Postmenopausal osteoporosis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of
 Osteoporosis itself has no symptoms; its main consequence is the increased risk of bone fractures. Osteoporotic fractures occur in situations where healthy people would not normally break a bone; they are therefore regarded as fragility fractures. Typical fragility fractures occur in the
Osteoporosis itself has no symptoms; its main consequence is the increased risk of bone fractures. Osteoporotic fractures occur in situations where healthy people would not normally break a bone; they are therefore regarded as fragility fractures. Typical fragility fractures occur in the
 There is an increased risk of falls associated with aging. These falls can lead to skeletal damage at the wrist, spine, hip, knee, foot, and ankle. Part of the fall risk is because of impaired eyesight due to many causes, (e.g.
There is an increased risk of falls associated with aging. These falls can lead to skeletal damage at the wrist, spine, hip, knee, foot, and ankle. Part of the fall risk is because of impaired eyesight due to many causes, (e.g.
 * The most important risk factors for osteoporosis are advanced age (in both men and women) and
* The most important risk factors for osteoporosis are advanced age (in both men and women) and
 Many diseases and disorders have been associated with osteoporosis. For some, the underlying mechanism influencing the bone metabolism is straightforward, whereas for others the causes are multiple or unknown.
* In general, immobilization causes bone loss (following the 'use it or lose it' rule). For example, localized osteoporosis can occur after prolonged immobilization of a fractured limb in a cast. This is also more common in active people with a high bone turn-over (for example, athletes). Other examples include bone loss during
Many diseases and disorders have been associated with osteoporosis. For some, the underlying mechanism influencing the bone metabolism is straightforward, whereas for others the causes are multiple or unknown.
* In general, immobilization causes bone loss (following the 'use it or lose it' rule). For example, localized osteoporosis can occur after prolonged immobilization of a fractured limb in a cast. This is also more common in active people with a high bone turn-over (for example, athletes). Other examples include bone loss during
 The underlying mechanism in all cases of osteoporosis is an imbalance between
The underlying mechanism in all cases of osteoporosis is an imbalance between
File:Osteoclast.jpg,
"Diagnosis of osteoporosis in men, premenopausal women, and children"
 Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
That is because patients with a fracture are more likely to experience a recurrent fracture, with marker increase in morbidity and mortality compared. Among the five bisphosphonates, no significant differences were found for a secondary fracture for all fracture endpoints combined. That being said, alendronate was identified as the most efficacious for secondary prevention of vertebral and hip fractures while zoledronate showed better performance for nonvertebral non-hip fracture prevention. There is concern that many people do not receive appropriate pharmacological therapy after a low-impact fracture. For those with osteoporosis but who have not had a fracture, evidence does not support a reduction in fracture risk with
 It is estimated that 200 million people have osteoporosis. Osteoporosis becomes more common with age. About 15% of Caucasians in their 50s and 70% of those over 80 are affected. It is more common in women than men. In the
It is estimated that 200 million people have osteoporosis. Osteoporosis becomes more common with age. About 15% of Caucasians in their 50s and 70% of those over 80 are affected. It is more common in women than men. In the
Handout on Health: Osteoporosis
nbsp; – US National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases
Osteoporosis
nbsp; – l NIH Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases – National Resource Center * * {{Authority control Aging-associated diseases Endocrine diseases Osteopathies Rheumatology Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate
bone tissue
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, a ...
leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone among the elderly. Bones that commonly break include the vertebrae
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristi ...
in the spine, the bones of the forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in ...
, and the hip. Until a broken bone occurs there are typically no symptoms. Bones may weaken to such a degree that a break may occur with minor stress or spontaneously. After the broken bone heals, the person may have chronic pain
Chronic pain is classified as pain that lasts longer than three to six months. In medicine, the distinction between acute and chronic pain is sometimes determined by the amount of time since onset. Two commonly used markers are pain that continue ...
and a decreased ability to carry out normal activities.
Osteoporosis may be due to lower-than-normal maximum bone mass and greater-than-normal bone loss. Bone loss increases after the menopause due to lower levels of estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
, and after ' andropause' due to lower levels of testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristi ...
. Osteoporosis may also occur due to a number of diseases or treatments, including alcoholism
Alcoholism is, broadly, any drinking of alcohol that results in significant mental or physical health problems. Because there is disagreement on the definition of the word ''alcoholism'', it is not a recognized diagnostic entity. Predomi ...
, anorexia
Anorexia nervosa, often referred to simply as anorexia, is an eating disorder characterized by low weight, food restriction, body image disturbance, fear of gaining weight, and an overpowering desire to be thin. ''Anorexia'' is a term of Gre ...
, hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidis ...
, kidney disease, and surgical removal of the ovaries. Certain medications increase the rate of bone loss, including some antiseizure medications, chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs ( chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemothe ...
, proton pump inhibitor
Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a class of medications that cause a profound and prolonged reduction of stomach acid production. They do so by irreversibly inhibiting the stomach's H+/K+ ATPase proton pump.
They are the most potent inhibitor ...
s, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and other psychological conditions.
SSRIs increase the extracellul ...
, and glucocorticosteroids. Smoking, and too little exercise are also risk factors. Osteoporosis is defined as a bone density
Bone density, or bone mineral density, is the amount of bone mineral in bone tissue. The concept is of mass of mineral per volume of bone (relating to density in the physics sense), although clinically it is measured by proxy according to optic ...
of 2.5 standard deviations below that of a young adult. This is typically measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA, or DEXA) is a means of measuring bone mineral density (BMD) using spectral imaging. Two X-ray beams, with different energy levels, are aimed at the patient's bones. When soft tissue absorption is subtracted ...
(DXA or DEXA).
Prevention of osteoporosis includes a proper diet during childhood, hormone replacement therapy
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), also known as menopausal hormone therapy or postmenopausal hormone therapy, is a form of hormone therapy used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause. These symptoms can include hot flashes, vaginal ...
for menopausal women, and efforts to avoid medications that increase the rate of bone loss. Efforts to prevent broken bones in those with osteoporosis include a good diet, exercise, and fall prevention
Fall prevention includes any action taken to help reduce the number of accidental falls suffered by susceptible individuals, such as the elderly (idiopathic) and people with neurological (Parkinson's, Multiple sclerosis, stroke survivors, Guilla ...
. Lifestyle changes such as stopping smoking and not drinking alcohol may help. Bisphosphonate medications are useful to decrease future broken bones in those with previous broken bones due to osteoporosis. In those with osteoporosis but no previous broken bones, they are less effective. They do not appear to affect the risk of death.
Osteoporosis becomes more common with age. About 15% of Caucasians in their 50s and 70% of those over 80 are affected. It is more common in women than men. In the developed world
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastruct ...
, depending on the method of diagnosis, 2% to 8% of males and 9% to 38% of females are affected. Rates of disease in the developing world are unclear. About 22 million women and 5.5 million men in the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
had osteoporosis in 2010. In the United States in 2010, about 8 million women and between 1 and 2 million men had osteoporosis. White and Asian people
Asian people (or Asians, sometimes referred to as Asiatic people)United States National Library of Medicine. Medical Subject Headings. 2004. November 17, 200Nlm.nih.gov: ''Asian Continental Ancestry Group'' is also used for categorical purpos ...
are at greater risk. The word "osteoporosis" is from the Greek terms for "porous bones".
Signs and symptoms
 Osteoporosis itself has no symptoms; its main consequence is the increased risk of bone fractures. Osteoporotic fractures occur in situations where healthy people would not normally break a bone; they are therefore regarded as fragility fractures. Typical fragility fractures occur in the
Osteoporosis itself has no symptoms; its main consequence is the increased risk of bone fractures. Osteoporotic fractures occur in situations where healthy people would not normally break a bone; they are therefore regarded as fragility fractures. Typical fragility fractures occur in the vertebral column
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord (a flexible rod of uniform composition) found in all chordate ...
, rib, hip and wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carp ...
.
Fractures
Fractures are a common symptom of osteoporosis and can result in disability. Acute and chronic pain in the elderly is often attributed to fractures from osteoporosis and can lead to further disability and early mortality. These fractures may also be asymptomatic. The most common osteoporotic fractures are of the wrist, spine, shoulder and hip. The symptoms of avertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristi ...
l collapse (" compression fracture") are sudden back pain
Back pain is pain felt in the back. It may be classified as neck pain (cervical), middle back pain (thoracic), lower back pain (lumbar) or coccydynia (tailbone or sacral pain) based on the segment affected. The lumbar area is the most common ...
, often with radicular pain
Radicular pain, or radiculitis, is pain "radiated" along the dermatome (sensory distribution) of a nerve due to inflammation or other irritation of the nerve root (radiculopathy) at its connection to the spinal column. A common form of radiculit ...
