Pseudopodia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
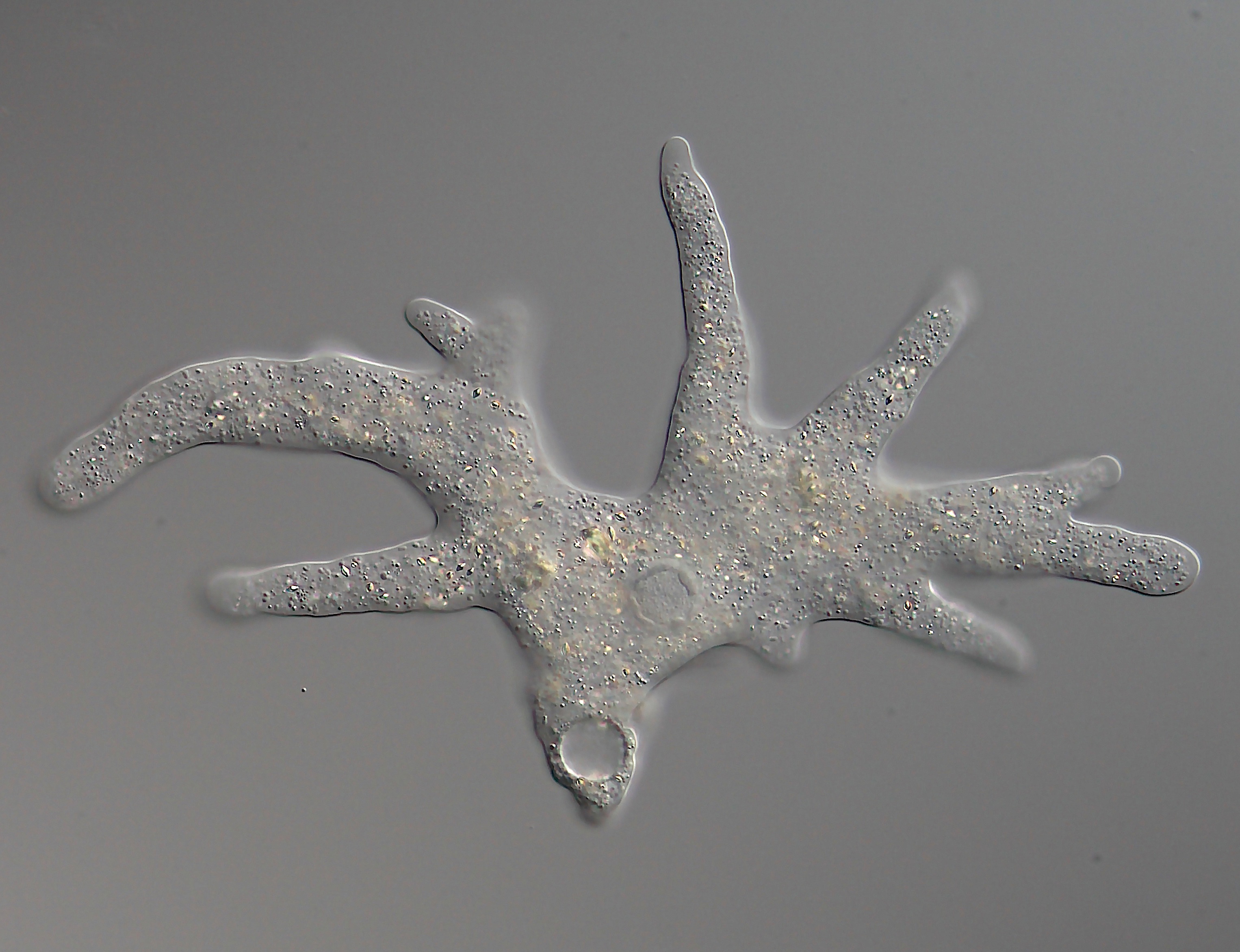 A pseudopod or pseudopodium (plural: pseudopods or pseudopodia) is a temporary arm-like projection of a
A pseudopod or pseudopodium (plural: pseudopods or pseudopodia) is a temporary arm-like projection of a
 Pseudopods can be classified into several varieties according to the number of projections (monopodia and polypodia), and according to their appearance:
Pseudopods can be classified into several varieties according to the number of projections (monopodia and polypodia), and according to their appearance:
 A pseudopod or pseudopodium (plural: pseudopods or pseudopodia) is a temporary arm-like projection of a
A pseudopod or pseudopodium (plural: pseudopods or pseudopodia) is a temporary arm-like projection of a eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
that is emerged in the direction of movement. Filled with cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
, pseudopodia primarily consist of actin filaments
Microfilaments, also called actin filaments, are protein filaments in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that form part of the cytoskeleton. They are primarily composed of polymers of actin, but are modified by and interact with numerous other p ...
