Rectenna on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A rectenna (''rec''tifying ant''enna'') is a special type of receiving antenna that is used for converting 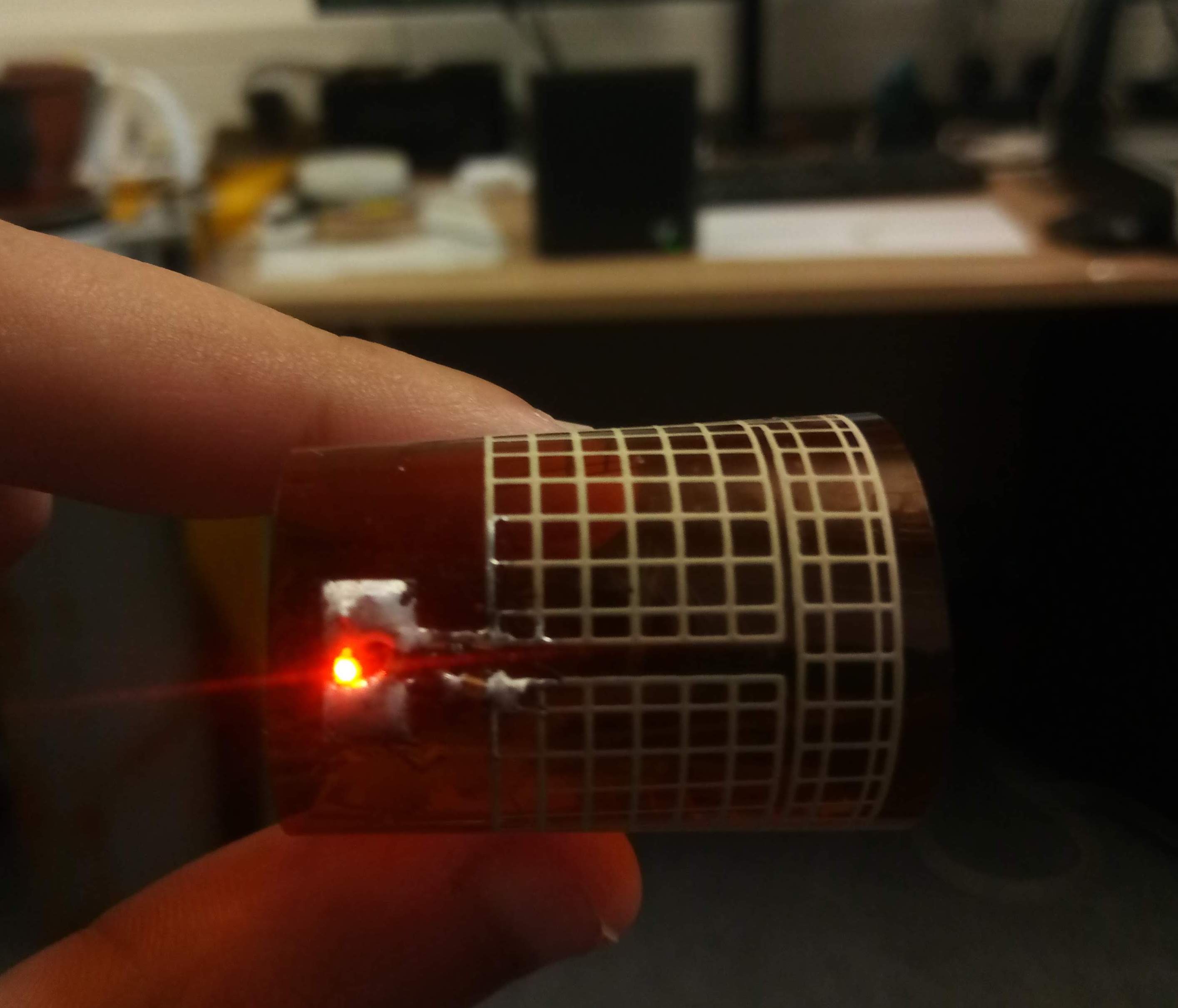
 In recent years, interest has turned to using rectennas as power sources for small wireless microelectronic devices. The largest current use of rectennas is in RFID tags,
In recent years, interest has turned to using rectennas as power sources for small wireless microelectronic devices. The largest current use of rectennas is in RFID tags,
William C. Brown's Distinguished Career
* ** {{Antenna Types Radio frequency antenna types Solar cells Antennas
electromagnetic
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions o ...
energy into direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or eve ...