(shooting pain due to nerve root compression) and rarely with spinal cord compression or cauda equina syndrome
Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is a condition that occurs when the bundle of nerves below the end of the spinal cord known as the cauda equina is damaged. Signs and symptoms include low back pain, pain that radiates down the leg, numbness around ...
. Multiple vertebral fractures lead to a stooped posture, loss of height, and chronic pain with resultant reduction in mobility.
Fractures of the long bones acutely impair mobility and may require surgery. Hip fracture
A hip fracture is a break that occurs in the upper part of the femur (thigh bone). Symptoms may include pain around the hip, particularly with movement, and shortening of the leg. Usually the person cannot walk.
They most often occur as a res ...
, in particular, usually requires prompt surgery, as serious risks are associated with it, such as deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enla ...
and pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream ( embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include shortness of breath, chest pain particularly upon breathin ...
, and increased mortality.
Fracture risk calculators assess the risk of fracture based upon several criteria, including bone mineral density, age, smoking, alcohol usage, weight, and gender. Recognized calculators include FRAX
FRAX (Fracture Risk Assessment Tool) is a diagnostic tool used to evaluate the 10-year probability of bone fracture risk. It was developed by the University of Sheffield. FRAX integrates clinical risk factors and bone mineral density at the femora ...
, the Garvan FRC calculator and QFracture as well as the open access FREM tool. The FRAX tool can also be applied in a modification adapted to routinely collected health data.
The term "established osteoporosis" is used when a broken bone due to osteoporosis has occurred. Osteoporosis is a part of frailty syndrome
Frailty is a common geriatric syndrome that embodies an elevated risk of catastrophic declines in health and function among older adults. Frailty is a condition associated with ageing, and it has been recognized for centuries. It is also a marker ...
.
Risk of falls
 There is an increased risk of falls associated with aging. These falls can lead to skeletal damage at the wrist, spine, hip, knee, foot, and ankle. Part of the fall risk is because of impaired eyesight due to many causes, (e.g.
There is an increased risk of falls associated with aging. These falls can lead to skeletal damage at the wrist, spine, hip, knee, foot, and ankle. Part of the fall risk is because of impaired eyesight due to many causes, (e.g. glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that result in damage to the optic nerve (or retina) and cause vision loss. The most common type is open-angle (wide angle, chronic simple) glaucoma, in which the drainage angle for fluid within the eye rem ...
, macular degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred or no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Over time, however, som ...
), balance disorder
A balance disorder is a disturbance that causes an individual to feel unsteady, for example when standing or walking. It may be accompanied by feelings of giddiness, or wooziness, or having a sensation of movement, spinning, or floating. Balance ...
, movement disorder
Movement disorder refers to any clinical syndrome with either an excess of movement or a paucity of voluntary and involuntary movements, unrelated to weakness or spasticity. Movement disorders are synonymous with basal ganglia or extrapyramidal ...
s (e.g. Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms becom ...
), dementia
Dementia is a disorder which manifests as a set of related symptoms, which usually surfaces when the brain is damaged by injury or disease. The symptoms involve progressive impairments in memory, thinking, and behavior, which negatively affe ...
, and sarcopenia (age-related loss of skeletal muscle). Collapse (transient loss of postural tone with or without loss of consciousness). Causes of syncope are manifold, but may include cardiac arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults ...
s (irregular heart beat), vasovagal syncope, orthostatic hypotension
Orthostatic hypotension, also known as postural hypotension, is a medical condition wherein a person's blood pressure drops when standing up or sitting down. Primary orthostatic hypertension is also often referred to as neurogenic orthostatic hyp ...
(abnormal drop in blood pressure on standing up), and seizure
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with l ...
s. Removal of obstacles and loose carpets in the living environment may substantially reduce falls. Those with previous falls, as well as those with gait or balance disorders, are most at risk.
Complication
As well as susceptibility to breaks and fractures, osteoporosis can lead to other complications. Bone fractures which are results from osteoporosis can lead to disability and even an increased chance of death after the injury. Depression is considered to a complication of osteoporosis. People with osteoporosis lose independence and risk being isolated due to less physical activity. This will further hinder the ability to manage health issues. Osteoporosis is also linked to respiratory and cardiovascular health issues, such as loss of lung capacity. Multiple fractures lead to a collapsed thoracic spine, which makes less air being able to move into the lungs. Every thoracic vertebral body collapsed results in the loss of nearly 10% of lung volume.Risk factors
Risk factors for osteoporotic fracture can be split between nonmodifiable and (potentially) modifiable. In addition, osteoporosis is a recognized complication of specific diseases and disorders. Medication use is theoretically modifiable, although in many cases, the use of medication that increases osteoporosis risk may be unavoidable.Caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine class. It is mainly used recreationally as a cognitive enhancer, increasing alertness and attentional performance. Caffeine acts by blocking binding of adenosine to ...
is not a risk factor for osteoporosis.
Nonmodifiable
 * The most important risk factors for osteoporosis are advanced age (in both men and women) and
* The most important risk factors for osteoporosis are advanced age (in both men and women) and female
Female ( symbol: ♀) is the sex of an organism that produces the large non-motile ova (egg cells), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete during sexual reproduction.
A female has larger gametes than a male. Females ...
sex; estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
deficiency following menopause or surgical removal of the ovaries is correlated with a rapid reduction in bone mineral density, while in men, a decrease in testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristi ...
levels has a comparable (but less pronounced) effect.
* Ethnicity: While osteoporosis occurs in people from all ethnic groups, European or Asian ancestry predisposes for osteoporosis.
* Heredity: Those with a family history
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kin ...
of fracture or osteoporosis are at an increased risk; the heritability of the fracture, as well as low bone mineral density, is relatively high, ranging from 25 to 80%. At least 30 genes are associated with the development of osteoporosis.
* Those who have already had a fracture are at least twice as likely to have another fracture compared to someone of the same age and sex.
* Build: A small stature is also a nonmodifiable risk factor associated with the development of osteoporosis.
Potentially modifiable
* Excessive alcohol: Although small amounts of alcohol might be beneficial (bone density increases with increasing alcohol intake, although the link has not been conclusively shown as causal), chronic heavy drinking (alcohol intake greater than three units/day) probably increases fracture risk despite any beneficial effects on bone density. *Vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency or hypovitaminosis D is a vitamin D level that is below normal. It most commonly occurs in people when they have inadequate exposure to sunlight, particularly sunlight with adequate ultraviolet B rays (UVB). Vitamin D defic ...
: Low circulating Vitamin D is common among the elderly worldwide. Mild vitamin D insufficiency is associated with increased parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid hormone (PTH), also called parathormone or parathyrin, is a peptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that regulates the serum calcium concentration through its effects on bone, kidney, and intestine.
PTH influences bone ...
(PTH) production. PTH increases bone resorption, leading to bone loss. A positive association exists between serum 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
Calcitriol is the active form of vitamin D, normally made in the kidney. It is also known as 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. It is a hormone which binds to and activates the vitamin D receptor in the nucleus of the cell, which then increases the ...
levels and bone mineral density, while PTH is negatively associated with bone mineral density.
* Tobacco smoking
Tobacco smoking is the practice of burning tobacco and ingesting the resulting smoke. The smoke may be inhaled, as is done with cigarettes, or simply released from the mouth, as is generally done with pipes and cigars. The practice is believed ...
: Many studies have associated smoking with decreased bone health, but the mechanisms are unclear. Tobacco smoking has been proposed to inhibit the activity of osteoblasts, and is an independent risk factor for osteoporosis. Smoking also results in increased breakdown of exogenous estrogen, lower body weight and earlier menopause, all of which contribute to lower bone mineral density.
* Malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues ...
: Nutrition has an important and complex role in maintenance of good bone. Identified risk factors include low dietary calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
and/or phosphorus, magnesium, zinc, boron, iron, fluoride, copper, vitamins A, K, E and C (and D where skin exposure to sunlight provides an inadequate supply). Excess sodium is a risk factor. High blood acidity may be diet-related, and is a known antagonist of bone. Some have identified low protein intake as associated with lower peak bone mass during adolescence and lower bone mineral density in elderly populations. Conversely, some have identified low protein intake as a positive factor, protein is among the causes of dietary acidity. Imbalance of omega-6 to omega-3 polyunsaturated fats is yet another identified risk factor.
* A diet high in protein may be optimal for bone health, as higher protein diets tend to increase absorption of calcium from the diet and are associated with higher bone density. No interventional trials have been performed on dietary protein in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis A meta-analysis of published medical studies shows that higher protein diet helps slightly with lower spine density but does not show significant improvement with other bones.
* Underweight
An underweight person is a person whose body weight is considered too low to be healthy. A person who is underweight is malnourished.
Assessment
The body mass index, a ratio of a person's weight to their height, has traditionally been used ...
/inactive
Inactive is a TRPV channel in invertebrates
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a groupin ...