and may also contain microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nm and have an inner diameter between 1 ...
s and intermediate filaments. Pseudopods are used for motility
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy.
Definitions
Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms th ...
and ingestion
Ingestion is the consumption of a substance by an organism. In animals, it normally is accomplished by taking in a substance through the mouth into the gastrointestinal tract, such as through eating or drinking. In single-celled organisms in ...
. They are often found in amoebas.
Different types of pseudopodia can be classified by their distinct appearances. Lamellipodia
The lamellipodium (plural lamellipodia) (from Latin ''lamella'', related to ', "thin sheet", and the Greek radical ''pod-'', "foot") is a cytoskeletal protein actin projection on the leading edge of the cell. It contains a quasi-two-dimensiona ...
are broad and thin. Filopodia
Filopodia (singular filopodium) are slender cytoplasmic projections that extend beyond the leading edge of lamellipodia in migrating cells. Within the lamellipodium, actin ribs are known as ''microspikes'', and when they extend beyond the lame ...
are slender, thread-like, and are supported largely by microfilaments. Lobopodia are bulbous and amoebic. Reticulopodia are complex structures bearing individual pseudopodia which form irregular nets. Axopodia are the phagocytosis type with long, thin pseudopods supported by complex microtubule arrays enveloped with cytoplasm; they respond rapidly to physical contact.
Some pseudopodial cells are able to use multiple types of pseudopodia depending on the situation: Most of them use a combination of lamellipodia and filopodia to migrate (such as metastatic cancer cells). The human foreskin fibroblasts can either use lamellipodia- or lobopodia-based migration in a 3D matrix depending on the matrix elasticity.
Generally, several pseudopodia arise from the surface of the body, (''polypodial'', for example, '' Amoeba proteus''), or a single pseudopod may form on the surface of the body (''monopodial'', such as '' Entamoeba histolytica'').
Cells which make pseudopods are generally referred to as amoeboids.
Formation
Via extracellular cue
To move towards a target, the cell uses chemotaxis. It senses extracellular signalling molecules, chemoattractants (e.g. cAMP for '' Dictyostelium'' cells), to extend pseudopodia at the membrane area facing the source of these molecules. The chemoattractants bind toG protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related p ...
s, which activate GTPases of the Rho family (e.g. Cdc42, Rac) via G-proteins
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell to its interior. Their ac ...
.
Rho GTPases are able to activate WASp
A wasp is any insect of the narrow-waisted suborder Apocrita of the order Hymenoptera which is neither a bee nor an ant; this excludes the broad-waisted sawflies (Symphyta), which look somewhat like wasps, but are in a separate suborder ...
which in turn activate Arp2/3 complex which serve as nucleation sites for actin polymerization
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ov ...
. The actin polymers then push the membrane as they grow, forming the pseudopod. The pseudopodium can then adhere to a surface via its adhesion proteins (e.g. integrin
Integrins are transmembrane receptors that facilitate cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. Upon ligand binding, integrins activate signal transduction pathways that mediate cellular signals such as regulation of the cell cycle ...
s), and then pull the cell's body forward via contraction of an actin-myosin complex in the pseudopod. This type of locomotion is called Amoeboid movement.
