Russian Armenia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Russian Armenia is the period of
Russian Armenia is the period of
''Russia at War: From the Mongol Conquest to Afghanistan, Chechnya, and Beyond''
pp 729 ABC-CLIO, 2 dec. 2014 Eastern Armenia remained part of the Russian Empire until its collapse in 1917.

 For hundreds of years, the inhabitants of Eastern Armenia lived under the rule of successive
For hundreds of years, the inhabitants of Eastern Armenia lived under the rule of successive
 Relations between the Russian authorities and their new Armenian subjects did not begin smoothly. Since Armenia was on Russia's frontline against the rival empires of the Ottomans and Persians, it was initially treated as a military zone. Until 1840, Russian Armenia was a separate administrative unit, the
Relations between the Russian authorities and their new Armenian subjects did not begin smoothly. Since Armenia was on Russia's frontline against the rival empires of the Ottomans and Persians, it was initially treated as a military zone. Until 1840, Russian Armenia was a separate administrative unit, the
 The new tsar, Alexander III, was ultra-conservative in outlook and wanted to create a highly centralised, autocratic state. He viewed any expression of a desire for increased freedom and autonomy by his subjects as evidence of rebellion.
The new tsar, Alexander III, was ultra-conservative in outlook and wanted to create a highly centralised, autocratic state. He viewed any expression of a desire for increased freedom and autonomy by his subjects as evidence of rebellion.

 The years between the 1905 Revolution and World War I saw a rapprochement between most Armenians and the Russian authorities. Russia became concerned when her enemy Germany began drawing closer to the
The years between the 1905 Revolution and World War I saw a rapprochement between most Armenians and the Russian authorities. Russia became concerned when her enemy Germany began drawing closer to the
 The Ottoman authorities embarked on the genocide of their Armenian subjects as early as April 1915 following the rapid Russian advance in the Caucasus Campaign and the Siege of Van. An
The Ottoman authorities embarked on the genocide of their Armenian subjects as early as April 1915 following the rapid Russian advance in the Caucasus Campaign and the Siege of Van. An
 The major problem confronting the new state was the advancing Ottoman army, which by now had recaptured much of western Armenia, but the interests of the three peoples were very different. For obvious reasons, defence against the invading army was of paramount importance to the Armenians, while the Muslim Azeris were sympathetic to the Turks. The Georgians felt that their interests could best be guaranteed by coming to a deal with the Germans rather than the Turks and on May 26, 1918, at German prompting, Georgia declared its independence from the Transcaucasian Republic. This move was followed two days later by Azerbaijan. Reluctantly, the Dashnak leaders, who were the most powerful Armenian politicians in the region, declared the formation of a new independent state, the
The major problem confronting the new state was the advancing Ottoman army, which by now had recaptured much of western Armenia, but the interests of the three peoples were very different. For obvious reasons, defence against the invading army was of paramount importance to the Armenians, while the Muslim Azeris were sympathetic to the Turks. The Georgians felt that their interests could best be guaranteed by coming to a deal with the Germans rather than the Turks and on May 26, 1918, at German prompting, Georgia declared its independence from the Transcaucasian Republic. This move was followed two days later by Azerbaijan. Reluctantly, the Dashnak leaders, who were the most powerful Armenian politicians in the region, declared the formation of a new independent state, the
 The
The
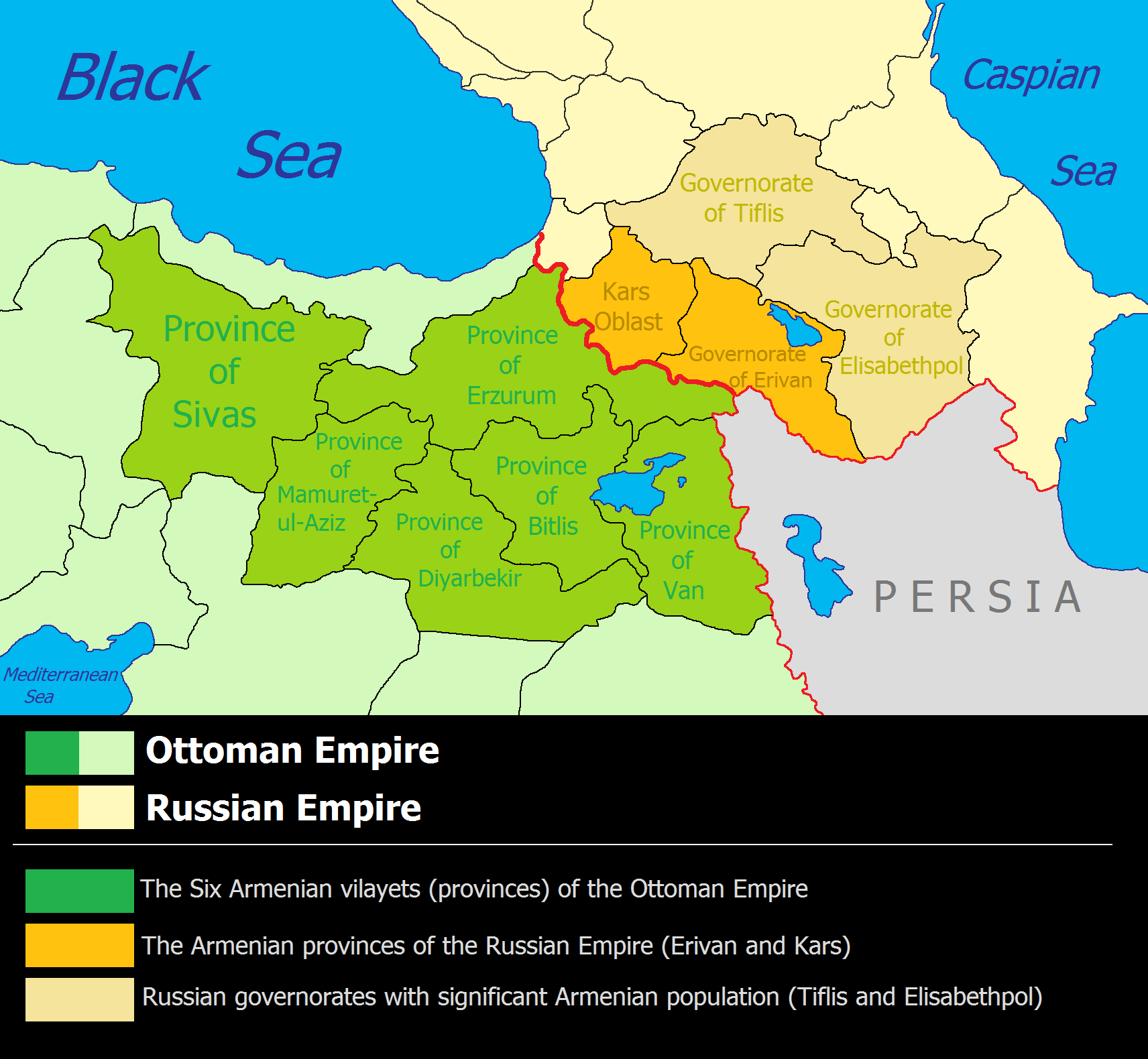
File:Administrative map of Kars Oblast-1913.png, Kars Oblast. Russian map.
