Recession of 1953 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Recession of 1953 was a
The Recession of 1953 was a
Bureau of Economic AnalysisBusiness Cycle Expansions and Contractions
* {{Federal Reserve System Recessions in the United States 1953 in the United States 1954 in the United States 1953 in economics 1954 in economics Presidency of Harry S. Truman Presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower

 The Recession of 1953 was a
The Recession of 1953 was a recession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction when there is a general decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending (an adverse demand shock). This may be triggered by various ...
in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
that began in the second quarter of 1953 and lasted until the first quarter of 1954. The total recession cost roughly $56 billion. It has been described by James L. Sundquist, a staff member of the Bureau of the Budget and speech-writer for President Harry S. Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. A leader of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 34th vice president from January to April 1945 under Franklin ...
as "relatively mild and brief."James L. Sundquist, ''Politics and Policy: The Eisenhower, Kennedy, and Johnson Years'', 1969, pg. 431, IBAN 0815782225
Preceding the recession
The recession from 1953 to 1954 occurred because of a combination of events during the earliest parts of the 1950s. In 1951, there was a post-Korean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
inflationary period and later in the year more funds were transferred into national security. Further inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduct ...
was expected into 1952 and the Federal Reserve set in motion restrictive monetary policy
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to control either the interest rate payable for very short-term borrowing (borrowing by banks from each other to meet their short-term needs) or the money supply, often a ...
.
Causes
The expected inflation never happened, but the policy was still implemented. During this time, the Treasury also lengthened the maturity of the national debt and pursued flexible interest rate policies. Alongside these policies, the Treasury also began to do debt-refunding which only increased interest rates further and subsequently issued a low percentage bond. The Federal Reserve recognized the increasing interest rates and decided to allow more reserves to be available. This worked, but interest rates plummeted sending the US into a demand-driven recession of output and employment. GDP declined because of government spending and investment.Type of recession
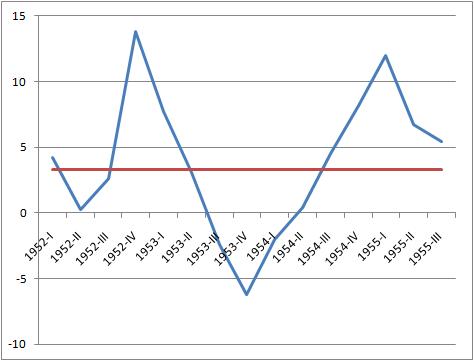
The recession of 1953 was demand-driven because the dramatic changes of interest rates earlier in the year led to an increase in pessimism towards the economy which led to a decrease in aggregate demand. Before the Federal Reserve stepped in to increase availability of reserves, the increase in interest rates continued to decrease aggregate demand. And finally, the actions of the Federal Reserve led to an increase in consumer expectation of an inevitable recession which led to an even further drop in aggregate demand and an increase in savings. Thus, the recession of 1953 began on the demand side. The sharp three quarter decline with a clear trough, followed by a sharp recovery means that the 1953 recession is an example of a V-shaped recession.See also
*Lists of recessions
The following articles contain lists of recessions:
*List of recessions in the United Kingdom
*List of recessions in the United States
There have been as many as 48 recessions in the United States dating back to the Articles of Confederation, ...
References
Further reading
* * *External links
Bureau of Economic Analysis
* {{Federal Reserve System Recessions in the United States 1953 in the United States 1954 in the United States 1953 in economics 1954 in economics Presidency of Harry S. Truman Presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower