Principalities of albania on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The term Albanian principalities refers to a number of
 * Principality of Arbanon
*
* Principality of Arbanon
*
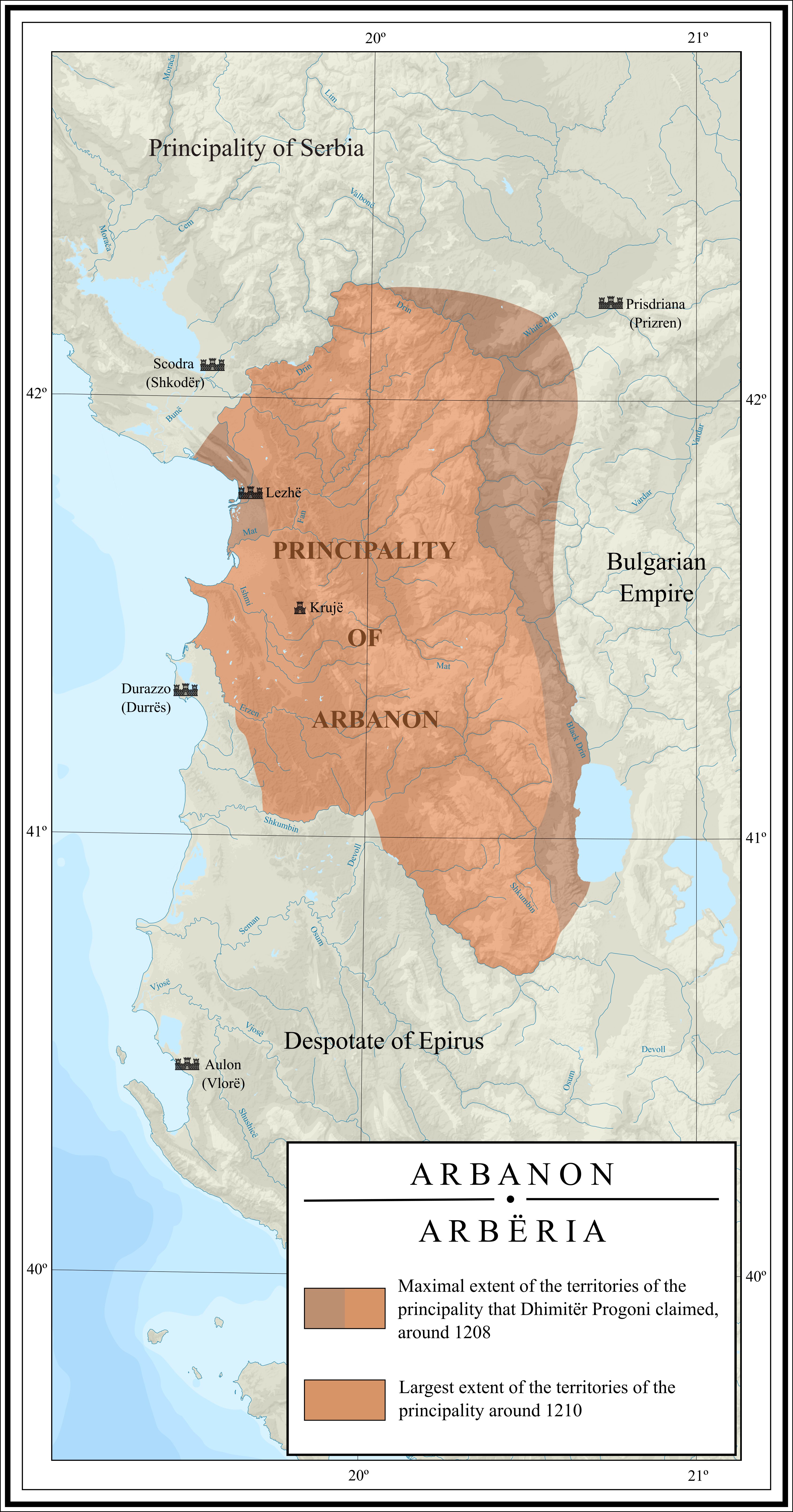 The Principality of Arbanon (1190–1255) was the first Albanian state during the
The Principality of Arbanon (1190–1255) was the first Albanian state during the
Volume 6, Scanderbeg section
/ref> abjured Islam and proclaimed himself the avenger of his family and country. Following the capture of Krujë, Skanderbeg managed to bring together all the Albanian princes in the town of LezhëMinna Skafte Jensen, 2006,
A Heroic Tale: Marin Barleti's Scanderbeg between orality and literacy
'' (see League of Lezhë, 1444). Gibbon reports that the ''"Albanians, a martial race, were unanimous to live and die with their hereditary prince"'' and that ''"in the assembly of the states of Epirus, Skanderbeg was elected general of the Turkish war and each of the allies engaged to furnish his respective proportion of men and money"''.
