Portland cement on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
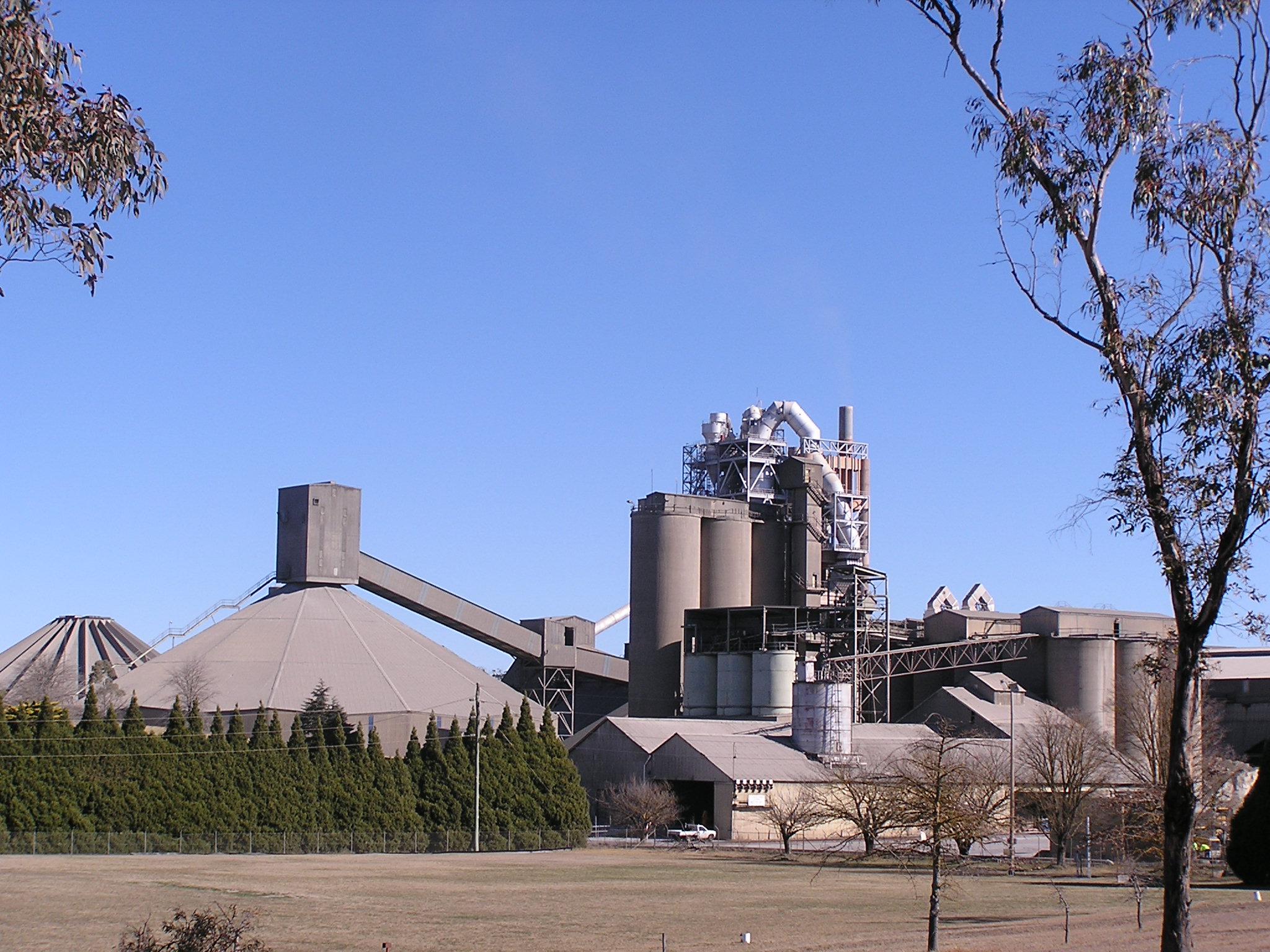
 Portland cement is the most common type of
Portland cement is the most common type of
 Portland cement was developed from natural cements made in Britain beginning in the middle of the 18th century. Its name is derived from its similarity to Portland stone, a type of building stone quarried on the
Portland cement was developed from natural cements made in Britain beginning in the middle of the 18th century. Its name is derived from its similarity to Portland stone, a type of building stone quarried on the
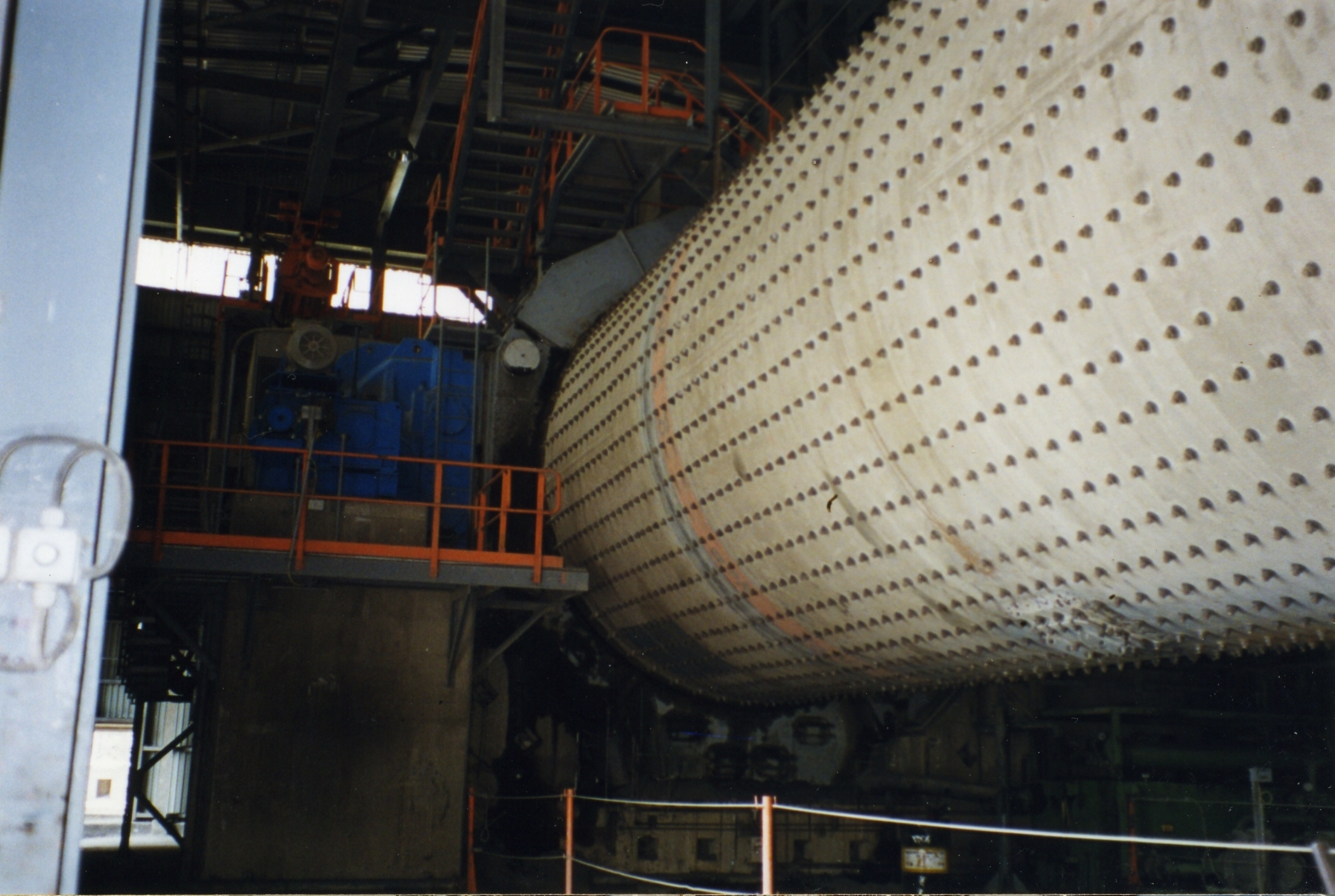
 Portland cement clinker is made by heating, in a
Portland cement clinker is made by heating, in a
 To achieve the desired setting qualities in the finished product, a quantity (2–8%, but typically 5%) of calcium sulfate (usually
To achieve the desired setting qualities in the finished product, a quantity (2–8%, but typically 5%) of calcium sulfate (usually
 The most common use for portland cement is in the production of concrete. Concrete is a composite material consisting of aggregate ( gravel and
The most common use for portland cement is in the production of concrete. Concrete is a composite material consisting of aggregate ( gravel and
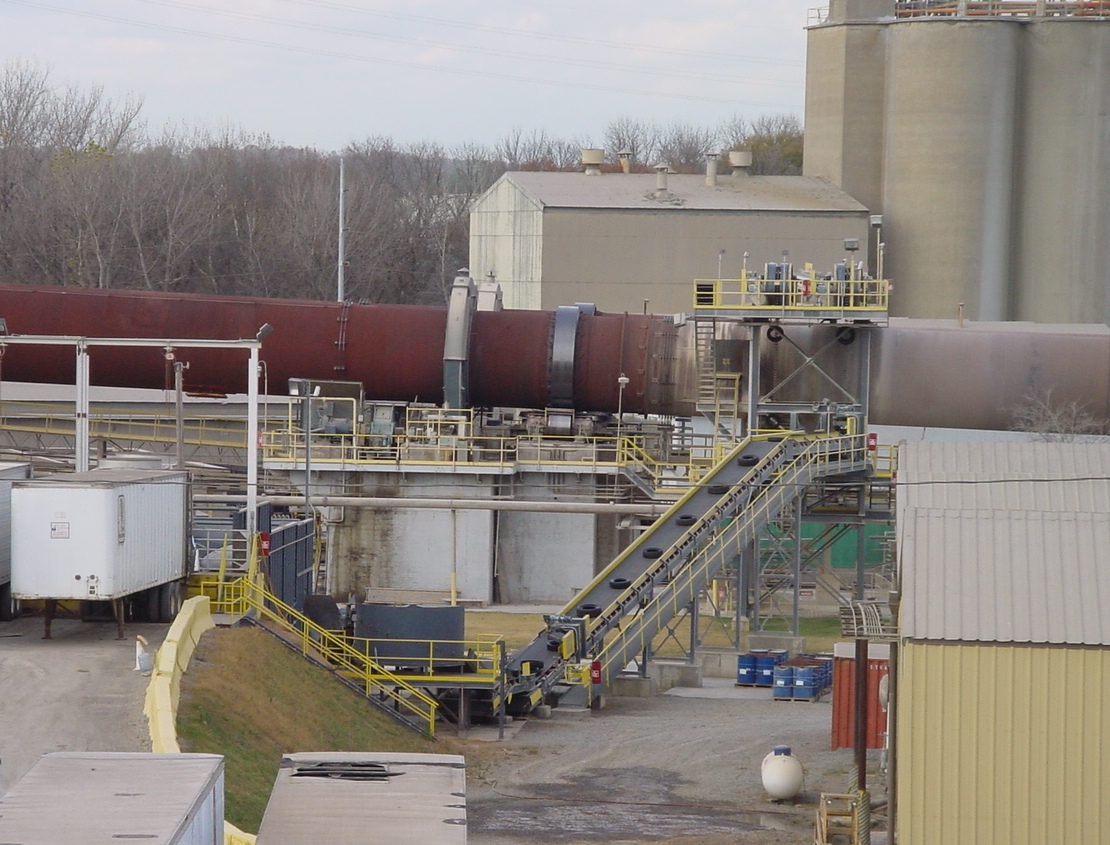 Due to the high temperatures inside
Due to the high temperatures inside
World Production of Hydraulic Cement, by CountryAlpha The Guaranteed Portland Cement Company: 1917 Trade Literature from Smithsonian Institution LibrariesCement Sustainability Initiative