File:Administrative map of Erivan Governorate - 1913.gif, Erivan Governorate. Russian map.
File:Administrative map of Elisabethpol Governorate - 1913.gif, Elisabethpol Governorate. Russian map.
 Russian Armenia is the period of
Russian Armenia is the period of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
n history under Russian rule from 1828, when Eastern Armenia
Eastern Armenia ( hy, Արևելյան Հայաստան ''Arevelyan Hayastan'') comprises the eastern part of the Armenian Highlands, the traditional homeland of the Armenian people. Between the 4th and the 20th centuries, Armenia was partitione ...
became part of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
following Qajar Iran
Qajar Iran (), also referred to as Qajar Persia, the Qajar Empire, '. Sublime State of Persia, officially the Sublime State of Iran ( fa, دولت علیّه ایران ') and also known then as the Guarded Domains of Iran ( fa, ممالک م ...
's loss in the Russo-Persian War (1826–1828)
The Russo-Persian War of 1826–1828 was the last major military conflict between the Russian Empire and Persia.
After the Treaty of Gulistan that concluded the previous Russo-Persian War in 1813, peace reigned in the Caucasus for thirteen ...
and the subsequent ceding of its territories that included Eastern Armenia per the out coming Treaty of Turkmenchay
The Treaty of Turkmenchay ( fa, عهدنامه ترکمنچای; russian: Туркманчайский договор) was an agreement between Qajar Iran and the Russian Empire, which concluded the Russo-Persian War (1826–28). It was second ...
of 1828.Timothy C. Dowlin''Russia at War: From the Mongol Conquest to Afghanistan, Chechnya, and Beyond''
pp 729 ABC-CLIO, 2 dec. 2014 Eastern Armenia remained part of the Russian Empire until its collapse in 1917.
Background


 For hundreds of years, the inhabitants of Eastern Armenia lived under the rule of successive
For hundreds of years, the inhabitants of Eastern Armenia lived under the rule of successive Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
ian empires. Starting from the early 16th century, up to 1828, Eastern Armenia was ruled by the Iranian Safavid
Safavid Iran or Safavid Persia (), also referred to as the Safavid Empire, '. was one of the greatest Iranian empires after the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia, which was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often conside ...
, Afsharid
Afsharid Iran ( fa, ایران افشاری), also referred as the Afsharid Empire was an Iranian empire established by the Turkoman Afshar tribe in Iran's north-eastern province of Khorasan, ruling Iran (Persia). The state was ruled by the A ...
, and Qajar
Qajar Iran (), also referred to as Qajar Persia, the Qajar Empire, '. Sublime State of Persia, officially the Sublime State of Iran ( fa, دولت علیّه ایران ') and also known then as the Guarded Domains of Iran ( fa, ممالک م ...
dynasties. Subsequent wars between the Ottoman and Safavid empires led to the destruction of many of the Armenian towns, and made Armenian life difficult. Added to this, the Christian Armenians were dhimmi
' ( ar, ذمي ', , collectively ''/'' "the people of the covenant") or () is a historical term for non-Muslims living in an Islamic state with legal protection. The word literally means "protected person", referring to the state's obligatio ...
subjects (forming a ''millet'') under Muslim rulers, whether Ottomans or Persians.
In 1678, the Armenian leadership secretly conducted a congress in Echmiadzin
Vagharshapat ( hy, Վաղարշապատ ) is the 4th-largest city in Armenia and the most populous municipal community of Armavir Province, located about west of the capital Yerevan, and north of the closed Turkish-Armenian border. It is comm ...
, and decided that Armenia had to be liberated from foreign domination. At this stage, the Armenians were unable to fight against two empires at once, so they searched for help from abroad. Israel Ori
Israel Ori () (1658–1711) was a prominent figure of the Armenian national liberation movement and a diplomat that sought the liberation of Armenia from Persia and the Ottoman Empire.
Early life
Ori was born in 1658 in the village of Sisian i ...
, an Armenian native of Karabagh, son of an Armenian melik
Мelik (also transliterated as ''Meliq'') ( ''melikʿ''; from ar, ملك '' malik'' (king)) was a hereditary Armenian noble title, in various Eastern Armenian principalities known as ''melikdom''s encompassing modern Yerevan, Kars, Nakhi ...
or prince, searched for help in many of the European capitals. Israel Ori died in 1711, without seeing the Armenian Dream realized. In 1722, the Tsar of Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
, Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
, declared war against the Safavid Iranians, who were at that time in heavy decline. Georgians
The Georgians, or Kartvelians (; ka, ქართველები, tr, ), are a nation and indigenous Caucasian ethnic group native to Georgia and the South Caucasus. Georgian diaspora communities are also present throughout Russia, Turkey, ...
and Karabagh's Armenians helped the Russians by rebelling against Safavid rule. David Bek
Davit Bek or David Beg (; died 1728) was an Armenian military commander and the leader of an Armenian rebellion against invading Ottoman forces and implanted Safavid Muslim tribes in the mountainous region of Zangezur (today the Armenian provin ...
commanded the rebellion for six years, until he died on the battlefield.
The Russian annexation and Persia's ceding
A turning-point came in 1801 when the Russiansannexed
Annexation (Latin ''ad'', to, and ''nexus'', joining), in international law, is the forcible acquisition of one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. It is generally held to be an illegal act ...
the Georgian Kingdom of Kartli-Kakheti
The Kingdom of Kartli-Kakheti ( ka, ქართლ-კახეთის სამეფო, tr) (1762–1801
) was created in 1762 by the unification of two Eastern Georgia (country), eastern Georgian kingdoms of Kingdom of Kartli, Kartli and ...
, giving them a foothold in Transcaucasia
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
. Over the next three decades, Russia sought to further expand its territory in the Caucasus at the expense of Ottoman Turkey and Qajar Iran. The Russian campaigns found enthusiastic support amongst the Armenians, led by the Bishop of Tbilisi
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), is the capital and the largest city of Georgia, lying on the banks of the Kura River with a population of approximately 1.5 million pe ...
, Nerses Ashtaraketsi, who took part in the fighting in person. The Russo-Persian War of 1804–1813 saw the Russians conquer a bit of territory in eastern Armenia only to renounce most of it at the Treaty of Gulistan
The Treaty of Gulistan (russian: Гюлистанский договор; fa, عهدنامه گلستان) was a peace treaty concluded between the Russian Empire and Iran on 24 October 1813 in the village of Gulistan (now in the Goranboy Distr ...
.
In 1826, in violation of the Gulistan treaty, the Russians occupied parts of Iran's Erivan Khanate. This sparked the final bout of hostilities between the two; the Russo-Persian War of 1826–1828. In the subsequent war that raged, (Russo-Persian War (1826–1828)
The Russo-Persian War of 1826–1828 was the last major military conflict between the Russian Empire and Persia.