5. Gropa
: "The sphere of influence of the Gropas was no doubt concentrated in the region between Pogradec, Ohrid and Dibra. They seem to have ruled in that area for two centuries" In 1218 a certain Andrea was mentioned as a powerful sebast. In 1273 is mentioned
principalities
A principality (or sometimes princedom) can either be a monarchical feudatory or a sovereign state, ruled or reigned over by a regnant-monarch with the title of prince and/or princess, or by a monarch with another title considered to fall under ...
created in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
in Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
and the surrounding regions in the western Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
that were ruled by Albanian
Albanian may refer to:
*Pertaining to Albania in Southeast Europe; in particular:
**Albanians, an ethnic group native to the Balkans
**Albanian language
**Albanian culture
**Demographics of Albania, includes other ethnic groups within the country ...
nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy (class), aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below Royal family, royalty. Nobility has often been an Estates of the realm, estate of the realm with many e ...
. The 12th century marked the first Albanian principality, the Principality of Arbanon. It was later, however, in the 2nd half of the 14th century that these principalities became stronger, especially with the fall of the Serbian Empire after 1355. Some of these principalities were notably united in 1444 under the military alliance called League of Lezhë up to 1480 which defeated the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
in more than 28 battles. They covered modern day Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
,western and central Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a partially recognised state in Southeast Euro ...
, Epirus, areas up to Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part o ...
, western North Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Socialist Feder ...
, southern Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
. The leaders of these principalities were some of the most noted Balkan figures in the 14th and 15th centuries such as Gjin Bue Shpata, Andrea II Muzaka, John Zenevisi
John Zenevisi or Gjon Zenebishi ( sq, Gjon Zenebishi or ''Gjin Zenebishi''; died 1418) was an Albanian magnate that held the estates in Epirus, such as Argyrokastro (Gjirokastër) and Vagenetia.
Name
Zenevisi can be found with different spellin ...
, Karl Topia
Karl Thopia ( sq, Karl Topia) was an Albanian feudal prince and warlord who ruled Albania from the middle of the 14th century until the first Ottoman conquest of Albania. Thopia usually maintained good relations with the Roman Curia.
Family ...
, Andrea Gropa
Andrea Gropa was a 14th-century Albanian nobleman who ruled the region and the city of Ohrid, first as a minor vassal for a very short time (župan) to Serbian King Vukašin Mrnjavčević (r. 1365–1371), then as independent after 1370. He was a ...
, Balsha family, Gjergj Arianiti
Gjergj Arianiti (1383–1462) was an Albanian feudal lord who led several successful campaigns against the Ottoman Empire. He was the father of Donika, Skanderbeg's wife, as well as the grand-uncle of Moisi Arianit Golemi. Gjergj Arianiti was ...
, Gjon Kastrioti
Gjon Kastrioti (1375/80 – 4 May 1437), was a member of the Albanian nobility, from the House of Kastrioti, and the father of future Albanian leader Gjergj Kastrioti (better known as Skanderbeg). He governed the territory between the Cape of ...
, Skanderbeg
, reign = 28 November 1443 – 17 January 1468
, predecessor = Gjon Kastrioti
, successor = Gjon Kastrioti II
, spouse = Donika Arianiti
, issue = Gjon Kastrioti II
, royal house = Kastrioti
, father ...
, Dukagjini family
The Dukagjini are an Albanian feudal noble family who ruled over an area of Northern Albania and Western Kosovo known as the Principality of Dukagjini in the 14th and 15th centuries. They may have been relatives or descendants of the earlier ...
and Lek Dukagjini
Lek or LEK may refer to:
* Lek mating, mating in a lek, a type of animal territory in which males of a species gather
* Albanian lek, the currency of Albania
* Lek (magazine), a Norwegian softcore pornographic magazine
* Lek (pharmaceutical comp ...