*Aerial views of the world's largest concentration of cement manufacturing capacity, Saraburi Province,
CDC – NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards

cement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel ( aggregate) together. Cement mi ...
in general use around the world as a basic ingredient of concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most wid ...
, mortar, stucco, and non-specialty grout. It was developed from other types of hydraulic lime in England in the early 19th century by Joseph Aspdin, and is usually made from limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
. It is a fine powder
A powder is a dry, bulk solid composed of many very fine particles that may flow freely when shaken or tilted. Powders are a special sub-class of granular materials, although the terms ''powder'' and '' granular'' are sometimes used to distin ...
, produced by heating limestone and clay minerals in a kiln
A kiln is a thermally insulated chamber, a type of oven, that produces temperatures sufficient to complete some process, such as hardening, drying, or chemical changes. Kilns have been used for millennia to turn objects made from clay int ...
to form clinker, grinding
Grind is the cross-sectional shape of a blade.
Grind, grinds, or grinding may also refer to:
Grinding action
* Grinding (abrasive cutting), a method of crafting
* Grinding (dance), suggestive club dancing
* Grinding (video gaming), repetitive and ...
the clinker, and adding 2 to 3 percent of gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywal ...
. Several types of portland cement are available. The most common, called ordinary portland cement (OPC), is grey, but white Portland cement is also available. Its name is derived from its resemblance to Portland stone which was quarried on the Isle of Portland
An isle is an island, land surrounded by water. The term is very common in British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct fr ...
in Dorset
Dorset ( ; archaically: Dorsetshire , ) is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The ceremonial county comprises the unitary authority areas of Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole and Dorset. Covering an area of , ...
, England. It was named by Joseph Aspdin who obtained a patent for it in 1824. His son William Aspdin is regarded as the inventor of "modern" portland cement due to his developments in the 1840s.
The low cost and widespread availability of the limestone, shales, and other naturally occurring materials used in portland cement make it a relatively cheap building material. Its most common use is in the production of concrete, a composite material consisting of aggregate (gravel and sand), cement, and water.
History

 Portland cement was developed from natural cements made in Britain beginning in the middle of the 18th century. Its name is derived from its similarity to Portland stone, a type of building stone quarried on the
Portland cement was developed from natural cements made in Britain beginning in the middle of the 18th century. Its name is derived from its similarity to Portland stone, a type of building stone quarried on the Isle of Portland
An isle is an island, land surrounded by water. The term is very common in British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct fr ...
in Dorset, England.
