Relay logic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Relay logic is a method of implementing
 The
The

combinational logic
In automata theory, combinational logic (also referred to as time-independent logic or combinatorial logic) is a type of digital logic which is implemented by Boolean circuits, where the output is a pure function of the present input only. This i ...
in electrical control circuits by using several electrical relays
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated switch ...
wired in a particular configuration.
Ladder logic
 The
The schematic diagrams
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a designed representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the key information the ...
for relay logic circuits are often called line diagrams, because the inputs and outputs are essentially drawn in a series of lines. A relay logic circuit is an electrical network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical components (e.g., batteries, resistors, inductors, capacitors, switches, transistors) or a model of such an interconnection, consisting of electrical elements (e.g., voltage sources ...
consisting of lines, or rungs, in which each line or rung must have continuity to enable the output device. A typical circuit consists of a number of rungs, with each rung controlling an output. This output is controlled by a combination of input or output conditions, such as input switch
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The most common type of ...
es and control relay
file:Delta Electronics DPS-350FB A - board 1 - OEG SDT-SS-112M - case removed-3045.jpg, A relay
file:Kontakt.svg, Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
file:R ...
s. The conditions that represent the inputs are connected in series, parallel, or series-parallel to obtain the logic required to drive the output. The relay logic circuit forms an electrical schematic diagram for the control of input and output devices. Relay logic diagrams represent the physical interconnection of devices.
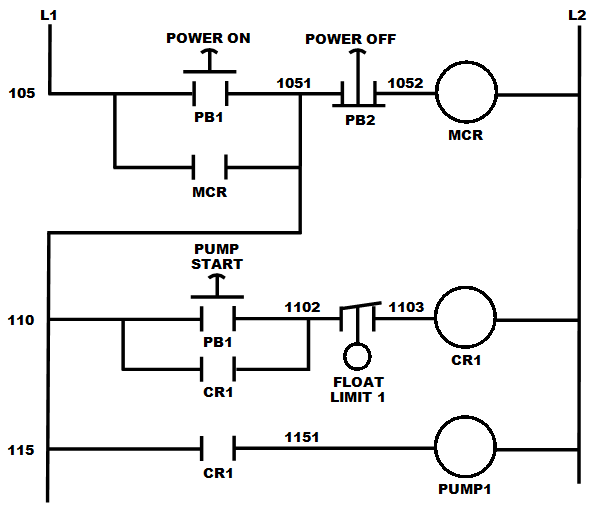
Each rung would have a unique identifying reference number and the individual wires on that rung would have wire numbers as a derivative of the rung number. Thus, if a rung was labelled as 105, the first independent wire would be 1051, the second as 1052, and so forth. A wire would be named for the top most rung to which it connected, even if it branched to lower rungs. When designing a system, it was common practice to skip numbers for the rungs to allow later additions as required.
When the rack was manufactured, as a wire was installed, each end would be marked with wire labels (a.k.a. wire markers). This also applied for pulling wire into the factory through conduit or in trays where each wire would have corresponding numbers. Wire labels were typically pieces of white tape with numbers or letters printed onto them and collected in small, pocket sized booklets. A number strip would be peeled out and wrapped around the wire near the end. Wire numbers were made up of a series of the number strips so wire 1051 would be four strips. There are also pocket sized printers that print onto an adhesive backed label that can be wrapped around the wire.
The basic format for relay logic diagrams is as follows:
1. The two vertical lines that connect all devices on the relay logic diagram are labeled L1 and L2. The space between L1 and L2 represents the voltage of the control circuit.
2. Output devices are always connected to L2. Any electrical overload
In an electric power system, overcurrent or excess current is a situation where a larger than intended electric current exists through a conductor, leading to excessive generation of heat, and the risk of fire or damage to equipment. Possible cau ...
s that are to be included must be shown between the output device and L2; otherwise, the output device must be the last component before L2.
3. Control devices are always shown between L1 and the output device. Control devices may be connected either in series or in parallel with each other.
4. Devices which perform a STOP function are usually connected in series, while devices that perform a START function are connected in parallel.
