually stabilized and less than satisfactory as the men manning them had difficulties keeping their sights on the horizon while the ship's motions were violent.
''Parizhskaya Kommuna'' finished the first stage of her reconstruction in January 1938 with unresolved stability issues derived from all of the additional topweight. The options to cure this were discussed at length until Marshal Voroshilov, the People's Commissar for Defense approved the addition of anti-torpedo bulges in 1939 which would increase the ship's underwater protection and rectify her stability problem. The second part of the reconstruction was carried out between December 1939 and July 1940. A pair of bulges were fitted that extended from the forward magazine to the rear magazine that increased the ship's beam by . They had an unusual form that consisted of an outer void compartment intended to weaken the explosive force of the torpedo backed by a relatively narrow section immediately adjacent to the original hull that extended from above the waterline to the bottom of the bilge
The bilge of a ship or boat is the part of the hull that would rest on the ground if the vessel were unsupported by water. The "turn of the bilge" is the transition from the bottom of a hull to the sides of a hull.
Internally, the bilges (us ...
. This was divided into two compartments; the lower of which was kept full of either fuel oil or water to absorb splinters and fragments from the explosion while the upper compartment was filled with small watertight tubes intended to preserve the ship's waterplane area and minimize flooding from gunfire hits around the waterline. The underwater torpedo tubes were incompatible with the bulges and were removed at this time. The bulges increased her standard displacement to , increased her metacentric height
The metacentric height (GM) is a measurement of the initial static stability of a floating body. It is calculated as the distance between the centre of gravity of a ship and its metacentre. A larger metacentric height implies greater initial stab ...
to and reduced her speed to . The Soviets took advantage of her extra stability to reinforce her deck armor by completely replacing her middle deck armor with cemented armor plates originally intended for s. These were not ideal as they were harder than desirable for deck plates, but they did have the prime virtue of being free. At some point, the exact date is unknown, her 45-mm guns were removed and sixteen ''70-K'' automatic AA guns were added, three each on the fore and aft turret tops and twelve in the superstructures.
World War II
Four of ''Parizhskaya Kommunas 120-mm guns were landed shortly before 22 June 1941.McLaughlin, p. 407 When the Germans invaded she was in Sevastopol,Rohwer, pp. 111, 119 and she was initially kept in reserve during the Soviet attack on the Romanian port of Constanța. She was evacuated toNovorossiysk
Novorossiysk ( rus, Новоросси́йск, p=nəvərɐˈsʲijsk; ady, ЦIэмэз, translit=Chəməz, p=t͡sʼɜmɜz) is a city in Krasnodar Krai, Russia. It is one of the largest ports on the Black Sea. It is one of the few cities hono ...
on 30 October after the Germans breached Soviet defensive lines near the Perekop Isthmus
The Isthmus of Perekop, literally Isthmus of the Trench ( uk, Перекопський перешийок; transliteration: ''Perekops'kyy pereshyyok''; russian: Перекопский перешеек; transliteration: ''Perekopskiy peresheek ...
. During 28–29 November she bombarded German and Romanian troops south of Sevastopol with 146 12-inch and 299 120-mm shells. On 29 November, three crew were washed overboard in a storm at Sevastopol and died. They were the only crew lost during the war. ''Parizhskaya Kommuna'' ran aground but was quickly refloated. She steamed into Sevastopol's South Bay on 29 December and fired 179 and 265 120-mm shells at German troops before embarking 1,025 wounded and departing in company with the cruiser on the 31st.McLaughlin, p. 402 She bombarded German positions south of Feodosiya
uk, Феодосія, Теодосія crh, Kefe
, official_name = ()
, settlement_type=
, image_skyline = THEODOSIA 01.jpg
, imagesize = 250px
, image_caption = Genoese fortress of Caffa
, image_shield = Fe ...
on the evening of 4–5 January 1942 and on 12 January. ''Parizhskaya Kommuna'' provided gunfire support during Soviet landings behind German lines along the southern coast of the Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
three days later. She bombarded German positions west and north of Feodosiya on the nights of 26–28 February in support of an offensive
Offensive may refer to:
* Offensive, the former name of the Dutch political party Socialist Alternative
* Offensive (military), an attack
* Offensive language
** Fighting words or insulting language, words that by their very utterance inflict inj ...
by the 44th Army
The 44th Army (russian: 44-я армия) of the Soviet Union's Red Army was an army-level command active during World War II. Initially part of the Transcaucasian Front, its main actions included the Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran and the Kerch a ...
. She fired her last shots of the war at targets near Feodosiya during the nights of 20–22 March 1942 before returning to Poti
Poti ( ka, ფოთი ; Mingrelian: ფუთი; Laz: ჶაში/Faşi or ფაში/Paşi) is a port city in Georgia, located on the eastern Black Sea coast in the region of Samegrelo-Zemo Svaneti in the west of the country. Built near t ...
, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, to have her worn-out 12-inch guns relined. By the time this was finished the Soviets were unwilling to expose such a prominent ship to German air attacks, which had already sunk a number of cruisers and destroyers. She returned to her original name on 31 May 1943, but remained in Poti until late 1944 when she led the surviving major units of the Black Sea Fleet back to Sevastopol on 5 November. Lend-Lease
Lend-Lease, formally the Lend-Lease Act and introduced as An Act to Promote the Defense of the United States (), was a policy under which the United States supplied the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union and other Allied nations with food, oil, ...
British Type 290 and 291 air-warning radars were fitted during the war. She was awarded the Order of the Red Banner
The Order of the Red Banner (russian: Орден Красного Знамени, Orden Krasnogo Znameni) was the first Soviet military decoration. The Order was established on 16 September 1918, during the Russian Civil War by decree of th ...
on 8 July 1945.
She was reclassified as a 'school battleship' on 24 July 1954 and stricken on 17 February 1956. She was scrap
Scrap consists of Recycling, recyclable materials, usually metals, left over from product manufacturing and consumption, such as parts of vehicles, building supplies, and surplus materials. Unlike waste, scrap Waste valorization, has monetary ...
ped at Sevastopol in 1956–1957.McLaughlin, p. 227
Notes
Footnotes
Bibliography
* * * * *External links
Specifications
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sevastopol (1911) Gangut-class battleships World War I battleships of Russia 1911 ships Ships built at the Baltic Shipyard Maritime incidents in 1915 Maritime incidents in 1916 Maritime incidents in 1929 Maritime incidents in November 1941