The development of modern portland cement (sometimes called ordinary or normal portland cement) began in 1756, when John Smeaton experimented with combinations of different limestones and additives, including trass and pozzolanas, intended for the construction of a lighthouse,Robert G. Blezard, "The History of Calcareous Cements" in Hewlett, Peter C., ed.. ''Leaʼs chemistry of cement and concrete''. 4. ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, 2004. 1–24. Print. now known as Smeaton's Tower. In the late 18th century, Roman cement was developed and patented in 1796 by James Parker.Saikia, Mimi Das. Bhargab Mohan Das, Madan Mohan Das. ''Elements of Civil Engineering''. New Delhie: PHI Learning Private Limited. 2010. 30. Print. Roman cement quickly became popular, but was largely replaced by portland cement in the 1850s. In 1811, James Frost
James Martin Frost (born 22 August 1986) is the guitarist, keyboardist and backing vocalist of Welsh band The Automatic, and guitarist and backing vocalist for Cardiff-based band Effort. As well as his musical duties for The Automatic, Frost ha ...
produced a cement he called British cement. James Frost is reported to have erected a manufactory for making of an artificial cement in 1826. In 1811 Edgar Dobbs of Southwark patented a cement of the kind invented 7 years later by the French engineer Louis Vicat
Louis Vicat (31 March 1786, Nevers – 10 April 1861, Grenoble) was a French engineer.
He graduated from the École Polytechnique in 1804 and the École des Ponts et Chaussées in 1806.
Vicat studied the setting of mortars and developed his own ...
. Vicat's cement is an artificial hydraulic lime, and is considered the "principal forerunner" of portland cement.
The name ''portland cement'' is recorded in a directory published in 1823 being associated with a William Lockwood and possibly others. In his 1824 cement patent, Joseph Aspdin called his invention "portland cement" because of its resemblance to Portland stone. Aspdin's cement was nothing like modern portland cement, but a first step in the development of modern portland cement, and has been called a "proto-portland cement".
William Aspdin had left his father's company, to form his own cement manufactury. In the 1840s William Aspdin, apparently accidentally, produced calcium silicates which are a middle step in the development of portland cement. In 1848, William Aspdin further improved his cement. Then, in 1853, he moved to Germany, where he was involved in cement making. William Aspdin made what could be called "meso-portland cement" (a mix of portland cement and hydraulic lime). Isaac Charles Johnson further refined the production of "meso-portland cement" (middle stage of development), and claimed to be the real father of portland cement.
In 1859, John Grant of the Metropolitan Board of Works, set out requirements for cement to be used in the London sewer project. This became a specification for portland cement. The next development in the manufacture of portland cement was the introduction of the rotary kiln, patented by Frederick Ransome
Frederick Ransome (1818–1893) was a British inventor and industrialist, creator of Ransome's artificial stone.
Frederick was the son of James Ransome, 1782–1849, a member of the Ransomes steel and agricultural equipment-making family of Ips ...
in 1885 (U.K.) and 1886 (U.S.); which allowed a stronger, more homogeneous mixture and a continuous manufacturing process. The Hoffmann "endless" kiln which was said to give "perfect control over combustion" was tested in 1860 and shown to produce a superior grade of cement. This cement was made at the Portland Cementfabrik Stern at Stettin, which was the first to use a Hoffmann kiln. The Association of German Cement Manufacturers issued a standard on portland cement in 1878.
Portland cement had been imported into the United States from Germany and England, and in the 1870s and 1880s, it was being produced by Eagle Portland cement near Kalamazoo, Michigan. In 1875, the first portland cement was produced in the Coplay Cement Company Kilns under the direction of David O. Saylor in Coplay, Pennsylvania. By the early 20th century, American-made portland cement had displaced most of the imported portland cement.
Composition
ASTM C150 defines portland cement as: TheEuropean Standard
European Standards (abbreviated EN, from the German name ("European Norm")) are technical standards which have been ratified by one of the three European standards organizations: European Committee for Standardization (CEN), European Committee ...
EN 197-1 uses the following definition:
(The last two requirements were already set out in the German Standard, issued in 1909).
Clinkers make up more than 90% of the cement, along with a limited amount of calcium sulfate
Calcium sulfate (or calcium sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the formula CaSO4 and related hydrates. In the form of γ-anhydrite (the anhydrous form), it is used as a desiccant. One particular hydrate is better known as plaster of Paris ...
(CaSO4, which controls the set time), and up to 5% minor constituents (fillers) as allowed by various standards. Clinkers are nodules (diameters, ) of a sintered material that is produced when a raw mixture of predetermined composition is heated to high temperature. The key chemical reaction distinguishing portland cement from other hydraulic limes occurs at these high temperatures (>) as belite (Ca2SiO4) combines with calcium oxide (CaO) to form alite
Alite is an impure form of tricalcium silicate, , sometimes formulated as ( in cement chemist notation), typically with 3-4% of substituent oxides. It is the major, and characteristic, phase in Portland cement. The name was given by Törnebohm i ...
(Ca3SiO5).