: Bone remodeling
Bone remodeling (or bone metabolism) is a lifelong process where mature bone tissue is removed from the skeleton (a process called ''bone resorption'') and new bone tissue is formed (a process called ''ossification'' or ''new bone formation''). ...
occurs in response to physical stress, so physical inactivity can lead to significant bone loss. Weight bearing In orthopedics, weight-bearing is the amount of weight a patient puts on an injured body part. Generally, it refers to a leg, ankle or foot that has been fractured or upon which surgery has been performed, but the term can also be used to refer to ...
exercise can increase peak bone mass achieved in adolescence, and a highly significant correlation between bone strength and muscle strength has been determined. The incidence of osteoporosis is lower in overweight people.
* Endurance training: In female endurance athletes, large volumes of training can lead to decreased bone density and an increased risk of osteoporosis. This effect might be caused by intense training suppressing menstruation, producing amenorrhea
Amenorrhea is the absence of a menstrual period in a woman of reproductive age. Physiological states of amenorrhoea are seen, most commonly, during pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding). Outside the reproductive years, there is absence of menses ...
, and it is part of the female athlete triad
Relative energy deficiency in sport (RED-S) is a syndrome in which disordered eating (or ''low energy availability''), amenorrhoea/ oligomenorrhoea (in women), and decreased bone mineral density (osteoporosis and osteopenia) are present. It is ca ...
. However, for male athletes, the situation is less clear, and although some studies have reported low bone density in elite male endurance athletes, others have instead seen increased leg bone density.
* Heavy metals: A strong association between cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Like zinc, it demonstrates oxidation state +2 in most of ...
and lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
with bone disease has been established. Low-level exposure to cadmium is associated with an increased loss of bone mineral density readily in both genders, leading to pain and increased risk of fractures, especially in the elderly and in females. Higher cadmium exposure results in osteomalacia
Osteomalacia is a disease characterized by the softening of the bones caused by impaired bone metabolism primarily due to inadequate levels of available phosphate, calcium, and vitamin D, or because of resorption of calcium. The impairment of bon ...
(softening of the bone).
* Soft drinks: Some studies indicate soft drinks (many of which contain phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid (orthophosphoric acid, monophosphoric acid or phosphoric(V) acid) is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, w ...
) may increase risk of osteoporosis, at least in women
A woman is an adult female human. Prior to adulthood, a female human is referred to as a girl (a female child or adolescent). The plural ''women'' is sometimes used in certain phrases such as "women's rights" to denote female humans regardl ...
. Others suggest soft drinks may displace calcium-containing drinks from the diet rather than directly causing osteoporosis.
* Proton pump inhibitors
Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a class of medications that cause a profound and prolonged reduction of stomach acid production. They do so by irreversibly inhibiting the stomach's H+/K+ ATPase proton pump.
They are the most potent inhibitor ...
(such as lansoprazole
Lansoprazole, sold under the brand name Prevacid among others, is a medication which reduces stomach acid. It is used to treat peptic ulcer disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and Zollinger–Ellison syndrome. Effectiveness is similar to ...
, esomeprazole
Esomeprazole, sold under the brand name Nexium among others, is a medication which reduces stomach acid. It is used to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease, peptic ulcer disease, and Zollinger–Ellison syndrome. Effectiveness is similar to ...
, and omeprazole
Omeprazole, sold under the brand names Prilosec and Losec, among others, is a medication used in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcer disease, and Zollinger–Ellison syndrome. It is also used to prevent upp ...
), which decrease the production of stomach acid
Gastric acid, gastric juice, or stomach acid is a digestive fluid formed within the stomach lining. With a pH between 1 and 3, gastric acid plays a key role in digestion of proteins by activating digestive enzymes, which together break down the ...
, are a risk factor for bone fractures if taken for two or more years, due to decreased absorption of calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
in the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
.
Medical disorders
 Many diseases and disorders have been associated with osteoporosis. For some, the underlying mechanism influencing the bone metabolism is straightforward, whereas for others the causes are multiple or unknown.
* In general, immobilization causes bone loss (following the 'use it or lose it' rule). For example, localized osteoporosis can occur after prolonged immobilization of a fractured limb in a cast. This is also more common in active people with a high bone turn-over (for example, athletes). Other examples include bone loss during
Many diseases and disorders have been associated with osteoporosis. For some, the underlying mechanism influencing the bone metabolism is straightforward, whereas for others the causes are multiple or unknown.
* In general, immobilization causes bone loss (following the 'use it or lose it' rule). For example, localized osteoporosis can occur after prolonged immobilization of a fractured limb in a cast. This is also more common in active people with a high bone turn-over (for example, athletes). Other examples include bone loss during space flight
Spaceflight (or space flight) is an application of astronautics to fly spacecraft into or through outer space, either with or without humans on board. Most spaceflight is uncrewed and conducted mainly with spacecraft such as satellites in ...
or in people who are bedridden or use wheelchairs for various reasons.
* Hypogonadal states can cause secondary osteoporosis. These include Turner syndrome
Turner syndrome (TS), also known as 45,X, or 45,X0, is a genetic condition in which a female is partially or completely missing an X chromosome. Signs and symptoms vary among those affected. Often, a short and webbed neck, low-set ears, low hair ...
, Klinefelter syndrome
Klinefelter syndrome (KS), also known as 47,XXY, is an aneuploid genetic condition where a male has an additional copy of the X chromosome. The primary features are infertility and small, poorly functioning testicles. Usually, symptoms are sub ...
, Kallmann syndrome
Kallmann syndrome (KS) is a genetic disorder that prevents a person from starting or fully completing puberty. Kallmann syndrome is a form of a group of conditions termed hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. To distinguish it from other forms of hypog ...
, anorexia nervosa
Anorexia nervosa, often referred to simply as anorexia, is an eating disorder characterized by low weight, food restriction, body image disturbance, fear of gaining weight, and an overpowering desire to be thin. ''Anorexia'' is a term of Gr ...
, andropause, hypothalamic amenorrhea or hyperprolactinemia
Hyperprolactinaemia is the presence of abnormally high levels of prolactin in the blood. Normal levels average to about 13 ng/mL in women, and 5 ng/mL in men, with an upper normal limit of serum prolactin levels being 15-25 ng/mL ...
. In females, the effect of hypogonadism is mediated by estrogen deficiency. It can appear as early menopause (<45 years) or from prolonged premenopausal amenorrhea (>1 year). Bilateral oophorectomy
Oophorectomy (; from Greek , , 'egg-bearing' and , , 'a cutting out of'), historically also called ''ovariotomy'' is the surgical removal of an ovary or ovaries. The surgery is also called ovariectomy, but this term is mostly used in reference ...
(surgical removal of the ovaries) and premature ovarian failure cause deficient estrogen production. In males, testosterone deficiency is the cause (for example, andropause or after surgical removal of the testes
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testoste ...
).
* Endocrine disorders that can induce bone loss include Cushing's syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, a ...
, hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is an increase in parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels in the blood. This occurs from a disorder either within the parathyroid glands (primary hyperparathyroidism) or as response to external stimuli (secondary hyperparathyroidism). ...
, hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidis ...
, hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
type 1 and 2, acromegaly, and adrenal insufficiency.
* Malnutrition, parenteral nutrition
Parenteral nutrition (PN) is the feeding of nutritional products to a person intravenously, bypassing the usual process of eating and digestion. The products are made by pharmaceutical compounding companies. The person receives a nutritional mi ...
and malabsorption
Malabsorption is a state arising from abnormality in absorption of food nutrients across the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Impairment can be of single or multiple nutrients depending on the abnormality. This may lead to malnutrition and a variety ...
can lead to osteoporosis. Nutritional and gastrointestinal disorders that can predispose to osteoporosis include undiagnosed and untreated coeliac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barle ...
(both symptomatic and asymptomatic people), Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a long-term condition that results in inflammation and ulcers of the colon and rectum. The primary symptoms of active disease are abdominal pain and diarrhea mixed with blood (hematochezia). Weight loss, fever, and ...
, cystic fibrosis, surgery (after gastrectomy, intestinal bypass surgery or bowel resection) and severe liver disease
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
Signs and symptoms
Some of the si ...
(especially primary biliary cirrhosis). People with lactose intolerance
Lactose intolerance is a common condition caused by a decreased ability to digest lactose, a sugar found in dairy products. Those affected vary in the amount of lactose they can tolerate before symptoms develop. Symptoms may include abdominal pai ...
or milk allergy
Milk allergy is an adverse immune reaction to one or more proteins in cow's milk. Among the possible symptoms is anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening condition that requires treatment with Epinephrine (medication), epinephrine, among o ...
may develop osteoporosis due to restrictions of calcium-containing foods. Individuals with bulimia
Bulimia nervosa, also known as simply bulimia, is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating followed by purging or fasting, and excessive concern with body shape and weight. The aim of this activity is to expel the body of calories eaten ...
can also develop osteoporosis. Those with an otherwise adequate calcium intake can develop osteoporosis due to the inability to absorb calcium and/or vitamin D. Other micronutrients such as vitamin K
Vitamin K refers to structurally similar, fat-soluble vitamers found in foods and marketed as dietary supplements. The human body requires vitamin K for post-synthesis modification of certain proteins that are required for blood coagulation ...
or vitamin B12 deficiency may also contribute.