After the Treaty of Gulistan that concluded the previous Russo-Persian War in 1813, peace reigned in the Caucasus for thirteen ...
), the Qajarid Iranians suffered an even bigger disaster, as Russia occupied as far as Tabriz
Tabriz ( fa, تبریز ; ) is a city in northwestern Iran, serving as the capital of East Azerbaijan Province. It is the sixth-most-populous city in Iran. In the Quru River valley in Iran's historic Azerbaijan region between long ridges of vo ...
in mainland Iran. At the end of the war, in 1828, with the Treaty of Turkmenchay
The Treaty of Turkmenchay ( fa, عهدنامه ترکمنچای; russian: Туркманчайский договор) was an agreement between Qajar Iran and the Russian Empire, which concluded the Russo-Persian War (1826–28). It was second ...
, Iran was forced to cede its territories comprising the Erivan Khanate (comprising modern-day Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
), the Nakhichevan Khanate
The Nakhichevan Khanate ( fa, خانات نخجوان, translit=Khānāt-e Nakhchevān; Azerbaijani:ناخچیوان خانلیغی,Naxçıvan xanlığı; hy, Նախիջեւանի խանութիւն, translit=Naxijewani xanowt'iwn) was a khanate ...
, as well as the remainder of the Republic of Azerbaijan that had not been ceded forcefully in 1813. By this time, in 1828, the century-long Iranian rule over Eastern Armenia
Eastern Armenia ( hy, Արևելյան Հայաստան ''Arevelyan Hayastan'') comprises the eastern part of the Armenian Highlands, the traditional homeland of the Armenian people. Between the 4th and the 20th centuries, Armenia was partitione ...
had thus officially come to an end.
Demographic shifts
Until the late fifteenth century, Armenians had constituted a majority inEastern Armenia
Eastern Armenia ( hy, Արևելյան Հայաստան ''Arevelyan Hayastan'') comprises the eastern part of the Armenian Highlands, the traditional homeland of the Armenian people. Between the 4th and the 20th centuries, Armenia was partitione ...
.
At the close of the fifteenth century, with the rise of the Safavids
Safavid Iran or Safavid Persia (), also referred to as the Safavid Empire, '. was one of the greatest Iranian empires after the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia, which was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often conside ...
, Islam had become the dominant faith, and Armenians became a minority in Eastern Armenia.
Some 80% of the population of Iranian Armenia were Muslims (Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian. ...
, Turkics
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to ...
, and Kurds ug:كۇردلار
Kurds ( ku, کورد ,Kurd, italic=yes, rtl=yes) or Kurdish people are an Iranian peoples, Iranian ethnic group native to the mountainous region of Kurdistan in Western Asia, which spans southeastern Turkey, northwestern Ir ...
) whereas Christian Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
constituted a minority of about 20%, mainly because of the sixteenth-century wars with the Ottomans and the early seventeenth-century forced deportations of Armenians from the region by Shah Abbas I
Abbas I ( fa, ; 27 January 157119 January 1629), commonly known as Abbas the Great (), was the 5th Safavid Shah (king) of Iran, and is generally considered one of the greatest rulers of Iranian history and the Safavid dynasty. He was the third s ...
. As a result of the Treaty of Gulistan
The Treaty of Gulistan (russian: Гюлистанский договор; fa, عهدنامه گلستان) was a peace treaty concluded between the Russian Empire and Iran on 24 October 1813 in the village of Gulistan (now in the Goranboy Distr ...
(1813) and the Treaty of Turkmenchay
The Treaty of Turkmenchay ( fa, عهدنامه ترکمنچای; russian: Туркманчайский договор) was an agreement between Qajar Iran and the Russian Empire, which concluded the Russo-Persian War (1826–28). It was second ...
(1828), Iran was forced to cede Iranian Armenia (which also constituted the present-day Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
), to the Russians.
After the Russian administration took hold of Iranian Armenia, the ethnic make-up shifted, and thus for the first time in three centuries, ethnic Armenians started to form a majority once again in one part of historic Armenia. The new Russian administration encouraged the return of ethnic Armenians from Iran proper and Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
to their homeland. As a result, by 1832, the number of ethnic Armenians had matched that of the Muslims. Anyhow, it would be only after the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the ...
and the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878, which brought another influx of Turkish Armenians, that ethnic Armenians once again established a solid majority in Eastern Armenia
Eastern Armenia ( hy, Արևելյան Հայաստան ''Arevelyan Hayastan'') comprises the eastern part of the Armenian Highlands, the traditional homeland of the Armenian people. Between the 4th and the 20th centuries, Armenia was partitione ...
. Nevertheless, the city of Erivan remained having a Muslim majority up to the twentieth century. According to the traveller H. F. B. Lynch, the city was about 50% Armenian and 50% Muslim (Azerbaijanis
Azerbaijanis (; az, Azərbaycanlılar, ), Azeris ( az, Azərilər, ), or Azerbaijani Turks ( az, Azərbaycan Türkləri, ) are a Turkic people living mainly in northwestern Iran and the Republic of Azerbaijan. They are the second-most nume ...
and Persians) in the early 1890s.
Establishment of Russian rule
Armenian patriots such as Bishop Nerses had hoped for an autonomous Armenia within the Russian Empire, but they were to be disappointed by the new government. Tsar Nicholas and his governor in Transcaucasia,Ivan Paskevich
Count Ivan Fyodorovich Paskevich-Erevansky, Serene Prince of Warsaw (russian: Ива́н Фёдорович Паске́вич-Эриванский, светлейший князь Варшавский, tr. ; – ) was an Imperial Russian mi ...
, had other plans. They wanted the Russian Empire to be a centralised state and when Nerses complained he was soon sent to Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds o ...
, far away from the Caucasus region.
In 1836 a regulation, the ''Polozhenie'' (charter) was enacted by the Russian government that greatly reduced the political powers of the Armenian religious leadership, including that of the Catholicos
Catholicos, plural Catholicoi, is a title used for the head of certain churches in some Eastern Christian traditions. The title implies autocephaly and in some cases it is the title of the head of an autonomous church. The word comes from ancient ...
, while preserving the autonomy of the Armenian Church. After 1836, in accordance with the new regulation, the Catholicos
Catholicos, plural Catholicoi, is a title used for the head of certain churches in some Eastern Christian traditions. The title implies autocephaly and in some cases it is the title of the head of an autonomous church. The word comes from ancient ...
of Echmiadzin
Vagharshapat ( hy, Վաղարշապատ ) is the 4th-largest city in Armenia and the most populous municipal community of Armavir Province, located about west of the capital Yerevan, and north of the closed Turkish-Armenian border. It is comm ...
was to be elected in congresses in Echmiadzin, in which religious and non-religious dignitaries would participate. The Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East and South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the ter ...
would have a last word in the choice of the Catholicos. Armenians greatly profited from the fact that the Catholicosate retained the authority to open schools. Notable ones are Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
's Lazarian Tiflis
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), is the capital and the largest city of Georgia, lying on the banks of the Kura River with a population of approximately 1.5 million pe ...
