Pre-modern human migration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
:'' This article focusses on prehistorical migration since the Neolithic period until AD 1800. See

 The proposed Indo-European migration has variously been dated to the end of the
The proposed Indo-European migration has variously been dated to the end of the
 The islands of the Pacific were populated during c. 1600 BC and AD 1000.
The Lapita people, who got their name from the archaeological site in Lapita, New Caledonia, where their characteristic pottery was first discovered, came from
The islands of the Pacific were populated during c. 1600 BC and AD 1000.
The Lapita people, who got their name from the archaeological site in Lapita, New Caledonia, where their characteristic pottery was first discovered, came from 

 The German term '' Landnahme'' ("land-taking") is sometimes used in historiography
for a migration event associated with a founding legend, e.g. of the
conquest of Canaan in the
The German term '' Landnahme'' ("land-taking") is sometimes used in historiography
for a migration event associated with a founding legend, e.g. of the
conquest of Canaan in the

 Western historians refer to the period of migrations that separated Antiquity from the
Western historians refer to the period of migrations that separated Antiquity from the
 The
The

 The migration of the Mongolic-speaking Kalmyks to the
The migration of the Mongolic-speaking Kalmyks to the
 European
European  The English colonists who came during this period were increasingly moved by economic necessity. Some colonies, including Georgia, were settled heavily by petty criminals and indentured servants who hoped to pay off their debts. By 1800, European emigration had transformed the demographic character of the American continent. This was due to the devastating effect of European diseases and warfare on Native American populations.
The European settlers' influence elsewhere was less pronounced as in South Asia and Africa, European settlement in this period was limited to a thin layer of administrators, traders and soldiers. Dutch-speaking settlers known as
The English colonists who came during this period were increasingly moved by economic necessity. Some colonies, including Georgia, were settled heavily by petty criminals and indentured servants who hoped to pay off their debts. By 1800, European emigration had transformed the demographic character of the American continent. This was due to the devastating effect of European diseases and warfare on Native American populations.
The European settlers' influence elsewhere was less pronounced as in South Asia and Africa, European settlement in this period was limited to a thin layer of administrators, traders and soldiers. Dutch-speaking settlers known as
Early human migrations
Early human migrations are the earliest migrations and expansions of archaic and modern humans across continents. They are believed to have begun approximately 2 million years ago with the early expansions out of Africa by '' Homo erect ...
for migration prior to the Neolithic, History of human migration
:''See Human migration.
Human migration is the movement by people from one place to another, particularly different countries, with the intention of settling temporarily or permanently in the new location. It typically involves movements over lon ...
for modern history, and human migration
Human migration is the movement of people from one place to another with intentions of settling, permanently or temporarily, at a new location (geographic region). The movement often occurs over long distances and from one country to another (ex ...
for contemporary migration.''
Paleolithic migration prior to end of the Last Glacial Maximum
spread anatomically modern humans
Early modern human (EMH) or anatomically modern human (AMH) are terms used to distinguish '' Homo sapiens'' (the only extant Hominina species) that are anatomically consistent with the range of phenotypes seen in contemporary humans from exti ...
throughout Afro-Eurasia and to the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
.
During the Holocene climatic optimum, formerly isolated populations began to move and merge, giving rise to the
pre-modern distribution of the world's major language families
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ''ancestral language'' or ''parental language'', called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in hi ...
.
In the wake of the population movements of the Mesolithic came the Neolithic revolution,
followed by the Indo-European expansion
The Indo-European migrations were hypothesized migrations of Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) speakers, and subsequent migrations of people speaking derived Indo-European languages, which took place approx. 4000 to 1000 BCE, potentially expla ...
in Eurasia and the Bantu expansion in Africa.
Population movements of the proto-historical or early historical period include the Migration period, followed by (or connected to) the Slavic, Magyar, Norse, Turkic and Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
expansions of the medieval period.
The last world regions to be permanently settled were the Pacific Islands and the Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, N ...
, reached during the 1st millennium AD.
Since the beginning of the Age of Exploration
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafari ...
and the beginning of the Early Modern period and its emerging colonial empires
A colonial empire is a collective of territories (often called colonies), either contiguous with the imperial center or located overseas, settled by the population of a certain state and governed by that state.
Before the expansion of early moder ...
, an accelerated pace of migration on the intercontinental scale became possible.
Prehistory

Neolithic to Chalcolithic
Agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
is believed to have first been practised around 10,000 BC in the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent ( ar, الهلال الخصيب) is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine and Jordan, together with the northern region of Kuwait, southeastern region of ...
(see Jericho). From there, it propagated as a "wave" across Europe, a view supported by Archaeogenetics
Archaeogenetics is the study of ancient DNA using various molecular genetic methods and DNA resources. This form of genetic analysis can be applied to human, animal, and plant specimens. Ancient DNA can be extracted from various fossilized specimen ...
