RNA vaccine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An mRNA vaccine is a type of
An mRNA vaccine is a type of
 The first successful
The first successful
* /** denote shared technology
 The goal of a vaccine is to stimulate the
The goal of a vaccine is to stimulate the
 The central component of a mRNA vaccine is its mRNA construct. The ''
The central component of a mRNA vaccine is its mRNA construct. The ''
 For a vaccine to be successful, sufficient mRNA must enter the host cell
For a vaccine to be successful, sufficient mRNA must enter the host cell
 The first time the FDA approved the use of lipid nanoparticles as a drug delivery system was in 2018, when the agency approved the first
The first time the FDA approved the use of lipid nanoparticles as a drug delivery system was in 2018, when the agency approved the first
 mRNA vaccines offer specific advantages over traditional
mRNA vaccines offer specific advantages over traditional
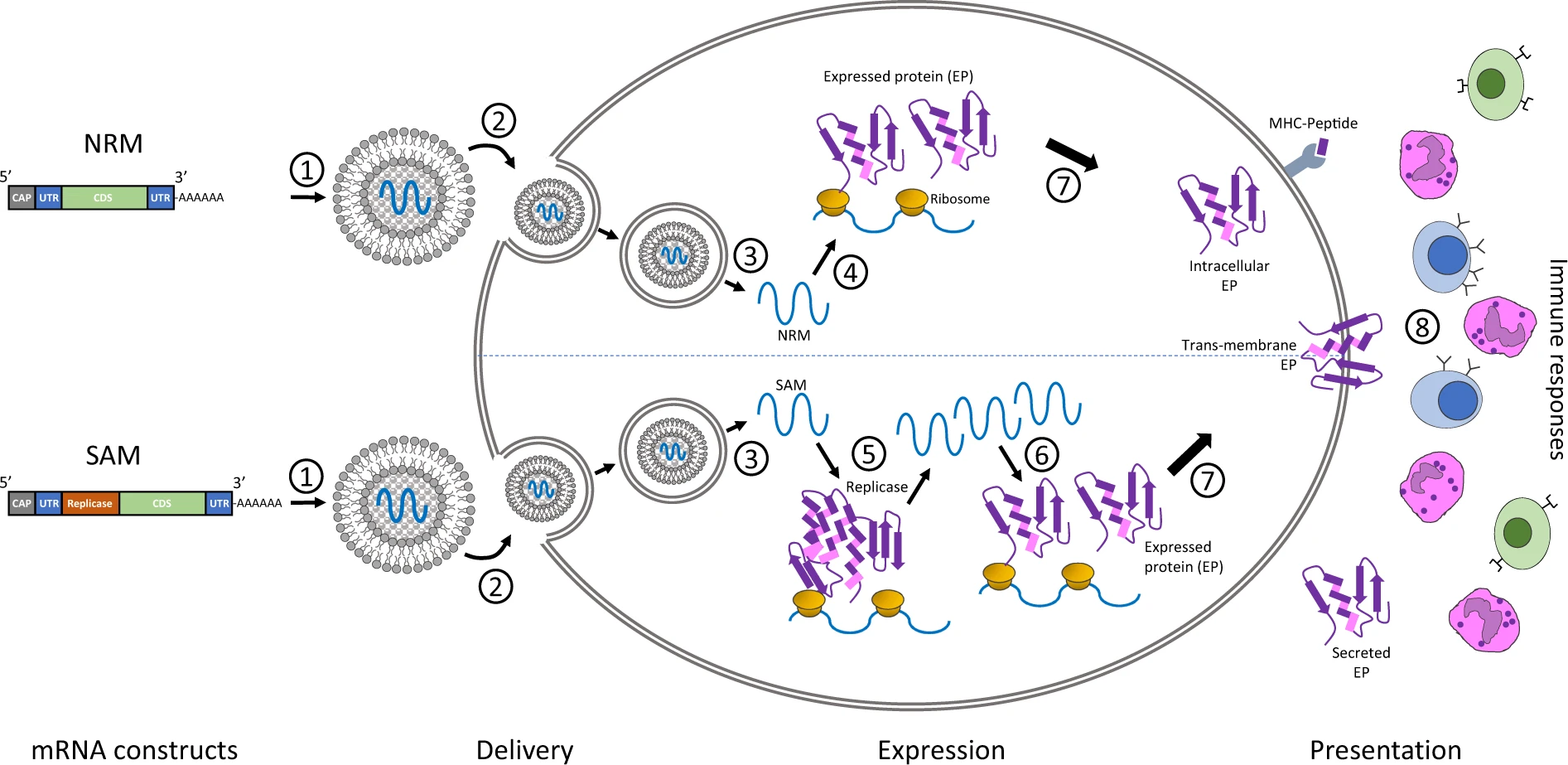 The initial mRNA vaccines use a non-amplifying mRNA construct. Non-amplifying mRNA has only one
The initial mRNA vaccines use a non-amplifying mRNA construct. Non-amplifying mRNA has only one
webcomic
explaining how the vaccine works using ''Star Wars'' characters and situations. {{DEFAULTSORT:MRNA Vaccine RNA . Articles containing video clips
 An mRNA vaccine is a type of
An mRNA vaccine is a type of vaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified.
that uses a copy of a molecule called messenger RNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the ...