' Nersessian schools. Moreover, the Catholicosate opened printing houses and encouraged the publication of Armenian newspapers
A newspaper is a periodical publication containing written information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background.
Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as politics, business, spor ...
.
Armenians within the Russian Empire
A significant number of Armenians were already living in the Russian Empire before the 1820s. After the destruction of the last remaining independent Armenian states in the Middle Ages, the nobility disintegrated, leaving Armenian society composed of a mass of peasants plus a middle class who were either craftsmen or merchants. Such Armenians were to be found in most towns of Transcaucasia; indeed, at the beginning of the 19th century they formed the majority of the population in cities such asTbilisi
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), is the capital and the largest city of Georgia, lying on the banks of the Kura River with a population of approximately 1.5 million pe ...
. Armenian merchants conducted their trade across the world and many had set up base within Russia. In 1778, Catherine the Great
, en, Catherine Alexeievna Romanova, link=yes
, house =
, father = Christian August, Prince of Anhalt-Zerbst
, mother = Joanna Elisabeth of Holstein-Gottorp
, birth_date =
, birth_name = Princess Sophie of Anha ...
invited Armenian merchants from the Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
to Russia and they established a settlement at Nor Nakhichevan near Rostov-on-Don
Rostov-on-Don ( rus, Ростов-на-Дону, r=Rostov-na-Donu, p=rɐˈstof nə dɐˈnu) is a port city and the administrative centre of Rostov Oblast and the Southern Federal District of Russia. It lies in the southeastern part of the Eas ...
. The Russian ruling classes welcomed the Armenians' entrepreneurial skills as a boost to the economy, but they also regarded them with some suspicion. The image of the Armenian as a "wily merchant" was already widespread. Russian nobles derived their income from their estates worked by serfs and, with their aristocratic distaste for engaging in business, they had little understanding or sympathy for the way of life of mercantile Armenians.
Nevertheless, middle-class Armenians prospered under Russian rule and they were the first to seize the new opportunities and transform themselves into a prosperous bourgeoisie
The bourgeoisie ( , ) is a social class, equivalent to the middle or upper middle class. They are distinguished from, and traditionally contrasted with, the proletariat by their affluence, and their great cultural and financial capital. Th ...
when capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, private ...
and industrialisation
Industrialisation ( alternatively spelled industrialization) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive re-organisation of an econo ...
came to Transcaucasia in the later half of the 19th century. The Armenians were much more skilled at adapting to the new economic circumstances than their neighbours in Transcaucasia, the Georgians and the Azeris
Azerbaijanis (; az, Azərbaycanlılar, ), Azeris ( az, Azərilər, ), or Azerbaijani Turks ( az, Azərbaycan Türkləri, ) are a Turkic people living mainly in northwestern Iran and the Republic of Azerbaijan. They are the second-most nume ...
. They became the most powerful element in the municipal life of Tbilisi, the city regarded by Georgians as their capital, and in the late 19th century they began to buy up the lands of the Georgian nobility, who had gone into decline after the emancipation of their serfs. Armenian entrepreneurs were quick to exploit the oil boom which began in Transcaucasia in the 1870s, having large investments in the oil-fields in Baku
Baku (, ; az, Bakı ) is the capital and largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and of the Caucasus region. Baku is located below sea level, which makes it the lowest lying national capital in the world an ...
in Azerbaijan and the refineries of Batumi
Batumi (; ka, ბათუმი ) is the List of cities and towns in Georgia (country), second largest city of Georgia (country), Georgia and the capital of the Autonomous Republic of Adjara, located on the coast of the Black Sea in Georgia's ...
on the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
coast. All this meant that the tensions between Armenians, Georgians and Azeris in Russian Transcaucasia were not simply ethnic or religious in nature but were due to social and economic factors too. Nevertheless, in spite of the popular image of the typical Armenian as a successful businessman, at the end of the 19th century 80 per cent of Russian Armenians were still peasants working the land.See Suny Chapter 2 "Images of Armenians in the Russian Empire" in ''Looking Toward Ararat: Armenia in Modern History''. Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 1993
Russian rule until 1877
 Relations between the Russian authorities and their new Armenian subjects did not begin smoothly. Since Armenia was on Russia's frontline against the rival empires of the Ottomans and Persians, it was initially treated as a military zone. Until 1840, Russian Armenia was a separate administrative unit, the
Relations between the Russian authorities and their new Armenian subjects did not begin smoothly. Since Armenia was on Russia's frontline against the rival empires of the Ottomans and Persians, it was initially treated as a military zone. Until 1840, Russian Armenia was a separate administrative unit, the Armenian Oblast
The Armenian Oblast was a province (''oblast'') of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire that existed from 1828 to 1840. It corresponded to most of present-day central Armenia, the Iğdır Province of Turkey, and the Nakhchivan excla ...
, but it was then merged into other Transcaucasian provinces with no regard to its national identity. Things improved when Nerses Ashtaraketsi was recalled from Bessarabia and made Catholicos of the Armenian Church in 1843. Moreover, Mikhail Vorontsov, who ruled Russian Armenia as Viceroy of the Caucasus between 1845 and 1854, was highly sympathetic to the Armenians.
As a consequence, by the mid-19th century, most of the Armenian intelligentsia
The intelligentsia is a status class composed of the university-educated people of a society who engage in the complex mental labours by which they critique, shape, and lead in the politics, policies, and culture of their society; as such, the i ...
had become highly Russophile. Armenian culture flourished in these years as the new unified province under Russian rule gave Armenians a sense of their shared identity once more. Being part of the Russian Empire also turned Armenia away from the Middle East and towards Europe and modern intellectual currents such as the Enlightenment and Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate ...
. A wide array of Armenian newspapers were published and there was a literary revival headed by Mikael Nalbandian
Mikayel Nalbandian ( hy, Միքայել Նալբանդյան; ) was a Russian-Armenian writer, poet, political theorist and activist.
Nalbandian was born in Nakhichevan-on-Don, an Armenian town in southern Russia, and traveled extensively, a ...
, who wanted to modernise the Armenian language
Armenian (Classical Armenian orthography, classical: , Armenian orthography reform, reformed: , , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language and an independent branch of that family of languages. It is the official language of Armenia ...
, and the poet and novelist Raffi
Raffi Cavoukian, ( hy, Րաֆֆի, born July 8, 1948), known professionally by the mononym Raffi, is a Canadian singer-lyricist and author of Armenian descent born in Egypt, best known for his children's music. He developed his career as a " ...
. The pro-Russian outlook of the Armenian intelligentsia continued under Tsar Alexander II
Alexander II ( rus, Алекса́ндр II Никола́евич, Aleksándr II Nikoláyevich, p=ɐlʲɪˈksandr ftɐˈroj nʲɪkɐˈlajɪvʲɪtɕ; 29 April 181813 March 1881) was Emperor of Russia, King of Poland and Grand Duke of Fin ...
, who was widely praised for his reforms.
