River systems on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
/ref>




StarHydro – software tool that covers concepts of fluvial geomorphology and watershed hydrology
{{Authority control Drainage basins Geomorphology Limnology Hydrology Rivers Water streams Water and the environment
 In
In geomorphology
Geomorphology (from Ancient Greek: , ', "earth"; , ', "form"; and , ', "study") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or ...
, drainage systems, also known as river systems, are the patterns formed by the stream
A stream is a continuous body of surface water flowing within the bed and banks of a channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a stream may be referred to by a variety of local or regional names. Long large streams ...
s, river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of ...
s, and lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much large ...
s in a particular drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
. They are governed by the topography of land, whether a particular region is dominated by hard or soft rocks, and the gradient of the land. Geomorphologist
Geomorphology (from Ancient Greek: , ', "earth"; , ', "form"; and , ', "study") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or ...
s and hydrologist
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is calle ...
s often view streams as part of drainage basins (and sub-basins). This is the topographic
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary scie ...
region from which a stream receives runoff
Runoff, run-off or RUNOFF may refer to:
* RUNOFF, the first computer text-formatting program
* Runoff or run-off, another name for bleed, printing that lies beyond the edges to which a printed sheet is trimmed
* Runoff or run-off, a stock marke ...
, throughflow, and its saturated equivalent, groundwater flow
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidate ...
. The number, size, and shape of the drainage basins varies and the larger and more detailed the topographic map
In modern mapping, a topographic map or topographic sheet is a type of map characterized by large- scale detail and quantitative representation of relief features, usually using contour lines (connecting points of equal elevation), but histori ...