(mRNA) to produce an immune response. The vaccine delivers molecules of antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respon ...
-encoding mRNA into immune cells
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mul ...
, which use the designed mRNA as a blueprint to build foreign protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
that would normally be produced by a pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a g ...
(such as a virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsk ...
) or by a cancer cell
Cancer cells are cells that divide continually, forming solid tumors or flooding the blood with abnormal cells. Cell division is a normal process used by the body for growth and repair. A parent cell divides to form two daughter cells, and these d ...
. These protein molecules stimulate an adaptive immune response
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system ...
that teaches the body to identify and destroy the corresponding pathogen or cancer cells. The mRNA is delivered
''Delivered'' is a 1998 thriller/crime film directed by Guy Ferland. A pizza boy finds a murdered man at his next delivery and becomes the murderer's next intended victim.
External links
*
*
1998 films
1998 crime thriller films
1998 comed ...
by a co-formulation of the RNA encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles that protect the RNA strands and help their absorption into the cells.
Reactogenicity, the tendency of a vaccine to produce adverse reactions, is similar to that of conventional non-RNA vaccines. People susceptible to an autoimmune response
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly a ...
may have an adverse reaction to messenger RNA vaccines. The advantages of mRNA vaccines over traditional vaccines are ease of design, speed and lower cost of production, the induction of both cellular and humoral immunity
Humoral immunity is the aspect of immunity that is mediated by macromolecules - including secreted antibodies, complement proteins, and certain antimicrobial peptides - located in extracellular fluids. Humoral immunity is named so because it i ...
, and lack of interaction with the genomic DNA. While some messenger RNA vaccines, such as the Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine
The Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine ( INN: tozinameran), sold under the brand name Comirnaty, is an mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine developed by the German biotechnology company BioNTech. For its development, BioNTech collaborated with Amer ...
, have the disadvantage of requiring ultracold storage before distribution, other mRNA vaccines, such as the Moderna
Moderna, Inc. ( ) is an American pharmaceutical and biotechnology company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts that focuses on RNA therapeutics, primarily mRNA vaccines. These vaccines use a copy of a molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA) to ...
, CureVac
CureVac N.V. is a German biopharmaceutical company that develops therapies based on messenger RNA (mRNA). Legally domiciled in the Netherlands and headquartered in Tübingen, Germany, the company was founded in 2000 by Ingmar Hoerr (CEO), St ...
, and Walvax COVID-19 vaccine
AWcorna, originally termed ARCoV and also known as the Walvax COVID-19 vaccine, is an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine developed by Walvax Biotechnology, Suzhou Abogen Biosciences, and the PLA Academy of Military Science. In contrast to other mRNA COVID ...
s, do not have such requirements.
In RNA therapeutics, messenger RNA vaccines have attracted considerable interest as COVID-19 vaccine
A COVID19 vaccine is a vaccine intended to provide acquired immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID19).
Prior to the COVID19 pandemic, an e ...
s. In December 2020, Pfizer–BioNTech and Moderna
Moderna, Inc. ( ) is an American pharmaceutical and biotechnology company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts that focuses on RNA therapeutics, primarily mRNA vaccines. These vaccines use a copy of a molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA) to ...
obtained authorization for their mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines. On 2 December, the UK Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency
The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) is an executive agency of the Department of Health and Social Care in the United Kingdom which is responsible for ensuring that medicines and medical devices work and are acceptab ...
(MHRA) became the first medicines regulator to approve an mRNA vaccine, authorizing the Pfizer–BioNTech vaccine for widespread use. On 11 December, the US Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
(FDA) issued an emergency use authorization
An Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) in the United States is an authorization granted to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) under sections of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act as added to and amended by various Acts of Congress, includ ...
for the Pfizer–BioNTech vaccine and a week later similarly authorized the Moderna vaccine.
History
Early research
 The first successful
The first successful transfection
Transfection is the process of deliberately introducing naked or purified nucleic acids into eukaryotic cells. It may also refer to other methods and cell types, although other terms are often preferred: " transformation" is typically used to des ...
of designed mRNA packaged within a liposomal nanoparticle into a cell was published in 1989. "Naked" (or unprotected) lab-made mRNA was injected a year later into the muscle of mice. These studies were the first evidence that ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called " test-tube experiments", these studies in biology a ...
'' transcribed mRNA with a chosen gene was able to deliver the genetic information to produce a desired protein within living cell tissue and led to the concept proposal of messenger RNA vaccines.