The Russo-Turkish War
The Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878 marked a watershed in the relationship between the Russian authorities and their Armenian subjects. Armenians still living inwestern Armenia
Western Armenia (Western Armenian: Արեւմտեան Հայաստան, ''Arevmdian Hayasdan'') is a term to refer to the eastern parts of Turkey (formerly the Ottoman Empire) that are part of the historical homeland of the Armenians. Weste ...
under the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
had grown increasingly discontented and looked towards Russia to free them from Turkish rule. In 1877, war broke out between the Russia and the Ottomans over the treatment of Christians in the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
. The Russians were keen to mobilise Armenian patriotism when they advanced on a second front against the Turks in the Caucasus, and many of the commanders they employed were of Armenian descent. The Russians made large territorial gains in western Armenia before an armistice was called in January, 1878.
The Treaty of San Stefano
The 1878 Treaty of San Stefano (russian: Сан-Стефанский мир; Peace of San-Stefano, ; Peace treaty of San-Stefano, or ) was a treaty between the Russian and Ottoman empires at the conclusion of the Russo-Turkish War of 1877-18 ...
, signed in March, 1878, did not grant Russia the whole of western Armenia but it contained a special clause, Article 16, by which Russia guaranteed the rights of Armenians still under Ottoman rule against oppression. However, Russia's Great Power rivals, Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
and Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, had been disturbed at the gains Russia had made at the expense of the Ottomans and pressed for a revision of the treaty. At the Congress of Berlin
The Congress of Berlin (13 June – 13 July 1878) was a diplomatic conference to reorganise the states in the Balkan Peninsula after the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–78, which had been won by Russia against the Ottoman Empire. Represented at th ...
, amongst other territories, Russia was forced to give up all its Armenian gains except the regions of Kars
Kars (; ku, Qers; ) is a city in northeast Turkey and the capital of Kars Province. Its population is 73,836 in 2011. Kars was in the ancient region known as ''Chorzene'', (in Greek Χορζηνή) in classical historiography (Strabo), part of ...
and Ardahan
Ardahan (, ka, არტაანი, tr, hy, Արդահան, translit=Ardahan Russian: Ардаган) is a city in northeastern Turkey, near the Georgian border.
It is the capital of Ardahan Province.
History
Ancient and medieval
Ardaha ...
and Article 16 was replaced by the "meaningless"Suny. ''Looking Toward Ararat'', p. 43 Article 61, which stated that reforms need only be carried out in the Ottoman Armenian provinces after the Russian army had withdrawn.
The reign of Alexander III, 1881–1894
After the assassination of the reform-minded Tsar Alexander II in 1881, the attitude of the Russian authorities towards the national minorities of the empire changed dramatically.Russification
The last decades of the 19th century also saw a rise in Russian chauvinism with non-Russians described in increasingly racist terms. Armenians came in for particular abuse in ways which often resembledanti-Semitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
. The first sign of this was the new regime's dismissal of Alexander II's leading minister, the Armenian Count Loris-Melikov
Count Mikhail Tarielovich Loris-Melikov (, hy, Միքայել Լորիս-Մելիքյան; – 24 December 1888) was a Russian- Armenian statesman, General of the Cavalry, and Adjutant General of H. I. M. Retinue.
The Princes of Lori - Lori ...
. Loris-Melikov was viewed as too liberal but he was also labeled a "frenzied Asiatic" and "not a true Russian patriot". The Russian authorities also began to be suspicious of Armenian economic dominance in Transcaucasia. Ironically, such suspicions of the Armenians - who were among the most Russophile of the tsar's subjects - as an untrustworthy people prone to revolutionary conspiracy led the Russians to introduce policies which produced the very thing they were aimed at preventing, as Armenians turned more and more towards new nationalist movements.
Russification began in earnest in 1885, when the Viceroy of the Caucasus, Dondukov-Korsakov, ordered the closure of all Armenian parish schools and their replacement by Russian ones. Though the Armenian schools were reopened the following year, they were now subject to strict tsarist control and the use of the Armenian language was discouraged in favour of Russian. The Russians also began to persecute the Armenian Church, which had been separate from the Orthodox Church
Orthodox Church may refer to:
* Eastern Orthodox Church
* Oriental Orthodox Churches
* Orthodox Presbyterian Church
* Orthodox Presbyterian Church of New Zealand
* State church of the Roman Empire
* True Orthodox church
See also
* Orthodox (d ...
since the year 451. The Russian attitude to the Ottoman Empire also changed and by the 1890s, Russia and Britain had exchanged roles. Now it was Russia who supported the status quo in western Armenia, with the British urging improvement in conditions for Christians in the region. The Russian authorities were disturbed by revolutionary Armenian nationalist movements within the Ottoman Empire and feared their links with eastern Armenians would increase subversion within Russian Transcaucasia too. The tsarist regime cracked down on any attempt by Russian Armenians to engage in action across the border, a leading example being the Gugunian Expedition of 1890.
The growth of Armenian nationalism
Armenians played little role in the revolutionary movements of the Russian Empire until the 1880s. Until that point, the ideas of Grigor Artsruni, the editor of the Tbilisi-based newspaper ''Mshak'' ("The Cultivator"), enjoyed great popularity among the Armenian intelligentsia. Artsruni believed that life under the Russian Empire represented the "lesser evil" for his people. Russian Armenians were deeply concerned about the plight of their compatriots under the Persian and Ottoman Empires, especially the peasants of western Armenia who were mostly ignored by Ottoman Armenian intellectuals far away inIstanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
and Smyrna
Smyrna ( ; grc, Σμύρνη, Smýrnē, or , ) was a Greek city located at a strategic point on the Aegean coast of Anatolia. Due to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence, and its good inland connections, Smyrna rose to prom ...
. Tbilisi and Yerevan were much more obvious choices for a base for promoting revolutionary activity among Armenians in the eastern Ottoman Empire. The importance of the unity of the Armenia, divided between three empires, ensured that Armenian political movements would have little in common with other political movements in the Russian Empire.
The growth of Armenian nationalism
Armenian nationalism in the modern period has its roots in the romantic nationalism of Mikayel Chamchian (1738–1823) and generally defined as the creation of a free, independent and united Armenia formulated as the Armenian Cause ( hy, Հայ ...
was given impetus by the Russian authorities' anti-Armenian measures of the 1880s. In 1889, Christapor Mikaelian
Christapor Mikaelian ( Armenian: , Krisdapor Mikaelyan/Chrisdapor Mikaelian; 18 October 1859 – 17 March 1905), also known by his ''noms de guerre'' Hellen (), Topal (), and Edward (), was one of the three founders of the Armenian Revolutionary ...
founded the "Young Armenia" movement in Tbilisi. Its aims were carrying out reprisals against Kurds ug:كۇردلار
Kurds ( ku, کورد ,Kurd, italic=yes, rtl=yes) or Kurdish people are an Iranian peoples, Iranian ethnic group native to the mountainous region of Kurdistan in Western Asia, which spans southeastern Turkey, northwestern Ir ...
believed to be guilty of persecuting Armenians in the Ottoman Empire, as well as smuggling arms and encouraging guerrilla action. They also established links with a new Ottoman Armenian nationalist party, the Hunchaks. In 1890, Mikaelian and his colleague Simon Zavarian replaced Young Armenia with a new party: the Armenian Revolutionary Federation
The Armenian Revolutionary Federation ( hy, Հայ Յեղափոխական Դաշնակցութիւն, ՀՅԴ ( classical spelling), abbr. ARF or ARF-D) also known as Dashnaktsutyun (collectively referred to as Dashnaks for short), is an Armenian ...