(DC) electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as describ ...
. They are used in wireless power transmission
Wireless power transfer (WPT), wireless power transmission, wireless energy transmission (WET), or electromagnetic power transfer is the transmission of electrical energy without wires as a physical link. In a wireless power transmission system ...
systems that transmit power by radio waves
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies of 300 gigahertz ( GHz) and below. At 300 GHz, the corresponding wavelength is 1 mm (s ...
. A simple rectenna element consists of a dipole antenna with an RF diode connected across the dipole elements. The diode rectifies the AC induced in the antenna by the microwaves, to produce DC power, which powers a load connected across the diode. Schottky diode
The Schottky diode (named after the German physicist Walter H. Schottky), also known as Schottky barrier diode or hot-carrier diode, is a semiconductor diode formed by the junction of a semiconductor with a metal. It has a low forward voltag ...
s are usually used because they have the lowest voltage drop and highest speed and therefore have the lowest power losses due to conduction and switching. Large rectennas consist of an array of many power receiving elements such as dipole antennas.

Power beaming applications
The invention of the rectenna in the 1960s made long distancewireless power transmission
Wireless power transfer (WPT), wireless power transmission, wireless energy transmission (WET), or electromagnetic power transfer is the transmission of electrical energy without wires as a physical link. In a wireless power transmission system ...
feasible. The rectenna was invented in 1964 and patented in 1969 by US electrical engineer William C. Brown
William C. Brown (May 22, 1916 – February 3, 1999) was an American electrical engineer who helped to invent the crossed-field amplifier in the 1950s and also pioneered microwave power transmission in the 1960s.
Brown received his BSEE fro ...
, who demonstrated it with a model helicopter powered by microwaves transmitted from the ground, received by an attached rectenna. Since the 1970s, one of the major motivations for rectenna research has been to develop a receiving antenna for proposed solar power satellites, which would harvest energy from sunlight in space with solar cell
A solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect, which is a physical and chemical phenomenon.
s and beam it down to Earth as microwaves to huge rectenna arrays. A proposed military application is to power drone
Drone most commonly refers to:
* Drone (bee), a male bee, from an unfertilized egg
* Unmanned aerial vehicle
* Unmanned surface vehicle, watercraft
* Unmanned underwater vehicle or underwater drone
Drone, drones or The Drones may also refer to:
...
reconnaissance aircraft with microwaves beamed from the ground, allowing them to stay aloft for long periods.
 In recent years, interest has turned to using rectennas as power sources for small wireless microelectronic devices. The largest current use of rectennas is in RFID tags,
In recent years, interest has turned to using rectennas as power sources for small wireless microelectronic devices. The largest current use of rectennas is in RFID tags, proximity card
A proximity card or prox card also known as a key card or keycard is a contactless smart card which can be read without inserting it into a reader device, as required by earlier magnetic stripe cards such as credit cards and contact type sma ...
s and contactless smart cards, which contain an integrated circuit ( IC) which is powered by a small rectenna element. When the device is brought near an electronic reader unit, radio waves from the reader are received by the rectenna, powering up the IC, which transmits its data back to the reader.
Radio frequency rectennas
The simplest crystal radio receiver, employing an antenna and a demodulating diode ( rectifier), is actually a rectenna, although it discards theDC component
DC, D.C., D/C, Dc, or dc may refer to:
Places
* Washington, D.C. (District of Columbia), the capital and the federal territory of the United States
* Bogotá, Distrito Capital, the capital city of Colombia
* Dubai City, as distinct from th ...
before sending the signal to the headphones. People living near strong radio transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the ...
s would occasionally discover that with a long receiving antenna, they could get enough electric power to light a light bulb.
However, this example uses only one antenna having a limited capture area. A rectenna array uses multiple antennas spread over a wide area to capture more energy.