Manufacturing
 Portland cement clinker is made by heating, in a
Portland cement clinker is made by heating, in a cement kiln
Cement kilns are used for the pyroprocessing stage of manufacture of portland and other types of hydraulic cement, in which calcium carbonate reacts with silica-bearing minerals to form a mixture of calcium silicates. Over a billion tonnes of ...
, a mixture of raw materials to a calcining
Calcination refers to thermal treatment of a solid chemical compound (e.g. mixed carbonate ores) whereby the compound is raised to high temperature without melting under restricted supply of ambient oxygen (i.e. gaseous O2 fraction of air), gener ...
temperature of above and then a fusion temperature, which is about for modern cements, to sinter the materials into clinker.
The materials in cement clinker are alite, belite, tricalcium aluminate
Tricalcium aluminate Ca3Al2O6, often formulated as 3CaO·Al2O3 to highlight the proportions of the oxides from which it is made, is the most basic of the calcium aluminates. It does not occur in nature, but is an important mineral phase in Port ...
, and tetracalcium alumino ferrite. The aluminium, iron, and magnesium oxides are present as a flux allowing the calcium silicates to form at a lower temperature, and contribute little to the strength. For special cements, such as low heat (LH) and sulfate resistant (SR) types, it is necessary to limit the amount of tricalcium aluminate (3 CaO·Al2O3) formed.
The major raw material for the clinker-making is usually limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
(CaCO3) mixed with a second material containing clay as source of alumino-silicate. Normally, an impure limestone which contains clay or SiO2 is used. The CaCO3 content of these limestones can be as low as 80%. Secondary raw materials (materials in the raw mix other than limestone) depend on the purity of the limestone. Some of the materials used are clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay par ...
, shale, sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class o ...
, iron ore, bauxite, fly ash, and slag. When a cement kiln is fired by coal, the ash of the coal acts as a secondary raw material.
Cement grinding
 To achieve the desired setting qualities in the finished product, a quantity (2–8%, but typically 5%) of calcium sulfate (usually
To achieve the desired setting qualities in the finished product, a quantity (2–8%, but typically 5%) of calcium sulfate (usually gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywal ...
or anhydrite
Anhydrite, or anhydrous calcium sulfate, is a mineral with the chemical formula CaSO4. It is in the orthorhombic crystal system, with three directions of perfect cleavage parallel to the three planes of symmetry. It is not isomorphous with the ...
) is added to the clinker, and the mixture is finely ground to form the finished cement powder. This is achieved in a cement mill. The grinding process is controlled to obtain a powder with a broad particle size range, in which typically 15% by mass consists of particles below 5 μm diameter, and 5% of particles above 45 μm. The measure of fineness usually used is the 'specific surface area
Specific surface area (SSA) is a property of solids defined as the total surface area of a material per unit of mass, (with units of m2/kg or m2/g) or solid or bulk volume (units of m2/m3 or m−1).
It is a physical value that can be used to dete ...
', which is the total particle surface area of a unit mass of cement. The rate of initial reaction (up to 24 hours) of the cement on addition of water is directly proportional
In mathematics, two sequences of numbers, often experimental data, are proportional or directly proportional if their corresponding elements have a constant ratio, which is called the coefficient of proportionality or proportionality constan ...
to the specific surface area. Typical values are 320–380 m2·kg−1 for general purpose cements, and 450–650 m2·kg−1 for 'rapid hardening' cements. The cement is conveyed by belt or powder pump to a silo for storage. Cement plants normally have sufficient silo space for one to 20 weeks of production, depending upon local demand cycles. The cement is delivered to end users either in bags, or as bulk powder blown from a pressure vehicle into the customer's silo. In industrial countries, 80% or more of cement is delivered in bulk.
Setting and hardening
Cement sets when mixed with water by way of a complex series of chemical reactions still only partly understood. The different constituents slowly crystallise, and the interlocking of their crystals gives cement its strength.Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
is slowly absorbed to convert the portlandite (Ca(OH)2) into insoluble calcium carbonate. After the initial setting, immersion in warm water will speed up setting. Gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywal ...
is added as an inhibitor to prevent flash (or quick) setting.
Use
 The most common use for portland cement is in the production of concrete. Concrete is a composite material consisting of aggregate ( gravel and
The most common use for portland cement is in the production of concrete. Concrete is a composite material consisting of aggregate ( gravel and sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class o ...
), cement, and water. As a construction material, concrete can be cast in almost any shape desired, and once hardened, can become a structural (load bearing) element. Concrete can be used in the construction of structural elements like panels, beams, and street furniture
Street furniture is a collective term for objects and pieces of equipment installed along streets and roads for various purposes. It includes benches, traffic barriers, bollards, post boxes, phone boxes, streetlamps, traffic lights, traf ...