, the more information is available.Pidwirny, M., (2006). "The Drainage Basin Concept". ''Fundamentals of Physical Geography,'' 2nd Edition./ref>
Drainage patterns
Per the lie of channels, drainage systems can fall into one of several categories, known as drainage patterns. These depend on thetopography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sc ...
and geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other Astronomical object, astronomical objects, the features or rock (geology), rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology ...
of the land.
All forms of transitions can occur between parallel, dendritic, and trellis patterns.
Accordant versus discordant drainage patterns
A drainage system is described as accordant if its pattern correlates to the structure and relief of the landscape over which it flows. A discordant system or pattern does not correlate to the topography and geology of the area. Discordant drainage patterns are classified into two main types: '' antecedent'' and ''superimposed'', while ''ante position'' drainage patterns combine the two. In ''antecedent'' drainage, a river's vertical incision ability matches that of land uplift due to tectonic forces. ''Superimposed'' drainage develops differently: initially, a drainage system develops on a surface composed of 'younger' rocks, but due to denudation activities this surface of younger rocks is removed and the river continues to flow over a seemingly new surface, but one in fact made up of rocks of old geological formation.
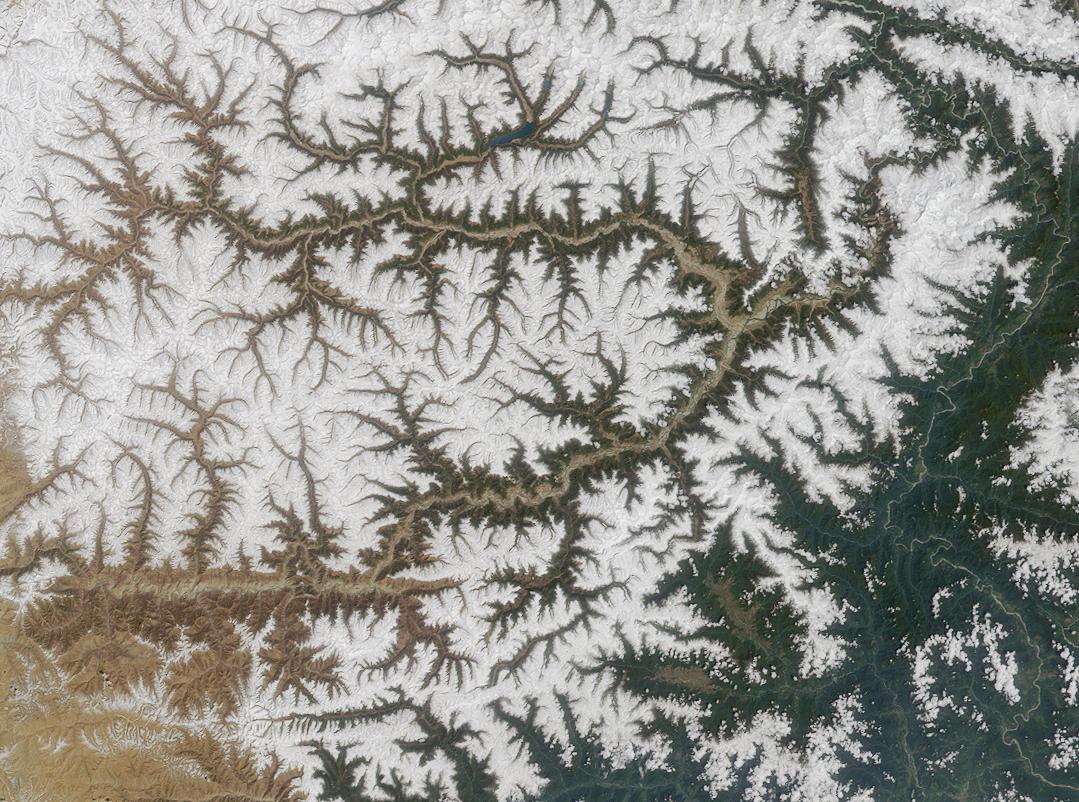
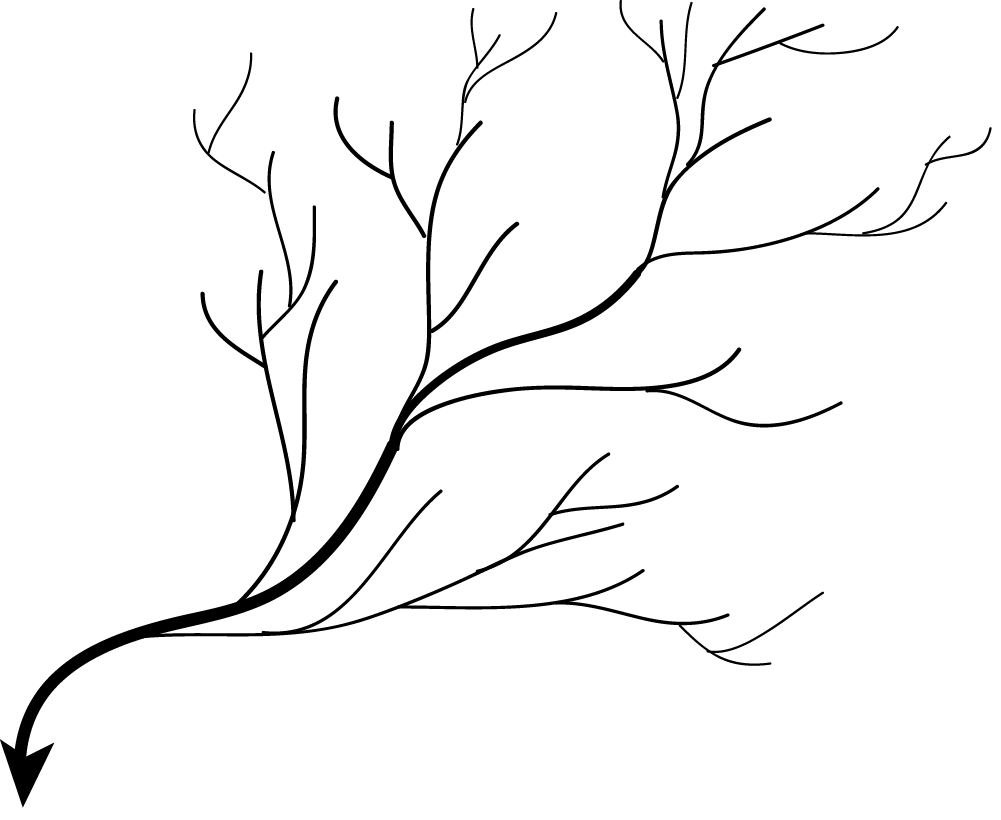
Dendritic drainage pattern
Dendritic drainage systems (fromGreek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, ''dendrites'', "of or like a tree") are not straight and are the most common form of the drainage system. In this, there are many sub-tributaries (analogous to the twigs of a tree), which merge into tributaries
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drain ...
of the main river (the branches and the trunk of the tree, respectively). They are seen to feed a river channel that matches and is strongly accordant to the overriding gradient of the land. Truly dendritic systems form in V-shaped valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over ...
s; as a result, the rock types must be impervious and non-porous.

