Renewable energy in developing countries on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Renewable energy in developing countries is an increasingly used alternative to
Renewable energy in developing countries is an increasingly used alternative to
pp. 7-9. In isolated rural areas,
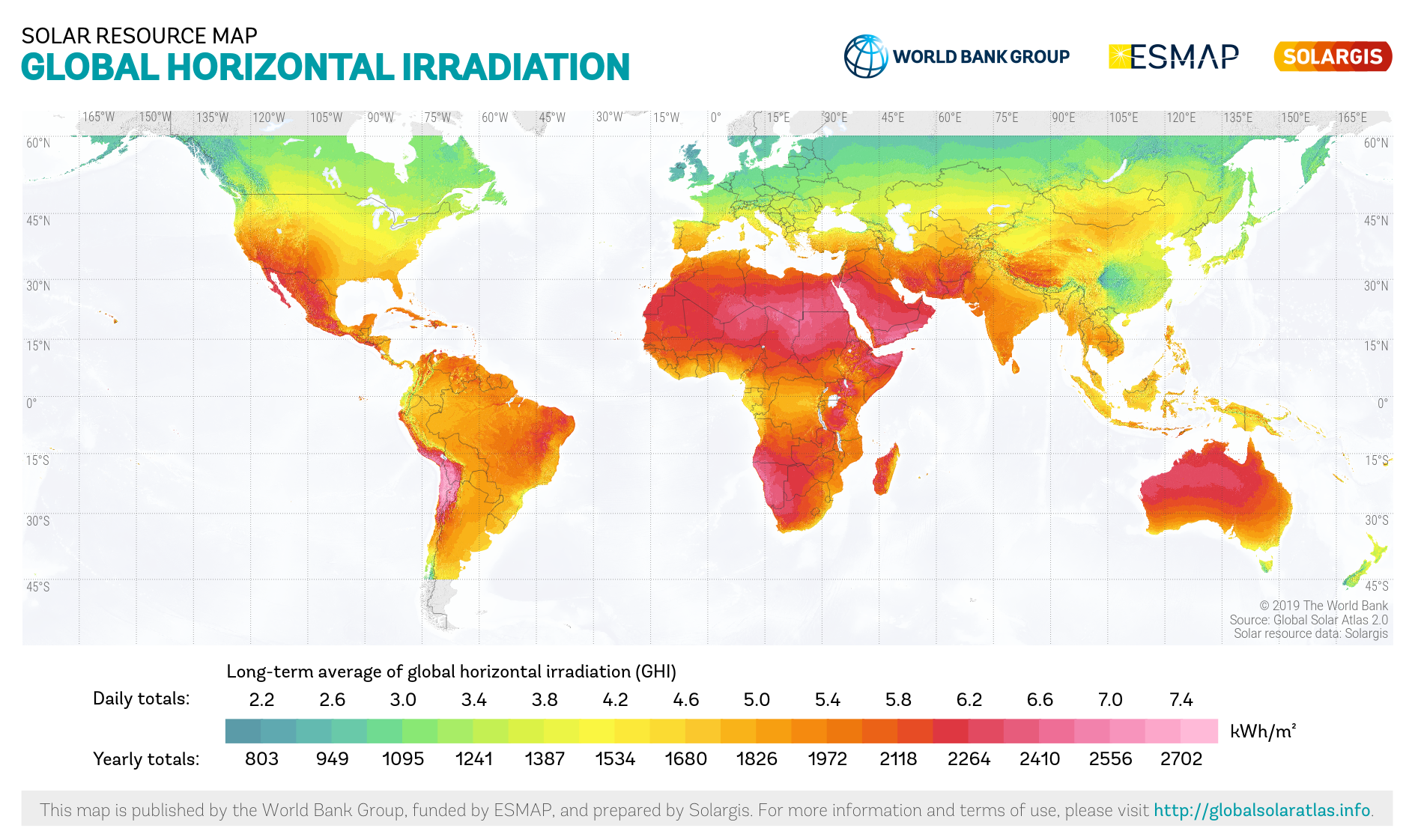 In 2009, about 1.4 billion of people in the world lived without electricity, and 2.7 billion relied on wood, charcoal, and dung for home energy requirements. This lack of access to modern energy technology limits income generation, blunts efforts to escape poverty, affects people's health, and contributes to global deforestation and climate change. Small-scale renewable energy technologies and distributed energy options, such as onsite solar power and improved cookstoves, offer rural households
modern energy services.