Liposome-encapsulated mRNA encoding a viral antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respon ...
was shown in 1993 to stimulate T cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
s in mice. The following year self-amplifying mRNA was developed by including both a viral antigen and replicase encoding gene. The method was used in mice to elicit both a humoral
Humoral immunity is the aspect of immunity that is mediated by macromolecules - including secreted antibodies, complement proteins, and certain antimicrobial peptides - located in extracellular fluids. Humoral immunity is named so because it invo ...
and cellular immune response against a viral pathogen. The next year mRNA encoding a tumor antigen
Tumor antigen is an antigenic substance produced in tumor cells, i.e., it triggers an immune response in the host. Tumor antigens are useful tumor markers in identifying tumor cells with diagnostic tests and are potential candidates for use in ...
was shown to elicit a similar immune response against cancer cells in mice.
Development
The first human clinical trial using ''ex vivo
''Ex vivo'' (Latin: "out of the living") literally means that which takes place outside an organism. In science, ''ex vivo'' refers to experimentation or measurements done in or on tissue from an organism in an external environment with minimal ...
'' dendritic cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. Th ...
s transfected with mRNA encoding tumor antigens ( therapeutic cancer mRNA vaccine) was started in 2001. Four years later, the successful use of modified nucleosides as a method to transport mRNA inside cells without setting off the body's defense system was reported. Clinical trial results of an mRNA vaccine directly injected into the body against cancer cells were reported in 2008.
BioNTech in 2008, and Moderna
Moderna, Inc. ( ) is an American pharmaceutical and biotechnology company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts that focuses on RNA therapeutics, primarily mRNA vaccines. These vaccines use a copy of a molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA) to ...
in 2010, were founded to develop mRNA biotechnologies. The US research agency DARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military.
Originally known as the A ...
launched at this time the biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used ...
research program ADEPT to develop emerging technologies for the US military
The United States Armed Forces are the Military, military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six Military branch, service branches: the United States Army, Army, United States Marine Corps, Marine Corps, United States N ...
. The agency recognized the potential of nucleic acid technology for defense against pandemic
A pandemic () is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has spread across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. A widespread endemic disease with a stable number of in ...
s and began to invest in the field. DARPA grants were seen as a vote of confidence that in turn encouraged other government agencies and private investors to invest in mRNA technology. DARPA awarded at the time a $25 million grant to Moderna.
The first human clinical trials using an mRNA vaccine against an infectious agent (rabies
Rabies is a viral disease that causes encephalitis in humans and other mammals. Early symptoms can include fever and tingling at the site of exposure. These symptoms are followed by one or more of the following symptoms: nausea, vomiting, ...
) began in 2013. Over the next few years, clinical trials of mRNA vaccines for a number of other viruses were started. mRNA vaccines for human use have been studied for infectious agents such as influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptom ...
, Zika virus
''Zika virus'' (ZIKV; pronounced or ) is a member of the virus family (biology), family ''Flaviviridae''. It is mosquito-borne disease, spread by daytime-active ''Aedes'' mosquitoes, such as ''Aedes aegypti, A. aegypti'' and ''Aedes albopict ...
, cytomegalovirus
''Cytomegalovirus'' (''CMV'') (from ''cyto-'' 'cell' via Greek - 'container' + 'big, megalo-' + -''virus'' via Latin 'poison') is a genus of viruses in the order '' Herpesvirales'', in the family '' Herpesviridae'', in the subfamily '' Betah ...
, and Chikungunya virus.
In March 2022 Moderna
Moderna, Inc. ( ) is an American pharmaceutical and biotechnology company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts that focuses on RNA therapeutics, primarily mRNA vaccines. These vaccines use a copy of a molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA) to ...
announced the development of mRNA vaccines for 15 diseases: Chikungunya virus, COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease quick ...
, Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever, Dengue
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. Symptoms typically begin three to fourteen days after infection. These may include a high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and joint pains, and a characteristic ...
, Ebola virus disease
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after becom ...
, HIV, Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. ...
, Marburg virus disease, Lassa fever
Lassa fever, also known as Lassa hemorrhagic fever (LHF), is a type of viral hemorrhagic fever caused by the Lassa virus. Many of those infected by the virus do not develop symptoms. When symptoms occur they typically include fever, weakness, ...
, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), Nipah
NIPA, Nipa or nipah may refer to:
* Shamim Ara Nipa, Bangladeshi dancer and choreographer
* Nipa hut, a type of stilt house indigenous to the cultures of the Philippines
* Nipah virus, a Henipavirus
NIPA
* National Income and Product Accounts ...
and henipaviral diseases, Rift Valley fever, Severe fever with Thrombocytopenia syndrome, Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, ...
and Zika
Zika fever, also known as Zika virus disease or simply Zika, is an infectious disease caused by the Zika virus. Most cases have no symptoms, but when present they are usually mild and can resemble dengue fever. Symptoms may include fever, red ...
.
Acceleration
TheCOVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
, and sequencing of the causative virus SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), the respiratory illness responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had a ...
at the beginning of 2020, led to the rapid development of the first approved mRNA vaccines. BioNTech and Moderna in December of the same year obtained approval for their mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine
A COVID19 vaccine is a vaccine intended to provide acquired immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID19).
Prior to the COVID19 pandemic, an e ...
s. On 2 December, seven days after its final eight-week trial, the UK Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency
The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) is an executive agency of the Department of Health and Social Care in the United Kingdom which is responsible for ensuring that medicines and medical devices work and are acceptab ...