Parallel drainage pattern
A parallel drainage system occurs on a common slope down linear ranges (or of rivers between linear series ofescarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''esca ...
s, parallel, elongate landforms like outcropping resistant rock bands), typically following natural faults or erosion (such as prevailing wind scars). The watercourses run swift and straight, with very few tributaries, and all flow in the same direction. This system forms on very long, uniform slopes, for instance, high rivers flowing southeast from the Aberdare Mountains
The Aberdare Range (formerly the Sattima Range, Kikuyu: ''Nyandarua'') is a 160 km (100 mile) long mountain range of upland, north of Kenya's capital Nairobi with an average elevation of . It straddles across the counties of Nyandarua, Nye ...
in Kenya and many rivers of Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
.
This sometimes indicates a major fault that cuts across an area of steeply folded bedrock.
Trellis drainage pattern
The geometry of a trellis drainage system is similar to that of a common garden trellis. Along a strike valley, smaller tributaries feed into the steep slopes of mountainsides. These tributaries enter the main river about perpendicular, causing a trellis-like appearance of the system. They form where hard and soft formations exist on both banks of the main river, and are reflective of height, accentuated by erosion. Trellis drainage is characteristic of folded mountains, such as theAppalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. The ...
in North America and in the north part of Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmos ...
.

Rectangular drainage pattern
Rectangular drainage develops on rocks that are of approximately uniform resistance toerosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is d ...
, but which have two directions of jointing at approximately right angles or 90 degrees. The joints are usually less resistant to erosion than the bulk rock so erosion tends to preferentially open the joints and streams eventually develop along the joints. The result is a stream system in which streams consist mainly of straight line segments with right-angle bends and tributaries join larger streams at right angles. This pattern can be found with the Arun River
The River Arun () is a river in the English county of West Sussex. At long, it is the longest river entirely in Sussex and one of the longest starting in Sussex after the River Medway, River Wey and River Mole. From the series of small stream ...
in Nepal.

Radial drainage pattern
In a radial drainage system, the streams radiate outwards from a central high point. Volcanos usually have archetypal features on which this commonly develops are modest or harddomes
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a m ...
pattern develops when streams flow in many general directions (meaning quite long-term)
In India, the Amarkantak
Amarkantak (NLK ''Amarakaṇṭaka'') is a pilgrim town and a Nagar Panchayat in Anuppur, Madhya Pradesh, India. The Amarkantak region is a unique natural heritage area and is the meeting point of the Vindhya and the Satpura Ranges, with the M ...
range and Ramgarh crater
Ramgarh crater, also known as ''Ramgarh structure'', ''Ramgarh Dome'' and ''Ramgarh astrobleme'', is a meteor impact crater of diameter in Kota plateau of Vindhya range located adjacent to Ramgarh village in Mangrol tehsil of Baran district ...
are most archetypal; and Dogu'a Tembien
Dogu'a Tembien (, "Upper Tembien", sometimes transliterated as Degua Tembien) is a woreda in Tigray Region, Ethiopia. It is named in part after the former province of Tembien. Nowadays, the mountainous district is part of the Southeastern Tigray ...
in Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
.

Centripetal drainage pattern
When the streams converge at a point, which is generally a depression or a basin they form centripetal or inland drainage pattern.Deranged drainage pattern
A deranged drainage system is a drainage system indrainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
s where there is no coherent pattern to the rivers and lakes. These can form in areas with extensive limestone deposits, where surface streams can disappear into the groundwater via caves and subterranean drainage routes. They can also form in areas where there has been much geological disruption.
A classic example is the Canadian Shield
The Canadian Shield (french: Bouclier canadien ), also called the Laurentian Plateau, is a geologic shield, a large area of exposed Precambrian igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks. It forms the North American Craton (or Laurentia), the anc ...
. During the last ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gre ...
, the topsoil
Topsoil is the upper layer of soil. It has the highest concentration of organic matter and microorganisms and is where most of the Earth's biological soil activity occurs.
Description
Topsoil is composed of mineral particles and organic matt ...
was scraped off, leaving mostly bare rock. The melting of the glaciers left land with many irregularities of elevation and a great deal of water to collect in the low points, explaining the large number of lakes which are found in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
. The drainage basins are young and are still sorting themselves out. Eventually the system will stabilize.

Annular drainage pattern
In an annular drainage pattern, streams trace a tangential or greater concentric path along a belt of weak rock so, with others, a roughly traced out ring can be seen. It is best displayed by streams draining a maturely dissected structural dome or basin where erosion has exposed rimmingsedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
strata of greatly varying degrees of hardness, as in the Red Valley, which nearly encircles the domal structure of the Black Hills
The Black Hills ( lkt, Ȟe Sápa; chy, Moʼȯhta-voʼhonáaeva; hid, awaxaawi shiibisha) is an isolated mountain range rising from the Great Plains of North America in western South Dakota and extending into Wyoming, United States. Black ...
of South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota and Dakota Sioux Native American tribes, who comprise a large po ...