Renewable energy can be particularly suitable for developing countries. In rural and remote areas, transmission and distribution of energy generated from
In 2009, about 1.4 billion of people in the world lived without electricity, and 2.7 billion relied on wood, charcoal, and dung for home energy requirements. This lack of access to modern energy technology limits income generation, blunts efforts to escape poverty, affects people's health, and contributes to global deforestation and climate change. Small-scale renewable energy technologies and distributed energy options, such as onsite solar power and improved cookstoves, offer rural households
modern energy services.
Renewable energy can be particularly suitable for developing countries. In rural and remote areas, transmission and distribution of energy generated from
p. 3. Renewable energy doesn't always have to come from a developing country. The Developing Areas Study Group session is a group of speakers from all over the energy businesses discusses the potential ideas to get developing countries the renewable energy that they need. Papers written by W. Morgan, R. Moss and P. Richard discuss the opportunities of renewable resources that lie within the developing country as well. Morgan and Richard claim firewood and agriculture could play a great role in an alternative energy solution in developing countries, while Richards claims that efficient use of agriculture could lead to renewable energy. Morgan also points out that green plants could play a great role in producing synthetic fuel alcohol, which would not only impact the developing country but the world as a whole in providing an alternative fuel source. Interest in renewable energies has increased in recent years due to environmental concern about
 Collectively, developing countries have more than half of global renewable power capacity. China and India are rapidly expanding markets for renewable energy. Brazil produces most of the world’s sugar-derived ethanol and has been adding new biomass and wind power plants. Many renewable markets are growing at rapid rates in countries such as Argentina, Costa Rica, Egypt, Indonesia, Kenya, Tanzania, Thailand, Tunisia, and Uruguay.
Collectively, developing countries have more than half of global renewable power capacity. China and India are rapidly expanding markets for renewable energy. Brazil produces most of the world’s sugar-derived ethanol and has been adding new biomass and wind power plants. Many renewable markets are growing at rapid rates in countries such as Argentina, Costa Rica, Egypt, Indonesia, Kenya, Tanzania, Thailand, Tunisia, and Uruguay.
Renewables 2010 Global Status Report
p. 9. In isolated rural areas, electricity grid extensions are often not economical. Off‐grid renewable technologies provide a sustainable and cost‐effective alternative to the diesel generators that would be otherwise be deployed in such areas. Renewable technologies can also help to displace other unsustainable energy sources such as kerosene lamps and traditional biomass. Technology advances are opening up a huge new market for solar power: the approximately 1.3 billion people around the world who don't have access to grid electricity. Even though they are typically very poor, these people have to pay far more for lighting than people in rich countries because they use inefficient kerosene lamps. Solar power costs half as much as lighting with kerosene. An estimated 3 million households get power from small solar PV systems.REN21 (2010)
Renewables 2010 Global Status Report
p. 12. Kenya is the world leader in the number of solar power systems installed per capita. More than 30,000 very small solar panels, each producing 12 to 30 watts, are sold in Kenya annually. Micro-hydro systems configured into village-scale or county-scale mini-grids serve many areas. More than 30 million rural households get lighting and cooking from biogas made in household-scale systems. These stoves are being manufactured in factories and workshops worldwide, and more than 160 million households now use them.
 The
The

 Renewable energy in developing countries is an increasingly used alternative to
Renewable energy in developing countries is an increasingly used alternative to fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels ma ...
energy, as these countries scale up their energy supplies and address energy poverty
Energy poverty is lack of access to modern energy services. It refers to the situation of large numbers of people in developing countries and some people in developed countries whose well-being is negatively affected by very low consumption of e ...
. Renewable energy technology was once seen as unaffordable for developing countries. However, since 2015, investment in non-hydro renewable energy has been higher in developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
than in developed countries, and comprised 54% of global renewable energy investment in 2019. The International Energy Agency
The International Energy Agency (IEA) is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organisation, established in 1974, that provides policy recommendations, analysis and data on the entire global energy sector, with a recent focus on curbing car ...
forecasts that renewable energy will provide the majority of energy supply growth through 2030 in Africa and Central and South America, and 42% of supply growth in China.
Most developing countries have abundant renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
resources, including solar energy
Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun that is harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar power to generate electricity, solar thermal energy (including solar water heating), and solar architecture. It is an essen ...
, wind power
Wind power or wind energy is mostly the use of wind turbines to generate electricity. Wind power is a popular, sustainable, renewable energy source that has a much smaller impact on the environment than burning fossil fuels. Historically ...