* People with rheumatologic disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are invol ...
, ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine typically where the spine joins the pelvis. Occasionally areas affected may include other joints such as the shoulders or hi ...
, systemic lupus erythematosus and polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) is the most common, chronic rheumatic disease of childhood, affecting approximately one per 1,000 children. ''Juvenile'', in this context, refers to disease onset before 16 years of age, while ''idiopathic'' r ...
are at increased risk of osteoporosis, either as part of their disease or because of other risk factors (notably corticosteroid therapy). Systemic diseases such as amyloidosis and sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (also known as ''Besnier-Boeck-Schaumann disease'') is a disease involving abnormal collections of inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly a ...
can also lead to osteoporosis.
* Chronic kidney disease can lead to renal osteodystrophy
Renal osteodystrophy/adynamic bone disease is currently defined as an alteration of bone morphology in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). It is one measure of the skeletal component of the systemic disorder of chronic kidney disease-min ...
.
* Hematologic disorders linked to osteoporosis are multiple myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies, lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enla ...
, leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ...
, mastocytosis
Mastocytosis, a type of mast cell disease, is a rare disorder affecting both children and adults caused by the accumulation of functionally defective mast cells (also called ''mastocytes'') and CD34+ mast cell precursors.
People affected by mas ...
, hemophilia, sickle-cell disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of blood disorders typically inherited from a person's parents. The most common type is known as sickle cell anaemia. It results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red blo ...
and thalassemia.
* Several inherited or genetic disorders have been linked to osteoporosis. These include osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta (; OI), colloquially known as brittle bone disease, is a group of genetic disorders that all result in bones that break easily. The range of symptoms—on the skeleton as well as on the body's other organs—may b ...
, Multicentric carpotarsal osteolysis syndrome, Multicentric Osteolysis, Nodulosis, and Arthropathy, Marfan syndrome, hemochromatosis
Iron overload or hemochromatosis (also spelled ''haemochromatosis'' in British English) indicates increased total accumulation of iron in the body from any cause and resulting organ damage. The most important causes are hereditary haemochromatos ...
, hypophosphatasia (for which it is often misdiagnosed), glycogen storage diseases, homocystinuria
Homocystinuria or HCU is an inherited disorder of the metabolism of the amino acid methionine due to a deficiency of cystathionine beta synthase or methionine synthase. It is an inherited autosomal recessive trait, which means a child needs to i ...
, Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, porphyria
Porphyria is a group of liver disorders in which substances called porphyrins build up in the body, negatively affecting the skin or nervous system. The types that affect the nervous system are also known as acute porphyria, as symptoms are ...
, Menkes' syndrome, epidermolysis bullosa
Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is a group of rare medical conditions that result in easy blistering of the skin and mucous membranes. Blisters occur with minor trauma or friction and are painful. Its severity can range from mild to fatal. Inherited E ...
and Gaucher's disease
Gaucher's disease or Gaucher disease () (GD) is a genetic disorder in which glucocerebroside (a sphingolipid, also known as glucosylceramide) accumulates in cells and certain organs. The disorder is characterized by bruising, fatigue, anemia, low ...
.
* People with scoliosis of unknown cause also have a higher risk of osteoporosis. Bone loss can be a feature of complex regional pain syndrome. It is also more frequent in people with Parkinson's disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce ...
.
* People with Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms becom ...
have a higher risk of broken bones. This is related to poor balance and poor bone density. In Parkinson's disease there may be a link between the loss of dopaminergic neuron
Dopaminergic cell groups, DA cell groups, or dopaminergic nuclei are collections of neurons in the central nervous system that synthesize the neurotransmitter dopamine. In the 1960s, dopaminergic neurons or ''dopamine neurons'' were first ident ...
s and altered calcium metabolism
Calcium metabolism is the movement and regulation of calcium ions (Ca2+) ''in'' (via the gut) and ''out'' (via the gut and kidneys) of the body, and ''between'' body compartments: the blood plasma, the extracellular and intracellular fluids, and ...
(and iron metabolism
Human iron metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that maintain human homeostasis of iron at the systemic and cellular level. Iron is both necessary to the body and potentially toxic. Controlling iron levels in the body is a critically impo ...
) causing a stiffening of the skeleton and kyphosis
Kyphosis is an abnormally excessive convex curvature of the spine as it occurs in the thoracic and sacral regions. Abnormal inward concave ''lordotic'' curving of the cervical and lumbar regions of the spine is called lordosis. It can result ...
.
Medication
Certain medications have been associated with an increase in osteoporosis risk; only glucocorticosteroids and anticonvulsants are classically associated, but evidence is emerging with regard to other drugs. *Steroid-induced osteoporosis
Steroid-induced osteoporosis is osteoporosis arising from the use of glucocorticoids (a class of steroid hormones) analogous to Cushing's syndrome but involving mainly the axial skeleton. The synthetic glucocorticoid prescription drug prednisone ...
(SIOP) arises due to use of glucocorticoids – analogous to Cushing's syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, a ...
and involving mainly the axial skeleton. The synthetic glucocorticoid prescription drug prednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium due to cancer and ad ...
is a main candidate after prolonged intake. Some professional guidelines recommend prophylaxis in patients who take the equivalent of more than 30 mg hydrocortisone (7.5 mg of prednisolone), especially when this is in excess of three months. It is recommended to use calcium or Vitamin D as prevention. Alternate day use may not prevent this complication.
* Barbiturates, phenytoin
Phenytoin (PHT), sold under the brand name Dilantin among others, is an anti-seizure medication. It is useful for the prevention of tonic-clonic seizures (also known as grand mal seizures) and focal seizures, but not absence seizures. The in ...
and some other enzyme-inducing antiepileptics – these probably accelerate the metabolism of vitamin D.
* L-Thyroxine over-replacement may contribute to osteoporosis, in a similar fashion as thyrotoxicosis does. This can be relevant in subclinical hypothyroidism.
* Several drugs induce hypogonadism, for example aromatase inhibitors
Aromatase inhibitors (AIs) are a class of drugs used in the treatment of breast cancer in postmenopausal women and in men, and gynecomastia in men. They may also be used off-label to reduce estrogen conversion when supplementing testosterone ...
used in breast cancer, methotrexate and other antimetabolite drugs, depot progesterone and gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist
A gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist (GnRH agonist) is a type of medication which affects gonadotropins and sex hormones. They are used for a variety of indications including in fertility medicine and to lower sex hormone levels in the treatm ...
s.
* Anticoagulants – long-term use of heparin is associated with a decrease in bone density, and warfarin
Warfarin, sold under the brand name Coumadin among others, is a medication that is used as an anticoagulant (blood thinner). It is commonly used to prevent blood clots such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, and to prevent st ...
(and related coumarins) have been linked with an increased risk in osteoporotic fracture in long-term use.
* Proton pump inhibitors
Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a class of medications that cause a profound and prolonged reduction of stomach acid production. They do so by irreversibly inhibiting the stomach's H+/K+ ATPase proton pump.
They are the most potent inhibitor ...
– these drugs inhibit the production of stomach acid
Gastric acid, gastric juice, or stomach acid is a digestive fluid formed within the stomach lining. With a pH between 1 and 3, gastric acid plays a key role in digestion of proteins by activating digestive enzymes, which together break down the ...
; this is thought to interfere with calcium absorption. Chronic phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
binding may also occur with aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
-containing antacids
An antacid is a substance which neutralizes stomach acidity and is used to relieve heartburn, indigestion or an upset stomach. Some antacids have been used in the treatment of constipation and diarrhea. Marketed antacids contain salts of alu ...
.
* Thiazolidinedione
The thiazolidinediones , abbreviated as TZD, also known as glitazones after the prototypical drug ciglitazone, are a class of heterocyclic compounds consisting of a five-membered C3NS ring. The term usually refers to a family of drugs used i ...
s (used for diabetes) – rosiglitazone
Rosiglitazone (trade name Avandia) is an antidiabetic drug in the thiazolidinedione class. It works as an insulin sensitizer, by binding to the PPAR in fat cells and making the cells more responsive to insulin. It is marketed by the pharmaceutica ...
and possibly pioglitazone
Pioglitazone, sold under the brand name Actos among others, is an anti-diabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It may be used with metformin, a sulfonylurea, or insulin. Use is recommended together with exercise and diet. It is not re ...
