Reconquista (Spanish America) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In the struggle for the independence of
Spanish America
Spanish America refers to the Spanish territories in the Americas during the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The term "Spanish America" was specifically used during the territories' imperial era between 15th and 19th centuries. To the e ...
, the Reconquista refers to the period of Colombian and Chilean history, following the defeat of Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
in 1814, during which royalist armies were able to gain the upper hand in the Spanish American wars of independence
The Spanish American wars of independence (25 September 1808 – 29 September 1833; es, Guerras de independencia hispanoamericanas) were numerous wars in Spanish America with the aim of political independence from Spanish rule during the early ...
. The term used in the past century by some Colombian and Chilean historians makes an analogy to the medieval Reconquista
The ' ( Spanish, Portuguese and Galician for "reconquest") is a historiographical construction describing the 781-year period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 and the fall of the N ...
, in which Christian forces retook the Iberian Peninsula from the Caliphate
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
.
During Napoleon's invasion of the Iberian Peninsula, a number of Spanish colonies in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
moved for greater autonomy or outright independence due to the political instability in Spain, which was eventually (1810) governed by the Cortes of Cádiz
The Cortes of Cádiz was a revival of the traditional '' cortes'' (Spanish parliament), which as an institution had not functioned for many years, but it met as a single body, rather than divided into estates as with previous ones.
The Genera ...
which served as a democratic Regency after Ferdinand VII was deposed.
By 1815 the general outlines of which areas were controlled by royalists and pro-independence forces had been established and the situation had reached a stalemate. With the exception of rural areas controlled by guerrillas, New Spain and Peru was under the control of royalists, and in South America only the Río de la Plata
The Río de la Plata (, "river of silver"), also called the River Plate or La Plata River in English, is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay River and the Paraná River at Punta Gorda. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean and fo ...
and New Granada New Granada may refer to various former national denominations for the present-day country of Colombia.
* New Kingdom of Granada, from 1538 to 1717
*Viceroyalty of New Granada, from 1717 to 1810, re-established from 1816 to 1819
*United Provinces of ...
remained outside of royalist control. After French forces left Spain in 1814, the restored Ferdinand VII, declared these developments in the Americas illegal, abolished the Spanish Constitution of 1812
The Political Constitution of the Spanish Monarchy ( es, link=no, Constitución Política de la Monarquía Española), also known as the Constitution of Cádiz ( es, link=no, Constitución de Cádiz) and as ''La Pepa'', was the first Constituti ...
passed by the Cortes of Cádiz, then sent expeditionary armies to quell the remaining rebellions. The impact of these expeditions was most notable in Pablo Morillo
Pablo Morillo y Morillo, Count of Cartagena and Marquess of La Puerta, a.k.a. ''El Pacificador'' (The Peace Maker) (5 May 1775 – 27 July 1837) was a Spanish general.
Biography
Morillo was born in Fuentesecas, Zamora, Spain. In 1791 ...
's expedition against New Granada New Granada may refer to various former national denominations for the present-day country of Colombia.
* New Kingdom of Granada, from 1538 to 1717
*Viceroyalty of New Granada, from 1717 to 1810, re-established from 1816 to 1819
*United Provinces of ...
, and Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
. The restoration of royal rule was short lived, reversed in these three countries.
Restoration of Ferdinand VII
The restoration of Ferdinand VII signified an important change, since most of the political and legal changes done on both sides of the Atlantic—the myriad ofjuntas
A military dictatorship is a dictatorship in which the military exerts complete or substantial control over political authority, and the dictator is often a high-ranked military officer.
The reverse situation is to have civilian control of the m ...
, the Cortes of Cádiz
The Cortes of Cádiz was a revival of the traditional '' cortes'' (Spanish parliament), which as an institution had not functioned for many years, but it met as a single body, rather than divided into estates as with previous ones.