, geothermal energy
Geothermal energy is the thermal energy in the Earth's crust which originates from the formation of the planet and from radioactive decay of materials in currently uncertain but possibly roughly equal proportions. The high temperature and pr ...
, and biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bio ...
, as well as the ability to manufacture the relatively labor-intensive systems that harness these. By developing such energy sources developing countries can reduce their dependence on oil and natural gas, creating energy portfolios that are less vulnerable to price rises. In many circumstances, these investments can be less expensive than fossil fuel energy systems.Energy for Development: The Potential Role of Renewable Energy in Meeting the Millennium Development Goalspp. 7-9. In isolated rural areas,
electricity grid
An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. It consists of:Kaplan, S. M. (2009). Smart Grid. Electrical Power ...
extensions are often not economical. Off‐grid renewable technologies provide a sustainable and cost‐effective alternative to the diesel generator
A diesel generator (DG) (also known as a diesel Genset) is the combination of a diesel engine with an electric generator (often an alternator) to generate electrical energy. This is a specific case of engine generator. A diesel compression-ig ...
s that would be otherwise be deployed in such areas. Renewable technologies can also help to displace other unsustainable energy sources such as kerosene lamp
A kerosene lamp (also known as a paraffin lamp in some countries) is a type of lighting device that uses kerosene as a fuel. Kerosene lamps have a wick or mantle as light source, protected by a glass chimney or globe; lamps may be used on a ta ...
s and traditional biomass.
Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
is the world leader in the number of solar power
Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovolta ...
systems installed per capita (but not the number of watts added). More than 30,000 small solar panel
A solar cell panel, solar electric panel, photo-voltaic (PV) module, PV panel or solar panel is an assembly of photovoltaic solar cells mounted in a (usually rectangular) frame, and a neatly organised collection of PV panels is called a photo ...
s, each producing 12 to 30 watts, are sold in Kenya annually. Kenya was the first African country to use geothermal power
Geothermal power is electrical power generated from geothermal energy. Technologies in use include dry steam power stations, flash steam power stations and binary cycle power stations. Geothermal electricity generation is currently used in 2 ...
, and still has the largest installed capacity
Nameplate capacity, also known as the rated capacity, nominal capacity, installed capacity, or maximum effect, is the intended full-load sustained output of a facility such as a power station,
of geothermal power in Africa at 200 MW, with a potential of up to 10 GW.
Rationale for renewable energy
 In 2009, about 1.4 billion of people in the world lived without electricity, and 2.7 billion relied on wood, charcoal, and dung for home energy requirements. This lack of access to modern energy technology limits income generation, blunts efforts to escape poverty, affects people's health, and contributes to global deforestation and climate change. Small-scale renewable energy technologies and distributed energy options, such as onsite solar power and improved cookstoves, offer rural households
modern energy services.
Renewable energy can be particularly suitable for developing countries. In rural and remote areas, transmission and distribution of energy generated from
In 2009, about 1.4 billion of people in the world lived without electricity, and 2.7 billion relied on wood, charcoal, and dung for home energy requirements. This lack of access to modern energy technology limits income generation, blunts efforts to escape poverty, affects people's health, and contributes to global deforestation and climate change. Small-scale renewable energy technologies and distributed energy options, such as onsite solar power and improved cookstoves, offer rural households
modern energy services.
Renewable energy can be particularly suitable for developing countries. In rural and remote areas, transmission and distribution of energy generated from fossil fuels
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels ma ...
can be difficult and expensive. Producing renewable energy locally can offer a viable alternative.Power for the Peoplep. 3. Renewable energy doesn't always have to come from a developing country. The Developing Areas Study Group session is a group of speakers from all over the energy businesses discusses the potential ideas to get developing countries the renewable energy that they need. Papers written by W. Morgan, R. Moss and P. Richard discuss the opportunities of renewable resources that lie within the developing country as well. Morgan and Richard claim firewood and agriculture could play a great role in an alternative energy solution in developing countries, while Richards claims that efficient use of agriculture could lead to renewable energy. Morgan also points out that green plants could play a great role in producing synthetic fuel alcohol, which would not only impact the developing country but the world as a whole in providing an alternative fuel source. Interest in renewable energies has increased in recent years due to environmental concern about
global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
and air pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different type ...
, reduced costs of the technologies themselves, and improved efficiency and reliability. In recent years, supportive programs from governments, businesses, nonprofit organizations, and community cooperatives have expanded access to these off-grid technologies and the energy services they provide. Program planners should select “low-hanging fruit” first, aiming for maximum access to modern energy services with the least effort.