, inhibitors of PPARγ
Peroxisome proliferator- activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ or PPARG), also known as the glitazone reverse insulin resistance
receptor, or NR1C3 (nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group C, member 3) is a type II nuclear receptor functioning as a tran ...
, have been linked with an increased risk of osteoporosis and fracture.
* Chronic lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid ...
therapy has been associated with osteoporosis.
Evolutionary
Age-related bone loss is common among humans due to exhibiting less dense bones than other primate species. Because of the more porous bones of humans, frequency of severe osteoporosis and osteoporosis related fractures is higher. The human vulnerability to osteoporosis is an obvious cost but it can be justified by the advantage of bipedalism inferring that this vulnerability is the byproduct of such. It has been suggested that porous bones help to absorb the increased stress that we have on two surfaces compared to our primate counterparts who have four surfaces to disperse the force. In addition, the porosity allows for more flexibility and a lighter skeleton that is easier to support. One other consideration may be that diets today have much lower amounts of calcium than the diets of other primates or the tetrapedal ancestors to humans which may lead to higher likelihood to show signs of osteoporosis.Fracture risk assessment
In the absence of risk factors other than sex and age a BMD measurement using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is recommended for women at age 65. For women with risk factors a clinical FRAX is advised at age 50.Pathogenesis
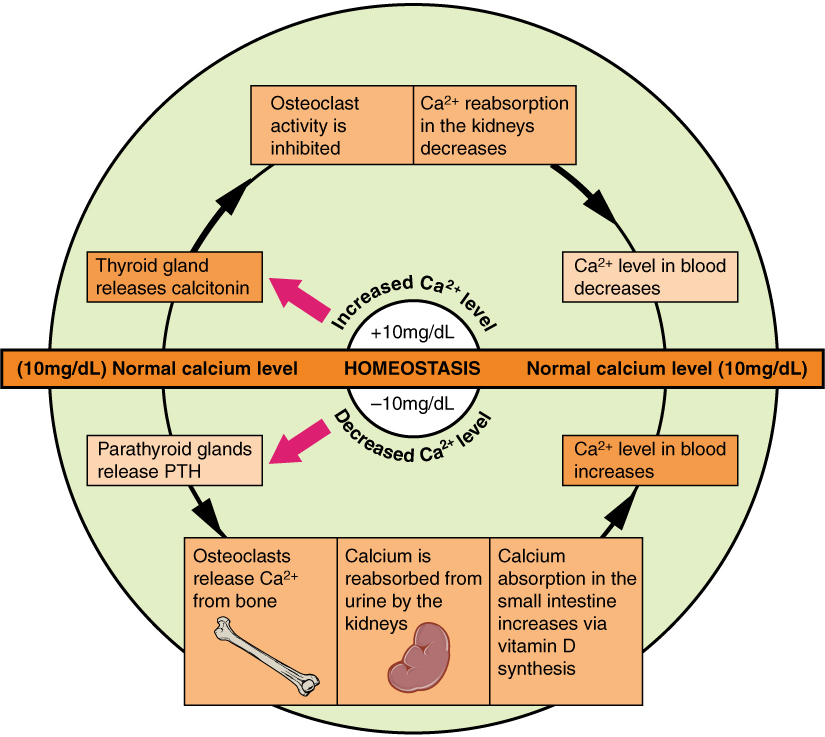
 The underlying mechanism in all cases of osteoporosis is an imbalance between
The underlying mechanism in all cases of osteoporosis is an imbalance between bone resorption
Bone resorption is resorption of bone tissue, that is, the process by which osteoclasts break down the tissue in bones and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone tissue to the blood.
The osteoclasts are multi-nuclea ...
and bone formation
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in th ...
. In normal bone, matrix remodeling of bone is constant; up to 10% of all bone mass may be undergoing remodeling at any point in time. The process takes place in bone multicellular units (BMUs) as first described by Frost & Thomas in 1963. Osteoclasts are assisted by transcription factor PU.1 to degrade the bone matrix, while osteoblasts
Osteoblasts (from the Greek combining forms for "bone", ὀστέο-, ''osteo-'' and βλαστάνω, ''blastanō'' "germinate") are cells with a single nucleus that synthesize bone. However, in the process of bone formation, osteoblasts function ...
rebuild the bone matrix. Low bone mass density can then occur when osteoclasts are degrading the bone matrix faster than the osteoblasts are rebuilding the bone.
The three main mechanisms by which osteoporosis develops are an inadequate peak bone mass (the skeleton develops insufficient mass and strength during growth), excessive bone resorption, and inadequate formation of new bone during remodeling, likely due to mesenchymal stem cells biasing away from the osteoblast and toward the marrow adipocyte lineage. An interplay of these three mechanisms underlies the development of fragile bone tissue. Hormonal factors strongly determine the rate of bone resorption; lack of estrogen (e.g. as a result of menopause) increases bone resorption, as well as decreasing the deposition of new bone that normally takes place in weight-bearing bones. The amount of estrogen needed to suppress this process is lower than that normally needed to stimulate the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The ...
and breast gland. The α-form of the estrogen receptor
Estrogen receptors (ERs) are a group of proteins found inside cells. They are receptors that are activated by the hormone estrogen (17β-estradiol). Two classes of ER exist: nuclear estrogen receptors ( ERα and ERβ), which are members of the ...
appears to be the most important in regulating bone turnover. In addition to estrogen, calcium metabolism
Calcium metabolism is the movement and regulation of calcium ions (Ca2+) ''in'' (via the gut) and ''out'' (via the gut and kidneys) of the body, and ''between'' body compartments: the blood plasma, the extracellular and intracellular fluids, and ...
plays a significant role in bone turnover, and deficiency of calcium and vitamin D leads to impaired bone deposition; in addition, the parathyroid gland
Parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands in the neck of humans and other tetrapods. Humans usually have four parathyroid glands, located on the back of the thyroid gland in variable locations. The parathyroid gland produces and secretes pa ...
s react to low calcium levels by secreting parathyroid hormone (parathormone, PTH), which increases bone resorption to ensure sufficient calcium in the blood. The role of calcitonin
Calcitonin is a 32 amino acid peptide hormone secreted by parafollicular cells (also known as C cells) of the thyroid (or endostyle) in humans and other chordates. in the ultimopharyngeal body. It acts to reduce blood calcium (Ca2+), opposing th ...
, a hormone generated by the thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thy ...
that increases bone deposition, is less clear and probably not as significant as that of PTH.
The activation of osteoclasts is regulated by various molecular signals, of which RANKL
Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa- ligand (RANKL), also known as tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11 (TNFSF11), TNF-related activation-induced cytokine (TRANCE), osteoprotegerin ligand (OPGL), and osteoclast differentiati ...
(receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand) is one of the best-studied. This molecule is produced by osteoblasts and other cells (e.g. lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic ad ...
s), and stimulates RANK
Rank is the relative position, value, worth, complexity, power, importance, authority, level, etc. of a person or object within a ranking, such as:
Level or position in a hierarchical organization
* Academic rank
* Diplomatic rank
* Hierarchy
* ...
(receptor activator of nuclear factor κB). Osteoprotegerin
Osteoprotegerin (OPG), also known as osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor (OCIF) or tumour necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 11B (TNFRSF11B), is a cytokine receptor of the tumour necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily encoded by the ...
(OPG) binds RANKL before it has an opportunity to bind to RANK, and hence suppresses its ability to increase bone resorption. RANKL, RANK, and OPG are closely related to tumor necrosis factor
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
and its receptors. The role of the Wnt signaling pathway
The Wnt signaling pathways are a group of signal transduction pathways which begin with proteins that pass signals into a cell through cell surface receptors. The name Wnt is a portmanteau created from the names Wingless and Int-1. Wnt signaling ...
is recognized, but less well understood. Local production of eicosanoid
Eicosanoids are signaling molecules made by the enzymatic or non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid or other polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) that are, similar to arachidonic acid, around 20 carbon units in length. Eicosanoids are a s ...
s and interleukin
Interleukins (ILs) are a group of cytokines (secreted proteins and signal molecules) that are expressed and secreted by white blood cells (leukocytes) as well as some other body cells. The human genome encodes more than 50 interleukins and related ...
s is thought to participate in the regulation of bone turnover, and excess or reduced production of these mediators may underlie the development of osteoporosis. Osteoclast maturation and activity is also regulated by activation of colony stimulating factor 1 receptor
Colony stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R), also known as macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor (M-CSFR), and CD115 (Cluster of Differentiation 115), is a cell-surface protein encoded by the human ''CSF1R'' gene (known also as c-FMS). CS ...
(CSF1R). Menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often ...
-associated increase production of TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
stimulates stromal cells to produce colony stimulating factor 1
The colony stimulating factor 1 (CSF1), also known as macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), is a secreted cytokine which causes hematopoietic stem cells to differentiate into macrophages or other related cell types. Eukaryotic cells also ...