(MHRA) became the first global medicines regulator in history to approve an mRNA vaccine, granting emergency authorization for Pfizer–BioNTech's BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine for widespread use. On 11 December, the FDA gave emergency use authorization
An Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) in the United States is an authorization granted to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) under sections of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act as added to and amended by various Acts of Congress, includ ...
for the Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine and a week later similar approval for the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine
The Moderna COVID19 vaccine ( INN: elasomeran), sold under the brand name Spikevax, is a COVID-19 vaccine developed by American company Moderna, the United States National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), and the Biomed ...
. Other mRNA vaccines continued under development.
Mechanism
adaptive immune system
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system ...
to create antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of ...
that precisely target that particular pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a g ...
. The markers on the pathogen that the antibodies target are called antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respon ...
s.
Traditional vaccines stimulate an antibody response by injecting either antigens
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. ...
, an attenuated (weakened) virus, an inactivated (dead) virus, or a recombinant antigen-encoding viral vector
Viral vectors are tools commonly used by molecular biologists to deliver genetic material into cells. This process can be performed inside a living organism (''in vivo'') or in cell culture (''in vitro''). Viruses have evolved specialized molecu ...
(harmless carrier virus with an antigen transgene
A transgene is a gene that has been transferred naturally, or by any of a number of genetic engineering techniques, from one organism to another. The introduction of a transgene, in a process known as transgenesis, has the potential to change t ...
) into the body. These antigens and viruses are prepared and grown outside the body.
In contrast, mRNA vaccines introduce a short-lived synthetically created fragment of the RNA sequence of a virus into the individual being vaccinated. These mRNA fragments are taken up by dendritic cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. Th ...
s through phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is ...
. The dendritic cells use their internal machinery (ribosome
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to fo ...
s) to read the mRNA and produce the viral antigens that the mRNA encodes. The body degrades the mRNA fragments within a few days of introduction. Although non-immune cells can potentially also absorb vaccine mRNA, produce antigens, and display the antigens on their surfaces, dendritic cells absorb the mRNA globules much more readily. The mRNA fragments are translated in the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
and do not affect the body's genomic DNA, located separately in the cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, h ...
.
Once the viral antigens are produced by the host cell, the normal adaptive immune system processes are followed. Antigens are broken down by proteasomes
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases.
Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by wh ...
. Class I and class II MHC molecules then attach to the antigen and transport it to the cellular membrane, "activating" the dendritic cell. Once activated, dendritic cells migrate to lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
s, where they present the antigen to T cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
s and B cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted o ...
s. This triggers the production of antibodies specifically targeted to the antigen, ultimately resulting in immunity
Immunity may refer to:
Medicine
* Immunity (medical), resistance of an organism to infection or disease
* ''Immunity'' (journal), a scientific journal published by Cell Press
Biology
* Immune system
Engineering
* Radiofrequence immunity de ...
.
mRNA
 The central component of a mRNA vaccine is its mRNA construct. The ''
The central component of a mRNA vaccine is its mRNA construct. The ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called " test-tube experiments", these studies in biology a ...
'' transcribed mRNA is generated from an engineered plasmid
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; how ...
DNA, which has an RNA polymerase promoter and sequence which corresponds to the mRNA construct. By combining T7 phage RNA polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.
Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens th ...
and the plasmid DNA, the mRNA can be transcribed in the lab. Efficacy of the vaccine is dependent on the stability and structure of the designed mRNA.
The ''in vitro'' transcribed mRNA has the same structural components as natural mRNA in eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bact ...
. It has a 5' cap
In molecular biology, the five-prime cap (5′ cap) is a specially altered nucleotide on the 5′ end of some primary transcripts such as precursor messenger RNA. This process, known as mRNA capping, is highly regulated and vital in the creation ...
, a 5'-untranslated region (UTR) and 3'-UTR
In molecular genetics, the three prime untranslated region (3′-UTR) is the section of messenger RNA (mRNA) that immediately follows the translation termination codon. The 3′-UTR often contains regulatory regions that post-transcriptionally ...
, an open reading frame
In molecular biology, open reading frames (ORFs) are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible readi ...
(ORF), which encodes the relevant antigen, and a 3'-poly(A) tail. By modifying these different components of the synthetic mRNA, the stability and translational ability of the mRNA can be enhanced, and in turn, the efficacy of the vaccine improved.