Use of renewables
 Collectively, developing countries have more than half of global renewable power capacity. China and India are rapidly expanding markets for renewable energy. Brazil produces most of the world’s sugar-derived ethanol and has been adding new biomass and wind power plants. Many renewable markets are growing at rapid rates in countries such as Argentina, Costa Rica, Egypt, Indonesia, Kenya, Tanzania, Thailand, Tunisia, and Uruguay.
Collectively, developing countries have more than half of global renewable power capacity. China and India are rapidly expanding markets for renewable energy. Brazil produces most of the world’s sugar-derived ethanol and has been adding new biomass and wind power plants. Many renewable markets are growing at rapid rates in countries such as Argentina, Costa Rica, Egypt, Indonesia, Kenya, Tanzania, Thailand, Tunisia, and Uruguay.REN21
REN21 (Renewable Energy Policy Network for the 21st Century) is a think tank and a multistakeholder governance group which is focused on renewable energy policy.
REN21's goal is to facilitate policy development, knowledge exchange, and joint a ...
(2010)Renewables 2010 Global Status Report
p. 9. In isolated rural areas, electricity grid extensions are often not economical. Off‐grid renewable technologies provide a sustainable and cost‐effective alternative to the diesel generators that would be otherwise be deployed in such areas. Renewable technologies can also help to displace other unsustainable energy sources such as kerosene lamps and traditional biomass. Technology advances are opening up a huge new market for solar power: the approximately 1.3 billion people around the world who don't have access to grid electricity. Even though they are typically very poor, these people have to pay far more for lighting than people in rich countries because they use inefficient kerosene lamps. Solar power costs half as much as lighting with kerosene. An estimated 3 million households get power from small solar PV systems.REN21 (2010)
Renewables 2010 Global Status Report
p. 12. Kenya is the world leader in the number of solar power systems installed per capita. More than 30,000 very small solar panels, each producing 12 to 30 watts, are sold in Kenya annually. Micro-hydro systems configured into village-scale or county-scale mini-grids serve many areas. More than 30 million rural households get lighting and cooking from biogas made in household-scale systems. These stoves are being manufactured in factories and workshops worldwide, and more than 160 million households now use them.
Poverty alleviation
Renewable energy projects in many developing countries have demonstrated that renewable energy can directly contribute topoverty alleviation
Poverty reduction, poverty relief, or poverty alleviation, is a set of measures, both economic and humanitarian, that are intended to permanently lift people out of poverty.
Measures, like those promoted by Henry George in his economics clas ...
by providing the energy needed for creating businesses and employment. Renewable energy technologies can also make indirect contributions to alleviating poverty by providing energy for cooking, space heating, and lighting.
Education
Renewable energy can also contribute to education, by providing electricity to schools. Renewable energy for cooking and heating can reduce the time that children spend out of school collecting fuel.Health
2.4 billion people use only traditional biomass, such as wood, residues and dung, for cooking and heating. The constant use of these types of energy sources exposes them to indoor particulate and carbon monoxide concentrations many times higher thanWorld Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
(WHO) standards. "Traditional stoves using dung and charcoal emit large amounts of carbon monoxide and other noxious gases. Women and children suffer most, because they are exposed for the longest periods of time. Acute respiratory illnesses affect as much as 6% of the world population. The WHO estimates that 2.5 million women and young children in developing countries die prematurely each year from breathing the fumes from indoor biomass stoves".
Renewable energy can improve this situation by reducing exposure to indoor pollutants.
Furthermore, renewable can also provide energy to refrigerate medicine and sterilize medical equipment in rural areas where the access to electricity is difficult. It can also provide power to supply the fresh water and sewerage services needed to reduce the spread of infectious diseases.
Government policies
More developing countries are implementing the public policies needed for the widespread development of renewable energy technologies and markets, which have traditionally been dominated by Europe, Japan, and North America. The exceptions include countries like Brazil, which has built the world’s leadingbiofuel
Biofuel is a fuel that is produced over a short time span from biomass, rather than by the very slow natural processes involved in the formation of fossil fuels, such as oil. According to the United States Energy Information Administration ...
s industry, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
, India, which are leaders in developing decentralized renewable sources such as small hydro
Small hydro is the development of hydroelectric power on a scale suitable for local community and industry, or to contribute to distributed generation in a regional electricity grid. Exact definitions vary, but a "small hydro" project is less ...
, small wind, biogas, and solar water heating.