.
List of Albanian principalities
 * Principality of Arbanon
*
* Principality of Arbanon
* Principality of Valona
The Principality of Valona and Kanina, also known as the Despotate of Valona and Kanina or simply the Principality of Valona (1346–1417) was a medieval principality in Albania, roughly encompassing the territories of the modern counties of Vlor� ...
* Principality of Muzaka
The Principality of Muzaka (Albanian: ''Principata e Muzakajve'') was an independent realm ruled by the Albanian Muzaka family with its capital at Berat, covering territories in Central and Southern Albania, and Western Macedonia. One of the fi ...
* Despotate of Angelokastron and Lepanto
Despot or ''despotes'' ( grc-gre, δεσπότης, despótēs, lord, master) was a senior Byzantine court title that was bestowed on the sons or sons-in-law of reigning emperors, and initially denoted the heir-apparent of the Byzantine emperor.
...
* Despotate of Arta
* Principality of Albania (medieval)
* Principality of Gjirokastër
A principality (or sometimes princedom) can either be a monarchical feudatory or a sovereign state, ruled or reigned over by a regnant-monarch with the title of prince and/or princess, or by a monarch with another title considered to fall under ...
* Principality of Kastrioti
* Principality of Mataranga
* Principality of Dukagjini
The Principality of Dukagjini ( sq, Principata e Dukagjinit) refers to the domains (''zotërimet'') of the Albanians, Albanian Dukagjini family in northern Albania and wester part of the modern-day territory of Kosovo in the 14th century and 15t ...
* Principality of Gropaj
* Principality of Zahariaj
* Principality of Mirdita
* Thopia family domains
* Arianiti family domains
Principality of Arbanon
 The Principality of Arbanon (1190–1255) was the first Albanian state during the
The Principality of Arbanon (1190–1255) was the first Albanian state during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
. The proclamation of the feudal state of Arbanon
Arbanon ( sq, Arbër or , el, Ἄρβανον, ''Árvanon''; la, Arbanum) was a principality ruled by the native Progoni family, and the first Albanian state to emerge in recorded history. The principality was established in 1190 by the native ...
, in the north of Albania, with Kruja as the capital took place in 1190. As the founder of this state is known Progoni and later on Gjini and Dhimiter. Nderfandina is known as the most important center of this principality. For this was spoken clearly by the emblem of Arbanon found carved on a stone in the Catholic Church of Saint Maria. After the fall of Progon Dynasty
The Progoni were an Albanian noble family which established the first Albanian state to be recorded in history, the Principality of Arbanon.: "By 1190, Byzantium's power had so receded that the archon Progon succeeded in establishing the first A ...
the principality came under Grigor Kamona and Gulam of Albania. Finally the principality was dissolved in 1255. The best period of the principality was under Dhimiter Progoni.
Despotate of Angelokastron and Lepanto
Despotate of Angelokastron and Lepanto (1358–1374) was aDespotate
Despot or ''despotes'' ( grc-gre, δεσπότης, despótēs, lord, master) was a senior Byzantine court title that was bestowed on the sons or sons-in-law of reigning emperors, and initially denoted the heir-apparent of the Byzantine emperor.
...
, ruled by Albanian chieftains of Epirus. It was created after the defeat of Nikephoros II Orsini in 1358 and ceased to exist in 1374, when its despot, Gjin Bua Shpata, unified the territory with Despotate of Arta."History of Albanian People" Albanian Academy of Science. John V.A. Fine Jr., The Late Medieval Balkans, Ann Arbor, 1987.The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium, Oxford University Press, 1991.
Principality of Valona
The Principality of Valona (1346–1417) was a medieval state roughly encompassing the territories of the modern Albanian counties ofVlorë
Vlorë ( , ; sq-definite, Vlora) is the third most populous city of the Republic of Albania and seat of Vlorë County and Vlorë Municipality. Located in southwestern Albania, Vlorë sprawls on the Bay of Vlorë and is surrounded by the foothi ...
(Valona) and Berat. Initially a vassal of the Serbian Empire, it became an independent lordship after 1355 until conquered by the Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
in 1417. Between 1355 and 1417, there were Bulgarian rulers from Asen family and rulers from the Balšić family.
Principality of Dukagjini
The Principality of Dukagjini ( sq, Principata e Dukagjinit) refers to the domains of theAlbanian
Albanian may refer to:
*Pertaining to Albania in Southeast Europe; in particular:
**Albanians, an ethnic group native to the Balkans
**Albanian language
**Albanian culture
**Demographics of Albania, includes other ethnic groups within the country ...
Dukagjini family
The Dukagjini are an Albanian feudal noble family who ruled over an area of Northern Albania and Western Kosovo known as the Principality of Dukagjini in the 14th and 15th centuries. They may have been relatives or descendants of the earlier ...
in northern Albania and western Kosovo in the 14th century and 15th century. At their maximum extent, the domains of the Dukagjini extended from Upper Zadrima in the northwest to the Plain of Dukagjini in western Kosovo. The political center of the Dukagjini family was Lezhë until 1393 when it was surrendered to Venice in order to not fall under the Ottomans. The Ottoman sanjak of Dukagjin
Sanjaks (liwāʾ) (plural form: alwiyāʾ)
* Armenian language, Armenian: նահանգ (''nahang''; meaning "province")
* Bulgarian language, Bulgarian: окръг (''okrǔg''; meaning "county", "province", or "region")
* el, Διοίκησι� ...
was named after the rule of the family in the areas that formed it. The principality formally existed until 1479, but in 1444 it was united by Skanderbeg
, reign = 28 November 1443 – 17 January 1468
, predecessor = Gjon Kastrioti
, successor = Gjon Kastrioti II
, spouse = Donika Arianiti
, issue = Gjon Kastrioti II
, royal house = Kastrioti
, father ...
with the other Albanian noble families.
Despotate of Arta
Despotate of Arta (1355–1416) was aDespotate
Despot or ''despotes'' ( grc-gre, δεσπότης, despótēs, lord, master) was a senior Byzantine court title that was bestowed on the sons or sons-in-law of reigning emperors, and initially denoted the heir-apparent of the Byzantine emperor.
...
, ruled by Albanian chieftains of Epirus. It was created after the defeat of Nikephoros II Orsini in 1358 and ceased to exist in 1416. After the death of Peter Losha in 1374, the Albanian despotates of Arta and Angelocastron were united under the rule of Despot Gjin Bua Shpata. The territory of this despotate was from the Corinth Gulf to Acheron River
The Acheron (; grc, Ἀχέρων ''Acheron'' or Ἀχερούσιος ''Acherousios''; ell, Αχέροντας ''Acherontas'') is a river located in the Epirus region of northwest Greece. It is long, and its drainage area is . Its source is ...
in the North, neighboring with the Principality
A principality (or sometimes princedom) can either be a monarchical feudatory or a sovereign state, ruled or reigned over by a regnant-monarch with the title of prince and/or princess, or by a monarch with another title considered to fall under ...
of John Zenevisi
John Zenevisi or Gjon Zenebishi ( sq, Gjon Zenebishi or ''Gjin Zenebishi''; died 1418) was an Albanian magnate that held the estates in Epirus, such as Argyrokastro (Gjirokastër) and Vagenetia.
Name
Zenevisi can be found with different spellin ...
, another state created in the area of the Despotate of Epirus
The Despotate of Epirus ( gkm, Δεσποτᾶτον τῆς Ἠπείρου) was one of the Greek successor states of the Byzantine Empire established in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade in 1204 by a branch of the Angelos dynasty. It claim ...
. The Despotate of Epirus managed to control in this period only the eastern part of Epirus, with its capital in Ioannina
Ioannina ( el, Ιωάννινα ' ), often called Yannena ( ' ) within Greece, is the capital and largest city of the Ioannina regional unit and of Epirus, an administrative region in north-western Greece. According to the 2011 census, the c ...
.
During this period the Despotate of Epirus was ruled by Thomas II Preljubović, who was in an open conflict with Gjin Bue Shpata. In 1375, Gjin Bue Shpata started an offensive in Ioannina
Ioannina ( el, Ιωάννινα ' ), often called Yannena ( ' ) within Greece, is the capital and largest city of the Ioannina regional unit and of Epirus, an administrative region in north-western Greece. According to the 2011 census, the c ...
, but he couldn't invade the city. Although Shpata married with the sister of Thomas II Preljubović, Helena their war did not stop. After the death of Gjin Bua Shpata in 1399, the Despotate of Arta weakened continuously. Among the animosities with the rulers of Janina
Ioannina ( el, Ιωάννινα ' ), often called Yannena ( ' ) within Greece, is the capital and largest city of the Ioannina regional unit and of Epirus, an administrative region in north-western Greece. According to the 2011 census, the c ...
Gjin's successor, Muriq Shpata }); ) was the Despotate of Arta, ruler of Arta from late 1399/early 1400 until his death in 1414 or 1415. Maurice's reign was dominated by his wars with Carlo I Tocco. Maurice was able to defend his capital of Arta, but despite some victories failed ...
, had to deal with the intentions of the Venetians and of Count
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: ...
Carlo I Tocco of Cefalonia
Kefalonia or Cephalonia ( el, Κεφαλονιά), formerly also known as Kefallinia or Kephallenia (), is the largest of the Ionian Islands in western Greece and the 6th largest island in Greece after Crete, Euboea, Lesbos, Rhodes and Chios. It ...
. In 1416 he defeated Jakup Shpata
Yaqub Spata or Shpata ( sq, Jakob Bua Shpata) was the last Lord of Arta, ruling from 1414/15 until 1416, with a brief interval when he was evicted by the local population. His rule ended after his capture and execution by Carlo I Tocco, who ...
and conquered Arta, ending the Shpata dynasty.
Principality of Gjirokastër
Principality of Gjirokastër (1373–1418) was a principality created byJohn Zenevisi
John Zenevisi or Gjon Zenebishi ( sq, Gjon Zenebishi or ''Gjin Zenebishi''; died 1418) was an Albanian magnate that held the estates in Epirus, such as Argyrokastro (Gjirokastër) and Vagenetia.
Name
Zenevisi can be found with different spellin ...
in 1386 and abolished after the Ottoman invasion in 1434. In 1380, John Zenevisi was appointed ''sebastocrator
''Sebastokrator'' ( grc-byz, Σεβαστοκράτωρ, Sevastokrátor, August Ruler, ; bg, севастократор, sevastokrator; sh, sebastokrator), was a senior court title in the late Byzantine Empire. It was also used by other rulers wh ...
'' or prefect of Vagenetia near Delvina and in 1386 he became prince. In 1399 Esau, supported by some Albanian clans, marched against his wife's brother-in-law John Zenevisi of Argyrokastron. Now Esau was routed and captured, and much of his land was occupied by Zenevisi. Esau returned to Ioannina in 1400, regaining the reign from Zenebishi. Zenebishi was defeated by the Turks, he fled to the Venetian island of Corfu, but was called back two years later (1416) by an uprising of the mountain tribes. With the support of Venice, he again set his sights on Gjirokastra, but was chased away once more by the Turks and died in Corfu in 1418.
Lordship of Berat
The Lordship of Berat was a principality ruled by theMuzaka
The Muzaka were an Albanian noble family that ruled over the region of Myzeqe (southern Albania) in the Late Middle Ages. The Muzaka are also referred to by some authors as a tribe or a clan. The earliest historical document that mention Muzaka ...
noble family. It's uncertain when the Muzaka family started to rule in central Albania, however, one of the first notable rulers is the sebastokrator
''Sebastokrator'' ( grc-byz, Σεβαστοκράτωρ, Sevastokrátor, August Ruler, ; bg, севастократор, sevastokrator; sh, sebastokrator), was a senior court title in the late Byzantine Empire. It was also used by other rulers wh ...
Andrea I Muzaka who ruled over Myzeqe. In 1335 the principality became a Despotate
Despot or ''despotes'' ( grc-gre, δεσπότης, despótēs, lord, master) was a senior Byzantine court title that was bestowed on the sons or sons-in-law of reigning emperors, and initially denoted the heir-apparent of the Byzantine emperor.
...
and was significantly expanded during the rule of Andrea II. The Muzaka family continued to be a formidable and influential dynasty in central Albania until 1417 when it eventually fell under the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
.
Kastrioti Principality
Principality of Kastrioti (1389–1444) was one of the most important principalities in Medieval Albania. It was created byGjon Kastrioti
Gjon Kastrioti (1375/80 – 4 May 1437), was a member of the Albanian nobility, from the House of Kastrioti, and the father of future Albanian leader Gjergj Kastrioti (better known as Skanderbeg). He governed the territory between the Cape of ...
and then ruled by the national hero of Albania, Gjergj Kastrioti Skanderbeg.
Gjon Kastrioti
Gjon Kastrioti (1375/80 – 4 May 1437), was a member of the Albanian nobility, from the House of Kastrioti, and the father of future Albanian leader Gjergj Kastrioti (better known as Skanderbeg). He governed the territory between the Cape of ...
had originally only two small villages, which probably emblem of the eagle family with a black two-headed, even if it can provide different interpretations. In short time Gjon Kastrioti managed to expand its lands so as to become the undisputed lord of Central Albania.
Gjon Kastrioti was among those who opposedJames Emerson Tennent
Sir James Emerson Tennent, 1st Baronet, FRS (born James Emerson; 7 April 1804 – 6 March 1869) was a British politician and traveller born in Ireland. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society on 5 June 1862.
Life
The third son of William ...
, 1845, ''The History of Modern Greece, from Its Conquest by the Romans B.C.146, to the Present Time'' the early incursion of Ottoman Bayezid I, however his resistance was ineffectual. The Sultan, having accepted his submissions, obliged him to pay tribute and to ensure the fidelity of local rulers, Gjergj Kastrioti and his three brothers were taken by the Sultan to his court as hostages.
Gjergj Kastrioti Skanderbeg was distinguished as one of the best officers in several Ottoman campaigns both in Asia Minor and in Europe, and the Sultan appointed him General.
On 28 November 1443, Skanderbeg saw his opportunity to rebel during a battle
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
against the Hungarians led by John Hunyadi in Niš
Niš (; sr-Cyrl, Ниш, ; names in other languages) is the third largest city in Serbia and the administrative center of the Nišava District. It is located in southern part of Serbia. , the city proper has a population of 183,164, while ...
as part of the Crusade of Varna. He switched sides along with 300 other Albanians serving in the Ottoman army. After a long trek to Albania he eventually captured Krujë by forging a letter from the Sultan to the Governor of Krujë, which granted him control of the territory. After capturing the castle, SkanderbegEdward Gibbon
Edward Gibbon (; 8 May 173716 January 1794) was an English historian, writer, and member of parliament. His most important work, ''The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'', published in six volumes between 1776 and 1788, is k ...
, 1788, ''History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire
''The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'' is a six-volume work by the English historian Edward Gibbon. It traces Western civilization (as well as the Islamic and Mongolian conquests) from the height of the Roman Empire to th ...
''Volume 6, Scanderbeg section
/ref> abjured Islam and proclaimed himself the avenger of his family and country. Following the capture of Krujë, Skanderbeg managed to bring together all the Albanian princes in the town of LezhëMinna Skafte Jensen, 2006,
A Heroic Tale: Marin Barleti's Scanderbeg between orality and literacy
'' (see League of Lezhë, 1444). Gibbon reports that the ''"Albanians, a martial race, were unanimous to live and die with their hereditary prince"'' and that ''"in the assembly of the states of Epirus, Skanderbeg was elected general of the Turkish war and each of the allies engaged to furnish his respective proportion of men and money"''.
Principality of Topiaj (medieval)
Principality of Albania was an Albanian principality ruled by the formidable Albanian dynasty of Thopia. One of the first notable rulers is Tanusio Thopia who was count of Mat since 1328. The most influential figure from this dynasty as well one of the most influential figures of medieval Albania was Karl Thopia. The principality changed hands between the Thopia dynasty and the Balšić dynasty, until 1392, when Durrës was annexed by theRepublic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
.
Principality of Mataranga
The Mataranga family, who were wealthy in thesouthern Albania
Southern Albania ( sq, Shqipëria jugore) is one of the three NUTS-2 Regions of Albania. This ethnographical territory is sometimes referred to as ''Toskeria'' ( sq, Toskëria).
