Relative age effect on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The term relative age effect (RAE), also known as birthdate effect or birth date effect, is used to describe a
 Relative age effects are caused by birth date eligibility rules but can be affected by parents, coaches and athletes through other mechanisms, the Pygmalian effect, Galatea effect, and Matthew effect are examples of effects which impact player motivation.
In addition to these social factors contextual differences change the distribution with decreased effects in female sports, unpopular sports, at different ages, individual sports or sports with a lower reliance on body size with an expected increased effect in male sports, popular sports, or competitive sports. The sports popularity in a geographical or cultural area will affect the relative age distribution relative with examples seen in
Relative age effects are caused by birth date eligibility rules but can be affected by parents, coaches and athletes through other mechanisms, the Pygmalian effect, Galatea effect, and Matthew effect are examples of effects which impact player motivation.
In addition to these social factors contextual differences change the distribution with decreased effects in female sports, unpopular sports, at different ages, individual sports or sports with a lower reliance on body size with an expected increased effect in male sports, popular sports, or competitive sports. The sports popularity in a geographical or cultural area will affect the relative age distribution relative with examples seen in
 The Academic year is decided by national education authorities with August or September being common cut-off dates in the Northern Hemisphere and February or March cut-off dates in the Southern Hemisphere.
The third graph illustrates the relative age effect in graduations from the
The Academic year is decided by national education authorities with August or September being common cut-off dates in the Northern Hemisphere and February or March cut-off dates in the Southern Hemisphere.
The third graph illustrates the relative age effect in graduations from the
Are There Really More Capricorns in the National Hockey League? Testing Astrology with Data Science
{{Authority control Sports science Educational assessment and evaluation Academia Epidemiology Ageism Social anthropology Pedagogy
bias
Bias is a disproportionate weight ''in favor of'' or ''against'' an idea or thing, usually in a way that is closed-minded, prejudicial, or unfair. Biases can be innate or learned. People may develop biases for or against an individual, a group ...
, evident in the upper echelons of youth sport and academia, where participation is higher amongst those born earlier in the relevant selection period (and lower for those born later in the selection period) than would be expected from the distribution of births. The selection period is usually the calendar year, the academic year or the sporting season.
The difference in maturity often contributes to the effect with age category, skill level and sport context also impacting the risk of the relative age effect. Mid to late adolescent, regional to nation, popular sports seeing the highest risk, and under 11, recreational, unpopular sports seeing the lowest risk.
The terms month of birth bias and season of birth bias are used to describe similar effect but are fundamentally different. Season of birth examines the influence of different prenatal and perinatal seasonal environmental factors like sunlight, temperature, or viral exposure during gestation, that relate to health outcomes. Whereas the relative age effect shifts with selection dates moving the advantage with the selection period. With influence from social agents children born soon after the cut-off date are typically included, and a child born soon before the cut-off date excluded.
In sport
Youth sport participation is often organized into annual age-groups. TheIOC
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; french: link=no, Comité international olympique, ''CIO'') is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swiss ...
, FIFA and the 6 international football confederations ( AFC, CAF, CONCACAF
The Confederation of North, Central America and Caribbean Association Football,, ; french: Confédération de football d'Amérique du Nord, d'Amérique centrale et des Caraïbes, . Dutch language, Dutch uses the English name. abbreviated as CON ...
, CONMEBOL, OFC and UEFA
Union of European Football Associations (UEFA ; french: Union des associations européennes de football; german: Union der europäischen Fußballverbände) is one of six continental bodies of governance in association football. It governs f ...
) all use 1 January as their administrative cut-off which is most commonly used but, 1 September is used in the UK like many other locations around the world. This grouping can be seen in the first graph showing the distribution of births, by month, for the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
over the ten years from 2000 to 2009. The birth rate correlates closely with the number of days in a month with a slight increase in the summer months. The second graph, by the month, shows the birth distribution of over 4,000 players involved in the qualifying squads for U17, U19 and U21 tournaments organised by UEFA
Union of European Football Associations (UEFA ; french: Union des associations européennes de football; german: Union der europäischen Fußballverbände) is one of six continental bodies of governance in association football. It governs f ...
in 2010–11.
This declining distribution from the beginning of the year for professional athlete participation has been seen in sports like: association football
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 players who primarily use their feet to propel the ball around a rectangular field called a pitch. The objective of the game is ...
, baseball
Baseball is a bat-and-ball sport played between two teams of nine players each, taking turns batting and fielding. The game occurs over the course of several plays, with each play generally beginning when a player on the fielding t ...
, cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by str ...
, gymnastics
Gymnastics is a type of sport that includes physical exercises requiring balance, strength, flexibility, agility, coordination, dedication and endurance. The movements involved in gymnastics contribute to the development of the arms, legs, s ...
, handball, ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice h ...
, rugby league
Rugby league football, commonly known as just rugby league and sometimes football, footy, rugby or league, is a full-contact sport played by two teams of thirteen players on a rectangular field measuring 68 metres (75 yards) wide and 11 ...
, running
Running is a method of terrestrial locomotion allowing humans and other animals to move rapidly on foot. Running is a type of gait characterized by an aerial phase in which all feet are above the ground (though there are exceptions). This is ...