Rho GTPases can also activate phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks), also called phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases, are a family of enzymes involved in cellular functions such as cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, motility, survival and intracellular trafficking, which i ...
(PI3K) which recruit PIP3 to the membrane at the leading edge and detach the PIP3-degrading enzyme PTEN from the same area of the membrane. PIP3 then activate GTPases back via GEF stimulation. This serves as a feedback loop to amplify and maintain the presence of local GTPase at the leading edge.
Otherwise, pseudopodia can't grow on other sides of the membrane than the leading edge because myosin filaments prevent them to extend. These myosin filaments are induced by cyclic GMP
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) is a cyclic nucleotide derived from guanosine triphosphate (GTP). cGMP acts as a second messenger much like cyclic AMP. Its most likely mechanism of action is activation of intracellular protein kinases in ...
in '' D. discoideum'' or Rho kinase in neutrophil
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying ...
s for example.
Different physical parameters were shown to regulate the length and time-scale of pseudopodia formation. For example, an increase in membrane tension inhibits actin assembly and protrusion formation. It was demonstrated that the lowered negative surface charge on the inner surface of the plasma membrane generates protrusions via activation of the Ras- PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway.
Without extracellular cue
In the case there is no extracellular cue, all moving cells navigate in random directions, but they can keep the same direction for some time before turning. This feature allows cells to explore large areas for colonization or searching for a new extracellular cue. In ''Dictyostelium'' cells, a pseudopodium can form either ''de novo'' as normal, or from an existing pseudopod, forming a Y-shaped pseudopodium. The Y-shaped pseudopods are used by ''Dictyostelium'' to advance relatively straight forward by alternating between retraction of the left or right branch of the pseudopod. The ''de novo'' pseudopodia form at different sides than pre-existing ones, they are used by the cells to turn. Y-shaped pseudopods are more frequent than ''de novo'' ones, which explain the preference of the cell to keep moving to the same direction. This persistence is modulated by PLA2 and cGMP signalling pathways.Functions
The functions of pseudopodia include locomotion and ingestion: * Pseudopodia are critical in sensing targets which can then be engulfed; the engulfing pseudopodia are called phagocytosis pseudopodia. A common example of this type of amoeboid cell is themacrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
.
* They are also essential to amoeboid-like locomotion. Human mesenchymal stem cells are a good example of this function: these migratory cells are responsible for in-utero remodeling; for example, in the formation of the trilaminar germ disc during gastrulation.
Morphology
 Pseudopods can be classified into several varieties according to the number of projections (monopodia and polypodia), and according to their appearance:
Pseudopods can be classified into several varieties according to the number of projections (monopodia and polypodia), and according to their appearance:
Lamellipodia
Lamellipodia
The lamellipodium (plural lamellipodia) (from Latin ''lamella'', related to ', "thin sheet", and the Greek radical ''pod-'', "foot") is a cytoskeletal protein actin projection on the leading edge of the cell. It contains a quasi-two-dimensiona ...
are broad and flat pseudopodia used in locomotion. They are supported by microfilaments which form at the leading edge, creating a mesh-like internal network.
Filopodia
Filopodia (or filose pseudopods) are slender and filiform with pointed ends, consisting mainly of ectoplasm. These formations are supported bymicrofilament
Microfilaments, also called actin filaments, are protein filaments in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that form part of the cytoskeleton. They are primarily composed of polymers of actin, but are modified by and interact with numerous other pr ...
s which, unlike the filaments of lamellipodia with their net-like actin, form loose bundles by cross-linking. This formation is partly due to bundling proteins such as fimbrins and fascins.
Filopodia are observed in some animal cells: in part of Filosa
Cercozoa is a phylum of diverse single-celled eukaryotes. They lack shared morphological characteristics at the microscopic level, and are instead defined by molecular phylogenies of rRNA and actin or polyubiquitin. They were the first major eu ...