The mRNA can be improved by using synthetic 5'-cap analogues which enhance the stability and increase protein translation. Similarly, regulatory elements
A regulatory sequence is a segment of a nucleic acid molecule which is capable of increasing or decreasing the expression of specific genes within an organism. Regulation of gene expression is an essential feature of all living organisms and vi ...
in the 5'-untranslated region and the 3'-untranslated region can be altered, and the length of the poly(A) tail optimized, to stabilize the mRNA and increase protein production. The mRNA nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecu ...
s can be modified to both decrease innate immune activation and increase the mRNA's half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ...
in the host cell. The nucleic acid sequence
A nucleic acid sequence is a succession of bases signified by a series of a set of five different letters that indicate the order of nucleotides forming alleles within a DNA (using GACT) or RNA (GACU) molecule. By convention, sequences are us ...
and codon usage impacts protein translation. Enriching the sequence with guanine-cytosine content
In molecular biology and genetics, GC-content (or guanine-cytosine content) is the percentage of nitrogenous bases in a DNA or RNA molecule that are either guanine (G) or cytosine (C). This measure indicates the proportion of G and C bases out ...
improves mRNA stability and half-life and, in turn, protein production. Replacing rare codon
The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material ( DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets, or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links ...
s with synonymous codons frequently used by the host cell also enhances protein production.
Delivery
 For a vaccine to be successful, sufficient mRNA must enter the host cell
For a vaccine to be successful, sufficient mRNA must enter the host cell cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
to stimulate production of the specific antigens. Entry of mRNA molecules, however, faces a number of difficulties. Not only are mRNA molecules too large to cross the cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
by simple diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical ...
, they are also negatively charged like the cell membrane, which causes a mutual electrostatic repulsion
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies electric charges at rest ( static electricity).
Since classical times, it has been known that some materials, such as amber, attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for a ...
. Additionally, mRNA is easily degraded by RNAases in skin and blood.
Various methods have been developed to overcome these delivery hurdles. The method of vaccine delivery can be broadly classified by whether mRNA transfer into cells occurs within (''in vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and p ...
'') or outside (''ex vivo
''Ex vivo'' (Latin: "out of the living") literally means that which takes place outside an organism. In science, ''ex vivo'' refers to experimentation or measurements done in or on tissue from an organism in an external environment with minimal ...
'') the organism.
''Ex vivo''
Dendritic cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. Th ...
s display antigens on their surfaces
A surface, as the term is most generally used, is the outermost or uppermost layer of a physical object or space.
Surface or surfaces may also refer to:
Mathematics
*Surface (mathematics), a generalization of a plane which needs not be flat
* Sur ...
, leading to interactions with T cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
s to initiate an immune response. Dendritic cells can be collected from patients and programmed with the desired mRNA, then administered back into patients to create an immune response.
The simplest way that ''ex vivo'' dendritic cells take up mRNA molecules is through endocytosis
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. ...
, a fairly inefficient pathway in the laboratory setting that can be significantly improved through electroporation
Electroporation, or electropermeabilization, is a microbiology technique in which an electrical field is applied to cells in order to increase the permeability of the cell membrane, allowing chemicals, drugs, electrode arrays or DNA to be introd ...
.
''In vivo''
Since the discovery that the direct administration of ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called " test-tube experiments", these studies in biology a ...
'' transcribed mRNA leads to the expression of antigens in the body, ''in vivo'' approaches have been investigated. They offer some advantages over ''ex vivo'' methods, particularly by avoiding the cost of harvesting and adapting dendritic cells from patients and by imitating a regular infection.
Different routes of injection, such as into the skin, blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
, or muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of mus ...
s, result in varying levels of mRNA uptake, making the choice of administration route a critical aspect of ''in vivo'' delivery. One study showed, in comparing different routes, that lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
injection leads to the largest T-cell response.
Naked mRNA injection
Naked mRNA injection means that the delivery of the vaccine is only done in abuffer solution
A buffer solution (more precisely, pH buffer or hydrogen ion buffer) is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or vice versa. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is ...
. This mode of mRNA uptake has been known since the 1990s. The first worldwide clinical studies used intradermal injection
Intradermal injection, often abbreviated ID, is a shallow or superficial injection of a substance into the dermis, which is located between the epidermis and the hypodermis. For certain substances, administration via an ID route can result in a ...
s of naked mRNA for vaccination. A variety of methods have been used to deliver naked mRNA, such as subcutaneous, intravenous, and intratumoral injections. Although naked mRNA delivery causes an immune response, the effect is relatively weak, and after injection the mRNA is often rapidly degraded.
Polymer and peptide vectors
Cationic polymer In chemistry, cationic polymerization is a type of chain growth polymerization in which a cationic initiator transfers charge to a monomer which then becomes reactive. This reactive monomer goes on to react similarly with other monomers to form a p ...
s can be mixed with mRNA to generate protective coatings called polyplexes. These protect the recombinant mRNA from ribonuclease
Ribonuclease (commonly abbreviated RNase) is a type of nuclease that catalyzes the degradation of RNA into smaller components. Ribonucleases can be divided into endoribonucleases and exoribonucleases, and comprise several sub-classes within the ...
s and assist its penetration in cells. Protamine
Protamines are small, arginine-rich, nuclear proteins that replace histones late in the haploid phase of spermatogenesis and are believed essential for sperm head condensation and DNA stabilization. They may allow for denser packaging of DNA in t ...
is a natural cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conven ...
ic peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. ...
and has been used to encapsulate mRNA for vaccination.