, skiing
Skiing is the use of skis to glide on snow. Variations of purpose include basic transport, a recreational activity, or a competitive winter sport. Many types of competitive skiing events are recognized by the International Olympic Committee ( ...
, swimming
Swimming is the self-propulsion of a person through water, or other liquid, usually for recreation, sport, exercise, or survival. Locomotion is achieved through coordinated movement of the limbs and the body to achieve hydrodynamic thrust that r ...
, tennis
Tennis is a racket sport that is played either individually against a single opponent ( singles) or between two teams of two players each ( doubles). Each player uses a tennis racket that is strung with cord to strike a hollow rubber ball ...
, and the Youth Olympic Games
The Youth Olympic Games (YOG) is an international multi-sport event for athletes between 15 and 18 years old, organized by the International Olympic Committee. The games are held every four years in staggered summer and winter events consiste ...
, as well as non-physical sports like shooting
Shooting is the act or process of discharging a projectile from a ranged weapon (such as a gun, bow, crossbow, slingshot, or blowpipe). Even the acts of launching flame, artillery, darts, harpoons, grenades, rockets, and guided missiles ...
.
Malcolm Gladwell
Malcolm Timothy Gladwell (born 3 September 1963) is an English-born Canadian journalist, author, and public speaker. He has been a staff writer for ''The New Yorker'' since 1996. He has published seven books: '' The Tipping Point: How Little ...
's book '' Outliers: The Story of Success'' and the book '' SuperFreakonomics'' by Steven Levitt and Stephen Dubner, popularised the issue in respect of Canadian ice-hockey players, European football players, and US Major League baseball players.
Contributing factors
 Relative age effects are caused by birth date eligibility rules but can be affected by parents, coaches and athletes through other mechanisms, the Pygmalian effect, Galatea effect, and Matthew effect are examples of effects which impact player motivation.
In addition to these social factors contextual differences change the distribution with decreased effects in female sports, unpopular sports, at different ages, individual sports or sports with a lower reliance on body size with an expected increased effect in male sports, popular sports, or competitive sports. The sports popularity in a geographical or cultural area will affect the relative age distribution relative with examples seen in
Relative age effects are caused by birth date eligibility rules but can be affected by parents, coaches and athletes through other mechanisms, the Pygmalian effect, Galatea effect, and Matthew effect are examples of effects which impact player motivation.
In addition to these social factors contextual differences change the distribution with decreased effects in female sports, unpopular sports, at different ages, individual sports or sports with a lower reliance on body size with an expected increased effect in male sports, popular sports, or competitive sports. The sports popularity in a geographical or cultural area will affect the relative age distribution relative with examples seen in Volleyball
Volleyball is a team sport in which two teams of six players are separated by a net. Each team tries to score points by grounding a ball on the other team's court under organized rules. It has been a part of the official program of the Sum ...
, and American football
American football (referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada), also known as gridiron, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular field with goalposts at each end. The offense, the team wi ...
.
The early maturation levels giving physical advantages to first quarter individuals can create the bias seen in players height in Basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular court, compete with the primary objective of shooting a basketball (approximately in diameter) through the defender's h ...
, dominant hand in Tennis
Tennis is a racket sport that is played either individually against a single opponent ( singles) or between two teams of two players each ( doubles). Each player uses a tennis racket that is strung with cord to strike a hollow rubber ball ...
, or size in a Cricket position, but physical size isn't always the cause. The older individuals also gaining more competence and self-efficacy increasing the performance gap, these advantages leading to increased dropout rates for Q1 births. However, the bias for sports where height and mass impedes flexibility, rotational speed and the strength to mass ratio, maturational delay may be preferred as seen in Gymnastics
Gymnastics is a type of sport that includes physical exercises requiring balance, strength, flexibility, agility, coordination, dedication and endurance. The movements involved in gymnastics contribute to the development of the arms, legs, s ...
.
With an adult group the relative age has the opposite meaning, as performance declines in age and is more significant with more physically demanding sports, depending on what age the average peak performance level is, in that sport. The "underdog effect" has shown that those late birth individuals may see better chances if they are selected to play, with the advantage decreasing after selection.
Playing position, federation membership, and individual and team performance also contribute to the effect with older players having a higher risk of injury.
Reducing the relative age effect
Various methods have been suggested and tested to reduce the relative age effect like moving the cut off dates, expanding the age group range, birthdate quotas for the players, the average team age (ATA) method for eligibility, or grouping by height and weight. Some methods have struggled to find success due to the effect moving with selection dates. Making the relative age known to the individuals in the environment have shown less bias in talent identification reducing the relative age effect. Birthday banding, and re-calculating scores based on relative age are other methods used to reduce the effects with bio-banding seeing the most research, showing benefit to early and late maturing players in both academy football and recreational football. Bio-banding can help promote appropriate training loads and reduce injury risk, while increasing technical demands from players however, sports already categorized by maturation metrics likeJudo
is an unarmed modern Japanese martial art, Olympic sport (since 1964), and the most prominent form of jacket wrestling competed internationally.『日本大百科全書』電子版【柔道】(CD-ROM version of Encyclopedia Nipponica, "Judo"). ...