, or may be cast-''in situ'' for superstructures like roads and dams. These may be supplied with concrete mixed on site, or may be provided with ' ready-mixed' concrete made at permanent mixing sites. Portland cement is also used in mortars (with sand and water only), for plasters and screed
Screed has three meanings in building construction:
# A flat board (screed board, floating screed) or a purpose-made aluminium tool used to smooth and to "true" materials like concrete, stucco and plaster after they have been placed on a surface ...
s, and in grouts (cement/water mixes squeezed into gaps to consolidate foundations, road-beds, etc.).
When water is mixed with portland cement, the product sets in a few hours, and hardens over a period of weeks. These processes can vary widely, depending upon the mix used and the conditions of curing of the product, but a typical concrete sets in about 6 hours and develops a compressive strength of 8 MPa in 24 hours. The strength rises to 15 MPa at 3 days, 23 MPa at 1 week, 35 MPa at 4 weeks, and 41 MPa at 3 months. In principle, the strength continues to rise slowly as long as water is available for continued hydration , but concrete is usually allowed to dry out after a few weeks and this causes strength growth to stop.
Types
General
ASTM C150
Five types of portland cements exist, with variations of the first three according to ASTM C150. Type I portland cement is known as common or general-purpose cement. It is generally assumed unless another type is specified. It is commonly used for general construction, especially when making precast, and precast-prestressed concrete that is not to be in contact with soils or ground water. The typical compound compositions of this type are: 55% (C3S), 19% (C2S), 10% (C3A), 7% (C4AF), 2.8% MgO, 2.9% (SO3), 1.0% ignition loss, and 1.0% free CaO (utilizingCement chemist notation
Cement chemist notation (CCN) was developed to simplify the formulas cement chemists use on a daily basis. It is a shorthand way of writing the chemical formula of oxides of calcium, silicon, and various metals.
Abbreviations of oxides
The ma ...
).
A limitation on the composition is that the (C3A) shall not exceed 15%.
Type II provides moderate sulfate resistance, and gives off less heat during hydration. This type of cement costs about the same as type I. Its typical compound composition is:
51% (C3S), 24% (C2S), 6% (C3A), 11% (C4AF), 2.9% MgO, 2.5% (SO3), 0.8% ignition loss, and 1.0% free CaO.
A limitation on the composition is that the (C3A) shall not exceed 8%, which reduces its vulnerability to sulfates. This type is for general construction exposed to moderate sulfate attack, and is meant for use when concrete is in contact with soils and ground water, especially in the western United States due to the high sulfur content of the soils. Because of similar price to that of type I, type II is much used as a general purpose cement, and the majority of portland cement sold in North America meets this specification.
Note: Cement meeting (among others) the specifications for types I and II has become commonly available on the world market.
Type III has relatively high early strength. Its typical compound composition is:
57% (C3S), 19% (C2S), 10% (C3A), 7% (C4AF), 3.0% MgO, 3.1% (SO3), 0.9% ignition loss, and 1.3% free CaO.
This cement is similar to type I, but ground finer. Some manufacturers make a separate clinker with higher C3S and/or C3A content, but this is increasingly rare, and the general purpose clinker is usually used, ground to a specific surface area
Specific surface area (SSA) is a property of solids defined as the total surface area of a material per unit of mass, (with units of m2/kg or m2/g) or solid or bulk volume (units of m2/m3 or m−1).
It is a physical value that can be used to dete ...
typically 50–80% higher. The gypsum level may also be increased a small amount. This gives the concrete using this type of cement a three-day compressive strength equal to the seven-day compressive strength of types I and II. Its seven-day compressive strength is almost equal to 28-day compressive strengths of types I and II. The only downside is that the six-month strength of type III is the same or slightly less than that of types I and II. Therefore, the long-term strength is sacrificed. It is usually used for precast concrete manufacture, where high one-day strength allows fast turnover of molds. It may also be used in emergency construction and repairs, and construction of machine bases and gate installations.
Type IV portland cement is generally known for its low heat of hydration. Its typical compound composition is:
28% (C3S), 49% (C2S), 4% (C3A), 12% (C4AF), 1.8% MgO, 1.9% (SO3), 0.9% ignition loss, and 0.8% free CaO.
The percentages of (C2S) and (C4AF) are relatively high and (C3S) and (C3A) are relatively low. A limitation on this type is that the maximum percentage of (C3A) is seven, and the maximum percentage of (C3S) is thirty-five. This causes the heat given off by the hydration reaction to develop at a slower rate. Consequently, the strength of the concrete develops slowly. After one or two years the strength is higher than the other types after full curing. This cement is used for very large concrete structures, such as dams, which have a low surface to volume ratio. This type of cement is generally not stocked by manufacturers, but some might consider a large special order. This type of cement has not been made for many years, because portland-pozzolan cements and ground granulated blast furnace slag addition offer a cheaper and more reliable alternative.
Type V is used where sulfate resistance is important. Its typical compound composition is:
38% (C3S), 43% (C2S), 4% (C3A), 9% (C4AF), 1.9% MgO, 1.8% (SO3), 0.9% ignition loss, and 0.8% free CaO.
