Qafzeh cave on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Qafzeh Cave, also known by other names, is a
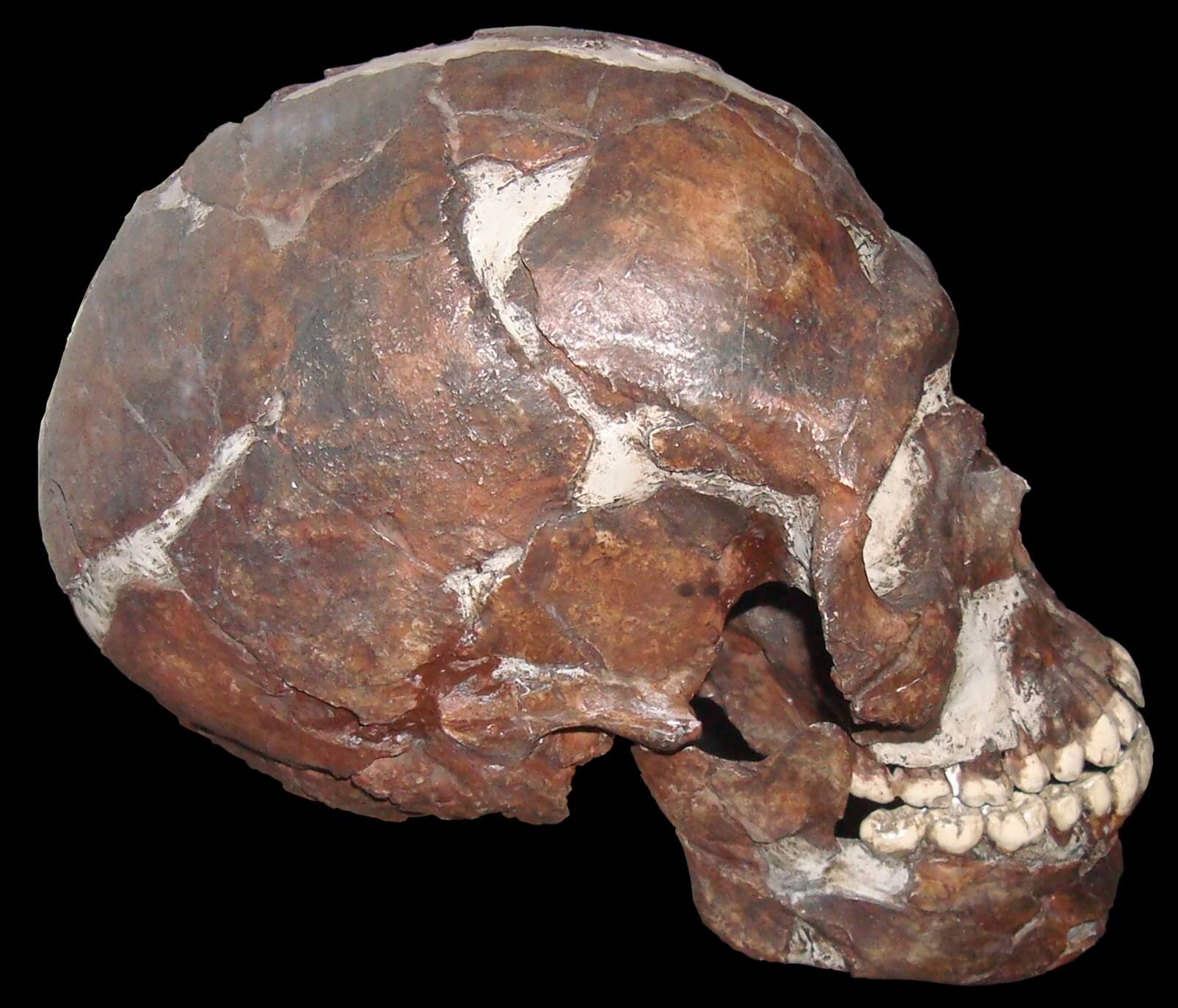 Among the finds on the site are
Among the finds on the site are
prehistoric
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The us ...
archaeological site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology an ...
located at the bottom of Mount Precipice in the Jezreel Valley
The Jezreel Valley (from the he, עמק יזרעאל, translit. ''ʿĒmeq Yīzrəʿēʿl''), or Marj Ibn Amir ( ar, مرج ابن عامر), also known as the Valley of Megiddo, is a large fertile plain and inland valley in the Northern Distr ...
of Lower Galilee The Lower Galilee (; ar, الجليل الأسفل, translit=Al Jalil Al Asfal) is a region within the Northern District (Israel), Northern District of Israel. The Lower Galilee is bordered by the Jezreel Valley to the south; the Upper Galilee to t ...
south of Nazareth
Nazareth ( ; ar, النَّاصِرَة, ''an-Nāṣira''; he, נָצְרַת, ''Nāṣəraṯ''; arc, ܢܨܪܬ, ''Naṣrath'') is the largest city in the Northern District of Israel. Nazareth is known as "the Arab capital of Israel". In ...