, may not see those effects. More longitudinal studies are needed alongside more reliable ways to band individuals as biological, psychological and social development doesn't progress in synchrony creating different imbalances in the groups.
In education
 The Academic year is decided by national education authorities with August or September being common cut-off dates in the Northern Hemisphere and February or March cut-off dates in the Southern Hemisphere.
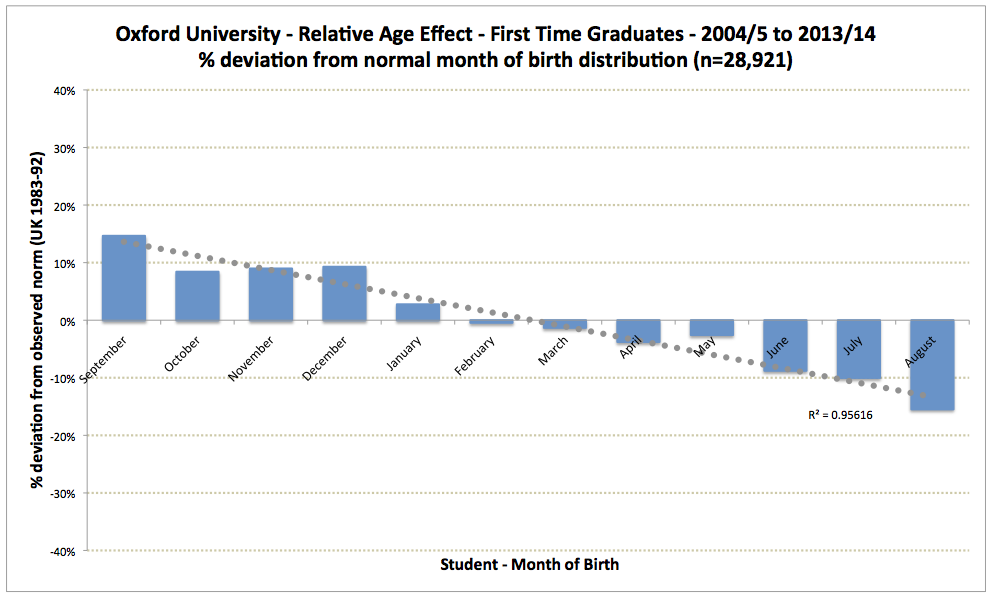
The third graph illustrates the relative age effect in graduations from the
The Academic year is decided by national education authorities with August or September being common cut-off dates in the Northern Hemisphere and February or March cut-off dates in the Southern Hemisphere.
The third graph illustrates the relative age effect in graduations from the University of Oxford
, mottoeng = The Lord is my light
, established =
, endowment = £6.1 billion (including colleges) (2019)
, budget = £2.145 billion (2019–20)
, chancellor ...
over a 10-year period, which has also been seen in UK Nobel laureates.
The relative age effect and reversal effect are evident in education with older students on average scoring higher marks, getting into gifted and talented programs, and are more likely to attend higher education in academic schools over vocational schools, not necessarily due to higher intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can be des ...
. The Matthew effect again playing a role, as the skills learned early in education compound overtime increasing the advantage, with older students becoming more likely to take up leadership roles. However, like in sport, the effect diminishes over time after middle school, and those born later in the year performing better in university education.
In leadership positions
A relative age effect has also been observed in the context of leadership. An over-representation starts in high-school leadership activities such as sports team captain or club president. Then in adult life, this over-representation has been observed in top managerial positions (CEOs of S&P 500 companies), and in top political positions, both in the USA (senators and representatives), and in Finland (MPs).Seasonal birth effect
Seasonal birth in humans varies, and alongside the relative age effect theepidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evide ...
of seasonal births show over-representations in health conditions like ADHD and schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social wit ...
with one study finding "that higher school starting age lowers the propensity to commit crime at young ages." However, other studies failed to replicate relative age effects on temperament, mood, or physical development.
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
has been linked to season of birth with increased chances, potentially due to surrounding temperature at birth with winter and spring having the highest correlation, but Physical inactivity Physical inactivity refers to the lack of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity in a person's lifestyle. It is distinct from sedentary behavior.
Health effects
The World Health Organization (WHO) has defined physical inactivity as a global public ...
is still a larger risk factor.
Summer babies having increased chances of specific learning difficulties, winter and spring babies related to schizophrenia and mania/bipolar disorder. Schizoaffective disorder can be related to December - March births, major depression to March - May births, and Autism to March births.
Increased rates in Seasonal affective disorder
Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) is a mood disorder subset, in which people who have normal mental health throughout most of the year exhibit depressive symptoms at the same time each year.
Common symptoms include sleeping too much, having li ...
relate to the Influence of seasonal birth in humans.
Further reading
Football. Ice Hockey. Tennis.References
External links
Are There Really More Capricorns in the National Hockey League? Testing Astrology with Data Science
{{Authority control Sports science Educational assessment and evaluation Academia Epidemiology Ageism Social anthropology Pedagogy