This cement has a very low (C3A) composition which accounts for its high sulfate resistance. The maximum content of (C3A) allowed is 5% for type V portland cement. Another limitation is that the (C4AF) + 2(C3A) composition cannot exceed 20%. This type is used in concrete to be exposed to alkali soil and ground water sulfates
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many a ...
which react with (C3A) causing disruptive expansion. It is unavailable in many places, although its use is common in the western United States and Canada. As with type IV, type V portland cement has mainly been supplanted by the use of ordinary cement with added ground granulated blast furnace slag or tertiary blended cements containing slag and fly ash.
Types Ia, IIa, and IIIa have the same composition as types I, II, and III. The only difference is that in Ia, IIa, and IIIa, an air-entraining agent is ground into the mix. The air-entrainment must meet the minimum and maximum optional specification found in the ASTM manual. These types are only available in the eastern United States and Canada, only on a limited basis. They are a poor approach to air-entrainment which improves resistance to freezing under low temperatures.
Types II(MH) and II(MH)a have a similar composition as types II and IIa, but with a mild heat.
EN 197 norm
The European norm EN 197-1 defines five classes of common cement that comprise portland cement as a main constituent. These classes differ from the ASTM classes. ''Constituents that are permitted in portland-composite cements are artificial pozzolans (blast furnace slag (in fact a latent hydraulic binder), silica fume, and fly ashes), or natural pozzolans (siliceous or siliceous aluminous materials such as volcanic ash glasses, calcined clays and shale).''CSA A3000-08
The Canadian standards describe six main classes of cement, four of which can also be supplied as a blend containing ground limestone (where a suffix L is present in the class names).White portland cement
White Portland cement or white ordinary portland cement (WOPC) is similar to ordinary, grey, portland cement in all respects, except for its high degree of whiteness. Obtaining this colour requires high purity raw materials (low Fe2O3 content), and some modification to the method of manufacture, among others a higher kiln temperature required to sinter the clinker in the absence of ferric oxides acting as a flux in normal clinker. As Fe2O3 contributes to decrease the melting point of the clinker (normally 1450 °C), the white cement requires a higher sintering temperature (around 1600 °C). Because of this, it is somewhat more expensive than the grey product. The main requirement is to have a low iron content which should be less than 0.5 wt.% expressed as Fe2O3 for white cement, and less than 0.9 wt.% for off-white cement. It also helps to have the iron oxide as ferrous oxide (FeO) which is obtained via slightly reducing conditions in the kiln, i.e., operating with zero excess oxygen at the kiln exit. This gives the clinker and cement a green tinge. Other metallic oxides such as Cr2O3 (green), MnO (pink), TiO2 (white), etc., in trace content, can also give colour tinges, so for a given project it is best to use cement from a single batch.Safety issues
Bags of cement routinely have health and safety warnings printed on them, because not only is cement highly alkaline, but the setting process is also exothermic. As a result, wet cement is strongly caustic and can easily cause severe skin burns if not promptly washed off with water. Similarly, dry cement powder in contact withmucous membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It i ...
s can cause severe eye or respiratory irritation. The reaction of cement dust with moisture in the sinuses and lungs can also cause a chemical burn, as well as headaches, fatigue, and lung cancer.
The production of comparatively low-alkalinity cements (pH<11) is an area of ongoing investigation.
In Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swe ...
, France, and the United Kingdom, the level of chromium(VI), which is considered to be toxic and a major skin irritant, may not exceed 2 parts per million
In science and engineering, the parts-per notation is a set of pseudo-units to describe small values of miscellaneous dimensionless quantities, e.g. mole fraction or mass fraction. Since these fractions are quantity-per-quantity measures, th ...
(ppm).
In the US, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set the legal limit ( permissible exposure limit) for portland cement exposure in the workplace as 50 mppcf (million particles per cubic foot) over an 8-hour workday. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, ) is the United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related injury and illness. NIOSH is part of the C ...
(NIOSH) has set a recommended exposure limit
A recommended exposure limit (REL) is an occupational exposure limit that has been recommended by the United States National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. The REL is a level that NIOSH believes would be protective of worker safet ...
(REL) of 10 mg/m3 total exposure and 5 mg/m3 respiratory exposure over an 8-hour workday. At levels of 5000 mg/m3, portland cement is immediately dangerous to life and health.
Environmental effects
Portland cement manufacture can cause environmental impacts at all stages of the process. These include emissions of airborne pollution in the form of dust; gases; noise and vibration when operating machinery and during blasting in quarries; consumption of large quantities of fuel during manufacture; release of from the raw materials during manufacture, and damage to countryside from quarrying. Equipment to reduce dust emissions during quarrying and manufacture of cement is widely used, and equipment to trap and separate exhaust gases are coming into increased use. Environmental protection also includes the re-integration of quarries into the countryside after they have been closed down by returning them to nature or re-cultivating them. Portland cement is caustic, so it can cause chemical burns. The powder can cause irritation or, with severe exposure, lung cancer, and can contain a number of hazardous components, including crystallinesilica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
and hexavalent chromium
Hexavalent chromium (chromium(VI), Cr(VI), chromium 6) is chromium in any chemical compound that contains the element in the +6 oxidation state (thus hexavalent). Virtually all chromium ore is processed via hexavalent chromium, specifically the ...