.
Angular drainage pattern
Angular drainage patterns form wherebedrock
In geology, bedrock is solid rock that lies under loose material ( regolith) within the crust of Earth or another terrestrial planet.
Definition
Bedrock is the solid rock that underlies looser surface material. An exposed portion of be ...
joints and faults intersect at angles other than rectangular drainage patterns. Angles can be more or less than 90 degrees.
Integrated drainage
An integrated drainage is a mature drainage system characteristic of arid climates. It is formed by coalescing of individual basins formerly separated by high ground, such as mountains or ridges. Headward erosion from a lower basin may breach the barrier, as may spilling over from a higher basin due toaggradation
Aggradation (or alluviation) is the term used in geology for the increase in land elevation, typically in a river system, due to the deposition of sediment. Aggradation occurs in areas in which the supply of sediment is greater than the amount of ...
(accumulation of sediments in the basin). The effect of integration of a drainage system is to replace local higher base level
In geology and geomorphology a base level is the lower limit for an erosion process. The modern term was introduced by John Wesley Powell in 1875. The term was subsequently appropriated by William Morris Davis who used it in his cycle of erosion ...
s with a single lower base level.
An example of an integrated drainage is the area drained by the Rio Grande River. The sedimentary basin
Sedimentary basins are region-scale depressions of the Earth's crust where subsidence has occurred and a thick sequence of sediments have accumulated to form a large three-dimensional body of sedimentary rock. They form when long-term subsiden ...
s forming the modern Rio Grande Valley were not integrated into a single river system draining into the Gulf of Mexico until relatively recent geologic time. Instead, the basins formed by the opening of the Rio Grande rift were initially bolson
A bolson is a desert valley or depression, usually draining into a playa or salt pan, and entirely surrounded by recently uplifted hills or mountains. Bolsons are sites of active deposition of sediments (aggradation).*
They are a type of endorh ...
s, with no external drainage and a central playa. An axial river existed in the Espanola Basin as early as 13 million years ago, reaching the Santo Domingo Basin by 6.9 million years ago. However, at this time, the river drained into a playa in the southern Albuquerque Basin
The Albuquerque Basin (or Middle Rio Grande Basin) is a structural basin and ecoregion within the Rio Grande rift in central New Mexico. It contains the city of Albuquerque.
Geologically, the Albuquerque Basin is a half-graben that slopes down ...
where it deposited the Popotosa Formation. The upper reach of this river corresponded to the modern Rio Chama
The Rio Chama, a major tributary river of the Rio Grande, is located in the U.S. states of Colorado and New Mexico. The river is about long altogether. From its source to El Vado Dam its length is about , from El Vado Dam to Abiquiu Dam is abo ...
, but by 5 million years ago, an ancestral Rio Grande draining the eastern San Juan Mountains
The San Juan Mountains is a high and rugged mountain range in the Rocky Mountains in southwestern Colorado and northwestern New Mexico. The area is highly mineralized (the Colorado Mineral Belt) and figured in the gold and silver mining industry ...
had joined the ancestral Rio Chama.
The ancestral Rio Grande progressively integrated basins to the south, reaching the Palomas basin by 4.5 million years ago, the Mesilla basin by 3.1 million years, to Texas by 2.06 million years, and finally joining the Pecos River at 800,000 years to drain into the Gulf of Mexico. Volcanism in the Taos Plateau reduced drainage from the San Luis basin until a spillover event 440,000 years ago that drained Lake Alamosa and fully reintegrated the San Luis basin into the Rio Grande basin.
Integrated drainages were widespread in western North America in the Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''pala ...
and Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', ...
, and there is evidence of integrated drainages on the surface of Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
.
See also
*Distributary
A distributary, or a distributary channel, is a stream that branches off and flows away from a main stream channel. Distributaries are a common feature of river deltas. The phenomenon is known as river bifurcation. The opposite of a distributar ...
* Integrated catchment management Integrated catchment management (ICM) is a subset of environmental planning which approaches sustainable resource management from a catchment perspective, in contrast to a piecemeal approach that artificially separates land management from water man ...
* List of unusual drainage systems
* River bifurcation
* Stream capture
Stream capture, river capture, river piracy or stream piracy is a geomorphological phenomenon occurring when a stream or river drainage system or watershed is diverted from its own bed, and flows instead down the bed of a neighbouring stream. T ...
References
External links
StarHydro – software tool that covers concepts of fluvial geomorphology and watershed hydrology
{{Authority control Drainage basins Geomorphology Limnology Hydrology Rivers Water streams Water and the environment