The Genera ...
and several of the congresses in the Americas, and many of the constitutions and new legal codes—had been done in his name. Once in Spain he realized that he had significant support from conservatives
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
in the general population and the hierarchy of the Spanish Catholic Church, and so on May 4, he repudiated the Spanish Constitution of 1812
The Political Constitution of the Spanish Monarchy ( es, link=no, Constitución Política de la Monarquía Española), also known as the Constitution of Cádiz ( es, link=no, Constitución de Cádiz) and as ''La Pepa'', was the first Constituti ...
, then on May 10 ordered the arrest of liberal leaders who had created it. Ferdinand justified his actions by stating that the Constitution and other changes had been made by a Cortes assembled in his absence and without his consent. He also declared all of the juntas and constitutions written in Spanish America invalid and restored the former law codes and political institutions. News of the events arrived through Spanish America during the next three weeks to nine months, depending on time it took goods and people to travel from Spain.
This, in effect, constituted a definitive break with two groups that could have been allies of Ferdinand VII: the autonomous governments, which had not yet declared formal independence, and Spanish liberals who had created a representative government that would fully include the overseas possessions and was seen as an alternative to independence by many in New Spain, Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
, the Caribbean, Quito (today Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ' ...
), Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
, Upper Peru
Upper Peru (; ) is a name for the land that was governed by the Real Audiencia of Charcas. The name originated in Buenos Aires towards the end of the 18th century after the Audiencia of Charcas was transferred from the Viceroyalty of Peru to t ...
(today, Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg
, flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center
, flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ...
) and Chile. Most Spanish Americans were moderates who decided to wait and see what would come out of the restoration of normalcy. Spanish Americans in royalist areas who were committed to independence had already joined guerrilla movements. Ferdinand's actions did set areas outside of the control of the royalist armies on the path to full independence. The governments of these regions, which had their origins in the juntas of 1810—and even moderates there who had entertained a reconciliation with the crown—now saw the need to separate from Spain, if they were to protect the reforms they had enacted.
Expeditionary campaigns
During this period royalist forces made advances into New Granada, which they controlled from 1815 to 1819, and into Chile, from 1814 to 1817. Except for royalist areas in the northeast and south, the provinces of New Granada had maintained independence from Spain since 1810, unlike neighboring Venezuela, where royalists and pro-independence forces had exchanged control of the country several times. To pacify Venezuela and to retake New Granada, Spain organized and sent in 1815 the largest armed force it ever sent to the New World, consisting of approximately 10,000 troops and nearly sixty ships under the command of generalPablo Morillo
Pablo Morillo y Morillo, Count of Cartagena and Marquess of La Puerta, a.k.a. ''El Pacificador'' (The Peace Maker) (5 May 1775 – 27 July 1837) was a Spanish general.
Biography
Morillo was born in Fuentesecas, Zamora, Spain. In 1791 ...
. Although this force was crucial in retaking a solidly pro-independence region like New Granada, its soldiers were eventually spread out throughout Venezuela, New Granada, Quito and Peru and lost to tropical diseases, diluting their impact on the war.Earle, ''Spain and the Independence of Colombia''. Ultimately, the majority of the royalist forces were composed, not of soldiers sent from Spain, but of Spanish Americans.
The expeditionary army of Tierra Firme
Leaving the port ofCádiz
Cádiz (, , ) is a city and port in southwestern Spain. It is the capital of the Province of Cádiz, one of eight that make up the autonomous community of Andalusia.
Cádiz, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in Western Europe, ...
on February 17, 1815, the force initially landed at Carupano (Venezuela) in April and later invaded the island of Margarita
A margarita is a cocktail consisting of Tequila, triple sec, and lime juice often served with salt on the rim of the glass. The drink is served shaken with ice (on the rocks), blended with ice (frozen margarita), or without ice (straight u ...
where no resistance was encountered. After leaving the island, Morillo's troops reinforced existing royalist forces in the Venezuelan mainland, entering Cumaná
Cumaná () is the capital city of Venezuela's Sucre State. It is located east of Caracas. Cumaná was one of the first cities founded by Spain in the mainland Americas and is the oldest continuously-inhabited Hispanic-established city in South ...
