QF 13 pounder 6 cwt AA gun on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
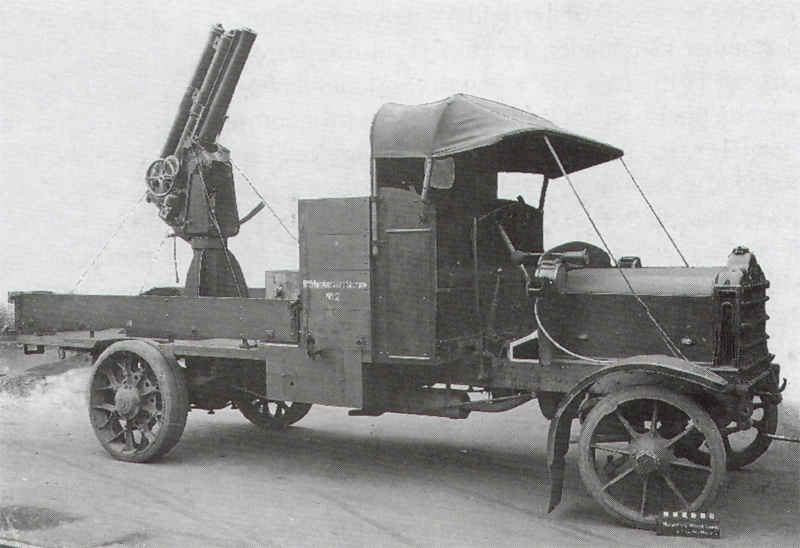
The Ordnance QF 13 pounder Mk III anti-aircraft gun, also known as 13 pounder 6 cwt, was an early British improvisation in World War I to adapt the QF 13-pounder field gun to anti-aircraft use. 6 cwt referred to the weight of barrel and breech (6 × 112 lb = 672 lb) to differentiate it from other "13 pounder" guns.
 This was a standard
This was a standard
History
 This was a standard
This was a standard QF 13 pounder
The Ordnance QF 13-pounder (British ordnance terms#QF, quick-firing) field gun was the standard equipment of the British and Canadian Royal Horse Artillery at the outbreak of World War I.
History
The QF 13-pounder was developed as a response t ...
field gun barrel and breech with the addition of a retaining catch to the breech to retain the round when loading at high angles.
It was first approved in October 1914 and was issued on Mk I high angle mounting, usually mounted on a motor lorry. The Mk I mounting had an additional recuperator
A recuperator is a special purpose counter-flow energy recovery heat exchanger positioned within the supply and exhaust air streams of an air handling system, or in the exhaust gases of an industrial process, in order to recover the waste heat. ...
housing mounted directly above the normal recuperator to facilitate gun runout at high angles. Hence the appearance was of a gun barrel with 2 slightly shorter tubes of similar diameter above it.
Mk II mount improved the usability, added deflection gear and the recoil system was improved so that the additional recuperator became unnecessary and was removed. On the Mk II mount the gun has the appearance of a standard 13 pounder.
The mount design was unusual in having both gunlayers on the left side.
Following World War I, the guns were returned to service as standard 13 pounder field guns.
Combat use
The gun's performance was "ballistically poor" and it was only marginally effective against aircraft. It was relegated to minor war theatres and the 13 pounder 9 cwt and 3 inch 20 cwt guns took over the major anti-aircraft role. At the end of World War I there were only 20 of the guns in service worldwide, with 12 in Egypt and Palestine, 4 inMesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
, 2 in Greece (Salonika front
The Macedonian front, also known as the Salonica front (after Thessaloniki), was a military theatre of World War I formed as a result of an attempt by the Allied Powers to aid Serbia, in the autumn of 1915, against the combined attack of German ...
) and 2 on the Western Front.
Performance
See also
*List of anti-aircraft guns
Anti-aircraft guns are weapons designed to attack aircraft. Such weapons commonly have a high rate of fire and are able to fire shells designed to damage aircraft. They also are capable of firing at high angles, but are also usually able to hit ...
References
Bibliography
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Qf 13 Pounder 6 Cwt Aa Gun World War I artillery of the United Kingdom World War I anti-aircraft guns 76 mm artillery