Lipid nanoparticle vector
 The first time the FDA approved the use of lipid nanoparticles as a drug delivery system was in 2018, when the agency approved the first
The first time the FDA approved the use of lipid nanoparticles as a drug delivery system was in 2018, when the agency approved the first siRNA
Small interfering RNA (siRNA), sometimes known as short interfering RNA or silencing RNA, is a class of double-stranded RNA at first non-coding RNA molecules, typically 20-24 (normally 21) base pairs in length, similar to miRNA, and operating ...
drug, Onpattro
Patisiran, sold under the brand name Onpattro, is a medication used for the treatment of polyneuropathy in people with hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis, a fatal rare disease that is estimated to affect 50,000 people worldwide.
It is ...
. Encapsulating the mRNA molecule in lipid nanoparticles was a critical breakthrough for producing viable mRNA vaccines, solving a number of key technical barriers in delivering the mRNA molecule into the host cell. Research into using lipids to deliver siRNA to cells became a foundation for similar research into using lipids to deliver mRNA. However, new lipids had to be invented to encapsulate mRNA strands, which are much longer than siRNA strands.
Principally, the lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids in ...
provides a layer of protection against degradation, allowing more robust translational output. In addition, the customization of the lipid's outer layer allows the targeting of desired cell types through ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's elect ...
interactions. However, many studies have also highlighted the difficulty of studying this type of delivery, demonstrating that there is an inconsistency between ''in vivo'' and ''in vitro'' applications of nanoparticles in terms of cellular intake. The nanoparticles can be administered to the body and transported via multiple routes, such as intravenously
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrie ...
or through the lymphatic system
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid ...
.
One issue with lipid nanoparticles is that several of the breakthroughs leading to the practical use of that technology involve the use of microfluidics. Microfluidic reaction chambers are difficult to scale up, since the entire point of microfluidics is to exploit the microscale behaviors of liquids. The only way around this obstacle is to run an extensive number of microfluidic reaction chambers in parallel, a novel task requiring custom-built equipment. For COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, this was the main manufacturing bottleneck. Pfizer used such a parallel approach to solve the scaling problem. After verifying that impingement jet mixers could not be directly scaled up, Pfizer made about 100 of the little mixers (each about the size of a U.S. half-dollar coin), connected them together with pumps and filters with a "maze of piping," and set up a computer system to regulate flow and pressure through the mixers.
Another issue, with the large-scale use of this delivery method, is the availability of the novel lipids used to create lipid nanoparticles, especially ionizable cationic lipids. Before 2020, such lipids were manufactured in small quantities measured in grams or kilograms, and they were used for medical research and a handful of drugs for rare conditions. As the safety and efficacy of mRNA vaccines became clear in 2020, the few companies able to manufacture the requisite lipids were confronted with the challenge of scaling up production to respond to orders for several tons of lipids.
Viral vector
In addition to non-viral delivery methods,RNA virus
An RNA virus is a virusother than a retrovirusthat has ribonucleic acid ( RNA) as its genetic material. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA virus ...
es have been engineered
Engineering is the use of scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more speciali ...
to achieve similar immunological responses. Typical RNA viruses used as vectors include retrovirus
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptas ...
es, lentivirus
''Lentivirus'' is a genus of retroviruses that cause chronic and deadly diseases characterized by long incubation periods, in humans and other mammalian species. The genus includes the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which causes AIDS. L ...
es, alphavirus
''Alphavirus'' is a genus of RNA viruses, the sole genus in the ''Togaviridae'' family. Alphaviruses belong to group IV of the Baltimore classification of viruses, with a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genome. There are 32 alphaviruses ...
es and rhabdoviruses
''Rhabdoviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Vertebrates (including mammals and humans), invertebrates, plants, fungi and protozoans serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with member virus ...
, each of which can differ in structure and function. Clinical studies have utilized such viruses on a range of diseases in model animals
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the working ...
such as mice
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus'' ...
, chicken
The chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') is a domesticated junglefowl species, with attributes of wild species such as the grey and the Ceylon junglefowl that are originally from Southeastern Asia. Rooster or cock is a term for an adu ...
and primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter includin ...
s.
Advantages
Traditional vaccines
 mRNA vaccines offer specific advantages over traditional
mRNA vaccines offer specific advantages over traditional vaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified.
s. Because mRNA vaccines are not constructed from an active pathogen (or even an inactivated pathogen), they are non-infectious. In contrast, traditional vaccines require the production of pathogens, which, if done at high volumes, could increase the risks of localized outbreaks of the virus at the production facility. Another biological advantage of mRNA vaccines is that since the antigens are produced inside the cell, they stimulate cellular immunity
Cell-mediated immunity or cellular immunity is an immune response that does not involve antibodies. Rather, cell-mediated immunity is the activation of phagocytes, antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, and the release of various cytokines ...
, as well as humoral immunity
Humoral immunity is the aspect of immunity that is mediated by macromolecules - including secreted antibodies, complement proteins, and certain antimicrobial peptides - located in extracellular fluids. Humoral immunity is named so because it i ...