. Important remains of prehistoric
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The us ...
people were discovered on the site - some of the oldest examples in the world, outside of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, of virtually anatomically modern human beings. These were discovered on the ledge just outside the cave, where 18 layers
Layer or layered may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Layers'' (Kungs album)
* ''Layers'' (Les McCann album)
* ''Layers'' (Royce da 5'9" album)
*"Layers", the title track of Royce da 5'9"'s sixth studio album
* Layer, a female Maveri ...
from the Middle Paleolithic
The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle Paleol ...
era were identified. The interior of the cave contains layers ranging from the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
era to the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
.
Names
The Arabic name of the mountain is Jebel el-Qafzeh, 'Mount of the Leap', and the cave's name is derived from it, Qafzeh Cave, sometimes spelled Qafza Cave, with article becoming al-Kafza (Cave). By translation toHebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
, the name becomes Meʿarat Har HaKfitza, 'Leap Mount Cave', or sometimes Mt. HaKfitza Cave, HaKfitza(h) Cave, or Meʿarat Qafzeh. Another Hebrew name is Meʿarat Kedumim or Kedumim Cave.
The various caves in the system are separately numbered using Roman numerals
Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and remained the usual way of writing numbers throughout Europe well into the Late Middle Ages. Numbers are written with combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet, ...
.
Excavations
Excavations
In archaeology, excavation is the exposure, processing and recording of archaeological remains. An excavation site or "dig" is the area being studied. These locations range from one to several areas at a time during a project and can be condu ...
of the site began in 1932, led by Moshe Stekelis and René Neuville, but were interrupted due to a collapse. In 1936, during the Arab rebellion in Palestine, the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
blew up the cave because it was being used as a hideout by gangs associated with the rebels. Excavations were renewed in 1965, by Bernard Vandermeersch, Ofer Bar-Yosef
Ofer Bar-Yosef ( he, עופר בר-יוסף; 29 August 1937 – 14 March 2020) was an Israeli archaeologist and anthropologist whose main field of study was the Palaeolithic period.
From 1967 Bar-Yosef was Professor of Prehistoric Archaeology at ...
, then continued, intermittently, until 1979.
Findings
stove
A stove or range is a device that burns fuel or uses electricity to generate heat inside or on top of the apparatus, to be used for general warming or cooking. It has evolved highly over time, with cast-iron and induction versions being develope ...
s, stone tool
A stone tool is, in the most general sense, any tool made either partially or entirely out of stone. Although stone tool-dependent societies and cultures still exist today, most stone tools are associated with prehistoric (particularly Stone A ...
s belonging to the Mousterian culture, and also human and animal bones, which attest to the fact that the cave had been used both for residence and as a burial site. The remains of 15 human skeletons
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure insid ...
were discovered on site, in a Mousterian archaeological context. Seven of them are skeletons of adults and the rest - of children. The high proportion of children skeletons is unique among Middle Palaeolithic sites, and it led researchers to look for signs of trauma or disease that might have led to their premature deaths. One child, Qafzeh 12, of around 3 years of age, by modern reference standards, had abnormalities indicating hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs within the brain. This typically causes increased pressure inside the skull. Older people may have headaches, double vision, poor balance, urinary i ...
. Five of these skeletons were found buried in an orderly fashion in the cave's floor, one being the remains of a 12-13 year old boy found with European fallow deer (Dama dama) horns next to his chest. He had been placed in a rectangular grave carved out of the bedrock, with his arms folded alongside his body and his hands placed on either side of his neck. The Deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the re ...
horns were most likely placed as an offering. The boy's skull bears signs of a head trauma
A head injury is any injury that results in trauma to the skull or brain. The terms ''traumatic brain injury'' and ''head injury'' are often used interchangeably in the medical literature. Because head injuries cover such a broad scope of inju ...
that had probably been the cause of death. The site was dated to circa 92,000 kya using thermoluminescence
Thermoluminescence is a form of luminescence that is exhibited by certain crystalline materials, such as some minerals, when previously absorbed energy from electromagnetic radiation or other ionizing radiation is re-emitted as light upon h ...
.