( Rhizaria), in " Testaceafilosia" , in Vampyrellidae
The family Vampyrellidae is a subgroup of the order Aconchulinida (formerly Vampyrellida) within the phylum Cercozoa. Based on molecular sequence data, the family currently comprises the genus '' Vampyrella'', and maybe several other vampyrel ...
and Pseudosporida
''Pseudospora'' is a genus of parasitic cercozoans.
It includes the species ''Pseudospora volvocis''.
Taxonomy
* Order Pseudosporida Hibberd 1983 sensu Cavalier-Smith 1993
** Family Pseudosporidae Kent 1880 emend. Berlese 1888
*** Genus ''Pseu ...
( Rhizaria) and in Nucleariida ( Opisthokonta).
Lobopodia
Lobopodia (or lobose pseudopods) are bulbous, short, and blunt in form. These finger-like, tubular pseudopodia contain both ectoplasm and endoplasm. They can be found in different kind of cells, notably in Lobosa and other Amoebozoa and in some Heterolobosea ( Excavata). High-pressure lobopodia can also be found in humanfibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of biological cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework ( stroma) for animal tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells ...
s travelling through a complex network of 3D matrix
Matrix most commonly refers to:
* ''The Matrix'' (franchise), an American media franchise
** '' The Matrix'', a 1999 science-fiction action film
** "The Matrix", a fictional setting, a virtual reality environment, within ''The Matrix'' (franchi ...
(e.g. mammalian dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided ...
, cell-derived matrix). Contrarily to other pseudopodia using the pressure exerted by actin polymerization on the membrane to extend, fibroblast lobopods use the nuclear piston mechanism consisting in pulling the nucleus via actomyosin contractility to push the cytoplasm that in turn push the membrane, leading to pseudopod formation. To occur, this lobopodia-based fibroblast migration needs nesprin 3, integrin
Integrins are transmembrane receptors that facilitate cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. Upon ligand binding, integrins activate signal transduction pathways that mediate cellular signals such as regulation of the cell cycle ...
s, RhoA
Transforming protein RhoA, also known as Ras homolog family member A (RhoA), is a small GTPase protein in the Rho family of GTPases that in humans is encoded by the ''RHOA'' gene. While the effects of RhoA activity are not all well known, it is ...
, ROCK and myosin II.
Otherwise, lobopods are often accompanied with small lateral blebs forming along the side of the cell, probably due to the high intracellular pressure during lobopodia formation increasing the frequency of plasma membrane-cortex rupture.
Reticulopodia
Reticulopodia (or reticulose pseudopods), are complex formations in which individual pseudopods are merged and form irregular nets. The primary function of reticulopodia, also known as myxopodia, is food ingestion, with locomotion a secondary function. Reticulopods are typical ofForaminifera
Foraminifera (; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of amoeboid protists characterized by streaming granular ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly ...
, Chlorarachnea
The chlorarachniophytes are a small group of exclusively marine algae widely distributed in tropical and temperate waters. They are typically mixotrophic, ingesting bacteria and smaller protists as well as conducting photosynthesis. Normally t ...
, '' Gromia'' and '' Filoreta'' (Rhizaria).
Axopodia
Axopodia (also known as actinopodia) are narrow pseudopodia containing complex arrays ofmicrotubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nm and have an inner diameter between 1 ...
s enveloped by cytoplasm. Axopodia are mostly responsible for phagocytosis by rapidly retracting in response to physical contact. Principally, these pseudopodia are food collecting structures. Also used in passive transportation by expanding their surface area , and being carried with the water stream. They are observed in " Radiolaria" and "Heliozoa
Heliozoa, commonly known as sun-animalcules, are microbial eukaryotes ( protists) with stiff arms (axopodia) radiating from their spherical bodies, which are responsible for their common name. The axopodia are microtubule-supported projections fr ...
".
References
{{Authority control Actin-based structures Cell anatomy Cell movement