.
mRNA vaccines have the production advantage that they can be designed swiftly. Moderna designed their mRNA-1273
The Moderna COVID19 vaccine ( INN: elasomeran), sold under the brand name Spikevax, is a COVID-19 vaccine developed by American company Moderna, the United States National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), and the Biomed ...
vaccine for COVID-19 in 2 days. They can also be manufactured faster, more cheaply, and in a more standardized fashion (with fewer error rates in production), which can improve responsiveness to serious outbreaks.
The Pfizer–BioNTech vaccine originally required 110 days to mass-produce (before Pfizer began to optimize the manufacturing process to only 60 days), which was substantially faster than traditional flu and polio vaccines. Within that larger timeframe, the actual production time is only about 22 days: two weeks for molecular cloning of DNA plasmids and purification of DNA, four days for DNA-to-RNA transcription and purification of mRNA, and four days to encapsulate mRNA in lipid nanoparticles followed by fill and finish. The majority of the days needed for each production run are allocated to rigorous quality control at each stage.
DNA vaccines
In addition to sharing the advantages of theoreticalDNA vaccine
A DNA vaccine is a type of vaccine that transfects a specific antigen-coding DNA sequence into the cells of an organism as a mechanism to induce an immune response.
DNA vaccines work by injecting genetically engineered plasmid containing the D ...
s over established traditional vaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified.
s, mRNA vaccines also have additional advantages over DNA vaccines. The mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the ...
is translated
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
in the cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondri ...
, so there is no need for the RNA to enter the cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, h ...
, and the risk of being integrated into the host genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
is averted. Modified nucleosides (for example, pseudouridine
Pseudouridine (abbreviated by the Greek letter psi- Ψ) is an isomer of the nucleoside uridine in which the uracil is attached via a carbon-carbon instead of a nitrogen-carbon glycosidic bond. (In this configuration, uracil is sometimes referred ...
s, 2'-O-methylated nucleosides) can be incorporated to mRNA to suppress immune response
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders. These invaders include a wide variety of different microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi which coul ...
stimulation to avoid immediate degradation and produce a more persistent effect through enhanced translation capacity. The open reading frame (ORF) and untranslated regions (UTR) of mRNA can be optimized for different purposes (a process called sequence engineering of mRNA), for example through enriching the guanine-cytosine content
In molecular biology and genetics, GC-content (or guanine-cytosine content) is the percentage of nitrogenous bases in a DNA or RNA molecule that are either guanine (G) or cytosine (C). This measure indicates the proportion of G and C bases out ...
or choosing specific UTRs known to increase translation. An additional ORF coding for a replication mechanism can be added to amplify antigen translation and therefore immune response, decreasing the amount of starting material needed.
Disadvantages
Storage
Because mRNA is fragile, some vaccines must be kept at very low temperatures to avoid degrading and thus giving little effective immunity to the recipient. Pfizer–BioNTech's BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine has to be kept between . Moderna says theirmRNA-1273
The Moderna COVID19 vaccine ( INN: elasomeran), sold under the brand name Spikevax, is a COVID-19 vaccine developed by American company Moderna, the United States National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), and the Biomed ...
vaccine can be stored between , which is comparable to a home freezer, and that it remains stable between for up to 30 days. In November 2020, ''Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are ...
'' reported, "While it's possible that differences in LNP formulations or mRNA secondary structures could account for the thermostability differences etween Moderna and BioNtech many experts suspect both vaccine products will ultimately prove to have similar storage requirements and shelf lives under various temperature conditions." Several platforms are being studied that may allow storage at higher temperatures.
Recent
Before 2020, no mRNA technology platform (drug or vaccine) had been authorized for use in humans, so there was a risk of unknown effects. The 2020 COVID-19 pandemic required faster production capability of mRNA vaccines, made them attractive to national health organisations, and led to debate about the type of initial authorization mRNA vaccines should get (includingemergency use authorization
An Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) in the United States is an authorization granted to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) under sections of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act as added to and amended by various Acts of Congress, includ ...
or expanded access authorization) after the eight-week period of post-final human trials.
Side effects
Reactogenicity is similar to that of conventional, non-RNA vaccines. However, those susceptible to anautoimmune response
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly a ...
may have an adverse reaction to mRNA vaccines. The mRNA strands in the vaccine may elicit an unintended immune reactionthis entails the body believing itself to be sick, and the person feeling as if they are as a result. To minimize this, mRNA sequences in mRNA vaccines are designed to mimic those produced by host cells.
Strong but transient reactogenic effects were reported in trials of novel COVID-19 mRNA vaccines; most people will not experience severe side effects which include fever and fatigue. Severe side effects are defined as those that prevent daily activity.