However, policies like feed-in tariff
A feed-in tariff (FIT, FiT, standard offer contract,Couture, T., Cory, K., Kreycik, C., Williams, E., (2010)Policymaker's Guide to Feed-in Tariff Policy Design National Renewable Energy Laboratory, U.S. Dept. of Energy advanced renewable tariff, ...
are applied. Besides, with the Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol was an international treaty which extended the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that (part ...
, the program called the Clean Development Mechanism
The Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) is a United Nations-run carbon offset scheme allowing countries to fund greenhouse gas emissions-reducing projects in other countries and claim the saved emissions as part of their own efforts to meet internat ...
(CDM) that allows for industrialized nations to invest in projects that reduce emissions in developing countries as an alternative to more expensive emission reductions in their own countries.
Developing-country Governments need to steer resources mobilized for large-scale investments into new production sectors and new technologies. Some argue that policies should base on active industrial policies, combining large scale investments and active policy interventions. There is a need of subsidizing these type of energy services to make them affordable to the major part of the population.
Asia
China
India
Pakistan
Philippines
Philippine
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
government sees the growth of the renewable energy sector essential for national energy security. The Philippines' fossil fuel sector is unsustainable, being dependent on the import of nonrenewable fuel, including petroleum, but has significant potential in the renewable energy sector. Based on a report of an Australian consulting firm, International Energy Consultants, the Philippines has the highest electricity rate in Asia, followed by Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
. Transmitting power and transporting fuel throughout the Philippine archipelago is problematic due to very high cost. Compared with neighboring Asian developing countries, the Philippines has relatively higher electricity prices due to the country’s dependence on imported fossil fuels, no government subsidy on electricity generation, fully cost-reflective, monopolized, and heavily taxed across the supply chain.
The Philippines could be considered a world leader in renewable energy, with its 30 percent of its power generation being powered by the renewable energy sector. The Philippines is the world's second largest generator of geothermal energy and was the first Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
n nation to invest in large-scale solar and wind technologies.
Promotion and support of renewable energy in the country was intensified with the passing of the Renewable Energy Act of 2008 which made a feed-in-tariff and a renewable portfolio standard. The Philippines aims to triple renewable energy supply by 2030.
Recently the government has concluded agreements with private developers for extensive projects in Oriental Mindoro with an eventual output of 48 MW, with plans for even larger development in the future.
Despite government efforts, some investors have criticized the government's lack of firmness in its feed-in-tariff policy, and the solar industry accused the government for hampering its progress in the country.
Africa
Algeria
On February 3, 2011, Algeria launched the National Development Programme for new and renewable energy and energy efficiency. The program, which spans the period from 2011 to 2013, aims to produce 22,000 MW of electricity from solar and wind power which 10,000 MW for export.Kenya
InKenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
, the Ministry of Energy and Petroleum is in charge of renewable energy policies. In March 2008, the country adopted the feed-in tariff
A feed-in tariff (FIT, FiT, standard offer contract,Couture, T., Cory, K., Kreycik, C., Williams, E., (2010)Policymaker's Guide to Feed-in Tariff Policy Design National Renewable Energy Laboratory, U.S. Dept. of Energy advanced renewable tariff, ...
policy. In January 2010, the policy was revised to urge private sectors to invest in electricity generation from renewable sources.
Kenya was the first African country to use geothermal power
Geothermal power is electrical power generated from geothermal energy. Technologies in use include dry steam power stations, flash steam power stations and binary cycle power stations. Geothermal electricity generation is currently used in 2 ...
, and still has the largest installed capacity of geothermal power in Africa at 200 MW, with a potential of up to 10 GW. The only other country in Africa utilising geothermal power is Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
.
Kenya is the world leader in the number of solar power systems installed per capita (but not the number of watts added). More than 30,000 small solar panels, each producing 12 to 30 watts, are sold in Kenya annually. For an investment of as little as $100 for the panel and wiring, the PV system can be used to charge a car battery, which can then provide power to run a fluorescent lamp or a small television for a few hours a day. More Kenyans are turning to solar power every year rather than making connections to the country’s electric grid. This is due to the high connectivity costs and the fact that there is an abundance of solar power in Kenya.
Latin America and the Caribbean
In 2021, theEuropean Investment Bank
The European Investment Bank (EIB) is the European Union's investment bank and is owned by the EU Member States. It is one of the largest supranational lenders in the world. The EIB finances and invests both through equity and debt solution ...
supported the renewable energy sector with €315 million in loans to two private sector project developers. Most of the loans in the area were made towards climate change and environmental sustainability, to public sector borrowers.