Researchers are experimenting with the use of rectennas to power sensors in remote areas and distributed networks of sensors, especially for IoT applications.
RF rectennas are used for several forms of wireless power transfer
Wireless power transfer (WPT), wireless power transmission, wireless energy transmission (WET), or electromagnetic power transfer is the transmission of electrical energy without wires as a physical link. In a wireless power transmission system ...
. In the microwave range, experimental devices have reached a power conversion efficiency of 85–90%. The record conversion efficiency for a rectenna is 90.6% for 2.45 GHz,McSpadden, J. O., Fan, L., and Kai Chang, "Design and Experiments of a High-Conversion-Efficiency 5.8-GHz Rectenna," ''IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory and Technique'', Vol. 46, No. 12, December 1998, pp. 2053–2060. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/739282 with lower efficiency of about 82% achieved at 5.82 GHz.
Optical rectennas
In principle, similar devices, scaled down to the proportions used in nanotechnology, can be used to convertlight
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 te ...
directly into electricity. This type of device is called an ''optical rectenna
An optical rectenna is a rectenna (rectifying antenna) that works with visible or infrared light. A rectenna is a circuit containing an antenna and a diode, which turns electromagnetic waves into direct current electricity. While rectennas have l ...
'' (or "nantenna"). Theoretically, high efficiencies can be maintained as the device shrinks, but to date efficiency has been limited, and so far there has not been convincing evidence that rectification has been achieved at optical frequencies. The University of Missouri
The University of Missouri (Mizzou, MU, or Missouri) is a public land-grant research university in Columbia, Missouri. It is Missouri's largest university and the flagship of the four-campus University of Missouri System. MU was founded in ...
previously reported on work to develop low-cost, high-efficiency optical-frequency rectennas. Other prototype devices were investigated in a collaboration between the University of Connecticut
The University of Connecticut (UConn) is a public land-grant research university in Storrs, Connecticut, a village in the town of Mansfield. The primary 4,400-acre (17.8 km2) campus is in Storrs, approximately a half hour's drive from H ...
and Penn State Altoona
Penn State Altoona is a commonwealth campus of The Pennsylvania State University located in Logan Township, Pennsylvania. It is one of four full-fledged four year institutions in the Commonwealth Campus network. The full-time student count was ...
using a grant from the National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National ...
. With the use of atomic layer deposition it has been suggested that conversion efficiencies of solar energy to electricity higher than 70% could eventually be achieved.
The creation of successful optical rectenna technology has two major complicating factors:
# Fabricating an antenna small enough to couple optical wavelengths.
# Creating an ultra-fast diode capable of rectifying the high frequency oscillations, at frequency of ~500 THz.
Below are a few examples of potential paths to creating diodes that would be fast enough to rectify optical and near-optical radiation.
Geometric diodes
A promising path towards creating these ultrafast diodes has been in the form of " geometric diodes". Graphene geometric diodes have been reported to rectifyterahertz radiation
Terahertz radiation – also known as submillimeter radiation, terahertz waves, tremendously high frequency
(THF), T-rays, T-waves, T-light, T-lux or THz – consists of electromagnetic waves within the ITU-designated band of fre ...
. In April 2020, geometric diodes were reported in silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ta ...
nanowires
A nanowire is a nanostructure in the form of a wire with the diameter of the order of a nanometre (10−9 metres). More generally, nanowires can be defined as structures that have a thickness or diameter constrained to tens of nanometers or less ...
. The wires were shown experimentally to rectify up to 40 GHz, but that was instrument limited, and theoretically may be able to rectify signals in the THz region as well.
See also
*Microstrip antenna
In telecommunication, a microstrip antenna (also known as a printed antenna) usually means an antenna fabricated using photolithographic techniques on a printed circuit board (PCB). It is a kind of internal antenna. They are mostly used at mic ...
* Wireless power transfer
Wireless power transfer (WPT), wireless power transmission, wireless energy transmission (WET), or electromagnetic power transfer is the transmission of electrical energy without wires as a physical link. In a wireless power transmission system ...
References
External links
William C. Brown's Distinguished Career
* ** {{Antenna Types Radio frequency antenna types Solar cells Antennas