(CSF-1) which activates CSF1R and stimulates osteoclasts to reabsorb bone.
Trabecular bone
A trabecula (plural trabeculae, from Latin for "small beam") is a small, often microscopic, tissue element in the form of a small beam, strut or rod that supports or anchors a framework of parts within a body or organ. A trabecula generally has ...
(or cancellous bone) is the sponge-like bone in the ends of long bones and vertebrae. Cortical bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and ...
is the hard outer shell of bones and the middle of long bones. Because osteoblasts and osteoclasts inhabit the surface of bones, trabecular bone is more active and is more subject to bone turnover and remodeling. Not only is bone density decreased, but the microarchitecture of bone is also disrupted. The weaker spicules of trabecular bone break ("microcracks"), and are replaced by weaker bone. Common osteoporotic fracture sites, the wrist, the hip, and the spine, have a relatively high trabecular bone to cortical bone ratio. These areas rely on the trabecular bone for strength, so the intense remodeling causes these areas to degenerate most when the remodeling is imbalanced. Around the ages of 30–35, cancellous or trabecular bone loss begins. Women may lose as much as 50%, while men lose about 30%.
Light micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a mi ...
of an osteoclast
An osteoclast () is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bones of the vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests the composite of hydrated pro ...
displaying typical distinguishing characteristics: a large cell with multiple nuclei and a "foamy" cytosol.
File:Active osteoblasts.jpg, Light micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a mi ...
of osteoblasts, several displaying a prominent Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles ...
, actively synthesizing osteoid
In histology, osteoid is the unmineralized, organic portion of the bone matrix that forms prior to the maturation of bone tissue. Osteoblasts begin the process of forming bone tissue by secreting the osteoid as several specific proteins. When ...
containing two osteocyte
An osteocyte, an oblate shaped type of bone cell with dendritic processes, is the most commonly found cell in mature bone. It can live as long as the organism itself. The adult human body has about 42 billion of them. Osteocytes do not divide an ...
s.
File:722 Feature Osteoprosis of Spine.jpg, Collapse of vertebra on the right, normal on the left
Diagnosis
Osteoporosis can be diagnosed using conventional radiography and by measuring the bone mineral density (BMD). The most popular method of measuring BMD isdual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA, or DEXA) is a means of measuring bone mineral density (BMD) using spectral imaging. Two X-ray beams, with different energy levels, are aimed at the patient's bones. When soft tissue absorption is subtracted ...
.
In addition to the detection of abnormal BMD, the diagnosis of osteoporosis requires investigations into potentially modifiable underlying causes; this may be done with blood tests. Depending on the likelihood of an underlying problem, investigations for cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
with metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then ...
to the bone, multiple myeloma, Cushing's disease
Cushing's disease is one cause of Cushing's syndrome characterised by increased secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the anterior pituitary (secondary hypercortisolism). This is most often as a result of a pituitary adenoma (spe ...
and other above-mentioned causes may be performed.
Conventional radiography
Conventional radiography is useful, both by itself and in conjunction with CT or MRI, for detecting complications ofosteopenia
Osteopenia, known as "low bone mass" or "low bone density", is a condition in which bone mineral density is low. Because their bones are weaker, people with osteopenia may have a higher risk of fractures, and some people may go on to develop osteop ...
(reduced bone mass; pre-osteoporosis), such as fractures; for differential diagnosis of osteopenia; or for follow-up examinations in specific clinical settings, such as soft tissue calcifications, secondary hyperparathyroidism, or osteomalacia in renal osteodystrophy. However, radiography is relatively insensitive to detection of early disease and requires a substantial amount of bone loss (about 30%) to be apparent on X-ray images.
The main radiographic features of generalized osteoporosis are cortical thinning and increased radiolucency. Frequent complications of osteoporosis are vertebral fractures for which spinal radiography can help considerably in diagnosis and follow-up. Vertebral height measurements can objectively be made using plain-film X-rays by using several methods such as height loss together with area reduction, particularly when looking at vertical deformity in T4-L4, or by determining a spinal fracture index that takes into account the number of vertebrae involved. Involvement of multiple vertebral bodies leads to kyphosis of the thoracic spine, leading to what is known as dowager's hump.
Dual-energy X-ray
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA, or DEXA) is a means of measuring bone mineral density (BMD) using spectral imaging. Two X-ray beams, with different energy levels, are aimed at the patient's bones. When soft tissue absorption is subtracted ...
(DEXA scan) is considered the gold standard
A gold standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the early 1920s, and from the l ...
for the diagnosis of osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is diagnosed when the bone mineral density is less than or equal to 2.5 standard deviations below that of a young (30–40-year-old:58), healthy adult women reference population. This is translated as a T-score
In statistics, the standard score is the number of standard deviations by which the value of a raw score (i.e., an observed value or data point) is above or below the mean value of what is being observed or measured. Raw scores above the mea ...
. But because bone density decreases with age, more people become osteoporotic with increasing age.:58 The World Health Organization has established the following diagnostic guidelines:
The International Society for Clinical Densitometry takes the position that a diagnosis of osteoporosis in men under 50 years of age should not be made on the basis of densitometric criteria alone. It also states, for premenopausal women, Z-scores (comparison with age group rather than peak bone mass) rather than T-scores should be used, and the diagnosis of osteoporosis in such women also should not be made on the basis of densitometric criteria alone. quoted in"Diagnosis of osteoporosis in men, premenopausal women, and children"
Biomarkers
Chemicalbiomarkers
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, pa ...
are a useful tool in detecting bone degradation. The enzyme cathepsin K
Cathepsin K, abbreviated CTSK, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CTSK'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a cysteine cathepsin, a lysosomal cysteine protease involved in bone remodeling and resorption. This pro ...
breaks down type-I collagen
Type I collagen is the most abundant collagen of the human body. It forms large, eosinophilic fibers known as collagen fibers.
It is present in scar tissue, the end product when tissue heals by repair, as well as tendons, ligaments, the endomys ...
, an important constituent in bones. Prepared antibodies can recognize the resulting fragment, called a neoepitope, as a way to diagnose osteoporosis. Increased urinary excretion of C-telopeptides, a type-I collagen breakdown product, also serves as a biomarker for osteoporosis.
Other measuring tools
Quantitative computed tomography (QCT) differs from DXA in that it gives separate estimates of BMD for trabecular and cortical bone and reports precise volumetric mineral density in mg/cm3 rather than BMD's relative Z-score. Among QCT's advantages: it can be performed at axial and peripheral sites, can be calculated from existing CT scans without a separate radiation dose, is sensitive to change over time, can analyze a region of any size or shape, excludes irrelevant tissue such as fat, muscle, and air, and does not require knowledge of the patient's subpopulation in order to create a clinical score (e.g. the Z-score of all females of a certain age). Among QCT's disadvantages: it requires a high radiation dose compared to DXA, CT scanners are large and expensive, and because its practice has been less standardized than BMD, its results are more operator-dependent. Peripheral QCT has been introduced to improve upon the limitations of DXA and QCT. Quantitativeultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
has many advantages in assessing osteoporosis. The modality is small, no ionizing radiation is involved, measurements can be made quickly and easily, and the cost of the device is low compared with DXA and QCT devices. The calcaneus is the most common skeletal site for quantitative ultrasound assessment because it has a high percentage of trabecular bone that is replaced more often than cortical bone, providing early evidence of metabolic change. Also, the calcaneus is fairly flat and parallel, reducing repositioning errors. The method can be applied to children, neonates, and preterm infants, just as well as to adults. Some ultrasound devices can be used on the tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
.
Screening
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommend that all women 65 years of age or older be screened by bone densitometry. Additionally they recommend screening younger women with risk factors. There is insufficient evidence to make recommendations about the intervals for repeated screening and the appropriate age to stop screening. In men the harm versus benefit of screening for osteoporosis is unknown. Prescrire states that the need to test for osteoporosis in those who have not had a previous bone fracture is unclear. The International Society for Clinical Densitometry suggest BMD testing for men 70 or older, or those who are indicated for risk equal to that of a 70‑year‑old. A number of tools exist to help determine who is reasonable to test.Prevention
Lifestyle prevention of osteoporosis is in many aspects the inverse of the potentially modifiable risk factors. As tobacco smoking and high alcohol intake have been linked with osteoporosis, smoking cessation and moderation of alcohol intake are commonly recommended as ways to help prevent it. In people withcoeliac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barle ...
adherence to a gluten-free diet
A gluten-free diet (GFD) is a nutritional plan that strictly excludes gluten, which is a mixture of proteins found in wheat (and all of its species and hybrids, such as spelt, kamut, and triticale), as well as barley, rye, and oats. The incl ...
decreases the risk of developing osteoporosis and increases bone density. The diet must ensure optimal calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
intake (of at least one gram daily) and measuring vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (c ...
levels is recommended, and to take specific supplements if necessary.