, usually known as the "Dashnaks". The Dashnaks tried to get the Hunchaks to join them but the two split in 1891 and rivalry between the parties would be a major feature of subsequent Armenian nationalism. Both parties were socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the ...
in their economic programmes. The primary focus of the Dashnaks was nationalism, however, and their chief concern was the fate of the Ottoman Armenians. They soon had branches in Russia, Persia and Turkey and after the fragmentation of the Hunchaks in the mid-1890s, they became the dominant nationalist force in Russian Armenia.
The reign of Nicholas II 1894–1917
Tsar Nicholas II
Nicholas II or Nikolai II Alexandrovich Romanov; spelled in pre-revolutionary script. ( 186817 July 1918), known in the Russian Orthodox Church as Saint Nicholas the Passion-Bearer,. was the last Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Polan ...
, who came to the throne in 1894, continued his father's policy of Russification. Anti-Armenian feeling among the Georgians and Azeris of Transcaucasia was also on the rise, inflamed by the editor of the official newspaper ''Kavkaz'' ("Caucasus"), V.L. Velichko, who was an ardent Russian chauvinist.
Edict on Armenian church property 1903–1904
In 1897, Tsar Nicholas appointed the Armenophobic Grigory Sergeyevich Golitsin as governor of Transcaucasia, and Armenian schools, cultural associations, newspapers and libraries were closed. Armenian nationalism as practised by the Dashnaks, with their penchant for revolutionary violence and socialist economic policies, had at first had little appeal for the Armenian bourgeoisie, but Russian cultural repression gained them more sympathy. Russified middle-class Armenians began changing their names back to their Armenian form (e.g. Mirzoev became Mirzoian) and engaged private tutors to teach their children the Armenian language. The tsar's Russification programme reached its peak with the decree of June 12, 1903 ordering the confiscation of the properties of the Armenian Church. The Catholicos of Armenia begged the Russians to overturn the decree but when they refused he turned to the Dashnaks. The Armenian clergy had previously been very wary of the Dashnaks, condemning their socialism asanti-clerical
Anti-clericalism is opposition to religious authority, typically in social or political matters. Historical anti-clericalism has mainly been opposed to the influence of Roman Catholicism. Anti-clericalism is related to secularism, which seeks to ...
, but now they saw them as their protectors. The Dashnaks formed a Central Committee for Self-Defence in the Caucasus and organised a series of protests among Armenians. At Gandzak the Russian army responded by firing into the crowd, killing ten, and further demonstrations were met with more bloodshed. The Dashnaks and Hunchaks began a campaign of assassinations against tsarist officials in Transcaucasia and they even succeeded in wounding Prince Golitsin. In 1904, the Dashnak congress specifically extended their programme to look after the rights of Armenians within the Russian Empire as well as Ottoman Turkey.
The 1905 Revolution
Unrest in Transcaucasia, which also included major strikes, reached a climax with the widespread uprisings throughout the Russian Empire known as the1905 Revolution
The Russian Revolution of 1905,. also known as the First Russian Revolution,. occurred on 22 January 1905, and was a wave of mass political and social unrest that spread through vast areas of the Russian Empire. The mass unrest was directed again ...
. 1905 saw a wave of mutinies, strikes and peasant uprisings across imperial Russia and events in Transcaucasia were particularly violent. In Baku, the centre of the Russian oil industry, class tensions mixed with ethnic rivalries. The city was almost wholly composed of Azeris and Armenians, but the Armenian middle-class tended to have a greater share in the ownership of the oil companies and Armenian workers generally had better salaries and working conditions than the Azeris. In December 1904, after a major strike was declared in Baku, the two communities began fighting each other on the streets and the violence spread to the countryside. By the time it was over, an estimated 1,500 Armenians and 700 Azeris were dead. The events of 1905 convinced Tsar Nicholas that he must reverse his policies. He replaced Golitsin with the Armenophile governor Count Illarion Ivanovich Vorontsov-Dashkov
Count Illarion Ivanovich Vorontsov-Dashkov (russian: Илларио́н Ива́нович Воронцов-Дашков; 27 May 1837 – 15 January 1916) was a notable representative of the Vorontsov family. He served as Minister of Imperial Pr ...
and returned the property of the Armenian Church. Gradually order was restored and the Armenian bourgeoisie once more began to distance itself from the revolutionary nationalists.
Tribune of People, 1912
In January 1912, a total of 159 Armenians were charged with membership of an anti-"Revolutionary" organization. During the revolution Armenian revolutionaries were split into "Old Dashnaks", allied with the Kadets and "Young Dashnaks" aligned with the SRs. To determine the position of Armenians all forms ofArmenian national movement
The Armenian national movement ( hy, Հայ ազգային-ազատագրական շարժում ''Hay azgayin-azatagrakan sharzhum'') included social, cultural, but primarily political and military movements that reached their height during Worl ...
put into trial. The entire Armenian intelligentsia, including writers, physicians, lawyers, bankers, and even merchants" on trial. When the tribune finished its work, 64 charges were dropped and the rest were either imprisoned or exiled for varying periods.
World War One and independence, 1914–1918

 The years between the 1905 Revolution and World War I saw a rapprochement between most Armenians and the Russian authorities. Russia became concerned when her enemy Germany began drawing closer to the
The years between the 1905 Revolution and World War I saw a rapprochement between most Armenians and the Russian authorities. Russia became concerned when her enemy Germany began drawing closer to the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
, which led the Russians to take a renewed interest in the welfare of the Ottoman Armenians.
When World War I broke out in August 1914, the Russians sought to mobilise Armenian patriotic sentiment. Most Armenian troops were transferred to the European theatre of World War I
Although considerable conflict took place outside Europe, the European theatre (also known as the First European War) was the main theatre of operations during World War I and was where the war began and ended. During the four years of conflic ...
(known as the Eastern Front). The Ottoman Empire did not join the world war until several months had passed and, as the possibility of a Caucasus Campaign
The Caucasus campaign comprised armed conflicts between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire, later including Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, the Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus, the German Empire, the Central Caspian Dict ...
come closer, in the summer of 1914, Count Illarion Ivanovich Vorontsov-Dashkov
Count Illarion Ivanovich Vorontsov-Dashkov (russian: Илларио́н Ива́нович Воронцов-Дашков; 27 May 1837 – 15 January 1916) was a notable representative of the Vorontsov family. He served as Minister of Imperial Pr ...
consulted with the Mayor of Tbilisi Alexandre Khatsian, the primate of Tbilisi, Bishop Mesrop, and the prominent civic leader Dr. Hakob Zavriev
Hakob Zavriev ( hy, Հակոբ Զավրիև), also known as Yakov Zavriev, was an Armenian politician.