Human remains found in the cave were preserved at the Institut de paléontologie humaine (IPH) de Paris and the largest part of Neville’s lithic series was preserved at the Rockefeller Museum
The Rockefeller Archeological Museum, formerly the Palestine Archaeological Museum ("PAM"; 1938–1967), and which before then housed The Imperial Museum of Antiquities (''Müze-i Hümayun''; 1901–1917), is an archaeology museum located in East ...
in Jerusalem.
One such burial is of a 10 year old boy from the earliest of the Middle Paleolithic
The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle Paleol ...
layers
Layer or layered may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Layers'' (Kungs album)
* ''Layers'' (Les McCann album)
* ''Layers'' (Royce da 5'9" album)
*"Layers", the title track of Royce da 5'9"'s sixth studio album
* Layer, a female Maveri ...
, who was buried in a rectangular grave carved out of the bedrock, with his arms folded alongside his body and his hands placed on either side of his neck. Deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the re ...
horns were laid on his hands, probably constituting one of the offerings put in the grave. The boy's skull bears signs of a head trauma
A head injury is any injury that results in trauma to the skull or brain. The terms ''traumatic brain injury'' and ''head injury'' are often used interchangeably in the medical literature. Because head injuries cover such a broad scope of inju ...
that had probably been the cause of death.
Skeletons, isolated bones and teeth found in the cave belong to at least 28 people. Remains of Qafzeh 9 and 10 that were found in a double burial, are nearly complete and belong to a young male and a child.
An additional important find was the remains of ochre
Ochre ( ; , ), or ocher in American English, is a natural clay earth pigment, a mixture of ferric oxide and varying amounts of clay and sand. It ranges in colour from yellow to deep orange or brown. It is also the name of the colours produced ...
that were found on human bones, and, also, 71 pieces of ochre that were associated with burial practices, which indicates that ceremonial funerary rites
A funeral is a ceremony connected with the final disposition of a corpse, such as a burial or cremation, with the attendant observances. Funerary customs comprise the complex of beliefs and practices used by a culture to remember and respect t ...
that included symbolic acts which held special meaning had already been common around 100,000 years ago. Ochre
Ochre ( ; , ), or ocher in American English, is a natural clay earth pigment, a mixture of ferric oxide and varying amounts of clay and sand. It ranges in colour from yellow to deep orange or brown. It is also the name of the colours produced ...
was used for body dyeing and ornamentation. It was also used during the burial of a brain damaged child that was found in the cave. Red, black and yellow ochre-painted seashells were found around the cave.
Stone tools
The stone tools discovered at the site - side scrapers, disc cores and points - were of the Levallois-Mousterian
The Mousterian (or Mode III) is an archaeological industry of stone tools, associated primarily with the Neanderthals in Europe, and to the earliest anatomically modern humans in North Africa and West Asia. The Mousterian largely defines the l ...
type. These tools are often associated with Neanderthal settlements. Animal remains of horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million yea ...
, woodland-adapted red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or hart, and a female is called a hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Iran, and parts of ...
, rhinoceros
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct specie ...
, fallow deer
''Dama'' is a genus of deer in the subfamily Cervinae, commonly referred to as fallow deer.
Name
The name fallow is derived from the deer's pale brown colour. The Latin word ''dāma'' or ''damma'', used for roe deer, gazelles, and antelopes ...
, wild ox and gazelle
A gazelle is one of many antelope species in the genus ''Gazella'' . This article also deals with the seven species included in two further genera, '' Eudorcas'' and '' Nanger'', which were formerly considered subgenera of ''Gazella''. A third ...
, land snail
A land snail is any of the numerous species of snail that live on land, as opposed to the sea snails and freshwater snails. ''Land snail'' is the common name for terrestrial gastropod mollusks that have shells (those without shells are known ...
s were also found at the site stand for Mousterian
The Mousterian (or Mode III) is an archaeological industry of stone tools, associated primarily with the Neanderthals in Europe, and to the earliest anatomically modern humans in North Africa and West Asia. The Mousterian largely defines the l ...
and Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coin ...
period.
See also
* Skhul Cave *Skhul and Qafzeh hominins
The Skhul/Qafzeh hominins or Qafzeh–Skhul early modern humans are hominin fossils discovered in Es-Skhul and Qafzeh caves in Israel. They are today classified as ''Homo sapiens'', among the earliest of their species in Eurasia. Skhul Cave ...
References
Citations
Bibliography
* . * . {{coord, 32, 41, 00, N, 35, 17, 50, E, type:landmark_region:IL, display=title 1932 archaeological discoveries Caves of Israel Prehistoric sites in Israel Lower Galilee Mousterian