5. Electrical devices are shown in their normal conditions. An NC contact would be shown as normally closed, and an NO contact would appear as a normally open device. All contacts associated with a device will change state when the device is energized.
Figure 1 shows a typical relay logic diagram. In this circuit, a STOP/START station is used to control two pilot light
Merker Tankless water heating, tankless gas-fired water heater from the 1930s, with pilot light clearly visible through the aperture in the front cover. The large opening allowed for the manual lighting of the pilot light by a lit match or taper
...
s. When the START button is pressed, the control relay energizes and its associated contacts change state. The green pilot light is now ON and the red lamp is OFF. When the STOP button is pressed, the contacts return to their resting state, the red pilot light is ON, and the green switches OFF.
Relay logic design
In many cases, it is possible to design a relay logic diagram directly from the narrative description of a control event sequence. In general, the following suggestions apply to designing a relay logic diagram: 1. Define the process to be controlled. 2. Draw a sketch of the operation process. Make sure all the components of the system are present in the drawing. 3. Determine the sequence of operations to be performed. List the sequence of operational steps in as much detail as possible. Write out the sequence in sentences, or put them in table form. 4. Write the relay logic diagram from the sequence of operations.Applications
A major application of relay logic is the control of routing and signalling on railways. This safety critical application usesinterlocking
In railway signalling, an interlocking is an arrangement of signal apparatus that prevents conflicting movements through an arrangement of tracks such as junctions or crossings. The signalling appliances and tracks are sometimes collectively re ...
to ensure conflicting routes can never be selected and helps reduce accidents.
Elevator
An elevator or lift is a wire rope, cable-assisted, hydraulic cylinder-assisted, or roller-track assisted machine that vertically transports people or freight between floors, levels, or deck (building), decks of a building, watercraft, ...
s are another common application - large relay logic circuits were employed from the 1930s onward to replace the human elevator operator
An elevator operator (North American English), liftman (in Commonwealth English, usually lift attendant), or lift girl (in British English), is a person specifically employed to operate a manually operated elevator.
Description
Being an effec ...
, but have been progressively superseded with modern solid-state controls in recent years.
Relay logic is also used for controlling and automation purposes in electro-hydraulics and electro-pneumatics.

Other kinds of relay logic
Most relay logic diagrams are in "ladder logic" form. Systems using relay logic diagrams in other forms include the Vernam cipher machine, the many 20th centurytelephone exchange
A telephone exchange, telephone switch, or central office is a telecommunications system used in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or in large enterprises. It interconnects telephone subscriber lines or virtual circuits of digital syst ...
s that controlled their crossbar switch
In electronics and telecommunications, a crossbar switch (cross-point switch, matrix switch) is a collection of switches arranged in a matrix configuration. A crossbar switch has multiple input and output lines that form a crossed pattern of int ...
es by relays, and the designs for the various electro-mechanical computers
In engineering, electromechanics combines processes and procedures drawn from electrical engineering and mechanical engineering. Electromechanics focuses on the interaction of electrical and mechanical systems as a whole and how the two systems ...
including the Harvard Mark II
The Harvard Mark II, also known as the Aiken Relay Calculator, was an electromechanical computer built under the direction of Howard Aiken at Harvard University, completed in 1947. It was financed by the United States Navy and used for ballistic c ...
. Design tools for these include Karnaugh map
The Karnaugh map (KM or K-map) is a method of simplifying Boolean algebra expressions. Maurice Karnaugh introduced it in 1953 as a refinement of Edward W. Veitch's 1952 Veitch chart, which was a rediscovery of Allan Marquand's 1881 ''logi ...
s and Boolean algebra
In mathematics and mathematical logic, Boolean algebra is a branch of algebra. It differs from elementary algebra in two ways. First, the values of the variables are the truth values ''true'' and ''false'', usually denoted 1 and 0, whereas in e ...
.
See also
*Programmable logic controller
A programmable logic controller (PLC) or programmable controller is an industrial computer that has been ruggedized and adapted for the control of manufacturing processes, such as assembly lines, machines, robotic devices, or any activity tha ...
- the modern replacement for complex relay logic in industry
{{DEFAULTSORT:Relay Logic
Electromagnetic components