Zavriev was a graduate of the St. Petersburg Army Medical Academy. He later joined the Armenian Revolutionary Federation. The viceroy of the ...
about the creation of Armenian volunteer detachments.Hovannisian “The Armenian People from Ancient to Modern Times “ p 280 The volunteer units would be made up from Armenians who were not subjects of the empire or not obliged to serve in the army. These units would be employed on the Caucasus Campaign. Many of them were living in the Caucasus and many were impatient to take up arms to liberate their homeland. During the course of the war 150,000 Armenians fought in the Russian Army.
Occupation of Turkish Armenia
 The Ottoman authorities embarked on the genocide of their Armenian subjects as early as April 1915 following the rapid Russian advance in the Caucasus Campaign and the Siege of Van. An
The Ottoman authorities embarked on the genocide of their Armenian subjects as early as April 1915 following the rapid Russian advance in the Caucasus Campaign and the Siege of Van. An Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
n provisional government
A provisional government, also called an interim government, an emergency government, or a transitional government, is an emergency governmental authority set up to manage a political transition generally in the cases of a newly formed state or ...
within the autonomous region was initially set up around Lake Van
Lake Van ( tr, Van Gölü; hy, Վանա լիճ, translit=Vana lič̣; ku, Gola Wanê) is the largest lake in Turkey. It lies in the far east of Turkey, in the provinces of Van and Bitlis in the Armenian highlands. It is a saline soda lake ...
. The Armenian government in the war zone was briefly referred to as "Free Vaspurakan", and after an Ottoman advance in June 1915. With the Ottoman advance in June 1915 250,000 Armenians from Van and the neighbouring region of Alashkerd retreated to the Russian frontier. Russian Transcaucasia was flooded with refugees from the massacres.
While it scored military successes against the Turks, the Russian war machine began to disintegrate on its front against Germany and in February 1917 the tsarist regime was overthrown by a revolution in Saint Petersburg.
Russian Armenians greeted the new government with enthusiasm, hoping it would secure Ottoman Armenia for them. The issue of the continuation of the war was a highly contentious one amongst the political parties of the new Russia, with most favouring a "democratic peace"; but since the provinces of Ottoman Armenia were under Russian military occupation at the time of the revolution, the Armenians believed that the government would agree to defend them. To help out, the Provisional Government began replacing Russian troops, whose commitment to continued fighting was in doubt, with Armenian ones on the Caucasian front. But as 1917 went on the Provisional Government lost support among Russian soldiers and workers and much of the army melted away from Transcaucasia.
Armenian Congress of Eastern Armenians
TheBolshevik Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mom ...
of October 1917 forced the issue of independence for the peoples of Transcaucasia, since the Bolsheviks enjoyed little support in the region. In February, 1918, the Armenians, Georgians and Azeris formed their own Transcaucasian parliament. Armenians united under Armenian Congress of Eastern Armenians. On April 22, 1918 it voted for independence, declaring itself to be the Democratic Federative Republic of Transcaucasia. The federation dissolved when Georgia declared its independence on May 26. Armenian Congress of Eastern Armenians followed on May 28.
The Armenian Congress of Eastern Armenians devised policies to direct the war efforts and the relief and repatriation of refugees. The council passed a law to organise the defense of the Caucasus against the Ottoman Empire using the vast quantity of supplies and ammunition left over from the departure of the Russian army. The congress specifically devised a local control and administrative structure for Transcaucasia. Even if the Congress did not devise specific solutions for the soldiers left in Baku, Tbilisi, Kars, and other militias under the Occupation of Turkish Armenia under the civil governor Hakob Zavriev
Hakob Zavriev ( hy, Հակոբ Զավրիև), also known as Yakov Zavriev, was an Armenian politician.
Zavriev was a graduate of the St. Petersburg Army Medical Academy. He later joined the Armenian Revolutionary Federation. The viceroy of the ...
, they did not resist the ongoing reality of these soldiers serving for the other forces. The Congress also selected a fifteen-member permanent executive committee, known as the "Armenian National Council", whose leader was Avetis Aharonyan
Avetis Aharonian () (4 January 1866 – 20 March 1948) was an Armenian politician, writer, public figure and revolutionary, also part of the Armenian national movement.
Biography
Aharonian was born in 1866 in Surmali, Erivan Governorate, ...
. This committee’s first task was to set the stage for the declaration of the First Republic of Armenia
The First Republic of Armenia, officially known at the time of its existence as the Republic of Armenia ( hy, Հայաստանի Հանրապետութիւն), was the first modern Armenian state since the loss of Armenian statehood in the Middle ...
.
First Republic of Armenia
 The major problem confronting the new state was the advancing Ottoman army, which by now had recaptured much of western Armenia, but the interests of the three peoples were very different. For obvious reasons, defence against the invading army was of paramount importance to the Armenians, while the Muslim Azeris were sympathetic to the Turks. The Georgians felt that their interests could best be guaranteed by coming to a deal with the Germans rather than the Turks and on May 26, 1918, at German prompting, Georgia declared its independence from the Transcaucasian Republic. This move was followed two days later by Azerbaijan. Reluctantly, the Dashnak leaders, who were the most powerful Armenian politicians in the region, declared the formation of a new independent state, the
The major problem confronting the new state was the advancing Ottoman army, which by now had recaptured much of western Armenia, but the interests of the three peoples were very different. For obvious reasons, defence against the invading army was of paramount importance to the Armenians, while the Muslim Azeris were sympathetic to the Turks. The Georgians felt that their interests could best be guaranteed by coming to a deal with the Germans rather than the Turks and on May 26, 1918, at German prompting, Georgia declared its independence from the Transcaucasian Republic. This move was followed two days later by Azerbaijan. Reluctantly, the Dashnak leaders, who were the most powerful Armenian politicians in the region, declared the formation of a new independent state, the First Republic of Armenia
The First Republic of Armenia, officially known at the time of its existence as the Republic of Armenia ( hy, Հայաստանի Հանրապետութիւն), was the first modern Armenian state since the loss of Armenian statehood in the Middle ...
on May 28, 1918.Suny. ''Looking Toward Ararat'', pp. 119-25
Republic of Mountainous Armenia
 The
The Treaty of Batum
The Treaty of Batum was signed in Batum on 4 June 1918, between the Ottoman Empire and the three Transcaucasian states: the First Republic of Armenia, the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic and the Democratic Republic of Georgia. It was the first ...
was signed between the First Republic of Armenia
The First Republic of Armenia, officially known at the time of its existence as the Republic of Armenia ( hy, Հայաստանի Հանրապետութիւն), was the first modern Armenian state since the loss of Armenian statehood in the Middle ...
and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
after the last battles of the Caucasus Campaign
The Caucasus campaign comprised armed conflicts between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire, later including Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, the Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus, the German Empire, the Central Caspian Dict ...