, reaching northern Europe some 5 millennia ago.
The earlier population of Europe were the Mesolithic hunter-gatherers. The Neolithic farmers, called the Early European Farmers
Early European Farmers (EEF), First European Farmers (FEF), Neolithic European Farmers, Ancient Aegean Farmers, or Anatolian Neolithic Farmers (ANF) are names used to describe a distinct group of early Neolithic farmers who brought agriculture to E ...
(EEF), migrated from Anatolia to the Balkans in large numbers during the 7th millennium BC. During the Chalcolithic
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular ...
and early Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
, the EEF-derived cultures of Europe were overwhelmed by successive invasions of Western Steppe Herders
In archaeogenetics, the term Western Steppe Herders (WSH), or Western Steppe Pastoralists, is the name given to a distinct ancestral component first identified in individuals from the Eneolithic steppe around the turn of the 5th millennium BCE, ...
(WSHs) from the Pontic–Caspian steppe
The Pontic–Caspian steppe, formed by the Caspian steppe and the Pontic steppe, is the steppeland stretching from the northern shores of the Black Sea (the Pontus Euxinus of antiquity) to the northern area around the Caspian Sea. It extend ...
, who carried about 60% Eastern Hunter-Gatherer
In archaeogenetics, the term Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG), sometimes East European Hunter-Gatherer, or Eastern European Hunter-Gatherer is the name given to a distinct ancestral component that represents descent from Mesolithic hunter-gatherers o ...
(EHG) and 40% Caucasus Hunter-Gatherer (CHG) admixture. These invasions led to EEF paternal
A father is the male parent of a child. Besides the paternal bonds of a father to his children, the father may have a parental, legal, and social relationship with the child that carries with it certain rights and obligations. An adoptive fathe ...
DNA lineages in Europe being almost entirely replaced with EHG/WSH paternal DNA (mainly R1b and R1a). EEF maternal
]
A mother is the female parent of a child. A woman may be considered a mother by virtue of having given birth, by raising a child who may or may not be her biological offspring, or by supplying her ovum for fertilisation in the case of gestat ...
DNA (mainly haplogroup N) also declined, being supplanted by steppe lineages, suggesting the migrations involved both males and females from the steppe. EEF mtDNA however remained frequent, suggesting admixture between WSH males and EEF females.
Some evidence (including a 2016 study by Busby et al.) suggests admixture from an ancient migration from Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
into parts of Sub-Saharan Africa. Another study (Ramsay et al. 2018) also shows evidence that ancient Eurasians migrated into Africa and that Eurasian admixture in modern Sub-Saharan Africans ranges from 0% to 50%, varying by region and generally highest (after North Africa) in the Horn of Africa and parts of the Sahel zone.
Bronze Age
 The proposed Indo-European migration has variously been dated to the end of the
The proposed Indo-European migration has variously been dated to the end of the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
(Marija Gimbutas
Marija Gimbutas ( lt, Marija Gimbutienė, ; January 23, 1921 – February 2, 1994) was a Lithuanian archaeologist and anthropologist known for her research into the Neolithic and Bronze Age cultures of " Old Europe" and for her Kurgan hypothesis ...
: Corded Ware culture
The Corded Ware culture comprises a broad archaeological horizon of Europe between ca. 3000 BC – 2350 BC, thus from the late Neolithic, through the Copper Age, and ending in the early Bronze Age. Corded Ware culture encompassed a v ...
, Yamna culture
The Yamnaya culture or the Yamna culture (russian: Ямная культура, ua, Ямна культура lit. 'culture of pits'), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, was a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archa ...
, Kurgan culture
The Kurgan hypothesis (also known as the Kurgan theory, Kurgan model, or steppe theory) is the most widely accepted proposal to identify the Proto-Indo-European homeland from which the Indo-European languages spread out throughout Europe and par ...
), the early Neolithic ( Colin Renfrew: Starčevo-Körös, Linearbandkeramic
The Linear Pottery culture (LBK) is a major archaeological horizon of the European Neolithic period, flourishing . Derived from the German ''Linearbandkeramik'', it is also known as the Linear Band Ware, Linear Ware, Linear Ceramics or Inci ...
) and the late Palaeolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος '' lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone to ...
( Marcel Otte, Paleolithic continuity theory).
The speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-E ...
are usually believed to have originated to the North of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
(today Eastern Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
and Southern Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
), and from there they gradually migrated into, and spread their language by cultural diffusion to, Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
, Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
, and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
and South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
starting from around the end of the Neolithic period (see Kurgan hypothesis
The Kurgan hypothesis (also known as the Kurgan theory, Kurgan model, or steppe theory) is the most widely accepted proposal to identify the Proto-Indo-European homeland from which the Indo-European languages spread out throughout Europe and par ...
). Other theories, such as that of Colin Renfrew, posit their development much earlier, in Anatolia, and claim that Indo-European languages and culture spread as a result of the agricultural revolution in the early Neolithic.
Relatively little is known about the inhabitants of pre-Indo-European " Old Europe". The Basque language remains from that era, as do the indigenous languages of the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
. The Sami
Acronyms
* SAMI, ''Synchronized Accessible Media Interchange'', a closed-captioning format developed by Microsoft
* Saudi Arabian Military Industries, a government-owned defence company
* South African Malaria Initiative, a virtual expertise ...
are genetically distinct among the peoples of Europe, but the Sami languages, as part of the Uralic languages
The Uralic languages (; sometimes called Uralian languages ) form a language family of 38 languages spoken by approximately 25million people, predominantly in Northern Eurasia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian (w ...
, spread into Europe about the same time as the Indo-European languages. However, since that period speakers of other Uralic languages such as the Finns and the Estonians have had more contact with other Europeans, thus today sharing more genes with them than the Sami. Like other Western Uralic and Baltic Finnic peoples, the Finns originate from the Volga region
The Volga Region (russian: Поволжье, ''Povolzhye'', literally: "along the Volga") is a historical region in Russia that encompasses the drainage basin of the Volga River, the longest river in Europe, in central and southern European Russ ...
in what is now Russia. Their ancestors migrated to Finland in the 8th century BC.
The earliest migrations we can reconstruct from historical sources are those of the 2nd millennium BC. The Proto-Indo-Iranians
Indo-Iranian peoples, also known as Indo-Iranic peoples by scholars, and sometimes as Arya or Aryans from their self-designation, were a group of Indo-European peoples who brought the Indo-Iranian languages, a major branch of the Indo-European l ...
began their expansion from c. 2000 BC, the Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one ...
documenting the presence of early Indo-Aryans
Indo-Aryan peoples are a diverse collection of Indo-European peoples speaking Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent. Historically, Aryan were the Indo-European pastoralists who migrated from Central Asia into South Asia and intr ...
in the Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising a ...
from the late 2nd millennium BC, and Iranian tribes
The Iranian peoples or Iranic peoples are a diverse grouping of Indo-European peoples who are identified by their usage of the Iranian languages and other cultural similarities.
The Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate ...
being attested in Assyrian sources as in the Iranian plateau
The Iranian plateau or Persian plateau is a geological feature in Western Asia, Central Asia, and South Asia. It comprises part of the Eurasian Plate and is wedged between the Arabian Plate and the Indian Plate; situated between the Zagros ...
from the 9th century BC. In the Late Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
, the Aegean and Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
were overrun by moving populations, summarized as the "Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples are a hypothesized seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions in the East Mediterranean prior to and during the Late Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BCE).. Quote: "First coined in 1881 by the Fren ...
", leading to the collapse of the Hittite Empire
The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750–1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-centr ...
and ushering in the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
.
A major archaeogenetics study uncovered a migration into southern Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
in the Bronze Age, during the 500-year period 1,300–800 BC. The newcomers were genetically most similar to ancient individuals from Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
.
Austronesian expansion
Austronesia
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austrone ...
, probably New Guinea, reaching the Solomon Islands, around 1600 BC, and later to Fiji, Samoa and Tonga. By the beginning of the 1st millennium BC, most of Polynesia was a loose web of thriving cultures who settled on the islands' coasts and lived off the sea. By 500 BC Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, and ...
was completely colonized; the last region of Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
to be reached was New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
in around 1000.

Bantu expansion
The Bantu expansion is the major prehistoric migratory pattern that shaped the ethno-linguistic composition of Sub-Saharan Africa. The Bantu, a branch of the Niger-Congo phylum, originated inWest Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, M ...
around the Benue-Cross
A cross is a geometrical figure consisting of two intersecting lines or bars, usually perpendicular to each other. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally. A cross of oblique lines, in the shape of the Latin letter X, is termed a sa ...
rivers area in southeastern Nigeria. Beginning in the 2nd millennium BC, they spread to Central Africa, and later, during the 1st millennium BC onward southeastern, spreading pastoralism
Pastoralism is a form of animal husbandry where domesticated animals (known as " livestock") are released onto large vegetated outdoor lands (pastures) for grazing, historically by nomadic people who moved around with their herds. The a ...
and agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
. During the 1st millennium AD, they populated Southern African. In the process, the Bantu languages displaced the Khoisan languages
The Khoisan languages (; also Khoesan or Khoesaan) are a group of African languages originally classified together by Joseph Greenberg. Khoisan languages share click consonants and do not belong to other African language families. For much of ...
indigenous to Central and Southern Africa.
Arctic peoples
The final region to be permanently settled by humans was theArctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, N ...
, reached by the Dorset culture
The Dorset was a Paleo-Eskimo culture, lasting from to between and , that followed the Pre-Dorset and preceded the Thule people (proto-Inuit) in the North American Arctic. The culture and people are named after Cape Dorset (now Kinngait) in ...
during about 500 BC to AD 1500. The Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories ...
are the descendants of the Thule culture
The Thule (, , ) or proto-Inuit were the ancestors of all modern Inuit. They developed in coastal Alaska by the year 1000 and expanded eastward across northern Canada, reaching Greenland by the 13th century. In the process, they replaced people o ...
, which emerged from western Alaska around AD 1000 and gradually displaced the Dorset culture.
Proto-historical and early historical migration

 The German term '' Landnahme'' ("land-taking") is sometimes used in historiography
for a migration event associated with a founding legend, e.g. of the
conquest of Canaan in the
The German term '' Landnahme'' ("land-taking") is sometimes used in historiography
for a migration event associated with a founding legend, e.g. of the
conquest of Canaan in the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' Indo-Aryan migration The Indo-Aryan migrations were the migrations into the Indian subcontinent of Indo-Aryan peoples, an ethnolinguistic group that spoke Indo-Aryan languages, the predominant languages of today's North India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lank ...
and expansion within India alluded to in the '' Indo-Aryan migration The Indo-Aryan migrations were the migrations into the Indian subcontinent of Indo-Aryan peoples, an ethnolinguistic group that spoke Indo-Aryan languages, the predominant languages of today's North India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lank ...
Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one ...
, the invasion traditions in the Irish Mythological Cycle
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not objectively true, the identification of a narrati ...
, accounting for how the Gaels
The Gaels ( ; ga, Na Gaeil ; gd, Na Gàidheil ; gv, Ny Gaeil ) are an ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man in the British Isles. They are associated with the Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic langu ...
came to Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
the arrival of the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
in Austrasia during the Migration period,
the Anglo-Saxon invasion of Britain
The Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain is the process which changed the language and culture of most of what became England from Romano-British to Germanic. The Germanic-speakers in Britain, themselves of diverse origins, eventually develo ...
,
the settlement of Iceland in the Viking Age
The Viking Age () was the period during the Middle Ages when Norsemen known as Vikings undertook large-scale raiding, colonizing, conquest, and trading throughout Europe and reached North America. It followed the Migration Period and the Germ ...
,
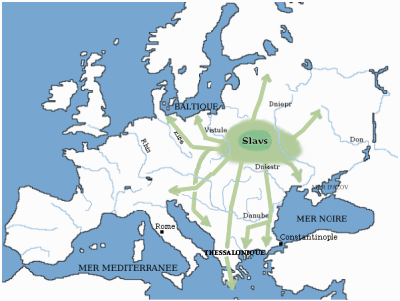
the Slavic migrations, the Hungarian conquest, etc.
Iron Age
The Dorian invasion of Greece led to the Greek Dark Ages. TheUrartians
Urartu (; Assyrian: ',Eberhard Schrader, ''The Cuneiform inscriptions and the Old Testament'' (1885), p. 65. Babylonian: ''Urashtu'', he, אֲרָרָט ''Ararat'') is a geographical region and Iron Age kingdom also known as the Kingdom of Va ...
were displaced by Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
, and the Cimmerians
The Cimmerians (Akkadian: , romanized: ; Hebrew: , romanized: ; Ancient Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people originating in the Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into Wes ...
and the Mushki
The Mushki (sometimes transliterated as Muški) were an Iron Age people of Anatolia who appear in sources from Assyria but not from the Hittites. Several authors have connected them with the Moschoi (Μόσχοι) of Greek sources and the Geor ...
migrated from the Caucasus into Anatolia. A Thraco-Cimmerian
Thraco-Cimmerian is a historiographical and archaeological term, composed of the names of the Thracians and the Cimmerians. It refers to 8th to 7th century BC cultures that are linked in Eastern Central Europe and in the area west of the Black Se ...
connection links these movements to the Proto-Celtic
Proto-Celtic, or Common Celtic, is the ancestral proto-language of all known Celtic languages, and a descendant of Proto-Indo-European. It is not attested in writing but has been partly reconstructed through the comparative method. Proto-Celti ...
world of central Europe, leading to the introduction of Iron to Europe and the Celtic expansion to western Europe and the British Isles around 500 BC.
Many scholars believe that the Ethiopian Semitic languages
Ethiopian Semitic (also Ethio-Semitic, Ethiosemitic, Ethiopic or Abyssinian) is a family of languages spoken in Ethiopia, Eritrea and Sudan. They form the western branch of the South Semitic languages, itself a sub-branch of Semitic, part of ...
descended from the South Semitic
South Semitic is a putative branch of the Semitic languages, which form a branch of the larger Afro-Asiatic language family, found in (North and East) Africa and Western Asia.
History
The "homeland" of the South Semitic languages is widely ...
branch which was spoken in the South Arabia. According to this theory, the speakers of the proto-Semitic language migrated from South Arabia to Ethiopia approximately 2800 years ago.
Beginning around 300 BC, the Japonic
Japonic or Japanese–Ryukyuan, sometimes also Japanic, is a language family comprising Japanese, spoken in the main islands of Japan, and the Ryukyuan languages, spoken in the Ryukyu Islands. The family is universally accepted by linguists, and ...
-speaking Yayoi people from the Korean Peninsula entered the Japanese islands and displaced or intermingled with the original Jōmon inhabitants. The linguistic homeland of Proto-Koreans
Koreans ( South Korean: , , North Korean: , ; see names of Korea) are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula.
Koreans mainly live in the two Korean nation states: North Korea and South Korea (collectively and simply re ...
is located somewhere in Southern Siberia/Manchuria, such the Liao river area or the Amur region. Proto-Koreans arrived in the southern part of the Korean Peninsula at around 300 BC, replacing and assimilating Japonic-speakers and likely causing the Yayoi
The started at the beginning of the Neolithic in Japan, continued through the Bronze Age, and towards its end crossed into the Iron Age.
Since the 1980s, scholars have argued that a period previously classified as a transition from the Jōmon p ...
migration.
Migration period

 Western historians refer to the period of migrations that separated Antiquity from the
Western historians refer to the period of migrations that separated Antiquity from the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
as the ''Great Migrations'' or as the Migrations Period. This period is further divided into two phases.
The first phase, from 300 to 500, saw the movement of Germanic, Sarmatian
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
and Hunnic tribes and ended with the settlement of these peoples in the areas of the former Western Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
. (See also: Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who ...
, Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
, Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area betw ...
, Burgundians, Suebi, Alamanni, Marcomanni
The Marcomanni were a Germanic people
*
*
*
that established a powerful kingdom north of the Danube, somewhere near modern Bohemia, during the peak of power of the nearby Roman Empire. According to Tacitus and Strabo, they were Suebian.
Or ...
).
The second phase, between 500 and 900, saw Slavic, Turkic and other tribes on the move, re-settling in Eastern Europe and gradually making it predominantly Slavic. Moreover, more Germanic tribes migrated within Europe during this period, including the Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the '' History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
(to Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
), and the Angles
The Angles ( ang, Ængle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ...
, Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
, and Jutes
The Jutes (), Iuti, or Iutæ ( da, Jyder, non, Jótar, ang, Ēotas) were one of the Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the departure of the Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic nation ...
(to the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, ...
). See also: Avars, Bulgars, Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
, Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and ...
, Varangian
The Varangians (; non, Væringjar; gkm, Βάραγγοι, ''Várangoi'';Varangian
" Online Etymo ...
s. The last phase of the migrations saw the coming of the " Online Etymo ...
Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
to the Pannonian plain
The Pannonian Basin, or Carpathian Basin, is a large basin situated in south-east Central Europe. The geomorphological term Pannonian Plain is more widely used for roughly the same region though with a somewhat different sense, with only the ...
.
German historians of the 19th century referred to these Germanic migrations as the ''Völkerwanderung'', the migrations of the peoples.
In the 4th or 5th century, Gaelic culture
The Gaels ( ; ga, Na Gaeil ; gd, Na Gàidheil ; gv, Ny Gaeil ) are an ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man in the British Isles. They are associated with the Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic languag ...
was brought to Scotland by settlers from Ireland, who founded the Gaelic kingdom of Dál Riata
Dál Riata or Dál Riada (also Dalriada) () was a Gaelic kingdom that encompassed the western seaboard of Scotland and north-eastern Ireland, on each side of the North Channel. At its height in the 6th and 7th centuries, it covered what is n ...
on Scotland's west coast. Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period ...
was settled by Britons
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs mod ...
from Britain between the 5th and 7th centuries.
The European migration period is connected with the simultaneous Turkic expansion
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West Asia, West, Central Asia, Central, East Asia, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose memb ...
which at first displaced other peoples towards the west, and by High Medieval times, the Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
themselves reached the Mediterranean.
Early medieval period
The main migration ofTurkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging t ...
occurred between the 5th and 10th centuries, when they spread across most of Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
. The Turkic peoples slowly replaced and assimilated the previous Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
-speaking locals, turning the population of Central Asia from largely Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
, into primarily of East Asian descent.
The medieval period, although often presented as a time of limited human mobility and slow social change in the history of Europe, in fact saw widespread movement of peoples. The Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and ...
from Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swe ...
raided all over Europe from the 8th century and settled in many places, including Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
, the north of England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a Anglo-Scottish border, border with England to the southeast ...
and Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
(most of whose urban centres were founded by the Vikings). The Normans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. ...
later conquered the Saxon Kingdom of England, most of Ireland, southern Italy and Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
.
Iberia was invaded by Muslim Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, Berbers and Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct or ...
in the 8th century, founding new Kingdoms such as al Andalus and bringing with them a wave of settlers from North Africa. The invasion of North Africa by the Banu Hilal
The Banu Hilal ( ar, بنو هلال, translit=Banū Hilāl) was a confederation of Arabian tribes from the Hejaz and Najd regions of the Arabian Peninsula that emigrated to North Africa in the 11th century. Masters of the vast plateaux of t ...
, a warlike Arab Bedouin tribe, in the 11th century was a major factor in the linguistic, cultural Arabization of the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
.
The Burmese-speaking people first migrated from present-day Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the C ...
, China to the Irrawaddy valley in the 7th century.
 The
The Tai peoples
Tai peoples are the populations who speak (or formerly spoke) the Tai languages. There are a total of about 93 million people of Tai ancestry worldwide, with the largest ethnic groups being Dai, Thais, Isan, Tai Yai (Shan), Lao, Tai Ahom, a ...
, from Guangxi began moving south – and westwards in the 1st millennium AD, eventually spreading across the whole of mainland Southeast Asia. Tai speaking tribes migrated southwestward along the rivers and over the lower passes into Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
, perhaps prompted by the Chinese expansion.
During the 4th–12th centuries, Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
people from the central plains migrated and settled in the South of China. This gave rise to the Cantonese people and other dialect groups of Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
during the Tang dynasty. Genetic studies have shown that the Hakka people
The Hakka (), sometimes also referred to as Hakka Han, or Hakka Chinese, or Hakkas are a Han Chinese subgroup whose ancestral homes are chiefly in the Hakka-speaking provincial areas of Guangdong, Fujian, Jiangxi, Guangxi, Sichuan, Hunan, Zhej ...
are largely descended from North Han Chinese. In a series of migrations, the Hakkas moved and settled in their present areas in South China.
Archaeological, historical and linguistic evidence suggest that the Nahuas
The Nahuas () are a group of the indigenous people of Mexico, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and Nicaragua. They comprise the largest indigenous group in Mexico and second largest in El Salvador. The Mexica (Aztecs) were of Nahua ethnicity, a ...
originally came from the deserts of northern Mexico and migrated into central Mexico in several waves. The Aztecs were descended of Nahua ancestry, and the Toltec
The Toltec culture () was a pre-Columbian Mesoamerican culture that ruled a state centered in Tula, Hidalgo, Mexico, during the Epiclassic and the early Post-Classic period of Mesoamerican chronology, reaching prominence from 950 to 1150 CE. T ...
s are often thought to have been as well. After the fall of the Toltecs a period of large population movements followed and some Nahua groups such as the Nicarao arrived as far south as Nicaragua.
Late Middle Ages
Massive migrations ofGermans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
took place into East Central and Eastern Europe, reaching its peak in the 12th to 14th centuries. These Ostsiedlung settlements in part followed territorial gains of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, but areas beyond were settled, too.
Arvanites
Arvanites (; Arvanitika: , or , ; Greek: , ) are a bilingual population group in Greece of Albanian origin. They traditionally speak Arvanitika, an Albanian language variety, along with Greek. Their ancestors were first recorded as settl ...
in Greece originate from Albanian settlers who moved south from areas in what is today southern Albania during the Middle Ages. They were the dominant population element of some regions in the south of Greece until the 19th century.
The Navajos and Apaches are believed to have migrated from northwestern Canada and eastern Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S. ...
, where the majority of Athabaskan speakers reside. Archaeological and historical evidence suggests the Athabaskan ancestors of the Navajos and Apaches entered the Southwest around 1400.
During the several centuries before Columbus's arrival in the Caribbean archipelago in 1492, the Caribs had in part displaced the Arawakan-speaking Taínos by warfare, extermination, and assimilation. The Taíno had settled the island chains earlier in history, migrating from the mainland.
At the end of the Middle Ages, the Romani arrived in Europe from the Middle East. They originate in India, probably an offshoot of the Domba
The Dom (Sanskrit ''ḍoma'', dialectally also Domra, Domba, Domaka, Dombari and variants) are castes, or groups, scattered across India. Dom were a caste of drummer. According to Tantra scriptures, the Dom were engaged in the occupations of sing ...
people of Northern India who had left for Sassanid Persia
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
around the 5th century.
Turkic-speaking Yakut tribes migrated north from the Lake Baikal region to their present homeland in Yakutia
Sakha, officially the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia),, is the largest republic of Russia, located in the Russian Far East, along the Arctic Ocean, with a population of roughly 1 million. Sakha comprises half of the area of its governing Far E ...
in central Siberia under pressure from the Mongol tribes during the 13th to 15th centuries.
The Fula people
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people ( ff, Fulɓe, ; french: Peul, links=no; ha, Fulani or Hilani; pt, Fula, links=no; wo, Pël; bm, Fulaw) are one of the largest ethnic groups in the Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region ...
are widely distributed, across the Sahel from the Atlantic coast to the Red Sea, particularly in West Africa. As their herds increased, small groups of Fulani herdsmen
Fulani herdsmen or Fulani pastoralists are nomadic or semi-nomadic Fulani people whose primary occupation is raising livestock. The Fulani herdsmen are largely located in the Sahel and semi-arid parts of West Africa, but due to relatively rec ...
found themselves forced to move eastward and further southwards and so initiated a series of migrations throughout West Africa, which endures to the present day. By the 15th century, there was a steady flow of Fulɓe immigrants into Hausaland and, later on, Bornu.
Early Modern period
Asia
Conflict between the Hmong people of southern China and newly arrivedHan
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
settlers increased during the 18th century. This led to armed conflict and large-scale migrations well into the late 19th century, the period during which many Hmong people immigrated to Southeast Asia. The most likely homeland of the Hmong–Mien languages
The Hmong–Mien languages (also known as Miao–Yao and rarely as Yangtzean) are a highly tonal language family of southern China and northern Southeast Asia. They are spoken in mountainous areas of southern China, including Guizhou, Hunan, Yunn ...
is in Southern China between the Yangtze
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows ...
and Mekong rivers, but speakers of these languages might have migrated from Central China
Central China () is a geographical and a loosely defined cultural region that includes the provinces of Henan, Hubei and Hunan. Jiangxi is sometimes also regarded to be part of this region. Central China is now officially part of South Centra ...
as part of the Han Chinese expansion or as a result of exile from an original homeland by Han Chinese.
Africa
The Oromo migrations were a series of expansions in the 16th and 17th centuries by the Oromo people from southern Ethiopia into more northerly regions of Ethiopia. Expansion of the Zulu Kingdom in South Africa in the early 19th century was a major factor of theMfecane
The Mfecane ( isiZulu, Zulu pronunciation: ̩fɛˈkǀaːne, also known by the Sesotho names Difaqane or Lifaqane (all meaning "crushing, scattering, forced dispersal, forced migration") is a historical period of heightened military conflict ...
, a mass-migration of tribes fleeing the Zulus. The Ngoni people
The Ngoni people are an ethnic group living in the present-day Southern African countries of Malawi, Mozambique, Tanzania, Zimbabwe, and Zambia. The Ngoni trace their origins to the Nguni and Zulu people of kwaZulu-Natal in South Africa. The d ...
fled as far north as Tanzania and Malawi. The Mfengu
The ''amaMfengu'' (in the Xhosa language ''Mfengu'', plural ''amafengu'') was a reference of Xhosa clans whose ancestors were refugees that fled from the Mfecane in the early 19th century to seek land and protection from the Xhosa and have sinc ...
refers to a variety of ethnic groups that fled from the Mfecane to enter into various Xhosa
Xhosa may refer to:
* Xhosa people, a nation, and ethnic group, who live in south-central and southeasterly region of South Africa
* Xhosa language, one of the 11 official languages of South Africa, principally spoken by the Xhosa people
See als ...
speaking areas.
North America
The Shoshone originated in the western Great Basin and spread north and east into present-day Idaho and Wyoming. By 1500, some Eastern Shoshone had crossed the Rocky Mountains into the Great Plains. After 1750, warfare and pressure pushed Eastern Shoshone south and westward. Some of them moved as far south as Texas, emerging as the Comanche by 1700.Siouan language
Siouan or Siouan–Catawban is a language family of North America that is located primarily in the Great Plains, Ohio and Mississippi valleys and southeastern North America with a few other languages in the east.
Name
Authors who call the entire ...
speakers may have originated in the lower Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
region. They were agriculturalists and may have been part of the Mound Builder civilization during the 9th–12th centuries AD. In the late 16th and early 17th centuries, Dakota-Lakota
Lakota may refer to:
* Lakota people, a confederation of seven related Native American tribes
*Lakota language, the language of the Lakota peoples
Place names
In the United States:
* Lakota, Iowa
* Lakota, North Dakota, seat of Nelson County
* La ...
speakers lived in the upper Mississippi Region. Wars with the Ojibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
and Cree peoples pushed the Lakota west onto the Great Plains in the mid- to late-17th century.
During the 1640s and 1650s, the Beaver Wars initiated by the Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
forced a massive demographic shift as their western neighbors fled the violence. They sought refuge west and north of Lake Michigan.
Early Modern Europe
Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchm ...
in the 17th century was the last wave of the westward expansion of Central Asian nomads.
Internal European migration stepped up in the Early Modern Period. In this period, major migration within Europe included the recruiting by monarchs of landless laborers to settle depopulated or uncultivated regions and a series of forced migration caused by religious persecution. Notable examples of this phenomenon include the expulsion of the Jews from Spain
The Expulsion of Jews from Spain was the expulsion from Spain following the Alhambra Decree in 1492, which was enacted in order to eliminate their influence on Spain's large ''converso'' population and to ensure its members did not revert to Judai ...
in 1492, mass migration of Protestants from the Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands (Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a ''pars pro toto'') was the H ...
to the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
after the 1580s, the expulsion of the Moriscos
The Expulsion of the Moriscos ( es, Expulsión de los moriscos) was decreed by King Philip III of Spain on April 9, 1609. The Moriscos were descendants of Spain's Muslim population who had been forced to convert to Christianity. Since the Span ...
(descendants of former Muslims) from Spain in 1609, and the expulsion of the Huguenots
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Be ...
from France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
in the 1680s. Since the 14th century, the Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language.
The majority of Serbs live in their na ...
started leaving the areas of their medieval Kingdom and Empire that was overrun by the Ottoman Turks and migrated to the north, to the lands of today's Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, Војводина}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital ...
(northern Serbia), which was ruled by the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
at that time. The Habsburg monarchs of Austria encouraged them to settle on their frontier with the Turks and provide military service by granting them free land and religious toleration. The two greatest migrations took place in 1690 and 1737. Other instances of labour recruitments include the Plantations of Ireland – the settling of Ireland with Protestant colonists from England, Scotland and Wales in the period 1560–1690 and the recruitment of German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
s by Catherine the Great of Russia to settle the Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchm ...
region in the 18th century.
Colonial empires
 European
European Colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colony, colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose the ...
from the 16th to the early 20th centuries led to an imposition of a European colonies
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
in many regions of the world, particularly in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
, South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
, Sub-Saharan Africa and Australia, where European languages remain either prevalent or in frequent use as administrative languages. Major human migration before the 18th century was largely state directed. For instance, Spanish emigration to the New World was limited to settlers from Castile who were intended to act as soldiers or administrators. Mass immigration was not encouraged due to a labour shortage in Europe (of which Spain was the worst affected by a depopulation of its core territories in the 17th century).
Europeans also tended to die of tropical diseases in the New World in this period and for this reason England, France and Spain preferred using slaves as free labor in their American possessions. Many historians attribute a change in this pattern in the 18th century to population increases in Europe.
However, in the less tropical regions of North America's east coast, large numbers of religious dissidents, mostly English Puritans
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to purify the Church of England of Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become more Protestant. ...
, settled during the early 17th century. Spanish restrictions on emigration to Latin America were revoked and the English colonies in North America also saw a major influx of settlers attracted by cheap or free land, economic opportunity and the continued lure of religious toleration.
A period in which various early English colonies had a significant amount of self-rule prevailed from the time of the Plymouth colony's founding in 1620 through 1676, as the mother country was wracked by revolution and general instability. However, King William III decisively intervened in colonial affairs after 1688 and the English colonies gradually came more directly under royal governance, with a marked effect on the type of emigration. During the early 18th century, significant numbers of non-English seekers of greater religious and political freedom were allowed to settle within the British colonies, including Protestant German Palatines
Palatines (german: Pfälzer), also known as the Palatine Dutch, are the people and princes of Palatinates ( Holy Roman principalities) of the Holy Roman Empire. The Palatine diaspora includes the Pennsylvania Dutch and New York Dutch.
In 1709 ...
displaced by French conquest, French Huguenots disenfranchised by an end of religious tolerance, Scotch-Irish Presbyterians, Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's abil ...
who were often Welsh, as well as Presbyterian and Catholic Scottish Highlanders seeking a new start after a series of unsuccessful revolts.
Boers
Boers ( ; af, Boere ()) are the descendants of the Dutch-speaking Free Burghers of the eastern Cape frontier in Southern Africa during the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries. From 1652 to 1795, the Dutch East India Company controlled this are ...
arrived in southern Africa in the mid-17th century.
See also
*Linguistic homeland
In historical linguistics, the homeland or ''Urheimat'' (, from German '' ur-'' "original" and '' Heimat'', home) of a proto-language is the region in which it was spoken before splitting into different daughter languages. A proto-language is th ...
* Nomadic pastoralism
Nomadic pastoralism is a form of pastoralism in which livestock are herded in order to seek for fresh pastures on which to graze. True nomads follow an irregular pattern of movement, in contrast with transhumance, where seasonal pastures are fix ...
* Trans-cultural diffusion
In cultural anthropology and cultural geography, cultural diffusion, as conceptualized by Leo Frobenius in his 1897/98 publication ''Der westafrikanische Kulturkreis'', is the spread of cultural items—such as ideas, styles, religions, technolo ...
* Timeline of maritime migration and exploration
This timeline is an incomplete list of significant events of human migration and exploration by sea. This timeline does not include migration and exploration over land, including migration across land that has subsequently submerged beneath the s ...
Further reading
*References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Historical Migration Demographic history