Efficacy
The COVID-19 mRNA vaccines from Moderna and Pfizer–BioNTech have efficacy rates of 90 to 95 percent. Prior mRNA, drug trials on pathogens other than COVID-19 were not effective and had to be abandoned in the early phases of trials. The reason for the efficacy of the new mRNA vaccines is not clear. Physician-scientist Margaret Liu stated that the efficacy of the new COVID-19 mRNA vaccines could be due to the "sheer volume of resources" that went into development, or that the vaccines might be "triggering a nonspecific inflammatory response to the mRNA that could be heightening its specific immune response, given that the modified nucleoside technique reduced inflammation but hasn't eliminated it completely", and that "this may also explain the intense reactions such as aches and fevers reported in some recipients of the mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccines". These reactions though severe were transient and another view is that they were believed to be a reaction to the lipid drug delivery molecules.Hesitancy
There is misinformation implying that mRNA vaccines could alter DNA in the nucleus. mRNA in thecytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondri ...
is very rapidly degraded before it would have time to gain entry into the cell nucleus. In fact, mRNA vaccines must be stored at very low temperature to prevent mRNA degradation. Retrovirus
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptas ...
can be single-stranded RNA (just as SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), the respiratory illness responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had a ...
vaccine is single-stranded RNA) which enters the cell nucleus and uses reverse transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genom ...
to make DNA from the RNA in the cell nucleus. A retrovirus has mechanisms to be imported into the nucleus, but other mRNA lack these mechanisms. Once inside the nucleus, creation of DNA from RNA cannot occur without a primer
Primer may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''Primer'' (film), a 2004 feature film written and directed by Shane Carruth
* ''Primer'' (video), a documentary about the funk band Living Colour
Literature
* Primer (textbook), a te ...
, which accompanies a retrovirus, but which would not exist for other mRNA if placed in the nucleus.
Amplification
mRNA vaccines use either non-amplifying (conventional) mRNA or self-amplifying mRNA. Pfizer–BioNTech and Moderna vaccines use non-amplifying mRNA. Both mRNA types continue to be investigated as vaccine methods against other potential pathogens and cancer.Non-amplifying
 The initial mRNA vaccines use a non-amplifying mRNA construct. Non-amplifying mRNA has only one
The initial mRNA vaccines use a non-amplifying mRNA construct. Non-amplifying mRNA has only one open reading frame
In molecular biology, open reading frames (ORFs) are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible readi ...
that codes for the antigen of interest. The total amount of mRNA available to the cell is equal to the amount delivered by the vaccine. Dosage strength is limited by the amount of mRNA that can be delivered by the vaccine. Non-amplifying vaccines replace uridine
Uridine (symbol U or Urd) is a glycosylated pyrimidine analog containing uracil attached to a ribose ring (or more specifically, a ribofuranose) via a β-N1-glycosidic bond. The analog is one of the five standard nucleosides which make up nucle ...
with N1-Methylpseudouridine in an attempt to reduce toxicity.
Self-amplifying
Self-amplifying mRNA (saRNA) vaccines replicate their mRNA after transfection. Self-amplifying mRNA has twoopen reading frame
In molecular biology, open reading frames (ORFs) are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible readi ...
s. The first frame, like conventional mRNA, codes for the antigen of interest. The second frame codes for an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) or RNA replicase is an enzyme that catalyzes the replication of RNA from an RNA template. Specifically, it catalyzes synthesis of the RNA strand complementary to a given RNA template. This is in contrast to ...
(and its helper proteins) which replicates the mRNA construct in the cell. This allows smaller vaccine doses. The mechanisms and consequently the evaluation of self-amplifying mRNA may be different, as self-amplifying mRNA is a much bigger molecule.
SaRNA vaccines being researched include a malaria vaccine
A malaria vaccine is a vaccine that is used to prevent malaria. The only approved use of a vaccine outside the EU, as of 2022, is RTS,S, known by the brand name ''Mosquirix''. In October 2021, the WHO for the first time recommended the large- ...
. Gritstone bio
Gritstone bio is a clinical-stage American biotechnology company which develops cancer and infectious disease immunotherapies and vaccines. It was founded in August 2015 as Gritstone Oncology, Inc., and is based in Emeryville, California.
In Sept ...
started in 2021 a phase 1 trial
The phases of clinical research are the stages in which scientists conduct experiments with a health intervention to obtain sufficient evidence for a process considered effective as a medical treatment. For drug development, the clinical phases ...
of an saRNA COVID-19 vaccine, used as a booster vaccine. The vaccine is designed to target both the spike protein of the SARS‑CoV‑2 virus, and viral proteins that may be less prone to genetic variation, to provide greater protection against SARS‑CoV‑2 variants. saRNA vaccines must use uridine, which is required for reproduction to occur.
See also
*DNA vaccine
A DNA vaccine is a type of vaccine that transfects a specific antigen-coding DNA sequence into the cells of an organism as a mechanism to induce an immune response.
DNA vaccines work by injecting genetically engineered plasmid containing the D ...
* Nucleoside-modified messenger RNA
* RNA therapeutics
* Timeline of human vaccines
References
Further reading
* *External links
* * * * * * ''xkcd
''xkcd'', sometimes styled ''XKCD'', is a webcomic created in 2005 by American author Randall Munroe. The comic's tagline describes it as "a webcomic of romance, sarcasm, math, and language". Munroe states on the comic's website that the name ...
'webcomic
explaining how the vaccine works using ''Star Wars'' characters and situations. {{DEFAULTSORT:MRNA Vaccine RNA . Articles containing video clips