The European Investment Bank is also collaborating with a private equity fund
A private equity fund (abbreviated as PE fund) is a collective investment scheme used for making investments in various equity (and to a lesser extent debt) securities according to one of the investment strategies associated with private equity ...
called GEF Latam Climate Solutions Fund to invest $200 million in small and medium-sized firms in Latin America that support climate action and environmental sustainability
Specific definitions of sustainability are difficult to agree on and have varied in the literature and over time. The concept of sustainability can be used to guide decisions at the global, national, and individual levels (e.g. sustainable livin ...
. This investment aims to contribute to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) or Global Goals are a collection of 17 interlinked objectives designed to serve as a "shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future".United Nations (2017) R ...
, specifically in climate change mitigation
Climate change mitigation is action to limit climate change by reducing emissions of greenhouse gases or removing those gases from the atmosphere. The recent rise in global average temperature is mostly caused by emissions from fossil fuels bu ...
.
Brazil

Renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
accounted for more than 85.4% of the domestically produced electricity used in Brazil, according to preliminary data from the 2009 National Energy Balance, conducted by the Energy Research Corporation (EPE). After the oil shocks of the 1970s, Brazil started focusing on developing alternative sources of energy, mainly sugarcane ethanol. Its large sugarcane farms helped. In 1985, 91% of cars produced that year ran on sugarcane ethanol. The success of flexible-fuel vehicle
A flexible-fuel vehicle (FFV) or dual-fuel vehicle ( colloquially called a flex-fuel vehicle) is an alternative fuel vehicle with an internal combustion engine designed to run on more than one fuel, usually gasoline blended with either ethan ...
s, introduced in 2003, together with the mandatory E25 blend throughout the country, have allowed ethanol fuel consumption in the country to achieve a 50% market share of the gasoline-powered fleet by February 2008.
In 2021, the country started establishing wind farms in the states of Paraiba, Piau and Bahia
Bahia ( , , ; meaning "bay") is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the Northeast Region of the country. It is the fourth-largest Brazilian state by population (after São Paulo, Minas Gerais, and Rio de Janeiro) and the 5th-larges ...
, and solar photovoltaic plants in Paraiba.
Costa Rica
Renewable energy in Costa Rica accounts for over 90% of the total output of the nation's energy. The country is the world leader in renewable use with massive investment in windmill technologies. The government's aim is to make the country the world's first carbon neutral country. In March 2015 the whole country was running over 75 straight days on100% renewable energy
100% renewable energy means getting all energy from renewable resources. The endeavor to use 100% renewable energy for electricity, heating, cooling and transport is motivated by climate change, pollution and other environmental issue ...
.
See also
*Agency for Non-conventional Energy and Rural Technology
The Agency for New and renewable Energy Research & Technology (ANERT) (earlier known as the Agency for Non-conventional Energy & Rural Technology) is a government agency in the Kerala, India. Its mission is gathering and disseminating knowledge a ...
* Ashden Awards for Sustainable Energy
*Clean-burning stove
A clean-burning stove is a stove with reduced toxic and polluting emissions. The term refers to solid-fuel stoves such as wood-burning stoves for either domestic heating, domestic cooking or both. In the context of a cooking stove, especially in l ...
* Gaspar Makale
* Global Solar Atlas
*Global Wind Atlas
The Global Wind Atlas is a web-based application developed to help policymakers and investors identify potential high-wind areas for wind power generation virtually anywhere in the world, and perform preliminary calculations. It provides free ...
*International Renewable Energy Agency
The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) is an intergovernmental organization mandated to facilitate cooperation, advance knowledge, and promote the adoption and sustainable use of renewable energy. It is the first international organis ...
* Renewable energy in Africa
* Renewable energy in Asia
*Solar powered refrigerator
A solar-powered refrigerator is a refrigerator which runs on energy directly provided by sun, and may include photovoltaic or solar thermal energy.
Solar-powered refrigerators are able to keep perishable goods such as meat and dairy cool in hot ...
*SolarAid
SolarAid is an international development charity which is working to create a sustainable market for solar lights in Africa. In line with the Sustainable Development Goal 7: "Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy f ...
*UN-Energy UN-Energy is an interagency mechanism within the system of the United Nations related to energy. It was created after the 2002 World Summit on Sustainable Development in Johannesburg, and its purpose is to create a coherent approach towards a sustai ...
*Wind power in Asia
Wind power in Asia is an important component in the Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continent ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Renewable Energy in Developing Countries Renewable energy policy Renewable energy commercialization International sustainable development Sustainable energy