, La Guaira
La Guaira () is the capital city of the Venezuelan state of the same name (formerly named Vargas) and the country's main port. It was founded in 1577 as an outlet for Caracas, to the southeast. The town and the port were badly damaged during ...
, Caracas
Caracas (, ), officially Santiago de León de Caracas, abbreviated as CCS, is the capital and largest city of Venezuela, and the center of the Metropolitan Region of Caracas (or Greater Caracas). Caracas is located along the Guaire River in th ...
, and Puerto Cabello
Puerto Cabello () is a city on the north coast of Venezuela. It is located in Carabobo State, about 210 km west of Caracas. As of 2011, the city had a population of around 182,400. The city is home to the largest and busiest port in the coun ...
in May. A small part of the main corps set off towards Panamá, while the main contingent was directed towards the Neogranadine coastal city of Santa Marta
Santa Marta (), officially Distrito Turístico, Cultural e Histórico de Santa Marta ("Touristic, Cultural and Historic District of Santa Marta"), is a city on the coast of the Caribbean Sea in northern Colombia. It is the capital of Magdalena ...
which was still in royalist hands.
After picking up supplies and militia volunteers in Santa Marta
Santa Marta (), officially Distrito Turístico, Cultural e Histórico de Santa Marta ("Touristic, Cultural and Historic District of Santa Marta"), is a city on the coast of the Caribbean Sea in northern Colombia. It is the capital of Magdalena ...
on July 23, the Spanish expeditionary forces besieged Cartagena de Indias
Cartagena ( , also ), known since the colonial era as Cartagena de Indias (), is a city and one of the major ports on the northern coast of Colombia in the Caribbean Coast Region, bordering the Caribbean sea. Cartagena's past role as a link ...
. After a five-month siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characteriz ...
the fortified city fell on December 1815. By May 6, 1816, the combined efforts of Spanish and colonial forces, marching south from Cartagena and north from royalist strongholds in Quito
Quito (; qu, Kitu), formally San Francisco de Quito, is the capital and largest city of Ecuador, with an estimated population of 2.8 million in its urban area. It is also the capital of the province of Pichincha. Quito is located in a valley on ...
, Pasto, and Popayán, completed the reconquest of New Granada, taking Bogotá
Bogotá (, also , , ), officially Bogotá, Distrito Capital, abbreviated Bogotá, D.C., and formerly known as Santa Fe de Bogotá (; ) during the Spanish period and between 1991 and 2000, is the capital city of Colombia, and one of the larges ...
. A permanent council of war
A council of war is a term in military science that describes a meeting held to decide on a course of action, usually in the midst of a battle. Under normal circumstances, decisions are made by a commanding officer, optionally communicated ...
was set up to judge those accused of treason and rebellion, resulting in the execution of more than a hundred notable republican officials, including Jorge Tadeo Lozano
Jorge Tadeo Lozano, Viscount of Pastrana (January 30, 1771 – July 6, 1816) was a Neogranadine (now Colombian) scientist, journalist, and politician who presided over the Constituent College of Cundinamarca and was elected President of Cundin ...
, Francisco José de Caldas
Francisco José de Caldas (October 4, 1768 – October 28, 1816) was a Colombian lawyer, military engineer
Military engineering is loosely defined as the art, science, and practice of designing and building military works and maintaining li ...
and José María Cabal. Units of the republican armies of New Granada were incorporated into the royalist army and sent to Peru.
The Chilean campaign
In August 1814 the Queen's Talavera Regiment, a unit which had fought in the Peninsular War, arrived inTalcahuano
Talcahuano () (From Mapudungun ''Tralkawenu'', "Thundering Sky") is a port city and commune in the Biobío Region of Chile. It is part of the Greater Concepción conurbation. Talcahuano is located in the south of the Central Zone of Chile.