Nutrition
Studies of the benefits of supplementation with calcium and vitamin D are conflicting, possibly because most studies did not have people with low dietary intakes. A 2018 review by the USPSTF found low-quality evidence that the routine use of calcium and vitamin D supplements (or both supplements together) did not reduce the risk of having an osteoporotic fracture in male and female adults living in the community who had no known history of vitamin D deficiency, osteoporosis, or a fracture. The USPSTF does not recommend low dose supplementation (less than 1 g of calcium and 400 IU of vitamin D) in postmenopausal women as there does not appear to be a difference in fracture risk. A 2015 review found little data that supplementation of calcium decreases the risk of fractures. While some meta-analyses have found a benefit of vitamin D supplements combined with calcium for fractures, they did not find a benefit of vitamin D supplements (800 IU/day or less) alone. While supplementation does not appear to affect the risk of death, an increased risk ofmyocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may ...
s kidney stones
Kidney stone disease, also known as nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis, is a crystallopathy where a calculus (medicine), solid piece of material (kidney stone) develops in the urinary tract. Kidney stones typically form in the kidney and leave the ...
, and stomach problems is associated with calcium supplementation.
Vitamin K deficiency
Vitamin K deficiency results from insufficient dietary vitamin K1 or vitamin K2 or both.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms include bruising, petechiae,
hematomas, oozing of blood at surgical or puncture sites, stomach pains; risk of massive uncontro ...
is also a risk factor for osteoporotic fractures. The gene gamma-glutamyl carboxylase (GGCX) is dependent on vitamin K. Functional polymorphisms in the gene could attribute to variation in bone metabolism and BMD. Vitamin K2
Vitamin K2 or menaquinone (MK) () is one of three types of vitamin K, the other two being vitamin K1 ( phylloquinone) and K3 ( menadione). K2 is both a tissue and bacterial product (derived from vitamin K1 in both cases) and is usually found in ...
is also used as a means of treatment for osteoporosis and the polymorphisms of GGCX could explain the individual variation in the response to treatment of vitamin K.
Dietary sources of calcium include dairy products, leafy greens, legumes, and beans. There has been conflicting evidence about whether or not dairy is an adequate source of calcium to prevent fractures. The National Academy of Sciences recommends 1,000 mg of calcium for those aged 19–50, and 1,200 mg for those aged 50 and above. A review of the evidence shows no adverse effect of higher protein intake on bone health.
Physical exercise
There is limited evidence indicating that exercise is helpful in promoting bone health. There is some evidence that physical exercise may be beneficial for bone density in postmenopausal women and lead to a slightly reduced risk of a bone fracture (absolute difference 4%). A position statement concluded that increased bone activity and weight-bearing exercises at a young age prevent bone fragility in adults. Bicycling and swimming are not considered weight-bearing exercise. Neither contribute to slowing bone loss with age, and professional bicycle racing has a negative effect on bone density. Low-quality evidence suggests that exercise may reduce pain and improve quality of life of people with vertebral fractures and there is moderate-quality evidence that exercise will likely improve physical performance in individuals with vertebral fractures.Physical therapy
People with osteoporosis are at higher risk of falls due to poor postural control, muscle weakness, and overall deconditioning. Postural control is important to maintaining functional movements such as walking and standing. Physical therapy may be an effective way to address postural weakness that may result from vertebral fractures, which are common in people with osteoporosis. Physical therapy treatment plans for people with vertebral fractures include balance training, postural correction, trunk and lower extremity muscle strengthening exercises, and moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity. The goal of these interventions are to regain normal spine curvatures, increase spine stability, and improve functional performance. Physical therapy interventions were also designed to slow the rate of bone loss through home exercise programs. Whole body vibration therapy has also been suggested as a physical therapy intervention. Moderate to low-quality evidence indicates that whole body vibration therapy may reduce the risk of falls. There are conflicting reviews as to whether vibration therapy improves bone mineral density. Physical therapy can aid in overall prevention in the development of osteoporosis through therapeutic exercise. Prescribed amounts of mechanical loading or increased forces on the bones promote bone formation and vascularization in various ways, therefore offering a preventative measure that is not reliant on drugs. Specific exercise interacts with the body's hormones and signaling pathways which encourages the maintenance of a healthy skeleton.Hormone therapy
Reducedoestrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal acti ...
levels increase the risk of osteoporosis, so hormone replacement therapy
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), also known as menopausal hormone therapy or postmenopausal hormone therapy, is a form of hormone therapy used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause. These symptoms can include hot flashes, vaginal ...
when women reach the menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often ...
may reduce the incidence of osteoporosis.
Management
Lifestyle
Weight-bearing endurance exercise and/or exercises to strengthen muscles improve bone strength in those with osteoporosis. Aerobics, weight bearing, and resistance exercises all maintain or increase BMD in postmenopausal women.Fall prevention
Fall prevention includes any action taken to help reduce the number of accidental falls suffered by susceptible individuals, such as the elderly (idiopathic) and people with neurological (Parkinson's, Multiple sclerosis, stroke survivors, Guilla ...
can help prevent osteoporosis complications. There is some evidence for hip protectors specifically among those who are in care homes.
Pharmacologic therapy
The US National Osteoporosis Foundation recommends pharmacologic treatment for patients with hip of spine fracture thought to be related to osteoporosis, those with BMD 2.5 SD or more below the young normal mean (T-score -2.5 or below), and those with BMD between 1 and 2.5 SD below normal mean whose 10-year risk, using FRAX, for hip fracture is equal or more than 3%.Bisphosphonate
Bisphosphonates are a class of drugs that prevent the loss of bone density, used to treat osteoporosis and similar diseases. They are the most commonly prescribed drugs used to treat osteoporosis. They are called bisphosphonates because they ...
s are useful in decreasing the risk of future fractures in those who have already sustained a fracture due to osteoporosis. This benefit is present when taken for three to four years. They do not appear to change the overall risk of death. Tentative evidence does not support the use of bisphosphonates as a standard treatment for secondary osteoporosis in children. Different bisphosphonates have not been directly compared, therefore it is unknown if one is better than another. Fracture risk reduction is between 25 and 70% depending on the bone involved. There are concerns of atypical femoral fractures and osteonecrosis of the jaw
Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) is a severe bone disease (osteonecrosis) that affects the jaws (the maxilla and the mandible). Various forms of ONJ have been described since 1861, and a number of causes have been suggested in the literature.
Oste ...
with long-term use, but these risks are low. With evidence of little benefit when used for more than three to five years and in light of the potential adverse events, it may be appropriate to stop treatment after this time. One medical organization recommends that after five years of medications by mouth or three years of intravenous medication among those at low risk, bisphosphonate treatment can be stopped. In those at higher risk they recommend up to ten years of medication by mouth or six years of intravenous treatment.
The goal of osteoporosis management is to prevent osteoporotic fractures, but for those who have sustained one already it is more urgent to prevent a secondary fracture. Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
That is because patients with a fracture are more likely to experience a recurrent fracture, with marker increase in morbidity and mortality compared. Among the five bisphosphonates, no significant differences were found for a secondary fracture for all fracture endpoints combined. That being said, alendronate was identified as the most efficacious for secondary prevention of vertebral and hip fractures while zoledronate showed better performance for nonvertebral non-hip fracture prevention. There is concern that many people do not receive appropriate pharmacological therapy after a low-impact fracture. For those with osteoporosis but who have not had a fracture, evidence does not support a reduction in fracture risk with
risedronate
Risedronic acid, often used as its sodium salt risedronate sodium, is a bisphosphonate. It slows down the cells which break down bone. It's used to treat or prevent osteoporosis, and treat Paget's disease of bone. It is taken by mouth.
It was pa ...
or etidronate. Alendronate
Alendronic acid, sold under the brand name Fosamax among others, is a bisphosphonate medication used to treat osteoporosis and Paget's disease of bone. It is taken by mouth. Use is often recommended together with vitamin D, calcium supplementati ...
decreases fractures of the spine but does not have any effect on other types of fractures. Half stop their medications within a year. When on treatment with bisphosphonates rechecking bone mineral density is not needed. There is tentative evidence of benefit in males with osteoporosis.
Fluoride supplementation does not appear to be effective in postmenopausal osteoporosis, as even though it increases bone density, it does not decrease the risk of fractures.
Teriparatide
Teriparatide, sold under the brand name Forteo, is a form of parathyroid hormone (PTH) consisting of the first ( N-terminus) 34 amino acids, which is the bioactive portion of the hormone. It is an effective anabolic (promoting bone formation) ag ...