. The Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
initially gained a considerable portion of the South Caucasus with the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers ( Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russi ...
signed with the Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
and then following Treaty of Batum
The Treaty of Batum was signed in Batum on 4 June 1918, between the Ottoman Empire and the three Transcaucasian states: the First Republic of Armenia, the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic and the Democratic Republic of Georgia. It was the first ...
with Armenia. Andranik Ozanian rejected these new borders and proclaimed the new state, where his activities were concentrated at the link between the Ottoman Empire to the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic
The Azerbaijan Democratic Republic), or simply as Azerbaijan in Paris Peace Conference, 1919–1920,''Bulletin d'Information de l'Azerbaidjan'', No. I, September 1, 1919, pp. 6–7''125 H.C.Debs.'', 58., February 24, 1920, p. 1467. Caucasian A ...
at Karabakh
Karabakh ( az, Qarabağ ; hy, Ղարաբաղ, Ġarabaġ ) is a geographic region in present-day southwestern Azerbaijan and eastern Armenia, extending from the highlands of the Lesser Caucasus down to the lowlands between the rivers Kura and ...
, Zanghezur and Nakhichevan. In January 1919, with Armenian troops advancing, the British forces (Lionel Dunsterville
Major General Lionel Charles Dunsterville, (9 November 1865 – 18 March 1946) was a British Army officer, who led Dunsterforce across present-day Iraq and Iran towards the Caucasus and Baku during the First World War.
Early life
Lionel Ch ...
) ordered Andranik back to Zangezur, and gave him assurances that this conflict could be solved with the Paris Peace Conference of 1919
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. ...
. The Paris Peace Conference proclaimed the First Republic of Armenia
The First Republic of Armenia, officially known at the time of its existence as the Republic of Armenia ( hy, Հայաստանի Հանրապետութիւն), was the first modern Armenian state since the loss of Armenian statehood in the Middle ...
an internationally recognized state and Republic of Mountainous Armenia dissolved.
Centrocaspian Dictatorship
TheCentrocaspian Dictatorship
The Centro-Caspian Dictatorship, also known as the Central-Caspian Dictatorship (russian: Диктатура Центрокаспия, ''Diktatura Tsentrokaspiya'') (Azerbaijani: Sentrokaspi Diktaturası), was a short-lived anti-Soviet administr ...
was a British-backed anti-Soviet government founded in Baku on August 1, 1918. The government was composed by the Socialist-Revolutionary Party and the Armenian national movement
The Armenian national movement ( hy, Հայ ազգային-ազատագրական շարժում ''Hay azgayin-azatagrakan sharzhum'') included social, cultural, but primarily political and military movements that reached their height during Worl ...
which majority was from Armenian Revolutionary Federation
The Armenian Revolutionary Federation ( hy, Հայ Յեղափոխական Դաշնակցութիւն, ՀՅԴ ( classical spelling), abbr. ARF or ARF-D) also known as Dashnaktsutyun (collectively referred to as Dashnaks for short), is an Armenian ...
(Dashnaks). British force the Dunsterforce occupied the city and helped the mainly Dashnak-Armenian forces to defend the capital during the Battle of Baku
The Battle of Baku ( az, Bakı döyüşü, tr, Bakü Muharebesi, russian: Битва за Баку) was a battle in World War I that took place between August–September 1918 between the Ottoman–Azerbaijani coalition forces led by Nuri Pas ...
. However, Baku fell on September 15, 1918 and an Azeri-Ottoman army entered the capital, causing British forces and much of the Armenian population to flee. The Ottoman Empire signed the Armistice of Mudros
Concluded on 30 October 1918 and taking effect at noon the next day, the Armistice of Mudros ( tr, Mondros Mütarekesi) ended hostilities in the Middle Eastern theatre between the Ottoman Empire and the Allies of World War I. It was signed by th ...
on November 30, 1918 and the British occupational force re-entered Baku.
Soviet rule
Eventually, the USSR annexed Eastern Armenia and rendered it theArmenian Soviet Socialist Republic
The Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic,; russian: Армянская Советская Социалистическая Республика, translit=Armyanskaya Sovetskaya Sotsialisticheskaya Respublika) also commonly referred to as Soviet A ...
.
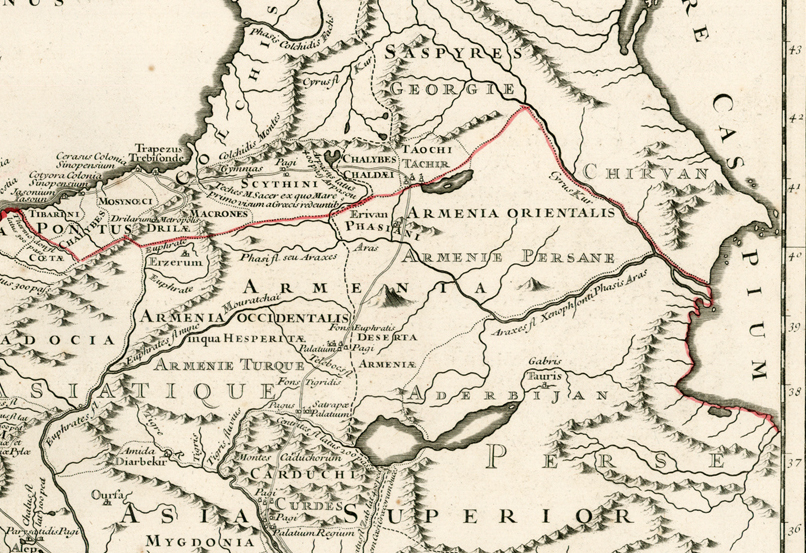
Maps
See also
*History of Armenia
The history of Armenia covers the topics related to the history of the Republic of Armenia, as well as the Armenian people, the Armenian language, and the regions historically and geographically considered ''Armenian''.
Armenia is locate ...
* Timeline of Armenian history
__NOTOC__
This is a timeline of Armenian history, comprising important legal and territorial changes and political events in Armenia and its predecessor states. To read about the background to these events, see History of Armenia. See also the l ...
* Armenian Oblast
The Armenian Oblast was a province (''oblast'') of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire that existed from 1828 to 1840. It corresponded to most of present-day central Armenia, the Iğdır Province of Turkey, and the Nakhchivan excla ...
* Erivan Governorate
The Erivan Governorate was a province ('' guberniya'') of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire, with its centеr in Erivan (present-day Yerevan). Its area was 27,830 sq. kilometеrs, roughly corresponding to what is now most of central ...
* Elisabethpol Governorate
* Kars Oblast
The Kars Oblast was a province ('' oblast'') of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire between 1878 and 1917. Its capital was the city of Kars, presently in Turkey. The ''oblast'' bordered the Ottoman Empire to the west, the Batum Obla ...
(since 1878)
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * {{Armenia topics, state=uncollapsed Modern history of Armenia * Armenia–Russia relations