Geo ...
, a royalist bastion in Chile under the command of Brigadier Mariano Osorio
Mariano de Osorio (; 1777–1819) was a Spanish general and Governor of Chile, from 1814 to 1815.
Early career
Osorio was born in Seville, Spain. He joined the Spanish army and as many of his contemporaries, his military career began during the S ...
, who was also the newly appointed governor. Osorio succeeded in organizing local recruits into a mobile army of some 5,000 men, of which the troops of the Talaveras Regiment were practically the only Spaniards. The new royalist force fought the patriot forces on October 1 in Rancagua
Rancagua () is a city and commune in central Chile and part of the Rancagua conurbation. It is the capital of the Cachapoal Province and of the O'Higgins Region, located south of the national capital of Santiago.
It was originally named Sant ...
, in which the patriots unsuccessfully tried to stop the expeditionaries from taking Santiago
Santiago (, ; ), also known as Santiago de Chile, is the capital and largest city of Chile as well as one of the largest cities in the Americas. It is the center of Chile's most densely populated region, the Santiago Metropolitan Region, whos ...
.
After royalist forces took Santiago
Santiago (, ; ), also known as Santiago de Chile, is the capital and largest city of Chile as well as one of the largest cities in the Americas. It is the center of Chile's most densely populated region, the Santiago Metropolitan Region, whos ...
, patriots found in the city—among whom were members of the First Junta—were exiled to the Juan Fernández Islands
The Juan Fernández Islands ( es, Archipiélago Juan Fernández) are a sparsely inhabited series of islands in the South Pacific Ocean reliant on tourism and fishing. Situated off the coast of Chile, they are composed of three main volcanic ...
. By November Spanish control had been reestablished in most of Chile. A member of the Talavera Regiment, Vicente San Bruno was put in charge of carrying out the orders to arrest civilians suspected of having helped or sympathised with the patriots. In 1816 Francisco Marcó del Pont
Francisco Casimiro Marcó del Pont y Ángel (; June 25, 1770 – May 19, 1819) was a Spanish soldier and the last Governor of Chile. He was one of the main figures of the Chilean independence process, being the final Spaniard to rule as Royal G ...
became the new governor and he initiated a new campaign of fierce political and military persecution. Marcó del Pont appointed San Bruno president of a Tribunal of Vigilance and Public Security.
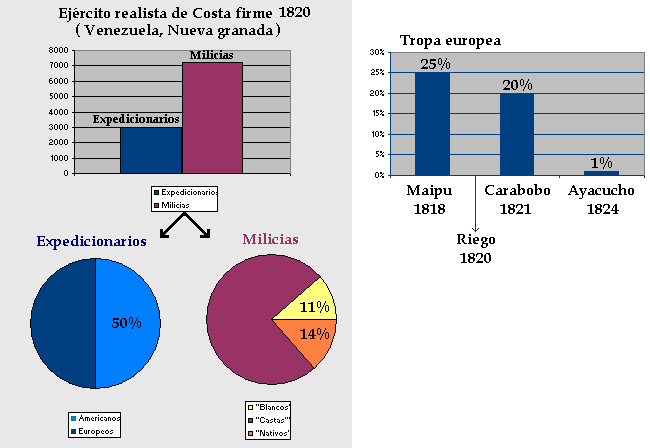
The royalist military
Overall, Europeans formed only about a tenth of the royalist armies in Spanish America, and only about half of the expeditionary units once they were deployed in the Americas. Since each European soldier casualty was substituted by a Spanish American soldier, over time, there were more and more Spanish American soldiers in the expeditionary units. For examplePablo Morillo
Pablo Morillo y Morillo, Count of Cartagena and Marquess of La Puerta, a.k.a. ''El Pacificador'' (The Peace Maker) (5 May 1775 – 27 July 1837) was a Spanish general.