It consists of five counties: Berat, Fier, Gjirokastër, Korçë ...
coastal region between Durazzo and Valona, whose first known members were recorded in a document from the Republic of Ragusa as rulers of the territory. Temporary vassals of the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
Emperors
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
, at the beginning of the 14th century they accepted the supremacy of Philip of Taranto, who recaptured Durazzo in 1304 for the House of Anjou
Angevin or House of Anjou may refer to:
* County of Anjou or Duchy of Anjou, a historical county, and later Duchy, in France
** Angevin (language), the traditional langue d'oïl spoken in Anjou
** Counts and Dukes of Anjou
*House of Ingelger, a Fra ...
of the Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was ...
. One of the last members was the ruler Blasius Matarango
Blasius Mataranga ( al, Vlash Matranga) was an Albanian prince of the Mataranga family, Matranga noble family.
Life
Blasius came from the noble family Mataranga family, who were wealthy in the Albania, southern Albania coastal region between ...
who after Dusan's death ruled from 1355 until his death in 1367, after his death the territories of the Mataranga family were incorporated into the Principality of Albania.
Principality of Gropaj
The Gropa family was one of the biggest and famous Albanian noble families in the eastern Albania. The dynasty controlled the region between Pogradec, Ohrid and Debar in the period 12th – 14th century.Vlora 19565. Gropa
: "The sphere of influence of the Gropas was no doubt concentrated in the region between Pogradec, Ohrid and Dibra. They seem to have ruled in that area for two centuries" In 1218 a certain Andrea was mentioned as a powerful sebast. In 1273 is mentioned
Pal Gropa
Pal (Paulo, Paulo) Gropa () was an Albanian feudal ruler of Ohrid and Debar from the 13th century.
Biography
Pal Gropa from Ohrid is known as the lord of Debar. It belongs to the medieval Gropa family. Chroniclers call him "a vassal of the Cr ...
which once again reconfirmed the domains of the Gropa family and were even given extended privileges by Charles I of Anjou
Charles I (early 1226/12277 January 1285), commonly called Charles of Anjou, was a member of the royal Capetian dynasty and the founder of the Capetian House of Anjou, second House of Anjou. He was Count of Provence (1246–85) and County of Fo ...
in order to ensure his loyalty. The Gropa noble family ruled until 1395 when it fell under the rapid expansion of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
.
Principality of Zahariaj
The first ruler of the Zaharia dynasty was Koja Zaharia who captured the castle of Dagnum in 1396 he proclaimed himself the Lord of Sati and Dagnum ''("dominus Sabatensis et Dagnensis")'' and from there he ruled the territory around it as an Ottoman vassal. In October 1400 Koja proposed to the Venetians to simulate a battle in which he and his cousinDhimitër Jonima
Dhimitër Jonima (? – 1409) was an Albanian nobleman from the Jonima family. Together with other Albanian noblemen he is mentioned as a participant of the Battle of Kosovo in 1389. He suffered another defeat from the Ottoman Empire shortly ...
would pretend to lose their possessions to the Venetians, in exchange for provision of 500 ducats annually. The Venetians did not promptly respond and Koja returned to the sultan. Koja continued to rule until 1430 when Ishak Bey
Ishak Bey or Ishak-Beg or Ishak-Beg Hranić was an Ottoman governor and soldier, the sanjakbey of Üsküb from 1415 to 1439.
Biography
According to some sources he was a member of the Bosnian Hranušić family, released slave and adopted son ...
captured Dagnum from Koja Zaharia in 1430 it was attached to the territory controlled by Ali Beg, while Koja was either imprisoned or expelled. After the Albanian Revolt of 1432–1436
Albanian may refer to:
*Pertaining to Albania in Southeast Europe; in particular:
** Albanians, an ethnic group native to the Balkans
**Albanian language
** Albanian culture
** Demographics of Albania, includes other ethnic groups within the coun ...
was crushed the sultan entrusted Koja's son Lekë Zaharia with a position of Dagnum's governor.
See also
* Principality of Albania *List of Albanian monarchs
This article includes a list of Albanian monarchs. Albania was first established by the Progon family in 1190, with Progon, Lord of Kruja as the nation's first monarch.
Princes of Arbanon (1190–1256)
House of Progon
* Progon (1190–1198)
...
References
Bibliography
* * * *''"History of Albanian People" Albanian Academy of Science. '' * {{Albania topics Former countries in Europe