(a recombinant parathyroid hormone) has been shown to be effective in treatment of women with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Some evidence also indicates strontium ranelate
Strontium ranelate, a strontium(II) salt of ranelic acid, is a medication for osteoporosis marketed as Protelos or Protos by Servier. Studies indicate it can also slow the course of osteoarthritis of the knee. The drug is unusual in that it bo ...
is effective in decreasing the risk of vertebral and nonvertebral fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Hormone replacement therapy, while effective for osteoporosis, is only recommended in women who also have menopausal symptoms. It is not recommended for osteoporosis by itself. Raloxifene
Raloxifene, sold under the brand name Evista among others, is a medication used to prevent and treat osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and those on glucocorticoids. For osteoporosis it is less preferred than bisphosphonates. It is also used to ...
, while effective in decreasing vertebral fractures, does not affect the risk of nonvertebral fracture. And while it reduces the risk of breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a r ...
, it increases the risk of blood clots and strokes. While denosumab
Denosumab (trade names Prolia and Xgeva) is a human monoclonal antibody for the treatment of osteoporosis, treatment-induced bone loss, metastases to bone, and giant cell tumor of bone.
Denosumab is contraindicated in people with low blood calci ...
is effective at preventing fractures in women, there is not clear evidence of benefit in males. In hypogonadal men, testosterone has been shown to improve bone quantity and quality, but, as of 2008, no studies evaluated its effect on fracture risk or in men with a normal testosterone levels. Calcitonin
Calcitonin is a 32 amino acid peptide hormone secreted by parafollicular cells (also known as C cells) of the thyroid (or endostyle) in humans and other chordates. in the ultimopharyngeal body. It acts to reduce blood calcium (Ca2+), opposing th ...
while once recommended is no longer due to the associated risk of cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
and questionable effect on fracture risk. Alendronic acid/colecalciferol can be taken to treat this condition in post-menopausal women.
Romosozumab
Romosozumab, sold under the brand name Evenity, is a medication used to treat osteoporosis. It has been found to decrease the risk of fractures of the spine.
Common side effect include headache, joint pain, and pain at the site of injection. ...
(sold under the brand name Evenity) is a monoclonal antibody against sclerostin
Sclerostin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SOST'' gene.
Sclerostin is a secreted glycoprotein with a C-terminal cysteine knot-like (CTCK) domain and sequence similarity to the DAN (differential screening-selected gene aberrative ...
. Romosozumab is usually reserved for patients with very high fracture risk and is the only available drug therapy for osteoporosis that leads to simultaneous inhibition of bone resorption
Bone resorption is resorption of bone tissue, that is, the process by which osteoclasts break down the tissue in bones and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone tissue to the blood.
The osteoclasts are multi-nuclea ...
together with an anabolic effect.
Certain medications like alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, raloxifene, and strontium ranelate can help to prevent osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Tentative evidence suggests that Chinese herbal medicines may have potential benefits on bone mineral density.
Prognosis
Although people with osteoporosis have increased mortality due to the complications of fracture, the fracture itself is rarely lethal. Hip fractures can lead to decreased mobility and additional risks of numerous complications (such asdeep venous thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enla ...
and/or pulmonary embolism, and pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severi ...
). The six-month mortality rate for those aged 50 and above following hip fracture was found to be around 13.5%, with a substantial proportion (almost 13%) needing total assistance to mobilize after a hip fracture.
Vertebral fractures, while having a smaller impact on mortality, can lead to severe chronic pain of neurogenic origin, which can be hard to control, as well as deformity. Though rare, multiple vertebral fractures can lead to such severe hunchback (kyphosis
Kyphosis is an abnormally excessive convex curvature of the spine as it occurs in the thoracic and sacral regions. Abnormal inward concave ''lordotic'' curving of the cervical and lumbar regions of the spine is called lordosis. It can result ...
), the resulting pressure on internal organs can impair one's ability to breathe.
Apart from risk of death and other complications, osteoporotic fractures are associated with a reduced health-related quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
.
The condition is responsible for millions of fractures annually, mostly involving the lumbar vertebrae, hip, and wrist. Fragility fractures of ribs are also common in men.
Fractures
Hip fractures are responsible for the most serious consequences of osteoporosis. In the United States, more than 250,000 hip fractures annually are attributable to osteoporosis. A 50-year-old white woman is estimated to have a 17.5% lifetime risk of fracture of the proximalfemur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates wit ...
. The incidence of hip fractures increases each decade from the sixth through the ninth for both women and men for all populations. The highest incidence is found among men and women ages 80 or older.
Between 35 and 50% of all women over 50 had at least one vertebral fracture. In the United States, 700,000 vertebral fractures occur annually, but only about a third are recognized. In a series of 9704 women aged 68.8 on average studied for 15 years, 324 had already sustained a vertebral fracture at entry into the study and 18.2% developed a vertebral fracture, but that risk rose to 41.4% in women who had a previous vertebral fracture.
In the United States, 250,000 wrist fractures annually are attributable to osteoporosis. Wrist fractures are the third most common type of osteoporotic fractures. The lifetime risk of sustaining a Colles' fracture is about 16% for white women. By the time women reach age 70, about 20% have had at least one wrist fracture.
Fragility fractures of the ribs are common in men as young as age 35. These are often overlooked as signs of osteoporosis, as these men are often physically active and develop the fracture in the course of physical activity, such as falling while water skiing
Water skiing (also waterskiing or water-skiing) is a surface water sport in which an individual is pulled behind a boat or a cable ski installation over a body of water, skimming the surface on two skis or one ski. The sport requires suffic ...
or jet skiing.
Epidemiology
developed world
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastruct ...
, depending on the method of diagnosis, 2% to 8% of males and 9% to 38% of females are affected. Rates of disease in the developing world are unclear.
Postmenopausal women have a higher rate of osteoporosis and fractures than older men. Postmenopausal women have decreased estrogen which contributes to their higher rates of osteoporosis. A 60-year-old woman has a 44% risk of fracture while a 60-year-old man has a 25% risk of fracture.
There are 8.9 million fractures worldwide per year due to osteoporosis. Globally, 1 in 3 women and 1 in 5 men over the age of 50 will have an osteoporotic fracture. Data from the United States shows a decrease in osteoporosis within the general population and in white women, from 18% in 1994 to 10% in 2006. White and Asian people
Asian people (or Asians, sometimes referred to as Asiatic people)United States National Library of Medicine. Medical Subject Headings. 2004. November 17, 200Nlm.nih.gov: ''Asian Continental Ancestry Group'' is also used for categorical purpos ...
are at greater risk. People of African descent are at a decreased risk of fractures due to osteoporosis, although they have the highest risk of death following an osteoporotic fracture.
It has been shown that latitude affects risk of osteoporotic fracture. Areas of higher latitude such as Northern Europe receive less Vitamin D through sunlight compared to regions closer to the equator, and consequently have higher fracture rates in comparison to lower latitudes. For example, Swedish men and women have a 13% and 28.5% risk of hip fracture by age 50, respectively, whereas this risk is only 1.9% and 2.4% in Chinese men and women. Diet may also be a factor that is responsible for this difference, as vitamin D, calcium, magnesium, and folate are all linked to bone mineral density.
There is also an association between Celiac Disease and increased risk of osteoporosis. In studies with premenopausal females and males, there was a correlation between Celiac Disease and osteoporosis and osteopenia. Celiac Disease can decrease absorption of nutrients in the small intestine such as calcium, and a gluten-free diet can help people with Celiac Disease to revert to normal absorption in the gut.
About 22 million women and 5.5 million men in the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
had osteoporosis in 2010. In the United States in 2010 about 8 million women and one to 2 million men had osteoporosis. This places a large economic burden on the healthcare system due to costs of treatment, long-term disability, and loss of productivity in the working population. The EU spends 37 billion euros per year in healthcare costs related to osteoporosis, and the US spends an estimated US$19 billion annually for related healthcare costs.
History
The link between age-related reductions in bone density goes back to the early 1800s. French pathologist Jean Lobstein coined the term ''osteoporosis''. The American endocrinologistFuller Albright
Fuller Albright (January 12, 1900 – December 8, 1969) was an American endocrinologist who made numerous contributions to his field, especially to the area of calcium metabolism. Albright made great strides and contributions to the understanding ...
linked osteoporosis with the postmenopausal state.
Anthropologists have studied skeletal remains that showed loss of bone density and associated structural changes that were linked to a chronic malnutrition in the agricultural area in which these individuals lived. "It follows that the skeletal deformation may be attributed to their heavy labor in agriculture as well as to their chronic malnutrition", causing the osteoporosis seen when radiographs of the remains were made.
See also
*Spaceflight osteopenia
Spaceflight osteopenia refers to the characteristic bone loss that occurs during spaceflight. Astronauts lose an average of more than 1% bone mass per month spent in space. There is concern that during long-duration flights, excessive bone loss ...
* World Osteoporosis Day
References
External links
Handout on Health: Osteoporosis
nbsp; – US National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases
Osteoporosis
nbsp; – l NIH Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases – National Resource Center * * {{Authority control Aging-associated diseases Endocrine diseases Osteopathies Rheumatology Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate