Astronomy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Astronomy () is a natural science that studies
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies
 ''Astronomy'' (from the
''Astronomy'' (from the

 A particularly important early development was the beginning of mathematical and scientific astronomy, which began among the Babylonians, who laid the foundations for the later astronomical traditions that developed in many other civilizations. The
A particularly important early development was the beginning of mathematical and scientific astronomy, which began among the Babylonians, who laid the foundations for the later astronomical traditions that developed in many other civilizations. The  Following the Babylonians, significant advances in astronomy were made in ancient Greece and the Hellenistic world. Greek astronomy is characterized from the start by seeking a rational, physical explanation for celestial phenomena. In the 3rd century BC, Aristarchus of Samos estimated the size and distance of the Moon and Sun, and he proposed a model of the Solar System where the Earth and planets rotated around the Sun, now called the heliocentric model. In the 2nd century BC, Hipparchus discovered
Following the Babylonians, significant advances in astronomy were made in ancient Greece and the Hellenistic world. Greek astronomy is characterized from the start by seeking a rational, physical explanation for celestial phenomena. In the 3rd century BC, Aristarchus of Samos estimated the size and distance of the Moon and Sun, and he proposed a model of the Solar System where the Earth and planets rotated around the Sun, now called the heliocentric model. In the 2nd century BC, Hipparchus discovered

 During the
During the
 Radio astronomy uses radiation with wavelengths greater than approximately one millimeter, outside the visible range. Radio astronomy is different from most other forms of observational astronomy in that the observed radio waves can be treated as waves rather than as discrete
Radio astronomy uses radiation with wavelengths greater than approximately one millimeter, outside the visible range. Radio astronomy is different from most other forms of observational astronomy in that the observed radio waves can be treated as waves rather than as discrete
 Infrared astronomy is founded on the detection and analysis of infrared radiation, wavelengths longer than red light and outside the range of our vision. The infrared spectrum is useful for studying objects that are too cold to radiate visible light, such as planets, circumstellar disks or nebulae whose light is blocked by dust. The longer wavelengths of infrared can penetrate clouds of dust that block visible light, allowing the observation of young stars embedded in
Infrared astronomy is founded on the detection and analysis of infrared radiation, wavelengths longer than red light and outside the range of our vision. The infrared spectrum is useful for studying objects that are too cold to radiate visible light, such as planets, circumstellar disks or nebulae whose light is blocked by dust. The longer wavelengths of infrared can penetrate clouds of dust that block visible light, allowing the observation of young stars embedded in
 Historically, optical astronomy, also called visible light astronomy, is the oldest form of astronomy. Images of observations were originally drawn by hand. In the late 19th century and most of the 20th century, images were made using photographic equipment. Modern images are made using digital detectors, particularly using
Historically, optical astronomy, also called visible light astronomy, is the oldest form of astronomy. Images of observations were originally drawn by hand. In the late 19th century and most of the 20th century, images were made using photographic equipment. Modern images are made using digital detectors, particularly using
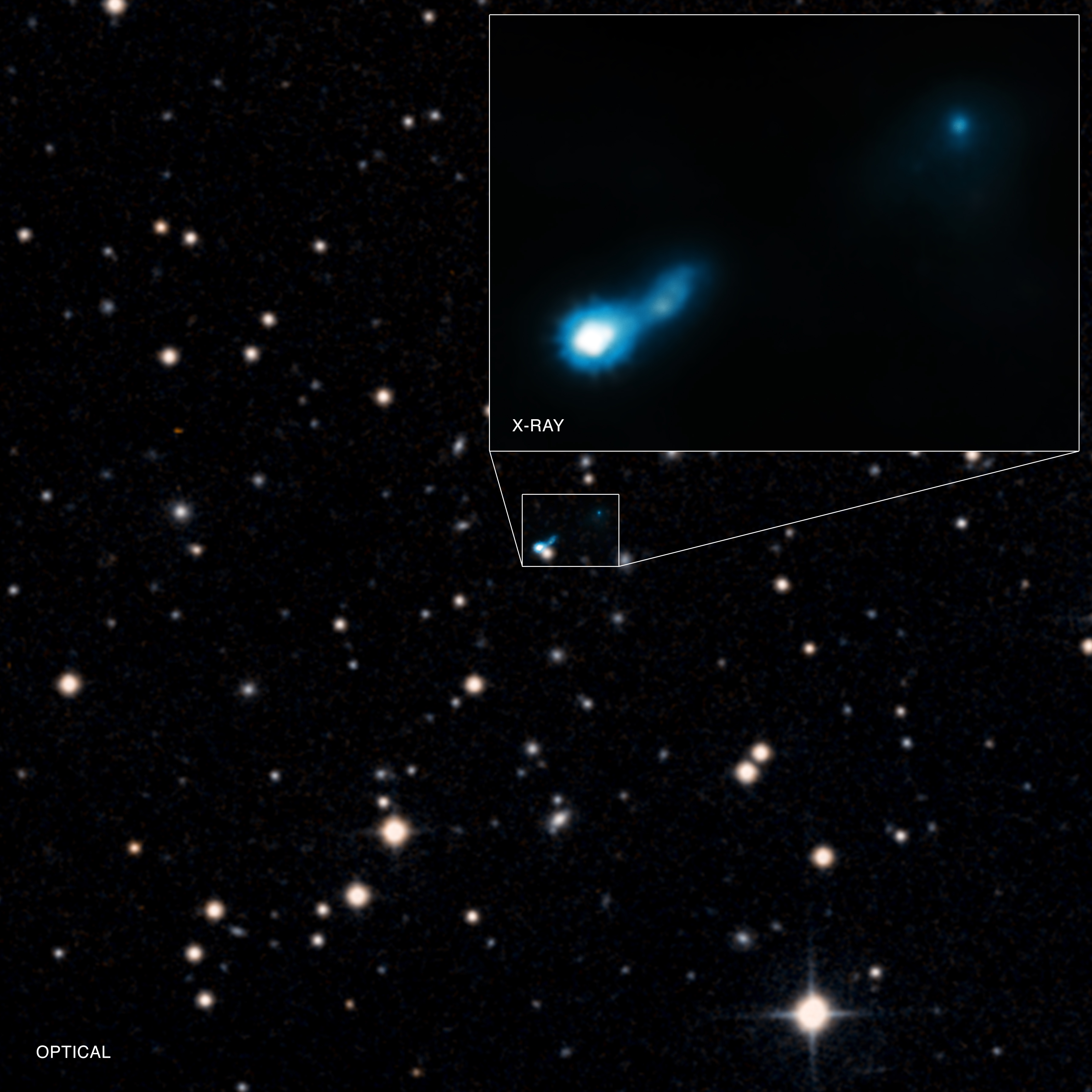 X-ray astronomy uses X-ray wavelengths. Typically, X-ray radiation is produced by
X-ray astronomy uses X-ray wavelengths. Typically, X-ray radiation is produced by
 One of the oldest fields in astronomy, and in all of science, is the measurement of the positions of celestial objects. Historically, accurate knowledge of the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets and stars has been essential in celestial navigation (the use of celestial objects to guide navigation) and in the making of calendars.
Careful measurement of the positions of the planets has led to a solid understanding of gravitational perturbations, and an ability to determine past and future positions of the planets with great accuracy, a field known as celestial mechanics. More recently the tracking of near-Earth objects will allow for predictions of close encounters or potential collisions of the Earth with those objects.
The measurement of stellar parallax of nearby stars provides a fundamental baseline in the cosmic distance ladder that is used to measure the scale of the Universe. Parallax measurements of nearby stars provide an absolute baseline for the properties of more distant stars, as their properties can be compared. Measurements of the radial velocity and proper motion of stars allow astronomers to plot the movement of these systems through the Milky Way galaxy. Astrometric results are the basis used to calculate the distribution of speculated dark matter in the galaxy.
During the 1990s, the measurement of the stellar wobble of nearby stars was used to detect large
One of the oldest fields in astronomy, and in all of science, is the measurement of the positions of celestial objects. Historically, accurate knowledge of the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets and stars has been essential in celestial navigation (the use of celestial objects to guide navigation) and in the making of calendars.
Careful measurement of the positions of the planets has led to a solid understanding of gravitational perturbations, and an ability to determine past and future positions of the planets with great accuracy, a field known as celestial mechanics. More recently the tracking of near-Earth objects will allow for predictions of close encounters or potential collisions of the Earth with those objects.
The measurement of stellar parallax of nearby stars provides a fundamental baseline in the cosmic distance ladder that is used to measure the scale of the Universe. Parallax measurements of nearby stars provide an absolute baseline for the properties of more distant stars, as their properties can be compared. Measurements of the radial velocity and proper motion of stars allow astronomers to plot the movement of these systems through the Milky Way galaxy. Astrometric results are the basis used to calculate the distribution of speculated dark matter in the galaxy.
During the 1990s, the measurement of the stellar wobble of nearby stars was used to detect large
 Observations of the large-scale structure of the Universe, a branch known as
Observations of the large-scale structure of the Universe, a branch known as
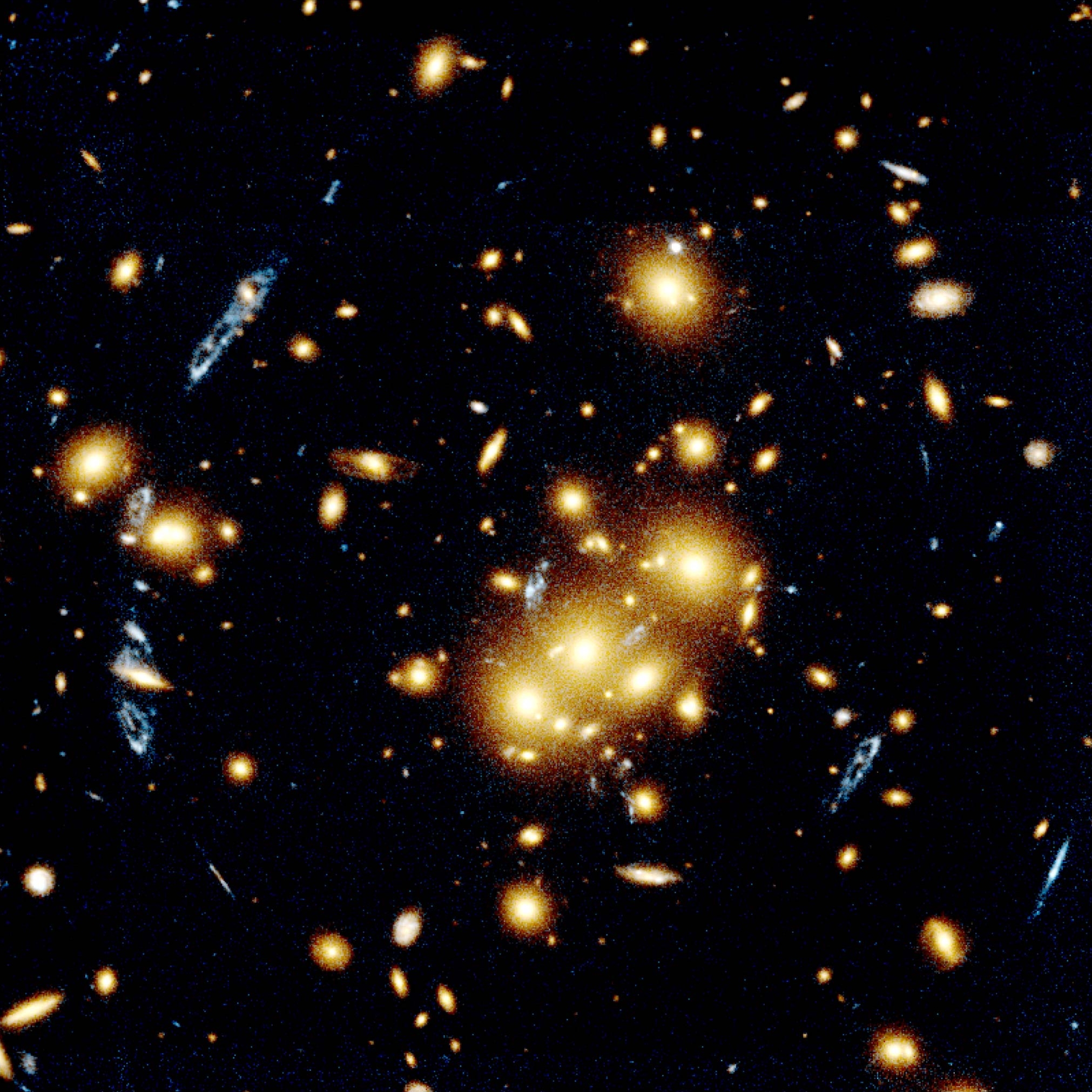 The study of objects outside our galaxy is a branch of astronomy concerned with the formation and evolution of Galaxies, their morphology (description) and classification, the observation of active galaxies, and at a larger scale, the groups and clusters of galaxies. Finally, the latter is important for the understanding of the
The study of objects outside our galaxy is a branch of astronomy concerned with the formation and evolution of Galaxies, their morphology (description) and classification, the observation of active galaxies, and at a larger scale, the groups and clusters of galaxies. Finally, the latter is important for the understanding of the
 The Solar System orbits within the Milky Way, a
The Solar System orbits within the Milky Way, a
 The study of stars and stellar evolution is fundamental to our understanding of the Universe. The astrophysics of stars has been determined through observation and theoretical understanding; and from computer simulations of the interior.Harpaz, 1994, pp. 7–18 Star formation occurs in dense regions of dust and gas, known as giant molecular clouds. When destabilized, cloud fragments can collapse under the influence of gravity, to form a
The study of stars and stellar evolution is fundamental to our understanding of the Universe. The astrophysics of stars has been determined through observation and theoretical understanding; and from computer simulations of the interior.Harpaz, 1994, pp. 7–18 Star formation occurs in dense regions of dust and gas, known as giant molecular clouds. When destabilized, cloud fragments can collapse under the influence of gravity, to form a
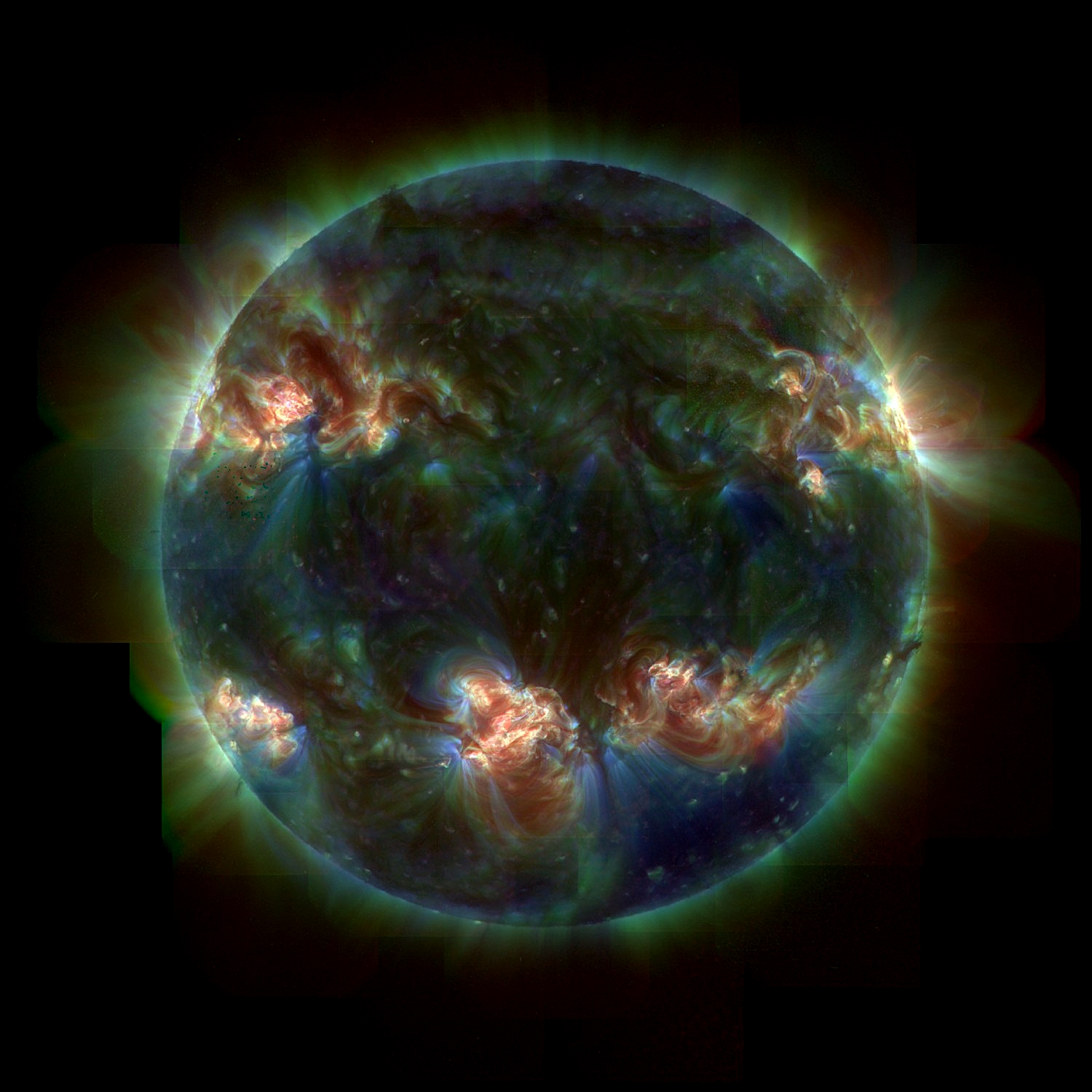
 At a distance of about eight light-minutes, the most frequently studied star is the
At a distance of about eight light-minutes, the most frequently studied star is the
 Planetary science is the study of the assemblage of planets,
Planetary science is the study of the assemblage of planets,
 Astronomy is one of the sciences to which amateurs can contribute the most.
Collectively, amateur astronomers observe a variety of celestial objects and phenomena sometimes with consumer-level equipment or equipment that they build themselves. Common targets of amateur astronomers include the Sun, the Moon, planets, stars, comets, meteor showers, and a variety of deep-sky objects such as star clusters, galaxies, and nebulae. Astronomy clubs are located throughout the world and many have programs to help their members set up and complete observational programs including those to observe all the objects in the Messier (110 objects) or Herschel 400 catalogues of points of interest in the night sky. One branch of amateur astronomy,
Astronomy is one of the sciences to which amateurs can contribute the most.
Collectively, amateur astronomers observe a variety of celestial objects and phenomena sometimes with consumer-level equipment or equipment that they build themselves. Common targets of amateur astronomers include the Sun, the Moon, planets, stars, comets, meteor showers, and a variety of deep-sky objects such as star clusters, galaxies, and nebulae. Astronomy clubs are located throughout the world and many have programs to help their members set up and complete observational programs including those to observe all the objects in the Messier (110 objects) or Herschel 400 catalogues of points of interest in the night sky. One branch of amateur astronomy,
NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database (NED)NED-Distances
International Year of Astronomy 2009
IYA2009 Main website
from the American Institute of Physics
Southern Hemisphere Astronomy
Celestia Motherlode
Educational site for Astronomical journeys through space
Kroto, Harry
Astrophysical Chemistry Lecture Series.
Core books
an
Core journals
in Astronomy, from the Smithsonian/NASA
A Journey with Fred Hoyle
by Wickramasinghe, Chandra.
Astronomy books from the History of Science Collection
at
 Astronomy () is a natural science that studies
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are often us ...
and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons
A natural satellite is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or small Solar System body (or sometimes another natural satellite). Natural satellites are often colloquially referred to as ''moons'' ...
, stars, nebulae
A nebula ('cloud' or 'fog' in Latin; pl. nebulae, nebulæ or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming region ...
, galaxies, and comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ...
s. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray burst
In gamma-ray astronomy, gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are immensely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the most energetic and luminous electromagnetic events since the Big Bang. Bursts can last from ten millise ...
s, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation
In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an early stage of the universe, also known as "relic radiation". The CMB is faint cosmic background radiation filling all space ...
. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. ...
as a whole.
Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonians
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. 1 ...
, Greeks, Indians, Egyptians, Chinese, Maya
Maya may refer to:
Civilizations
* Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and northern Central America
** Maya civilization, the historical civilization of the Maya peoples
** Maya language, the languages of the Maya peoples
* Maya (Ethiopia), a popul ...
, and many ancient indigenous peoples of the Americas. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as astrometry, celestial navigation, observational astronomy, and the making of calendars. Nowadays, professional astronomy is often said to be the same as astrophysics.
Professional astronomy is split into observational
Observation is the active acquisition of information from a primary source. In living beings, observation employs the senses. In science, observation can also involve the perception and recording of data (information), data via the use of scienti ...
and theoretical
A theory is a rational type of abstract thinking about a phenomenon, or the results of such thinking. The process of contemplative and rational thinking is often associated with such processes as observational study or research. Theories may be ...
branches. Observational astronomy is focused on acquiring data from observations of astronomical objects. This data is then analyzed using basic principles of physics. Theoretical astronomy is oriented toward the development of computer or analytical models to describe astronomical objects and phenomena. These two fields complement each other. Theoretical astronomy seeks to explain observational results and observations are used to confirm theoretical results.
Astronomy is one of the few sciences in which amateurs play an active role. This is especially true for the discovery and observation of transient events. Amateur astronomers have helped with many important discoveries, such as finding new comets.
Etymology

Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
ἀστρονομία from ἄστρον ''astron'', "star" and -νομία '' -nomia'' from νόμος ''nomos'', "law" or "culture") means "law of the stars" (or "culture of the stars" depending on the translation). Astronomy should not be confused with astrology, the belief system which claims that human affairs are correlated with the positions of celestial objects. Although the two fields share a common origin, they are now entirely distinct.
Use of terms "astronomy" and "astrophysics"
"Astronomy" and "astrophysics" are synonyms. Based on strict dictionary definitions, "astronomy" refers to "the study of objects and matter outside the Earth's atmosphere and of their physical and chemical properties," while "astrophysics" refers to the branch of astronomy dealing with "the behavior, physical properties, and dynamic processes of celestial objects and phenomena". In some cases, as in the introduction of the introductory textbook ''The Physical Universe'' byFrank Shu
Frank Hsia-San Shu (; born June 2, 1943), is a Chinese-American astrophysicist, astronomer and author. He is currently a University Professor Emeritus at the University of California, Berkeley and University of California, San Diego. He is be ...
, "astronomy" may be used to describe the qualitative study of the subject, whereas "astrophysics" is used to describe the physics-oriented version of the subject. However, since most modern astronomical research deals with subjects related to physics, modern astronomy could actually be called astrophysics. Some fields, such as astrometry, are purely astronomy rather than also astrophysics. Various departments in which scientists carry out research on this subject may use "astronomy" and "astrophysics", partly depending on whether the department is historically affiliated with a physics department, and many professional astronomers have physics rather than astronomy degrees. Some titles of the leading scientific journals in this field include '' The Astronomical Journal'', '' The Astrophysical Journal'', and '' Astronomy & Astrophysics''.
History

Ancient times
In early historic times, astronomy only consisted of the observation and predictions of the motions of objects visible to the naked eye. In some locations, early cultures assembled massive artifacts that possibly had some astronomical purpose. In addition to their ceremonial uses, these observatories could be employed to determine the seasons, an important factor in knowing when to plant crops and in understanding the length of the year.Forbes, 1909 Before tools such as the telescope were invented, early study of the stars was conducted using the naked eye. As civilizations developed, most notably inMesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
, Persia, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, China, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, and Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
, astronomical observatories were assembled and ideas on the nature of the Universe began to develop. Most early astronomy consisted of mapping the positions of the stars and planets, a science now referred to as astrometry. From these observations, early ideas about the motions of the planets were formed, and the nature of the Sun, Moon and the Earth in the Universe were explored philosophically. The Earth was believed to be the center of the Universe with the Sun, the Moon and the stars rotating around it. This is known as the geocentric model of the Universe, or the Ptolemaic system
In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, often exemplified specifically by the Ptolemaic system) is a superseded description of the Universe with Earth at the center. Under most geocentric models, the Sun, Moon, stars, an ...
, named after Ptolemy.
 A particularly important early development was the beginning of mathematical and scientific astronomy, which began among the Babylonians, who laid the foundations for the later astronomical traditions that developed in many other civilizations. The
A particularly important early development was the beginning of mathematical and scientific astronomy, which began among the Babylonians, who laid the foundations for the later astronomical traditions that developed in many other civilizations. The Babylonians
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. 1 ...
discovered that lunar eclipses recurred in a repeating cycle known as a saros.
 Following the Babylonians, significant advances in astronomy were made in ancient Greece and the Hellenistic world. Greek astronomy is characterized from the start by seeking a rational, physical explanation for celestial phenomena. In the 3rd century BC, Aristarchus of Samos estimated the size and distance of the Moon and Sun, and he proposed a model of the Solar System where the Earth and planets rotated around the Sun, now called the heliocentric model. In the 2nd century BC, Hipparchus discovered
Following the Babylonians, significant advances in astronomy were made in ancient Greece and the Hellenistic world. Greek astronomy is characterized from the start by seeking a rational, physical explanation for celestial phenomena. In the 3rd century BC, Aristarchus of Samos estimated the size and distance of the Moon and Sun, and he proposed a model of the Solar System where the Earth and planets rotated around the Sun, now called the heliocentric model. In the 2nd century BC, Hipparchus discovered precession
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In oth ...
, calculated the size and distance of the Moon and invented the earliest known astronomical devices such as the astrolabe. Hipparchus also created a comprehensive catalog of 1020 stars, and most of the constellations of the northern hemisphere derive from Greek astronomy. The Antikythera mechanism (–80 BC) was an early analog computer
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computer that uses the continuous variation aspect of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities (''analog signals'') to model the problem being solved. In ...
designed to calculate the location of the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
, Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
, and planets for a given date. Technological artifacts of similar complexity did not reappear until the 14th century, when mechanical astronomical clock
An astronomical clock, horologium, or orloj is a clock with special mechanisms and dials to display astronomical information, such as the relative positions of the Sun, Moon, zodiacal constellations, and sometimes major planets.
Definition ...
s appeared in Europe.
Middle Ages
Medieval Europe housed a number of important astronomers.Richard of Wallingford
Richard of Wallingford (1292–1336) was an English mathematician, astronomer, horologist, and cleric who made major contributions to astronomy and horology while serving as abbot of St Albans Abbey in Hertfordshire.
Biography
Richard was bor ...
(1292–1336) made major contributions to astronomy and horology
Horology (; related to Latin '; ; , interfix ''-o-'', and suffix ''-logy''), . is the study of the measurement of time. Clocks, watches, clockwork, sundials, hourglasses, clepsydras, timers, time recorders, marine chronometers, and atomic clo ...
, including the invention of the first astronomical clock, the Rectangulus which allowed for the measurement of angles between planets and other astronomical bodies, as well as an equatorium called the ''Albion'' which could be used for astronomical calculations such as lunar, solar and planetary longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east– west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lette ...
s and could predict eclipses. Nicole Oresme
Nicole Oresme (; c. 1320–1325 – 11 July 1382), also known as Nicolas Oresme, Nicholas Oresme, or Nicolas d'Oresme, was a French philosopher of the later Middle Ages. He wrote influential works on economics, mathematics, physics, astrology an ...
(1320–1382) and Jean Buridan
Jean Buridan (; Latin: ''Johannes Buridanus''; – ) was an influential 14th-century French philosopher.
Buridan was a teacher in the faculty of arts at the University of Paris for his entire career who focused in particular on logic and the wor ...
(1300–1361) first discussed evidence for the rotation of the Earth, furthermore, Buridan also developed the theory of impetus (predecessor of the modern scientific theory of inertia
Inertia is the idea that an object will continue its current motion until some force causes its speed or direction to change. The term is properly understood as shorthand for "the principle of inertia" as described by Newton in his first law ...
) which was able to show planets were capable of motion without the intervention of angels. Georg von Peuerbach
Georg von Peuerbach (also Purbach, Peurbach; la, Purbachius; born May 30, 1423 – April 8, 1461) was an Austrian astronomer, poet, mathematician and instrument maker, best known for his streamlined presentation of Ptolemaic astronomy in the ''Th ...
(1423–1461) and Regiomontanus
Johannes Müller von Königsberg (6 June 1436 – 6 July 1476), better known as Regiomontanus (), was a mathematician, astrologer and astronomer of the German Renaissance, active in Vienna, Buda and Nuremberg. His contributions were instrument ...
(1436–1476) helped make astronomical progress instrumental to Copernicus's development of the heliocentric model decades later.
Astronomy flourished in the Islamic world and other parts of the world. This led to the emergence of the first astronomical observatories in the Muslim world by the early 9th century. In 964, the Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy (IPA: ), also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224 and originally the Andromeda Nebula, is a barred spiral galaxy with the diameter of about approximately from Earth and the nearest large galaxy to the Milky Way. The gal ...
, the largest galaxy in the Local Group, was described by the Persian Muslim astronomer Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi in his ''Book of Fixed Stars
The ''Book of Fixed Stars'' ( ar, كتاب صور الكواكب ', literally ''The Book of the Shapes of Stars'') is an astronomical text written by Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi (Azophi) around 964. Following the translation movement in the 9th centu ...
''. The SN 1006 supernova, the brightest apparent magnitude stellar event in recorded history, was observed by the Egyptian Arabic astronomer Ali ibn Ridwan and Chinese astronomers in 1006. Some of the prominent Islamic (mostly Persian and Arab) astronomers who made significant contributions to the science include Al-Battani, Thebit, Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi, Biruni, Abū Ishāq Ibrāhīm al-Zarqālī, Al-Birjandi, and the astronomers of the Maragheh
Maragheh ( fa, مراغه, Marāgheh or ''Marāgha''; az, ماراغا ) is a city and capital of Maragheh County, East Azerbaijan Province, Iran. Maragheh is on the bank of the river Sufi Chay. The population consists mostly of Iranian Azerba ...
and Samarkand observatories. Astronomers during that time introduced many Arabic names now used for individual stars.