Biography
Morillo was born in Fuentesecas, Zamora, Spain. In 1791 ...
, commander in chief of the expeditionary force sent South America, reported that he only had 2,000 European soldiers under his command in 1820, in other words, only half of the soldiers of his expeditionary force were European. It is estimated that in the Battle of Maipú
The Battle of Maipú ( es, Batalla de Maipú) was a battle fought near Santiago, Chile on April 5, 1818, between South American rebels and Spanish royalists, during the Chilean War of Independence. The Patriot rebels led by Argentine general J ...
only a quarter of the royalist forces were European soldiers, in the Battle of Carabobo
The Battle of Carabobo, on 24 June 1821, was fought between independence fighters, led by Venezuelan General Simón Bolívar, and the Royalist forces, led by Spanish Field Marshal Miguel de la Torre. Bolívar's decisive victory at Carabobo le ...
about a fifth, and in the Battle of Ayacucho
The Battle of Ayacucho ( es, Batalla de Ayacucho, ) was a decisive military encounter during the Peruvian War of Independence. This battle secured the independence of Peru and ensured independence for the rest of South America. In Peru it is co ...
less than 1% was European.
The American militias reflected the racial make-up of the local population. For example, in 1820 the royalist army in Venezuela had 843 white (''español''), 5,378 Casta
() is a term which means "lineage" in Spanish and Portuguese and has historically been used as a racial and social identifier. In the context of the Spanish Empire in the Americas it also refers to a now-discredited 20th-century theoretical f ...
and 980 Indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
soldiers.

Reverses
Far from pacifying the patriots, these actions served to incite them to the military solution, and soon even moderates, who had previously envisioned a negotiation with the Spanish crown, concluded that war of independence was the only way to guarantee their newfound freedoms. In New Granada, patriots reacted to the expeditionary force with disunity, aiding Morillo's advance. Several Neogranadine and Venezuelan exiles fled toHaiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and s ...
, where they were well received. Others fled to the Llanos
The Llanos ( Spanish ''Los Llanos'', "The Plains"; ) is a vast tropical grassland plain situated to the east of the Andes in Colombia and Venezuela, in northwestern South America. It is an ecoregion of the tropical and subtropical grassla ...
, where they were out of reach of Morillo's forces. Haitian president Alexandre Pétion
Alexandre Sabès Pétion (; April 2, 1770 – March 29, 1818) was the first president of the Republic of Haiti from 1807 until his death in 1818. He is acknowledged as one of Haiti's founding fathers; a member of the revolutionary quartet tha ...
gave the exiles military and monetary aid, which allowed them to resume the struggle for independence in conjunction with the patriots who had organized the Llaneros into guerrilla bands.
In the Southern Cone, San Martín as the governor of Cuyo, had been organizing an army as early as 1814 in preparation for an invasion of Chile. Chilean patriots who escaped the royalist reprisals fled to Mendoza, an Argentine Andean province under Buenos Aires control. They were reorganized under José de San Martín
José Francisco de San Martín y Matorras (25 February 177817 August 1850), known simply as José de San Martín () or '' the Liberator of Argentina, Chile and Peru'', was an Argentine general and the primary leader of the southern and centr ...
. While Argentinean forces prepared to invade Chile, San Martín and O'Higgins initiated a guerrilla campaign under Manuel Rodríguez to keep the royalist forces off balance. The black people
Black is a racialized classification of people, usually a political and skin color-based category for specific populations with a mid to dark brown complexion. Not all people considered "black" have dark skin; in certain countries, often in ...
, slave and freemen, recruits from Mendoza and Buenos Aires was the nucleus of the Army of the Andes
The Army of the Andes ( es, Ejército de los Andes) was a military force created by the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata (Argentina) and mustered by general José de San Martín in his campaign to free Chile from the Spanish Empire. In 181 ...