. Environmental concerns are the high energy consumption required to mine, manufacture, and transport the cement, and the related air pollution, including the release of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
, dioxin, , , and particulates. Production of portland cement contributes about 10% of world carbon dioxide emissions. The International Energy Agency has estimated that cement production will increase by between 12 and 23% by 2050 to meet the needs of the world's growing population. There are several ongoing researches targeting a suitable replacement of portland cement by supplementary cementitious materials.
''Epidemiologic Notes and Reports Sulfur Dioxide Exposure in Portland Cement Plants'', from the Centers for Disease Control
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgi ...
, states:
An independent research effort of AEA Technology to identify critical issues for the cement industry today concluded the most important environment, health and safety performance issues facing the cement industry are atmospheric releases (including greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and ...
, dioxin, , , and particulates), accidents, and worker exposure to dust.
The associated with portland cement manufacture comes mainly from four sources:
Overall, with nuclear or hydroelectric power, and efficient manufacturing, generation can be reduced to per kg cement, but can be twice as high. The thrust of innovation for the future is to reduce sources 1 and 2 by modification of the chemistry of cement, by the use of wastes, and by adopting more efficient processes. Although cement manufacturing is clearly a very large emitter, concrete (of which cement makes up about 15%) compares quite favourably with other modern building systems in this regard.. Traditional materials such as lime based mortars as well as timber and earth based construction methods emit significantly less CO2.
Cement plants used for waste disposal or processing
 Due to the high temperatures inside
Due to the high temperatures inside cement kiln
Cement kilns are used for the pyroprocessing stage of manufacture of portland and other types of hydraulic cement, in which calcium carbonate reacts with silica-bearing minerals to form a mixture of calcium silicates. Over a billion tonnes of ...
s, combined with the oxidising (oxygen-rich) atmosphere and long residence times, cement kilns are used as a processing option for various types of waste streams; indeed, they efficiently destroy many hazardous organic compounds. The waste streams also often contain combustible materials which allow the substitution of part of the fossil fuel normally used in the process.
Waste materials used in cement kilns as a fuel supplement:
*Car and truck tire
A tire (American English) or tyre (British English) is a ring-shaped component that surrounds a wheel's rim to transfer a vehicle's load from the axle through the wheel to the ground and to provide traction on the surface over which t ...
s – steel belts are easily tolerated in the kilns
*Paint sludge from automobile industries
*Waste solvents and lubricants
*Meat and bone meal
Meat and bone meal (MBM) is a product of the rendering industry. It is typically about 48–52% protein, 33–35% ash, 8–12% fat, and 4–7% water. It is primarily used in the formulation of animal feed to improve the amino acid profile of t ...
– slaughterhouse waste due to bovine spongiform encephalopathy
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), commonly known as mad cow disease, is an incurable and invariably fatal neurodegenerative disease of cattle. Symptoms include abnormal behavior, trouble walking, and weight loss. Later in the course of t ...
contamination concerns
*Waste plastics
*Sewage sludge
Sludge is a semi-solid slurry that can be produced from a range of industrial processes, from water treatment, wastewater treatment or on-site sanitation systems. For example, it can be produced as a settled suspension obtained from conventional ...
*Rice hulls
Rice hulls (or rice husks) are the hard protecting coverings of grains of rice. In addition to protecting rice during the growing season, rice hulls can be put to use as building material, fertilizer, insulation material, or fuel. Rice hulls are p ...
* Sugarcane waste
*Used wooden railroad ties (railway sleepers)
* Spent cell liner from the aluminium smelting industry (also called spent pot liner)
Portland cement manufacture also has the potential to benefit from using industrial byproducts from the waste stream. These include in particular:
* Slag
* Fly ash (from power plants)
*Silica fume
Silica fume, also known as microsilica, (CAS number 69012-64-2, EINECS number 273-761-1) is an amorphous (non-crystalline) polymorph of silicon dioxide, silica. It is an ultrafine powder collected as a by-product of the silicon and ferrosilicon a ...
(from steel mills)
*Synthetic gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywal ...
(from desulfurisation)
See also
* * * * * * * *External links
World Production of Hydraulic Cement, by Country
*Aerial views of the world's largest concentration of cement manufacturing capacity, Saraburi Province,
Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
, at
*CDC – NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Portland Cement Cement Concrete English inventions LimestoneCement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel ( aggregate) together. Cement mi ...
Building materials
19th-century inventions
de:Zement#Portlandzement