It is also believed that the ruins at Great Zimbabwe and Timbuktu may have housed astronomical observatories. In Post-classical
In world history, post-classical history refers to the period from about 500 AD to 1500, roughly corresponding to the European Middle Ages. The period is characterized by the expansion of civilizations geographically and development of trade ...
West Africa, Astronomers studied the movement of stars and relation to seasons, crafting charts of the heavens as well as precise diagrams of orbits of the other planets based on complex mathematical calculations. Songhai historian Mahmud Kati documented a meteor shower in August 1583.
Europeans had previously believed that there had been no astronomical observation in sub-Saharan Africa during the pre-colonial Middle Ages, but modern discoveries show otherwise.
For over six centuries (from the recovery of ancient learning during the late Middle Ages into the Enlightenment), the Roman Catholic Church gave more financial and social support to the study of astronomy than probably all other institutions. Among the Church's motives was finding the date for Easter.
Scientific revolution

 During the
During the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
, Nicolaus Copernicus proposed a heliocentric model of the solar system. His work was defended by Galileo Galilei and expanded upon by Johannes Kepler. Kepler was the first to devise a system that correctly described the details of the motion of the planets around the Sun. However, Kepler did not succeed in formulating a theory behind the laws he wrote down. It was Isaac Newton, with his invention of celestial dynamics
Celestial mechanics is the branch of astronomy that deals with the motions of objects in outer space. Historically, celestial mechanics applies principles of physics (classical mechanics) to astronomical objects, such as stars and planets, ...
and his law of gravitation
Newton's law of universal gravitation is usually stated as that every particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distanc ...
, who finally explained the motions of the planets. Newton also developed the reflecting telescope
A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is a telescope that uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century by Isaac Newton as an alternati ...
.Forbes, 1909, pp. 58–64
Improvements in the size and quality of the telescope led to further discoveries. The English astronomer John Flamsteed
John Flamsteed (19 August 1646 – 31 December 1719) was an English astronomer and the first Astronomer Royal. His main achievements were the preparation of a 3,000-star catalogue, ''Catalogus Britannicus'', and a star atlas called '' Atlas C ...
catalogued over 3000 stars, More extensive star catalogues were produced by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille. The astronomer William Herschel
Frederick William Herschel (; german: Friedrich Wilhelm Herschel; 15 November 1738 – 25 August 1822) was a German-born British astronomer and composer. He frequently collaborated with his younger sister and fellow astronomer Caroline ...
made a detailed catalog of nebulosity and clusters, and in 1781 discovered the planet Uranus, the first new planet found.
During the 18–19th centuries, the study of the three-body problem
In physics and classical mechanics, the three-body problem is the problem of taking the initial positions and velocities (or momenta) of three point masses and solving for their subsequent motion according to Newton's laws of motion and Newton's ...
by Leonhard Euler, Alexis Claude Clairaut
Alexis Claude Clairaut (; 13 May 1713 – 17 May 1765) was a French mathematician, astronomer, and geophysicist. He was a prominent Newtonian whose work helped to establish the validity of the principles and results that Sir Isaac Newton had ou ...
, and Jean le Rond d'Alembert
Jean-Baptiste le Rond d'Alembert (; ; 16 November 1717 – 29 October 1783) was a French mathematician, mechanician, physicist, philosopher, and music theorist. Until 1759 he was, together with Denis Diderot, a co-editor of the '' Encyclopéd ...
led to more accurate predictions about the motions of the Moon and planets. This work was further refined by Joseph-Louis Lagrange and Pierre Simon Laplace
Pierre-Simon, marquis de Laplace (; ; 23 March 1749 – 5 March 1827) was a French scholar and polymath whose work was important to the development of engineering, mathematics, statistics, physics, astronomy, and philosophy. He summarized ...
, allowing the masses of the planets and moons to be estimated from their perturbations.
Significant advances in astronomy came about with the introduction of new technology, including the spectroscope
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify mate ...
and photography
Photography is the art, application, and practice of creating durable images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is employe ...
. Joseph von Fraunhofer discovered about 600 bands in the spectrum of the Sun in 1814–15, which, in 1859, Gustav Kirchhoff
Gustav Robert Kirchhoff (; 12 March 1824 – 17 October 1887) was a German physicist who contributed to the fundamental understanding of electrical circuits, spectroscopy, and the emission of black-body radiation by heated objects.
He ...
ascribed to the presence of different elements. Stars were proven to be similar to the Earth's own Sun, but with a wide range of temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various Conversion of units of temperature, temp ...
s, masses, and sizes.
The existence of the Earth's galaxy, the Milky Way, as its own group of stars was only proved in the 20th century, along with the existence of "external" galaxies. The observed recession of those galaxies led to the discovery of the expansion of the Universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. ...
. Theoretical astronomy led to speculations on the existence of objects such as black holes and neutron stars, which have been used to explain such observed phenomena as quasars, pulsars, blazars, and radio galaxies
A radio galaxy is a galaxy with giant regions of radio emission extending well beyond its visible structure. These energetic radio lobes are powered by jets from its active galactic nucleus. They have luminosities up to 1039 W at radio wav ...
. Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology is a branch of cosmology concerned with the study of cosmological models. A cosmological model, or simply cosmology, provides a description of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and allows study of f ...
made huge advances during the 20th century. In the early 1900s the model of the Big Bang theory was formulated, heavily evidenced by cosmic microwave background radiation
In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an early stage of the universe, also known as "relic radiation". The CMB is faint cosmic background radiation filling all space ...
, Hubble's law
Hubble's law, also known as the Hubble–Lemaître law, is the observation in physical cosmology that galaxies are moving away from Earth at speeds proportional to their distance. In other words, the farther they are, the faster they are moving a ...
, and the cosmological abundances of elements. Space telescope
A space telescope or space observatory is a telescope in outer space used to observe astronomical objects. Suggested by Lyman Spitzer in 1946, the first operational telescopes were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory, OAO-2 launch ...
s have enabled measurements in parts of the electromagnetic spectrum normally blocked or blurred by the atmosphere. In February 2016, it was revealed that the LIGO
The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) is a large-scale physics experiment and observatory designed to detect cosmic gravitational waves and to develop gravitational-wave observations as an astronomical tool. Two large ...
project had detected evidence of gravitational waves in the previous September.
Observational astronomy
The main source of information about celestial bodies and other objects is visible light, or more generally electromagnetic radiation. Observational astronomy may be categorized according to the corresponding region of the electromagnetic spectrum on which the observations are made. Some parts of the spectrum can be observed from the Earth's surface, while other parts are only observable from either high altitudes or outside the Earth's atmosphere. Specific information on these subfields is given below.Radio astronomy
 Radio astronomy uses radiation with wavelengths greater than approximately one millimeter, outside the visible range. Radio astronomy is different from most other forms of observational astronomy in that the observed radio waves can be treated as waves rather than as discrete
Radio astronomy uses radiation with wavelengths greater than approximately one millimeter, outside the visible range. Radio astronomy is different from most other forms of observational astronomy in that the observed radio waves can be treated as waves rather than as discrete photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they a ...
s. Hence, it is relatively easier to measure both the amplitude and phase of radio waves, whereas this is not as easily done at shorter wavelengths.
Although some radio waves are emitted directly by astronomical objects, a product of thermal emission, most of the radio emission that is observed is the result of synchrotron radiation, which is produced when electrons orbit magnetic fields. Additionally, a number of spectral lines produced by interstellar gas
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter and radiation that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstella ...
, notably the hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
spectral line at 21 cm, are observable at radio wavelengths.
A wide variety of other objects are observable at radio wavelengths, including supernovae, interstellar gas, pulsars, and active galactic nuclei
An active galactic nucleus (AGN) is a compact region at the center of a galaxy that has a much-higher-than-normal luminosity over at least some portion of the electromagnetic spectrum with characteristics indicating that the luminosity is not prod ...
.
Infrared astronomy
 Infrared astronomy is founded on the detection and analysis of infrared radiation, wavelengths longer than red light and outside the range of our vision. The infrared spectrum is useful for studying objects that are too cold to radiate visible light, such as planets, circumstellar disks or nebulae whose light is blocked by dust. The longer wavelengths of infrared can penetrate clouds of dust that block visible light, allowing the observation of young stars embedded in
Infrared astronomy is founded on the detection and analysis of infrared radiation, wavelengths longer than red light and outside the range of our vision. The infrared spectrum is useful for studying objects that are too cold to radiate visible light, such as planets, circumstellar disks or nebulae whose light is blocked by dust. The longer wavelengths of infrared can penetrate clouds of dust that block visible light, allowing the observation of young stars embedded in molecular cloud
A molecular cloud, sometimes called a stellar nursery (if star formation is occurring within), is a type of interstellar cloud, the density and size of which permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydroge ...
s and the cores of galaxies. Observations from the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) have been particularly effective at unveiling numerous galactic protostar
A protostar is a very young star that is still gathering mass from its parent molecular cloud. The protostellar phase is the earliest one in the process of stellar evolution. For a low-mass star (i.e. that of the Sun or lower), it lasts about 50 ...
s and their host star clusters.
With the exception of infrared wavelengths
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tr ...
close to visible light, such radiation is heavily absorbed by the atmosphere, or masked, as the atmosphere itself produces significant infrared emission. Consequently, infrared observatories have to be located in high, dry places on Earth or in space. Some molecules radiate strongly in the infrared. This allows the study of the chemistry of space; more specifically it can detect water in comets.
Optical astronomy
charge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a ...
s (CCDs) and recorded on modern medium. Although visible light itself extends from approximately 4000 Å to 7000 Å (400 nm to 700 nm), that same equipment can be used to observe some near-ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
and near-infrared radiation.
Ultraviolet astronomy
Ultraviolet astronomy employs ultraviolet wavelengths between approximately 100 and 3200 Å (10 to 320 nm). Light at those wavelengths is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, requiring observations at these wavelengths to be performed from the upper atmosphere or from space. Ultraviolet astronomy is best suited to the study of thermal radiation and spectral emission lines from hot blue stars (OB star
OB stars are hot, massive stars of spectral types O or early-type B that form in loosely organized groups called OB associations. They are short lived, and thus do not move very far from where they formed within their life. During their lifet ...
s) that are very bright in this wave band. This includes the blue stars in other galaxies, which have been the targets of several ultraviolet surveys. Other objects commonly observed in ultraviolet light include planetary nebula
A planetary nebula (PN, plural PNe) is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.