, which received crucial political and material support in 1816 when Juan Martín de Pueyrredón
Juan Martín de Pueyrredón y O'Dogan (December 18, 1777 – March 13, 1850) was an Argentine general and politician of the early 19th century. He was appointed Supreme Director of the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata after the Argentine ...
became Supreme Director of the United Provinces. From January to February 1817, San Martín led the Army over the Andes in an audacious move that turned the tables on the royalists in Chile. By February 10, San Martín had control of northern and central Chile, and a year later had control of the south. Chile was secured from royalist control and independence was declared in 1818. San Martín and his allies spent the next two years planning an invasion of Peru, which began in 1820.
In northern South America, Simón Bolívar
Simón José Antonio de la Santísima Trinidad Bolívar y Palacios (24 July 1783 – 17 December 1830) was a Venezuelan military and political leader who led what are currently the countries of Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, Panama and B ...
devised a change the center of military operations from Caracas to New Granada. Like San Martín, Bolívar personally undertook the efforts to create an army to invade a neighboring country and collaborated with pro-independence exiles from that region. Unlike San Martín, Bolívar did not have the approval of the Venezuelan congress. From June to July 1819, using the rainy season
The rainy season is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs.
Rainy Season may also refer to:
* ''Rainy Season'' (short story), a 1989 short horror story by Stephen King
* "Rainy Season", a 2018 song by Monni
* '' ...
as cover, Bolívar led an army composed mostly of '' Llaneros'' and British Legions
The British Legion () or British Legions were foreign volunteer units that fought under Simón Bolívar against Spain for the independence of Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador and José de San Martín for the independence of Peru in the Spanish Ameri ...
over the cold, forbidding passes of the Andes, but the gamble paid off. By August Bolívar was in control of Bogotá
Bogotá (, also , , ), officially Bogotá, Distrito Capital, abbreviated Bogotá, D.C., and formerly known as Santa Fe de Bogotá (; ) during the Spanish period and between 1991 and 2000, is the capital city of Colombia, and one of the larges ...
and gained the support of New Granada, which still resented the harsh reconquest carried out under Morillo. With the resources of New Granada, Bolívar became the undisputed leader of the patriots in Venezuela and orchestrated the union of the two regions in a new state, Gran Colombia
Gran Colombia (, "Great Colombia"), or Greater Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia ( Spanish: ''República de Colombia''), was a state that encompassed much of northern South America and part of southern Central America from 1819 to ...
.
See also
* Royalist (Spanish American Revolution) * Spanish attempts to reconquer Mexico *Venezuelan War of Independence
The Venezuelan War of Independence ( es, Guerra de Independencia de Venezuela, links=no, 1810–1823) was one of the Spanish American wars of independence of the early nineteenth century, when independence movements in Latin America fought agai ...
References
Bibliography
*Timothy Anna. ''Spain & the Loss of Empire''. Lincoln, University of Nebraska Press, 1983. *Christon I. Archer (ed.). ''The Wars of Independence in Spanish America''. Willmington, SR Books, 2000. *Michael P. Costeloe. ''Response to Revolution: Imperial Spain and the Spanish American Revolutions, 1810-1840''. Cambridge University Press, 1986. *Jorge I. Domínguez. ''Insurrection or Loyalty: The Breakdown of the Spanish American Empire''. Cambridge, Harvard University Press, 1980. * Rebecca Earle. ''Spain and the Independence of Colombia, 1810-1825''. Exter: University of Exter Press, 2000. *Jaime E. Rodríguez O. ''The Independence of Spanish America''. Cambridge University Press, 1998. {{ISBN, 0-521-62673-0 *Stephen K. Stoan. ''Pablo Morillo and Venezuela, 1815-1820''. Columbus: Ohio State University Press, 1959. Spanish American wars of independence 19th century in Spain Spanish colonization of the Americas