The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelate ...
e, supernova remnant
A supernova remnant (SNR) is the structure resulting from the explosion of a star in a supernova. The supernova remnant is bounded by an expanding shock wave, and consists of ejected material expanding from the explosion, and the interstellar mat ...
s, and active galactic nuclei. However, as ultraviolet light is easily absorbed by interstellar dust, an adjustment of ultraviolet measurements is necessary.
X-ray astronomy
 X-ray astronomy uses X-ray wavelengths. Typically, X-ray radiation is produced by
X-ray astronomy uses X-ray wavelengths. Typically, X-ray radiation is produced by synchrotron emission
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in ...
(the result of electrons orbiting magnetic field lines), thermal emission from thin gases above 107 (10 million) kelvins, and thermal emission from thick gases above 107 Kelvin. Since X-rays are absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, all X-ray observations must be performed from high-altitude balloons, rockets, or X-ray astronomy satellites. Notable X-ray sources include X-ray binaries, pulsars, supernova remnant
A supernova remnant (SNR) is the structure resulting from the explosion of a star in a supernova. The supernova remnant is bounded by an expanding shock wave, and consists of ejected material expanding from the explosion, and the interstellar mat ...
s, elliptical galaxies
An elliptical galaxy is a type of galaxy with an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless image. They are one of the four main classes of galaxy described by Edwin Hubble in his Hubble sequence and 1936 work ''The Real ...
, clusters of galaxies, and active galactic nuclei
An active galactic nucleus (AGN) is a compact region at the center of a galaxy that has a much-higher-than-normal luminosity over at least some portion of the electromagnetic spectrum with characteristics indicating that the luminosity is not prod ...
.
Gamma-ray astronomy
Gamma ray astronomy observes astronomical objects at the shortest wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. Gamma rays may be observed directly by satellites such as theCompton Gamma Ray Observatory
The Compton Gamma Ray Observatory (CGRO) was a space observatory detecting photons with photon energy, energies from 20 kElectronvolt#Properties, eV to 30 GeV, in Earth orbit from 1991 to 2000. The observatory featured four main tele ...
or by specialized telescopes called atmospheric Cherenkov telescopes. The Cherenkov telescopes do not detect the gamma rays directly but instead detect the flashes of visible light produced when gamma rays are absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere.
Most gamma-ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically sh ...
emitting sources are actually gamma-ray burst
In gamma-ray astronomy, gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are immensely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the most energetic and luminous electromagnetic events since the Big Bang. Bursts can last from ten millise ...
s, objects which only produce gamma radiation for a few milliseconds to thousands of seconds before fading away. Only 10% of gamma-ray sources are non-transient sources. These steady gamma-ray emitters include pulsars, neutron stars, and black hole candidates such as active galactic nuclei.
Fields not based on the electromagnetic spectrum
In addition to electromagnetic radiation, a few other events originating from great distances may be observed from the Earth. Inneutrino astronomy
Neutrino astronomy is the branch of astronomy that observes astronomical objects with neutrino detectors in special observatories. Neutrinos are created as a result of certain types of radioactive decay, nuclear reactions such as those that take ...
, astronomers use heavily shielded underground facilities such as SAGE, GALLEX, and Kamioka II/III for the detection of neutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is a fermion (an elementary particle with spin of ) that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass ...
s. The vast majority of the neutrinos streaming through the Earth originate from the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
, but 24 neutrinos were also detected from supernova 1987A. Cosmic rays, which consist of very high energy particles (atomic nuclei) that can decay or be absorbed when they enter the Earth's atmosphere, result in a cascade of secondary particles which can be detected by current observatories. Some future neutrino detector
A neutrino detector is a physics apparatus which is designed to study neutrinos. Because neutrinos only weakly interact with other particles of matter, neutrino detectors must be very large to detect a significant number of neutrinos. Neutrino d ...
s may also be sensitive to the particles produced when cosmic rays hit the Earth's atmosphere.
Gravitational-wave astronomy is an emerging field of astronomy that employs gravitational-wave detectors to collect observational data about distant massive objects. A few observatories have been constructed, such as the ''Laser Interferometer Gravitational Observatory'' LIGO
The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) is a large-scale physics experiment and observatory designed to detect cosmic gravitational waves and to develop gravitational-wave observations as an astronomical tool. Two large ...
. LIGO made its first detection on 14 September 2015, observing gravitational waves from a binary black hole. A second gravitational wave was detected on 26 December 2015 and additional observations should continue but gravitational waves require extremely sensitive instruments.
The combination of observations made using electromagnetic radiation, neutrinos or gravitational waves and other complementary information, is known as multi-messenger astronomy
Multi-messenger astronomy is astronomy based on the coordinated observation and interpretation of disparate "messenger" signals. Interplanetary probes can visit objects within the Solar System, but beyond that, information must rely on "extrasolar ...
.
Astrometry and celestial mechanics
 One of the oldest fields in astronomy, and in all of science, is the measurement of the positions of celestial objects. Historically, accurate knowledge of the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets and stars has been essential in celestial navigation (the use of celestial objects to guide navigation) and in the making of calendars.
Careful measurement of the positions of the planets has led to a solid understanding of gravitational perturbations, and an ability to determine past and future positions of the planets with great accuracy, a field known as celestial mechanics. More recently the tracking of near-Earth objects will allow for predictions of close encounters or potential collisions of the Earth with those objects.
The measurement of stellar parallax of nearby stars provides a fundamental baseline in the cosmic distance ladder that is used to measure the scale of the Universe. Parallax measurements of nearby stars provide an absolute baseline for the properties of more distant stars, as their properties can be compared. Measurements of the radial velocity and proper motion of stars allow astronomers to plot the movement of these systems through the Milky Way galaxy. Astrometric results are the basis used to calculate the distribution of speculated dark matter in the galaxy.
During the 1990s, the measurement of the stellar wobble of nearby stars was used to detect large
One of the oldest fields in astronomy, and in all of science, is the measurement of the positions of celestial objects. Historically, accurate knowledge of the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets and stars has been essential in celestial navigation (the use of celestial objects to guide navigation) and in the making of calendars.
Careful measurement of the positions of the planets has led to a solid understanding of gravitational perturbations, and an ability to determine past and future positions of the planets with great accuracy, a field known as celestial mechanics. More recently the tracking of near-Earth objects will allow for predictions of close encounters or potential collisions of the Earth with those objects.
The measurement of stellar parallax of nearby stars provides a fundamental baseline in the cosmic distance ladder that is used to measure the scale of the Universe. Parallax measurements of nearby stars provide an absolute baseline for the properties of more distant stars, as their properties can be compared. Measurements of the radial velocity and proper motion of stars allow astronomers to plot the movement of these systems through the Milky Way galaxy. Astrometric results are the basis used to calculate the distribution of speculated dark matter in the galaxy.
During the 1990s, the measurement of the stellar wobble of nearby stars was used to detect large extrasolar planet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
s orbiting those stars.
Theoretical astronomy
Theoretical astronomers use several tools including analytical models and computational numerical simulations; each has its particular advantages. Analytical models of a process are better for giving broader insight into the heart of what is going on. Numerical models reveal the existence of phenomena and effects otherwise unobserved. Theorists in astronomy endeavor to create theoretical models and from the results predict observational consequences of those models. The observation of a phenomenon predicted by a model allows astronomers to select between several alternate or conflicting models as the one best able to describe the phenomena. Theorists also try to generate or modify models to take into account new data. In the case of an inconsistency between the data and the model's results, the general tendency is to try to make minimal modifications to the model so that it produces results that fit the data. In some cases, a large amount of inconsistent data over time may lead to the total abandonment of a model. Phenomena modeled by theoretical astronomers include: stellar dynamics and evolution; galaxy formation; large-scale distribution ofmatter
In classical physics and general chemistry, matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume. All everyday objects that can be touched are ultimately composed of atoms, which are made up of interacting subatomic part ...
in the Universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. ...
; origin of cosmic rays; general relativity and physical cosmology
Physical cosmology is a branch of cosmology concerned with the study of cosmological models. A cosmological model, or simply cosmology, provides a description of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and allows study of f ...
, including string cosmology and astroparticle physics. Astrophysical relativity serves as a tool to gauge the properties of large scale structures for which gravitation plays a significant role in physical phenomena investigated and as the basis for black hole (''astro'') physics and the study of gravitational waves.
Some widely accepted and studied theories and models in astronomy, now included in the Lambda-CDM model are the Big Bang, dark matter and fundamental theories of physics.
A few examples of this process:
Along with Cosmic inflation, dark matter and dark energy are the current leading topics in astronomy, as their discovery and controversy originated during the study of the galaxies.
Specific subfields
Astrophysics
Astrophysics is the branch of astronomy that employs the principles of physics and chemistry "to ascertain the nature of the astronomical objects, rather than their positions or motions in space". Among the objects studied are theSun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
, other stars, galaxies, extrasolar planet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
s, the interstellar medium and the cosmic microwave background. Their emissions are examined across all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, and the properties examined include luminosity, density, temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various Conversion of units of temperature, temp ...
, and chemical
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., w ...
composition. Because astrophysics is a very broad subject, ''astrophysicists'' typically apply many disciplines of physics, including mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, thermodynamics, quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistr ...
, relativity, nuclear and particle physics, and atomic and molecular physics.
In practice, modern astronomical research often involves a substantial amount of work in the realms of theoretical
A theory is a rational type of abstract thinking about a phenomenon, or the results of such thinking. The process of contemplative and rational thinking is often associated with such processes as observational study or research. Theories may be ...
and observational physics. Some areas of study for astrophysicists include their attempts to determine the properties of dark matter, dark energy, and black holes; whether or not time travel is possible, wormholes can form, or the multiverse exists; and the origin and ultimate fate of the universe. Topics also studied by theoretical astrophysicists include Solar System formation and evolution; stellar dynamics and evolution; galaxy formation and evolution
The study of galaxy formation and evolution is concerned with the processes that formed a heterogeneous universe from a homogeneous beginning, the formation of the first galaxies, the way galaxies change over time, and the processes that have gen ...
; magnetohydrodynamics
Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD; also called magneto-fluid dynamics or hydromagnetics) is the study of the magnetic properties and behaviour of electrically conducting fluids. Examples of such magnetofluids include plasmas, liquid metals, ...
; large-scale structure of matter
In classical physics and general chemistry, matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume. All everyday objects that can be touched are ultimately composed of atoms, which are made up of interacting subatomic part ...
in the universe; origin of cosmic rays; general relativity and physical cosmology
Physical cosmology is a branch of cosmology concerned with the study of cosmological models. A cosmological model, or simply cosmology, provides a description of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and allows study of f ...
, including string cosmology and astroparticle physics.
Astrochemistry
Astrochemistry
Astrochemistry is the study of the abundance and reactions of molecules in the Universe, and their interaction with radiation. The discipline is an overlap of astronomy and chemistry. The word "astrochemistry" may be applied to both the Solar Syst ...
is the study of the abundance and reactions of molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
s in the Universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. ...
, and their interaction with radiation. The discipline is an overlap of astronomy and chemistry. The word "astrochemistry" may be applied to both the Solar System and the interstellar medium. The study of the abundance of elements and isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numb ...
ratios in Solar System objects, such as meteorites, is also called cosmochemistry
Cosmochemistry (from Greek κόσμος ''kósmos'', "universe" and χημεία ''khemeía'') or chemical cosmology is the study of the chemical composition of matter in the universe and the processes that led to those compositions. This is done ...
, while the study of interstellar atoms and molecules and their interaction with radiation is sometimes called molecular astrophysics. The formation, atomic and chemical composition, evolution and fate of molecular gas clouds is of special interest, because it is from these clouds that solar systems form.
Studies in this field contribute to the understanding of the formation of the Solar System, Earth's origin and geology, abiogenesis
In biology, abiogenesis (from a- 'not' + Greek bios 'life' + genesis 'origin') or the origin of life is the natural process by which life has arisen from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The prevailing scientific hypothes ...
, and the origin of climate and oceans.
Astrobiology
Astrobiology is an interdisciplinary scientific field concerned with the origins, early evolution, distribution, and future oflife
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for Cell growth, growth, reaction to Stimu ...
in the universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. ...
. Astrobiology considers the question of whether extraterrestrial life exists, and how humans can detect it if it does. The term exobiology is similar.
Astrobiology makes use of molecular biology, biophysics
Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that applies approaches and methods traditionally used in physics to study biological phenomena. Biophysics covers all scales of biological organization, from molecular to organismic and populations. ...
, biochemistry, chemistry, astronomy, physical cosmology
Physical cosmology is a branch of cosmology concerned with the study of cosmological models. A cosmological model, or simply cosmology, provides a description of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and allows study of f ...
, exoplanetology and geology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biosphere
The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also ...
s that might be different from that on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data
In the pursuit of knowledge, data (; ) is a collection of discrete values that convey information, describing quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpr ...
, and although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories
A scientific theory is an explanation of an aspect of the natural world and universe that has been repeatedly tested and corroborated in accordance with the scientific method, using accepted protocols of observation, measurement, and evaluatio ...
.
This interdisciplinary field encompasses research on the origin of planetary systems, origins of organic compounds in space, rock-water-carbon interactions, abiogenesis
In biology, abiogenesis (from a- 'not' + Greek bios 'life' + genesis 'origin') or the origin of life is the natural process by which life has arisen from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The prevailing scientific hypothes ...
on Earth, planetary habitability
Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and maintain environments hospitable to life. Life may be generated directly on a planet or satellite endogenously or be transferred to it from ...
, research on biosignatures for life detection, and studies on the potential for life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in outer space.
Physical cosmology
Cosmology (from the Greek κόσμος (''kosmos'') "world, universe" and λόγος (''logos'') "word, study" or literally "logic") could be considered the study of the Universe as a whole. Observations of the large-scale structure of the Universe, a branch known as
Observations of the large-scale structure of the Universe, a branch known as physical cosmology
Physical cosmology is a branch of cosmology concerned with the study of cosmological models. A cosmological model, or simply cosmology, provides a description of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and allows study of f ...
, have provided a deep understanding of the formation and evolution of the cosmos. Fundamental to modern cosmology is the well-accepted theory of the Big Bang, wherein our Universe began at a single point in time, and thereafter expanded over the course of 13.8 billion years to its present condition. The concept of the Big Bang can be traced back to the discovery of the microwave background radiation in 1965.
In the course of this expansion, the Universe underwent several evolutionary stages. In the very early moments, it is theorized that the Universe experienced a very rapid cosmic inflation, which homogenized the starting conditions. Thereafter, nucleosynthesis
Nucleosynthesis is the process that creates new atomic nuclei from pre-existing nucleons (protons and neutrons) and nuclei. According to current theories, the first nuclei were formed a few minutes after the Big Bang, through nuclear reactions in ...
produced the elemental abundance of the early Universe. (See also nucleocosmochronology
Nucleocosmochronology or nuclear cosmochronology is a technique used to determine timescales for astrophysical objects and events. It compares the observed ratios of abundances of heavy radioactive and stable nuclides to the primordial ratios pred ...
.)
When the first neutral atoms formed from a sea of primordial ions, space became transparent to radiation, releasing the energy viewed today as the microwave background radiation. The expanding Universe then underwent a Dark Age due to the lack of stellar energy sources.
A hierarchical structure of matter began to form from minute variations in the mass density of space. Matter accumulated in the densest regions, forming clouds of gas and the earliest stars, the Population III stars. These massive stars triggered the reionization
In the fields of Big Bang theory and cosmology, reionization is the process that caused matter in the universe to reionize after the lapse of the " dark ages".
Reionization is the second of two major phase transitions of gas in the universe (t ...
process and are believed to have created many of the heavy elements in the early Universe, which, through nuclear decay, create lighter elements, allowing the cycle of nucleosynthesis to continue longer.
Gravitational aggregations clustered into filaments, leaving voids in the gaps. Gradually, organizations of gas and dust merged to form the first primitive galaxies. Over time, these pulled in more matter, and were often organized into groups and clusters of galaxies, then into larger-scale superclusters.
Various fields of physics are crucial to studying the universe. Interdisciplinary studies involve the fields of quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistr ...
, particle physics, , condensed matter physics, statistical mechanics, optics, and nuclear physics
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter.
Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies the ...
.
Fundamental to the structure of the Universe is the existence of dark matter and dark energy. These are now thought to be its dominant components, forming 96% of the mass of the Universe. For this reason, much effort is expended in trying to understand the physics of these components.
Extragalactic astronomy
 The study of objects outside our galaxy is a branch of astronomy concerned with the formation and evolution of Galaxies, their morphology (description) and classification, the observation of active galaxies, and at a larger scale, the groups and clusters of galaxies. Finally, the latter is important for the understanding of the
The study of objects outside our galaxy is a branch of astronomy concerned with the formation and evolution of Galaxies, their morphology (description) and classification, the observation of active galaxies, and at a larger scale, the groups and clusters of galaxies. Finally, the latter is important for the understanding of the large-scale structure of the cosmos
The observable universe is a ball-shaped region of the universe comprising all matter that can be observed from Earth or its space-based telescopes and exploratory probes at the present time, because the electromagnetic radiation from these obj ...
.
Most galaxies are organized into distinct shapes that allow for classification schemes. They are commonly divided into spiral, elliptical and Irregular galaxies.
As the name suggests, an elliptical galaxy has the cross-sectional shape of an ellipse. The stars move along random orbits with no preferred direction. These galaxies contain little or no interstellar dust, few star-forming regions, and older stars. Elliptical galaxies are more commonly found at the core of galactic clusters, and may have been formed through mergers of large galaxies.
A spiral galaxy is organized into a flat, rotating disk, usually with a prominent bulge or bar at the center, and trailing bright arms that spiral outward. The arms are dusty regions of star formation within which massive young stars produce a blue tint. Spiral galaxies are typically surrounded by a halo of older stars. Both the Milky Way and one of our nearest galaxy neighbors, the Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy (IPA: ), also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224 and originally the Andromeda Nebula, is a barred spiral galaxy with the diameter of about approximately from Earth and the nearest large galaxy to the Milky Way. The gal ...
, are spiral galaxies.
Irregular galaxies are chaotic in appearance, and are neither spiral nor elliptical. About a quarter of all galaxies are irregular, and the peculiar shapes of such galaxies may be the result of gravitational interaction.
An active galaxy is a formation that emits a significant amount of its energy from a source other than its stars, dust and gas. It is powered by a compact region at the core, thought to be a supermassive black hole that is emitting radiation from in-falling material.
A radio galaxy
A radio galaxy is a galaxy with giant regions of radio emission extending well beyond its visible structure. These energetic radio lobes are powered by jets from its active galactic nucleus. They have luminosities up to 1039 W at radio wav ...
is an active galaxy that is very luminous in the radio portion of the spectrum, and is emitting immense plumes or lobes of gas. Active galaxies that emit shorter frequency, high-energy radiation include Seyfert galaxies
Seyfert galaxies are one of the two largest groups of active galaxies, along with quasars. They have quasar-like nuclei (very luminous, distant and bright sources of electromagnetic radiation) with very high surface brightnesses whose spectra ...
, Quasars, and Blazars. Quasars are believed to be the most consistently luminous objects in the known universe.
The large-scale structure of the cosmos
The observable universe is a ball-shaped region of the universe comprising all matter that can be observed from Earth or its space-based telescopes and exploratory probes at the present time, because the electromagnetic radiation from these obj ...
is represented by groups and clusters of galaxies. This structure is organized into a hierarchy of groupings, with the largest being the superclusters. The collective matter is formed into filaments and walls, leaving large voids between.
Galactic astronomy
barred spiral galaxy
A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. Bars are found in about two thirds of all spiral galaxies, and generally affect both the motions of stars and interstellar gas within spiral galaxies ...
that is a prominent member of the Local Group of galaxies. It is a rotating mass of gas, dust, stars and other objects, held together by mutual gravitational attraction. As the Earth is located within the dusty outer arms, there are large portions of the Milky Way that are obscured from view.
In the center of the Milky Way is the core, a bar-shaped bulge with what is believed to be a supermassive black hole
A supermassive black hole (SMBH or sometimes SBH) is the largest type of black hole, with its mass being on the order of hundreds of thousands, or millions to billions of times the mass of the Sun (). Black holes are a class of astronomical ob ...
at its center. This is surrounded by four primary arms that spiral from the core. This is a region of active star formation that contains many younger, population I
During 1944, Walter Baade categorized groups of stars within the Milky Way into stellar populations.
In the abstract of the article by Baade, he recognizes that Jan Oort originally conceived this type of classification in 1926:
Baade noticed th ...
stars. The disk is surrounded by a spheroid halo of older, population II
During 1944, Walter Baade categorized groups of stars within the Milky Way into stellar populations.
In the abstract of the article by Baade, he recognizes that Jan Oort originally conceived this type of classification in 1926:
Baade noticed ...
stars, as well as relatively dense concentrations of stars known as globular cluster
A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars. Globular clusters are bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards their centers. They can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of membe ...
s.
Between the stars lies the interstellar medium, a region of sparse matter. In the densest regions, molecular cloud
A molecular cloud, sometimes called a stellar nursery (if star formation is occurring within), is a type of interstellar cloud, the density and size of which permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydroge ...
s of molecular hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, ...
and other elements create star-forming regions. These begin as a compact pre-stellar core
Pre-stellar cores are the nurseries of new stars, and are an early phase in the formation of low-mass stars, before gravitational collapse produces a central protostar. The spatial distribution of pre-stellar cores shows the history of their forma ...
or dark nebulae, which concentrate and collapse (in volumes determined by the Jeans length) to form compact protostars.
As the more massive stars appear, they transform the cloud into an H II region
An H II region or HII region is a region of interstellar atomic hydrogen that is ionized. It is typically in a molecular cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place, with a size ranging from one to hundreds ...
(ionized atomic hydrogen) of glowing gas and plasma. The stellar wind and supernova explosions from these stars eventually cause the cloud to disperse, often leaving behind one or more young open clusters of stars. These clusters gradually disperse, and the stars join the population of the Milky Way.
Kinematic studies of matter in the Milky Way and other galaxies have demonstrated that there is more mass than can be accounted for by visible matter. A dark matter halo appears to dominate the mass, although the nature of this dark matter remains undetermined.
Stellar astronomy
 The study of stars and stellar evolution is fundamental to our understanding of the Universe. The astrophysics of stars has been determined through observation and theoretical understanding; and from computer simulations of the interior.Harpaz, 1994, pp. 7–18 Star formation occurs in dense regions of dust and gas, known as giant molecular clouds. When destabilized, cloud fragments can collapse under the influence of gravity, to form a
The study of stars and stellar evolution is fundamental to our understanding of the Universe. The astrophysics of stars has been determined through observation and theoretical understanding; and from computer simulations of the interior.Harpaz, 1994, pp. 7–18 Star formation occurs in dense regions of dust and gas, known as giant molecular clouds. When destabilized, cloud fragments can collapse under the influence of gravity, to form a protostar
A protostar is a very young star that is still gathering mass from its parent molecular cloud. The protostellar phase is the earliest one in the process of stellar evolution. For a low-mass star (i.e. that of the Sun or lower), it lasts about 50 ...
. A sufficiently dense, and hot, core region will trigger nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei are combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles ( neutrons or protons). The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manife ...
, thus creating a main-sequence star
In astronomy, the main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Hert ...
.
Almost all elements heavier than hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
and helium were created inside the cores of stars.
The characteristics of the resulting star depend primarily upon its starting mass. The more massive the star, the greater its luminosity, and the more rapidly it fuses its hydrogen fuel into helium in its core. Over time, this hydrogen fuel is completely converted into helium, and the star begins to evolve. The fusion of helium requires a higher core temperature. A star with a high enough core temperature will push its outer layers outward while increasing its core density. The resulting red giant formed by the expanding outer layers enjoys a brief life span, before the helium fuel in the core is in turn consumed. Very massive stars can also undergo a series of evolutionary phases, as they fuse increasingly heavier elements.Harpaz, 1994
The final fate of the star depends on its mass, with stars of mass greater than about eight times the Sun becoming core collapse supernovae; while smaller stars blow off their outer layers and leave behind the inert core in the form of a white dwarf. The ejection of the outer layers forms a planetary nebula
A planetary nebula (PN, plural PNe) is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.
The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelate ...
. The remnant of a supernova is a dense neutron star, or, if the stellar mass was at least three times that of the Sun, a black hole. Closely orbiting binary stars can follow more complex evolutionary paths, such as mass transfer onto a white dwarf companion that can potentially cause a supernova. Planetary nebulae and supernovae distribute the " metals" produced in the star by fusion to the interstellar medium; without them, all new stars (and their planetary systems) would be formed from hydrogen and helium alone.
Solar astronomy

 At a distance of about eight light-minutes, the most frequently studied star is the
At a distance of about eight light-minutes, the most frequently studied star is the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
, a typical main-sequence dwarf star
A dwarf star is a star of relatively small size and low luminosity. Most main sequence stars are dwarf stars. The meaning of the word "dwarf" was later extended to some star-sized objects that are not stars, and compact stellar remnants which ar ...
of stellar class G2 V, and about 4.6 billion years (Gyr) old. The Sun is not considered a variable star, but it does undergo periodic changes in activity known as the sunspot cycle. This is an 11-year oscillation in sunspot number. Sunspots are regions of lower-than- average temperatures that are associated with intense magnetic activity.
The Sun has steadily increased in luminosity by 40% since it first became a main-sequence star. The Sun has also undergone periodic changes in luminosity that can have a significant impact on the Earth. The Maunder minimum, for example, is believed to have caused the Little Ice Age phenomenon during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
.
The visible outer surface of the Sun is called the photosphere. Above this layer is a thin region known as the chromosphere. This is surrounded by a transition region of rapidly increasing temperatures, and finally by the super-heated corona
Corona (from the Latin for 'crown') most commonly refers to:
* Stellar corona, the outer atmosphere of the Sun or another star
* Corona (beer), a Mexican beer
* Corona, informal term for the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, which causes the COVID-19 di ...
.
At the center of the Sun is the core region, a volume of sufficient temperature and pressure for nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei are combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles ( neutrons or protons). The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manife ...
to occur. Above the core is the radiation zone
A radiation zone, or radiative region is a layer of a star's interior where energy is primarily transported toward the exterior by means of radiative diffusion and thermal conduction, rather than by convection. Energy travels through the radiatio ...
, where the plasma conveys the energy flux by means of radiation. Above that is the convection zone
A convection zone, convective zone or convective region of a star is a layer which is unstable due to convection. Energy is primarily or partially transported by convection in such a region. In a radiation zone, energy is transported by radiatio ...
where the gas material transports energy primarily through physical displacement of the gas known as convection. It is believed that the movement of mass within the convection zone creates the magnetic activity that generates sunspots.
A solar wind of plasma particles constantly streams outward from the Sun until, at the outermost limit of the Solar System, it reaches the heliopause. As the solar wind passes the Earth, it interacts with the Earth's magnetic field ( magnetosphere) and deflects the solar wind, but traps some creating the Van Allen radiation belts that envelop the Earth. The aurora
An aurora (plural: auroras or aurorae), also commonly known as the polar lights, is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly seen in high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic). Auroras display dynamic patterns of bri ...
are created when solar wind particles are guided by the magnetic flux lines into the Earth's polar regions where the lines then descend into the atmosphere.
Planetary science
 Planetary science is the study of the assemblage of planets,
Planetary science is the study of the assemblage of planets, moons
A natural satellite is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or small Solar System body (or sometimes another natural satellite). Natural satellites are often colloquially referred to as ''moons'' ...
, dwarf planet
A dwarf planet is a small planetary-mass object that is in direct orbit of the Sun, smaller than any of the eight classical planets but still a world in its own right. The prototypical dwarf planet is Pluto. The interest of dwarf planets to ...
s, comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ...
s, asteroids, and other bodies orbiting the Sun, as well as extrasolar planets. The Solar System has been relatively well-studied, initially through telescopes and then later by spacecraft. This has provided a good overall understanding of the formation and evolution of the Sun's planetary system, although many new discoveries are still being made.
The Solar System is divided into the inner Solar System (subdivided into the inner planets and the asteroid belt
The asteroid belt is a torus-shaped region in the Solar System, located roughly between the orbits of the planets Jupiter and Mars. It contains a great many solid, irregularly shaped bodies, of many sizes, but much smaller than planets, c ...
), the outer Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar S ...
(subdivided into the outer planets and centaurs), comets, the trans-Neptunian region (subdivided into the Kuiper belt, and the scattered disc
The scattered disc (or scattered disk) is a distant circumstellar disc in the Solar System that is sparsely populated by icy small solar system bodies, which are a subset of the broader family of trans-Neptunian objects. The scattered-disc obje ...
) and the farthest regions (e.g., boundaries of the heliosphere
The heliosphere is the magnetosphere, astrosphere and outermost atmospheric layer of the Sun. It takes the shape of a vast, bubble-like region of space. In plasma physics terms, it is the cavity formed by the Sun in the surrounding interstell ...
, and the Oort Cloud
The Oort cloud (), sometimes called the Öpik–Oort cloud, first described in 1950 by the Dutch astronomer Jan Oort, is a theoretical concept of a cloud of predominantly icy planetesimals proposed to surround the Sun at distances ranging from ...
, which may extend as far as a light-year). The inner terrestrial planet
A terrestrial planet, telluric planet, or rocky planet, is a planet that is composed primarily of silicate rocks or metals. Within the Solar System, the terrestrial planets accepted by the IAU are the inner planets closest to the Sun: Mercury, ...
s consist of Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
. The outer giant planet
The giant planets constitute a diverse type of planet much larger than Earth. They are usually primarily composed of low-boiling-point materials (volatiles), rather than rock or other solid matter, but massive solid planets can also exist. The ...
s are the gas giant
A gas giant is a giant planet composed mainly of hydrogen and helium. Gas giants are also called failed stars because they contain the same basic elements as a star. Jupiter and Saturn are the gas giants of the Solar System. The term "gas giant" ...
s ( Jupiter and Saturn) and the ice giants ( Uranus and Neptune).
The planets were formed 4.6 billion years ago in the protoplanetary disk
A protoplanetary disk is a rotating circumstellar disc of dense gas and dust surrounding a young newly formed star, a T Tauri star, or Herbig Ae/Be star. The protoplanetary disk may also be considered an accretion disk for the star itself, be ...
that surrounded the early Sun. Through a process that included gravitational attraction, collision, and accretion, the disk formed clumps of matter that, with time, became protoplanets. The radiation pressure
Radiation pressure is the mechanical pressure exerted upon any surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength that is a ...
of the solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the sol ...
then expelled most of the unaccreted matter, and only those planets with sufficient mass retained their gaseous atmosphere. The planets continued to sweep up, or eject, the remaining matter during a period of intense bombardment, evidenced by the many impact crater
An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact crater ...
s on the Moon. During this period, some of the protoplanets may have collided and one such collision may have formed the Moon.
Once a planet reaches sufficient mass, the materials of different densities segregate within, during planetary differentiation
In planetary science, planetary differentiation is the process by which the chemical elements of a planetary body accumulate in different areas of that body, due to their physical or chemical behavior (e.g. density and chemical affinities). The p ...
. This process can form a stony or metallic core, surrounded by a mantle and an outer crust. The core may include solid and liquid regions, and some planetary cores generate their own magnetic field, which can protect their atmospheres from solar wind stripping.
A planet or moon's interior heat is produced from the collisions that created the body, by the decay of radioactive materials (''e.g.'' uranium, thorium, and 26Al), or tidal heating
Tidal heating (also known as tidal working or tidal flexing) occurs through the tidal friction processes: orbital and rotational energy is dissipated as heat in either (or both) the surface ocean or interior of a planet or satellite. When an objec ...
caused by interactions with other bodies. Some planets and moons accumulate enough heat to drive geologic processes such as volcanism and tectonics. Those that accumulate or retain an atmosphere can also undergo surface erosion from wind or water. Smaller bodies, without tidal heating, cool more quickly; and their geological activity ceases with the exception of impact cratering.
Interdisciplinary studies
Astronomy and astrophysics have developed significant interdisciplinary links with other major scientific fields. Archaeoastronomy is the study of ancient or traditional astronomies in their cultural context, utilizing archaeological and anthropological evidence. Astrobiology is the study of the advent and evolution of biological systems in the Universe, with particular emphasis on the possibility of non-terrestrial life. Astrostatistics is the application of statistics to astrophysics to the analysis of a vast amount of observational astrophysical data. The study ofchemical
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., w ...
s found in space, including their formation, interaction and destruction, is called astrochemistry
Astrochemistry is the study of the abundance and reactions of molecules in the Universe, and their interaction with radiation. The discipline is an overlap of astronomy and chemistry. The word "astrochemistry" may be applied to both the Solar Syst ...
. These substances are usually found in molecular cloud
A molecular cloud, sometimes called a stellar nursery (if star formation is occurring within), is a type of interstellar cloud, the density and size of which permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydroge ...
s, although they may also appear in low-temperature stars, brown dwarfs and planets. Cosmochemistry
Cosmochemistry (from Greek κόσμος ''kósmos'', "universe" and χημεία ''khemeía'') or chemical cosmology is the study of the chemical composition of matter in the universe and the processes that led to those compositions. This is done ...
is the study of the chemicals found within the Solar System, including the origins of the elements and variations in the isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numb ...
ratios. Both of these fields represent an overlap of the disciplines of astronomy and chemistry. As "forensic astronomy
Forensic astronomy is the use of astronomy, the scientific study of celestial objects, to determine the appearance of the sky at specific times in the past. This has been used, if relatively rarely, in forensic science (that is, for solving problem ...
", finally, methods from astronomy have been used to solve problems of law and history.
Amateur astronomy
 Astronomy is one of the sciences to which amateurs can contribute the most.
Collectively, amateur astronomers observe a variety of celestial objects and phenomena sometimes with consumer-level equipment or equipment that they build themselves. Common targets of amateur astronomers include the Sun, the Moon, planets, stars, comets, meteor showers, and a variety of deep-sky objects such as star clusters, galaxies, and nebulae. Astronomy clubs are located throughout the world and many have programs to help their members set up and complete observational programs including those to observe all the objects in the Messier (110 objects) or Herschel 400 catalogues of points of interest in the night sky. One branch of amateur astronomy,
Astronomy is one of the sciences to which amateurs can contribute the most.
Collectively, amateur astronomers observe a variety of celestial objects and phenomena sometimes with consumer-level equipment or equipment that they build themselves. Common targets of amateur astronomers include the Sun, the Moon, planets, stars, comets, meteor showers, and a variety of deep-sky objects such as star clusters, galaxies, and nebulae. Astronomy clubs are located throughout the world and many have programs to help their members set up and complete observational programs including those to observe all the objects in the Messier (110 objects) or Herschel 400 catalogues of points of interest in the night sky. One branch of amateur astronomy, astrophotography
Astrophotography, also known as astronomical imaging, is the photography or imaging of astronomical objects, celestial events, or areas of the night sky. The first photograph of an astronomical object (the Moon) was taken in 1840, but it was no ...
, involves the taking of photos of the night sky. Many amateurs like to specialize in the observation of particular objects, types of objects, or types of events that interest them.
Most amateurs work at visible wavelengths, but many experiment with wavelengths outside the visible spectrum. This includes the use of infrared filters on conventional telescopes, and also the use of radio telescopes. The pioneer of amateur radio astronomy was Karl Jansky, who started observing the sky at radio wavelengths in the 1930s. A number of amateur astronomers use either homemade telescopes or use radio telescopes which were originally built for astronomy research but which are now available to amateurs (''e.g.'' the One-Mile Telescope
The One-Mile Telescope at the Mullard Radio Astronomy Observatory (MRAO), Cambridge, UK is an array of radio telescopes (two fixed and one moveable, fully steerable 60-ft-diameter parabolic reflectors operating simultaneously at 1407 MHz ...
).
Amateur astronomers continue to make scientific contributions to the field of astronomy and it is one of the few scientific disciplines where amateurs can still make significant contributions. Amateurs can make occultation measurements that are used to refine the orbits of minor planets. They can also discover comets, and perform regular observations of variable stars. Improvements in digital technology have allowed amateurs to make impressive advances in the field of astrophotography.
Unsolved problems in astronomy
Although the scientific discipline of astronomy has made tremendous strides in understanding the nature of the Universe and its contents, there remain some important unanswered questions. Answers to these may require the construction of new ground- and space-based instruments, and possibly new developments in theoretical and experimental physics. * What is the origin of the stellar mass spectrum? That is, why do astronomers observe the same distribution of stellar masses—theinitial mass function
In astronomy, the initial mass function (IMF) is an empirical function that describes the initial distribution of masses for a population of stars. The IMF is an output of the process of star formation. The IMF is often given as a probability d ...
—apparently regardless of the initial conditions? A deeper understanding of the formation of stars and planets is needed.
* Is there other life in the Universe? Especially, is there other intelligent life? If so, what is the explanation for the Fermi paradox
The Fermi paradox is the discrepancy between the lack of conclusive evidence of advanced extraterrestrial life and the apparently high a priori likelihood of its existence, and by extension of obtaining such evidence. As a 2015 article put it, ...
? The existence of life elsewhere has important scientific and philosophical implications.
* Is the Solar System normal or atypical?
* What are dark matter and dark energy? These dominate the evolution and fate of the cosmos, yet their true nature remains unknown.
* What will be the ultimate fate of the universe?
* How did the first galaxies form?
* How did supermassive black holes
A supermassive black hole (SMBH or sometimes SBH) is the largest type of black hole, with its mass being on the order of hundreds of thousands, or millions to billions of times the mass of the Sun (). Black holes are a class of astronomical ob ...
form?
* What is creating ultra-high-energy cosmic rays?
* Why is the abundance of lithium in the cosmos four times lower than predicted by the standard Big Bang model?
* What happens beyond the event horizon
In astrophysics, an event horizon is a boundary beyond which events cannot affect an observer. Wolfgang Rindler coined the term in the 1950s.
In 1784, John Michell proposed that gravity can be strong enough in the vicinity of massive compact ob ...
of a black hole?
See also
*Airmass
In astronomy, air mass or airmass is a measure of the amount of air along the line of sight when observing a star or other celestial source from below Earth's atmosphere ( Green 1992). It is formulated as the integral of air density along the lig ...
* Astronomical instruments
* Cosmogony
* International Year of Astronomy
* List of astronomy acronyms
* List of Russian astronomers and astrophysicists
* List of software for astronomy research and education
* Outline of space science
The following outline is provided as an overview and topical guide to space science:
Space science encompasses all of the scientific disciplines that involve space exploration and study natural phenomena and physical bodies occurring in outer ...
* Science tourism
* Space exploration
* Starlight
* Stellar collision
A stellar collision is the coming together of two stars caused by stellar dynamics within a star cluster, or by the orbital decay of a binary star due to stellar mass loss or gravitational radiation, or by other mechanisms not yet well understood ...
* Portal:Astronomy
* :Astronomical events
* :Astronomical objects
References
Bibliography
* * *External links
NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database (NED)
International Year of Astronomy 2009
IYA2009 Main website
from the American Institute of Physics
Southern Hemisphere Astronomy
Celestia Motherlode
Educational site for Astronomical journeys through space
Kroto, Harry
Astrophysical Chemistry Lecture Series.
Core books
an
Core journals
in Astronomy, from the Smithsonian/NASA
Astrophysics Data System
The SAO/NASA Astrophysics Data System (ADS) is an online database of over 16 million astronomy and physics papers from both peer reviewed and non-peer reviewed sources. Abstracts are available free online for almost all articles, and full scanned ...
A Journey with Fred Hoyle
by Wickramasinghe, Chandra.
Astronomy books from the History of Science Collection
at
Linda Hall Library
The Linda Hall Library is a privately endowed American library of science, engineering and technology located in Kansas City, Missouri, sitting "majestically on a urban arboretum." It is the "largest independently funded public library of scien ...
{{Use dmy dates, date=April 2019
Physical sciences